Antimicrobial Activity of Human C-Type Lectin Domain Family 3 Member A (CLEC3A)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Recombinant Proteins
2.2. Bacteria
2.3. SDS-PAGE and Immunoblot
2.4. Antimicrobial Activity
2.5. Bacterial Cleavage
2.6. Biostability
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
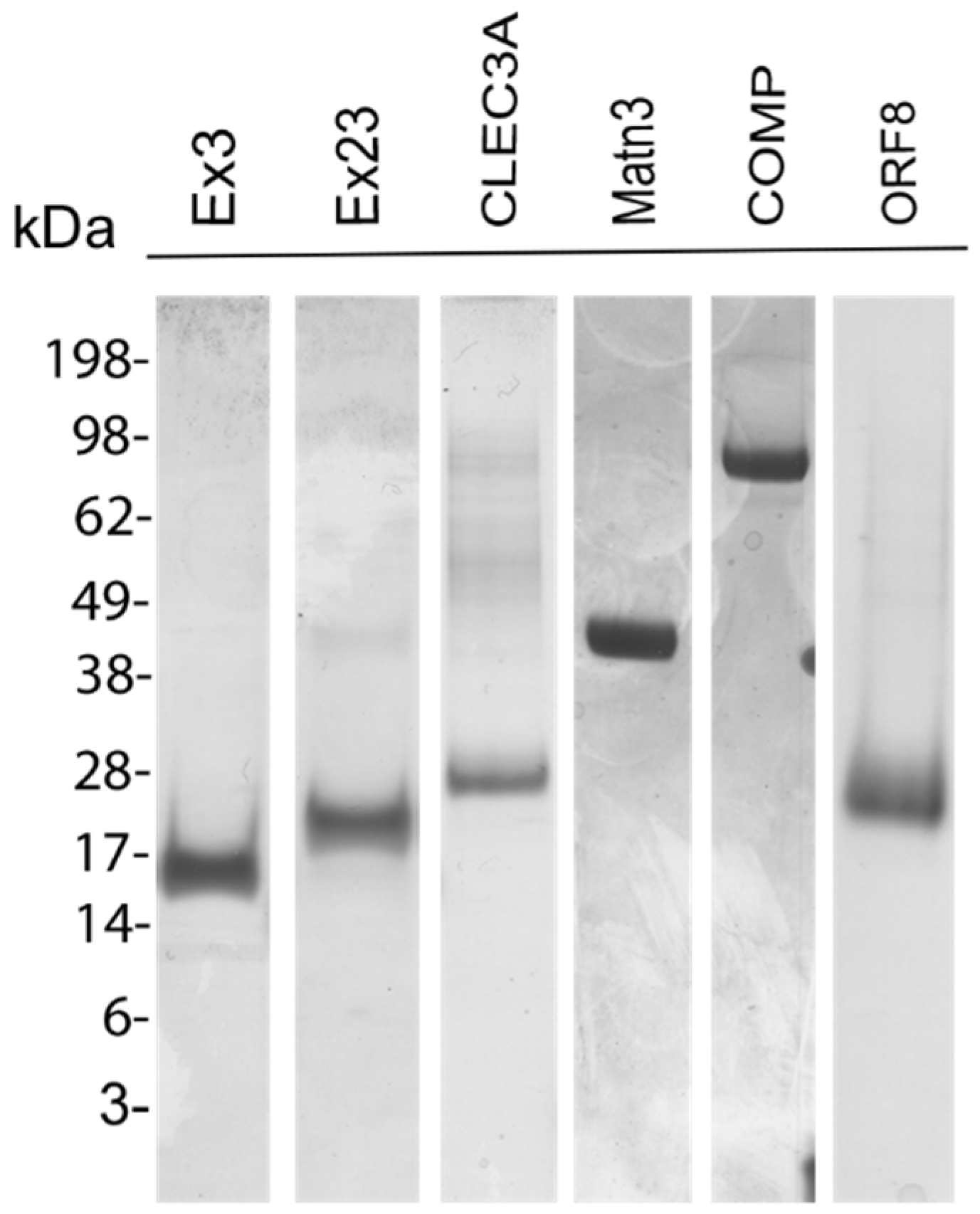
3.1. Recombinant Proteins
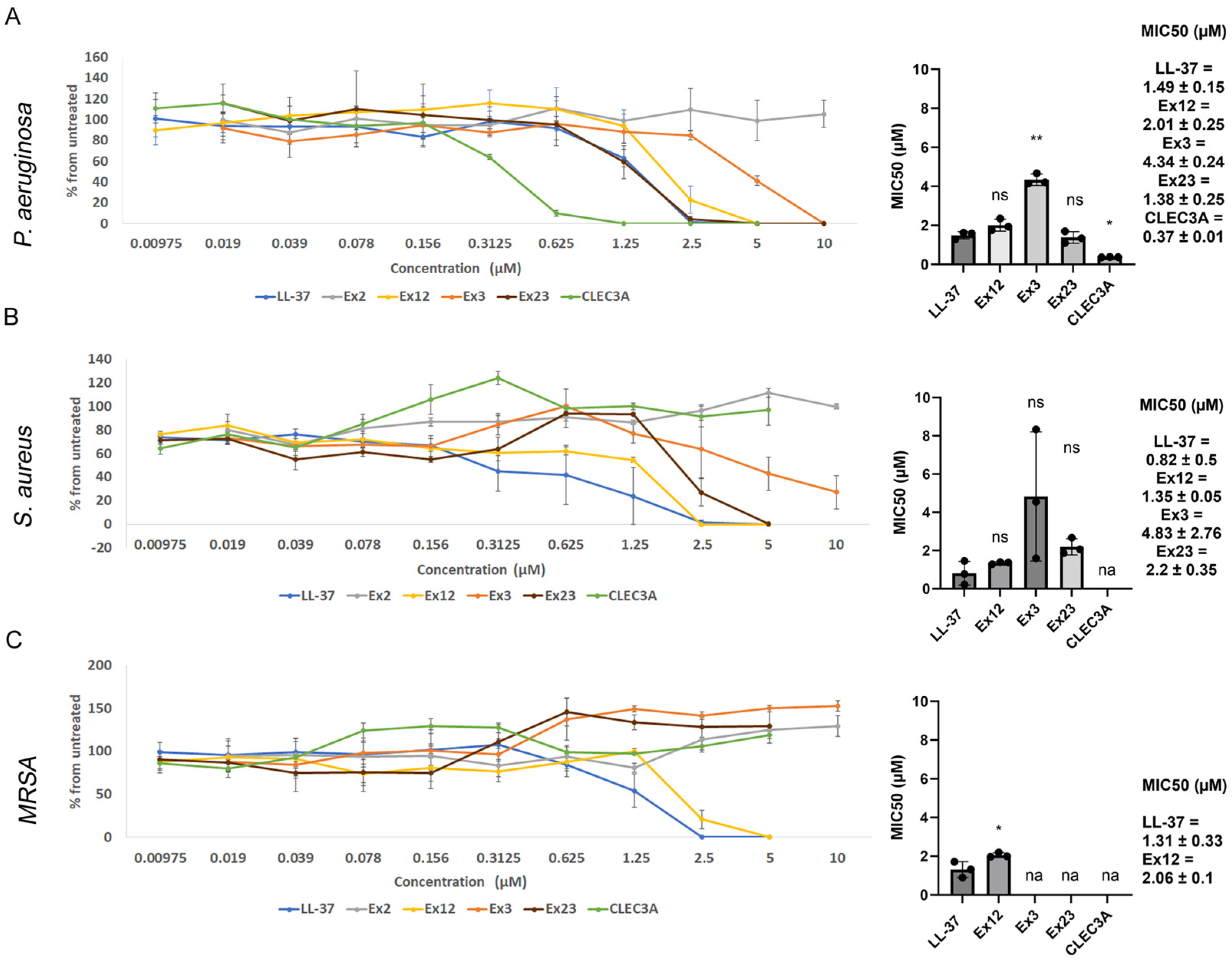
3.2. Antimicrobial Activity
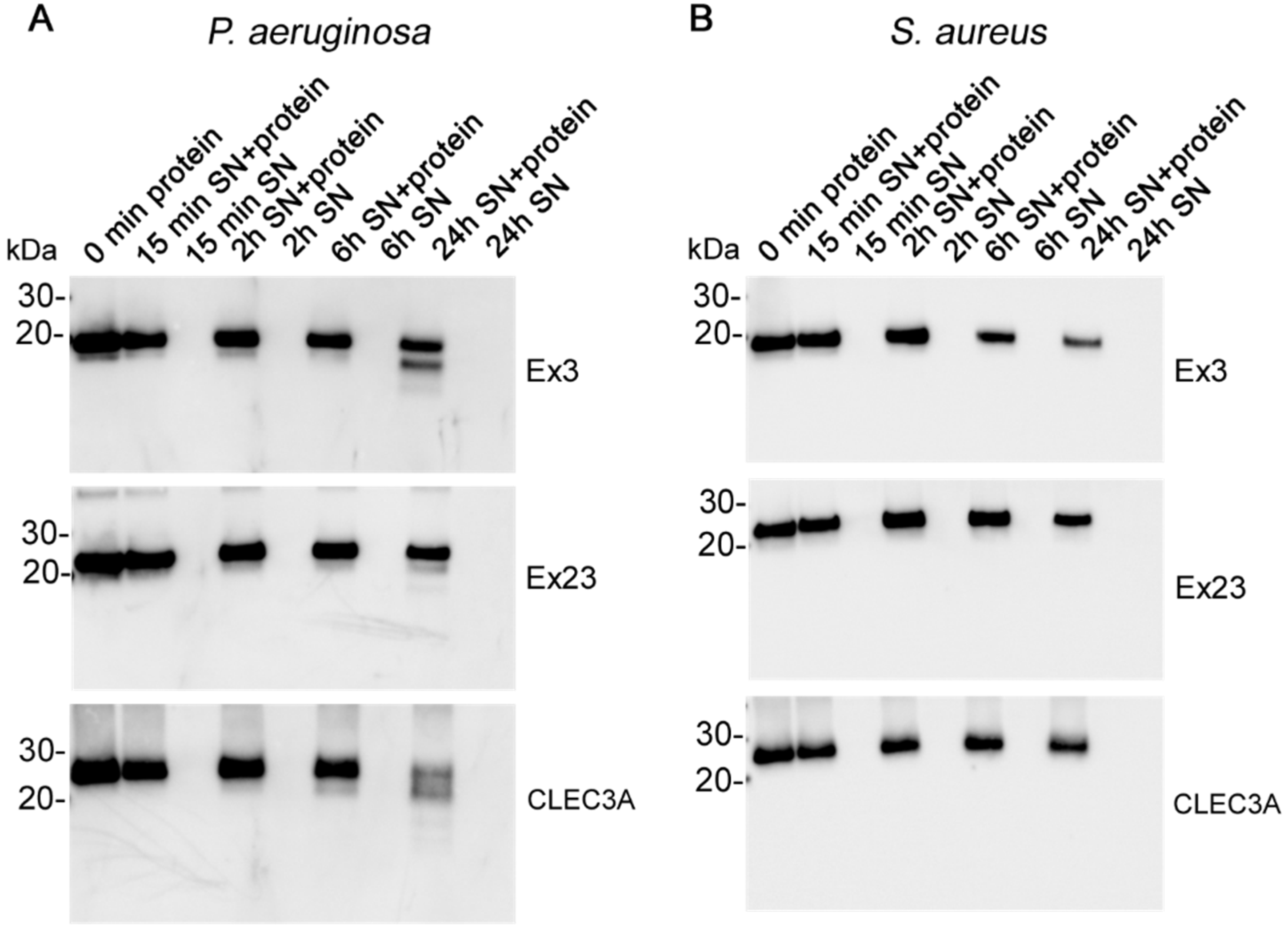
3.3. Bacterial Cleavage
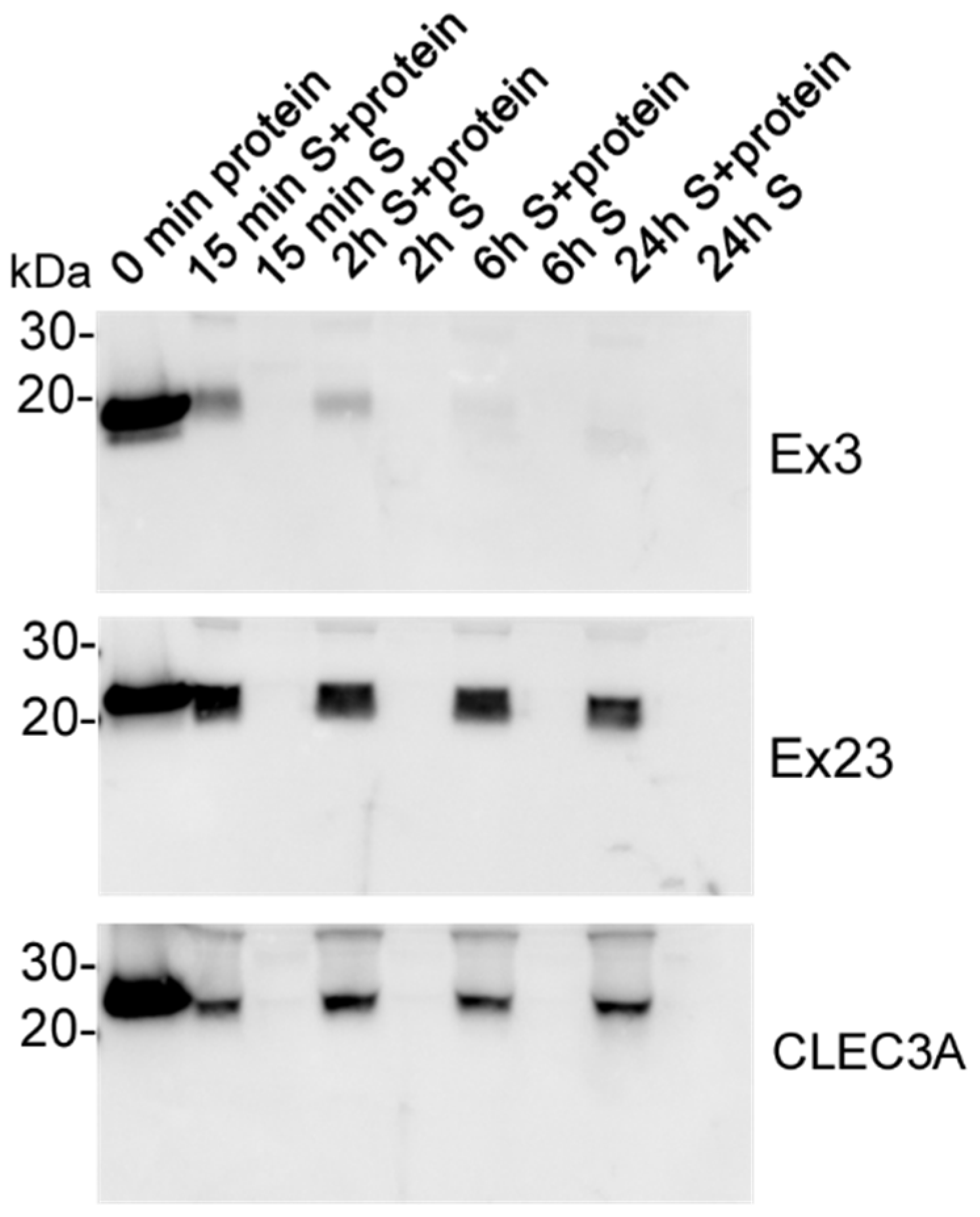
3.4. Biostability of CLEC3A
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Medina, E.; Pieper, D.H. Tackling Threats and Future Problems of Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2016, 398, 3–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boparai, J.K.; Sharma, P.K. Mini Review on Antimicrobial Peptides, Sources, Mechanism and Recent Applications. Protein Pept. Lett. 2020, 27, 4–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, P.; Kizhakkedathu, J.N.; Straus, S.K. Antimicrobial Peptides: Diversity, Mechanism of Action and Strategies to Improve the Activity and Biocompatibility In Vivo. Biomolecules 2018, 8, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breitenbach Barroso Coelho, L.C.; Marcelino Dos Santos Silva, P.; Felix de Oliveira, W.; de Moura, M.C.; Viana Pontual, E.; Soares Gomes, F.; Guedes Paiva, P.M.; Napoleão, T.H.; Dos Santos Correia, M.T. Lectins as antimicrobial agents. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2018, 125, 1238–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zelensky, A.N.; Gready, J.E. The C-type lectin-like domain superfamily. FEBS J. 2005, 272, 6179–6217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, G.D.; Willment, J.A.; Whitehead, L. C-type lectins in immunity and homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2018, 18, 374–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukherjee, S.; Zheng, H.; Derebe, M.G.; Callenberg, K.M.; Partch, C.L.; Rollins, D.; Propheter, D.C.; Rizo, J.; Grabe, M.; Jiang, Q.X.; et al. Antibacterial membrane attack by a pore-forming intestinal C-type lectin. Nature 2014, 505, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Bi, J.; Zhang, P.; Wang, Z.; Zhong, Y.; Xu, S.; Wang, L.; Li, B. Functions of a C-type lectin with a single carbohydrate-recognition domain in the innate immunity and movement of the red flour beetle, Tribolium castaneum. Insect. Mol. Biol. 2021, 30, 90–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Runsaeng, P.; Puengyam, P.; Utarabhand, P. A mannose-specific C-type lectin from Fenneropenaeus merguiensis exhibited antimicrobial activity to mediate shrimp innate immunity. Mol. Immunol. 2017, 92, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.D.; Fu, L.D.; Jia, Y.P.; Du, X.J.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Y.H.; Zhao, X.F.; Yu, X.Q.; Wang, J.X. A hepatopancreas-specific C-type lectin from the Chinese shrimp Fenneropenaeus chinensis exhibits antimicrobial activity. Mol. Immunol. 2008, 45, 348–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Wang, L.; Sun, W.; Zhang, M.; Ma, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, S. C-type lectin B (SpCTL-B) regulates the expression of antimicrobial peptides and promotes phagocytosis in mud crab Scylla paramamosain. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2018, 84, 213–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.L.; Wang, Y.Q.; Dai, Y.J.; Zhao, L.J.; Qin, Q.; Lin, L.; Ren, Q.; Lan, J.F. A novel C-type lectin with four CRDs is involved in the regulation of antimicrobial peptide gene expression in Hyriopsis cumingii. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2016, 55, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.T.; Zhang, X.; Wang, S.C.; Li, W.W.; Wang, Q. Antimicrobial functions of EsLecH, a C-type lectin, via JNK pathway in the Chinese mitten crab, Eriocheir sinensis. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2016, 61, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neame, P.J.; Tapp, H.; Grimm, D.R. The cartilage-derived, C-type lectin (CLECSF1): Structure of the gene and chromosomal location. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1999, 1446, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elezagic, D.; Mörgelin, M.; Hermes, G.; Hamprecht, A.; Sengle, G.; Lau, D.; Höllriegl, S.; Wagener, R.; Paulsson, M.; Streichert, T.; et al. Antimicrobial peptides derived from the cartilage.-specific C-type Lectin Domain Family 3 Member A (CLEC3A)–potential in the prevention and treatment of septic arthritis. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2019, 27, 1564–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, D.; Elezagic, D.; Hermes, G.; Mörgelin, M.; Wohl, A.P.; Koch, M.; Hartmann, U.; Höllriegl, S.; Wagener, R.; Paulsson, M.; et al. The cartilage-specific lectin C-type lectin domain family 3 member A (CLEC3A) enhances tissue plasminogen activator-mediated plasminogen activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meinberger, D.; Koch, M.; Roth, A.; Hermes, G.; Stemler, J.; Cornely, O.A.; Streichert, T.; Klatt, A.R. Analysis of IgM, IgA, and IgG isotype antibodies Directed against SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein and ORF8 in the course of COVID-19. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 8920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruthard, J.; Hermes, G.; Hartmann, U.; Sengle, G.; Pongratz, G.; Ostendorf, B.; Schneider, M.; Höllriegl, S.; Zaucke, F.; Wagener, R.; et al. Identification of antibodies against extracellular matrix proteins in human osteoarthritis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 503, 1273–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meinberger, D.; Drexelius, M.G.; Grabeck, J.; Hermes, G.; Roth, A.; Elezagic, D.; Neundorf, I.; Streichert, T.; Klatt, A.R. Modified CLEC3A-Derived Antimicrobial Peptides Lead to Enhanced Antimicrobial Activity against Drug-Resistant Bacteria. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdimarsson, H.; Stefansson, M.; Vikingsdottir, T.; Arason, G.J.; Koch, C.; Thiel, S.; Jensenius, J.C. Reconstitution of opsonizing activity by infusion of mannan-binding lectin (MBL) to MBL-deficient humans. Scand J. Immunol. 1998, 48, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilpatrick, D.C. Mannan-binding lectin: Clinical significance and applications. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2002, 1572, 401–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, G.Y.C.; Bae, J.S.; Otto, M. Pathogenicity and virulence of Staphylococcus aureus. Virulence 2021, 12, 547–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyczak, J.B.; Cannon, C.L.; Pier, G.B. Establishment of Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection: Lessons from a versatile opportunist. Microbes Infect. 2000, 2, 1051–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heyland, D.K.; Cook, D.J.; Griffith, L.; Keenan, S.P.; Brun-Buisson, C. The attributable morbidity and mortality of ventilator-associated pneumonia in the critically ill patient. The Canadian Critical Trials Group. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1999, 159, 1249–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsunezumi, J.; Higashi, S.; Miyazaki, K. Matrilysin (MMP-7) cleaves C-type lectin domain family 3 member A (CLEC3A) on tumor cell surface and modulates its cell adhesion activity. J. Cell. Biochem. 2009, 106, 693–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.W.; Yang, C.H.; Zhang, H.Q.; Pan, X.T.; Jin, Z.Y.; Zhang, H.W.; Xia, X.H. A C-type lectin with antibacterial activity in weather loach, Misgurnus anguillicaudatus. J. Fish Dis. 2020, 43, 1531–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Q.; Huo, H.; Fu, Q.; Yang, N.; Xue, T.; Zhuang, C.; Liu, X.; Wang, B.; Su, B.; Li, C. Identification and characterization of a C-type lectin in turbot (Scophthalmus maximus) which functioning as a pattern recognition receptor that binds and agglutinates various bacteria. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2021, 115, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abergel, C.; Chenivesse, S.; Stinnakre, M.G.; Guasco, S.; Bréchot, C.; Claverie, J.M.; Devinoy, E.; Christa, L. Crystallization and preliminary crystallographic study of HIP/PAP, a human C-lectin overexpressed in primary liver cancers. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 1999, 55, 1487–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peacock, S.J.; Paterson, G.K. Mechanisms of Methicillin Resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2015, 84, 577–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Larrota, J.S.; Eckhard, U. An Introduction to Bacterial Biofilms and Their Proteases, and Their Roles in Host Infection and Immune Evasion. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werle, M.; Bernkop-Schnürch, A. Strategies to improve plasma half life time of peptide and protein drugs. Amino Acids 2006, 30, 351–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Woggon, K.S.; Meinberger, D.; Hermes, G.; Roth, A.; Streichert, T.; Klatt, A.R. Antimicrobial Activity of Human C-Type Lectin Domain Family 3 Member A (CLEC3A). Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 184. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14010184
Woggon KS, Meinberger D, Hermes G, Roth A, Streichert T, Klatt AR. Antimicrobial Activity of Human C-Type Lectin Domain Family 3 Member A (CLEC3A). Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(1):184. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14010184
Chicago/Turabian StyleWoggon, Katharina S., Denise Meinberger, Gabriele Hermes, Annika Roth, Thomas Streichert, and Andreas R. Klatt. 2024. "Antimicrobial Activity of Human C-Type Lectin Domain Family 3 Member A (CLEC3A)" Applied Sciences 14, no. 1: 184. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14010184
APA StyleWoggon, K. S., Meinberger, D., Hermes, G., Roth, A., Streichert, T., & Klatt, A. R. (2024). Antimicrobial Activity of Human C-Type Lectin Domain Family 3 Member A (CLEC3A). Applied Sciences, 14(1), 184. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14010184





