How Does the Concentration of Technetium-99m Radiolabeled Gold Nanoparticles Affect Their In Vivo Biodistribution?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemical Reagents
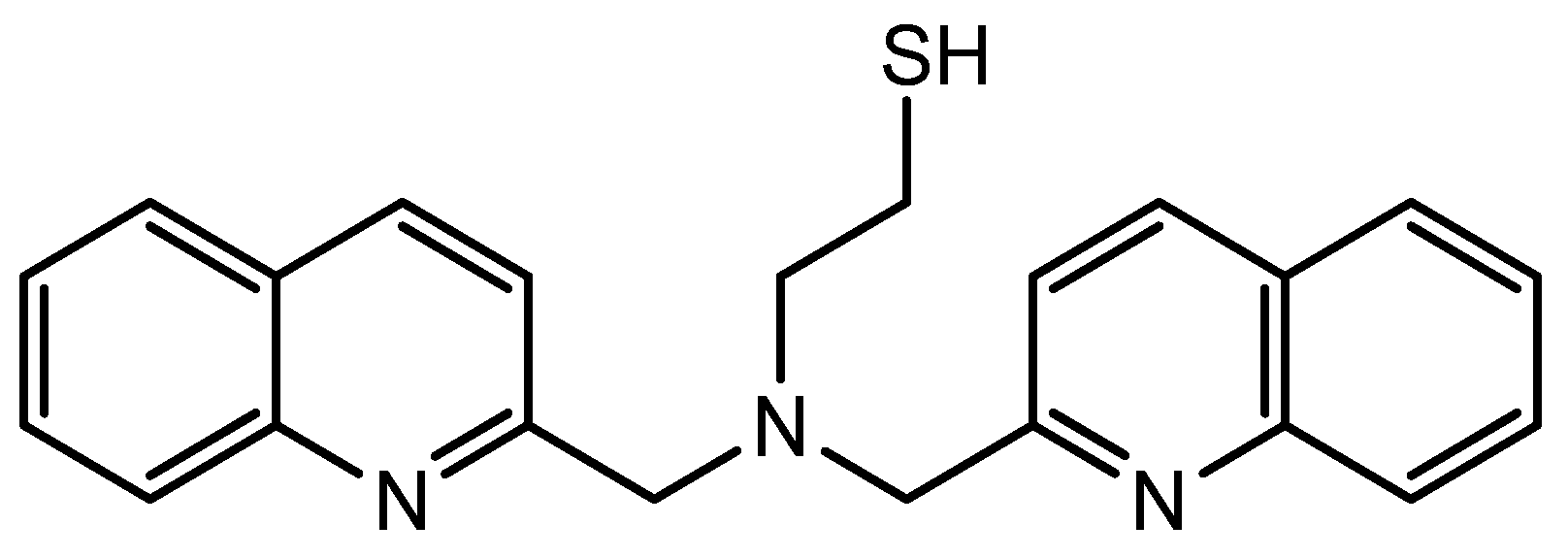
2.2. Functionalization of Gold Nanoparticles with a Thiol Tridentate Ligand
2.3. Characterization of AuNPs by Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS)
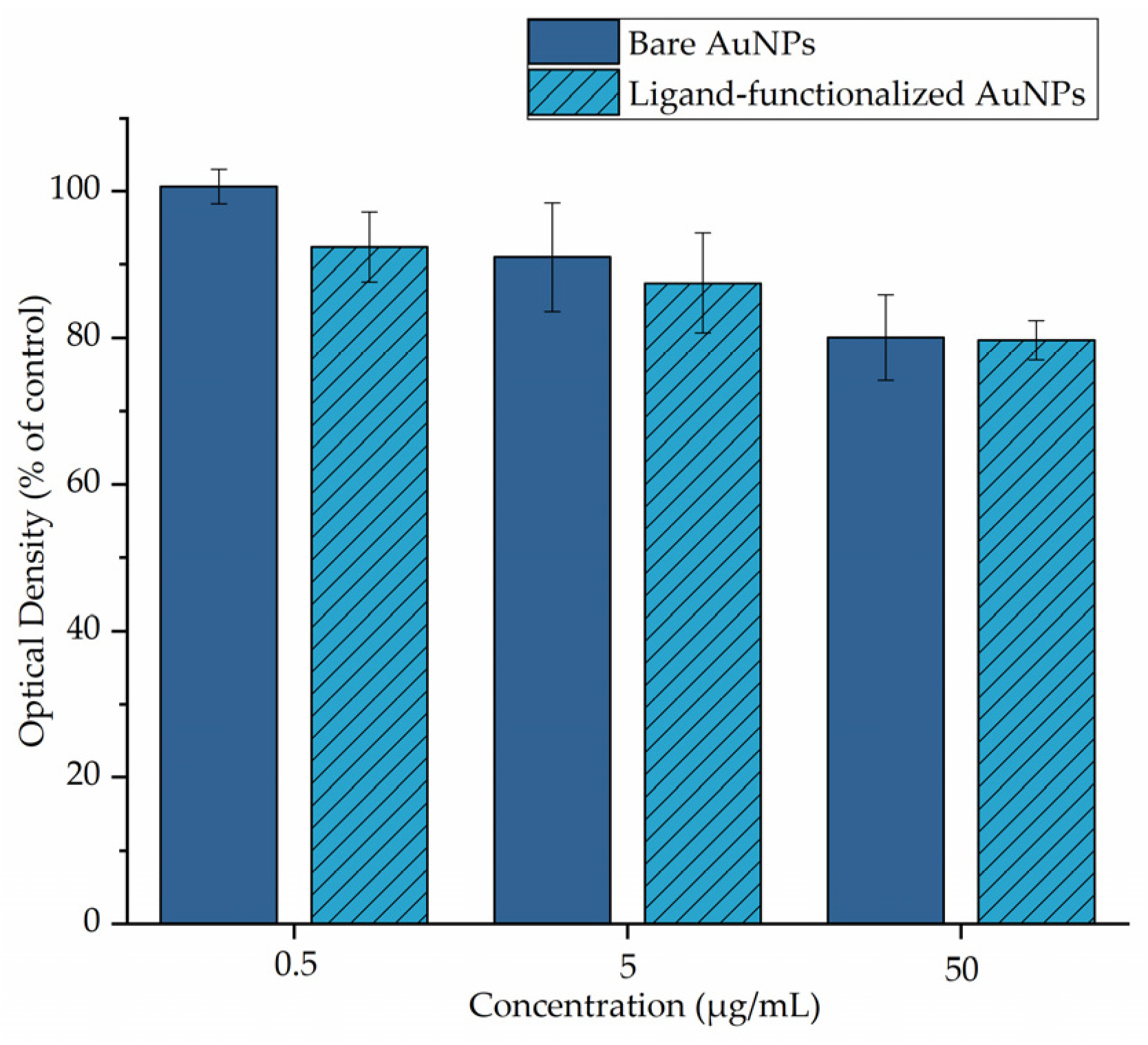
2.4. Cell Viability by MTT Assay
2.5. Radiolabeling with [99mTc][Tc(H2O)3(CO)3]+
2.6. In Vitro Stability Studies
2.7. Ex Vivo Biodistribution Studies
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of AuNPs by DLS
3.2. MTT [3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-Diphenyltetrazolium Bromide] Assay
3.3. Functionalization and Radiolabeling of AuNPs with [99mTc][Tc(H2O)3(CO)3]+
3.4. Stability Studies
3.5. Biodistribution Studies
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Silva, F.; Cabral Campello, M.P.; Paulo, A. Radiolabeled Gold Nanoparticles for Imaging and Therapy of Cancer. Materials 2020, 14, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dreaden, E.C.; Austin, L.A.; Mackey, M.A.; El-Sayed, M.A. Size Matters: Gold Nanoparticles in Targeted Cancer Drug Delivery. Ther. Deliv. 2012, 3, 457–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuckerman, J.E.; Choi, C.H.J.; Han, H.; Davis, M.E. Polycation-siRNA Nanoparticles Can Disassemble at the Kidney Glomerular Basement Membrane. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 3137–3142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoshyar, N.; Gray, S.; Han, H.; Bao, G. The Effect of Nanoparticle Size on in Vivo Pharmacokinetics and Cellular Interaction. Nanomedicine 2016, 11, 673–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulkarni, S.A.; Feng, S.-S. Effects of Particle Size and Surface Modification on Cellular Uptake and Biodistribution of Polymeric Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery. Pharm. Res. 2013, 30, 2512–2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraji, A.H.; Wipf, P. Nanoparticles in Cellular Drug Delivery. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 2950–2962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arvizo, R.R.; Miranda, O.R.; Moyano, D.F.; Walden, C.A.; Giri, K.; Bhattacharya, R.; Robertson, J.D.; Rotello, V.M.; Reid, J.M.; Mukherjee, P. Modulating Pharmacokinetics, Tumor Uptake and Biodistribution by Engineered Nanoparticles. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, 24374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balogh, L.; Nigavekar, S.S.; Nair, B.M.; Lesniak, W.; Zhang, C.; Sung, L.Y.; Kariapper, M.S.T.; El-Jawahri, A.; Llanes, M.; Bolton, B.; et al. Significant Effect of Size on the in Vivo Biodistribution of Gold Composite Nanodevices in Mouse Tumor Models. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2007, 3, 281–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moghimi, S.M.; Hunter, A.C.; Andresen, T.L. Factors Controlling Nanoparticle Pharmacokinetics: An Integrated Analysis and Perspective. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2012, 52, 481–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonavane, G.; Tomoda, K.; Makino, K. Biodistribution of Colloidal Gold Nanoparticles after Intravenous Administration: Effect of Particle Size. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2008, 66, 274–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohane, D.S.; Tse, J.Y.; Yeo, Y.; Padera, R.; Shubina, M.; Langer, R. Biodegradable Polymeric Microspheres and Nanospheres for Drug Delivery in the Peritoneum. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2006, 77A, 351–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Rao, Y.; Liu, X.; Sun, L.; Gong, J.; Zhang, H.; Shen, L.; Bao, A.; Yang, H. Administration Route Governs the Therapeutic Efficacy, Biodistribution and Macrophage Targeting of Anti-Inflammatory Nanoparticles in the Lung. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2021, 19, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Black, K.C.L.; Wang, Y.; Luehmann, H.P.; Cai, X.; Xing, W.; Pang, B.; Zhao, Y.; Cutler, C.S.; Wang, L.V.; Liu, Y.; et al. Radioactive 198Au-Doped Nanostructures with Different Shapes for In Vivo Analyses of Their Biodistribution, Tumor Uptake, and Intratumoral Distribution. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 4385–4394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Same, S.; Aghanejad, A.; Akbari Nakhjavani, S.; Barar, J.; Omidi, Y. Radiolabeled Theranostics: Magnetic and Gold Nanoparticles. Bioimpacts 2016, 6, 169–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Connor, D.M.; Broome, A.-M. Gold Nanoparticles for the Delivery of Cancer Therapeutics. Adv. Cancer Res. 2018, 139, 163–184. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fan, M.; Han, Y.; Gao, S.; Yan, H.; Cao, L.; Li, Z.; Liang, X.-J.; Zhang, J. Ultrasmall Gold Nanoparticles in Cancer Diagnosis and Therapy. Theranostics 2020, 10, 4944–4957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, E.J.; Choi, D.G.; Shim, M.S. Targeted and Effective Photodynamic Therapy for Cancer Using Functionalized Nanomaterials. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2016, 6, 297–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Zhao, L.; Yang, J.; Chen, L.; Shi, J.; Zhao, J.; Shi, X. 99mTc-Labeled Polyethylenimine-Entrapped Gold Nanoparticles with pH-Responsive Charge Conversion Property for Enhanced Dual Mode SPECT/CT Imaging of Cancer Cells. Langmuir 2019, 35, 13405–13412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Avila, E.; Ferro-Flores, G.; Ocampo-García, B.E.; De León-Rodríguez, L.M.; Santos-Cuevas, C.L.; García-Becerra, R.; Medina, L.A.; Gómez-Oliván, L. Multimeric System of 99mTc-Labeled Gold Nanoparticles Conjugated to c[RGDfK(C)] for Molecular Imaging of Tumor α(v)β(3) Expression. Bioconjugate Chem. 2011, 22, 913–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanda, N.; Kattumuri, V.; Shukla, R.; Zambre, A.; Katti, K.; Upendran, A.; Kulkarni, R.R.; Kan, P.; Fent, G.M.; Casteel, S.W.; et al. Bombesin Functionalized Gold Nanoparticles Show in Vitro and in Vivo Cancer Receptor Specificity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 8760–8765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xiong, Z.; Xu, X.; Luo, Y.; Peng, C.; Shen, M.; Shi, X. 99mTc-Labeled Multifunctional Low-Generation Dendrimer-Entrapped Gold Nanoparticles for Targeted SPECT/CT Dual-Mode Imaging of Tumors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 19883–19891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alric, C.; Miladi, I.; Kryza, D.; Taleb, J.; Lux, F.; Bazzi, R.; Billotey, C.; Janier, M.; Perriat, P.; Roux, S.; et al. The Biodistribution of Gold Nanoparticles Designed for Renal Clearance. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 5930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apostolopoulou, A.; Chiotellis, A.; Salvanou, E.-A.; Makrypidi, K.; Tsoukalas, C.; Kapiris, F.; Paravatou-Petsotas, M.; Papadopoulos, M.; Pirmettis, I.C.; Koźmiński, P.; et al. Synthesis and In Vitro Evaluation of Gold Nanoparticles Functionalized with Thiol Ligands for Robust Radiolabeling with 99mTc. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dexter, D.L.; Kowalski, H.M.; Blazar, B.A. Heterogeneity of Tumor Cells from a Single Mouse Mammary Tumor. Cancer Res. 1978, 38, 3174–3181. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Krystofiak, E.S.; Matson, V.Z.; Steeber, D.A.; Oliver, J.A. Elimination of Tumor Cells Using Folate Receptor Targeting by Antibody-Conjugated, Gold-Coated Magnetite Nanoparticles in a Murine Breast Cancer Model. J. Nanomater. 2012, 2012, 431012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heppner, G.H.; Miller, F.R.; Malathy Shekhar, P. Nontransgenic Models of Breast Cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2000, 2, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prokop, A. (Ed.) Intracellular Delivery: Fundamentals and Applications; Fundamental Biomedical Technologies; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; Volume 5, pp. 73–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Q.; Liu, X.; Yang, T.; Cui, K.; Kong, L.; Yang, C.; Zhang, Z. Nanomedicine for Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: The Latest Application, Targeting Strategy, and Rational Design. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2021, 11, 3060–3091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Upton, R.; Doolette, D. Kinetic Aspects of Drug Disposition in the Lungs. Clin. Exp. Pharma. Physio. 1999, 26, 381–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brun, E.; Sicard-Roselli, C. Could Nanoparticle Corona Characterization Help for Biological Consequence Prediction? Cancer Nano 2014, 5, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forest, V.; Pourchez, J. Preferential Binding of Positive Nanoparticles on Cell Membranes Is Due to Electrostatic Interactions: A Too Simplistic Explanation That Does Not Take into Account the Nanoparticle Protein Corona. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 70, 889–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Concentration of Functionalized AuNPs | Hydrodynamic Diameter (nm) | Zeta Potential (mV) |
|---|---|---|
| 312.5 μg/mL | 198.0 | +18.0 ± 0.4 |
| 312.5 × 10−1 μg/mL | 168.8 | −34.0 ± 0.6 |
| 312.5 × 10−2 μg/mL | 140.9 | −17.3 ± 0.4 |
| 312.5 × 10−3 μg/mL | 112.8 | −11.0 ± 0.5 |
| Concentration of Radiolabeled AuNPs | Radiochemical Purity (%) (1 h) | Radiochemical Purity (%) (24 h) |
|---|---|---|
| 500 μg/radiolabeling | 98.31 ± 1.43 | 98.51 ± 2.36 |
| 500 × 10−1 μg/radiolabeling | 97.76 ± 2.62 | 97.59 ± 0.55 |
| 500 × 10−2 μg/radiolabeling | 94.48 ± 3.21 | 96.42 ± 1.89 |
| 500 × 10−3 μg/radiolabeling | 97.75 ± 1.26 | 97.8 ± 1.62 |
| Concentration of Radiolabeled AuNPs | Cysteine Challenge (%) (1 h) | Cysteine Challenge (%) (24 h) |
|---|---|---|
| 500 μg/radiolabeling | 97.46 ± 2.04 | 95.15 ± 1.69 |
| 500 × 10−1 μg/radiolabeling | 95.63 ± 1.83 | 97.36 ± 2.14 |
| 500 × 10−2 μg/radiolabeling | 91.19 ± 1.81 | 94.56 ± 2.84 |
| 500 × 10−3 μg/radiolabeling | 96.84 ± 1.45 | 96.51 ± 2.78 |
| Concentration of Radiolabeled AuNPs | Histidine Challenge (%) (1 h) | Histidine Challenge (%) (24 h) |
|---|---|---|
| 500 μg/radiolabeling | 98.52 ± 1.09 | 98.74 ± 0.52 |
| 500 × 10−1 μg/radiolabeling | 94.14 ± 4.23 | 97.56 ± 1.23 |
| 500 × 10−2 μg/radiolabeling | 94.38 ± 2.12 | 93.65 ± 3.12 |
| 500 × 10−3 μg/radiolabeling | 96.02 ± 3.21 | 95.12 ± 1.80 |
| Concentration of Radiolabeled AuNPs | Serum Challenge (%) (1 h) | Serum Challenge (%) (24 h) |
|---|---|---|
| 500 μg/radiolabeling | 99.01 ± 0.63 | 98.47 ± 0.66 |
| 500 × 10−1 μg/radiolabeling | 96.41 ± 1.12 | 96.23 ± 1.52 |
| 500 × 10−2 μg/radiolabeling | 94.52 ± 1.69 | 97.21 ± 0.41 |
| 500 × 10−3 μg/radiolabeling | 97.81 ± 1.45 | 94.23 ± 1.48 |
| 1 h | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Organ | 312.5 μg/mL | 312.5 × 10−1 μg/mL | 312.5 × 10−2 μg/mL | 312.5 × 10−3 μg/mL |
| Blood | 0.26 ± 0.01 | 1.90 ± 0.35 | 9.61 ± 1.25 | 4.40 ± 0.75 |
| Liver | 10.95 ± 0.73 | 59.08 ± 22.69 | 59.19 ± 2.50 | 34.54 ± 1.79 |
| Heart | 1.73 ± 0.49 | 2.52 ± 0.48 | 3.72 ± 0.11 | 5.65 ± 1.64 |
| Kidney | 8.96 ± 0.82 | 7.29 ± 0.88 | 16.33 ± 1.96 | 7.40 ± 1.23 |
| Stomach | 0.92 ± 0.19 | 1.97 ± 1.06 | 2.68 ± 1.29 | 2.18 ± 0.51 |
| Intestine | 0.85 ± 0.22 | 10.48 ± 4.39 | 25.49 ± 14.79 | 4.13 ± 3.41 |
| Spleen | 5.20 ± 1.54 | 28.10 ± 6.61 | 11.77 ± 4.01 | 11.83 ± 2.30 |
| Muscle | 0.24 ± 0.07 | 0.47 ± 0.22 | 0.84 ± 0.11 | 0.76 ± 0.21 |
| Lung | 153.83 ± 49.40 | 86.32 ± 17.33 | 47.31 ± 8.36 | 105.21 ± 32.37 |
| Bone | 0.26 ± 0.09 | 0.95 ± 0.23 | 1.81 ± 0.63 | 0.97 ± 0.27 |
| Pancreas | 0.45 ± 0.11 | 0.63 ± 0.15 | 1.63 ± 0.24 | 1.24 ± 0.27 |
| Brain | 0.21 ± 0.03 | 0.23 ± 0.09 | 0.09 ± 0.06 | 0.44 ± 0.25 |
| 4 h | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Organ | 312.5 μg/mL | 312.5 × 10−1 μg/mL | 312.5 × 10−2 μg/mL | 312.5 × 10−3 μg/mL |
| Blood | 0.18 ± 0.03 | 1.21 ± 0.24 | 1.77 ± 0.06 | 1.08 ± 0.12 |
| Liver | 14.78 ± 6.81 | 32.19 ± 16.43 | 43.05 ± 10.70 | 22.67 ± 7.38 |
| Heart | 2.19 ± 0.39 | 2.02 ± 0.51 | 2.53 ± 0.74 | 5.11 ± 1.01 |
| Kidney | 7.35 ± 1.51 | 4.82 ± 0.42 | 7.85 ± 0.38 | 7.32 ± 0.62 |
| Stomach | 1.70 ± 1.44 | 2.56 ± 1.07 | 4.11 ± 0.88 | 3.02 ± 1.15 |
| Intestine | 2.74 ± 1.07 | 16.99 ± 6.29 | 32.66 ± 1.27 | 17.98 ± 4.99 |
| Spleen | 11.10 ± 4.10 | 13.95 ± 1.17 | 14.90 ± 4.73 | 18.37 ± 5.60 |
| Muscle | 0.41 ± 0.08 | 0.28 ± 0.12 | 0.84 ± 0.48 | 0.57 ± 0.11 |
| Lung | 370.68 ± 25.73 | 104.32 ± 20.98 | 59.79 ± 12.58 | 119.90 ± 8.64 |
| Bone | 0.64 ± 0.11 | 0.68 ± 0.10 | 1.44 ± 0.45 | 0.88 ± 0.17 |
| Pancreas | 0.50 ± 0.26 | 0.60 ± 0.41 | 0.66 ± 0.19 | 0.90 ± 0.29 |
| Brain | 0.28 ± 0.07 | 0.24 ± 0.11 | 0.16 ± 0.04 | 0.37 ± 0.12 |
| 24 h | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Organ | 312.5 μg/mL | 312.5 × 10−1 μg/mL | 312.5 × 10−2 μg/mL | 312.5 × 10−3 μg/mL |
| Blood | 0.08 ± 0.01 | 0.54 ± 0.11 | 0.83 ± 0.13 | 0.50 ± 0.06 |
| Liver | 9.89 ± 0.04 | 16.00 ± 4.46 | 23.69 ± 4.90 | 11.22 ± 2.77 |
| Heart | 0.78 ± 0.27 | 0.77 ± 0.16 | 1.62 ± 0.18 | 1.43 ± 0.37 |
| Kidney | 2.32 ± 0.16 | 3.09 ± 0.38 | 5.91 ± 0.88 | 2.48 ± 0.36 |
| Stomach | 0.30 ± 0.12 | 0.48 ± 0.01 | 0.73 ± 0.22 | 0.56 ± 0.18 |
| Intestine | 0.69 ± 0.41 | 0.58 ± 0.12 | 1.09 ± 0.07 | 0.87 ± 0.55 |
| Spleen | 9.33 ± 2.52 | 8.38 ± 3.12 | 6.59 ± 2.48 | 16.56 ± 4.12 |
| Muscle | 0.07 ± 0.02 | 0.12 ± 0.01 | 0.29 ± 0.04 | 0.18 ± 0.04 |
| Lung | 51.58 ± 0.54 | 19.56 ± 8.01 | 9.75 ± 2.63 | 10.27 ± 1.94 |
| Bone | 0.31 ± 0.07 | 0.46 ± 0.05 | 0.72 ± 0.16 | 0.73 ± 0.26 |
| Pancreas | 0.16 ± 0.09 | 0.33 ± 0.11 | 0.51 ± 0.11 | 0.25 ± 0.03 |
| Brain | 0.06 ± 0.05 | 0.19 ± 0.11 | 0.05 ± 0.01 | 0.08 ± 0.03 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Apostolopoulou, A.; Salvanou, E.-A.; Chiotellis, A.; Pirmettis, N.N.; Pirmettis, I.C.; Xanthopoulos, S.; Koźmiński, P.; Bouziotis, P. How Does the Concentration of Technetium-99m Radiolabeled Gold Nanoparticles Affect Their In Vivo Biodistribution? Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 4324. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14104324
Apostolopoulou A, Salvanou E-A, Chiotellis A, Pirmettis NN, Pirmettis IC, Xanthopoulos S, Koźmiński P, Bouziotis P. How Does the Concentration of Technetium-99m Radiolabeled Gold Nanoparticles Affect Their In Vivo Biodistribution? Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(10):4324. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14104324
Chicago/Turabian StyleApostolopoulou, Adamantia, Evangelia-Alexandra Salvanou, Aristeidis Chiotellis, Nektarios N. Pirmettis, Ioannis C. Pirmettis, Stavros Xanthopoulos, Przemysław Koźmiński, and Penelope Bouziotis. 2024. "How Does the Concentration of Technetium-99m Radiolabeled Gold Nanoparticles Affect Their In Vivo Biodistribution?" Applied Sciences 14, no. 10: 4324. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14104324
APA StyleApostolopoulou, A., Salvanou, E.-A., Chiotellis, A., Pirmettis, N. N., Pirmettis, I. C., Xanthopoulos, S., Koźmiński, P., & Bouziotis, P. (2024). How Does the Concentration of Technetium-99m Radiolabeled Gold Nanoparticles Affect Their In Vivo Biodistribution? Applied Sciences, 14(10), 4324. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14104324








