DAMP-YOLO: A Lightweight Network Based on Deformable Features and Aggregation for Meter Reading Recognition
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- The proposal of a deformable CSP bottleneck (DCB) module that adapts by learning the kernel offset for objects, making the network resilient to noise interference from objects with similar shapes and structures, thus achieving high accuracy;
- The design of the aggregated triplet attention (ATA) mechanism enhances global information interaction by aggregating diverse branches, effectively capturing attention across all dimensions.
- Aiming at the particularity of meter images: meter data augmentation (MDA) is used to generate training data that are similar to natural scenes to improve the robustness of the model in complex environments;
- Utilize network slimming to prune unimportant network channels to achieve model compression and accelerated computing;
- Deploy the recognition pipeline to the Jetson TX1-based intelligent car to realize meter reading recognition in real-world scenarios;
- Our model can still enhance accuracy even with reduced parameters in general object-detection datasets.
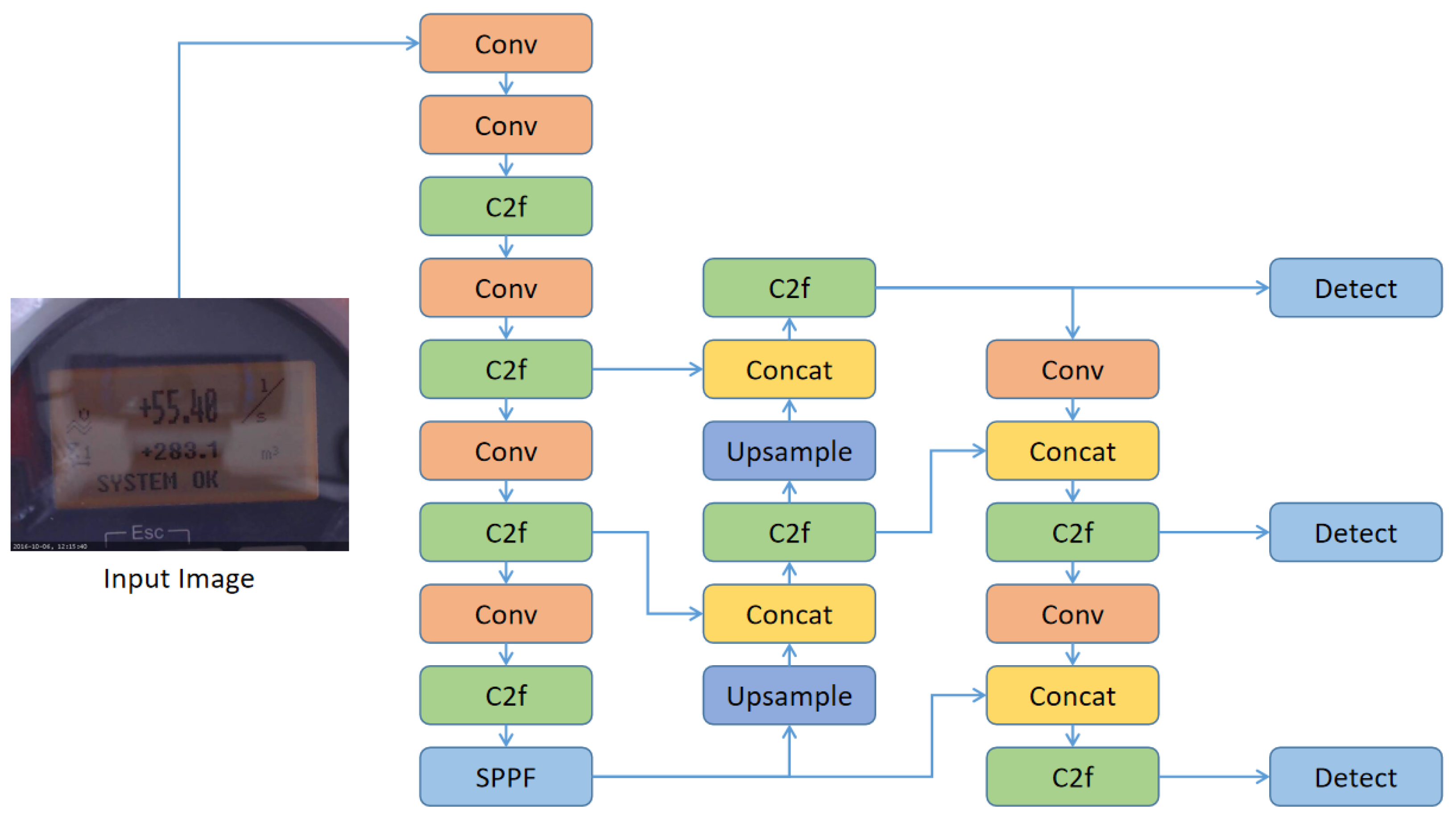
2. YOLOv8 Network
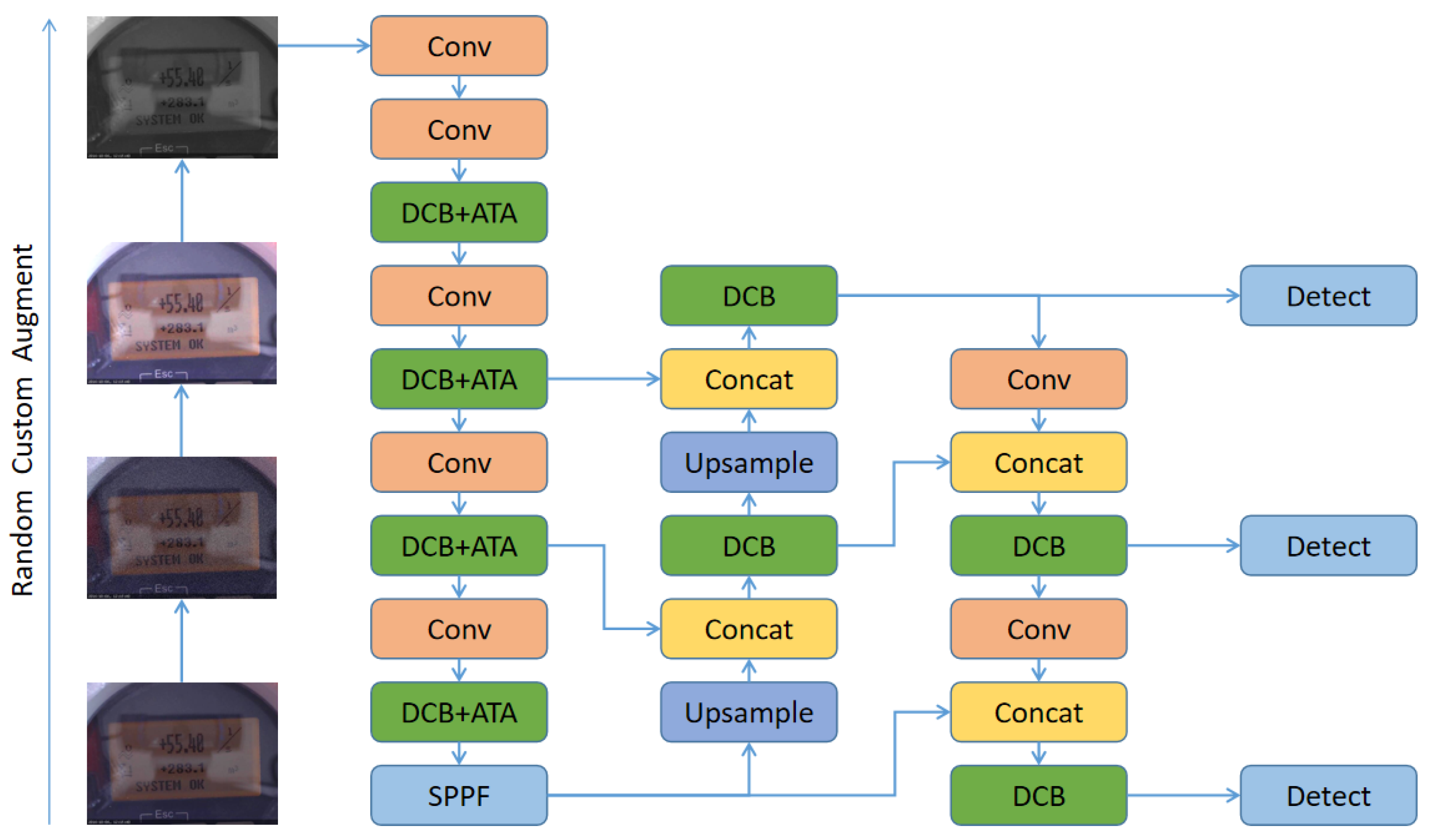
3. DAMP-YOLO Network
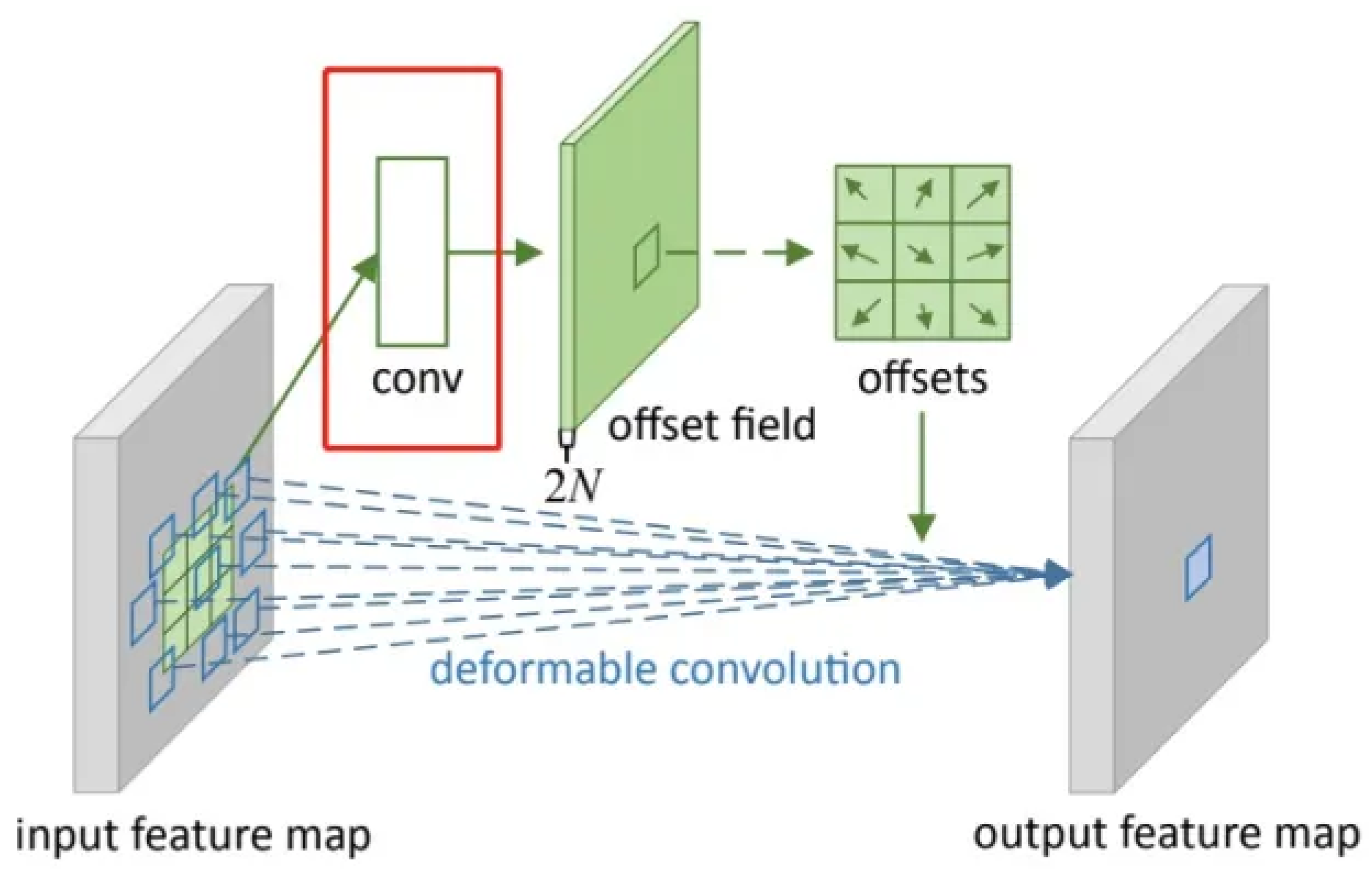
3.1. Deformable CSP Bottleneck
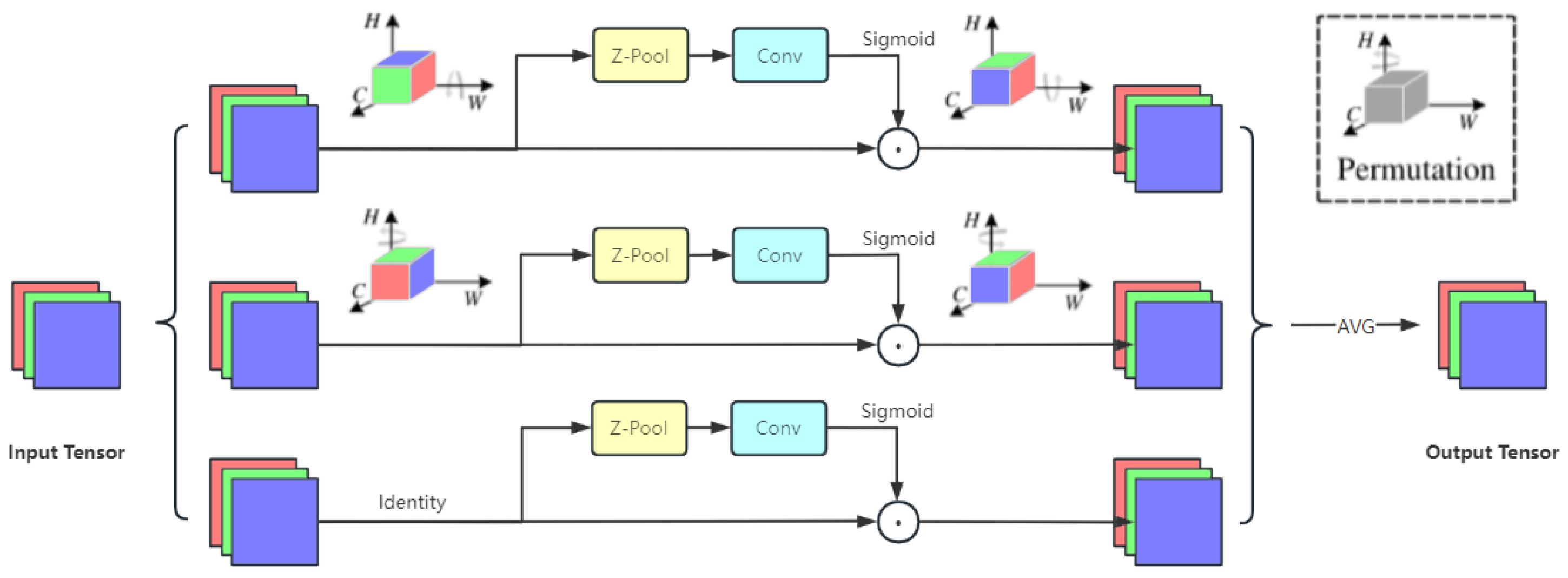
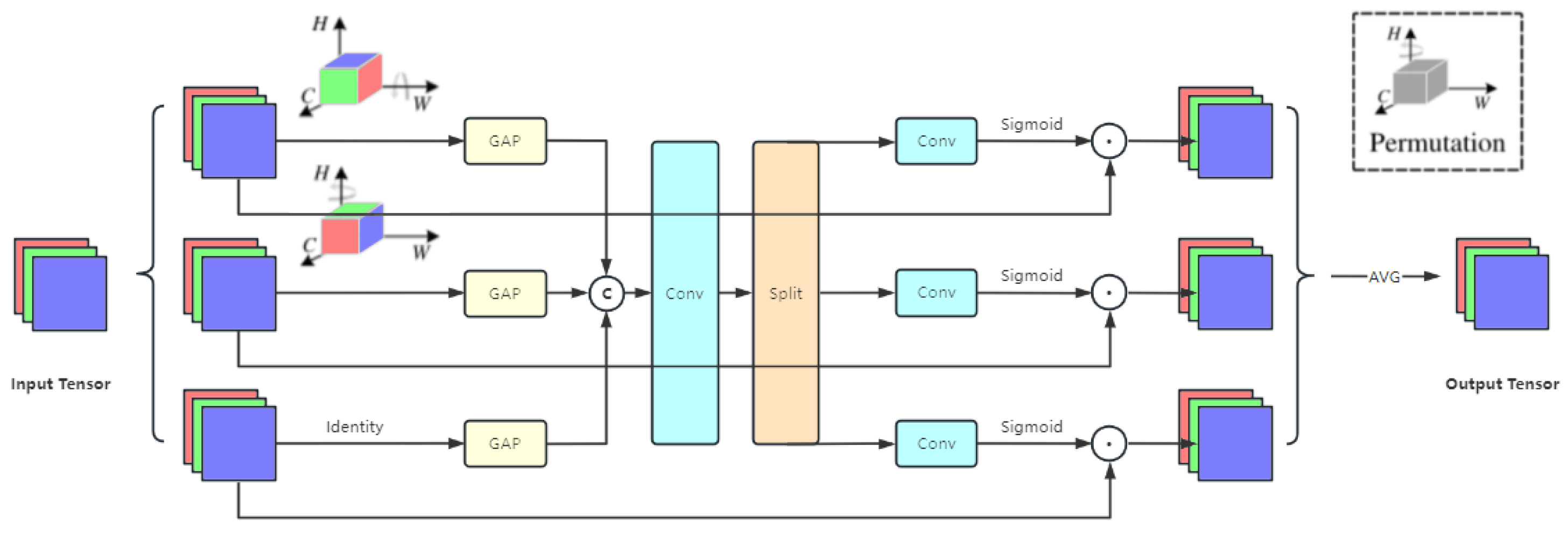
3.2. Aggregated Triplet Attention
3.3. Meter Data Augmentation
- Background color: The digital display area of the meter image is usually dominated by light colors (such as light green or light grey), and the peripheral areas of the meter are usually dark colors (such as dark black and dark brown).
- Font labels: Meter images contain text labels such as meter readings and timestamps. Meter readings are the core of meter recognition and are usually presented using specific digital fonts, which cannot be flipped left and right or up and down.
- Shape layout: Meters of the same model have similar shapes and layouts, and the numbers and labels in the meter reading image are primarily located in the center of the image with the same fonts.
- Noise interference: The meter image may be affected by noise interference, such as day and night light changes, stains, reflections, and shadow occlusion. These interferences may affect the accuracy and stability of readings.
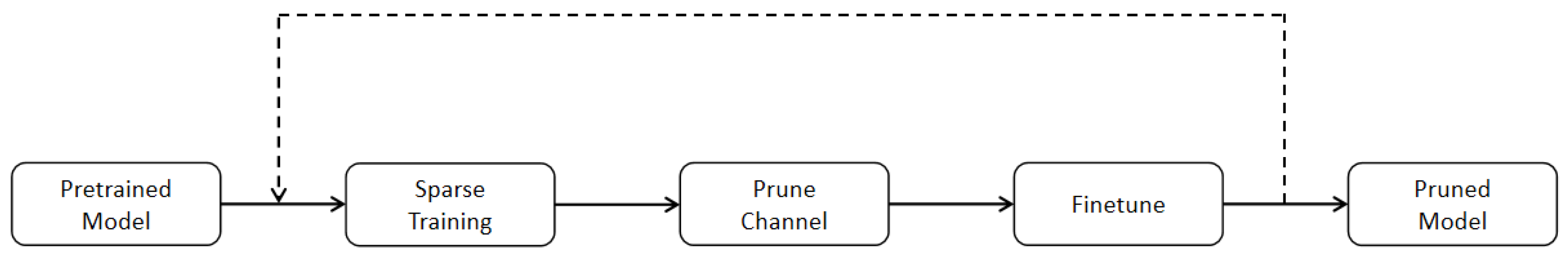
3.4. Network Pruning
3.4.1. Sparse Training
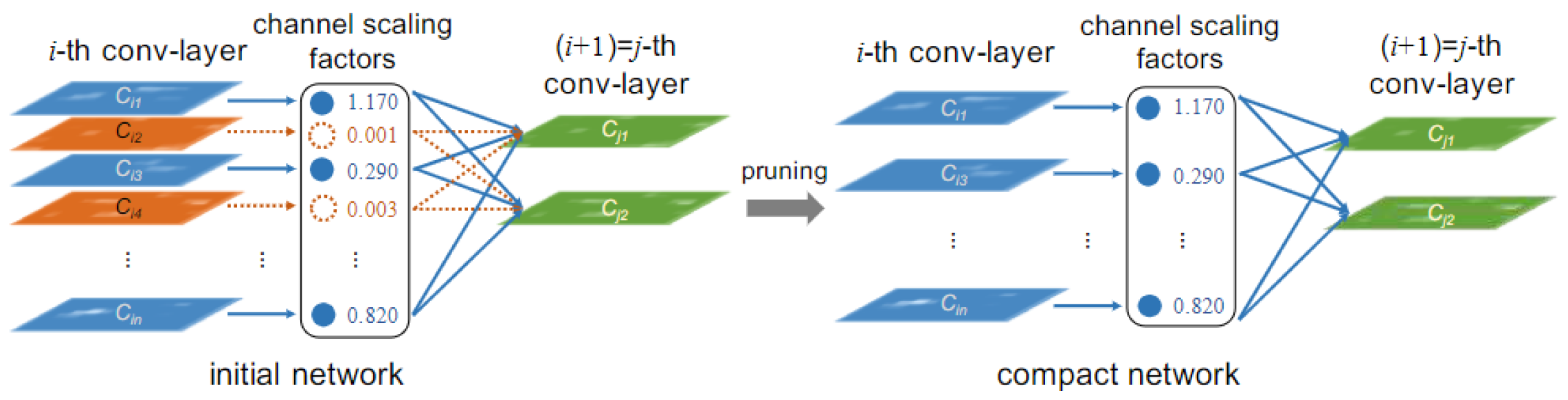
3.4.2. Channel Prune and Finetune
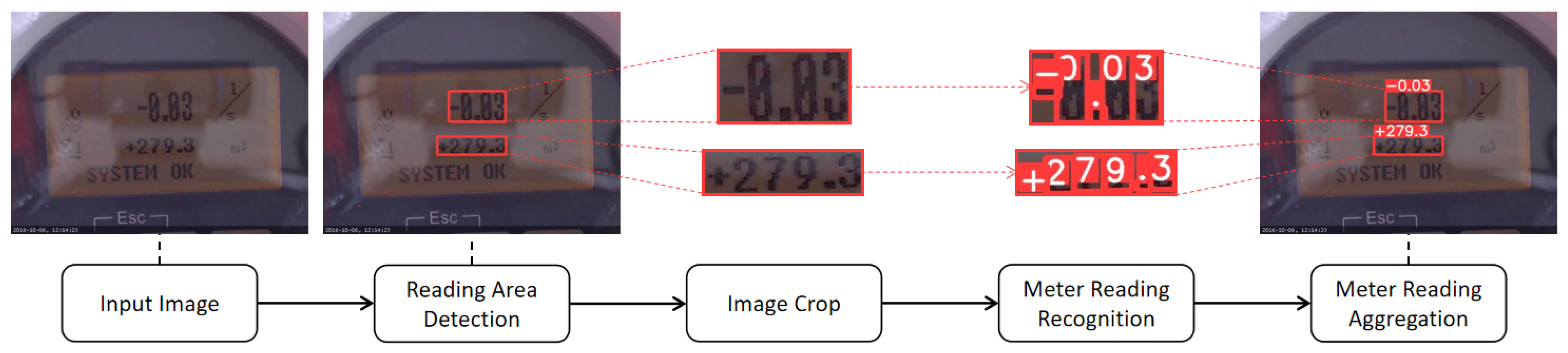
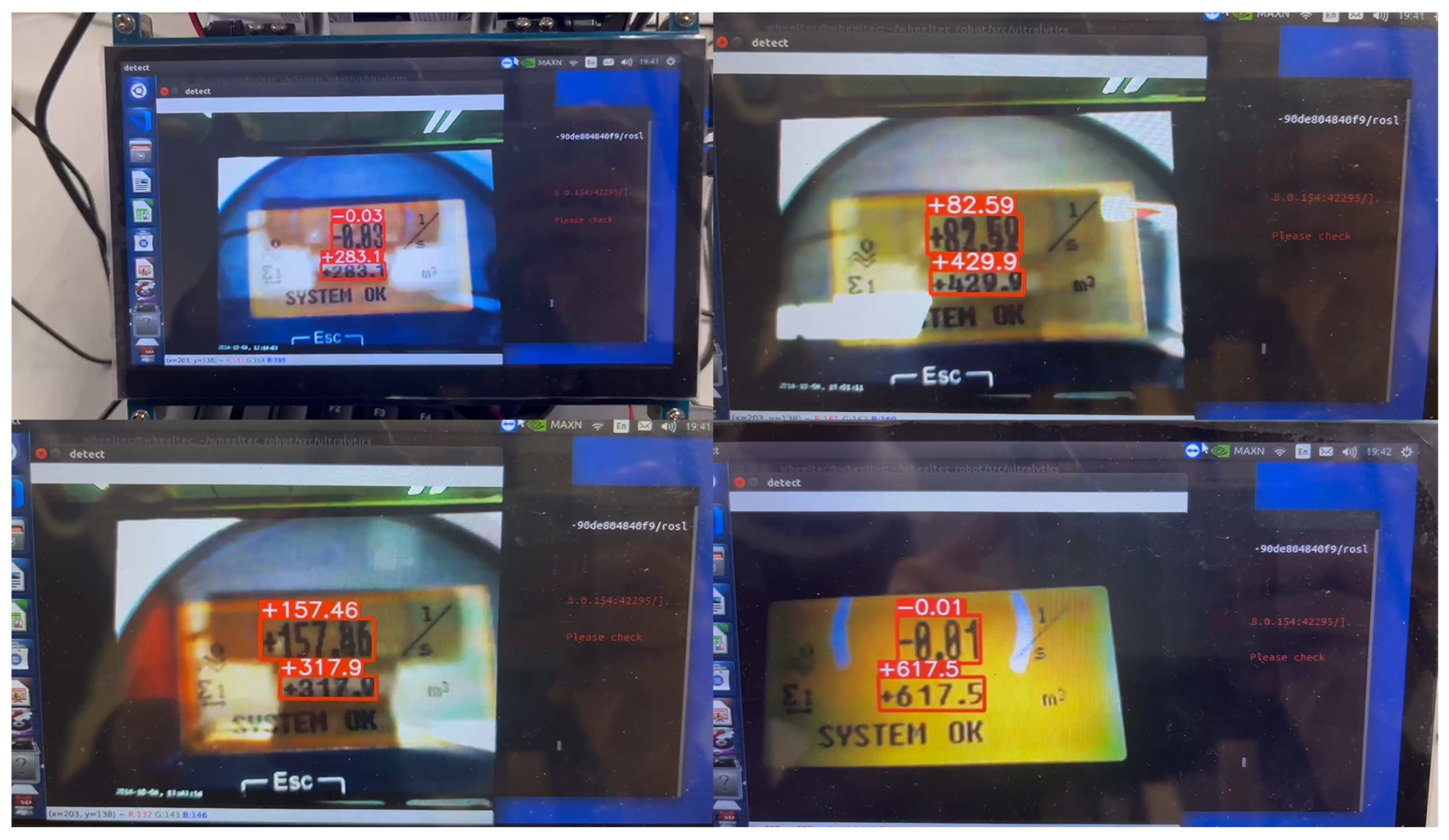
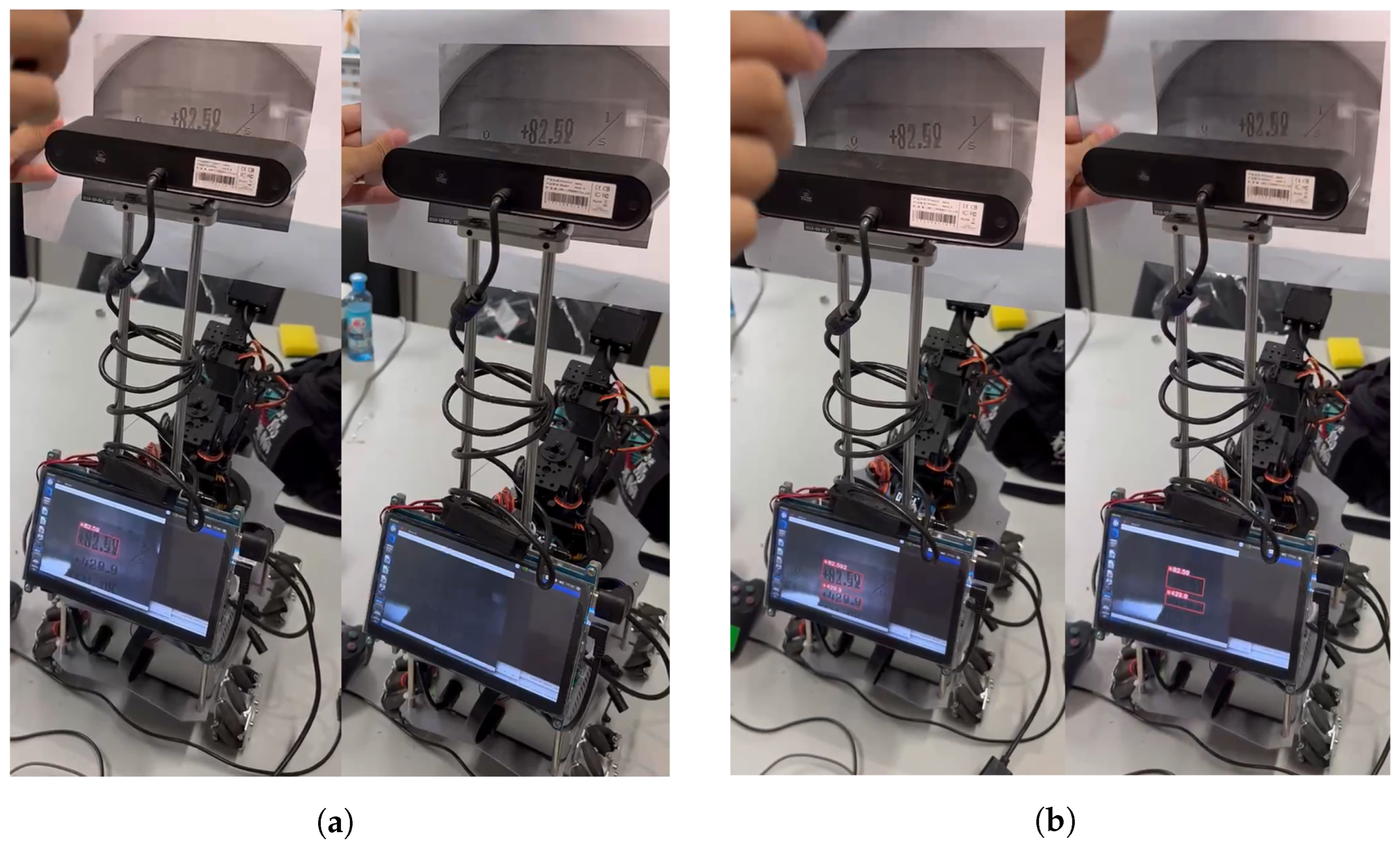
4. Embedded Deployment
5. Experiment and Results
5.1. Dataset Setup
5.2. Evaluation Metrics
5.3. Environment Details
5.4. Experiments and Discussion
5.4.1. Meter Reading Recognition Results
5.4.2. PASCAL VOC Object Detection Results
5.4.3. Meter Reading Area Detection Results
5.4.4. Ablation Experiments
5.4.5. Embedded Deployed Results
5.4.6. Inference Speed Results
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Duan, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, S.; Shou, S.; Liu, H. Reasearch of meter digits recognition based on fuzzy theory. Instrum. Tech. Sens. 2004, 1, 37–39. [Google Scholar]
- Shuang, G. Study on automatic identification method of digital tube. Commun. Technol. 2012, 1, 91–93. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, S.; Li, B.; Yuan, J.; Cui, G. Research on remote meter automatic reading based on computer vision. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE/PES Transmission & Distribution Conference & Exposition: Asia and Pacific, Dalian, China, 18 August 2005; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Vanetti, M.; Gallo, I.; Nodari, A. Gas meter reading from real world images using a multi-net system. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2013, 34, 519–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Liu, C.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, H. A method for digital instrument character recognition based on template matching. Mod. Comput. 2008, 1, 70–72. [Google Scholar]
- He, H.; Kong, H. A new processing method of nixie tube computer vision recognition. Electron. Eng. 2007, 33, 65–69. [Google Scholar]
- Nodari, A.; Gallo, I. A multi-neural network approach to image detection and segmentation of gas meter counter. In MVA; Citeseer: Centre County, PA, USA, 2011; pp. 239–242. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, X.; Hua, F.; Yang, G. A new method of digital number recognition for substation inspection robot. In Proceedings of the 2016 4th International Conference on Applied Robotics for the Power Industry (CARPI), Jinan, China, 11–13 October 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Sampath, A.; Gomathi, N. Fuzzy-based multi-kernel spherical support vector machine for effective handwritten character recognition. Sādhanā 2017, 42, 1513–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girshick, R.; Donahue, J.; Darrell, T.; Malik, J. Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014; pp. 580–587. [Google Scholar]
- Girshick, R. Fast r-cnn. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 1440–1448. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster r-cnn: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2015, 28, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, K.; Gkioxari, G.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R. Mask r-cnn. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2961–2969. [Google Scholar]
- Redmon, J.; Divvala, S.; Girshick, R.; Farhadi, A. You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 779–788. [Google Scholar]
- Jocher, G. Ultralytics yolov5. 2020. Available online: https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5 (accessed on 26 September 2023).
- Li, C.; Li, L.; Jiang, H.; Weng, K.; Geng, Y.; Li, L.; Ke, Z.; Li, Q.; Cheng, M.; Nie, W.; et al. Yolov6: A single-stage object detection framework for industrial applications. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2209.02976. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.-Y.; Bochkovskiy, A.; Liao, H.-Y.M. Yolov7: Trainable bag-of-freebies sets new state-of-the-art for real-time object detectors. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 7464–7475. [Google Scholar]
- Jocher, G.; Chaurasia, A.; Qiu, J. Ultralytics yolov8. 2023. Available online: https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics (accessed on 26 September 2023).
- Liu, W.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Szegedy, C.; Reed, S.; Fu, C.-Y.; Berg, A.C. Ssd: Single shot multibox detector. In Computer Vision–ECCV 2016: 14th European Conference, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016; Proceedings, Part I 14; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 21–37. [Google Scholar]
- Gómez, L.; Rusinol, M.; Karatzas, D. Cutting sayre’s knot: Reading scene text without segmentation. Application to utility meters. In Proceedings of the 2018 13th IAPR International Workshop on Document Analysis Systems (DAS), Vienna, Austria, 24–27 April 2018; pp. 97–102. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, M.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Mo, J. A fully convolution network based approach for character recognition in digital meter. Mod. Comput. 2018, 1, 38–43. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, L.; Han, R.; Cheng, X. Digital instrument identification method based on deformable convolutional neural network. Comput. Sci. 2020, 47, 187–193. [Google Scholar]
- Waqar, M.; Waris, M.A.; Rashid, E.; Nida, N.; Nawaz, S.; Yousaf, M.H. Meter digit recognition via faster r-cnn. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Robotics and Automation in Industry (ICRAI), Rawalpindi, Pakistan, 21–22 October 2019; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Laroca, R.; Barroso, V.; Diniz, M.A.; Gonçalves, G.R.; Schwartz, W.R.; Menotti, D. Convolutional neural networks for automatic meter reading. J. Electron. Imaging 2019, 28, 013023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Yang, T. Instrument target detection algorithm based on deep learning. Instrum. Tech. Sens. 2021, 6, 104–108. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.; Hou, J.; Gao, W. Instrument reading recognition by deep learning of capsules network model for digitalization in industrial internet of things. Eng. Rep. 2022, 4, e12547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinton, G.E.; Krizhevsky, A.; Wang, S.D. Transforming auto-encoders. In Artificial Neural Networks and Machine Learning–ICANN 2011: 21st International Conference on Artificial Neural Networks, Espoo, Finland, 14–17 June 2011; Proceedings, Part I 21; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 44–51. [Google Scholar]
- Martinelli, F.; Mercaldo, F.; Santone, A. Water meter reading for smart grid monitoring. Sensors 2023, 23, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, W.; Zhao, Z.; Tao, J.; Lian, C.; Zhang, C. Research on digital meter reading method of inspection robot based on deep learning. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 7146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, R.; Melo, J.; Graça, R.; Santos, G.; Vasconcelos, M.J.M. Deep learning-powered system for real-time digital meter reading on edge devices. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandler, M.; Howard, A.; Zhu, M.; Zhmoginov, A.; Chen, L.-C. Mobilenetv2: Inverted residuals and linear bottlenecks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 4510–4520. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Yao, C.; Wen, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, S.; He, W.; Liang, J. East: An efficient and accurate scene text detector. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 5551–5560. [Google Scholar]
- Borisyuk, F.; Gordo, A.; Sivakumar, V. Rosetta: Large scale system for text detection and recognition in images. In Proceedings of the 24th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining, London, UK, 19–23 August 2018; pp. 71–79. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.-Y.; Goyal, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Dollár, P. Focal loss for dense object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2980–2988. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Spatial pyramid pooling in deep convolutional networks for visual recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2015, 37, 1904–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Qi, H.; Xiong, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, G.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y. Deformable convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 764–773. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 7132–7141. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Wu, B.; Zhu, P.; Li, P.; Zuo, W.; Hu, Q. Eca-net: Efficient channel attention for deep convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 11534–11542. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, Z.; Zhang, P.; Wu, F.; Li, X. Fcanet: Frequency channel attention networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 783–792. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, S.; Park, J.; Lee, J.-Y.; Kweon, I.S. Cbam: Convolutional block attention module. In Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision (ECCV), Tel Aviv, Israel, 23–27 October 2018; pp. 3–19. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, Q.; Zhou, D.; Feng, J. Coordinate attention for efficient mobile network design. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 13713–13722. [Google Scholar]
- Misra, D.; Nalamada, T.; Arasanipalai, A.U.; Hou, Q. Rotate to attend: Convolutional triplet attention module. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 3–8 January 2021; pp. 3139–3148. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Li, J.; Shen, Z.; Huang, G.; Yan, S.; Zhang, C. Learning efficient convolutional networks through network slimming. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2736–2744. [Google Scholar]
- Everingham, M.; Gool, L.V.; Williams, C.K.I.; Winn, J.; Zisserman, A. The PASCAL Visual Object Classes Challenge 2007 (VOC2007) Results. Available online: http://www.pascal-network.org/challenges/VOC/voc2007/workshop/index.html (accessed on 26 September 2023).
- de Vitry, M.M.; Dicht, S.; Leitão, J.P. floodx: Urban flash flood experiments monitored with conventional and alternative sensors. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2017, 9, 657–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, A.; Sandler, M.; Chu, G.; Chen, L.-C.; Chen, B.; Tan, M.; Wang, W.; Zhu, Y.; Pang, R.; Vasudevan, V.; et al. Searching for mobilenetv3. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 1314–1324. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, N.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, H.-T.; Sun, J. Shufflenet v2: Practical guidelines for efficient cnn architecture design. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 116–131. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, X.; Zhang, X.; Ma, N.; Han, J.; Ding, G.; Sun, J. Repvgg: Making vgg-style convnets great again. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on computer Vision and PATTERN Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 13733–13742. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, C.; Zhong, Y.; Gao, Y.; Scott, M.R.; Huang, W. Tood: Task-aligned one-stage object detection. In 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV); IEEE Computer Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2021; pp. 3490–3499. [Google Scholar]








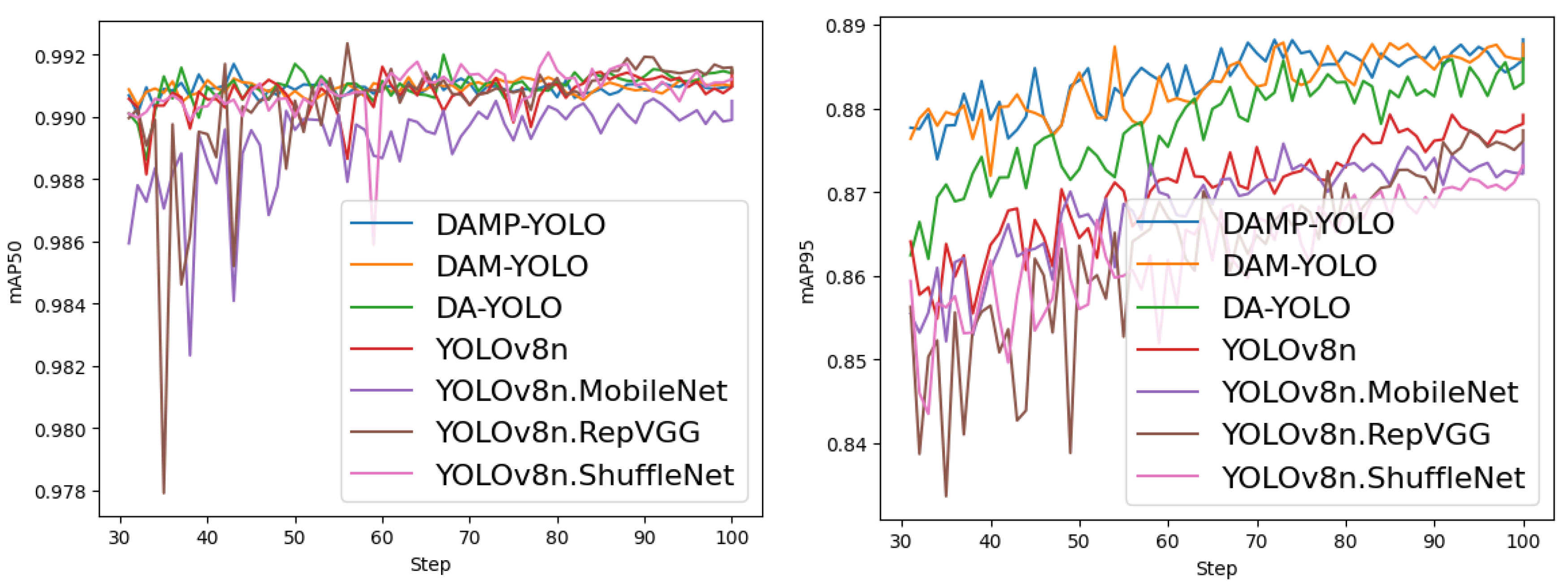

| Model | mAP@50/% | mAP@50:95/% | Parameters/M |
|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv8n | 62.02 | 41.03 | 3.15 |
| +SE | 62.29 | 41.35 | 3.16 |
| +ECA | 62.14 | 41.12 | 3.15 |
| +CA | 61.95 | 40.67 | 3.17 |
| +FCA | 61.89 | 40.61 | 3.16 |
| +CBAM | 61.65 | 40.48 | 3.16 |
| +TripletAttention | 62.92 | 41.87 | 3.15 |
| Model | Precision/% | Recall/% | mAP@50/% | mAP@50:95/% | Parameters/M |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv8s | 99.44 | 98.84 | 99.14 | 88.61 | 11.16 |
| SSD300 | - | - | 98.38 | 82.44 | 25.35 |
| Retinanet | 96.02 | 96.01 | 98.80 | 84.10 | 20.02 |
| TOOD | - | - | 98.70 | 84.61 | 32.05 |
| MobileNetV2-SSDLite | - | - | 98.52 | 83.65 | 3.21 |
| YOLOv8n | 99.50 | 98.81 | 99.14 | 87.92 | 3.15 |
| YOLOv8n-MobileNetV3 | 99.28 | 98.14 | 99.05 | 87.58 | 2.25 |
| YOLOv8n-ShuffleNetV2 | 98.85 | 98.15 | 99.12 | 87.31 | 1.86 |
| YOLOv8n-RepVGG | 99.17 | 98.81 | 99.14 | 87.74 | 2.89 |
| YOLOv5n | 99.46 | 98.56 | 99.02 | 85.57 | 1.79 |
| YOLOv6n | - | - | 98.93 | 85.34 | 4.70 |
| YOLOv7-tiny | 99.53 | 98.76 | 99.00 | 84.95 | 6.07 |
| DA-YOLO | 99.57 | 98.82 | 99.15 | 88.60 | 3.46 |
| DAM-YOLO | 99.58 | 98.86 | 99.12 | 88.77 | 3.46 |
| DAMP-YOLO | 99.44 | 98.41 | 99.10 | 88.82 | 2.40 |
| Model | Precision/% | Recall/% | mAP@50/% | mAP@50:95/% | Parameters/M |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv8s | 72.22 | 61.23 | 67.86 | 45.76 | 11.16 |
| SSD300 | - | - | 71.01 | 41.35 | 26.29 |
| Retinanet | 49.64 | 56.23 | 60.67 | 33.38 | 20.17 |
| TOOD | - | - | 69.93 | 44.54 | 32.05 |
| MobileNetV2-SSDLite | - | - | 59.89 | 34.89 | 3.32 |
| YOLOv8n | 64.83 | 58.02 | 62.02 | 41.03 | 3.15 |
| YOLOv8n-MobileNetV3 | 57.37 | 46.63 | 49.49 | 31.36 | 2.25 |
| YOLOv8n-ShuffleNetV2 | 59.98 | 48.53 | 52.53 | 32.50 | 1.86 |
| YOLOv8n-RepVGG | 65.59 | 53.06 | 58.64 | 36.89 | 2.89 |
| YOLOv5n | 55.21 | 49.65 | 50.34 | 25.74 | 1.79 |
| YOLOv6n | - | - | 62.11 | 39.36 | 4.70 |
| YOLOv7-tiny | 57.17 | 55.76 | 55.66 | 30.74 | 6.07 |
| DA-YOLO | 69.79 | 59.88 | 66.11 | 45.64 | 3.46 |
| DAP-YOLO | 70.09 | 56.80 | 63.88 | 43.57 | 2.42 |
| Model | mAP@50:95/% | Parameters/M |
|---|---|---|
| YOLOv8s | 96.01 | 11.16 |
| YOLOv8n | 96.47 | 3.15 |
| YOLOv8n-MobileNetV3 | 92.76 | 2.25 |
| YOLOv8n-ShuffleNetV2 | 93.27 | 1.86 |
| YOLOv8n-RepVGG | 95.38 | 2.89 |
| DAM-YOLO | 97.95 | 3.46 |
| DAMP-YOLO | 95.72 | 1.94 |
| Model | DCB | ATA | MDA | Prune | mAP@50:95 | Parameters/M | Inference/ms (Jetson TX1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv8n | 87.92 | 3.15 | 76.0 | ||||
| D-YOLOv8n | √ | 88.36 | 3.46 | 126.2 | |||
| A-YOLOv8n | √ | 88.21 | 3.15 | 84.4 | |||
| M-YOLOv8n | √ | 88.46 | 3.15 | 76.0 | |||
| DA-YOLOv8n | √ | √ | 88.60 | 3.46 | 136.5 | ||
| DAM-YOLOv8n | √ | √ | √ | 88.77 | 3.46 | 136.5 | |
| DAMP-YOLOv8n | √ | √ | √ | √ | 88.82 | 2.40 | 129.6 |
| Model | mAP@50:95/% | Parameters/M |
|---|---|---|
| YOLOv8n | 87.92 | 3.15 |
| YOLOv8n+MDA | 88.46 | 3.15 |
| YOLOv8n-MobileNetV3 | 87.58 | 2.25 |
| YOLOv8n-MobileNetV3+MDA | 87.64 | 2.25 |
| DA-YOLO | 88.60 | 3.46 |
| DA-YOLO+MDA | 88.77 | 3.46 |
| DAP-YOLO | 88.34 | 2.40 |
| DAP-YOLO+MDA | 88.82 | 2.40 |
| Model | mAP@50:95/% | Parameters/M | Inference/ms (MX350) | Inference/ms (Jetson TX1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv8s | 88.61 | 11.16 | 44.2 | 184.5 |
| SSD300 | 82.44 | 25.35 | 86.2 | - |
| Retinanet | 84.10 | 20.02 | 267.4 | - |
| TOOD | 84.61 | 32.05 | 414.3 | - |
| MobileNetV2-SSDLite | 83.65 | 3.21 | 25.7 | - |
| YOLOv8n | 87.92 | 3.15 | 23.5 | 76.0 |
| YOLOv8n-MobileNetV3 | 87.58 | 2.25 | 23.7 | 83.9 |
| YOLOv8n-ShuffleNetV2 | 87.31 | 1.86 | 18.6 | 62.1 |
| YOLOv8n-RepVGG | 87.74 | 2.89 | 25.1 | 78.1 |
| DAM-YOLO | 88.77 | 3.46 | 40.2 | 136.5 |
| DAMP-YOLO | 88.82 | 2.40 | 37.3 | 129.6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhuo, S.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Z.; Wei, W.; Wang, F.; Li, Q.; Guan, Y. DAMP-YOLO: A Lightweight Network Based on Deformable Features and Aggregation for Meter Reading Recognition. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 11493. https://doi.org/10.3390/app132011493
Zhuo S, Zhang X, Chen Z, Wei W, Wang F, Li Q, Guan Y. DAMP-YOLO: A Lightweight Network Based on Deformable Features and Aggregation for Meter Reading Recognition. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(20):11493. https://doi.org/10.3390/app132011493
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhuo, Sichao, Xiaoming Zhang, Ziyi Chen, Wei Wei, Fang Wang, Quanlong Li, and Yufan Guan. 2023. "DAMP-YOLO: A Lightweight Network Based on Deformable Features and Aggregation for Meter Reading Recognition" Applied Sciences 13, no. 20: 11493. https://doi.org/10.3390/app132011493
APA StyleZhuo, S., Zhang, X., Chen, Z., Wei, W., Wang, F., Li, Q., & Guan, Y. (2023). DAMP-YOLO: A Lightweight Network Based on Deformable Features and Aggregation for Meter Reading Recognition. Applied Sciences, 13(20), 11493. https://doi.org/10.3390/app132011493









