The Inverse Optimization of an Optical Lithographic Source with a Hybrid Genetic Algorithm
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
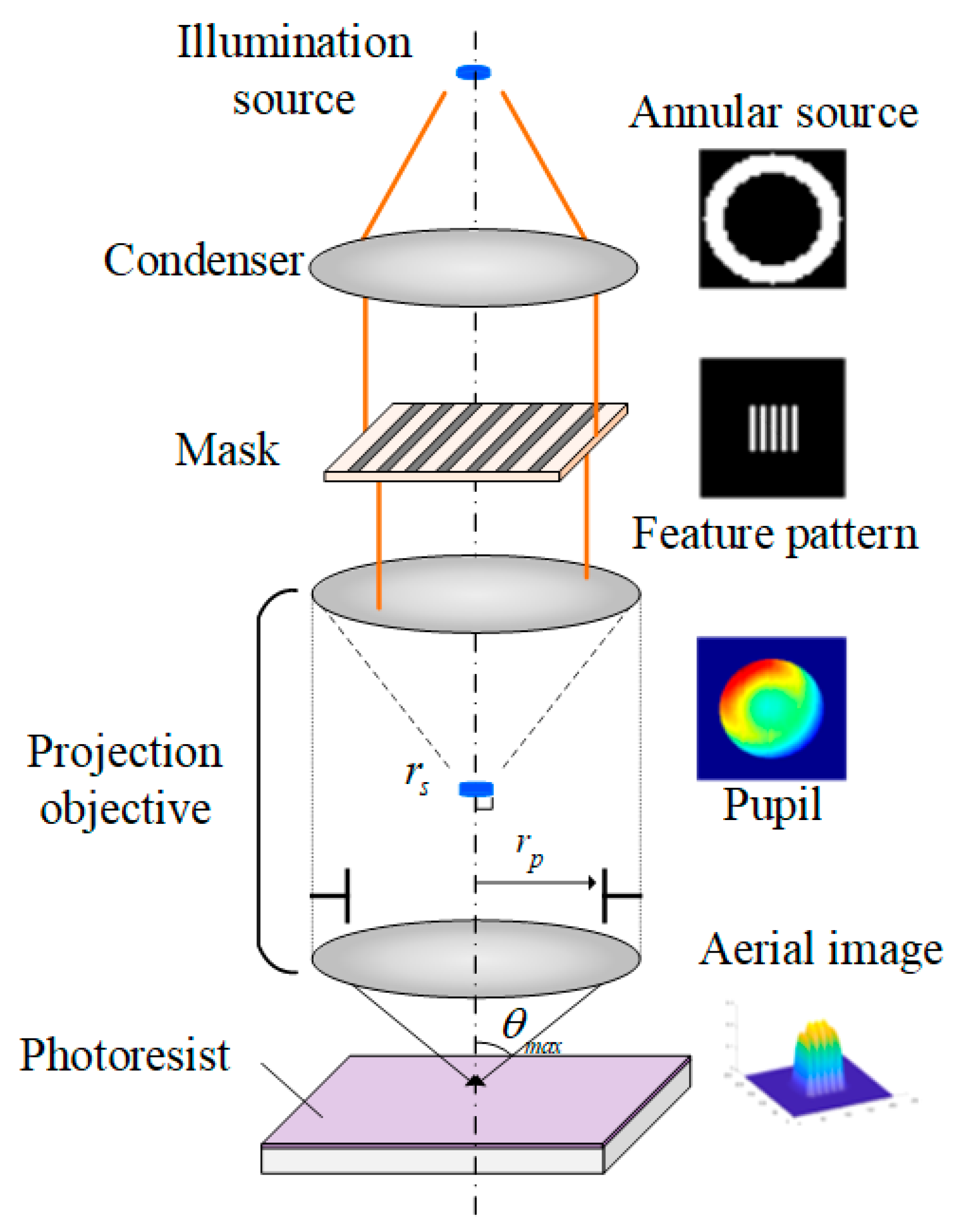
2.1. Partially Coherent Imaging Model
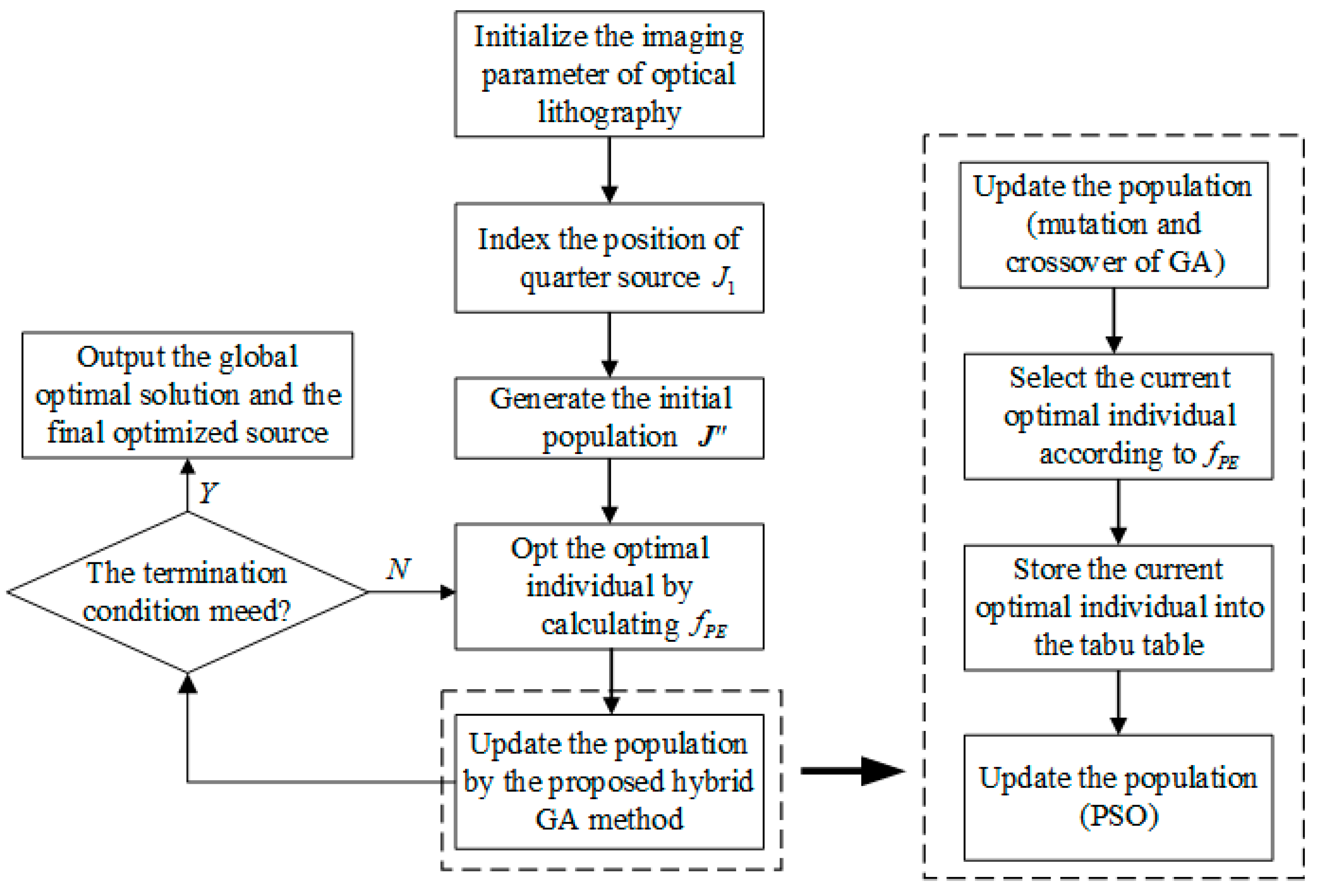
2.2. Flow of Hybrid-GA-Based SO
2.2.1. Pattern Error Minimization Problem
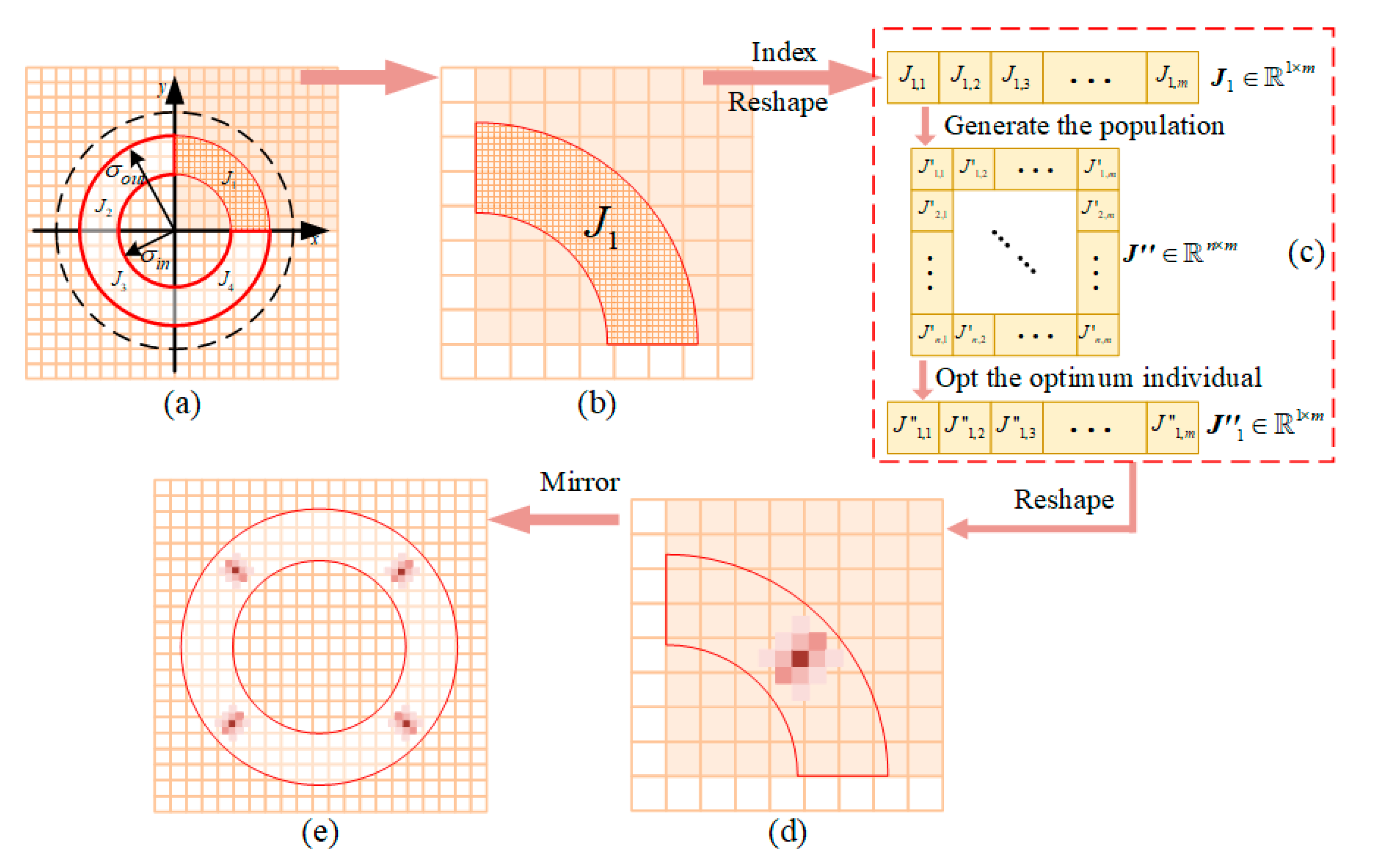
2.2.2. The Optimization Strategy for the Illumination Source
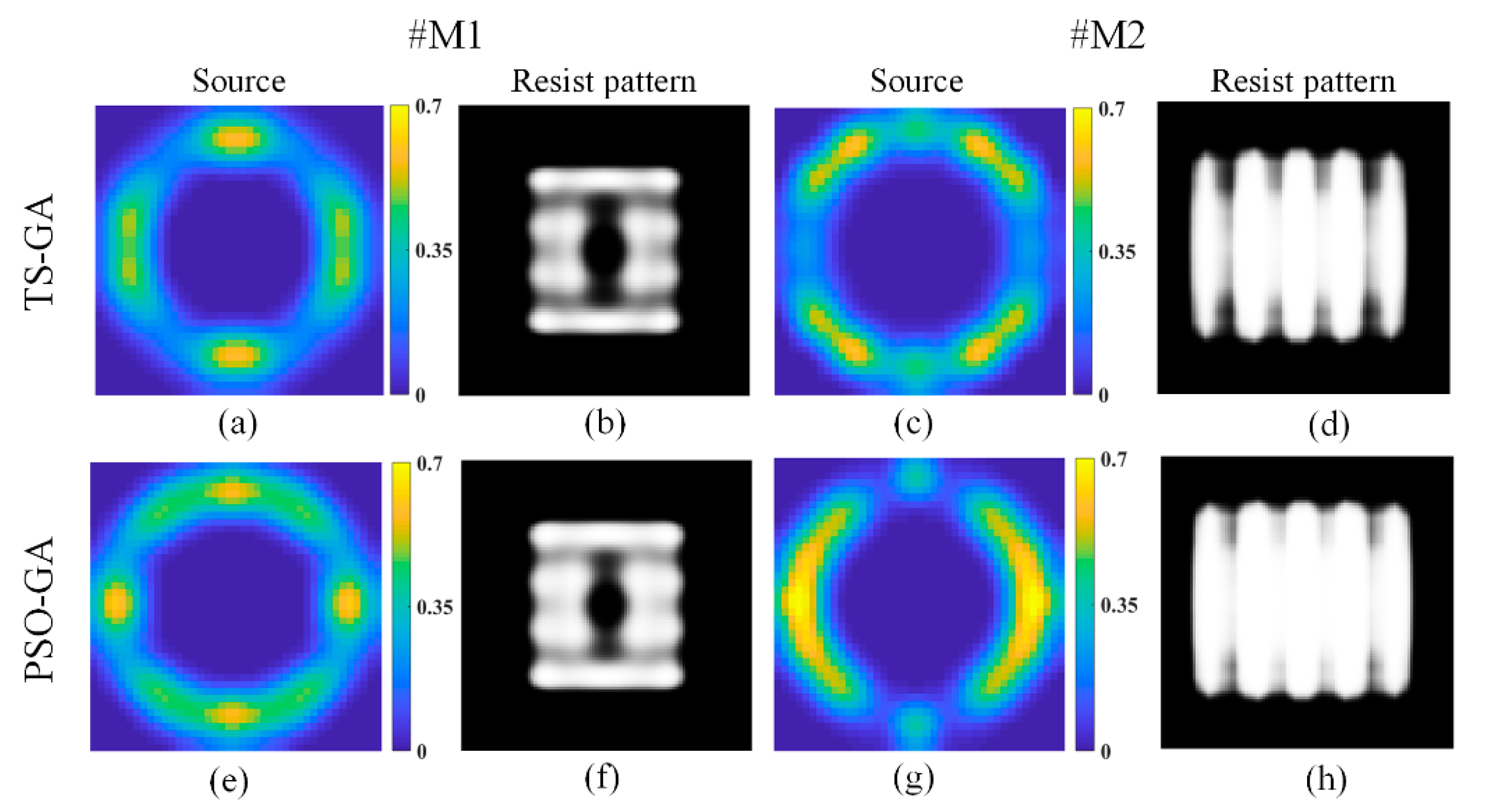
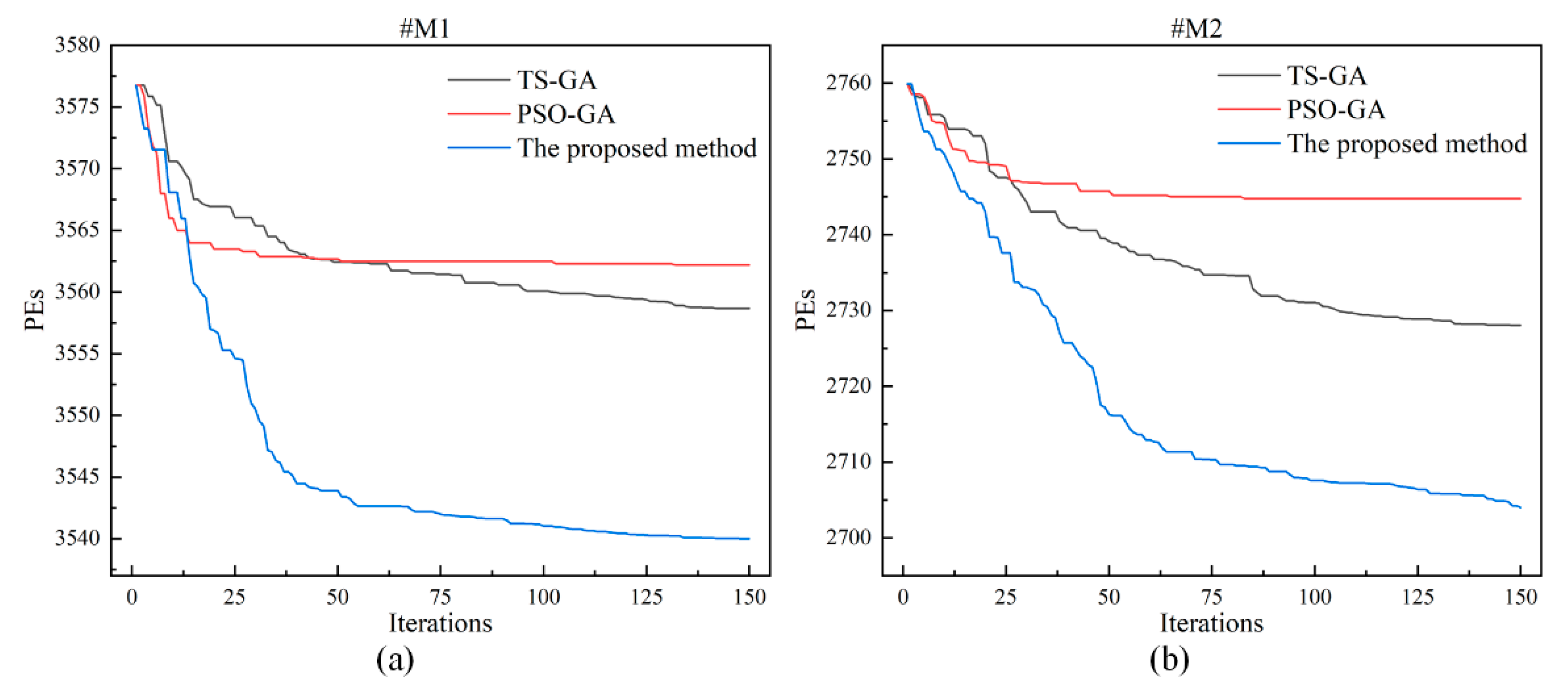
3. Simulations
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wong, A.K.-K. Optical Imaging in Projection Microlithography; SPIE Optical Engineering Press: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2005; ISBN 978-0-8194-5829-2. [Google Scholar]
- Levinson, H.J. Principles of Lithography, 3rd ed.; SPIE Press Monograph: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2010; ISBN 978-0-8194-8324-9. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, A.K. Resolution Enhancement Techniques in Optical Lithography; SPIE: Bellingham, DC, USA, 2001; ISBN 978-0-8194-7881-8. [Google Scholar]
- Schellenberg, F.M. Resolution Enhancement Technology: The Past, the Present, and Extensions for the Future. In Proceedings of the SPIE—The International Society for Optical Engineering, Santa Clara, CA, USA, 28 May 2004; p. 1. [Google Scholar]
- Liebmann, L.W. Resolution Enhancement Techniques in Optical Lithography: It’s Not Just a Mask Problem. In Proceedings of the Photomask and Next Generation Lithography Mask Technology VIII, Kanagawa, Japan, 5 September 2001; p. 23. [Google Scholar]
- Isoyan, A.; Melvin, L.S. Optical Proximity Correction Using Holographic Imaging Technique. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 2014, 32, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Peng, F.; Zhang, Z. Efficient Optical Proximity Correction Based on Semi-Implicit Additive Operator Splitting. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hakko, M.; Suzuki, K. Resolution Enhancement with Source-Wavelength Optimization According to Illumination Angle in Optical Lithography. J. Micro/Nanolithogr. MEMS MOEMS 2020, 19, 043201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X. Resolution Enhancement Optimization Methods in Optical Lithography with Improved Manufacturability. J. Micro/Nanolithogr. MEMS MOEMS 2011, 10, 023009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Arce, G.R. Pixel-Based Simultaneous Source and Mask Optimization for Resolution Enhancement in Optical Lithography. Opt. Express 2009, 17, 5783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Mei, Q.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y. Illumination System with Freeform Fly’s Eye to Generate Pixelated Pupil Prescribed by Source-Mask Optimization in Extreme Ultraviolet Lithography. Opt. Eng. 2017, 56, 065101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, W.; Liu, S.; Wu, X.; Lam, E.Y. Illumination Source Optimization in Optical Lithography via Derivative-Free Optimization. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 2014, 31, B19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Wang, Z.; Lin, H.; Li, Y.; Arce, G.R.; Zhang, L. Optimization of Lithography Source Illumination Arrays Using Diffraction Subspaces. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 3738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, H.-F.; Wu, W.-C. Forming Freeform Source Shapes by Utilizing Particle Swarm Optimization to Enhance Resolution in Extreme UV Nanolithography. IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 2015, 14, 322–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, J.; Gräupner, P.; Neumann, J.T.; Hellweg, D.; Jürgens, D.; Patra, M.; Hennerkes, C.; Maul, M.; Geh, B.; Engelen, A.; et al. Generation of Arbitrary Freeform Source Shapes Using Advanced Illumination Systems in High-NA Immersion Scanners. In Proceedings of the SPIE—The International Society for Optical Engineering, San Jose, CA, USA, 11 March 2010; p. 764005. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Yu, Z. High Performance Source Optimization Using a Gradient-Based Method in Optical Lithography. In Proceedings of the 2010 11th International Symposium on Quality Electronic Design (ISQED), San Jose, CA, USA, 22–24 March 2010; pp. 108–113. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, N.; Lam, E.Y. Pixelated Source Mask Optimization for Process Robustness in Optical Lithography. Opt. Express 2011, 19, 19384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Lam, E.Y. Robust Source and Mask Optimization Compensating for Mask Topography Effects in Computational Lithography. Opt. Express 2014, 22, 9471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Han, C.; Li, Y.; Dong, L.; Arce, G.R. Pixelated Source and Mask Optimization for Immersion Lithography. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 2013, 30, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, N.; Lam, E.Y. Stochastic Gradient Descent for Robust Inverse Photomask Synthesis in Optical Lithography. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, Hong Kong, China, 26–29 September 2010; pp. 4173–4176. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, M.; Niu, Z.; Zhang, F.; Zhu, L.; Shi, W.; Zeng, A.; Huang, H. Gradient-Based Source Mask and Polarization Optimization with the Hybrid Hopkins–Abbe Model. J. Micro/Nanolithogr. MEMS MOEMS 2020, 19, 033201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitley, D. A Genetic Algorithm Tutorial. Stat. Comput. 1994, 4, 65–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haldurai, L.; Madhubala, T.; Rajalakshmi, R. A Study on Genetic Algorithm and Its Applications. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Eng. 2016, 4, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Sortrakul, N.; Nachtmann, H.L.; Cassady, C.R. Genetic Algorithms for Integrated Preventive Maintenance Planning and Production Scheduling for a Single Machine. Comput. Ind. 2005, 56, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, J. Image Segmentation Method Based on Improved Genetic Algorithm and Fuzzy Clustering. Adv. Mater. Res. 2010, 143–144, 379–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, T.-P.; Chen, C.-H.; Wu, Y.-L.; Lee, Y.-C. A GA-Based Fuzzy Mining Approach to Achieve a Trade-off Between Number of Rules and Suitability of Membership Functions. Soft Comput. 2006, 10, 1091–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fühner, T.; Erdmann, A.; Farkas, R.; Tollkühn, B.; Kókai, G. Genetic Algorithms to Improve Mask and Illumination Geometries in Lithographic Imaging Systems. In Applications of Evolutionary Computing; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Raidl, G.R., Cagnoni, S., Branke, J., Corne, D.W., Drechsler, R., Jin, Y., Johnson, C.G., Machado, P., Marchiori, E., Rothlauf, F., et al., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004; Volume 3005, pp. 208–218. ISBN 978-3-540-21378-9. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Yu, S.-M.; Li, Y.-L. Intelligent Optical Proximity Correction Using Genetic Algorithm with Model- and Rule-Based Approaches. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2009, 12, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, L.; Fan, J.; Tritchkov, A.; Word, J.; Zhang, D. Inverse Lithography Recipe Optimization Using Genetic Algorithm. In Proceedings of the Optical Microlithography XXXI, San Jose, CA, USA, 27 February–1 March 2018; p. 53. [Google Scholar]
- Deb, K.; Pratap, A.; Agarwal, S.; Meyarivan, T. A Fast and Elitist Multiobjective Genetic Algorithm: NSGA-II. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2002, 6, 182–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Q.; Qian, F. A Hybrid Genetic Algorithm for Twice Continuously Differentiable NLP Problems. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2010, 34, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dziwinski, P.; Bartczuk, L. A New Hybrid Particle Swarm Optimization and Genetic Algorithm Method Controlled by Fuzzy Logic. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2020, 28, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drezner, Z.; Misevičius, A. Enhancing the Performance of Hybrid Genetic Algorithms by Differential Improvement. Comput. Oper. Res. 2013, 40, 1038–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Arce, G.R. Computational Lithography; Wiley Series in Pure and Applied Optics; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010; ISBN 978-0-470-59697-5. [Google Scholar]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, J.; Zhou, J.; Yu, D.; Sun, H.; Hu, S.; Wang, J. The Inverse Optimization of an Optical Lithographic Source with a Hybrid Genetic Algorithm. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 5708. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13095708
Liu J, Zhou J, Yu D, Sun H, Hu S, Wang J. The Inverse Optimization of an Optical Lithographic Source with a Hybrid Genetic Algorithm. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(9):5708. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13095708
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Junbo, Ji Zhou, Dajie Yu, Haifeng Sun, Song Hu, and Jian Wang. 2023. "The Inverse Optimization of an Optical Lithographic Source with a Hybrid Genetic Algorithm" Applied Sciences 13, no. 9: 5708. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13095708
APA StyleLiu, J., Zhou, J., Yu, D., Sun, H., Hu, S., & Wang, J. (2023). The Inverse Optimization of an Optical Lithographic Source with a Hybrid Genetic Algorithm. Applied Sciences, 13(9), 5708. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13095708





