Abstract
The aim of this study was to analyse the cytotoxicity of heavy metals (HMs) and nanoparticles (NPs) on populations of the ciliated protist Euplotes aediculatus. We used ecotoxicological tests, antioxidant assays, and the MixTOX tool in Microsoft® Excel to evaluate the toxic effect of HMs and NPs in single and binary mixtures on E. aediculatus and to detect the type of interaction between them. Based on our results, the order of toxicity was Cu > Cd >> Zn (1 h and 24 h) for HMs and ZnO > CuO >> TiO2 >> SiO2 (1 h) and CuO > ZnO >> TiO2 >> SiO2 (24 h) for NPs. The interaction between metals in binary mixtures was predominantly synergistic at low doses and antagonistic at high doses. The type of interaction depende on the metals present and their respective concentrations. Furthermore, both HMs and NPs were shown to trigger effective antioxidant responses in E. aediculatus. Our research highlights the importance of considering the combined effects of HMs and NP exposure and their potency in risk assessment.
1. Introduction
Freshwater ecosystems contain a heterogeneous mixture of inorganic and organic pollutants [1], including heavy metals [2], nanoparticles [3], nitrates, phosphorus, domestic sewage, food processing waste, oil and oil dispersants, pesticides, pathogens, and emerging contaminants (endocrine disruptors, flame retardants, etc.), among others [4,5,6,7,8]. These pollutants reach freshwater ecosystems through various sources, such as industrial waste runoff, sewage treatment plants, feedlots, urban and agricultural runoff, septic systems, and illegal disposal of solid waste [1,7]. Heavy metals (HMs) and nanoparticles (NPs) are recognized as important toxic pollutants, with extensive literature describing their accumulation in different ecosystems. HMs and NPs pose a significant threat to a wide range of habitats, inducing harmful effects on organisms within polluted ecosystems. Some HMs are essential for cellular metabolism and growth at minimal concentrations [9], while others can cause harm even at very low concentrations [10]. Nanoparticles are introduced into freshwater ecosystems at various stages, from production to disposal, raising concerns about ecological risks, i.e., immediate responses and long-term damage to the environment [11,12]. NPs are extremely small particles, typically ranging from 1 to 100 nanometers in size. Due to their small size, NPs have unique physical and chemical properties that are different from larger particles, including a high surface area-to-volume ratio and increased reactivity. These properties make them valuable in various applications, such as medicine for drug delivery, electronics for developing advanced materials, environmental science for pollution remediation, and potential antimicrobial applications in food packaging [13]. However, their increased use has raised concerns about potential environmental and health impacts, particularly their behaviour and effects in natural ecosystems. In aquatic environments, NPs can interact with biological organisms in complex ways, potentially causing toxicity. Research focuses on understanding how NPs affect aquatic microorganisms and examining factors such as bioaccumulation, oxidative stress, and disruption of biological processes. Aquatic ecotoxicity research on NPs has increased in recent years, with a greater focus on freshwater compared to other ecosystems, such as salt water and soil [14,15,16,17,18]. Despite the unknown concentrations of most HMs and NPs in the environment, exposure modelling suggests that freshwater and soil could act as significant sinks for these pollutants, accumulating at higher levels than in the air [19,20,21]. Ciliated protists, an important group of primary consumers, are unicellular eukaryotic microorganisms well adapted to life in freshwater, soil, and many other ecosystems, from the subterranean groundwater ecosystem (i.e., caves) to the Antarctic coastal seawater [22,23,24]. Due to their widespread presence in different ecosystems, these microorganisms are a good model for monitoring the effects of various physical and chemical factors on biological communities [25,26,27]. Additionally, their rapid response to various toxic chemicals, coupled with a short generation time and a delicate cell membrane without external covering, makes them valuable for such studies [28,29,30,31,32]. Studies and reviews have explored ciliate tolerance to HMs and NPs [33,34,35,36,37]. In recent years, the research focus has shifted to the interactions between HMs and NPs with microorganisms, particularly freshwater ciliates. Generally, ciliates demonstrate the ability to endure long-term exposure to areas polluted by HMs and NPs, suggesting the existence of mechanisms for tolerance, resistance, or detoxification [36,37,38,39]. Euplotes aediculatus is a freshwater ciliate belonging to the class Hypotrichea and the family Euplotidae. Although this and other congeneric species have been extensively studied in various biological aspects, including toxicity assessment [40,41,42,43], to the best of our knowledge, only one recent study has attempted to analyse the toxic effects induced by NPs, specifically Cu and CuO, on E. aediculatus [44]. In this regard, our study further extends this analysis by increasing the number of NPs tested (i.e., ZnO, CuO, TiO2, and SiO2) and for the first time, assessing their acute and chronic effects in combination with heavy metals (i.e., Cd, Zn, and Cu) on E. aediculatus. In addition, the present study also analyses the antioxidant defences of E. aediculatus in response to both single and binary mixtures of these pollutants by using three different types of antioxidant assays, namely total phenol content (TPC), α,α-diphenyl-β-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH), and hydroxyl radical scavenging assay (HRSA). The ultimate goal is to confirm E. aediculatus as a suitable eukaryotic model organism, to demonstrate its potential as a bioindicator of HMs and NPs in polluted habitats, and, ultimately, to establish its effectiveness as a biomarker for robust environmental monitoring initiatives. Overall, this study will provide novel information about the antioxidant defence responses elicited by HMs and NPs in ciliates and their prospective application as biomarkers in risk assessment (RA) studies.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ciliate Strain and Culture Conditions
For our study, the freshwater ciliate Euplotes aediculatus was employed, which was isolated from the Frasassi cave complex (Genga, AN, Italy) [20] and kindly provided by Prof. Claudio Ortenzi and Prof. Federico Buonanno, University of Macerata (Italy). Euplotes aediculatus was cultivated in a salt basal medium (SMB) [45] at a temperature of 18 ± 1 °C. The cells were fed with the green algae Chlorogonium elongatum. Concurrently, the algae C. elongatum was cultured in Jaworski’s medium (JM) [46] at a temperature of 18 ± 1 °C. The experiments were conducted using cells of E. aediculatus in the logarithmic growth phase.
2.2. Metal Salts (Chemicals)
High-grade analytical chemicals with a purity of ≥99% were employed for the ecotoxicological assays as sources of metal ions. Specifically, cadmium chloride (anhydrous CdCl2), zinc sulfate heptahydrate (ZnSO4·7H2O), copper (II) sulfate pentahydrate (CuSO4·5H2O), zinc oxide (ZnO) (nanopowder with a particle size < 100 nm), titanium (IV) oxide (TiO2) (a mixture of rutile and anatase nanopowder, < 100 nm particle size as per BET, 99.5% trace metals basis), silicon dioxide (SiO2) (nanopowder with a particle size of 10–20 nm as per BET, 99.5% trace metals basis), and copper (II) oxide (CuO) (nanopowder with a particle size < 50 nm as per TEM) were procured from Sigma-Aldrich (Milan, Italy).
2.3. Single HM and NP Toxicity Tests at 1 h and 24 h
To determine the toxicity of HMs and NPs to E. aediculatus, we conducted preliminary toxicity range-finding tests using different concentrations of HMs and NPs. These tests aimed to establish the concentration range for the final assays. Each test included 5–7 different concentrations, ranging from the lowest concentration with no observed effect on cell viability to the highest concentration, resulting in 100% cell death. We prepared 0.1 M stock solutions for HMs and 1 M stock solutions for NPs by dissolving each chemical in a salt basal medium (SMB) with a pH of 7. Daily working solutions were then prepared by diluting the stock solutions to nominal concentrations as follows: 10–100 mg Cd/L, 0–2 mg Cu/L, 50–250 mg Zn/L, 10–150 mg ZnO/L, 1–10 mg CuO/L, 500–8000 mg TiO2/L, and 1000–15,000 mg SiO2/L. We conducted ecotoxicity assays at 1 h and 24 h using specific 3-well depression glass slides. One hundred cells from an exponentially growing culture were inoculated into each well, resulting in a final volume of 1 mL of ciliate culture medium containing the specified chemical concentration. The setup was covered to prevent evaporation and incubated for 1 h and 24 h in a humid chamber at 18 ± 1 °C in the dark, without feeding the ciliates during the test period. After the 1 h and 24 h incubation periods, Euplotes cells were examined under a stereoscopic microscope (20–40× magnification) to determine mortality and survival at different test concentrations. The ciliates were considered dead if they were missing due to a cell burst or if they remained stationary at the bottom of the well, unresponsive to gentle mechanical stimulation with the tip of the micropipette. The control wells contained the same number of ciliates but lacked HMs and NP solutions. Replicates (n = 3) were averaged for each concentration treatment. Cytotoxicity assessment endpoints included median lethal concentration (LC) LC20 (concentration causing 20% mortality) and LC50 (concentration causing 50% mortality) at 1 h and 24 h. Mean mortality was determined using a regression equation. Due to the number of exposed organisms, each analysis required a larger amount of working solution, resulting in minimal absorption of HMs and NPs due to bioaccumulation. To minimize chemical adsorption/release levels, we used 3-well depression glass slides, aiming to reduce these levels compared to conventional toxicity test setups.
2.4. Bimetallic Mixture (Cd + Zn, Cd + ZnO) Toxicity Tests at 1 h and 24 h
Toxicity assessment in binary mixtures followed the same procedure as in single-metal treatment assays. We structured the data in a full factorial design, including all possible combinations of binary mixtures to ensure comprehensive coverage. For this toxicity test involving binary mixtures, we included a control (medium only) and examined 16 binary mixtures of Cd + Zn, and Cd + ZnO based on the total concentration of the two chemicals in the mixture. The concentration of each chemical was expressed using the toxic unit (TU) approach according to Sprague [47]. In this study, the binary mixtures were prepared by combining the toxicants according to their individual LC50 values, where 1TU corresponds to the LC50 values of single-metal toxicities. Seven total concentrations were tested: 0.5, 0.75, 1, 1.25, 1.5, 1.75, and 2TUs. The total concentrations were calculated as the sum of the TUs of the single chemicals constituting the mixture. Expected mortality rates were determined as the sum of the single-metal toxicities obtained for each metal in the mixture at the same concentration. An interaction was considered synergistic if the observed mortality rate was higher than the expected mortality rate, and antagonistic if the observed mortality rate was lower than the expected mortality rate at the same concentration.
2.5. Total Phenolic Content and Antioxidant Activity Assays
To evaluate the presence of antioxidant activity in the ciliate exposed to different concentrations of the single and binary mixture of HMs and NPs, three different types of antioxidant assays, namely total phenol content (TPC), α,α-diphenyl-β-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH), and hydroxyl radical scavenging assay (HRSA), were applied. To analyse the antioxidant activity of these ciliate cells, 2000 cells/mL were taken from an exponentially growing culture flask and transferred to Petri plates in a volume of 10 mL and exposed to different concentrations of single and binary mixtures of HMs and NPs for 1 h and 24 h. For single-metal exposure, concentrations 0.25, 0.5, 0.75, and 1 TUs of Cd, Zn, and ZnO, respectively, were selected and used to analyse the antioxidant activity and enzyme assays. In the binary mixture, minimal cut-off concentrations (less than or equal to 50% mortality) were selected. Based on this minimal cut-off, we selected seven concentrations in the binary mixture of Cd + Zn (0.25 + 0.25, 0.5 + 0.25, 0.25 + 0.5, 0.75 + 0.25, 0.25 + 0.75, 0.75 + 0.5, and 0.75 + 0.75) at 1 h, nine concentrations in the binary mixture of Cd + Zn (0.25 + 0.25, 0.5 + 0.25, 0.25 + 0.5, 0.75 + 0.25, 0.5 + 0.5, 0.25 + 0.75, 1 + 0.75, 0.5 + 1, and 0.75 + 0.75) at 24 h, and six concentrations in the binary mixture of Cd + ZnO (0.25 + 0.25, 0.5 + 0.25, 0.25 + 0.5, 0.75 + 0.25, 0.5 + 0.5, and 1 + 0.25) at 24 h and used them to analyse the antioxidant activity. In the binary mixture of Cd + ZnO at 1 h toxicity test, we could not select any concentrations for the analysis of antioxidant activity assays, because in this test, all the concentrations were above the minimal cut-off concentration. Nanoparticles were not conditioned before antioxidant activity. Antioxidant activity assays were measured in the supernatant of the cell extract (intracellular) according to Ravindran et al. [48].
The analysis of TPC was based on the Folin assay of Vattem and Shetty [49] with minor modifications. In this method, 100 μLof cell extract was added to a test tube, mixed with 2 mL of sodium bicarbonate, and incubated for 2 min at 18 ± 2 °C. Then, 100 μLof the Folin–Ciocalteu reagent was added and incubated in the dark at 18 ± 2 °C for 30 min. After the incubation period, the absorbance was measured at λ = 725 nm using a spectrophotometer. Gallic acid 1 mg/mL was used as standard, and standard curves were obtained using different concentrations of gallic acid. We also used the culture medium (without cells) as a control, as no phenols were observed. We used the DPPH scavenging assay to determine the antioxidant capacity of the Euplotes extracts. Antioxidant activity was determined by its ability to scavenge α,α-diphenyl-β-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) radicals. This analysis is based on the procedure of Yıldırım et al. [50] with minor changes. Briefly, 1 mM DPPH stock solution was prepared in 95% ethanol. Then, 800 μLof 1 mM DPPH solution was added to 200 μLof sample extract. The samples were mixed well and incubated for 30 min in the dark at room temperature. After incubation, the samples were transferred to centrifuge tubes and centrifuged at 14,000 rpm for 5 min. The supernatant was collected and the absorbance measured at λ = 517 nm using a spectrophotometer. In total, 200 μLof 95% ethanol was used as a control. Butylated hydroxy anisole (BHA) was used as a reference compound. Antioxidant activity is expressed as a percentage (%). The percentage of DPPH scavenging was calculated using the formula below:
The HRSA assay is based on the Fenton reaction of Kunchandy and Rao [51] and follows the procedure of Ravindran et al. [48] with slight modifications. The hydroxyl radical is generated by the Fe3+ ascorbate EDTA H2O2 system i.e., Fenton reaction. To analyse this reaction, the chemicals of 2–deoxyribose (2.8 mM), FeCl3 (100 µM), H2O2 (1 mM), and EDTA (100 µM) were dissolved in 20 mM phosphate buffer at pH 7.4. From this mixture, 800 µL was then transferred to another test tube. Then, 10 µL of ascorbic acid (10 mM) and 100 µL sample extract were added. Finally, ascorbic acid was added and incubated at 37 °C for 1 h. After the incubation, 1 mL of 2.8% TCA and 1 mL of 1% aqueous TBA were added, and the mixture was heated at 90 °C for 15 min to develop colour. After cooling, the absorbance was measured at 532 nm against a suitable blank solution. Mannitol was used as a reference compound. The percentage of scavenging was determined according to the formula below:
2.6. Statistical Analysis
Statistical analysis was performed using InfoStat software ver. 2012 and Microsoft® Excel v.2010 spreadsheet; the difference between control and test groups was evaluated using one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni corrected post-hoc t-test and correlation coefficient (R). And p ˂ 0.05 was considered statistically significant. All experiments were performed at least in triplicate (n = 3), and the results were presented as mean ± standard error (SE) values.
Toxicity data from binary mixtures of the different compounds were analysed using the Microsoft® Excel spreadsheet MixTOX tool [52]. Concentration addition (CA) and independent action (IA) models were used to analyse the bimetallic mixtures. This tool assesses if and how the observed data deviate from both models and a better significance of the observed data could be realized using deviation functions such as synergism or antagonism (S/A), dose level-dependent deviation (DL), and doseratio-dependent deviation (DR). The strict concentration addition model occurs when the toxic unit value of a mixture equals 1 [52,53]. In the independent action model, the dose–response relationship of chemical mixtures can be expressed by multiplying the non-response of each chemical in the mixture at a given exposure concentration [52,53]. The deviation arrays of the 1 h Cd + Zn (1a), 24 h Cd + Zn (1b), 1 h Cd + ZnO (1c), and 24 h Cd +ZnO (1d) mixtures were analysed using the MixTOX tool. The Solver program and Visual Basic functions in Microsoft Excel v.2010 were used to guide the software design. The different types of toxicity data of the binary mixtures (1a, 1b, 1c, and 1d) were fitted to the deviation functions (S/A, DL, and DR) using the maximum likelihood method, while minimizing the sum of squared residuals (SS). Chi-square (χ2) tests were used to calculate the statistical significance of the improved model fit from additional parameters. In this study, a p(χ2) value < 5% it was considered statistically significant. A detailed description of these mixture models can be found in Jonker et al. [52].
3. Results
3.1. Acute and Chronic Cytotoxicity of Single HMs (Cd, Cu, and Zn) and NPs (CuO, ZnO, TiO2, and SiO2)
The LC20 and LC50 values were determined from the mortality curve based on the regression equation for 1 h and 24 h exposures of HMs and NPs to E. aediculatus. In the case of single-metal exposures (HMs and NPs), E. aediculatus showed higher resistance to HM Zn at both 1 h and 24 h. E. aediculatus cells also showed greater resistance to NP SiO2 at both time points, with no mortality observed at 1 h and 24 h in the control group. Analysing the mean lethal concentration values after 1 h exposure (1 h LC20 and LC50) and 24 h exposure (24 h LC20 and LC50), Cu emerged as the most toxic metal to E. aediculatus, with LC20 and LC50 values of 0.18 and 0.43 mg/L, respectively (Table 1). At the same time, the cellular toxicity of TiO2, SiO2, and CuO NPs was lower than that of ZnO at 1 h LC20 and LC50 values, while CuO exhibited greater toxicity compared to all other NPs at 24 h LC20 and LC50 values. The 1 h LC20 and LC50 values for E. aediculatus were 282.41 and 283.95 mg/L for Zn, and 7.05 and 7.36 g/L for TiO2, respectively. The 24 h LC20 and LC50 values for Zn were 76.47 and 137.65 mg/L, and for TiO2they were 2.61 and 4.44 g/L, respectively (Table 1). The order of toxicity of HMs was Cu > Cd > Zn at both 1 h and 24 h. For NPs, the toxicity order was ZnO > CuO > TiO2 > SiO2 at 1 h and CuO > ZnO > TiO2 > SiO2 at 24 h.

Table 1.
LC20 and LC50 values of E.aediculatus for HMs and NPs at 1 h and 24 h.
3.2. 1 h Binary Mixture of Cd + Zn—MixTOX Analysis
The simplest CA module does not appear to adequately capture the overall toxicity data; in fact, the squared R2 value is only 34%, indicating that a significant proportion of the variance in the data is not explained by the model. This limitation is not only due to the binary mixture toxicity data but also extends to the data for Zn, which shows a threshold effect above 280 mg/L, which the CA model is unable to predict. Attempts to fit the slope with a value lower than −39 resulted in an error. This is not the case for the SA, DR, and DL subsystems (as well as with the IA model). For cadmium toxicity, a good fit can be achieved. Consequently, we relied on modules that take into account deviations from additivity, which have much better predictive capabilities. The most conservative (lower L) among them, the DL module, with its positive and negative a and b values, respectively (Table 2), suggests antagonism, indicating a decrease in toxic effects with increasing doses. In addition, positive a and b parameters for the DR model suggest antagonism in scenarios where the toxicity of the mixture is primarily due to one component (e.g., high Cd with low zinc, and vice versa).

Table 2.
Fitting results of the toxicity data of the bimetallic mixture (Cd + Zn) to the four models describing the deviations from concentration addition (CA) and independent action (IA) of Euplotes aediculatus using the MixTOX tool.
3.3. 24 h Binary Mixture of Cd + Zn—MixTOX Analysis
In the 24 h dataset for Cd + Zn exposure in E. aediculatus, the concentration addition (CA) module is statistically significant, although it explains a relatively small proportion of the data variance. The inclusion of different sub-models improves the explanation of the data variance up to 77%. However, these models generally struggle to accurately predict mixture toxicity (Table 2). Specifically, the S/A model and the DR models both yield positive values for their parameters (a and b), which typically indicate antagonism in CA systems. However, the DR model shows synergism at low doses and antagonism at high doses. Notably, a strong synergistic effect was observed at the lowest concentrations of chemical 1 (Cd) and chemical 2 (Zn) (0.25 TU), followed by antagonism in the central dose range and again synergism at the highest tested concentrations tested. This non-linear dynamic could be attributed to hormesis, as observed in previous studies [54,55,56].
3.4. 1 h and 24 h Binary Mixture of Cd + ZnO—MixTOX Analysis
The dataset for Cd + ZnO conspicuously shows synergistic effects, as predicted by both the CA and IA sub-modules (Table 3) at 1 h.

Table 3.
Fitting results of the toxicity data of the bimetallic mixture (Cd + ZnO) to the four models describing deviations from concentration addition (CA) and independent action (IA) of Euplotes aediculatus using the MixTOX tool.
The concentration addition (CA) module is statistically significant at 24 h, but the dose ratio (DR) dependence module outperforms it. Notably, this module explains 91% of the variance in the data. A negative “a” parameter indicates synergism, while a positive “b” parameter indicates antagonism at specific dose ratios. When the data were examined, strong antagonism was observed when Cd toxicity was particularly high. These results are consistent with the results of the IA sub-modules (Table 3).
3.5. Antioxidant Properties of E. aediculatus Extracts Treated with Single and Binary Mixture at 1 h and 24 h
The total phenolic content has been identified as the major naturally occurring antioxidant component in the extracts of the freshwater ciliate E. aediculatus. In this study, the total phenolic content (TPC) of ciliate extracts treated with single metals (Cd, Zn, and ZnO) and bimetallic mixtures (Cd + Zn and Cd + ZnO) at 1 h and 24 h was evaluated. The Folin–Ciocalteu Method was used for the measurement, revealing concentrations ranging from 95.44 to 148.65 µg/L. E. aediculatus showed the lowest phenolic value at concentrations of 1 TU ZnO, while the maximum was observed at 0.5 TU Cd and 0.5 TU Zn at 1 h and 24 h, respectively, with a significant level of p < 0.001. In the case of single-metal treatments, the TPC of E. aediculatus was higher after 24 h of exposure compared to 1 h. In the bimetallic mixture treatments, the TPC was lower in the binary mixture of Cd + ZnO compared to the binary mixture of Cd + Zn at 24 h (Figure 1).
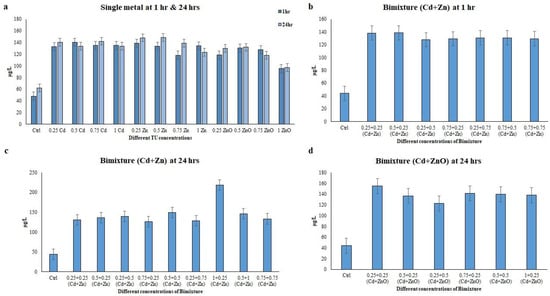
Figure 1.
Total phenolic content measured in the Euplotes aediculatus cell extracts at single-metal (Cd, Zn, and ZnO) and bimetallic mixture concentrations. (a) Single metal, (b) bimetallic mixture of Cd + Zn at 1 h exposure period, (c) bimetallic mixture of Cd + Zn at 24 h exposure period, and (d) bimetallic mixture of Cd + ZnO at 24 h exposure time. The results are presented as means of three replicate experiments.
In the binary mixture, the TPC ranged from 122.58 to 218.54 µg/L. The highest TPC was observed in the binary mixtures of 1 + 0.25 TU (Cd + Zn) and 0.25 + 0.25 TU (Cd + ZnO) ciliate extracts after a 24 h exposure period, respectively (p < 0.001) (Figure 1). Importantly, the TPC of the ciliate extract, an indicator of antioxidant capacity, was significantly increased in cells exposed to different single heavy metal conditions and bimetallic mixtures compared to untreated cells (p < 0.001). The free radical scavenging activity of the ciliate extracts were evaluated using the DPPH assay, with BHT employed as a standard. Extracts obtained from E. aediculatus showed a maximum scavenging activity of 34.90% at the concentration of 0.75 TU Cd (p < 0.001) and a minimum activity of 26.97% at the concentration of 0.25 TU ZnO (p < 0.001) after 1 h. After 24 h, the maximum activity was found at 0.25 TU Cd, while the minimum activity was found at 0.5 TU Cd, with values of 48.97% and 33.04% (p < 0.001), respectively (Figure 2).
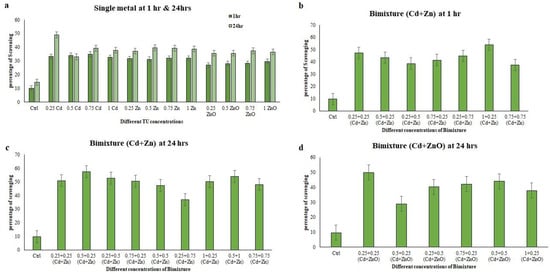
Figure 2.
DPPH scavenging activity measured in Euplotes aediculatus cell extracts at single-metal (Cd, Zn, and ZnO) and bimetallic mixture concentrations. (a) Single metal, (b) bimetallic mixture of Cd + Zn at 1 h exposure time, (c) bimetallic mixture of Cd +Zn at 24 h exposure time, and (d) bimetallic mixture of Cd + ZnO at 24 h exposure time. The results are ± SD of three parallel experiments.
The DPPH scavenging activity ranged from 25.69% to 48.97%. In the single-metal treatments, concentrations of 0.75 TU and 0.25 TU Cd showed higher DPPH scavenging activity, with significant values of p < 0.001 at 1 h and 24 h, respectively (Figure 2). In the bimetallic mixtures, Cd + Zn showed higher DPPH activity during chronic exposure compared to other bimetallic mixture exposure periods. The maximum activity was observed with 0.5 + 0.25 TU (Cd + Zn) ciliate extracts at 24 h (p < 0.001), while the minimum value was found at the concentration of 0.5 + 0.25 TU (Cd + ZnO) at 24 h (p < 0.001) (Figure 2). Among the concentrations of the bimetallic mixture, the values ranged from 28.87% to 57.56%. To establish correlations between the results obtained by different methods, a regression analysis was conducted, and the correlation coefficients (R) are presented in Table 4.

Table 4.
Correlation coefficient (R) between single and binary mixture metal exposure of different antioxidant assays on Euplotes aediculatus.
Significant correlations were observed between different methods used to determine the antioxidant potential, with notable associations between total phenolic content (TPC) and DPPH assays showing positive correlations of R = 0.90 and R = 0.80 at 1 h and 24 h, respectively. For the bimetallic mixture of Cd + Zn at acute exposure, a robust correlation of R = 0.93 was observed between the TPC and DPPH assays at 24 h. Similarly, Cd + ZnO showed very strong correlations in TPC and DPPH assays, with R = 0.95 at 24 h (Table 4). A significant positive correlation was observed between DPPH and TPC, as well as DPPH and HRSA (R = 0.90; R = 0.86; p < 0.001), reflecting the antioxidant capacity of the single-metal treatments at both 1 h and 24 h (Table 4). In the acute exposure of the bimetallic mixture Cd + Zn, strong correlations (R = 0.93) were found between DPPH and HRSA, as well as between DPPH and TPC. However, lower correlations were identified between the antioxidant assays in the chronic condition of this mixture (Table 4). At the same time, in the bimetallic mixture of Cd + ZnO during chronic exposure, DPPH and HRSA as well as DPPH and TPC showed a strong correlation R = 0.91 and R = 0.95 at 24 h, respectively (Table 4). The hydroxyl radical is a highly important and reactive free radical formed in biological systems, capable of interacting with all molecules within living cells and causing severe damage. The ability of E. aediculatus cell extracts to scavenge hydroxyl radicals is expressed as the percentage of scavenged hydroxyl radicals, using ascorbic acid used as a standard. As shown in Figure 3, the cell extracts showed varying levels of radical scavenging ability in single-metal treatments, ranging from 31.20% to 68.98% at 1 h and from 48.83% to 71.92% at 24 h.
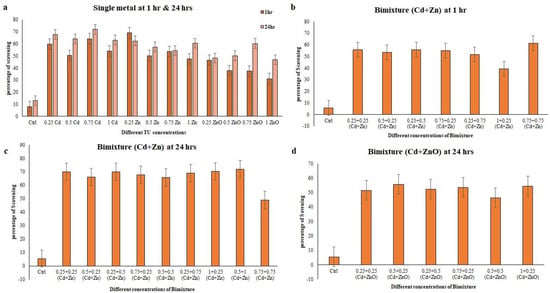
Figure 3.
Hydroxyl radical scavenging activity measured in Euplotes aediculatus cell extracts at single -metal (Cd, Zn, and ZnO) and bimetallic mixture concentrations. (a) Single metal, (b) bimetallic mixture of Cd + Zn at 1 h exposure time, (c) bimetallic mixture of Cd +Zn at 24 h exposure time, and (d) bimetallic mixture of Cd + ZnO at 24 h exposure time. The results are ± SD of three parallel experiments.
In the case of binary mixtures, the hydroxyl radical scavenging activity ranged from 39.39% to 71.88% (Figure 3). The minimum and maximum hydroxyl radical scavenging activity was observed in the 0.5 + 1 mixture at 1 h and 24 h of Cd + Zn, respectively. In the binary mixture of Cd + ZnO, higher activity was observed in the mixture of 0.5 + 0.25 (55.74%), and in Cd + Zn at 24 h, higher scavenging activity was observed in the binary mixture of 0.5 + 1 (71.88%) (Figure 3) with a significant p-value of < 0.001. Generally, Cd + Zn at 1 h and Cd + ZnO at 24 h showed a wide range of scavenging abilities (39.39–61.38% and 46.31–55.74%, respectively), with Cd + Zn at 24 h consistently showing higher scavenging activity (49–71.88%). In the present study, a significant and positive correlation was observed between HRSA and TPC assays in single-metal treatments at both 1 h (R = 0.85) and 24 h (R = 0.86). The correlation was stronger in the bimetallic mixture compared to single-metal exposure, with the lowest correlations found between the antioxidant assays of HRSA and TPC at 1 h in the binary mixture of Cd + Zn (Table 4). However, strong correlations were found in Cd + Zn and Cd + ZnO at 24 h, with R values of 0.89 and 0.81, respectively.
4. Discussion
Anthropogenic activities contribute significantly to ecosystem pollution, a global challenge, with heavy metals (HMs) and nanoparticles (NPs) emerging as key pollutants [2,3]. Research on the interaction between HMs/NPs and ciliated protists is limited [29,31,36,41,57], especially compared to studies on other organisms [37,58,59,60,61,62,63,64]. Cell biomass plays a pivotal role in bioassay treatments, modifying pollutant bioavailability and enhancing data accuracy [65]. The order of toxicity of HMs is Cu > Cd > Zn at 1 h and 24 h, a pattern consistent with the findings of Pudpong and Chantangsi [66] and Martín-González et al. [29] for HMs. Martín-González et al. [29] used Euplotes sp. in their study and found concentrations of 0.7, 4.8, and 110.2 mg/1 for Cd, Cu, and Zn, respectively, after a 24 h exposure. Notably, these concentrations are lower than those observed in our study, except for the Cu LC50 value. The ciliate Bresslauides sp. showed lower LC50 values for Cd and Zn compared to our study [66]. Díaz et al. [67] and Rico et al. [68] observed higher LC50 values for Cu and Zn in Colpoda genus isolates compared to our study, except for the Cd LC50 value. Our NP LC50 values exceed those reported by Blinova et al. [69] for the ciliate Tetrahymena thermophila. Mortimer et al. [38] found ZnO values lower and CuO values higher than our results for the ciliated protozoa T. thermophila at 24 h exposure. According to a study by Zhao et al. [44], the LC50 value of CuO on E. aediculatus was found to be 1.24 mg/L after a 24 h exposure. However, our study showed a higher 24 h LC50 value of CuO compared to the study by Zhao et al. [44]. These different sensitivities may be due to the different origins of the E. aediculatus strains used in the experiments. Overall, Zn shows fewer toxic effects compared to other HMs, as ciliated protists adapt quickly to excess Zn without adverse effects. In contrast, the E. aediculatus cells used in this study showed lower resistance to Cu compared to previous studies [29]. In general, the mixtures of Cd + ZnO showed predominantly synergistic effects at both 1 h and 24 h. This particular interaction (Cd + Zn) has been studied and documented in various organisms, with consistent outcomes [37,67,70,71]. On the other hand, the differing responses of E. aediculatus to heavy metals and nanoparticles can be attributed to the distinct physical and chemical properties of these substances, their differing mechanisms of uptake and bioavailability, and the unique ways in which they interact with biological systems and the environment. Moreover, the toxicity of nanoparticles (NPs) can vary depending on the duration of exposure. Some nanoparticles dissolve slowly, releasing toxic ions over time, which can lead to a delayed onset of toxicity. The level of toxicity may increase or decrease based on the duration of exposure. These differences highlight the complexity of nanoparticle toxicity and the need for further research to fully understand their impacts on soil microorganisms and ecosystems.
In our analyses, the independent action (IA) module outperformed the concentration addition (CA) module, as evidenced by the R2 value, which explains 82% of the data variance. Modules taking into account deviations from the norm performed even better. The synergism/antagonism (S/A) sub-module provides a broad indication of synergisms, while the dose ratio-dependent deviation (DR) and the dose level-dependent deviation (DL) sub-modules show a more complex pattern, moving from synergism to antagonism. DR has the most conservative score, yet it is very similar to DL. Specifically, in the case of DR, a negative “a” and a positive “b” indicate the presence of antagonism, where the toxicity of the mixture is primarily due to one component (either high Cd or high Zn). The DL sub-module suggests a shift from synergism to antagonism at toxic values higher than LC50. It is noteworthy that the responses identified by the two systems (CA, IA, and their derived models) are not identical. However, it should be pointed out that they account for additivity in markedly different ways. In particular, CA tends to overestimate mixture toxicity, making it relatively simpler to highlight an antagonistic effect from its derived sub-modules. In the IA module, each sub-module explains a very similar amount of data variance, approximately 77%. Among these sub-modules, DL stands out as the best performer, significantly outperforming both IA and SA. The parameters of the DL sub-module, labelled as “a” and “b,” indicate synergism at low dose levels and antagonism at high doses. It is noteworthy that although the results of the CA and IA modules are not identical, their significant DL modules are similar in their predictions. In particular, they both indicate synergism at very low doses, such as the no observed adverse effect levels (NOAELs) for either Cd or Zn. This study represents a novel exploration, marking the first analysis of the MixTOX tool in the context of bimetallic mixtures involving Cd, Zn, and ZnO in the freshwater ciliate E. aediculatus. The data analysis shows no substantial differences in the predictability of joint effects using CA and IA for the tested bimetallic system. Both models explain between 34% and 88% of the variance in the 1a–1b bimetallic mixture, and between 35% and 99% in the 1c–1d binary mixture. The MixTOX tool emerged as the superior and predominant method, demonstrating statistically significant deviations in bimetallic mixtures by incorporating additional parameters to tailor the dataset. For instance, with the exception of the Cd + Zn and Cd + ZnO mixtures, the inclusion of S/A, DR, and DL deviation parameters in the reference models results in a modest increase of less than 5% in the goodness of fit, as measured by R2. While CA and IA predictions are nearly identical in most cases, there are subtle differences. For instance, in the case of the Cd + Zn mixture, positive “a” values at 1 h and 24 h are observed in all deviation patterns of the CA module, except DL, while the opposite is true for the IA module. Conversely, in the case of Cd + ZnO, both modules give similar results at 1 h and 24 h. In general, the CA models explain the mixture toxicity of the 1a–1d mixtures based on free ion activity. For Cd + Zn mixtures, the CA model explains the variation, showing an increase from 34% to 72% at 24 h, while the IA model shows a decrease from 82% to 77% over the same period. For the bimetallic mixture of Cd + ZnO, the CA model shows an increase from 47% to 87%, while the IA module shows an increase from 35% to 86%. Notably, IA predictions are consistently lower than CA predictions, as exemplified by the mixture of Cd + ZnO at 1 h, where IA accounts for 35% of the model predictability compared to 47% for CA. The lower predictability of IA has been studied in various organisms, with particular emphasis on chemicals known to interact with xenobiotic metabolism [72,73,74]. We observed that the presence of one metal does not significantly affect the free ion activity of another metal in the mixed solution. Our results indicate that the joint toxicity effect of Cd, Zn, and ZnO, after different exposure times, is predominantly antagonistic at chronic levels, whereas it shows synergism at acute levels. This behaviour can be attributed to the consideration of free ion activity and is significantly enhanced in the MixTOX tool when incorporating deviations from both models. Our findings are in agreement with the observations of Jonker et al. [52], who reported similar joint toxic effects of Cd and Zn mixtures in their reference model. Furthermore, He et al. [75] investigated mixtures of Ni and Co in the soil-dwelling annelid Enchytraeus crypticus and reported a shift from synergism at low concentrations to antagonism at high concentrations, indicating that the effects depend on metal uptake and elimination processes [76]. We encountered difficulty in distinguishing between the CA- and IA-based models, as both models performed comparably well in assessing the overall toxicity of 1a, 1b, 1c, and 1d mixtures. This observation is consistent with the findings of Farley and Meyer [77] and Cedergreen et al. [73], who reported similar results, indicating that neither the CA nor the IA model showed significant superiority over the other. As a result, researchers are often faced with the challenge of decisively selecting or favouring one reference model for mixture toxicity over the other. Their toxicity often follows a dose–response curve, where low concentrations may be tolerable or even essential (as trace nutrients), while higher concentrations become toxic. Additionally, biological systems have the capacity to detoxify and excrete metals up to a certain limit. Once this threshold is exceeded, toxic effects become more pronounced. The type of interaction can shift from being tolerable or beneficial at low concentrations to being harmful at high concentrations. In our test model system, the response closely matched that of the CA model, making it difficult to distinguish the joint toxicity results from those predicted by the IA model. The difficulty arises from the unknown action of the chemicals; they may have a similar mode of action or different specific modes of action, contributing to the challenge of model selection. No prior total phenolic content (TPC) studies have been conducted on ciliate species. Before this study, numerous phenolic compounds demonstrated effective antioxidant properties in various organisms, including fungi, bacteria, various plant species, marine algae, and natural products, among others. Previous research has highlighted the antioxidant activity of marine algae extracts, particularly their polyphenols [78]. Additionally, phenolic content plays a crucial role in an organism’s ability to withstand various environmental factors or stresses by acting as a component of the cell’s antioxidant defence system. This aspect is particularly important for plants, fungi, and protozoa due to their hydroxyl radical scavenging activity. The presence of HMs and NPs can lead to the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in E. aediculatus, either directly or indirectly. This oxidative stress causes damage to the cells, prompting a strong antioxidant response. The response includes the activation of transcription factors, increased production of antioxidant and antioxidant enzymes, synthesis of metal-binding proteins (metallothioneins and phytochelatins), and the activation of repair mechanisms to counteract oxidative damage. These defence mechanisms collectively assist the organism in managing and neutralizing the toxic effects of HMs and NPs. Thus, the defence mechanisms help the ciliate E. aediculatus cope with an increase in the production of antioxidants. Therefore, in our experiment, we evaluated the total phenolic content of E. aediculatus cell extracts to understand their antioxidant activity against different concentrations of HM and NP stresses, using a series of antioxidant assays. DPPH scavenging activity was assessed for both single and bimetallic mixtures at acute and chronic exposures. Remarkably, the bimetallic mixture at 24 h showed robust DPPH scavenging activity, surpassing other bimetallic mixtures such as Cd + Zn at 1 h and Cd + ZnO at 24 h. Additionally, while the DPPH scavenging activity of single metals showed lower activity at both 1 h and 24 h, the combination of single metals with other metals resulted in higher activity. This phenomenon can be attributed to the joint toxicity of the chemical mixture (p < 0.001). In this study, the bimetallic mixtures showed potent antioxidant capacity. Consistent with our findings, a bimetallic mixture of Cd + Zn at chronic exposure has previously demonstrated effective antioxidant activity using the DPPH radical scavenging method [48]. Although no data are available for the analysis of DPPH scavenging activity in ciliated protists, DPPH has been extensively used as a radical to evaluate reducing substances in food materials [79]. Sanaye et al. [80] analysed the antioxidant activity in alligator pipefish and showed lower DPPH scavenging activity compared to our values. It is worth noting that DPPH is a stable free radical that becomes a diamagnetic molecule when it accepts an electron or hydrogen radical.
As previously stated, there are no available data on hydroxyl radical scavenging activity (HRSA) in ciliated protists, but numerous results are available for other organisms. For instance, Sanaye et al. [80] demonstrated HRSA ranging from 84.89% to 91.02%, and these levels of activity are relatively higher than those observed in our results. The robust correlation observed between TPC and HRSA strongly suggests that phenolic compounds play a crucial role in donating electrons to hydroxyl radicals, effectively neutralizing them into water [81]. The efficiency of E. aediculatus cell extract is demonstrated by the significant positive correlation (p < 0.001) between HRSA and other kinds of antioxidant activity. This positive correlation suggests that the ciliate cell extract stabilizes lipid peroxidation through its hydrogen-donating potential, contributing to its overall antioxidant capacity. This study has some limitations. First, the findings are based on a single ciliate species, which may not be representative of other aquatic organisms. Additionally, the experiments were conducted in controlled environments, which may not fully replicate natural conditions, potentially limiting the applicability of results to real-world scenarios. Furthermore, the study tested only specific combinations of heavy metals and nanoparticles, leaving out numerous possible mixtures and interactions that could occur in natural settings. The study primarily focused on acute toxicity (1 h) and chronic toxicity (24 h), as well as immediate antioxidant responses, potentially overlooking long-term ecological impacts such as effects over 2 days, 4 days, 6 days, and one week for long-term chronic exposure. Moreover, the study may have used concentrations that do not accurately reflect environmental levels, either being too high or too low compared to what is typically found in polluted habitats. Addressing these limitations in future research could provide a more comprehensive understanding of the ecological risks posed by heavy metals and nanoparticles.
5. Conclusions
Our results indicate that both HMs and NPs have statistically significant toxic effects on the selected ciliate species. In particular:
- E. aediculatus shows different sensitivities to the two types of pollutants, with a higher resistance to HMs than to NPs. Furthermore, both HMs and NPs can induce effective antioxidant responses in E. aediculatus, as evidenced by an increase in antioxidant properties and activity.
- Despite being exposed to oxidative stress, E. aediculatus exhibits a strong response with greater effectiveness.
- Various antioxidant assays reveal a significantly increased level of antioxidant activity and free radical scavenging activity in E. aediculatus when exposed to both single and bimetallic mixtures.
- In conclusion, our results suggest that E. aediculatus can be used as a bioindicator organism for the detection of the bioavailable fraction of various toxic pollutants, such as HMs and NPs, in real environmental samples. The observed differential sensitivity of this species to the toxic effects of HMs and NPs suggests that they can be used in the development of rapid, simple, and cost-effective ciliate test arrays for the detection of specific pollutants in different environmental matrices.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.L.T.; methodology, G.R.V., A.C., F.D., D.B., S.K., and A.L.T.; software, G.R.V., A.C., and F.D.; validation, G.R.V., A.C., F.D., D.B., S.K., and A.L.T.; formal analysis, G.R.V., A.C., D.B., S.K. and A.L.T.; investigation, G.R.V., A.C., and A.L.T.; writing—original draft preparation, G.R.V.; writing—review and editing, A.C., F.D., D.B., S.K., and A.L.T.; supervision; A.L.T.; funding acquisition, A.L.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the 2017 FFABR—”Fund for Financing Basic Research Activities”—of the Italian Ministry of Education (BVI120008) to A.L.T.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study did not require ethical approval according to the legislation in force—that is, Directive2010/63/EU of the European Parliament and of the Council.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data are available when required under the responsibility of the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to privacy.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Amoatey, P.; Baawain, M.S. Effects of pollution on freshwater aquatic organisms. Water Environ. Res. 2019, 91, 1272–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadim, M.K.; Risjani, Y. Biomarker for monitoring heavy metal pollution in aquatic environment: An overview toward molecular perspectives. Emerg. Contam. 2022, 8, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Liu, W. Emerging investigator series: Metal nanoparticles in freshwater: Transformation, bioavailability and effects on invertebrates. Environ. Sci. Nano 2022, 9, 2237–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, K.E.; Thomas, S.M.; Bodour, A.A. Prioritizing research for trace pollutants and emerging contaminants in the freshwater environment. Environ. Pollut. 2010, 158, 3462–3471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, J.; Zhai, M.; Liu, Q.; Sun, J.; Guo, J. Residues of organochlorine pesticides (OCPs) in upper reach of the Huaihe River, East China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2011, 74, 2252–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puri, M.; Gandhi, K.; Kumar, M.S. Emerging environmental contaminants: A global perspective on policies and regulations. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 332, 117344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Deng, Q.; Bai, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, N.; Gong, Y. Management system for engineering and decoration waste: An exploratory study in Shenzhen. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 314, 115085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Somasundaram, S.; Abraham, J.S.; Maurya, S.; Toteja, R.; Gupta, R.; Makhija, S. Molecular characterization and transcriptional modulation of stress-responsive genes under heavy metal stress in freshwater ciliate, Euplotes aediculatus. Ecotoxicology 2022, 31, 271–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovley, D.R. Fe (III) and Mn (IV) reduction. In Environmental Microbe-Metal Interactions; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2000; pp. 1–30. [Google Scholar]
- Beveridge, T.; Hughes, M.; Lee, H.; Leung, K.; Poole, R.; Savvaidis, I.; Silver, S.; Trevors, J. Metal-microbe interactions: Contemporary approaches. Adv. Microb. Physiol. 1996, 38, 177–243. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Chen, B.; Fath, B.D. Ecological risk assessment on the system scale: A review of state-of-the-art models and future perspectives. Ecol. Model. 2013, 250, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, Y.; Shan, B.; Song, Z. Pollution, toxicity, and ecological risk of heavy metals in surface river sediments of a large basin undergoing rapid economic development. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2017, 36, 1149–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkatesan, R.; Rajeswari, N. ZnO/PBAT nanocomposite films: Investigation on the mechanical and biological activity for food packaging. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2017, 28, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corsi, I.; Cherr, G.N.; Lenihan, H.S.; Labille, J.; Hassellov, M.; Canesi, L.; Dondero, F.; Frenzilli, G.; Hristozov, D.; Puntes, V. Common strategies and technologies for the ecosafety assessment and design of nanomaterials entering the marine environment. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 9694–9709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Libralato, G.; Devoti, A.C.; Zanella, M.; Sabbioni, E.; Mičetić, I.; Manodori, L.; Pigozzo, A.; Manenti, S.; Groppi, F.; Ghirardini, A.V. Phytotoxicity of ionic, micro-and nano-sized iron in three plant species. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2016, 123, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vale, G.; Mehennaoui, K.; Cambier, S.; Libralato, G.; Jomini, S.; Domingos, R.F. Manufactured nanoparticles in the aquatic environment-biochemical responses on freshwater organisms: A critical overview. Aquat. Toxicol. 2016, 170, 162–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbas, Q.; Yousaf, B.; Ullah, H.; Ali, M.U.; Ok, Y.S.; Rinklebe, J. Environmental transformation and nano-toxicity of engineered nano-particles (ENPs) in aquatic and terrestrial organisms. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 50, 2523–2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azhar, W.; Khan, A.R.; Salam, A.; Ulhassan, Z.; Qi, J.; Shah, G.; Liu, Y.; Chunyan, Y.; Yang, S.; Gan, Y. Ethylene accelerates copper oxide nanoparticle-induced toxicity at physiological, biochemical, and ultrastructural levels in rice seedlings. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 26137–26149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Wang, X.; Hoang, S.A.; Bolan, N.S.; Kirkham, M.; Liu, J.; Xia, X.; Li, Y. Silver nanoparticles in aquatic sediments: Occurrence, chemical transformations, toxicity, and analytical methods. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 418, 126368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Castro, I.; Molina, L.; Prieto-Fernández, M.-Á.; Segura, A. Past, present and future trends in the remediation of heavy-metal contaminated soil-Remediation techniques applied in real soil-contamination events. Heliyon 2023, 9, e16692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garg, V.; Arora, A.; Prakash, A. A Review on Bioremediation Using Nanobiotechnology and Microbial Heavy Metal Resistance Mechanisms. Curr. Mater. Sci. Former. Recent Pat. Mater. Sci. 2024, 17, 289–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valbonesi, A.; Luporini, P. Description of two new species of Euplotes and Euplotes rariseta from Antarctica. Polar Biol. 1990, 11, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, A.; Patterson, D.J.; Dunthorn, M.; Clamp, J.C.; Achilles-Day, U.E.; Aescht, E.; Al-Farraj, S.A.; Al-Quraishy, S.; Al-Rasheid, K.; Carr, M.; et al. Beyond the “Code”: A guide to the description and documentation of biodiversity in ciliated protists (Alveolata, Ciliophora). J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 2017, 64, 539–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bharti, D.; Santosh, K.; Federico, B.; Ortenzi, C.; Montanari, A.; Pablo, Q.-A.; La Terza, A. Free living ciliated protists from the chemoautotrophic cave ecosystem of Frasassi (Italy). Subterr. Biol. 2022, 44, 167–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madoni, P.; Davoli, D.; Gorbi, G.; Vescovi, L. Toxic effect of heavy metals on the activated sludge protozoan community. Water Res. 1996, 30, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulgentini, L.; Passini, V.; Colombetti, G.; Miceli, C.; La Terza, A.; Marangoni, R. UV radiation and visible light induce hsp70 gene expression in the antarctic psychrophilic ciliate euplotes focardii. Microb. Ecol. 2015, 70, 372–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Terza, A.; Papa, G.; Miceli, C.; Luporini, P. Divergence between two Antarctic species of the ciliate Euplotes, E. focardii and E. nobilii, in the expression of heat-shock protein 70 genes. Mol. Ecol. 2001, 10, 1061–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutiérrez, J.C.; Martín-González, A.; Díaz, S.; Ortega, R. Ciliates as a potential source of cellular and molecular biomarkers/biosensors for heavy metal pollution. Eur. J. Protistol. 2003, 39, 461–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-González, A.; Díaz, S.; Borniquel, S.; Gallego, A.; Gutiérrez, J.C. Cytotoxicity and bioaccumulation of heavy metals by ciliated protozoa isolated from urban wastewater treatment plants. Res. Microbiol. 2006, 157, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Terza, A.; Barchetta, S.; Buonanno, F.; Ballarini, P.; Miceli, C. The protozoan ciliate Tetrahymena thermophila as biosensor of sublethal levels of toxicants in the soil. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2008, 17, 1144–1150. [Google Scholar]
- Gertler, C.; Näther, D.J.; Gerdts, G.; Malpass, M.C.; Golyshin, P.N. A mesocosm study of the changes in marine flagellate and ciliate communities in a crude oil bioremediation trial. Microb. Ecol. 2010, 60, 180–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorusso, C.; Calisi, A.; Sanchez-Hernandez, J.C.; Varodi, C.; Pogăcean, F.; Pruneanu, S.; Dondero, F. Carbon nanomaterial functionalization with pesticide-detoxifying carboxylesterase. Chemosphere 2022, 309, 136594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Terza, A.; Miceli, C.; Luporini, P. The gene for the heat-shock protein 70 of Euplotes focardii, an Antarctic psychrophilic ciliate. Antarct. Sci. 2004, 16, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baun, A.; Hartmann, N.B.; Grieger, K.; Kusk, K.O. Ecotoxicity of engineered nanoparticles to aquatic invertebrates: A brief review and recommendations for future toxicity testing. Ecotoxicology 2008, 17, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahru, A.; Dubourguier, H.-C.; Blinova, I.; Ivask, A.; Kasemets, K. Biotests and biosensors for ecotoxicology of metal oxide nanoparticles: A minireview. Sensors 2008, 8, 5153–5170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.-W.; Wang, Y.; Huang, B.; Wang, N.-X.; Wei, Z.-B.; Luo, J.; Miao, A.-J.; Yang, L.-Y. TiO2 nanoparticles act as a carrier of Cd bioaccumulation in the ciliate Tetrahymena thermophila. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 7568–7575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djibril Sekou, K.; Hannah Akasi, A.; Bachir Yaou, B.; Irédon, A.; Manka, M.; Patel, H. A Review on the Impact of Nanoparticles on Heavy Metals in the Soils. SSRG Int. J. Agric. Environ. Sci. 2023, 10, 16–28. [Google Scholar]
- Mortimer, M.; Kasemets, K.; Vodovnik, M.a.; Marinšek-Logar, R.; Kahru, A. Exposure to CuO nanoparticles changes the fatty acid composition of protozoa Tetrahymena thermophila. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 6617–6624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djibril Sekou, K.; Patel, H. A Review on the interaction between Nanoparticles and Toxic metals in Soil: Meta-analysis of their effects on soil, plants and human health. Soil Sediment Contam. Int. J. 2023, 32, 417–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-H.; Jung, M.-Y.; Lee, Y.-M. Effect of heavy metals on the antioxidant enzymes in the marine ciliate Euplotes crassus. Toxicol. Environ. Health Sci. 2011, 3, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomiero, A.; Dagnino, A.; Nasci, C.; Viarengo, A. The use of protozoa in ecotoxicology: Application of multiple endpoint tests of the ciliate E. crassus for the evaluation of sediment quality in coastal marine ecosystems. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 442, 534–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.-H.; Kim, S.-J.; Lee, J.-S.; Lee, Y.-M. Acute effects of heavy metals on the expression of glutathione-related antioxidant genes in the marine ciliate Euplotes crassus. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 85, 455–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marín-Leal, J.C.; Rincón-Miquilena, N.J.; Díaz-Borrego, L.C.; Pire-Sierra, M.C. Acute toxicity of potentially toxic elements on ciliated protozoa from Lake Maracaibo (Venezuela). Acta Limnol. Bras. 2022, 34, e21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Fan, X.; Gong, Z.; Gao, X.; Wang, Y.; Ni, B. The toxic effects of Cu and CuO nanoparticles on Euplotes aediculatus. Microb. Ecol. 2023, 85, 544–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyake, A. Physiology and biochemistry of conjugation in ciliates. Biochem. Physiol. Protozoa 1981, 2, 125–198. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, C.; Lee, J.; Soldo, A. Protocols in Protozoology; Society of Protozoology: Lawrence, KS, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Sprague, J.B. Measurement of pollutant toxicity to fish, I.I. Utilizing and applying bioassay results. Water Res. 1970, 4, 3–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravindran, C.; Varatharajan, G.R.; Rajasabapathy, R.; Vijayakanth, S.; Kumar, A.H.; Meena, R.M. A role for antioxidants in acclimation of marine derived pathogenic fungus (NIOCC 1) to salt stress. Microb. Pathog. 2012, 53, 168–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vattem, D.A.; Shetty, K. Solid-state production of phenolic antioxidants from cranberry pomace by Rhizopus oligosporus. Food Biotechnol. 2002, 16, 189–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yıldırım, A.; Mavi, A.; Kara, A.A. Determination of antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of Rumex crispus L. extracts. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 4083–4089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunchandy, E.; Rao, M. Oxygen radical scavenging activity of curcumin. Int. J. Pharm. 1990, 58, 237–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonker, M.J.; Svendsen, C.; Bedaux, J.J.; Bongers, M.; Kammenga, J.E. Significance testing of synergistic/antagonistic, dose level-dependent, or dose ratio-dependent effects in mixture dose-response analysis. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. Int. J. 2005, 24, 2701–2713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Vijver, M.G.; Qiu, H.; Baas, J.; Peijnenburg, W.J. Statistically significant deviations from additivity: What do they mean in assessing toxicity of mixtures? Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 122, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belz, R.G.; Cedergreen, N.; Sørensen, H. Hormesis in mixtures—Can it be predicted? Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 404, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Wang, D.; Lin, Z.; An, Q.; Yin, C.; Huang, Q. Prediction of mixture toxicity from the hormesis of a single chemical: A case study of combinations of antibiotics and quorum-sensing inhibitors with gram-negative bacteria. Chemosphere 2016, 150, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, X.; Xiao, X.; He, Y.; Hu, L.; Hu, C.; Huang, X. Hormetic effects of metal ions upon V. fischeri and the application of a new parameter for the quantitative assessment of hormesis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 322, 454–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández-Flores, S.; Santos-Medrano, G.E.; Rico-Martínez, R. Integral Study of Paramecium caudatum Acute and Chronic Toxicity, Sites of Entry and Distribution, Bioconcentration and Body Burdens of Five Metals. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2023, 111, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baek, Y.-W.; An, Y.-J. Microbial toxicity of metal oxide nanoparticles (CuO, NiO, ZnO, and Sb2O3) to Escherichia coli, Bacillus subtilis, and Streptococcus aureus. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 1603–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maurer-Jones, M.A.; Gunsolus, I.L.; Murphy, C.J.; Haynes, C.L. Toxicity of engineered nanoparticles in the environment. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 3036–3049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Liao, A.; Hu, S.; Zheng, Y.; Liang, S.; Han, S.; Lin, Y. Acute and chronic toxicity of binary mixtures of bisphenol A and heavy metals. Toxics 2022, 10, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karri, V.; Kumar, V.; Ramos, D.; Oliveira, E.; Schuhmacher, M. An in vitro cytotoxic approach to assess the toxicity of heavy metals and their binary mixtures on hippocampal HT-22 cell line. Toxicol. Lett. 2018, 282, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Xu, A.; Liu, Y. Combined biological effects of silver nanoparticles and heavy metals in different target cell lines. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 16324–16331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahamed, M.; Akhtar, M.J.; Alaizeri, Z.M.; Alhadlaq, H.A. TiO2 nanoparticles potentiated the cytotoxicity, oxidative stress and apoptosis response of cadmium in two different human cells. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 10425–10435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansour, W.A.; Abdelsalam, N.R.; Tanekhy, M.; Khaled, A.A.; Mansour, A.T. Toxicity, inflammatory and antioxidant genes expression, and physiological changes of green synthesis silver nanoparticles on Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) fingerlings. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2021, 247, 109068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wells, P.G.; Depledge, M.H.; Butler, J.N.; Manock, J.J.; Knap, A.H. Rapid toxicity assessment and biomonitoring of marine contaminants—Exploiting the potential of rapid biomarker assays and microscale toxicity tests. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2001, 42, 799–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pudpong, S.; Chantangsi, C. Effects of Four Heavy Metals on Cell Morphology and Survival Rate of the Ciliate Bresslauides sp`. Trop. Nat. Hist. 2015, 15, 117–125. [Google Scholar]
- Díaz, S.; Martín-González, A.; Gutiérrez, J.C. Evaluation of heavy metal acute toxicity and bioaccumulation in soil ciliated protozoa. Environ. Int. 2006, 32, 711–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rico, D.; Martín-González, A.; Díaz, S.; de Lucas, P.; Gutiérrez, J.-C. Heavy metals generate reactive oxygen species in terrestrial and aquatic ciliated protozoa. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2009, 149, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blinova, I.; Ivask, A.; Heinlaan, M.; Mortimer, M.; Kahru, A. Ecotoxicity of nanoparticles of CuO and ZnO in natural water. Environ. Pollut. 2010, 158, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rainbow, P.; Amiard-Triquet, C.; Amiard, J.; Smith, B.; Langston, W. Observations on the interaction of zinc and cadmium uptake rates in crustaceans (amphipods and crabs) from coastal sites in UK and France differentially enriched with trace metals. Aquat. Toxicol. 2000, 50, 189–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barata, C.; Markich, S.J.; Baird, D.J.; Taylor, G.; Soares, A.M. Genetic variability in sublethal tolerance to mixtures of cadmium and zinc in clones of Daphnia magna Straus. Aquat. Toxicol. 2002, 60, 85–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, T.D.; Lydy, M.J. Increased toxicity to invertebrates associated with a mixture of atrazine and organophosphate insecticides. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. Int. J. 2002, 21, 1507–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cedergreen, N.; Christensen, A.M.; Kamper, A.; Kudsk, P.; Mathiassen, S.K.; Streibig, J.C.; Sørensen, H. A review of independent action compared to concentration addition as reference models for mixtures of compounds with different molecular target sites. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. Int. J. 2008, 27, 1621–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cedergreen, N.; Kamper, A.; Streibig, J.C. Is prochloraz a potent synergist across aquatic species? A study on bacteria, daphnia, algae and higher plants. Aquat. Toxicol. 2006, 78, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, E.; Baas, J.; Van Gestel, C.A. Interaction between nickel and cobalt toxicity in Enchytraeus crypticus is due to competitive uptake. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2015, 34, 328–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franklin, N.M.; Stauber, J.L.; Lim, R.P.; Petocz, P. Toxicity of metal mixtures to a tropical freshwater alga (Chlorella sp.): The effect of interactions between copper, cadmium, and zinc on metal cell binding and uptake. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. Int. J. 2002, 21, 2412–2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farley, K.J.; Meyer, J.S. Metal mixture modeling evaluation project: 3. Lessons learned and steps forward. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2015, 34, 821–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuda, T.; Tsunekawa, M.; Goto, H.; Araki, Y. Antioxidant properties of four edible algae harvested in the Noto Peninsula, Japan. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2005, 18, 625–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawidowicz, A.L.; Wianowska, D.; Olszowy, M. On practical problems in estimation of antioxidant activity of compounds by DPPH method (Problems in estimation of antioxidant activity). Food Chem. 2012, 131, 1037–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanaye, S.; Pise, N.; Pawar, A.; Parab, P.; Sreepada, R.; Pawar, H.; Murugan, A. Total phenolic Content and In-Vitro Antioxidant Activities from Methanolic Extract of Alligator Pipefish, Syngnathoides biaculeatus (Bloch, 1785). 2015. Available online: http://drs.nio.org/drs/handle/2264/7679 (accessed on 20 February 2015).
- Rabiei, K.; Bekhradnia, S.; Nabavi, S.; Nabavi, S.; Ebrahimzadeh, M. Antioxidant activity of polyphenol and ultrasonic extracts from fruits of Crataegus pentagyna subsp. elburensis. Nat. Prod. Res. 2012, 26, 2353–2357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).