Short-Term Load Forecasting Based on Spiking Neural P Systems
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- We propose a variant of NSNP systems, which is inspired from the nonlinear spiking mechanism of biological neurons.
- (2)
- Based on the variant, we deduce a new type of neuron model, NSNP neuron model, which is a recurrent-like neuron model.
- (3)
- Based on the NSNP neuron model, we develop a prediction model for short-term load forecasting, called the LF-NSNP model. The LF-NSNP model can be implemented in the RNN framework due to its recurrent-like structure.
- (4)
- Extensive experiment is conducted to verify the effectiveness of the proposed LF-NSNP model for short-term load forecasting.
2. Proposed Prediction Model
2.1. NSNP Systems
- (1)
- denotes a singleton alphabet (a indicates the spike).
- (2)
- is the ith neuron, , wherein
- (a)
- denotes the primary state of .
- (b)
- denotes the nonlinear firing rule, and the modality is , wherein , and both the functions and are nonlinear.
- (3)
- with , (synapses).
- (4)
- x denotes the external input of the model.
- (5)
- y denotes the external output of the model.
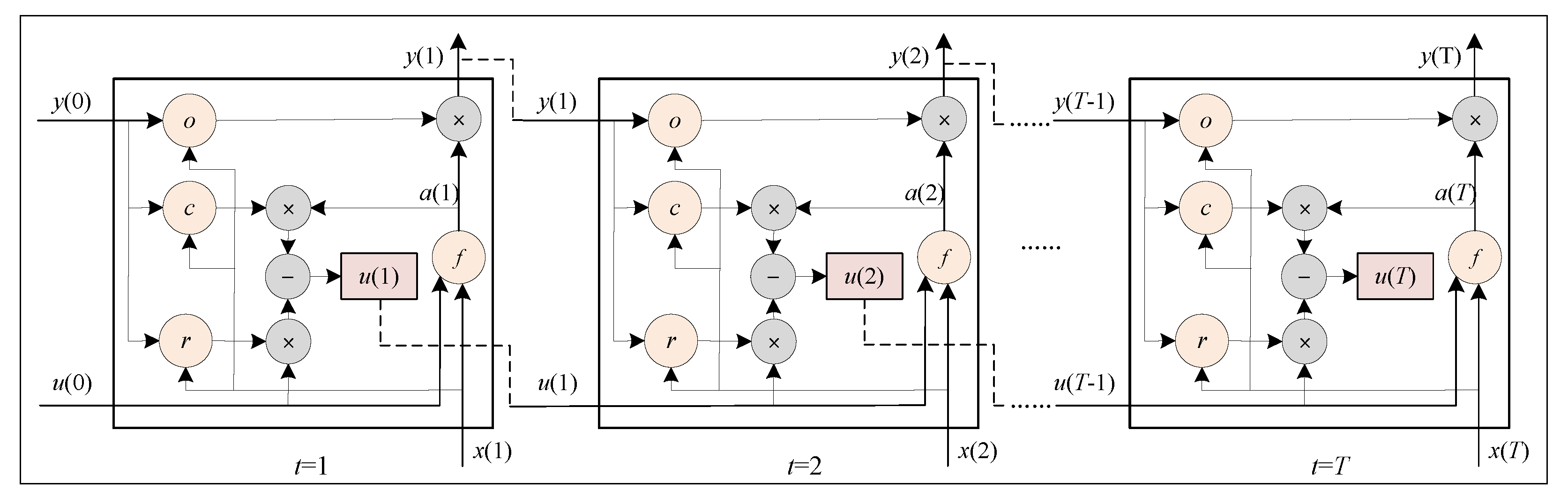
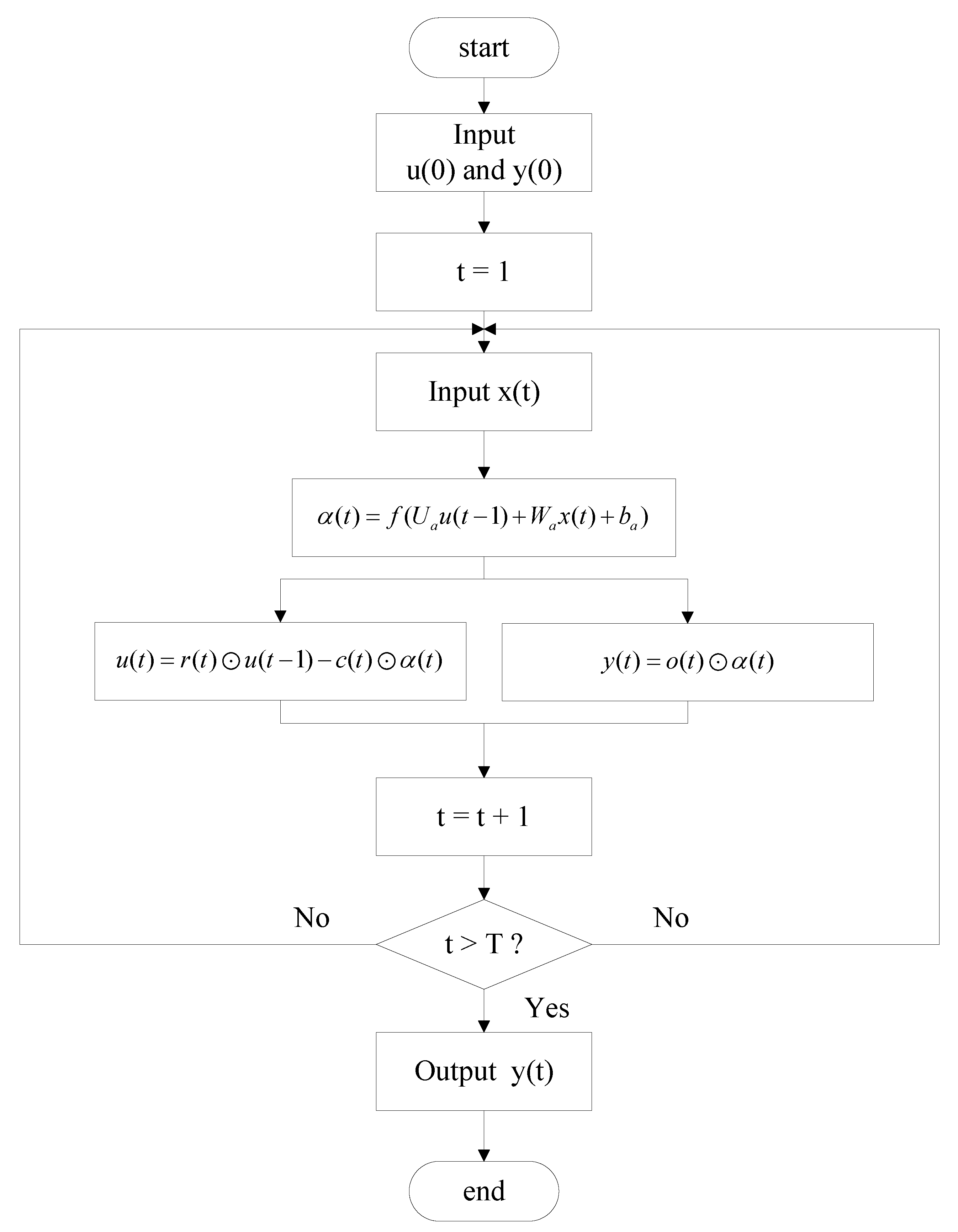
2.2. LF-NSNP Model
3. Experiments
3.1. Dataset
3.2. Evaluation Metrics
3.3. Experimental Results
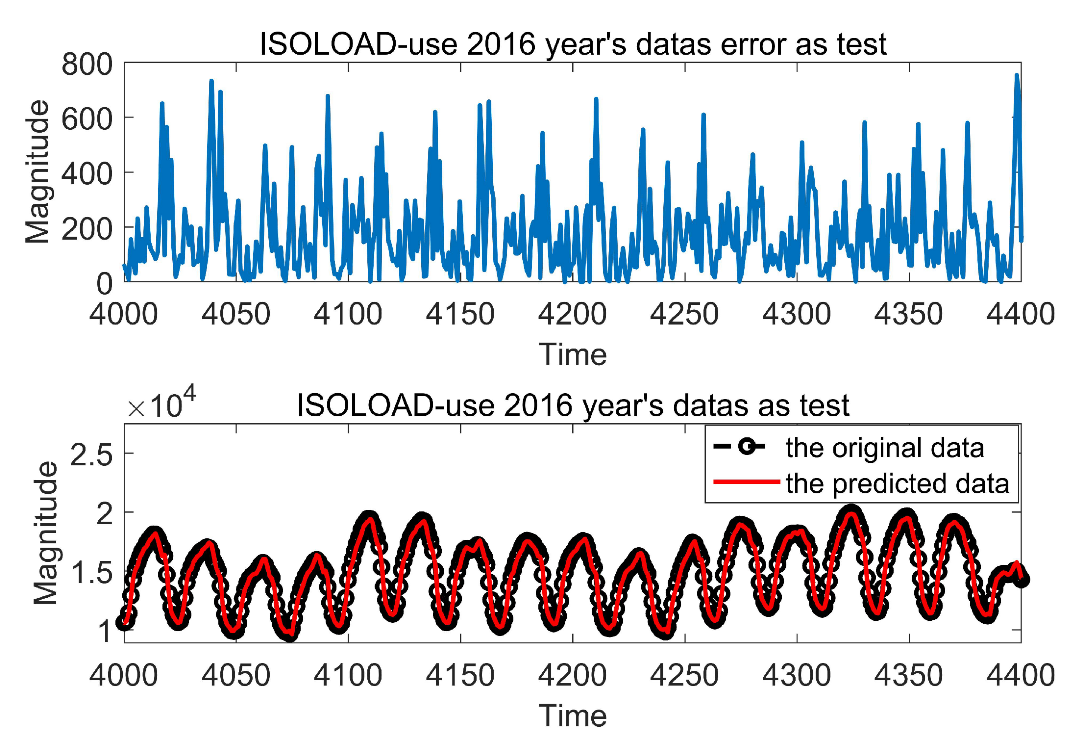
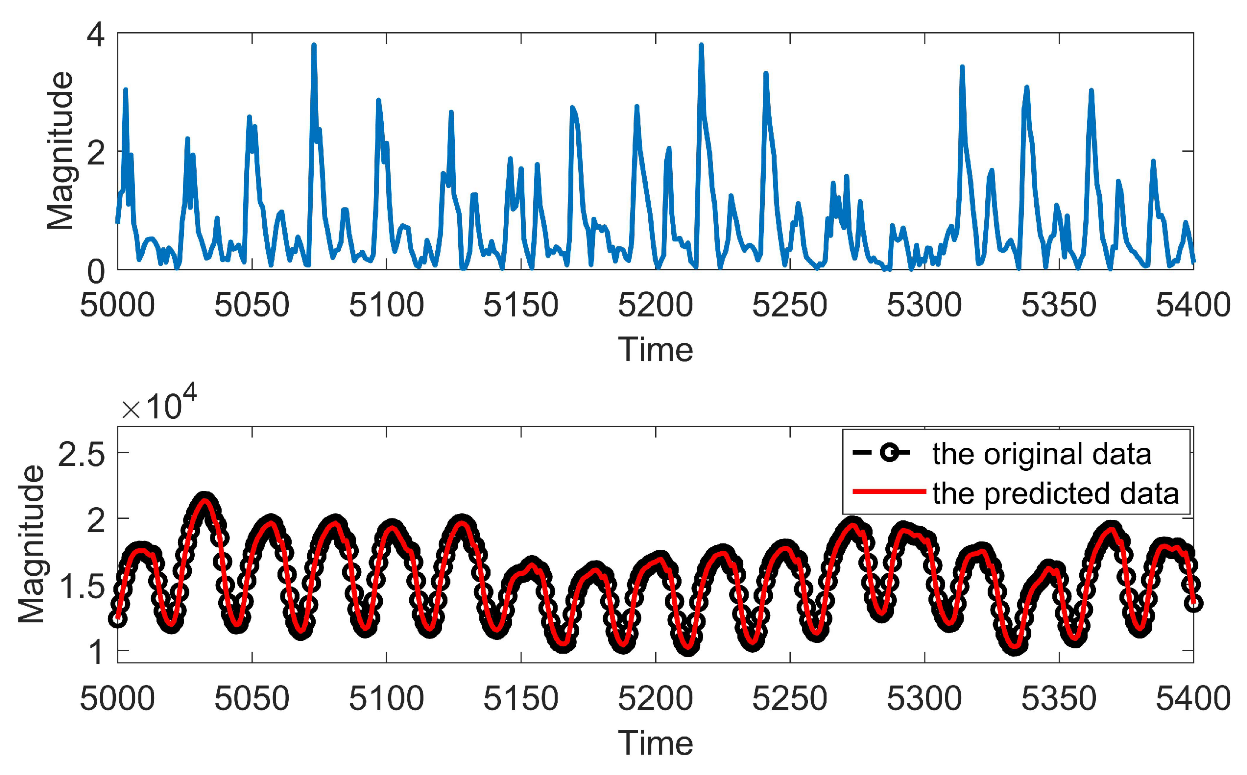
3.3.1. Case A
3.3.2. Case B
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| STLF | Short-term load forecasting |
| SVR | support vector regression |
| MLP | multilayer perceptron |
| RBF | radial basis function |
| ELM | extreme learning machine |
| CNN | convolutional neural network |
| LSTM | long short-term memory |
| GRU | gated recurrent unit |
| SNP | Spiking neural P systems |
| NSNP | Nonlinear spiking neural P |
| LF-NSNP | Load Forecasting Based on Nonlinear Spiking Neural P Systems |
| RNN | recurrent neural networks |
| MIMO | multiple input multiple output |
| MAE | mean absolute error |
| MAPE | mean absolute percentage error |
| RMSE | root mean square error |
| CRM | conditional residual modeling |
References
- Gonzalez-Romera, E.; Jaramillo-Moran, M.A.; Carmona-Fernandez, D. Monthlyelectric energy demand forecasting based on trend extraction. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2006, 21, 1946–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charytoniuk, W.; Chen, M.S.; Olinda, P.V. Nonparametric regression based short-term load forecasting. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 1998, 13, 725–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.-B.; Baek, Y.-S.; Hong, D.H.; Jang, G. Short-term load forecasting for the holidays using fuzzy linear regression method. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2005, 20, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, J.W. Short-term electricity demand forecasting using double seasonal exponential smoothing. J. Oper. Res. Soc. 2003, 54, 799–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elattar, E.E.; Goulermas, J.; Wu, Q.H. Electric load forecasting based on locally weighted support vector regression. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man, Cybern. Part C 2010, 40, 438–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rejc, M.; Pantos, M. Short-term transmission-loss forecast for the Slovenian transmission power system based on a fuzzy-logic decision approach. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2011, 26, 1511–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hippert, H.S.; Pedreira, C.E.; Souza, R.C. Neural networks for short-term load forecasting: A review and evaluation. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2001, 16, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, Q.; Hong, T.; Kang, C. Review of smart meter data analytics: Applications, methodologies, and challenges. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2019, 10, 3125–3148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charytoniuk, W.; Chen, M.S. Very short-term load forecasting using artificialneural networks. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2000, 15, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cecati, C.; Kolbusz, J.; Ró˙zycki, P.; Siano, P.; Wilamowski, B.M. A novel RBF training algorithm for short-term electric load forecasting and comparative studies. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2015, 62, 6519–6529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Luh, P.B.; Guan, C.; Zhao, Y.; Michel, L.D.; Coolbeth, M.A.; Friedl, P.B.; Rourke, S.J. Short-term load forecasting: Similar day-based wavelet neural networks. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2010, 25, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Dong, Z.Y.; Xu, Y.; Meng, K.; Wong, K.P. Short-term load forecasting of Australian national electricity market by an ensemble model of extreme learning machine. IET Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2013, 7, 391–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doveh, E.; Feigin, P.; Greig, D.; Hyams, L. Experience with FNN models formedium term power demand predictions. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 1999, 14, 538–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodfellow, I.; Bengio, Y.; Courville, A. Deep Learning; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ryu, S.; Noh, J.; Kim, H. Deep neural network based demand side short term load forecasting. Energies 2016, 10, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merkel, G.; Povinelli, R.J.; Brown, R.H. Deep neural network regression for short-term load forecasting of natural gas. In Proceedings of the 37th Annual International Symposium on Forecasting 2017, Boston, MA, USA, 25–28 June 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, N.; Wang, Y. Conditional Residual Modeling for Probabilistic Load Forecasting. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2018, 33, 7327–7330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Chen, Q.; Yan, J.; Zhang, S.; Xu, J. A novel asynchronous deep reinforcement learning model with adaptive early forecasting method and reward incentive mechanism for short-term load forecasting. Energy 2021, 236, 121492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ionescu, M.; Păun, G.; Yokomori, T. Spiking neural P systems. Fundam. Inform. 2006, 71, 279–308. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, H.; Lv, Z.; Li, B.; Luo, X.; Wang, J.; Song, X.; Wang, T.; Pérez-Jiménez, M.J.; Riscos-Núñez, A. Nonlinear spiking neural P systems. Int. J. Neural Syst. 2020, 30, 2050008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Yang, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, T.; Sun, Z.; Song, X.; Luo, X.; Huang, X. Spiking neural P systems with multiple channels. Neural Netw. 2017, 95, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Wang, J. Coupled neural P systems. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2019, 30, 1672–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Wang, J.; Pérez-Jiménez, M.J.; Riscos-Núñez, A. Dynamic threshold neural P systems. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2019, 163, 875–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Li, B.; Wang, J.; Song, X.; Wang, T.; Valencia-Cabrera, L.; Pérez-Hurtado, I.; Riscos-Núñez, A.; Pérez-Jiménez, M.J. Spiking neural P systems with inhibitory rules. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2020, 188, 105064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Bao, T.; Luo, X.; Wang, J.; Song, X.; Riscos-Núñez, A.; Pérez-Jiménez, M.J. Dendrite P systems. Neural Netw. 2020, 127, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ISO New England. ISO New England Zonal Information. 2017. Available online: https://www.iso-ne.com/isoexpress/web/reports/load-anddemand (accessed on 1 January 2022).
- Nowotarski, J.; Liu, B.; Weron, R.; Hong, T. Improving Short Term Load Forecast Accuracy via Combining Sister Forecasts. Energy 2016, 98, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Models | Metrics | CT | ME | NH | RI | VT | NEMASS | SEMASS | WCMASS | SYS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CRM | RMSE | 171.82 | 49.06 | 59.74 | 40.60 | 34.81 | 133.21 | 94.54 | 91.85 | 582.09 |
| MAE | 127.25 | 37.44 | 44.22 | 29.95 | 25.79 | 99.01 | 68.99 | 69.06 | 433.44 | |
| MAPE | 3.78 | 2.95 | 3.36 | 3.28 | 4.21 | 3.55 | 4.17 | 3.68 | 3.16 | |
| LF-NSNP | RMSE | 75.95 | 26.90 | 27.07 | 19.21 | 14.43 | 48.39 | 40.87 | 36.03 | 251.59 |
| MAE | 54.77 | 18.84 | 19.88 | 14.10 | 10.39 | 35.33 | 31.414 | 27.06 | 172.68 | |
| MAPE | 1.56 | 1.45 | 1.51 | 1.52 | 1.65 | 1.22 | 1.89 | 1.40 | 1.20 |
| Models | MAPE |
|---|---|
| TA | 2.10 |
| WA | 2.10 |
| OLS | 2.14 |
| LAD | 2.14 |
| PW | 2.12 |
| CLS | 2.11 |
| IRMSE | 2.10 |
| EWA | 2.18 |
| FS | 2.11 |
| ML-poly | 2.11 |
| LF-NSNP |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, L.; Guo, L.; Wang, J.; Peng, H. Short-Term Load Forecasting Based on Spiking Neural P Systems. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 792. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13020792
Li L, Guo L, Wang J, Peng H. Short-Term Load Forecasting Based on Spiking Neural P Systems. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(2):792. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13020792
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Lin, Lin Guo, Jun Wang, and Hong Peng. 2023. "Short-Term Load Forecasting Based on Spiking Neural P Systems" Applied Sciences 13, no. 2: 792. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13020792
APA StyleLi, L., Guo, L., Wang, J., & Peng, H. (2023). Short-Term Load Forecasting Based on Spiking Neural P Systems. Applied Sciences, 13(2), 792. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13020792





