Abstract
Synthesis of gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) using phytochemicals has become tremendously prominent in biomedical applications because of its enhanced bioactivity and biocompatibility. In this study, water extracts from the leaves of Cyclopia genistoides (C. genistoides), commonly known as honeybush (HB), were used to synthesize honeybush gold nanoparticles (HB-AuNPs). The HB water extracts (HBE) served as both reducing and capping agents in the synthesis of HB-AuNPs. The HB-AuNPs were characterized by UV–Vis spectrophotometry, dynamic light scattering (DLS), and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). The cytotoxicity and apoptotic effects of the HBE and HB-AuNPs, alone and in combination with doxorubicin (Dox), were examined against various human cell lines. Spherical-shaped HB-AuNPs with a hydrodynamic diameter range of 63 to 121 nm were produced. The HB-AuNPs conferred selective cytotoxicity against colon (Caco-2), breast (MCF-7), and prostate (PC-3) cancer cells and did not display any cytotoxicity to non-cancerous skin fibroblast (KMST-6) and human embryonic kidney (HEK)-293 cells. Moreover, co-treatment of Caco-2 cells with HB-AuNPs and Dox (at non-toxic concentrations) significantly enhanced the anti-cancer effects of Dox towards the Caco-2 cells. Furthermore, it was demonstrated that HB-AuNPs induced PC-3 cell death through apoptosis. Further studies are warranted to elucidate the mechanisms by which the HB-AuNPs influence cell death when used alone or in combination with drugs, as well as the type of phytochemicals involved in AuNPs synthesis and activity.
1. Introduction
Plants are among the natural products that have significantly contributed to modern medicine. There are several chemically profiled phytochemicals that were used in drug formulation and development, some are still used in clinical treatment of various infectious and chronic diseases. To date, nature proves to be an infinite source of highly potent drug candidates and is continuously being explored for novel drug leads [1,2]. South Africa contributes 10% of the world’s flora and is blessed with a remarkable diversity of indigenous plants [3]. Some of these plants exhibit various medicinal properties that have been used for centuries in the treatment of a diverse range of diseases. Motivated by the sparsely explored medicinal properties of indigenous South African plants, honeybush (HB), of the genus Cyclopia, became a medicinal plant of interest as a mangiferin (MGF)-rich plant [4]. MGF has many health benefits [5] and is believed to be among the phytochemicals that are responsible for HB’s bioactivity [4,6]. Cyclopia are classified into 20 species of flowering plants, examples include C. intermedia, C. genistoides, C. maculata, C. sessiliflora, and C. longifolia that are endemic to the Cape Floristic Region of South Africa. HB leaves are commonly used to make medicinal beverages and a herbal tea [7,8] that is caffeine-free and recognized for its many health benefits [4,9,10], such as anti-oxidant, anti-mutagenic, and anti-carcinogenic activities [8,11,12]. HB tea has been used by indigenous South African people for many centuries in folk medicine [7,8] to treat various ailments such as respiratory infections and digestive problems, to soothe the central nervous system, and to boost the immune system [9]. It has also been reported to have the inherent ability to prevent the development of skin cancer [13,14] and confer protection against oxidative stress via radical scavenging activity, iron-reducing potential, and inhibition of lipid peroxidation [7]. Although there is a notion that plant-derived medicines are safe, some of the phytochemicals are associated with serious health issues [15]. Moreover the pure active compounds tend to have low solubility, permeability, and bioavailability, which has limited their clinical application [16].
The emergence of green nanotechnology proved vital for phytotherapy, to help improve drug delivery, bioavailability, and reduce bystander effects. Nanotechnology deals with the synthesis and application of materials within a size range of 1 to 100 nm [16,17,18]. Among the various types of NPs, metallic NPs have drawn considerable attention due to their unique catalytic, optical, and electronic properties [18,19,20]. Generally, these NPs are synthesized by physical and chemical methods using top-down and bottom-up approaches. However, both these methods are potentially hazardous to the environment and living organisms, as they use toxic chemical additives and high temperatures [18,19]. As a corollary, recent developments in nanotechnology are focused on environmentally friendly, cost-effective, and biocompatible green synthesis methods. Green synthesis utilizes natural products as reducing, capping, and stabilizing agents in a one-step protocol. Plant-mediated synthesis was proven to be more economical than using microbial systems [20,21]. Plant biodiversity is a potential reservoir for phytochemicals that can be used for the green synthesis of metallic NPs with enhanced biological applications [22,23,24]. Aspalathus linearis (rooibos tea) has been used to synthesize AuNPs [19,22], palladium, and palladium oxide NPs [25]. Salvia africana-lutea and Sutherlandia frutescens were also used to synthesize AuNPs and silver NPs [23]. HB species were also explored in the synthesis of HB-AuNPs using water extracts from C. intermedia [4,6]. These NPs were reported to inhibit microbial (fungi and bacteria) [22,23,24,26] and cancer cell [4,27] growth, alone or in combination with conventional treatments [4,6].
In addition to the selective anticancer activity of the HB-AuNPs synthesized from C. intermedia (HB-AuNPs_ci), the AuNPs demonstrated a unique property of drug sensitization. When co-administered with a chemotherapeutic drug (Dox), HB-AuNPs_ci were reported to increase the biocompatibility of Dox by sensitizing its therapeutic activity at a non-active dose, which might help reduce the drug’s bystander effects [4,6]. In the current study, another HB species (C. genistoides) was investigated to determine if species under the same genus will behave in a similar manner; either in AuNPs synthesis or their bioactivity. The HB-AuNPs from C. genistoides significantly promoted the cytotoxic effects of Dox in Caco-2 cells during co-treatment, further highlighting the potential clinical value of biogenic nanomaterials. The clinical benefits of AuNPs-chemotherapeutic drug co-treatment were demonstrated in a pilot clinical trial performed on humans, where administration of Nano Swarna bhasma (AuNPs synthesized using mango peel and combined with five plant extracts) with Dox and cyclophosphamide showed no adverse effects in breast cancer patients [28].
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
The water-soluble tetrazolium (WST)-1 cell proliferation reagent was purchased from Roche Diagnostics (Mannheim, Germany) and sodium tetrachloroaurate (III) dihydrate (NaAuCl4·2H2O) from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA). The ApopercentageTM assay kit (product ID: A1000) was obtained from Biocolor Ltd. (County Antrim, UK); fetal bovine serum (FBS), Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle’s Media (DMEM), and Roswell Park Memorial Institute Medium (RPMI)-1640 were purchased from Gibco (Rockville, MD, USA), and penicillin/streptomycin was from Lonza (Basel, Switzerland). All the chemicals used in the study were bought from reputable companies and are of good quality.
2.2. Plant Collection
Fresh leaves of C. genistoides plants were collected from the commercial farms situated in the Boland and Overberg regions of the Western Cape Province (South Africa) and were purchased from local nurseries. The identification of the plant was performed according to the taxonomic revision of the Cyclopia genus [29].
Preparation of HBE
The HB leaves were thoroughly washed with deionized water, cut into small pieces, and dried in the shade for 48 h. Then, 5 g of the dried plant material was transferred into 50 mL of boiling distilled water and stirred for 24 h without heating as per the methods previously described [30]. The HBE was filtered using glass wool to remove the large plant materials. The filtrate was centrifuged at 3750 rpm in an ALLEGRA X-12R centrifuge (Beckman Coulter, Indianapolis, IN, USA) for 1 h and then filtered through 0.45 μm syringe filters to obtain a clear filtrate. The supernatant was frozen at −20 °C, freeze-dried using Virtis Model 10-020 (The Virtis Company Inc., Gardiner, NY, USA), and stored in a desiccator until further analysis.
2.3. Biosynthesis of HB-AuNPs
Synthesis of the HB-AuNPs was optimized following a protocol described by Elbagory et al., with some modifications [19]. The stock concentration (50 mg/mL) of the HBE was freshly prepared in distilled water, the extract was serially diluted from 8 to 0.25 mg/mL. Then, 50 µL of the HBE was added into 200 µL of 1 mM NaAuCl4·2H2O solution in a 96-well plate. The mixture was incubated at 25 °C and 70 °C while shaking at 40 rpm for 30 min, followed by UV–Vis spectrum analysis of the AuNPs ranging from 300 nm to 800 nm using a POLARstar Omega microplate reader (BMG Labtech, Offenberg, Germany) [19]. The optimal synthesis conditions, i.e., the HBE concentration which produced the best AuNPs (based on the UV-Vis spectrum), were used to upscale HB-AuNPs synthesis to 30 mL using a 1:5 ratio of HBE to 1 mM NaAuCl4·2H2O. Following synthesis, the HB-AuNPs were collected by centrifugation at 14,000 rpm for 10 min, and the HB-AuNPs pellet was washed twice with distilled water to remove unreacted plant material and NaAuCl4·2H2O. A stock solution of the HB-AuNPs was prepared by suspending the pellet in distilled water and was kept at 4 °C until further use.
2.3.1. Optical Properties and DLS Analysis of HB-AuNPs
The surface plasmon resonance (SPR) of the HB-AuNPs was measured using a POLARstar Omega microplate reader. The size distribution, zeta potential, and PDI measurements for the HB-AuNPs were analyzed using a Nano-ZS90 Zetasizer instrument (Malvern Panalytical Ltd., Enigma Business Park, UK).
2.3.2. High-Resolution TEM (HRTEM) Analyses
The shape, morphology, and dispersity of the HB-AuNPs were analyzed by HRTEM and elemental mapping was performed by energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX) in a Hitachi HT7800 TEM (Tokyo, Japan) operated in a bright field mode and accelerating voltage of 200 kV. One drop of HB-AuNPs was placed on a carbon-coated copper grid, dried at room temperature, and analyzed under a TEM-EDX instrument. The core size distribution was analyzed using ImageJ Software (National Institutes of Health, Stapleton, NY, USA).
2.4. Evaluation of HB-AuNPs Stability
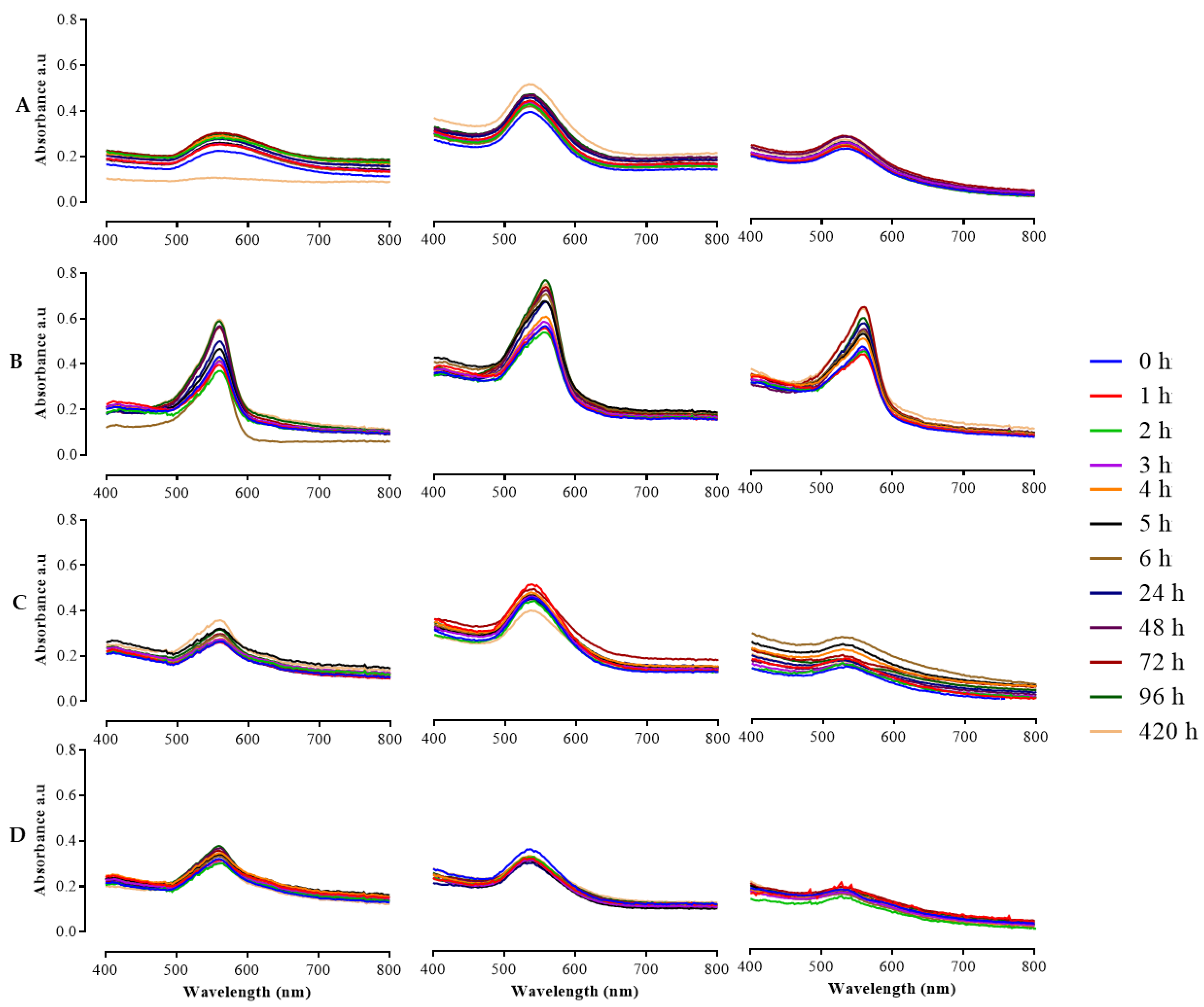
The in vitro stability of HB-AuNPs was monitored for a 420 h period (7 days) at 1 h intervals for the first 6 h, then at 24 h intervals from 24 to 420 h using UV–Vis absorption spectrophotometer as previously described [31]. The stability of the HB-AuNPs was evaluated in distilled water, Phosphate-Buffered Saline (PBS), RPMI-1640, and DMEM. The media were supplemented with 10% FBS and 1% penicillin/streptomycin. At the respective time points, 100 μL of the HB-AuNPs solutions were added into a 96-well plate and the UV–Vis was measured on a POLARstar Omega microplate reader.
2.5. Investigation of the In Vitro Cytotoxicity of HBE and HB-AuNPs
2.5.1. Effects of HB-AuNPs on Cell Viability: WST-1 Assay
The effect of HB-AuNPs was evaluated on human cancer cell lines (Caco-2, PC-3, MCF-7) and non-cancer cell lines (KMST-6, HEK-293) using the WST-1 assay as described elsewhere [32]. The cells were purchased from the American Type Culture Collection (Manassas, VA, USA). Briefly, the PC-3 cells were cultured in RPMI-1640, whereas the KMST-6, HEK-293, Caco-2, and MCF-7 cells were cultured in DMEM. The cells were seeded at a density of 1 × 105 cells/mL in a 96-well microplate in their respective media containing 10% FBS and 1% penicillin/streptomycin. The cells were treated for 24 h with increasing concentrations of HB-AuNPs (0 to 100 µg/mL) and HBE (0 to 8 mg/mL). The effect of the treatments on cell viability was evaluated using the WST-1 assay as previously described [32]. The absorbance of the samples was measured at 440 nm (with a reference wavelength of 600 nm) using a POLARstar Omega microplate reader. The percentage cell viability was calculated as follows:
2.5.2. HB-AuNPs Uptake: Dark-Field Microscopic Analysis
Internalization of the HB-AuNPs was evaluated by a dark-field microscope following a previously described method [33]. The cells were seeded (≤5000 cells/well) on 12 mm coverslips placed in a 12-well plate and incubated for 24 h at 37 °C. The growth media was replaced with media containing 1 mL of HB-AuNPs and incubated for 24 h. The cells were washed thrice with PBS and fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde for 15 min. The fixative was washed off with PBS, and the coverslips were mounted on the slides with fluoroshield with 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI, Sigma) and viewed under a dark-field microscope using a Leica DM2500 LED optical microscope (Leica Microsystems CMS GmbH, Mannheim, Germany).
2.5.3. Apoptotic Effects of HB-AuNPs against Prostate Cancer Cells
The induction of apoptosis in PC-3 cells treated with HBE and HB-AuNPs was assessed using the ApopercentageTM assay, following a previously reported protocol [32,34]. The PC-3 cells were seeded at a density of 2 × 105 cells/mL in a 12-well culture plate and treated for 24 h with the concentrations of HBE or HB-AuNPs that killed 50% of the cells. Ceramide was used as a positive control at 50 µM. All treatments were performed in triplicate. The cells were harvested and stained with ApopercentageTM dye reagent for 30 min and washed with PBS. The cells were resuspended in PBS and analyzed using an AccuriTM C6 flow Cytometer (BD Biosciences, Erembodegem, Belgium) within 30 min.
2.6. Statistical Analysis
Each experiment was performed in triplicate, and statistical analysis was conducted using one-way ANOVA and Graph Pad Prism software. A p-value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis and Characterization of HB-AuNPs
The overall hazardous effects associated with the physical and chemical synthesis methods have necessitated the use of less toxic natural products for the synthesis of biogenic NPs. The number of studies describing the use of plant-mediated NPs has increased significantly in the past decade, as well as research describing the possible health benefits of these biogenic NPs in pre-clinical [4,31,35] and clinical studies [28]. As a follow-up to our previous studies [4,6], in the current study we investigated the effect of HB-AuNPs synthesized from C. genistoides on cancer cells either alone or in combination with Dox. Phytochemicals in the HBE served as reducing and capping agents in the synthesis of stable and bioactive HB-AuNPs following optimization of temperature, HBE concentration, and time of synthesis. These parameters are among other factors that control the shape and size of NPs [23,24,36].
3.1.1. Effect of Temperature, HBE Concentration, and Time
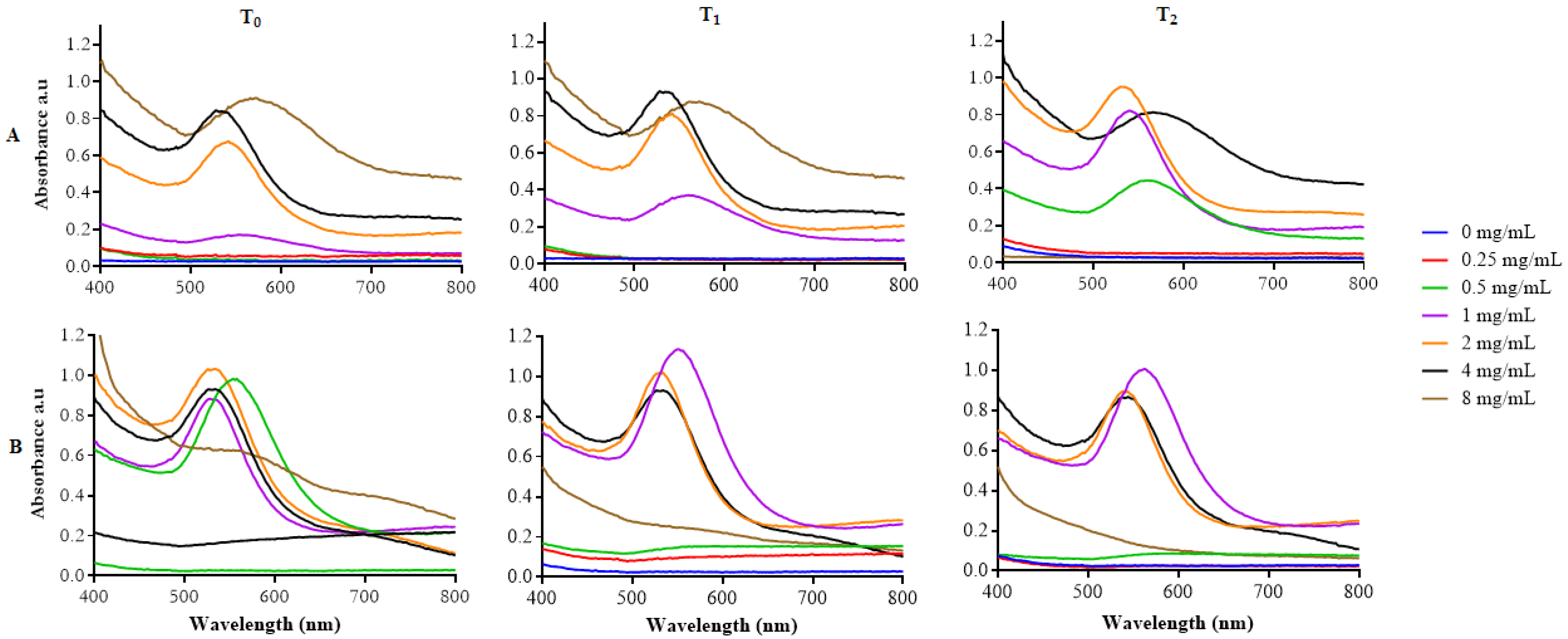
The successful synthesis of the HB-AuNPs was indicated by the appearance of a wine red color, which results in a sharp and intense absorption band in a visible region at 500–600 nm [37,38]. Likewise, the HB-AuNPs had an absorption peak or SPR in the range of 542 to 564 nm for HBE concentrations starting from 0.5 mg/mL at both 25 °C (Figure 1A) and 70 °C (Figure 1B) at 0–2 h (T0–T2). The SPR of the HB-AuNPs stabilized at 542 nm for HB-AuNPs synthesized with 2 and 4 mg/mL (summarized in Table 1). There were also notable broad peaks and red shift in the SPR of 8 mg/mL_HB-AuNPs, an indication that larger and non-uniform NPs were formed at this concentration. The SPR of NPs is reflective of some factors such as their size, shape, refractive index of dispersive medium, and distance of neighboring NPs [39].
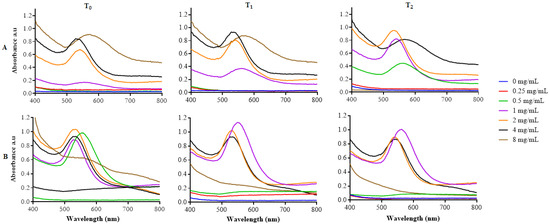
Figure 1.
Synthesis of HB-AuNPs using different concentrations of HBE at 25 °C (A) and 70 °C (B). Optical properties of the HB-AuNPs were measured at 0–2 h, designated as T0–T2.

Table 1.
Optical and DLS analysis of the HB-AuNPs synthesized at various HBE concentrations at 70 °C.
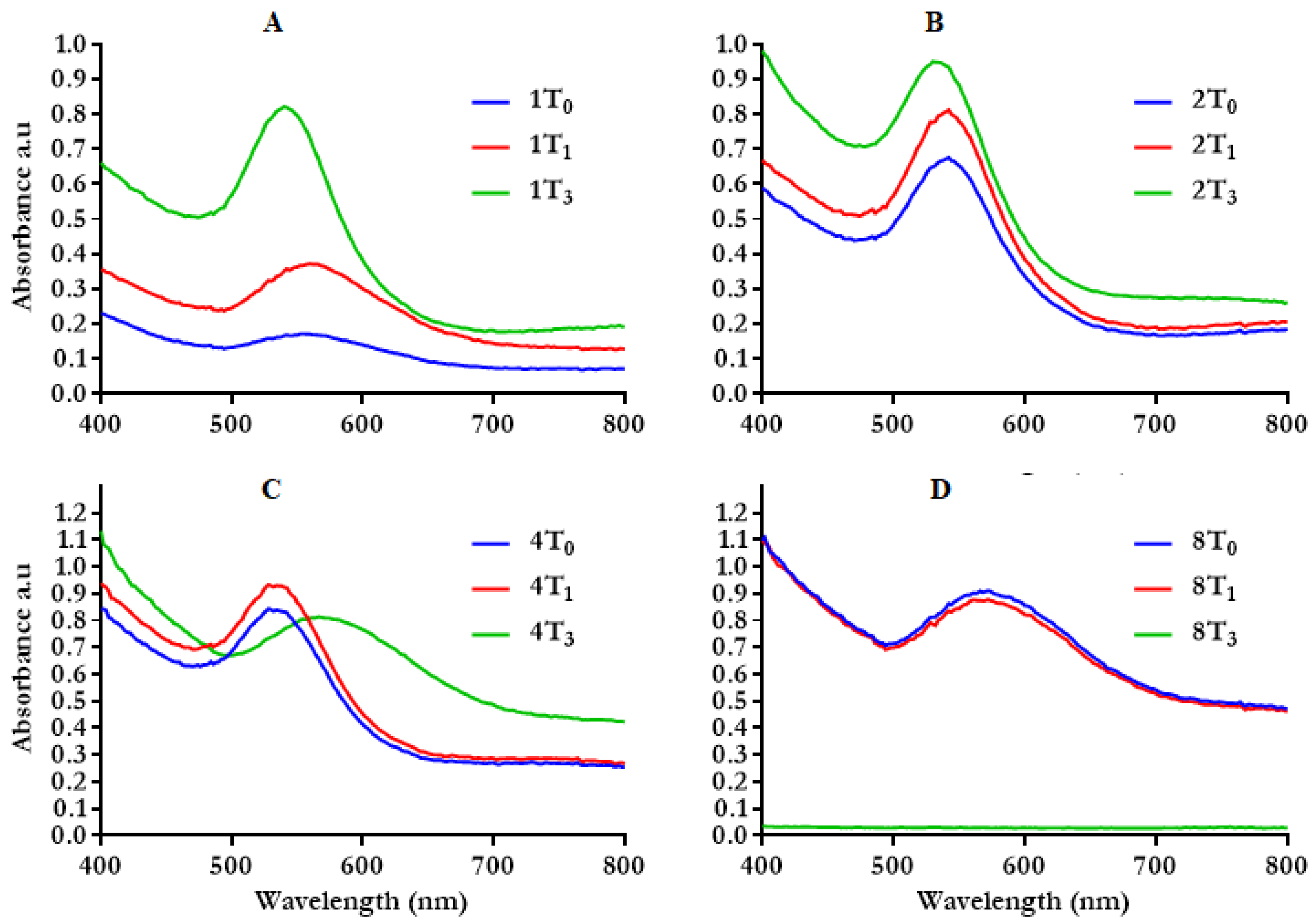
The time of reaction is one of the important factors that influences the physicochemical properties of NPs. The rate of HB-AuNPs synthesized with 1 to 8 mg/mL HBE at an optimal temperature (70 °C) at different time points is shown in Figure 2. The synthesis of HB-AuNPs was immediate, starting at time zero (T0) for the selected HBE concentrations. The absorption peaks increased with an increase in reaction time (T0–T2), which was most evident in HB-AuNPs synthesized with 1 and 2 mg/mL of HBE (Figure 2A,B). Synthesis of HB-AuNPs was time and concentration dependent, i.e., synthesis with 1mg/mL of HBE took a longer time compared with the higher HBE concentrations (2–8 mg/mL). The 2 mg/mL_HB-AuNPs did not show a significant variation in SPR with change in time (Figure 2B). However, the peak for 4 mg/mL_HB-AuNPs became broader at T2, causing a blue shift in SPR (Figure 2C); the same behavior was also observed with 8 mg/mL_HB-AuNPs at both T0 and T1 (Figure 2D). The broadening of the peaks suggested that the size and shape of AuNPs has changed, and this was further confirmed by aggregation of 8 mg/mL_HB-AuNPs at T2. Thus, reaction time and temperature, in addition to other parameters such as the pH of the solution and the reducing agents influences the physical parameters of the NPs. Shorter reaction times mainly produce smaller and spherical sizes, whereas longer times change the nanospheres to other shapes such as nanoprisms [40].
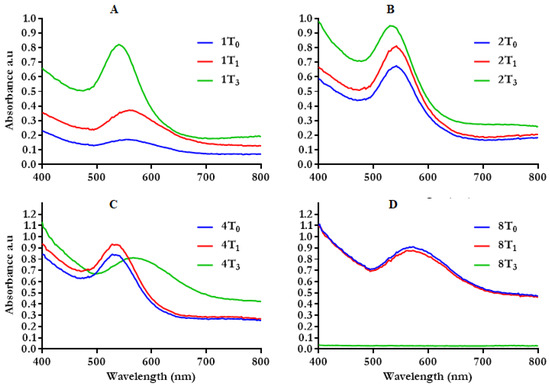
Figure 2.
Effect of reaction time on the synthesis of HB-AuNPs at 70 °C using 1 mg/mL (A), 2 mg/mL (B), 4 mg/mL (C), and 8 mg/mL (D) of HBE. The numbers (1, 2, 4, and 8) represent the concentration of HBE in mg/mL; T0–T2 represent the reaction time from 0–2 h.
3.1.2. DLS Properties of HB-AuNPs
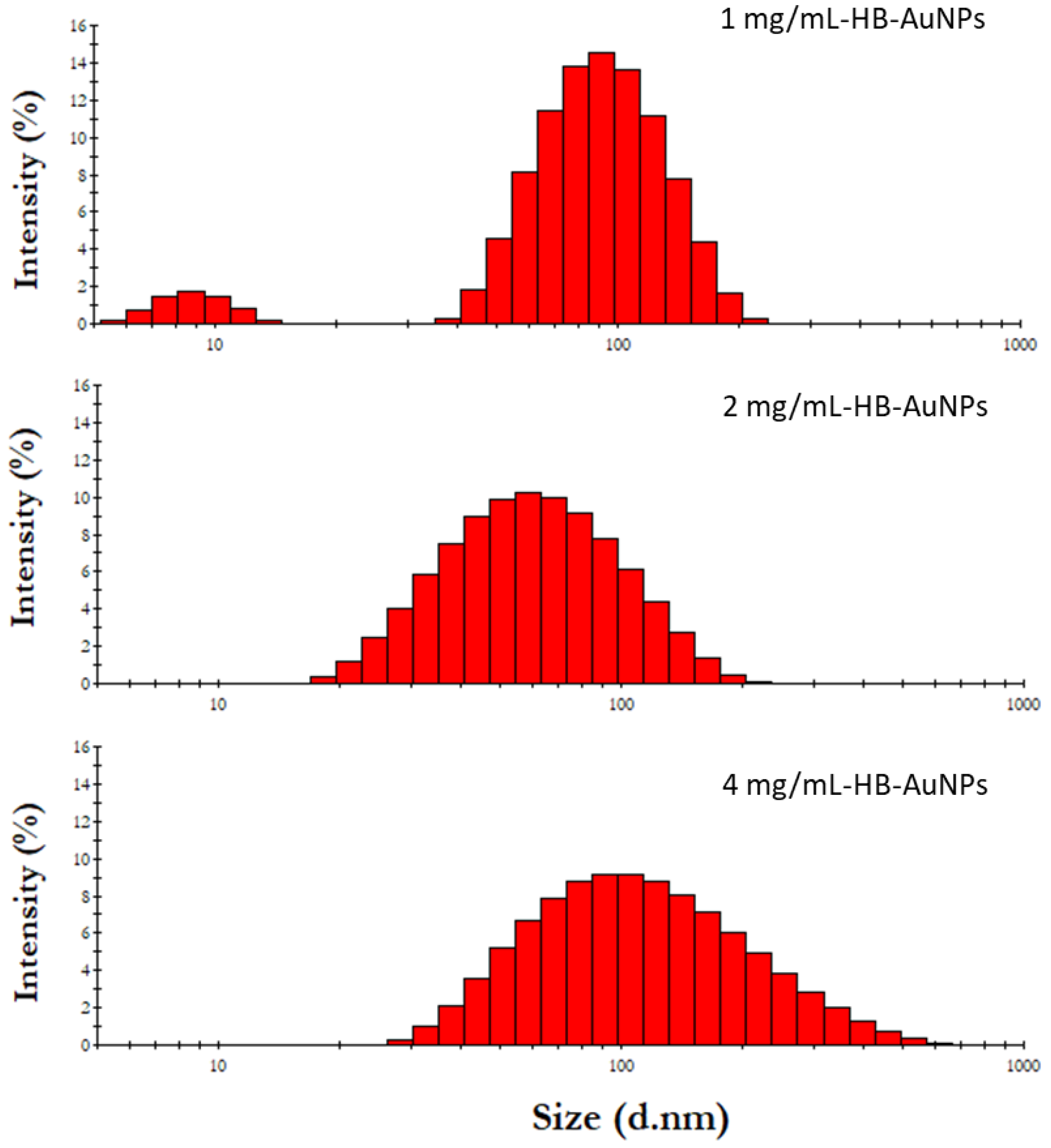
The representative hydrodynamic sizes of the HB-AuNPs are shown in Figure 3. As summarized in Table 1, the 4 mg_HB-AuNPs had the largest hydrodynamic diameter of 121 nm, followed by 1 mg/mL_HB-AuNPs that had a hydrodynamic size of 98 nm and 2 mg/mL_HB-AuNPs that that had a hydrodynamic size of 63 nm. Their zeta potentials were also measured to determine the physiochemical stability of the HB-AuNPs. The zeta potential provides information about the long-term stability of the AuNPs in a solution, which relies on the repulsion forces between the particles. All the HB-AuNPs had a negative zeta potential (Table 1) ranging from −18.1 to −22 mV. Colloids with zeta potential values that are within the −30 and +30 mV range are considered to be stable and provide sufficient repulsive forces to keep the colloids stable for a longer period [41]. The PDI of the HB-AuNPs confirmed that 2 mg/mL_HB-AuNPs (0.31) and 4 mg/mL_HB-AuNPs (0.39) were more stable than the 1 mg/mL_HB-AuNPs (0.58).
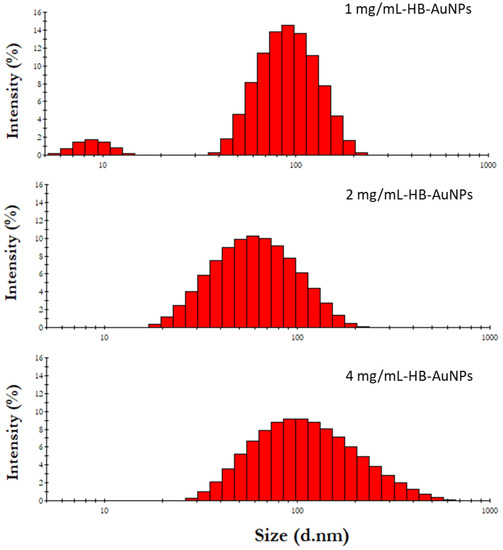
Figure 3.
Hydrodynamic size distribution of HB-AuNPs synthesized at various HBE concentrations at 70 °C.
3.1.3. HRTEM Analysis of 2 mg/mL_HB-AuNPs
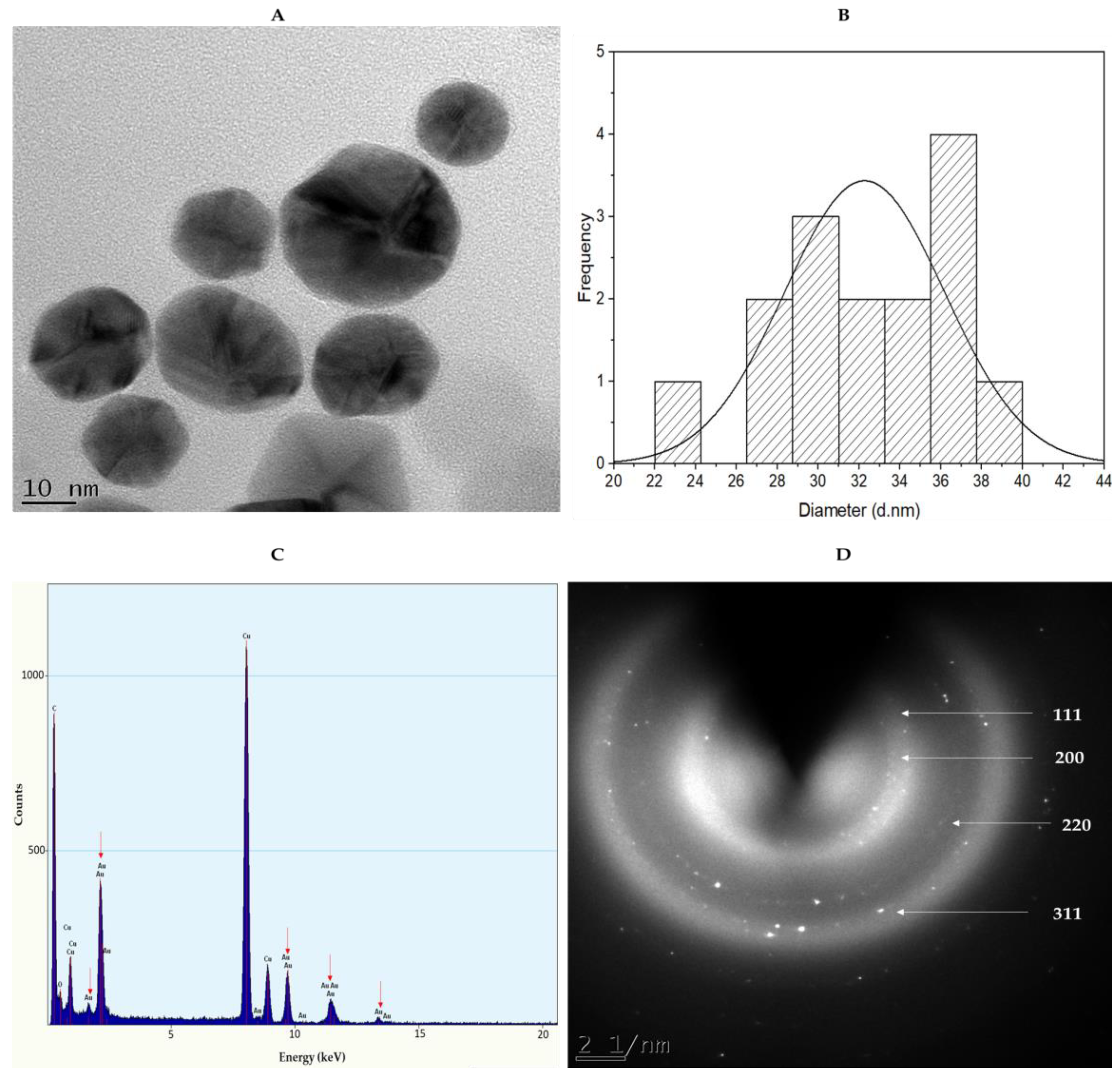
The smaller-sized HB-AuNPs obtained with 2 mg/mL HBE concentrations were selected for HRTEM analysis to acquire insight into the shape and core size distribution of the NPs. The micrograph in Figure 4A shows that HBE formed spherical- and pentagonal-shaped AuNPs with an average core size of 37 nm (Figure 4B). AuNPs synthesized using plant extracts often exhibit polydispersity, which could be due to the fact that the extracts contain a variety of phytochemicals acting synergistically in the reduction and stabilization of AuNPs [4,19,36]. The size of the NPs is of critical importance since it influences their bioavailability, bioaccumulation, and toxicity in a biological system [38]. The EDX spectroscopy in Figure 4C further confirmed the formation of HB-AuNPs through the presence of elemental gold (Au) atoms around 2.30, 8.10, 9.40, and 11.30 keV. The crystalline nature of the HB-AuNPs was illustrated by the selected area electron diffraction (SAED) pattern (Figure 4D) corresponding to (111), (200), (220), and (311) reflections of face-centered cubic gold. These findings were consistent with the previous observations reported for AuNPs synthesized from Memecylon umbellatum [42], Terminalia mantaly [36], Salvia africana-lutea, and Sutherlandia fructescens [23].
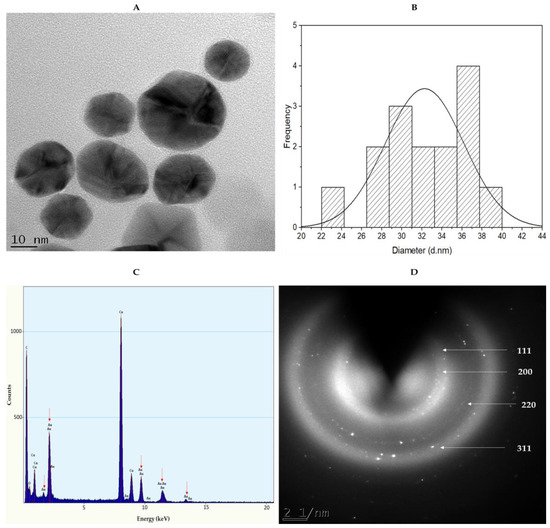
Figure 4.
TEM micrograph (A), core size (B), EDX (C), and SAED patterns (D) of the 2 mg/mL_HB-AuNPs. Red arrows in the EDX show Au peaks.
The 2 mg/mL_HB-AuNPs synthesized from Cyclopia genistoides had a similar profile to the ones previously synthesized from C. intermedia. These two species (C. genistoides and C. intermedia) out of the twenty-three registered HB species are so far the only ones to have been used to synthesize AuNPs. The HB-AuNPs from C. intermedia (HB-AuNPs_ci) were synthesized following the optimal conditions used to synthesize 2 mg/mL_HB-AuNPs by C. genistoides and had similar physicochemical properties: SPR of 540 nm, hydrodynamic size of 67 nm, 0.57 PDI, and a zeta potential of −23 mV [4]. These similarities suggested that the two species most probably have the same phytochemical profiles, which might be responsible for HB-AuNPs synthesis.
3.1.4. In Vitro Stability of HB-AuNPs
Colloidal stability of NPs in relevant media is very crucial for in vivo downstream applications [24,43]. The biologically stable NPs do not aggregate when incubated in various media that simulate biological conditions [44]. In this study, the stability of HB-AuNPs was examined in water, DMEM, RPMI-1640, and PBS at various time points between 0 and 420 h at 37 °C. As shown in Figure 5, the HB-AuNPs incubated in water, RPMI-1640, and PBS demonstrated excellent stability for the entire period, as shown by the retention of their UV–Vis spectra. However, a shift in their SPR band was observed over time in DMEM (Figure 5B). The shift could be due to their interaction with the media components such inorganic salts, vitamins, amino acids, proteins, glucose, and supplements such as FBS and antibiotics [45,46,47]. This behavior was reported for both the chemically (citrate) and green synthesized AuNPs, where pronounced changes in the absorption peak and hydrodynamic size were observed in the AuNPs suspended in DMEM compared with those in the RPMI-1640 [48]. The broad curves in 4 mg/mL_HB-AuNPs in PBS (Figure 5D) demonstrated a formation of larger-sized NPs [47] or NP aggregation. Aggregation of AuNPs can be immediate and visually detected by the color change of the medium to blue [47,48]. The alteration in the SPR of the HB-AuNPs was not accompanied by aggregation in the test solutions, except for 4 mg/mL_HB-AuNPs in PBS. The HB-AuNPs remained stable in these solutions for 420 h and did not change color or aggregate. Aggregation of NPs in biological media can often compromise their biological functions by modifying their cellular uptake and toxicity and can produce misleading results [49,50]. So, it became evident that 1 and 2 mg/mL HB-AuNPs can be used in these test solutions for various biomedical applications [48].
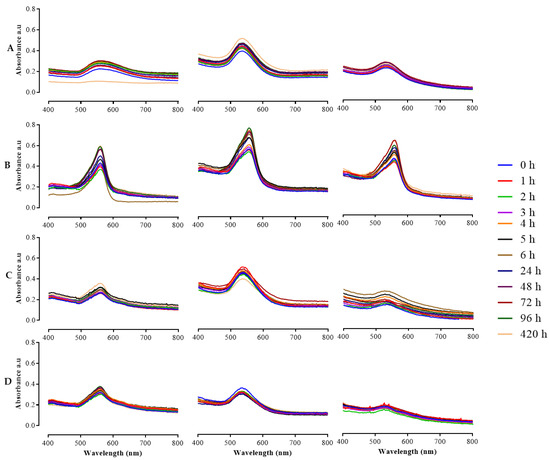
Figure 5.
In vitro stability testing of HB-AuNPs. The AuNPs were incubated for 0 to 420 h in water (A), DMEM (B), RPMI-1640 (C), and PBS (D); and their stability was measured through UV–Vis spectroscopy.
3.2. Cytotoxicity of HB-AuNPs
Investigation of the cytotoxicity of nanomaterials is pivotal to assess how cells will respond when exposed to the nanomaterials either intentionally or accidentally. Various methods have been used to evaluate cytotoxicity [17,51]. Among others, the tetrazolium-based assays have dominated since the introduction of the 3-(4,5-dimethyl-2-thiazolyl)-2,5-diphenyl-2H-tetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay in 1983. These assays do not actually measure the number of viable cells but rather provide information about the enzymatic activities that are related to cellular metabolism in live cells [52]. In the current study, the cytotoxicity of HBE and HB-AuNPs was investigated on a panel of human cancer cells (Caco-2, MCF-7 and PC-3) and non-cancer cells (KMST-6 and HEK-293) using the WST-1 assay. The WST-1 assay is based on the cleavage of tetrazolium salt to a yellow formazan product by cellular mitochondrial dehydrogenases, which is directly related to a number of metabolically active or live cells [32,52]. The WST-1 assay offers various advantages over the other assays when used in the investigation of the cytotoxicity of AuNPs [32]. Unlike the MTT assay, the WST-1 assay excludes the addition of DMSO as it converts tetrazolium salt to water-soluble formazan products. It is also considered to be less toxic compared with other water-soluble variants such as 2,3-bis-(2-methoxy-4-nitro-5-sulfophenyl)-2H-tetrazolium-5-carboxanilide (XTT) assay. Most importantly, the formazan product produced in the MTT assay absorbs at the same wavelength range (570 nm) [52] as AuNPs and might interfere with the assay [31].
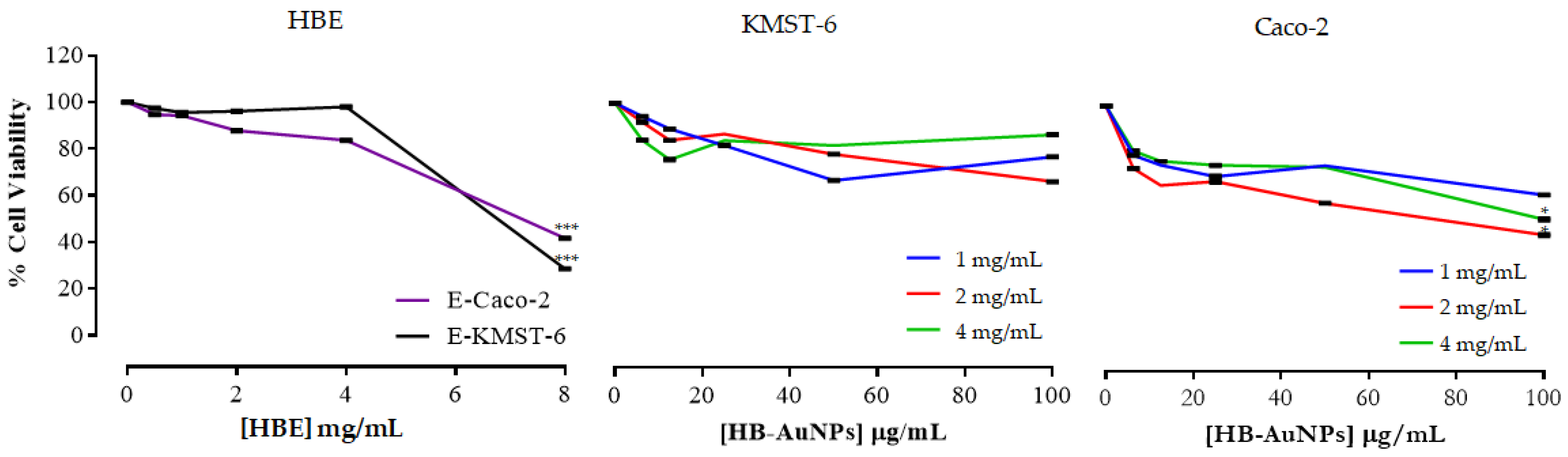
The HBE was non-toxic to KMST-6 cells up to 4 mg/mL and showed a significant toxicity only at 8 mg/mL (Figure 6). On the contrary, the viability of Caco-2 cells was reduced in a dose-dependent manner after HBE treatment. Similarly, 2 mg/mL_HB-AuNPs were not toxic to KMST-6 cells but were effective in inhibiting the cell viability of Caco-2 cells. The 1 and 4 mg/mL HB-AuNPs were least effective in inhibiting the cell viability of both KMST-6 and Caco-2 cells, and showed low cytotoxicity towards cancer cells when compared with the 2 mg/mL_HB-AuNPs.
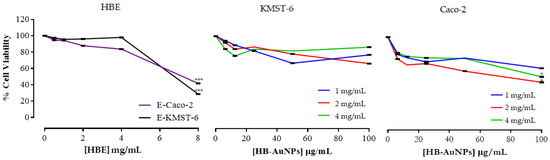
Figure 6.
Cytotoxicity of HBE and HB-AuNPs on KMST-6 and Caco-2 cells. p ≤ 0.05 was considered as statistical significant for untreated vs. treated samples, * p ≤ 0.05, *** p ≤ 0.001.
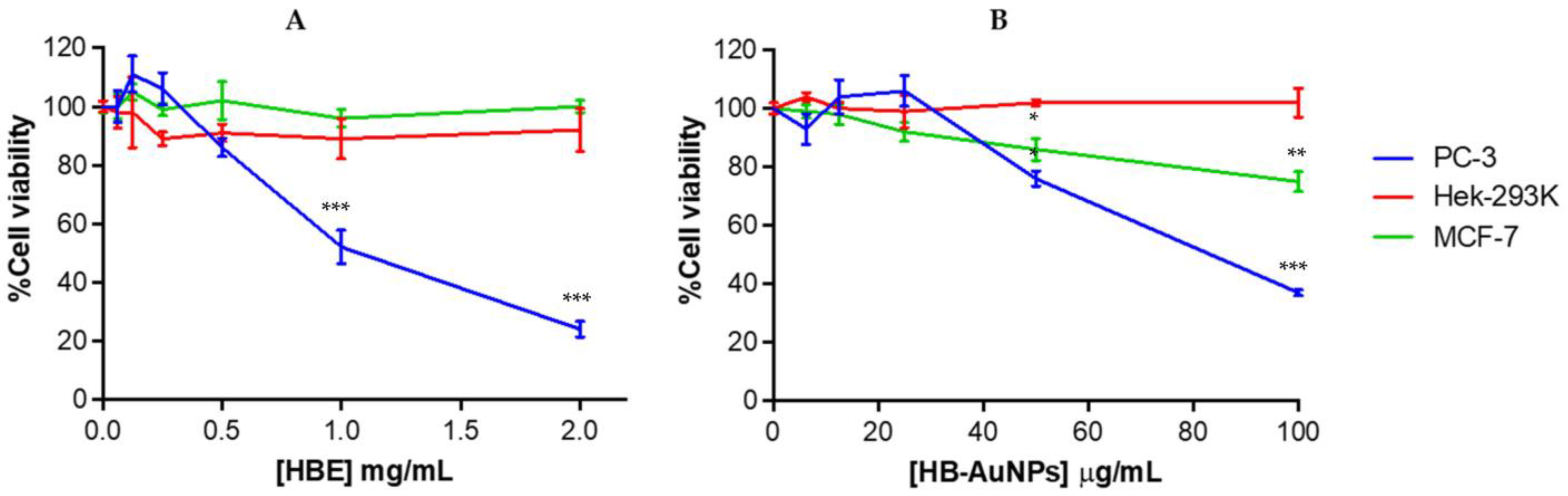
HBE was non-toxic to HEK-293 and MCF-7 cells and exhibited selective cytotoxicity towards PC-3 cells at ≥0.5 mg/mL (Figure 7A). The 2 mg/mL_HB-AuNPs also displayed a selective and significant cytotoxicity towards the PC-3 and MCF-7 cells as shown in Figure 7B; at 100 µg/mL the PC-3 cell death (63%) was 2.5-fold higher than the MCF-7 cells (25%). These selective cytotoxic effects were also reported for HB-AuNPs_Ci against U87 (brain glioblastoma) and PC-3 cells. Interestingly, HB-AuNPs_Ci were also non-toxic to non-cancer breast (MCF-12A) cells [4]. This confirmed that the HB-AuNPs might be biocompatible when used in vivo and will selectively hamper or disrupt the activities of diseased cells. Biogenic AuNPs have been reported to have negligible cytotoxicity towards normal cells and will have therapeutic potential at concentrations that are non-toxic to healthy cells.
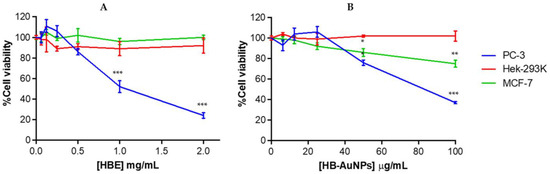
Figure 7.
Cytotoxicity of HBE (A) and HB-AuNPs (B) in PC-3, KMST-6, HEK-293, and MCF-7 cells after 24 h. p ≤ 0.05 was considered as statistical significant for untreated vs. treated samples, * p ≤ 0.05, ** p ≤ 0.01 and *** p ≤ 0.001.
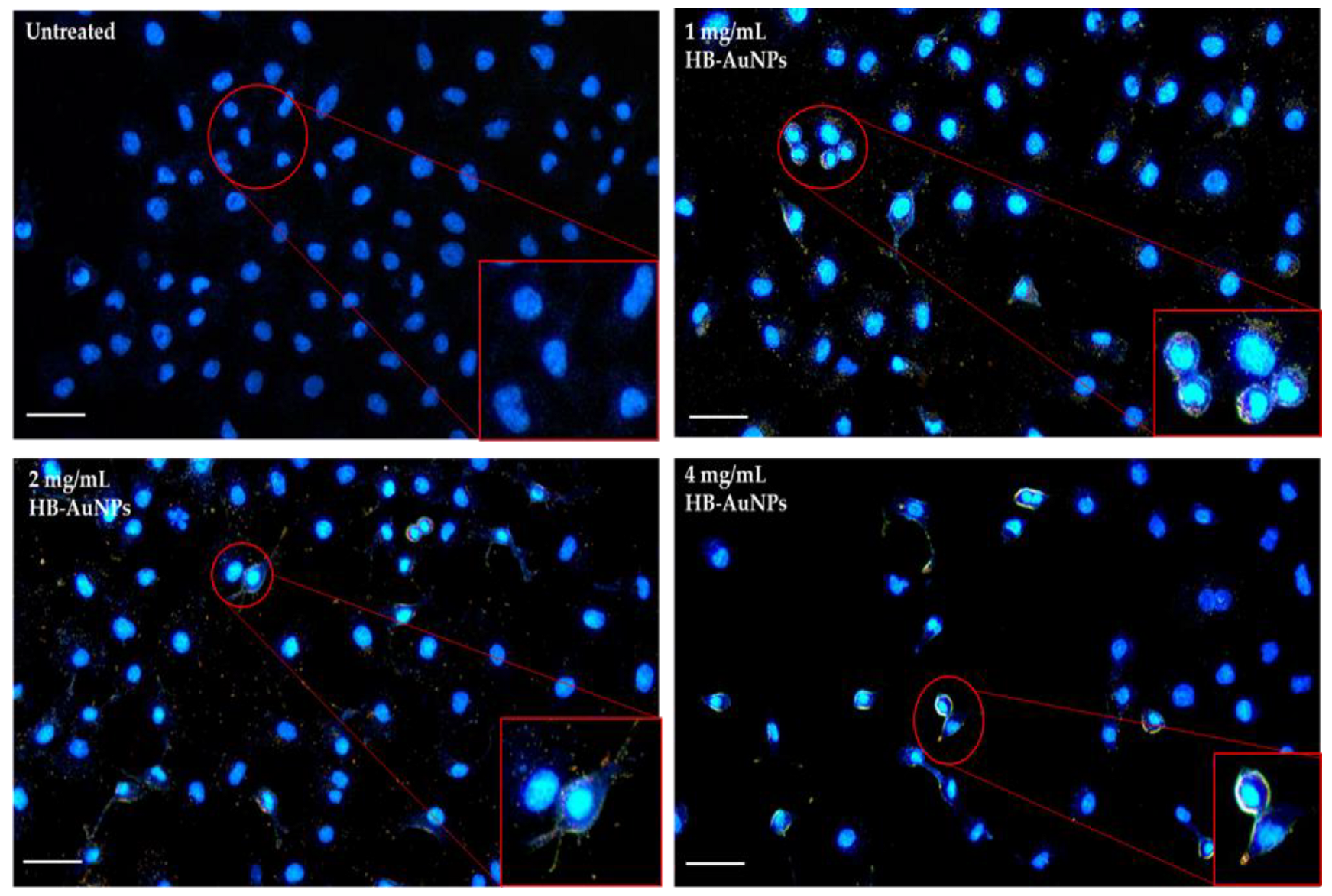
3.3. Internalization of HB-AuNPs
The remarkable application of AuNPs in therapeutics is due to their ability to penetrate the biological barrier and target the cells. In nanomedicine, safe delivery of the NPs into cells is imperative for achieving their higher therapeutic efficacy. In this study, dark-field microscopy in Figure 8 demonstrated that 1 mg/mL_HB-AuNPs, 2 mg/mL_HB-AuNPs, and 4 mg/mL_HB-AuNPs were efficiently internalized by Caco-2 cells. The AuNPs appeared as yellow spots surrounding the nucleus of the Caco-2 cells. Uptake and biodistribution of AuNPs are dependent on their sizes, where ≤5 nm AuNPs can transverse the nuclear membrane and are often associated with genotoxicity and 14–40 nm AuNPs accumulate in the cytosolic spaces [18].
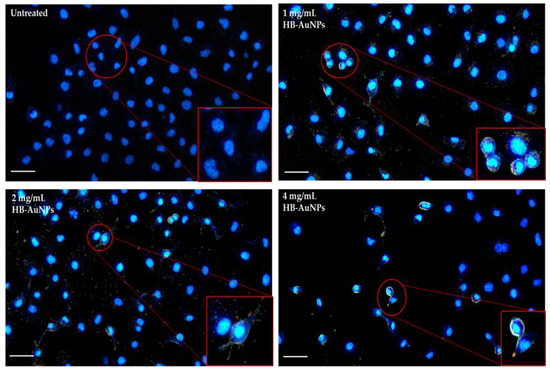
Figure 8.
Uptake of HB-AuNPs by Caco-2 cells. Blue represents the nucleus of the cells stained by DAPI and yellow represents the distribution of the HB-AuNPs within the cells. Scalebar was set at 100 µm. The red circle represent the part that was zoomed in the red frame.
3.4. Co-Treatment of Caco-2 Cells with 2 mg/mL_HB-AuNPs and Dox
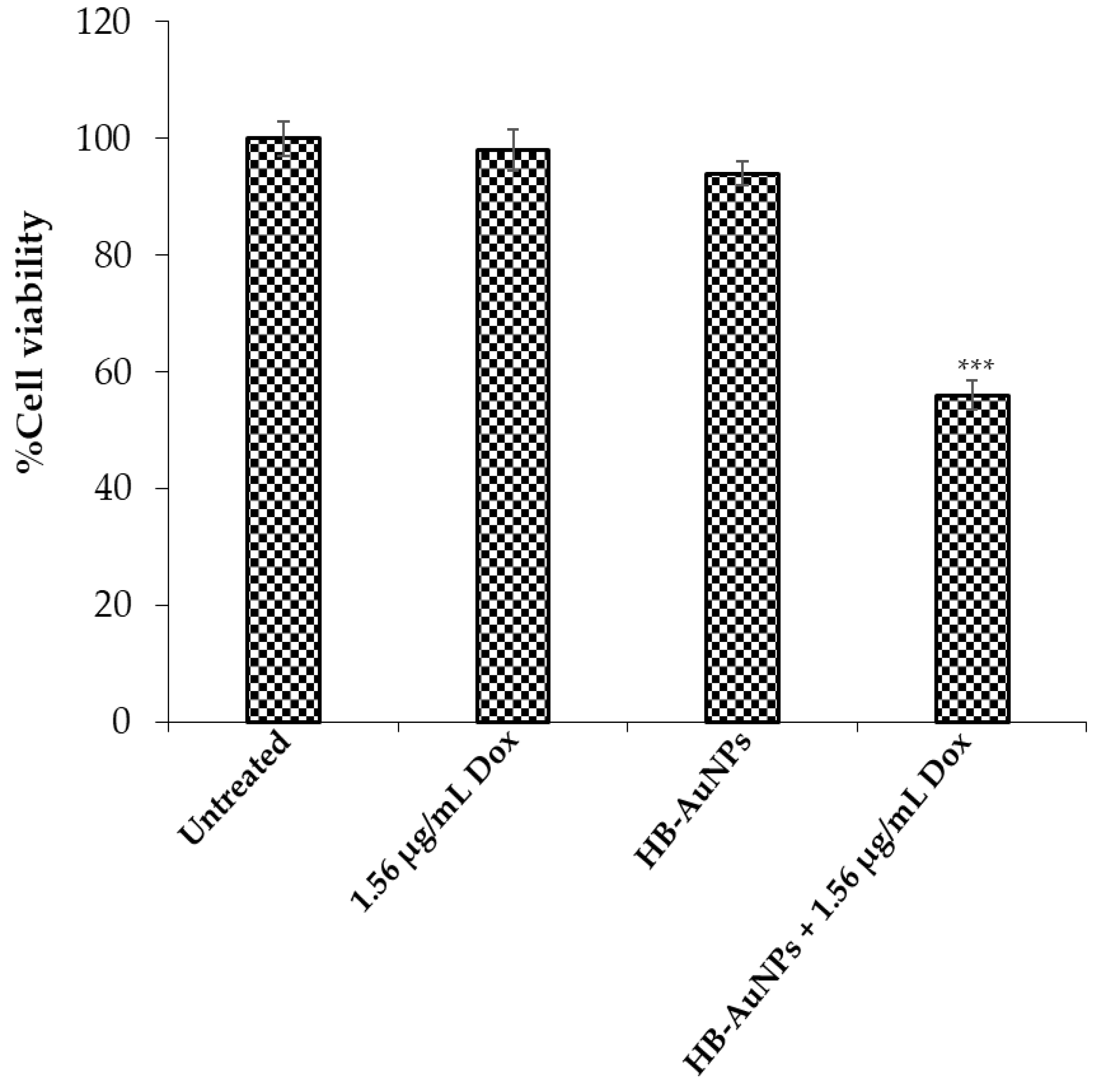
The unique optical properties of AuNPs resulted in multifunctional biomedical activities such as drug delivery, photothermal, and drug-sensitizing agents, etc. [18]. The drug-sensitizing effects of AuNPs are currently being explored in the fight against cancer to enhance chemotherapeutic drug efficacy while reducing their side effects. Previous studies have demonstrated that co-administration of plant-mediated AuNPs and Dox has the potential to enhance the anti-cancer effects of Dox [6,53]. Of interest, unlike other studies, HB-AuNPs_ci were able to augment the cytotoxicity of Dox when used at a very low and non-toxic dose [4]. This finding was especially interesting as Dox is one of the most potent chemotherapeutic drugs but has limited application due to cardiotoxicity and nephrotoxicity. The idea of using chemotherapeutic drugs (not limited to Dox) at non-toxic doses therefore holds promise in the development of highly potent cancer treatment strategies. Nano-based strategies have shown the ability to enhance the drug’s biocompatibility, bio-availability, and efficacy [6]. The current study also investigated the drug-sensitizing effects of HB-AuNPs on Dox-treated Caco-2 cells to investigate whether the two HB species behaved in a similar manner. Co-treatment of Caco-2 cells with Dox (1.56 µg/mL) and 100 µg/mL of 2 mg/mL_HB-AuNPs resulted in a significant reduction in the cell viability (Figure 9) when compared with their individual treatments. Unlike HB-AuNPs_ci, the concentration of 2 mg/mL_HB-AuNPs was ten-times lower [4], suggesting that these NPs can also be effective at a very low dosage. Co-treatment was also investigated in clinical trials, where orally administered biogenic AuNPs in combination with Dox and cyclophosphamide were well tolerated in metastatic stage III breast cancer patients [28]. These studies suggest that biogenic AuNPs can be safely used alone or in combination with conventional therapy for disease treatment to enhance drug efficacy.
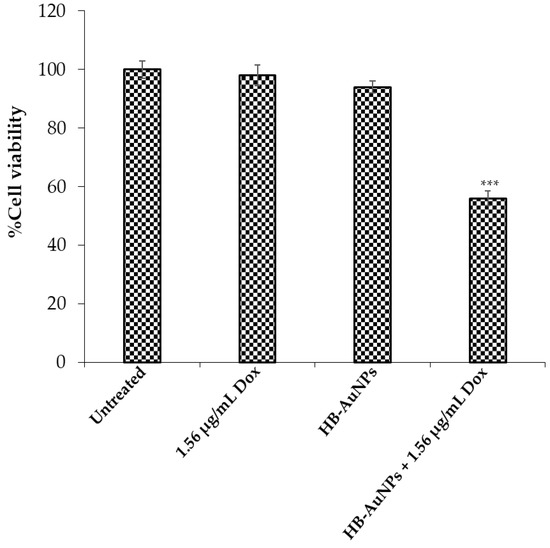
Figure 9.
Co-treatment with 2 mg/mL_HB-AuNPs and Dox enhanced cell death in Caco-2 cells. Individual treatments demonstrated insignificant effect on the viability of Caco-2 cells after 24 h exposure, whereas combination of Dox (1.56 µg/mL) and 2 mg/mL_HB-AuNPs (100 µg/mL) significantly reduced cell viability. p ≤ 0.05 was considered as statistical significant for untreated vs. treated samples, *** p value = 0.001.
3.5. Pro-Apoptotic Effects of 2 mg/mL_HB-AuNPs
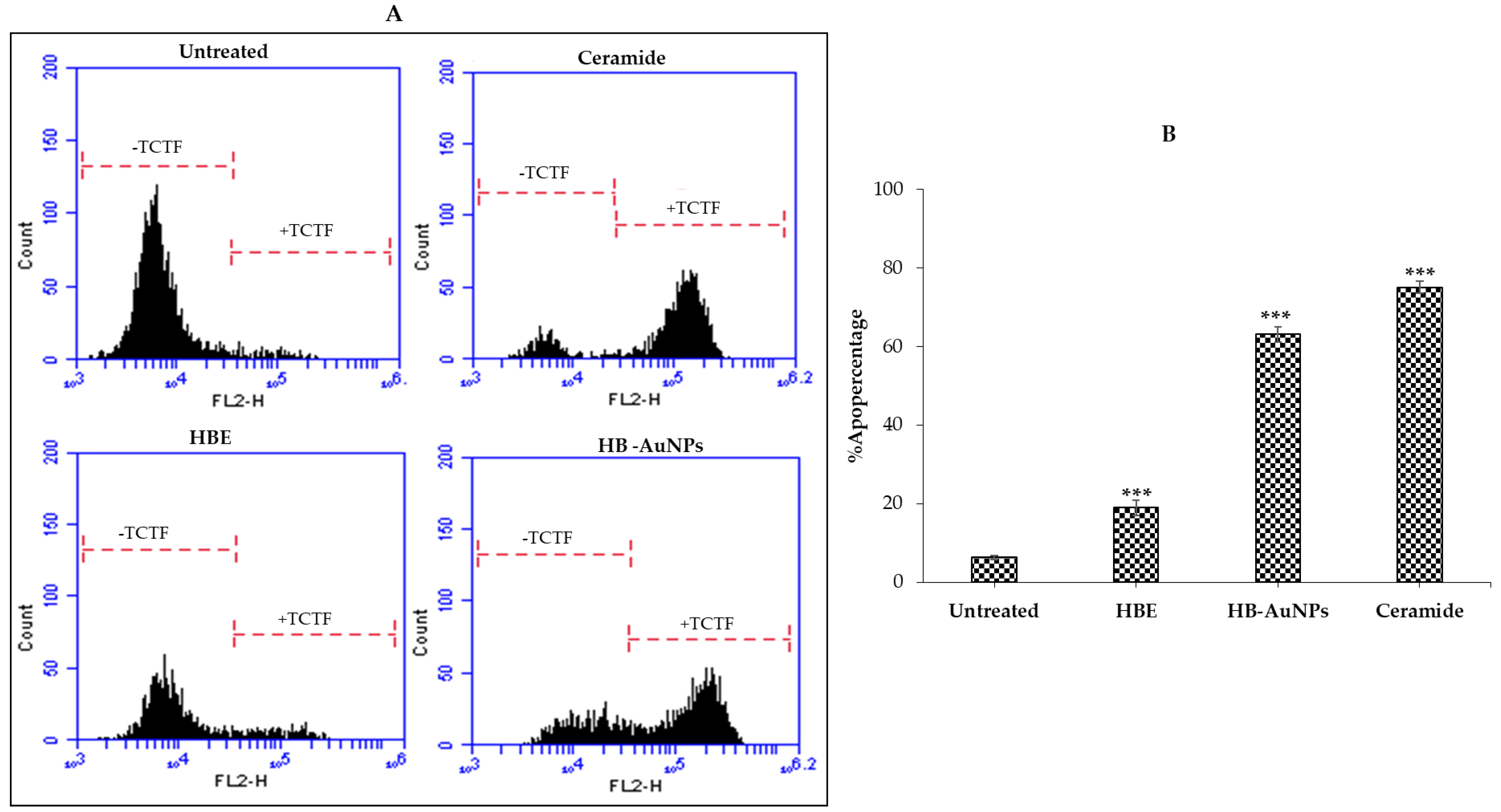
The study further evaluated the mechanism of HB-AuNPs that resulted in the death of PC-3 cells using the ApopercentageTM assay. The assay is based on the uptake of the ApopercentageTM (3,4,5, tetrachloro-2′,4′,5′,7′-tetraiodofluorescein/TCTF) dye by cells undergoing apoptosis, that have their phosphatidylserine translocated to the cell surface [34]. Treatment with HBE and 2 mg/mL_HB-AuNPs induced changes in cell shape or morphology, such as rounded shape and detachment (data not shown), that implicated apoptosis as one of the possible mechanisms of cell death [34]. These effects were more pronounced in cells treated with the HB-AuNPs and ceramide when compared with cells treated with HBE. Ceramide, as an inducer of apoptosis, was used as a positive control. Figure 10 confirmed that the PC-3 cells treated with ceramide (positive control), HB-AuNPs, and HBE were undergoing apoptotic cell death. It should also be noted that a significant effect with HBE treatment occurred at a concentration that was ten-times (1 mg/mL) higher than the HB-AuNPs (100 µg/mL) and these effects were three-fold lower (19.5%) than the HB-AuNPs (64%).
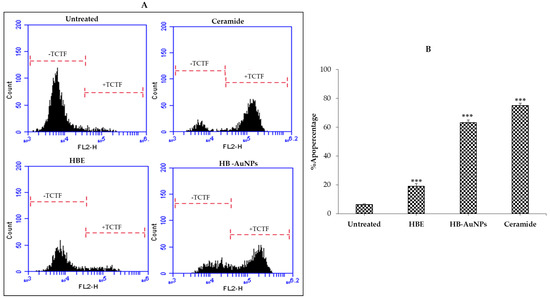
Figure 10.
Apoptosis-mediated PC-3 cell death induced by HB-AuNPs. The cells were treated with 1 mg/mL of HBE and 100 µg/mL of HB-AuNPs for 24 h; apoptosis was assessed by the ApopercentageTM assay. Distribution (A) and quantification (B) of PC-3 cells that were positive for TCTF. −TCTF, unstained cells; +TCTF, ApopercentageTM-dye-stained cells. p < 0.05 was considered to be statistically significant for untreated vs. treated samples. *** p ≤ 0.001.
It was reported in previous studies that the majority of the polyphenolic constituents of HB (in particular MGF and hesperidin) can modulate inflammatory and apoptotic signaling pathways related to oxidative stress [13]. It is not clear at this stage which mechanism is responsible for the selective anti-cancer activity of the 2 mg/mL_HB-AuNPs. However, several studies have shown that plant-mediated AuNPs usually target receptors that are differentially expressed in cancer cells, such as laminin [54,55]. Laminin receptors are overexpressed in PC-3 cells and were targeted by MGF-AuNPs in PC-3 cell tumor xenografts in mice. However, confirmatory studies are warranted to study or identify the genes affected by the 2 mg/mL_HB-AuNPs and the polyphenols responsible for these actions [54].
4. Conclusions
This study demonstrated that water extracts of HB leaves can be used to synthesize bioactive HB-AuNPs. The HB-AuNPs were stable in media for up to 420 h at 37 °C. The 2 mg/mL_HB-AuNPs showed selective cytotoxicity towards cancer cells and were more enhanced in the PC-3 cells, whereas the HBE was cytotoxic at moderately high concentrations (≥0.5 mg/mL). It is unclear at this stage why the PC-3 cells had this apparent susceptibility to HBE and HB-AuNPs. Mechanistically, 2 mg/mL_HB-AuNPs induced cell death in PC-3 cells through apoptosis. Any therapeutic agent capable of selectively inducing apoptosis in cancer cells could be a promising anti-tumor therapy and must be explored further. Interestingly, co-treatment of Caco-2 cells with non-toxic concentrations of 2 mg/mL_HB-AuNPs and Dox resulted in significantly higher cell death. Studies are required to investigate the mechanism of HB-AuNPs on cancer cells and identify the receptors targeted by the HB-AuNPs, which could be explored as targets for AuNPs-based therapy.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.M.; methodology, J.R.S., N.R.S.S., S.M., A.M.M., M.M. and K.K.; formal analysis, J.R.S., N.R.S.S., A.O.F. and S.M.; investigation, J.R.S., N.R.S.S. and A.O.F.; resources, M.M., writing—original draft preparation, J.R.S., N.R.S.S. and A.O.F.; writing review and editing, J.R.S., N.R.S.S., A.O.F., S.M., A.M.M., M.M. and K.K.; supervision, M.M., A.M.M. and K.K.; project administration, J.R.S. and A.O.F.; funding acquisition, M.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
This study was financially supported by the DSI/Mintek NIC—UWC Biolabels Research Node. The authors would like to thank the University of Missouri South African Education Program (UMSAEP) for funding J.R.S’s research visit to the Institute of Green Nanotechnology and Cancer Nanotechnology, MU.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Fürst, R.; Zündorf, I. Plant-Derived Anti-Inflammatory Compounds: Hopes and Disappointments Regarding the Translation of Preclinical Knowledge into Clinical Progress. Mediators Inflamm. 2014, 2014, 146832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fridlender, M.; Kapulnik, Y.; Koltai, H. Plant Derived Substances with Anti-Cancer Activity: From Folklore to Practice. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Germishuizen, G.; Meyer, N.L. Plants of Southern Africa: An Annotated Checklist; National Botanical Institute: Pretoria, South Africa, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Aboyewa, J.A.; Sibuyi, N.R.S.; Meyer, M.; Oguntibeju, O.O. Gold Nanoparticles Synthesized Using Extracts of Cyclopia Intermedia, Commonly Known as Honeybush, Amplify the Cytotoxic Effects of Doxorubicin. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeda, T.; Tsubaki, M.; Kino, T.; Kawamura, A.; Isoyama, S.; Itoh, T.; Imano, M.; Tanabe, G.; Muraoka, O.; Matsuda, H.; et al. Mangiferin Enhances the Sensitivity of Human Multiple Myeloma Cells to Anticancer Drugs through Suppression of the Nuclear Factor ΚB Pathway. Int. J. Oncol. 2016, 48, 2704–2712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboyewa, J.A.; Sibuyi, N.R.; Goboza, M.; Murtz, L.-A.; Oguntibeju, O.O.; Meyer, M. Co-Treatment of Caco-2 Cells with Doxorubicin and Gold Nanoparticles Produced from Cyclopia Intermedia Extracts or Mangiferin Enhances Drug Effects. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 3918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joubert, E.; Gelderblom, W.C.A.; Louw, A.; de Beer, D. South African Herbal Teas: Aspalathus Linearis, Cyclopia Spp. and Athrixia Phylicoides-A Review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2008, 119, 376–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joubert, E.; Joubert, M.E.; Bester, C.; de Beer, D.; De Lange, J.H. Honeybush (Cyclopia Spp.): From Local Cottage Industry to Global Markets—The Catalytic and Supporting Role of Research. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2011, 77, 887–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, S.; Miura, Y.; Hattori, M.; Matsuda, H.; Malherbe, C.J.; Muller, C.J.F.; Joubert, E.; Yoshida, T. Cyclopia Extracts Enhance Th1-, Th2-, and Th17-Type T Cell Responses and Induce Foxp3 + Cells in Murine Cell Culture. Planta Med. 2018, 84, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magcwebeba, T.; Swart, P.; Swanevelder, S.; Joubert, E.; Gelderblom, W. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Aspalathus Linearis and Cyclopia Spp. Extracts in a UVB/Keratinocyte (HaCaT) Model Utilising Interleukin-1-Accumulation as Biomarker. Molecules 2016, 21, 1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Wyk, B.-E. The Potential of South African Plants in the Development of New Food and Beverage Products. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2011, 77, 857–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKay, D.L.; Blumberg, J.B. A Review of the Bioactivity of South African Herbal Teas: Rooibos (Aspalathus Linearis) and Honeybush (Cyclopia Intermedia). Phyther. Res. 2007, 21, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marnewick, J.; Joubert, E.; Joseph, S.; Swanevelder, S.; Swart, P.; Gelderblom, W. Inhibition of Tumour Promotion in Mouse Skin by Extracts of Rooibos (Aspalathus Linearis) and Honeybush (Cyclopia Intermedia), Unique South African Herbal Teas. Cancer Lett. 2005, 224, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrova, A. Modulation of Ultraviolet Light-Induced Skin Carcinogenesis by Extracts of Rooibos and Honeybush Using a Mouse Model: Elucidating Possible Protective Mechanisms; Cape Peninsula University of Technology: Cape Town, South Africa, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Ekor, M.; Pistelli, L. The Growing Use of Herbal Medicines: Issues Relating to Adverse Reactions and Challenges in Monitoring Safety. Front. Pharmacol. 2014, 4, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conte, R.; De Luca, I.; De Luise, A.; Petillo, O.; Calarco, A.; Peluso, G. New Therapeutic Potentials of Nanosized Phytomedicine. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2016, 16, 8176–8187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Lai, X.; Shao, L.; Li, L. Evaluation of Immunoresponses and Cytotoxicity from Skin Exposure to Metallic Nanoparticles. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 4445–4459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibuyi, N.R.S.; Moabelo, K.L.; Fadaka, A.O.; Meyer, S.; Onani, M.O.; Madiehe, A.M.; Meyer, M. Multifunctional Gold Nanoparticles for Improved Diagnostic and Therapeutic Applications: A Review. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbagory, A.; Cupido, C.; Meyer, M.; Hussein, A. Large Scale Screening of Southern African Plant Extracts for the Green Synthesis of Gold Nanoparticles Using Microtitre-Plate Method. Molecules 2016, 21, 1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboyewa, J.A.; Sibuyi, N.R.S.; Meyer, M.; Oguntibeju, O.O. Green Synthesis of Metallic Nanoparticles Using Some Selected Medicinal Plants from Southern Africa and Their Biological Applications. Plants 2021, 10, 1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sargazi, S.; Laraib, U.; Er, S.; Rahdar, A.; Hassanisaadi, M.; Zafar, M.N.; Díez-Pascual, A.M.; Bilal, M. Application of Green Gold Nanoparticles in Cancer Therapy and Diagnosis. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thipe, V.C.; Njobeh, P.B.; Mhlanga, S.D. Optimization of Commercial Antibiotic Agents Using Gold Nanoparticles Against Toxigenic Aspergillus Spp. Proc. Mater. Today Proc. 2015, 2, 4136–4148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dube, P.; Meyer, S.; Madiehe, A.; Meyer, M. Antibacterial Activity of Biogenic Silver and Gold Nanoparticles Synthesized from Salvia Africana-Lutea and Sutherlandia Frutescens. Nanotechnology 2020, 31, 505607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elbagory, A.; Meyer, M.; Cupido, C.; Hussein, A.A. Inhibition of Bacteria Associated with Wound Infection by Biocompatible Green Synthesized Gold Nanoparticles from South African Plant Extracts. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ismail, E.; Khenfouch, M.; Dhlamini, M.; Dube, S.; Maaza, M. Green Palladium and Palladium Oxide Nanoparticles Synthesized via Aspalathus Linearis Natural Extract. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 695, 3632–3638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.S.; Wang, J.T.; Tai, H.M.; Chang, P.C.; Huang, H.C.; Yang, P.C. Metal Nanoparticles and Nanoparticle Composites Are Effective against Haemophilus Influenzae, Streptococcus Pneumoniae, and Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2022, 55, 708–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahlaule-Glory, L.M.; Mbita, Z.; Mathipa, M.M.; Tetana, Z.N.; Hintsho-Mbita, N.C. Biological Therapeutics of AgO Nanoparticles against Pathogenic Bacteria and A549 Lung Cancer Cells. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 105402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoobchandani, M.; Katti, K.K.; Karikachery, A.R.; Thipe, V.C.; Srisrimal, D.; Mohandoss, D.K.D.; Darshakumar, R.D.; Joshi, C.M.; Katti, K.V. New Approaches in Breast Cancer Therapy through Green Nanotechnology and Nano-Ayurvedic Medicine—Pre-Clinical and Pilot Human Clinical Investigations. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 181–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schutte, A.L. Systematics of the Genus Cyclopia Vent. (Fabaceae, Podalyrieae). Edinb. J. Bot. 1997, 54, 125–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbagory, A.M.; Hussein, A.A.; Meyer, M. The In Vitro Immunomodulatory Effects of Gold Nanoparticles Synthesized From Hypoxis Hemerocallidea Aqueous Extract and Hypoxoside on Macrophage and Natural Killer Cells. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 9007–9018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibuyi, N.R.S.; Thipe, V.C.; Panjtan-Amiri, K.; Meyer, M.; Katti, K.V. Green Synthesis of Gold Nanoparticles Using Acai Berry and Elderberry Extracts and Investigation of Their Effect on Prostate and Pancreatic Cancer Cells. Nanobiomedicine 2021, 8, 184954352199531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibuyi, N.R.S.; Thovhogi, N.; Gabuza, K.B.; Meyer, M.D.; Drah, M.; Onani, M.O.; Skepu, A.; Madiehe, A.M.; Meyer, M. Peptide-Functionalized Nanoparticles for the Selective Induction of Apoptosis in Target Cells. Nanomedicine 2017, 12, 1631–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbs-flournoy, E.A.; Bromberg, P.A.; Hofer, T.P.J.; Samet, J.M.; Zucker, R.M. Darkfield-Confocal Microscopy Detection of Nanoscale Particle Internalization by Human Lung Cells. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2011, 8, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, M.; Essack, M.; Kanyanda, S.; Rees, J.G. A Low-Cost Flow Cytometric Assay for the Detection and Quantification of Apoptosis Using an Anionic Halogenated Fluorescein Dye. Biotechniques 2008, 45, 317–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubey, S.P.; Lahtinen, M.; Sillanpää, M. Green Synthesis and Characterizations of Silver and Gold Nanoparticles Using Leaf Extract of Rosa Rugosa. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2010, 364, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majoumouo, M.S.; Sharma, J.R.; Sibuyi, N.R.S.; Tincho, M.B.; Boyom, F.F.; Meyer, M. Synthesis of Biogenic Gold Nanoparticles from Terminalia Mantaly Extracts and the Evaluation of Their in Vitro Cytotoxic Effects in Cancer Cells. Molecules 2020, 25, 4469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Link, S.; El-Sayed, M.A. Optical Properties and Ultrafast Dynamics of Metallic Nanocrystals. Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 2003, 54, 331–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sengani, M.; Grumezescu, A.M.; Rajeswari, V.D. Recent Trends and Methodologies in Gold Nanoparticle Synthesis—A Prospective Review on Drug Delivery Aspect. OpenNano 2017, 2, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Jackman, J.A.; Yang, H.H.; Chen, P.; Cho, N.J.; Kim, D.H. Strategies for Enhancing the Sensitivity of Plasmonic Nanosensors. Nano Today 2015, 10, 213–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aji, A.; Santosa, J.; Kunarti, E.S. Effect of Reaction Time and Stability Properties of Gold Nanoparticles Synthesized by P-Aminobenzoic Acid and p-Aminosalicylic Acid. Indones. J. Chem. 2020, 2020, 413–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco-Ulloa, S.; Tatulli, G.; Bore, S.L.; Moglianetti, M.; Pompa, P.P.; Cascella, M.; De Vivo, M. Dispersion State Phase Diagram of Citrate-Coated Metallic Nanoparticles in Saline Solutions. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arunachalam, K.D.; Annamalai, S.K.; Hari, S. One-Step Green Synthesis and Characterization of Leaf Extract-Mediated Biocompatible Silver and Gold Nanoparticles from Memecylon Umbellatum. Int. J. Nanomed. 2013, 8, 1307–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katti, K.; Chanda, N.; Shukla, R.; Zambre, A.; Suibramanian, T.; Kulkarni, R.R.; Kannan, R.; Katti, K.V. Green Nanotechnology from Cumin Phytochemicals: Generation of Biocompatible Gold Nanoparticles. Int. J. Green Nanotechnol. Biomed. 2009, 1, B39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, S.R.; Oh, S.; Baba, R.; Zhou, H.; Hwang, S.; Lee, J.; Park, E.Y. Synthesis of Gold Nanoparticles with Buffer-Dependent Variations of Size and Morphology in Biological Buffers. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foo, Y.Y.; Periasamy, V.; Kiew, L.V.; Kumar, G.G.; Malek, S.N.A. Curcuma Mangga-Mediated Synthesis of Gold Nanoparticles: Characterization, Stability, Cytotoxicity, and Blood Compatibility. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yallapu, M.M.; Chauhan, N.; Othman, S.F.; Khalilzad-Sharghi, V.; Ebeling, M.C.; Khan, S.; Jaggi, M.; Chauhan, S.C. Implications of Protein Corona on Physico-Chemical and Biological Properties of Magnetic Nanoparticles. Biomaterials 2015, 46, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreto, Â.; Luis, L.G.; Girão, A.V.; Trindade, T.; Soares, A.M.V.M.; Oliveira, M. Behavior of Colloidal Gold Nanoparticles in Different Ionic Strength Media. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2015, 17, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boldeiu, A.; Simion, M.; Mihalache, I.; Radoi, A.; Banu, M.; Varasteanu, P.; Nadejde, P.; Vasile, E.; Acasandrei, A.; Popescu, R.C.; et al. Comparative Analysis of Honey and Citrate Stabilized Gold Nanoparticles: In Vitro Interaction with Proteins and Toxicity Studies. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2019, 197, 111519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albanese, A.; Chan, W.C.W. Effect of Gold Nanoparticle Aggregation on Cell Uptake and Toxicity. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 5478–5489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkilany, A.M.; Murphy, C.J. Toxicity and Cellular Uptake of Gold Nanoparticles: What We Have Learned so Far? J. Nanoparticle Res. 2010, 12, 2313–2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clichici, S.; Filip, A. In Vivo Assessment of Nanomaterials Toxicity. In Nanomaterials—Toxicity and Risk Assessment; InTech: London, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Kamiloglu, S.; Sari, G.; Ozdal, T.; Capanoglu, E. Guidelines for Cell Viability Assays. Food Front. 2020, 1, 332–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louisa, M.; Soediro, T.M.; Suyatna, F.D. In Vitro Modulation of P-Glycoprotein, MRP-1 and BCRP Expression by Mangiferin in Doxorubicin-Treated MCF-7 Cells. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2014, 15, 1639–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Yasiri, A.Y.; Khoobchandani, M.; Cutler, C.S.; Watkinson, L.; Carmack, T.; Smith, C.J.; Kuchuk, M.; Loyalka, S.K.; Lugão, A.B.; Katti, K.V. Mangiferin Functionalized Radioactive Gold Nanoparticles (MGF-198AuNPs) in Prostate Tumor Therapy: Green Nanotechnology for Production: In Vivo Tumor Retention and Evaluation of Therapeutic Efficacy. Dalt. Trans. 2017, 46, 14561–14571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shukla, R.; Chanda, N.; Zambre, A.; Upendran, A.; Katti, K.; Kulkarni, R.R.; Nune, S.K.; Casteel, S.W.; Smith, C.J.; Vimal, J.; et al. Laminin Receptor Specific Therapeutic Gold Nanoparticles (198AuNP-EGCg) Show Efficacy in Treating Prostate Cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 12426–12431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).