Development of Fiber Reinforced Sustainable Dredge Bricks
Abstract
Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
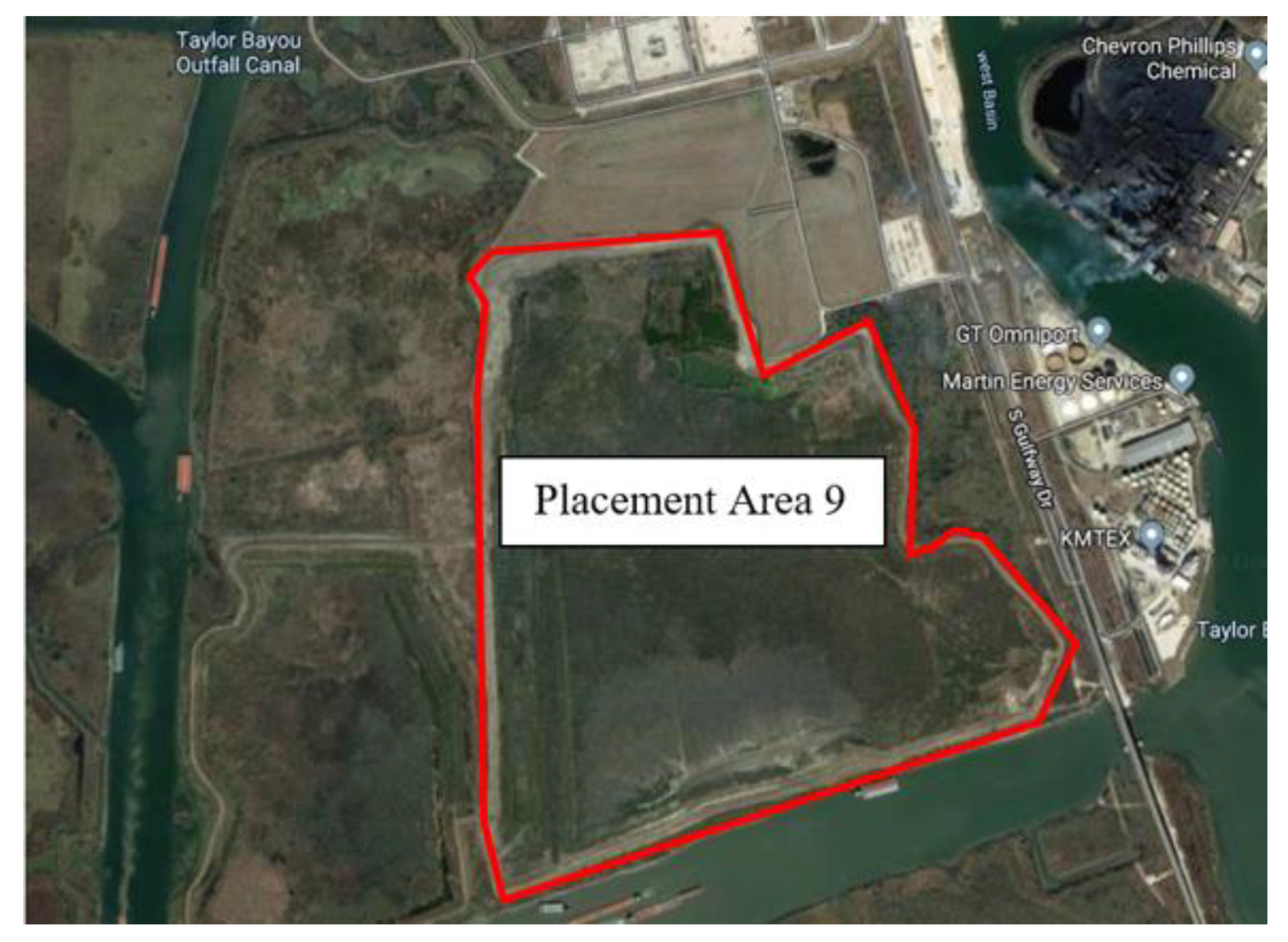
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Dredge Material Property Test
2.3. Brick Mixture Combinations
2.4. Mixing Dredged Materials with Agents
2.5. Equipment for Dredge Brick Production
2.6. Brick Property Tests
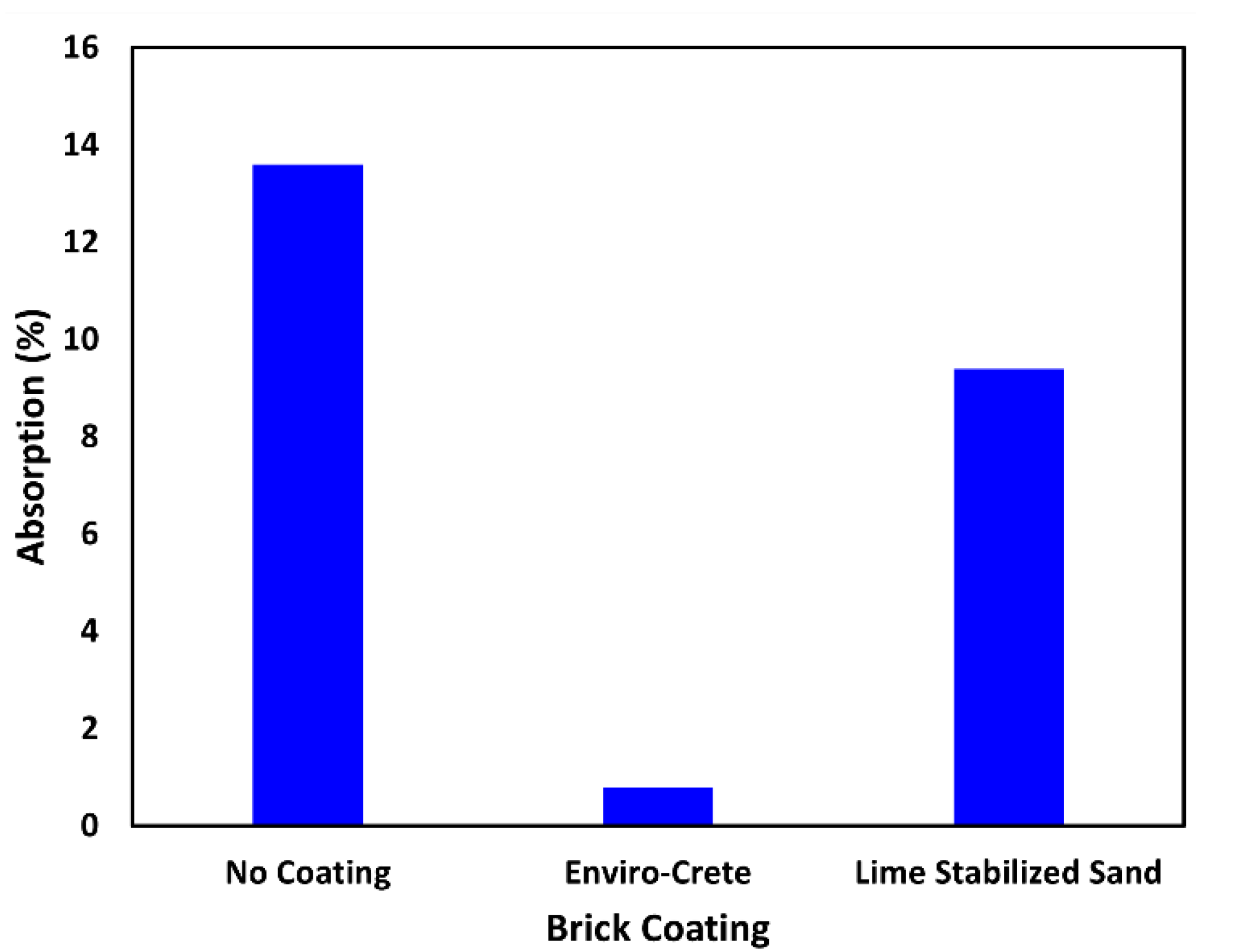
2.7. Control Coatings to Minimize Erosion
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Soil Characteristics and Classification
3.2. Brick Mechanical Tests
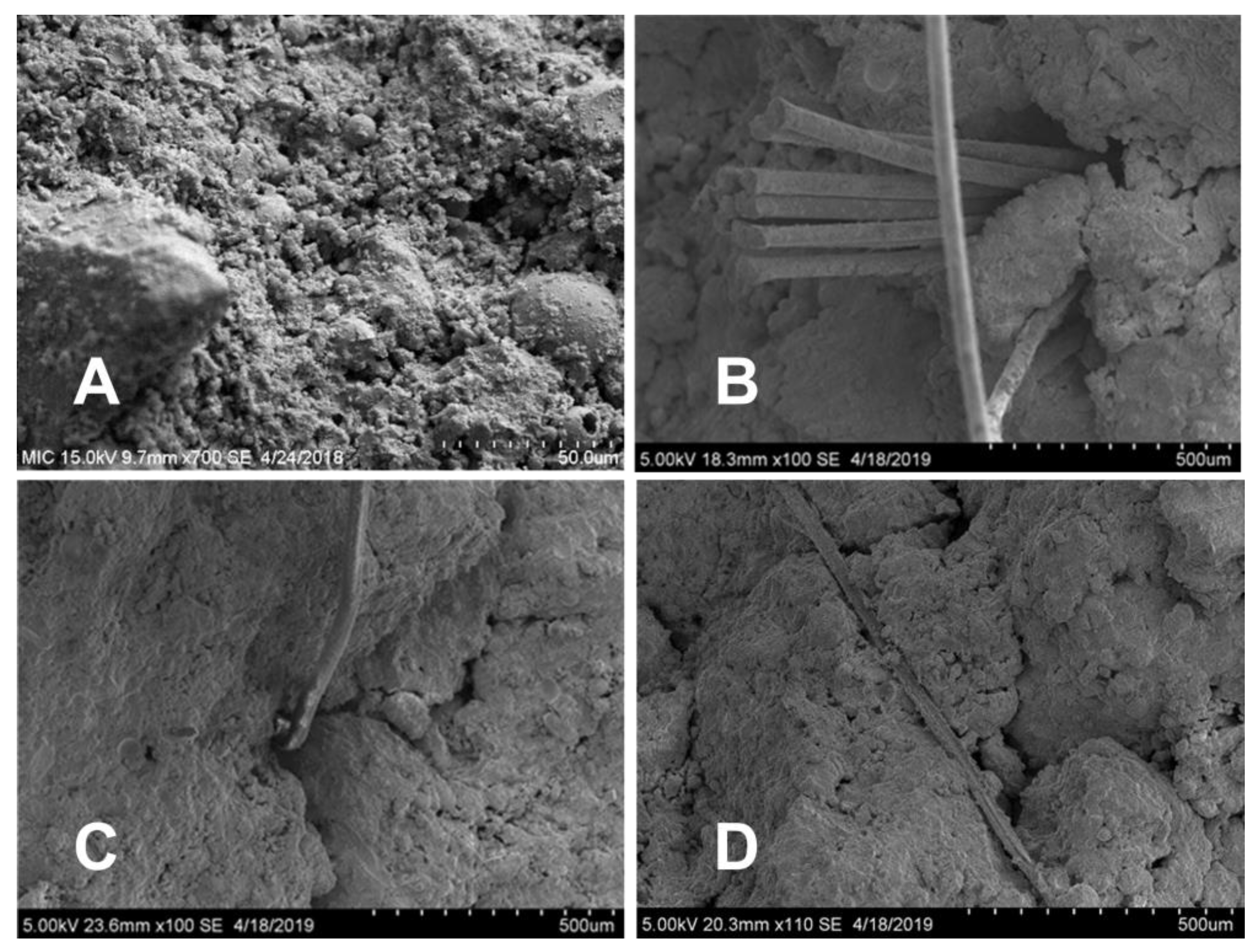
3.3. SEM Images
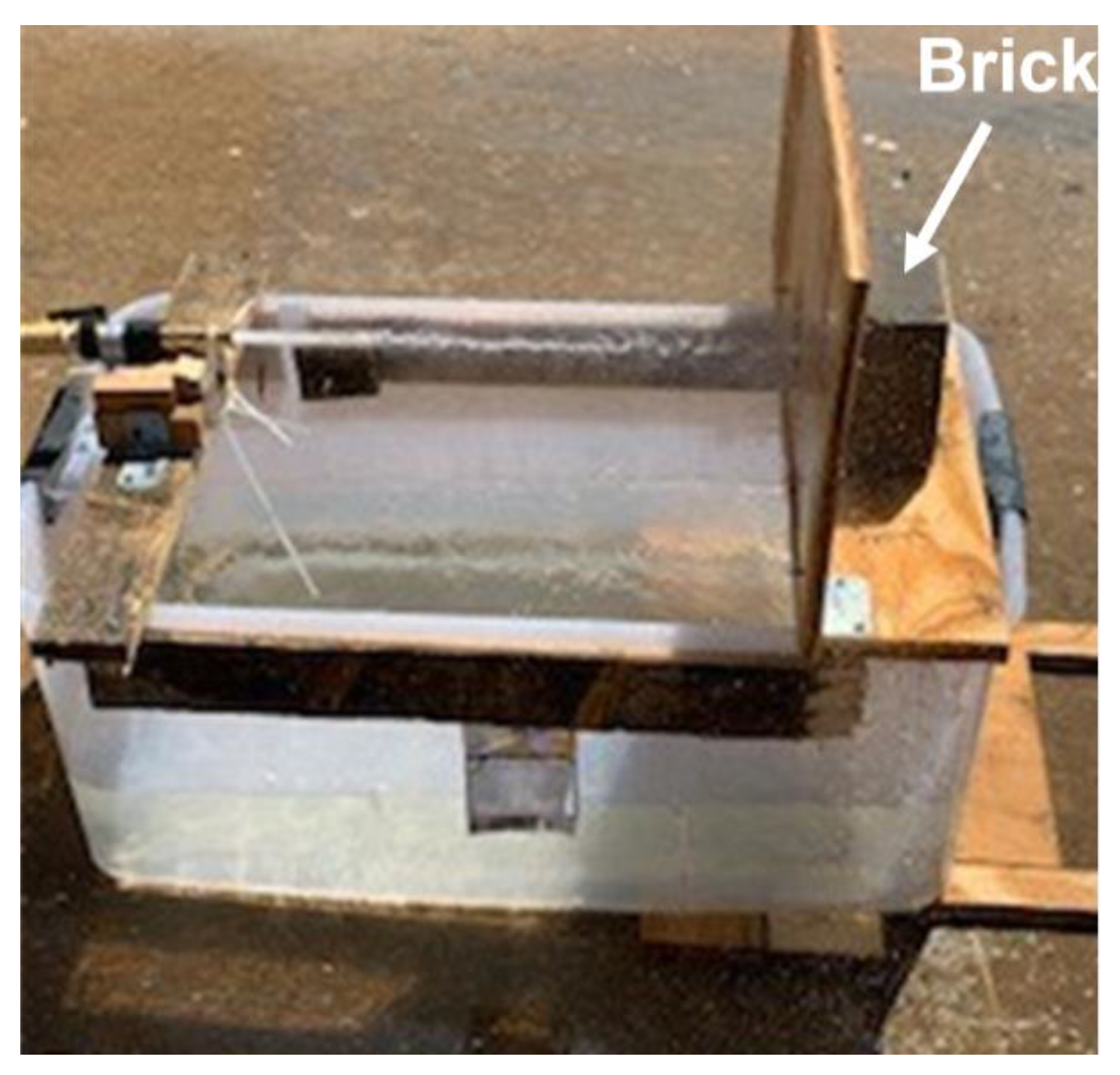
3.4. Erosion Tests
3.5. Rainfall Simulation Tests
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Maher, A.; Douglas, W.S.; Jafari, F. Field placement and evaluation of stabilized dredged material from New York New Jersey Harbor. Mar. GeoResour. Geotechnol. 2006, 24, 251–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brils, J.; de Boer, P.; Mulder, J.; de Boer, E. Reuse of dredged material as a way to tackle societal challenges. J. Soils Sediments 2014, 14, 1638–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cevikbilen, G.; Basar, H.M.; Karadogan, U.; Teymur, B.; Dagli, S.; Tolun, L. Assessment of the use of dredged marine materials in sanitary landfills: A case study from the Marmara sea. Waste Manag. 2020, 113, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamsawang, P.; Charoensil, S.; Namjan, T.; Jongpradist, P.; Likitlersuang, S. Mechanical and microstructural properties of dredged sediments treated with cement and fly ash for use as road materials. Road Mat. Pavement Design 2021, 22, 2498–2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.D.; Cong, X.; Zhu, L.P.; Kong, L.P.; Zhang, Z.F.; Tian, A.G.; Li, L. Experimental study on recycling dredged marine sediment and phosphate tailing to produce earth fill. Mar. GeoResour. Geotechnol. 2017, 35, 586–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamer, K.; Karius, V. Brick production with dredged harbour sediments. An industrial-scale experiment. Waste Manag. 2002, 22, 521–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubenstein, M. Emissions from the Cement Industry. State of the Planet. 2012. Available online: https://news.climate.columbia.edu/2012/05/09/emissions-from-the-cement-industry/ (accessed on 12 December 2022).
- Grubb, D.G.; Chrysochoou, M.; Smith, C.J.; Malasavage, N.E. Stabilized Dredged Material. I: Parametric Study. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2010, 136, 1011–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serbah, B.; Abou-Bekr, N.; Bouchemella, S.; Eid, J.; Taibi, S. Dredged Sediments Valorisation in Compressed Earth Blocks: Suction and Water Content Effect on Their Mechanical Properties. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 158, 503–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Chen, L.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Li, S.J.; Baek, K.; Hou, D.; Ding, S.; Poon, C.S. Recycling Dredged Sediment into Fill Materials, Partition Blocks, and Paving Blocks: Technical and Economic Assessment. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 199, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, R.; Bonner, B.; Fernande, D.; Aleman, F.; Defrancis, J. Dredged Stone Erosion Mitigation. Final Report; Lamar University: Beaumont, TX, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Laborel-Preneron, A.; Aubert, J.E.; Magniont, C.; Tribout, C.; Bertron, A. Plant Aggregates and Fibers in Earth Construction Materials: A Review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 111, 719–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M.; Levacher, D.; Saouti, L.; Leblanc, N.; Zmamou, H.; Djeran-Maigre, I.; Razakamanantsoa, A. Implementation on a Preparation and Controlled Compaction Procedure for Waste-Fiber-Reinforced Raw Earth Samples. J. Compos. Sci. 2022, 6, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Ju, C.G.; Yan, W.Z.; Yang, M.; Wan, Q.Q.; Li, Q.Q.; Wu, Y. Performance improvement of non-sintering permeable brick with the addition of fibers at a low content. J. Build. Eng. 2021, 43, 103191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Walia, B.A.; Bajaj, A. Influence of fly ash, lime, and polyester fibers on compaction and strength properties of expansive soil. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2007, 19, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S. Effect of Fiber Reinforcement and Distribution on Confined Compressive Strength of Fiber-Reinforced Cemented Sand. Geotext. Geomembr. 2009, 27, 162–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millogo, Y.; Aubert, J.M.; Hamard, E.; Morel, J.C. How Properties of Kenaf Fibers from Burkina Faso Contribute to the Reinforcement of Earth Blocks. Materials 2015, 8, 2332–2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.M.; Rabbanifar, S.; Brake, N.A.; Qian, Q.; Kibodeaux, K.; Crochet, H.E.; Oruji, S.; Whitt, R.; Farrow, J.; Belaire, B.; et al. Stabilization of Silty Clayey Dredged Material. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2018, 30, 04018199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treloar, G.J.; Owen, C.; Fay, R. Environmental assessment of rammed earth construction systems. Struct. Surv. 2001, 19, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Gao, X. Evaluation of the Anti-Erosion Characteristics of an MICP Coating on the Surface of Tabia. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2020, 32, 04020304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Environmental Protection Agency. Architectural Coating Rule for Volatile Organic Compounds. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/production/files/2015-11/documents/aim_coatings_detailed_factsheet.pdf (accessed on 12 December 2022).
- Webb, P. Natural Hydraulic Limes: A Plaster in a League of Its Own. Traditional Building. 2016. Available online: https://www.traditionalbuilding.com/opinions/natural-hydraulic-limes-plaster-league (accessed on 12 December 2022).
- Google Map Image (Latitude: 29.82821, Longitude: −93.97543). Available online: https://www.google.com/maps/place/29%C2%B049’41.6%22N+93%C2%B058’31.6%22W/@29.8296707,-93.9826311,3432m/data=!3m1!1e3!4m5!3m4!1s0x0:0x7082890fe16d0369!8m2!3d29.82821!4d-93.97543!5m1!1e8 (accessed on 12 December 2022).
- Obonyo, E.; Exelbirt, J.; Baskaran, M. Durability of compressed earth bricks: Assessing erosion resistance using the modified spray testing. Sustainability 2010, 2, 3639–3649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- New Mexico Earthen Building Materials Code. Construction Industries Division of the Regulation and Licensing Department. Title 14: Housing and Construction Chapter 7: Building Codes General. 2009. Available online: http://www.udcinc.org/2009%20New%20Mexico%20Earthen%20Building%20Materials%20Code.pdf (accessed on 12 December 2022).
- Gowda, R.P.C. Experimental Study of Cement Stabilized Fiber Reinforced Compressed Earth Blocks as an Alternative Building Material. Master’s Thesis, Arizona State University, Tempe, AZ, USA, 2016; pp. 10–127. [Google Scholar]
- Milburn, J.; Parsons, R. Performance of Soil Stabilization Agents. Univ. of Kansas and Kansas Dept. of Transportation. 2004. Available online: https://rosap.ntl.bts.gov/view/dot/38749 (accessed on 12 December 2022).
- Mitchell, J.K.; Soga, K. Fundamentals of Soil Behavior; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Rabbanifar, S.; Nguyen, T.T.M.; Yao, C.W.; Qian, Q.; Bernazzani, P.; Jao, M. Adding Value to Dredged Material Using Lime and Ash Products. In Proceedings of the Recent Trends in Geotechnical Geo-Environmental Engineering and Education RTG2EE International Conference, Online, 10–11 September 2020; pp. 94–98, ISBN-13: 978-0-6489449-0-4. [Google Scholar]
- NOAA 2019. Climate Information, NOAA’s National Weather Service, 2 January 2019. Available online: https://www.weather.gov/lch/bptclimategraphs (accessed on 12 December 2022).


| Fiber | Application Rate (%) | 7-Day UCS | 28-Day UCS | Flexural Strength |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| None | - | 1070 | 1394 | 381 |
| PVA | 0.25 | 724 | 907 | 201 |
| 0.50 | 354 | 666 | 108 | |
| 0.75 | 240 | 497 | 108 | |
| Polyester | 0.05 | 740 | 1123 | 195 |
| Kenaf | 0.10 | 872 | 1151 | 260 |
| Brick | Average Pit Depth (mm) | Maximum Pit Depth (mm) | Mass Before Spray Test (lb) | Mass after Spray Test (lb) | Mass Loss (lb) | Mass Loss (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No Coating/No Fiber | 3.1 | 5.0 | 7.061 | 6.952 | 0.109 | 1.544 |
| Enviro-Crete | 0.0 | 0.0 | 6.840 | 6.916 | −0.076 | −1.111 |
| Lime-Sand Mortar | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| No Coating/Kenaf Fiber | 2.1 | 3.3 | 6.534 | 6.344 | 0.190 | 2.908 |
| No Coating/PVA Fiber | 7.2 | 10.0 | 5.617 | 5.357 | 0.260 | 4.629 |
| No Coating/Polyester Fiber | 2.2 | 2.8 | 6.582 | 6.378 | 0.204 | 3.099 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nguyen, T.T.M.; Rabbanifar, S.; Luo, Z.; Huddleston, C.; O’Connor, T.; Richard, A.; Michel, M.; Moon, R.; Yao, C.-W.; Jao, M.; et al. Development of Fiber Reinforced Sustainable Dredge Bricks. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 789. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13020789
Nguyen TTM, Rabbanifar S, Luo Z, Huddleston C, O’Connor T, Richard A, Michel M, Moon R, Yao C-W, Jao M, et al. Development of Fiber Reinforced Sustainable Dredge Bricks. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(2):789. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13020789
Chicago/Turabian StyleNguyen, Thi Thuy Minh, Saeed Rabbanifar, Zhe Luo, Christopher Huddleston, Trey O’Connor, Adam Richard, Malik Michel, Ryan Moon, Chun-Wei Yao, Mien Jao, and et al. 2023. "Development of Fiber Reinforced Sustainable Dredge Bricks" Applied Sciences 13, no. 2: 789. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13020789
APA StyleNguyen, T. T. M., Rabbanifar, S., Luo, Z., Huddleston, C., O’Connor, T., Richard, A., Michel, M., Moon, R., Yao, C.-W., Jao, M., & Bernazzani, P. (2023). Development of Fiber Reinforced Sustainable Dredge Bricks. Applied Sciences, 13(2), 789. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13020789






