Enhancing Transferability of Near-Infrared Spectral Models for Soluble Solids Content Prediction across Different Fruits
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
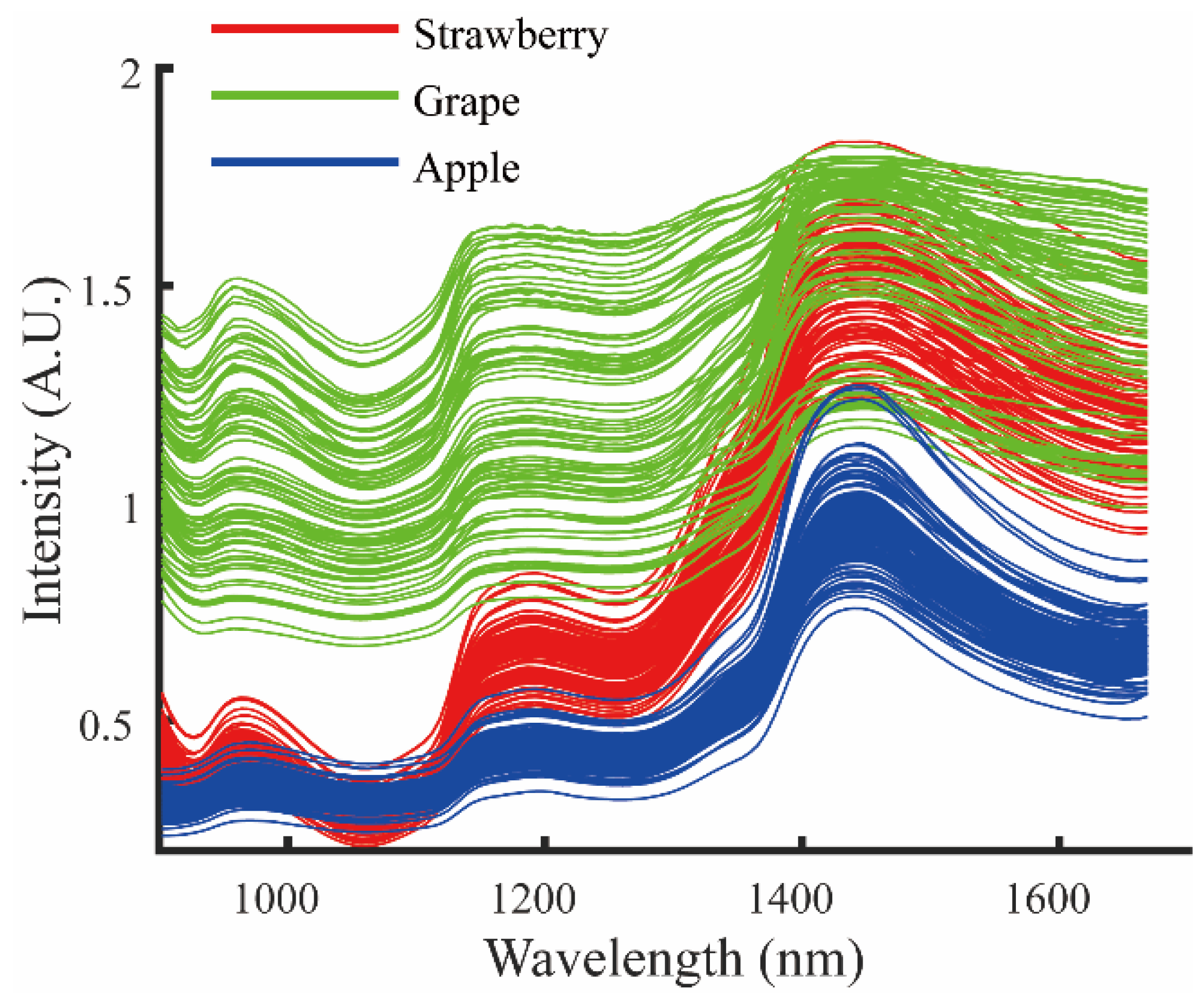
2.1. Fruit Sample Preparation and NIR Spectra Measurement
2.2. Soluble Solids Content Measurement
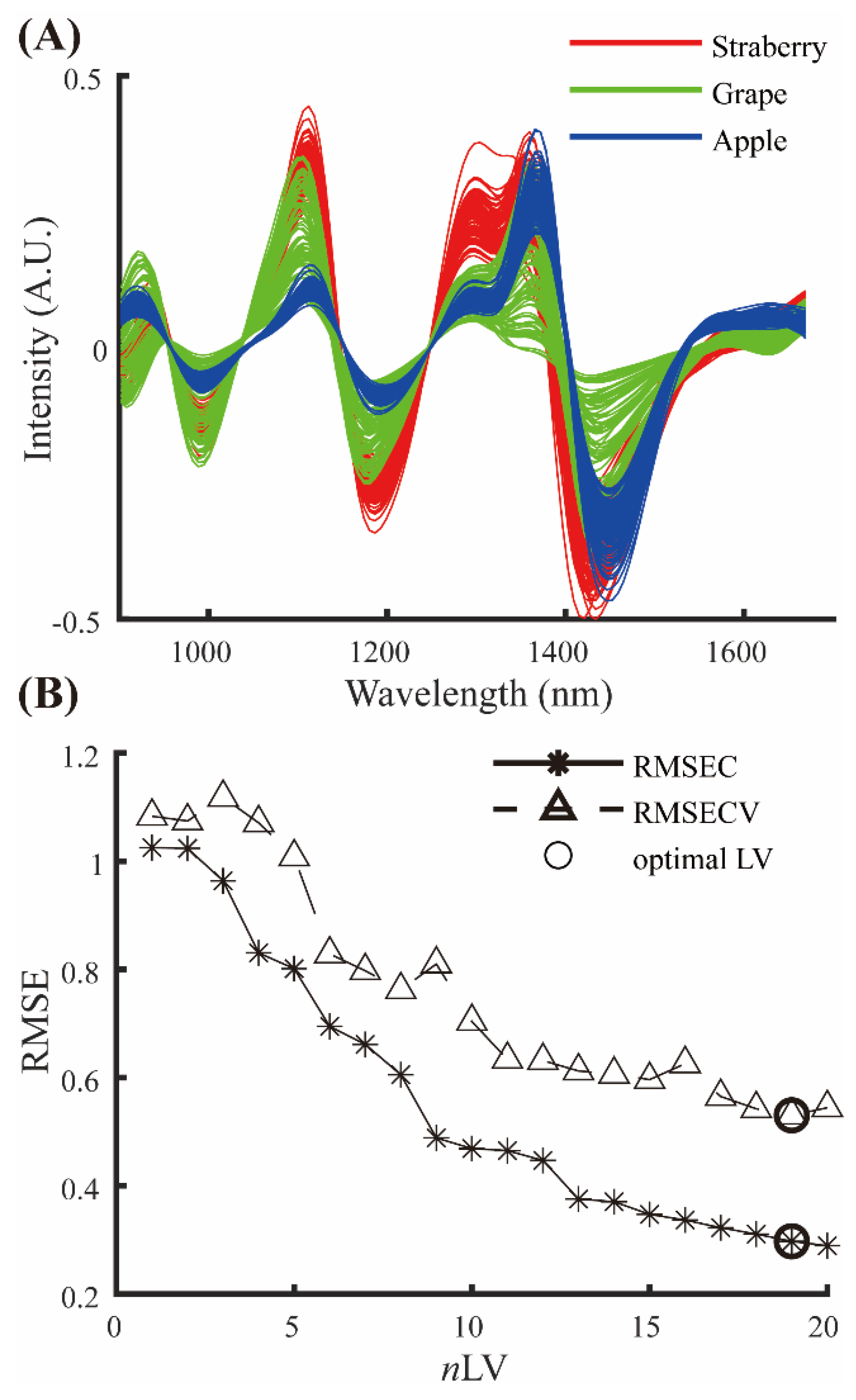
2.3. Calibration
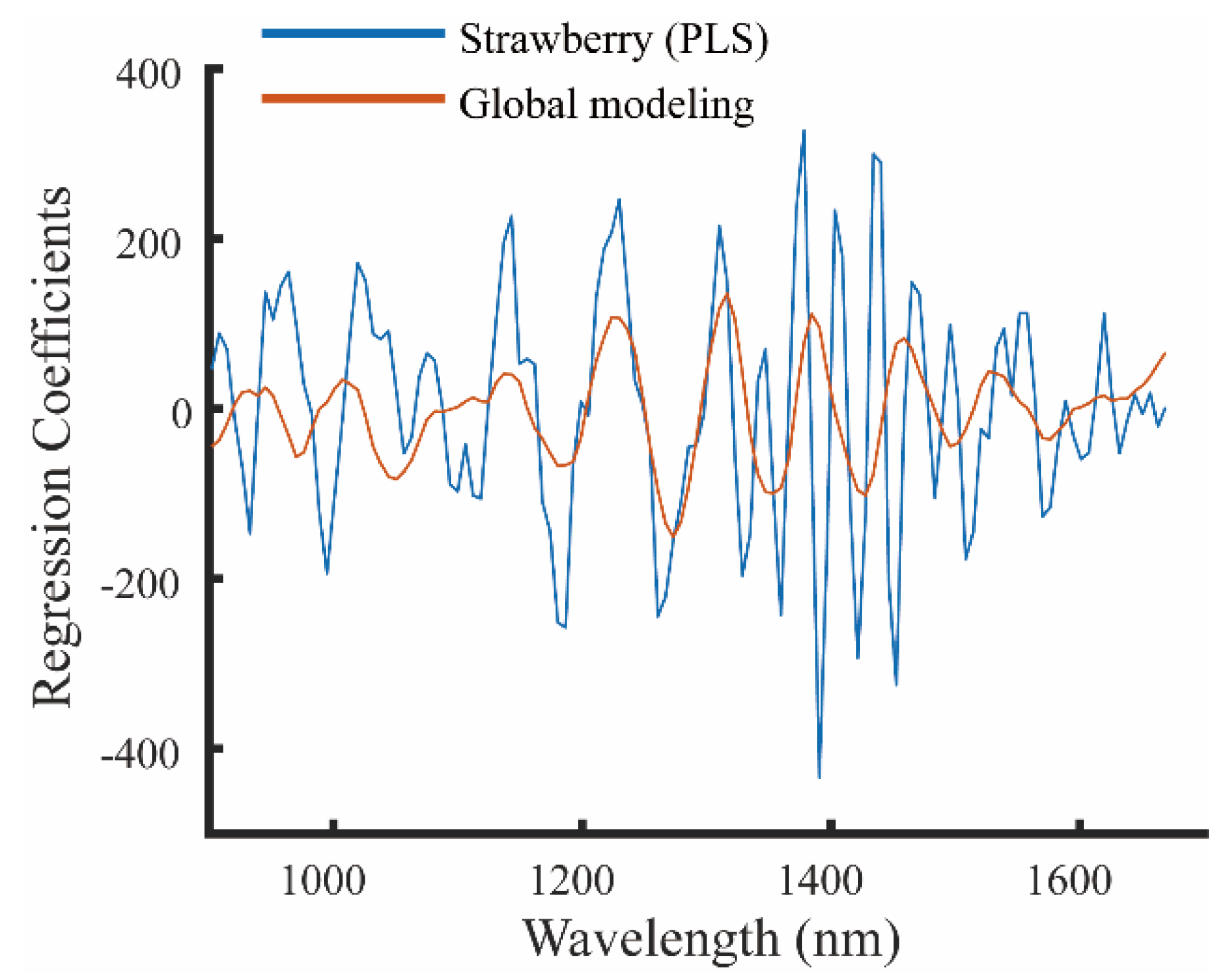
2.4. Global Modeling
2.5. Calibration Transfer
3. Results and Discussion
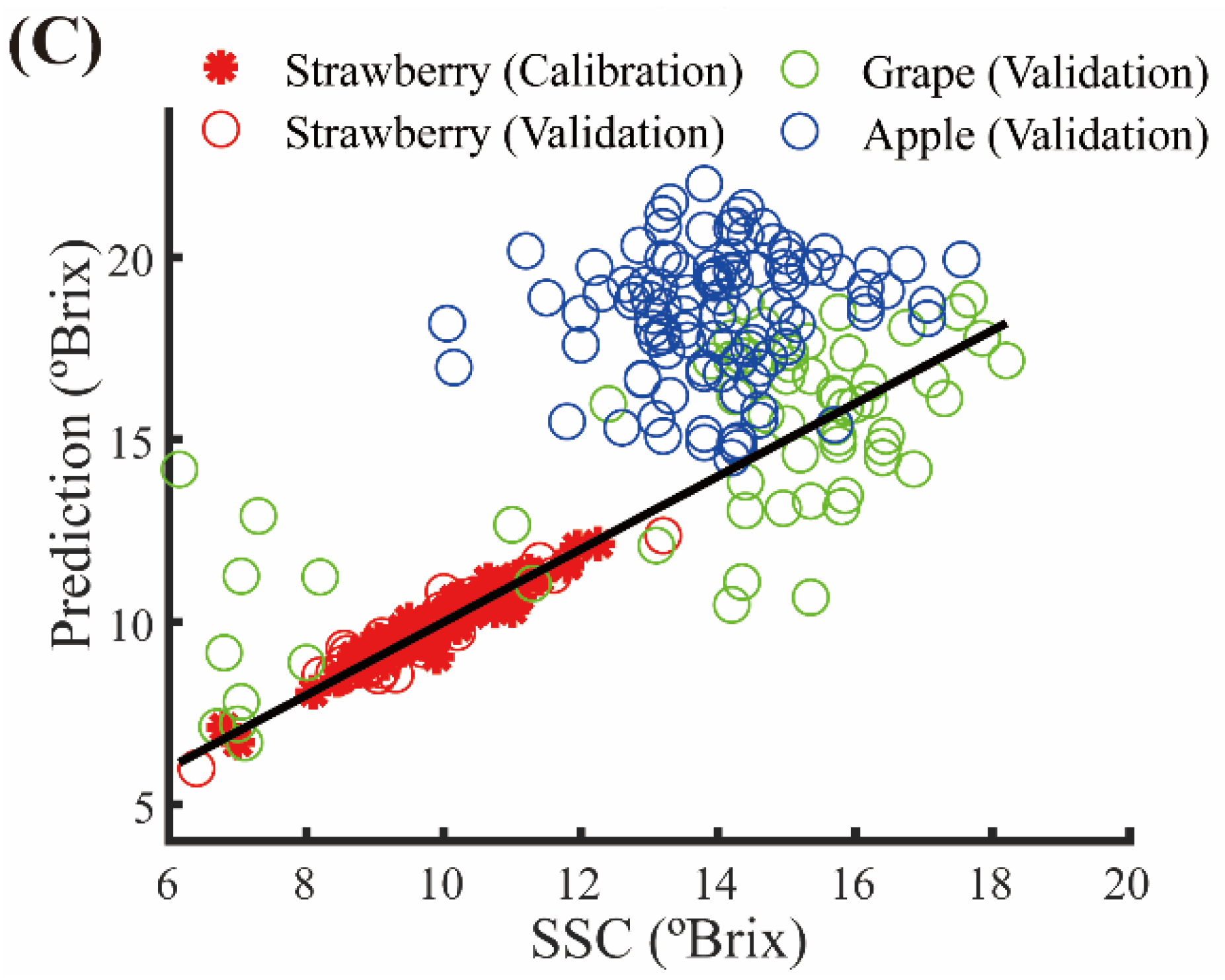
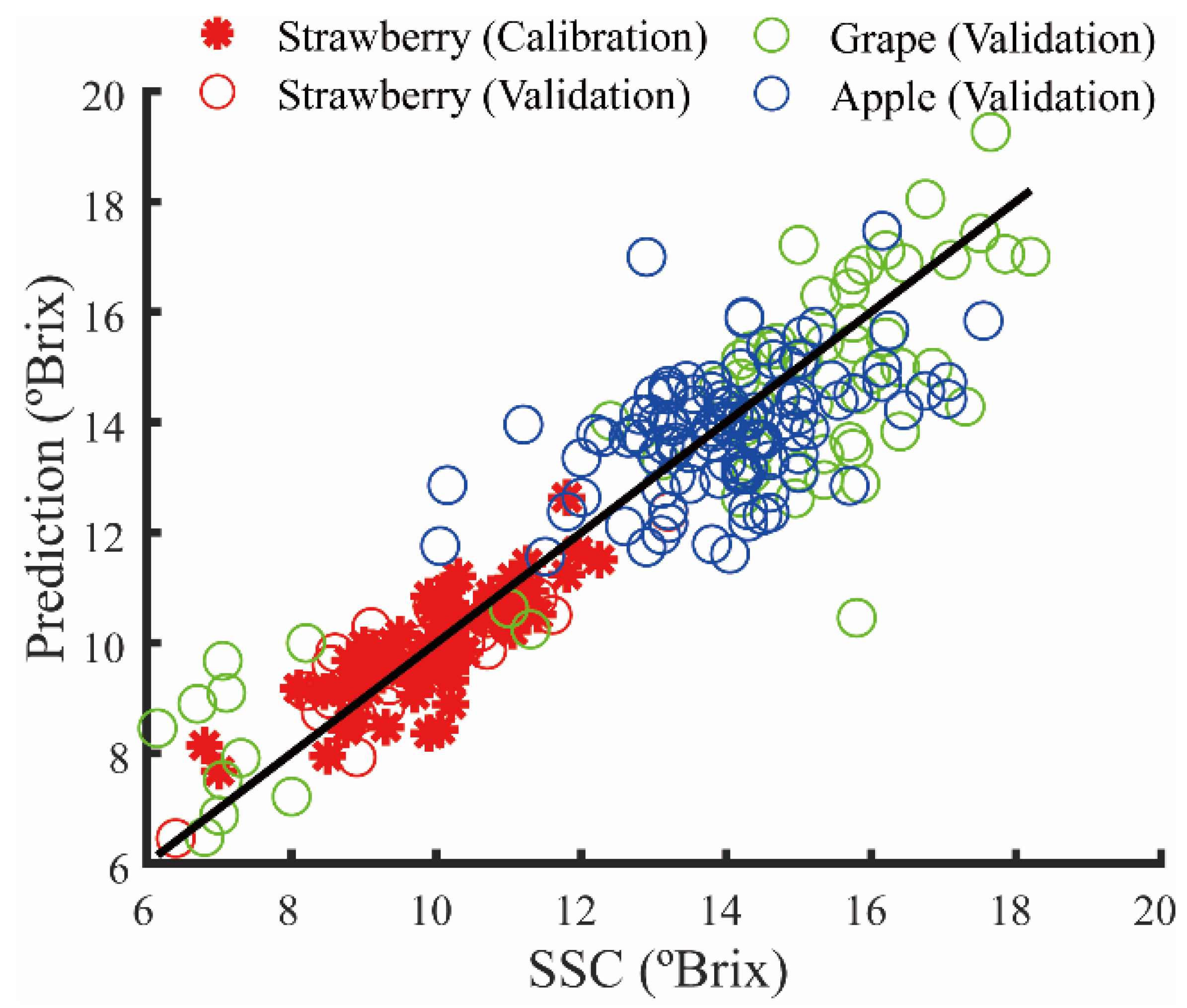
3.1. Calibration Results
3.2. Global Modeling
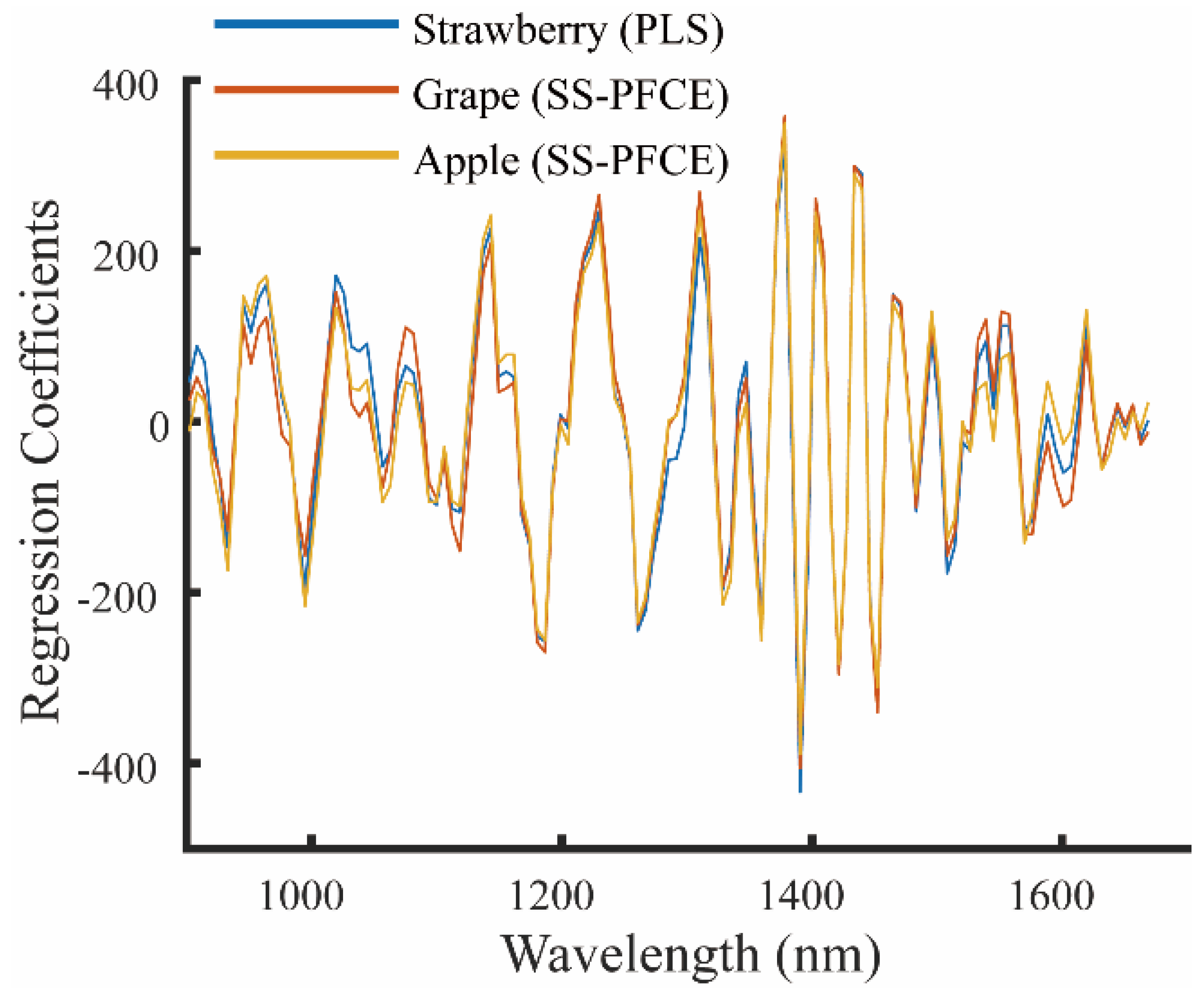
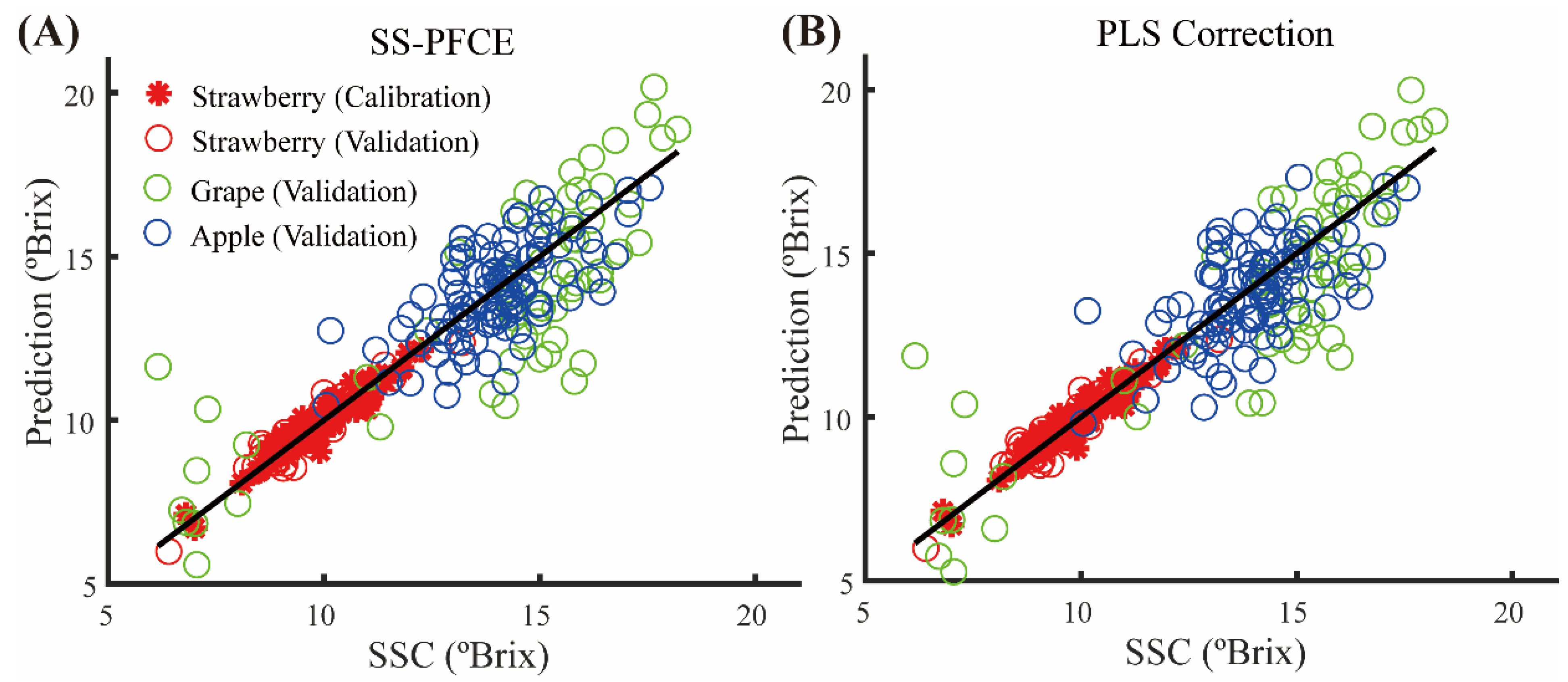
3.3. Calibration Transfer without Standards
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pasquini, C. Near infrared spectroscopy: A mature analytical technique with new perspectives—A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1026, 8–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gan, F.; Luo, J. Simple dilated convolutional neural network for quantitative modeling based on near infrared spectroscopy techniques. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2023, 232, 104710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, P.; Rutledge, D.N.; Roger, J.M.; Wali, K.; Khan, H.A. Chemometric pre-processing can negatively affect the performance of near-infrared spectroscopy models for fruit quality prediction. Talanta 2021, 229, 122303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sohaib Ali Shah, S.; Zeb, A.; Qureshi, W.S.; Arslan, M.; Ullah Malik, A.; Alasmary, W.; Alanazi, E. Towards fruit maturity estimation using NIR spectroscopy. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2020, 111, 103479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, D.; Wang, X.; Yu, L.; Zhang, W.; Li, P. Review of NIR spectroscopy methods for nondestructive quality analysis of oilseeds and edible oils. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 101, 172–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, J.J.; Cozzolino, D. An overview on the application of chemometrics in food science and technology—An approach to quantitative data analysis. Food Anal. Methods 2016, 9, 3258–3267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Ma, Y.; Han, B.X. Rapid detection of the component contents in caryophylli flos by a handheld near infrared spectrometer based on digital light processing technology. J. Near Infrared Spectrosc. 2018, 26, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Guo, C.; Cui, X.Y.; Cai, W.S.; Shao, X.G. A two-level strategy for standardization of near infrared spectra by multi-level simultaneous component analysis. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1050, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortés, V.; Blasco, J.; Aleixos, N.; Cubero, S.; Talens, P. Monitoring strategies for quality control of agricultural products using visible and near-infrared spectroscopy: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 85, 138–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Xiao, Q.; Bai, X.; Zhou, L.; Liu, F.; Zhang, C. Recent progress of nondestructive techniques for fruits damage inspection: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 5476–5494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.; Li, J.; Xia, Y.; Tian, X.; Guo, Z.; Huang, W. Long-term evaluation of soluble solids content of apples with biological variability by using near-infrared spectroscopy and calibration transfer method. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2019, 151, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Xu, Y.; Siesler, H.W.; Han, B.X.; Zhang, G.Z. Hand-held near-infrared spectroscopy for authentication of fengdous and quantitative analysis of mulberry fruits. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, N.T.; Walsh, K.B. The evolution of chemometrics coupled with near infrared spectroscopy for fruit quality evaluation. J. Near Infrared Spectrosc. 2022, 30, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Huang, W.; Lin, L.; Fan, S. Effects of orientations and regions on performance of online soluble solids content prediction models based on near-infrared spectroscopy for peaches. Foods 2022, 11, 1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jie, D.; Xie, L.; Rao, X.; Ying, Y. Using visible and near infrared diffuse transmittance technique to predict soluble solids content of watermelon in an on-line detection system. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2014, 90, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, H.; Liu, D.; Wang, L.; Sun, D.-W. Soluble solids content and pH prediction and maturity discrimination of lychee fruits using visible and near infrared hyperspectral imaging. Food Anal. Methods 2016, 9, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moros, J.; Garrigues, S.; Guardia, M.d.l. Vibrational spectroscopy provides a green tool for multi-component analysis. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2010, 29, 578–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, X.G.; Bian, X.H.; Liu, J.; Zhang, M.; Cai, W.S. Multivariate calibration methods in near infrared spectroscopic analysis. Anal. Methods 2010, 2, 1662–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boido, E.; Fariña, L.; Carrau, F.; Cozzolino, D.; Dellacassa, E. Application of near-infrared spectroscopy/artificial neural network to quantify glycosylated norisoprenoids in Tannat grapes. Food Chem. 2022, 387, 132927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Shao, X.G. Continuous Wavelet Transform applied to removing the fluctuating background in near-Infrared spectra. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 2004, 44, 907–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rady, A.; Fischer, J.; Reeves, S.; Logan, B.; James Watson, N. The effect of light intensity, sensor height, and spectral pre-processing methods when using NIR spectroscopy to identify different allergen-containing powdered foods. Sensors 2019, 20, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bian, X.H.; Cai, W.S.; Shao, X.G.; Chen, D.; Grant, E.R. Detecting influential observations by cluster analysis and Monte Carlo cross-validation. Analyst 2010, 135, 2841–2847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Liu, Z.; Cai, W.S.; Shao, X.G. A wavelength selection method based on randomization test for near-infrared spectral analysis. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2009, 97, 189–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, Y.H.; Bin, J.; Liu, D.L.; Xu, L.; Yan, T.L.; Cao, D.S.; Xu, Q.S. A hybrid variable selection strategy based on continuous shrinkage of variable space in multivariate calibration. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1058, 58–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, X.G.; Bian, X.H.; Cai, W.S. An improved boosting partial least squares method for near-infrared spectroscopic quantitative analysis. Anal. Chim. Acta 2010, 666, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Huang, W.; Wang, Z.; Liu, S.; He, X.; Fan, S. Calibration transfer between developed portable Vis/NIR devices for detection of soluble solids contents in apple. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2022, 183, 111720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinnan, Å.; van den Berg, F.; Engelsen, S.B. Review of the most common pre-processing techniques for near-infrared spectra. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2009, 28, 1201–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Workman, J.J. A review of calibration transfer practices and instrument differences in spectroscopy. Appl. Spectrosc. 2018, 72, 340–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.J.; Li, Z.F.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Cai, W.S.; Shao, X.G. A dual model strategy to transfer multivariate calibration models for near-infrared spectral analysis. Spectrosc. Lett. 2016, 48, 348–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, P.; Nikzad-Langerodi, R.; Marini, F.; Roger, J.M.; Biancolillo, A.; Rutledge, D.N.; Lohumi, S. Are standard sample measurements still needed to transfer multivariate calibration models between near-infrared spectrometers? The answer is not always. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2021, 143, 116331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Cai, W.S.; Shao, X.G. Linear model correction: A method for transferring a near-infrared multivariate calibration model without standard samples. Spectrochim. Acta Part A 2016, 169, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, X.Y.; Yu, X.; Cai, W.S.; Shao, X.G. Water as a probe for serum–based diagnosis by temperature–dependent near–infrared spectroscopy. Talanta 2019, 204, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Li, B.; Hu, Y.; Zhou, L.; Wang, G.; Guo, G.; Zhang, Q.; Lei, S.; Zhang, A. A parameter-free framework for calibration enhancement of near-infrared spectroscopy based on correlation constraint. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1142, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Cai, W.S.; Shao, X.G. Correcting multivariate calibration model for near infrared spectral analysis without using standard samples. J. Near Infrared Spectrosc. 2015, 23, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Fruits | SSC Range (°Brix) | Number of Samples |
|---|---|---|
| Strawberry | 6.40–13.20 | 94 |
| Grape | 6.15–18.20 | 80 |
| Apple | 9.35–17.55 | 125 |
| Preprocessing Methods | nLV | Calibration | Validation | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSEC (°Brix) | Rc | RMSEP (°Brix) | Rp | ||
| None | |||||
| Strawberry | 15 | 0.32 | 0.95 | 0.53 | 0.91 |
| Grape | - | - | - | 3.47 | 0.84 |
| Apple | - | - | - | 16.40 | 0.01 |
| CWT | |||||
| Strawberry | 19 | 0.30 | 0.96 | 0.41 | 0.95 |
| Grape | - | - | - | 2.40 | 0.74 |
| Apple | - | - | - | 4.90 | 0.12 |
| SG Smooth | |||||
| Strawberry | 12 | 0.54 | 0.86 | 0.78 | 0.80 |
| Grape | - | - | - | 2.94 | 0.67 |
| Apple | - | - | - | 25.44 | 0.28 |
| SNV | |||||
| Strawberry | 19 | 0.18 | 0.99 | 0.41 | 0.95 |
| Grape | - | - | - | 6.48 | 0.34 |
| Apple | - | - | - | 14.45 | 0.11 |
| Prediction Set | RMSEP (°Brix) | Rp |
|---|---|---|
| Strawberry | 0.66 | 0.86 |
| Grape | 1.55 | 0.89 |
| Apple | 1.28 | 0.45 |
| Model | Prediction Set | RMSEP (°Brix) | Rp |
|---|---|---|---|
| Strawberry | Strawberry | 0.41 | 0.95 |
| Strawberry | Grape | 2.40 | 0.74 |
| Strawberry | Apple | 4.90 | 0.12 |
| SS-PFCE | Grape | 1.99 | 0.84 |
| SS-PFCE | Apple | 1.14 | 0.65 |
| PLS Correction | Grape | 1.77 | 0.87 |
| PLS Correction | Apple | 1.22 | 0.64 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, C.; Zhang, J.; Cai, W.; Shao, X. Enhancing Transferability of Near-Infrared Spectral Models for Soluble Solids Content Prediction across Different Fruits. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 5417. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13095417
Guo C, Zhang J, Cai W, Shao X. Enhancing Transferability of Near-Infrared Spectral Models for Soluble Solids Content Prediction across Different Fruits. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(9):5417. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13095417
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Cheng, Jin Zhang, Wensheng Cai, and Xueguang Shao. 2023. "Enhancing Transferability of Near-Infrared Spectral Models for Soluble Solids Content Prediction across Different Fruits" Applied Sciences 13, no. 9: 5417. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13095417
APA StyleGuo, C., Zhang, J., Cai, W., & Shao, X. (2023). Enhancing Transferability of Near-Infrared Spectral Models for Soluble Solids Content Prediction across Different Fruits. Applied Sciences, 13(9), 5417. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13095417






