Abstract
Semantic segmentation stands as a prominent domain within remote sensing that is currently garnering significant attention. This paper introduces a pioneering semantic segmentation model based on TransUNet architecture with improved coordinate attention for remote-sensing imagery. It is composed of an encoding stage and a decoding stage. Notably, an enhanced and improved coordinate attention module is employed by integrating two pooling methods to generate weights. Subsequently, the feature map undergoes reweighting to accentuate foreground information and suppress background information. To address the issue of time complexity, this paper introduces an improvement to the transformer model by sparsifying the attention matrix. This reduces the computing expense of calculating attention, making the model more efficient. Additionally, the paper uses a combined loss function that is designed to enhance the training performance of the model. The experimental results conducted on three public datasets manifest the efficiency of the proposed method. The results indicate that it excels in delivering outstanding performance for semantic segmentation tasks pertaining to remote-sensing images.
1. Introduction
The processing and analysis of remote-sensing images have gained increasing importance in light of the rapid advancements in imaging technologies. Consequently, the automated extraction of essential information from remote-sensing images has emerged as a critical research domain within the field of remote-sensing image processing. In particular, semantic segmentation has proven to be one of the most significant advances in remote-sensing image technology [1,2,3], which is applied to a variety of fields, including environmental monitoring, land resource utilization, and urban planning. Compared with natural images, remote-sensing images exhibit the properties of high resolution, complex content, and large differences in object scale. Additionally, because of the intricate nature of the image content, segmentation accuracy is higher in real-world applications. Semantic segmentation of remote-sensing images presents a significant challenge due to the complexity of imaging, diverse object categories, and substantial scale variations among objects [4,5].
A remote-sensing image contains rich information about ground objects; how to accurately segment the real area is still a long-term challenge [6]. The traditional remote-sensing image segmentation methods usually use threshold segmentation [7], edge detection [8], pixel clustering [9], etc. The robustness of classic segmentation algorithms is poor, and deep semantic information is hard to extract. Deep learning has been developing quickly lately, and, as a result, it is becoming a necessary tool for computer vision [5]. Convolutional neural networks (CNNs) have strong learning abilities and can autonomously acquire rich spectral and spatial characteristics from images. Therefore, several scholars have successfully employed it in tasks related to remote-sensing image segmentation [10,11]. Different from traditional CNN, a full convolutional network (FCN) [12] can achieve pixel-level image classification. It replaces the fully connected layer of traditional CNNs and employs upsampling to restore the image to its original size for pixel-level segmentation. Semantic segmentation methods based on FCN are constantly developed and improved for remote-sensing images. For instance, Kampffmeyer et al. [13] introduced FCN to semantic segmentation to improve the segmentation effect and achieve pixel-to-pixel segmentation. Building upon FCN, Ronneberger et al. [14] established the U-Net model, utilizing a symmetric coding structure combined with feature fusion to enhance segmentation accuracy. U-Net has earned widespread adoption in image segmentation applications [15]. Another notable approach, SegNet [16] was proposed with a coding–decoding structure based on FCN and used atrous convolution and a conditional random field to improve segmentation outcomes.
The utilization of classical semantic segmentation networks for remote-sensing images often leads to non-ideal segmentation accuracy, primarily due to the substantial variations in target scale and the intricate nature of edge details. Therefore, semantic segmentation often utilizes two kinds of strategies. One strategy is multiscale feature fusion. For instance, Ma et al. [17] presented a convolutional network with a multiscale and skip connection structure to extract both shallow and deep features at varying scales, established upon the U-Net architecture. Similarly, Zhou et al. [18] presented a multiscale fusion model to obtain multimodal features using the nonlocal mechanism and dilated convolutional layers for remote-sensing images. Zeng et al. [19] proposed a new cross-scale semantic feature network by using the multiscale convolution module to obtain multiscale context from different receptive fields. Liu et al. [20] developed a multi-resolution attention model based on multiscale channel and spatial attention for exacting important features. Xu et al. [21] proposed a multiscale fusion network with atrous spatial pyramid pooling and varisized convolutions to effectively extract and fuse the features from multi-modal images. The other strategy is using attention mechanisms. For example, Ding et al. [22] designed a patch attention component to enhance the segmentation effect based on CNN. In another study, Liu et al. [23] constructed a novel spatial pyramid pooling network by combining the channel and position attention modules to address the issue of gradient disappearance for image segmentation. Furthermore, Li et al. [24] presented a synergistic attention architecture by combining both spatial and channel details to refine contextual representations for segmentation. Hu et al. [25] proposed a segmentation network with a global–local self-attention mechanism containing the global atrous self-attention and local window self-attention modules for considering both global and local contexts. This attention model resulted in improved segmentation accuracy. The transformer architecture has also been utilized in image segmentation. For example, Wang et al. [26] developed an innovative UNet-based model to enable the extraction of both global and local features, thereby improving urban scene segmentation. Based on the strategies, Xu et al. [27] developed a segmentation network based on a mixed-mask transformer mechanism and multiscale learning strategy to enhance the model’s performance. Wu et al. [28] put forward a CNN-transformer fusion network with a lightweight W/P transformer block to capture global information, which used the channel and spatial attention fusion module for semantic segmentation. A novel encoder–decoder fusion model [29] was also proposed by embedding multiscale and channel information into the transformer module, resulting in an impressive performance in semantic segmentation tasks.
Although there has been substantial advancement with deep networks for semantic segmentation, the majority of current techniques still face the following issues: The remote-sensing imagery does not contain significant discrepancies that make it challenging to gather detailed and contextual information for the complex process of classifying object pixels. Moreover, the varying number of samples across different categories within remote-sensing image datasets poses another significant challenge, with some categories containing significantly more samples than others. These imbalances can lead to issues such as class imbalance and inadequate representation of certain classes, which, in turn, can hinder the performance of classification algorithms. In addition, extensive features of remote-sensing images are extracted to improve the accuracy, resulting in an increase in the time complexity.
To address the aforementioned limitations, an enhanced semantic segmentation model is presented by utilizing the power of attention mechanisms for remote-sensing images. TransUNet [30] is used as a network backbone to extract the hierarchical semantic features. The proposed method builds two attention modules to emphasize the detailed and context information. The coordinate attention module is improved to effectively focus on the regions of interest and their corresponding spatial locations for capturing small features. The transformer module is improved with some attention mechanisms to reduce the computation burden and refine local features. Lastly, to encourage the network to focus more on the few categories, the joint loss function is employed, combining with the Dice and Cross Entropy loss functions to address the challenge of imbalanced class distribution. The main contributions are reflected in the aspects that follow.
- (1)
- The proposed approach introduces an encoder–decoder framework based on TransUNet specifically designed for the semantic segmentation of remote-sensing images. This framework leverages detailed information and global context to enhance the quality of feature representation. Additionally, the Content-Aware ReAssembly of Features (CARAFE++) method is employed to effectively upsample feature maps, thereby preserving important details during the decoding process.
- (2)
- To improve the model’s performance, an efficient improved coordinate attention module is incorporated, which utilizes four pooling enhancements to suppress background information and accentuate small features. The h-swish activation function is utilized to enhance the model’s nonlinear fitting capability. Furthermore, a weight generation submodule is designed to assist the network in precisely localizing the object of interest.
- (3)
- The transformer module is improved to reduce the time complexity associated with calculating attention. This is achieved by sparsifying the attention matrix and introducing a row–column attention (RCA) mechanism, which replaces the multi-head attention in the transformer model. It can also supplement the contextual information in the attention. Additionally, the layer normalization (LN) layer and multi-layer perceptron (MLP) layer are substituted with an asymmetric convolutional block (ACB) and a Leaky ReLU activation layer.
2. Methods
2.1. Datasets
Vaihingen dataset [31]: It contains 33 images, each measuring 2494 × 2064 pixels. With a 9 cm spatial resolution, each image in the collection includes red, green, and near-infrared channels. Additionally, each image includes a digital surface model that is registered with the image data. The imagery is classified into six distinct categories, namely impervious surfaces, buildings, low vegetation, trees, cars, and background.
Potsdam dataset [31]: It includes 38 images with a size of 6000 × 6000 pixels. The sample distance from the ground is 5 cm. Three bands—red, green, and near-infrared—make up the 8-bit TIFF file format used for remote-sensing images. The additional data contain the digital surface model data. The Potsdam dataset has six categories as well.
LoveDA dataset [32]: It contains 5987 images with RGB channels with 1024 × 1024 pixels, and is from the images constructed from Nanjing, Changzhou, and Wuhan using Google Earth data. There is a 0.3 m ground sampling distance. Because every research area has a unique development approach, the ratio of rural to urban areas varies. The National Bureau of Statistics’ urban and rural zoning codes were used to guide the collection of data for both urban and rural areas. We chose nine heavily populated urban regions from areas with affluent economies. Undeveloped areas were the source of the remaining nine rural areas.
2.2. Methodology
2.2.1. Network Architecture
The architecture of the network is displayed in Figure 1, integrating attention mechanisms to enhance the segmentation capability. The network is constructed based on the TransUNet framework, serving as its backbone. It comprises the encoding phase and the decoding phase. During the encoding phase, the image undergoes an improved coordinate attention module, which effectively extracts comprehensive contextual semantic features following a 3 × 3 convolutional layer. The original TransUNet feature extraction uses the ResNet50 network, which is divided into three blocks, and features are extracted after each block. In this work, an improved coordinate attention module (ICAM) is placed after extracting features from each CNN block to enhance feature expression. Specifically, the extracting features from the last block of the ResNet50 architecture are divided into N pixel blocks and added with positional information before being sent to the improved vision transformer (IViT) for global information extraction. The sequence output by an improved vision transformer module is then convolved and integrated into 3D image features to prepare for upsampling. In the decoder phase, the CARAFE++ technique is employed for upsampling the feature map output by the encoder to obtain high-resolution features instead of traditional bilinear interpolation. Then, it jumps and connects with the features extracted from the corresponding blocks in the encoder to achieve a fusion of high- and low-resolution feature information. To reduce parameter calculations, depthwise separable convolutions are used instead of ordinary convolutions to gradually restore the fused features to the original image size. With a cascade approach, features with multiscale fusion are obtained with two jumps.
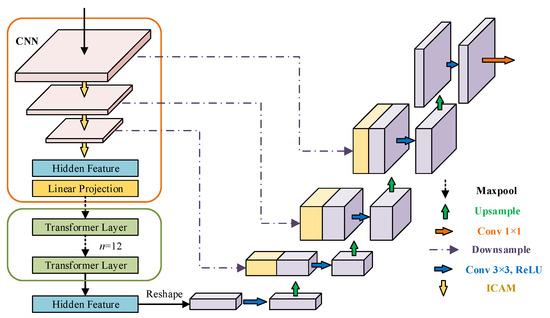
Figure 1.
Overview of the proposed method.
2.2.2. Improved Coordinate Attention Module
Inspired by coordinate attention module [33], ICAM is designed to suppress background interference and enhance small features, as depicted in Figure 2. The ICAM module attempts to strengthen the segmentation performance by selectively attending to key regions and their corresponding spatial locations. Firstly, the original feature map is represented as , where , , and signify the channel number, height, and width in the feature map separately. Both one-dimensional (1D) global average pooling (GAP) and 1D global max pooling (GMP) are performed for each channel along horizontal and vertical directions in 4 spatial dimensions. Then, the orientation-aware features and are obtained as
where is the average function, , , , and are the intermediate feature maps of GAP and GMP in the horizontal and vertical directions, respectively.
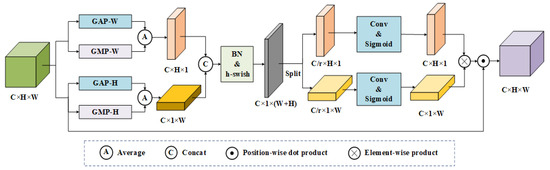
Figure 2.
Complemented attention module.
The concat operation is used to fuse the orientation-aware features on the channel dimension before the batch normalization (BN) operation, followed by the h-swish activation function to increase the nonlinear fitting ability of the model. Additionally, a weight generation submodule is devised to produce attention weights. The fused feature map is split into the two feature vectors and along the horizontal and vertical directions, respectively. Then, they are processed using a 1 × 1 convolution with a Sigmoid activation function, yielding the attention weight.
where is the Sigmoid activation function and is the convolution function.
Finally, the original feature map is weighted with the attention weight to generate an attention map.
2.2.3. Improved Vision Transformer Module
- (1)
- Classical Transformer model
The transformer model was initially proposed for natural language processing by the team at Google [34]. Recently, the Transformer model was successfully adapted for visual tasks. The key innovation of the transformer model is a self-attention mechanism, which enables parallel training and facilitates the capture of global information. When applied to visual data, this architecture can effectively process image information in a manner analogous to its success in NLP tasks. In the transformer model, there are two main components: the encoding component consists of multiple encoder layers, while the decoding component consists of an equivalent number of decoder layers. In order to address the sequence-related challenges at both the input of the encoder and decoder, locational encoding information is added. The position is encoded with sine and cosine functions as follows:
where represents the position of the sequence of words in the sentence, represents the dimensional position of the vector, and represents the size of the vector dimension.
The self-attention mechanism plays a pivotal role by simulating a human in the transformer model cognitive behavior, dynamically focusing on specific regions. The attention mechanism comprises two essential components: The first component is the transformation layer, which performs linear transformations on the input sequence information , to three distinct sequence vectors, respectively, with linear transformation. These three vectors are called query vector Q, key vector K, and value vector V. Here, n and d are the input sequence length and dimension, respectively. The self-attention mechanism is manifested with the following:
where are the three input matrices, and their dimensions are .
The limitation of the single-headed attention layer is that it can only focus on a specific location and cannot focus on other important locations at the same time. To solve this problem, the multi-head attention mechanism uses to calculate multiple information selected in parallel from the input information for linear projection, and each attention is focused on a different part of the input information and output the content. Finally, the output values are again concatenated and projected to generate the output value. The multi-head attention mechanism is presented as follows:
where , , and are parameter matrices for linear projection, n is the head number, and is the projection weight.
- (2)
- Improved vision Transformer module
Vision transformers (ViT), which is a transformer model for computer vision, substitute transformer structures for convolutional structures. Suppose the input feature map is , and it is subdivided into two-dimensional patches with a size of . Then the length of the transformer input sequence is . patches are projected onto a -dimensional space with a projection matrix. Its output is called patch embedding. The position information of each patch is preserved by inserting the learnable positional embedding into the patch embedding to obtain . After standardization, are obtained and sent to Multi-Head Attention for attention operations. Transformers primarily use self-attention techniques to extract global contextual semantic information from images, yet this process is known to be computationally intensive. The time complexity during the calculation process is .
In the context of optimizing the time complexity of calculating attention in transformer models, we attempt to sparsify the attention matrix. Inspired by [35], row–column attention (RCA) is introduced to replace the multi-head attention block, as shown in Figure 3. Meanwhile, in order to make use of the position relationship between different regions, positional encoding is added to the RCA. In this work, the improved module refers to the convolution process, which calculates within a fixed receptive field range. Therefore, the receptive field is first fixed as each column on the feature map (). patches of columns are projected onto a -dimensional space. By adding the positional encoding , is obtained. Finally, the attention results are calculated row by row and concatenated as the output features. Obviously, the features fully cover the contextual information of elements between rows in the vertical direction. Meanwhile, the receptive field is fixed on each row of the output feature map and perform similar operations to obtain features with global information interaction. The time complexity during the calculation process is . In addition, the layer norm (LN) layer and multi-layer perceptron (MLP) layer are replaced with an asymmetric convolutional block (ACB) and a Leaky ReLU activation layer to reduce the computational burden brought by MLP and make up for the local information of RCA.
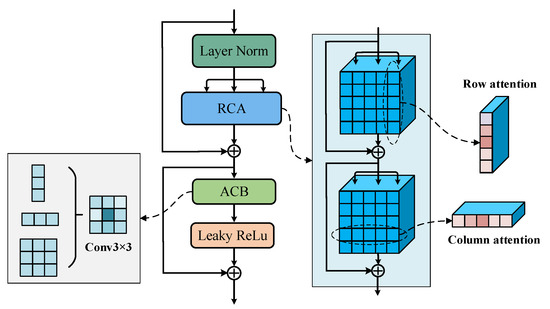
Figure 3.
Improved vision transformer module.
2.2.4. CAPAFE++ Upsampling Module
To create feature maps with rich semantic information, the CAPAFE++ method [36] is employed as an upsampling operator to decrease the loss of upsampled information and enhance the receptive field. The content-aware reassembly submodule and the kernel prediction submodule make up the CARAFE++ module. The function of the kernel prediction submodule is to generate the upsampling reorganization kernel in a content-aware form so that the reassembly submodule can achieve the upsampling work. Suppose a feature map size is , and an upsampling ratio is . Firstly, the input feature map channel from to is compressed via a 1 × 1 convolution layer, reducing the parameters of the following steps. Secondly, based on the compressed feature map, a convolution layer of a kernel size of is used to generate the upsampled reassembly kernel. The channel dimension is expanded on the spatial dimension. The size of the reassembly kernel is . Here, is the upper sampling rate. Finally, the values for the reassembly kernel with a size of are normalized using a softmax function so that the sum of the kernel values is 1. In the content-aware reassembly submodule, each position in the output feature is mapped to the input feature map to gain the feature . Then, the region of each location center is taken out for dot-product operation with the reassembly kernel . Then, the upsampling feature map with a size of is obtained.
2.2.5. Loss Function
The cross-entropy loss function [14] may result in the model excessively emphasizing categories that possess substantial samples, then inadvertently disregarding categories that possess fewer ones. This issue is particularly problematic in pixel-level segmentation tasks where class imbalance is prevalent. To reduce attention towards the background class, the Dice loss function [37] is introduced. Then a combined loss function is designed using the following:
where is the cross entropy loss function, and is Dice the loss function, and are set as 0.5.
3. Results
3.1. Evaluation Metrics
For the objective evaluation of the proposed method, three widely recognized indicators were selected: mean intersection over union (mIoU), mean F1 score (mF1), and overall accuracy (OA). The evaluation metrics can be computed as follows:
where is the precision, and is the recall. The test results can be divided into TP, FP, TN, and FN, which signify true positive, false positive, true negative, and false negative values of a particular class.
3.2. Dataset Settings and Implementation Details
To measure the effectiveness of the suggested methodology, the comparison experiments were performed on the three public datasets, namely the Vaihingen dataset, the Potsdam dataset, and the LoveDA dataset. Particularly for the Vaihingen and Potsdam datasets, the images were cropped to 512 × 512 pixels. The images in the Val dataset were selected for testing. The selected samples were randomly divided into a training set and a test set at a ratio of about 1.4:1.
The experiments were taken by using an NVIDIA GPU (11G), and the framework was created using Pytorch. The network was trained by applying the Adam optimizer, the batch size was set to eight, the initial learning rate was set as 0.001, and 100 epochs were utilized for training.
3.3. Comparison of Different Methods
For confirming the efficacy of the suggested approach in semantic segmentation, the OA, mIoU, and mF1 indexes after 100 trainings with various classical segmentation algorithms in the three datasets were calculated. The classical semantic segmentation algorithms include the following: Deeplabv3+ [38], Segformer [39], DNLNet [40], Segmenter [41], SegNeXt [42], CMTFNet [29], and SAN [43].
For the Vaihingen dataset, the comparisons were made with other advanced algorithms, as exhibited in Table 1. This technique achieved the best mIoU (71.48%), mF1 (81.81%), and OA (90.50%) on the Vaihingen dataset, outperforming other networks. Specifically, the proposed approach not only outperforms the multiscale feature model Deeplabv3+ by 3.5% in terms of mIoU but also outperforms the self-attention-based model, DNLNet, by 3.21%. The segmentation in the background category, in particular, showed a surprising advantage that was far ahead of other methods with IoU. Figure 4 exhibits the semantic segmentation effects of the networks on the Vaihingen dataset. Particularly in the red box, it is evident that the effectiveness of the proposed method is superior to the others, especially in the red box. The ground truth is obviously mislabeled because of a car in the red box.

Table 1.
Comparisons of the methods on Vaihingen dataset (%).
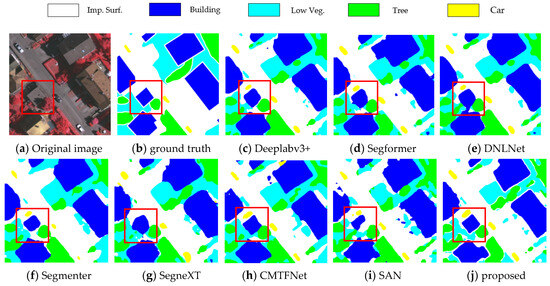
Figure 4.
Visualization results for Vaihingen.
Table 2 presents the comparisons with other techniques on the Potsdam dataset. In comparison to previous networks, the proposed technique produced the mIoU (74.34%), mF1 (83.77%), and OA (88.90%) in the Potsdam dataset. Note that the approach just in the car category earned an IoU of 84.06%, less than 5% lower than the two recent networks, CMTFNet and SAN, resulting in the lower mIoU. It is seen that the OA of the proposed method is the best in Table 2. Figure 5 illustrates how the boundary segmentation detail using the suggested method is more accurate than most of the other networks. The border of the segmented objects in the remote-sensing images can be more accurately depicted about buildings using the suggested way.

Table 2.
Comparisons of the methods on Potsdam (%).
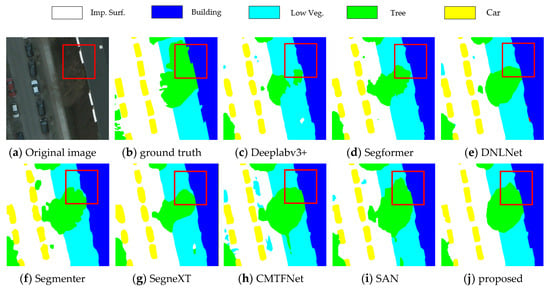
Figure 5.
Visualization results for Potsdam.
For the LoveDA dataset, comparative experiments were conducted, further estimating the performance of the presented approach. Table 3 illustrates that the suggested approach can gain superior results on the LoveDA dataset. According to Table 3, the suggested method produced satisfactory results with regard to mIoU (52.57%), mF1 (67.98%), and OA (70.80%). The classification of buildings, roads, and forests shows outstanding advantages. Figure 6 demonstrates the visual results of the LoveDA dataset. It can be observed that a portion of the forest in the red box is identified as water or background in these classical methods. The suggested strategy can significantly enhance the performance, according to the aforementioned experimental results.

Table 3.
Comparisons of the methods on LoveDA (%).
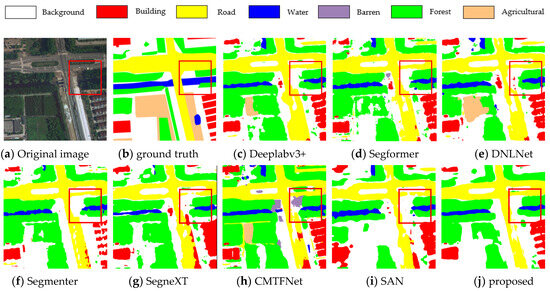
Figure 6.
Visualization results of LoveDA.
4. Discussion
4.1. Analysis of the Attention Mechanism
This case is used for confirming the impact of the attention mechanism, by comparing the results of the model with and without the attention mechanism. The baseline method is designed without the improved attention modules of the proposed method. The three datasets were utilized in the studies for the baseline and suggested techniques. The comparable results of the suggested and the baseline methods are displayed in Table 4. It is clear that the mIoUs of the suggested method in the three datasets are enhanced by 3.58%, 3.19%, and 3.69%, respectively, in comparison to the baseline method. The ablation experiment demonstrates how well the enhanced attention modules can enhance the semantic segmentation effect. By emphasizing small-scale characteristics and suppressing unnecessary background information, the attention mechanism helps to improve feature representation, which leads to enhanced segmentation performance.

Table 4.
Comparisons with the baseline method (%).
4.2. Limitations
The proposed method demonstrates promising results, but there are still some limitations. For instance, the model misidentifies objects that are similar, and the accuracy of the object boundaries needs to be further enhanced. In future work, we will continue to focus on improving the performance of semantic segmentation by introducing an advanced backbone; thereby, the presented model may attain more precision for the boundary details under more complex situations.
5. Conclusions
In this paper, a TransUNet-based semantic segmentation technique is presented with sparse matrix and coordinate attention for remote-sensing images. To minimize the background interference and highlight the small features, an improved coordinate attention module is used to focus on interest goals and the goal location. The transformer model is improved to enhance the computation efficiency and refine segmentation results. To reduce the category imbalance, the loss function is coupled with both the cross-entropy loss and Dice loss functions. The experimental results demonstrate that, when compared to alternative approaches on the three datasets, the suggested algorithm has a superior segmentation effect. The attention mechanism can be also applied to other computer vision tasks, and its influence on different network performance is worthy of further study.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.G.; methodology, S.G.; software, Y.H.; investigation, L.D. and Y.H.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.H.; writing—review and editing, L.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, grant number, 42101017, in part by the funding project of the Northeast Geological S&T Innovation Center of China Geological Survey, grant number, QCJJ2022-23, QCJJ2022-24, QCJJ2022-26, in part by the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation, grant number, 2020M680979, and in part by the Basic Scientific Research Project of the Higher Education Institutions of Liaoning Province, grant number, JYTMS20231165.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors on request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Yuan, X.; Shi, J.; Gu, L. A review of deep learning methods for semantic segmentation of remote sensing imagery. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 169, 114417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, D.; Yao, R.; Xue, Y. Swin transformer embedding unet for remote sensing image semantic segmentation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Jiang, B.; Lv, S.; Liu, Y.; Fu, Y. Deep-Learning-Based Semantic Segmentation of Remote Sensing Images: A Survey. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2024, 17, 8370–8396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diakogiannis, F.I.; Waldner, F.; Caccetta, P.; Wu, C. Resunet-a: A deep learning framework for semantic segmentation of remotely sensed data. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2020, 162, 94–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, Y.; Gang, S.; Guan, C. Fcihmrt: Feature cross-layer interaction hybrid method based on res2net and transformer for remote sensing scene classification. Electronics 2023, 12, 4362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Wang, L.; Wu, C.; Guo, C.; Yan, H.; Qiao, Z. Semantic segmentation of remote sensing images using multiway fusion network. Signal Process. 2024, 215, 109272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, S.K.; Ghosh, A.; Shankar, B.U. Segmentation of remotely sensed images with fuzzy thresholding, and quantitative evaluation. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2000, 21, 2269–2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Zhang, G.; Wu, Z.; Yi, L. An edge embedded marker-based watershed algorithm for high spatial resolution remote sensing image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2010, 19, 2781–2787. [Google Scholar]
- Saha, I.; Maulik, U.; Bandyopadhyay, S.; Plewczynski, D. Svmefc: Svm ensemble fuzzy clustering for satellite image segmentation. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2012, 9, 52–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, A.; Quan, Y.; Yu, R.; Guo, W.; Wang, X.; Hong, D.; Zhang, H.; Chen, J.; Hu, Q.; He, P. Deep learning methods for semantic segmentation in remote sensing with small data: A survey. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, C.; Li, W.; Zhao, T. Semantic segmentation of urban buildings from vhr remote sensing imagery using a deep convolutional neural network. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.; Shelhamer, E.; Darrell, T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2015, 39, 640–651. [Google Scholar]
- Kampffmeyer, M.; Salberg, A.-B.; Jenssen, R. Semantic segmentation of small objects and modeling of uncertainty in urban remote sensing images using deep convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26 June–1 July 2016; pp. 680–688. [Google Scholar]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention—MICCAI 2015, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Huo, Y.; Li, X.; Tu, B. Image measurement of crystal size growth during cooling crystallization using high-speed imaging and a u-net network. Crystals 2022, 12, 1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badrinarayanan, V.; Kendall, A.; Cipolla, R. Segnet: A deep convolutional encoder-decoder architecture for image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 39, 2481–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, B.; Chang, C.-Y. Semantic segmentation of high-resolution remote sensing images using multiscale skip connection network. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 22, 3745–3755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Jin, J.; Lei, J.; Yu, L. Cimfnet: Cross-layer interaction and multiscale fusion network for semantic segmentation of high-resolution remote sensing images. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 2022, 16, 666–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.; Zhou, J.; Niu, X. Cross-Scale Feature Propagation Network for Semantic Segmentation of High-Resolution Remote Sensing Images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2023, 20, 6008305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Gu, H.; Li, Z.; Chen, H.; Chen, H. Multi-Scale Feature Fusion Attention Network for Building Extraction in Remote Sensing Images. Electronics 2024, 13, 923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Li, Z.; Feng, H.; Wu, F.; Wang, Y. Multi-Scale Feature Fusion Network with Symmetric Attention for Land Cover Classification Using SAR and Optical Images. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Tang, H.; Bruzzone, L. Lanet: Local attention embedding to improve the semantic segmentation of remote sensing images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 59, 426–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Tao, F.; Liu, X.; Na, J.; Leng, H.; Wu, J.; Zhou, T. Raanet: A residual aspp with attention framework for semantic segmentation of high-resolution remote sensing images. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xu, F.; Liu, F.; Lyu, X.; Tong, Y.; Xu, Z.; Zhou, J. A Synergistical Attention Model for Semantic Segmentation of Remote Sensing Images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 5400916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, Q.; Yuan, F. GLSANet: Global-Local Self-Attention Network for Remote Sensing Image Semantic Segmentation. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2023, 20, 6000105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, R.; Zhang, C.; Fang, S.; Duan, C.; Meng, X.; Atkinson, P.M. Unetformer: A unet-like transformer for efficient semantic segmentation of remote sensing urban scene imagery. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2022, 190, 196–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Geng, J.; Jiang, W. MMT: Mixed-Mask Transformer for Remote Sensing Image Semantic Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 5613415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Huang, P.; Zhang, M.; Tang, W. CTFNet: CNN-Transformer Fusion Network for Remote-Sensing Image Semantic Segmentation. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2024, 21, 5000305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Huang, P.; Zhang, M.; Tang, W.; Yu, X. Cmtfnet: Cnn and multiscale transformer fusion network for remote sensing image semantic segmentation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 2004612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Lu, Y.; Yu, Q.; Luo, X.; Adeli, E.; Wang, Y.; Lu, L.; Yuille, A.L.; Zhou, Y. Transunet: Transformers make strong encoders for medical image segmentation. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2102.04306. [Google Scholar]
- Ghamisi, P.; Yokoya, N. Img2dsm: Height simulation from single imagery using conditional generative adversarial net. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2018, 15, 794–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zheng, Z.; Ma, A.; Lu, X.; Zhong, Y. Loveda: A remote sensing land-cover dataset for domain adaptive semantic segmentation. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2110.08733. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, Q.; Zhou, D.; Feng, J. Coordinate attention for efficient mobile network design. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 13708–13717. [Google Scholar]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. In Proceedings of the 31th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4 December 2017; pp. 6000–6010. [Google Scholar]
- Tay, Y.; Dehghani, M.; Bahri, D.; Metzler, D. Efficient Transformers: A Survey. ACM Comput. 2022, 55, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, K.; Xu, R.; Liu, Z.; Loy, C.C.; Lin, D. Carafe++: Unified content-aware reassembly of features. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2022, 44, 4674–4687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Sun, X.; Meng, Y.; Liang, J.; Wu, F.; Li, J. Dice loss for data-imbalanced NLP tasks. In Proceedings of the the 58th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Online, 5–10 July 2020; pp. 465–476. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.-C.; Zhu, Y.; Papandreou, G.; Schroff, F.; Adam, H. Encoder-decoder with atrous separable convolution for semantic image segmentation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 833–851. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, E.; Wang, W.; Yu, Z.; Anandkumar, A.; Alvarez, J.M.; Luo, P. Segformer: Simple and efficient design for semantic segmentation with transformers. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2021, 34, 12077–12090. [Google Scholar]
- Ni, J.; Wu, J.; Elazab, A.; Tong, J.; Chen, Z. Dnl-net: Deformed non-local neural network for blood vessel segmentation. BMC Med. Imaging 2022, 22, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strudel, R.; Garcia, R.; Laptev, I.; Schmid, C. Segmenter: Transformer for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 7262–7272. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, M.-H.; Lu, C.-Z.; Hou, Q.; Liu, Z.; Cheng, M.-M.; Hu, S.-M. Segnext: Rethinking convolutional attention design for semantic segmentation. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2022, 35, 1140–1156. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, M.; Zhang, Z.; Wei, F.; Hu, H.; Bai, X. Side adapter network for open-vocabulary semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 17–21 June 2023; pp. 2945–2954. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).