Dynamic Measuring Method of Laser Beam Incident Angle for Laser Doppler Vibrometer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Basic Measurement Principles
2.1. Measurement Principle of LDV
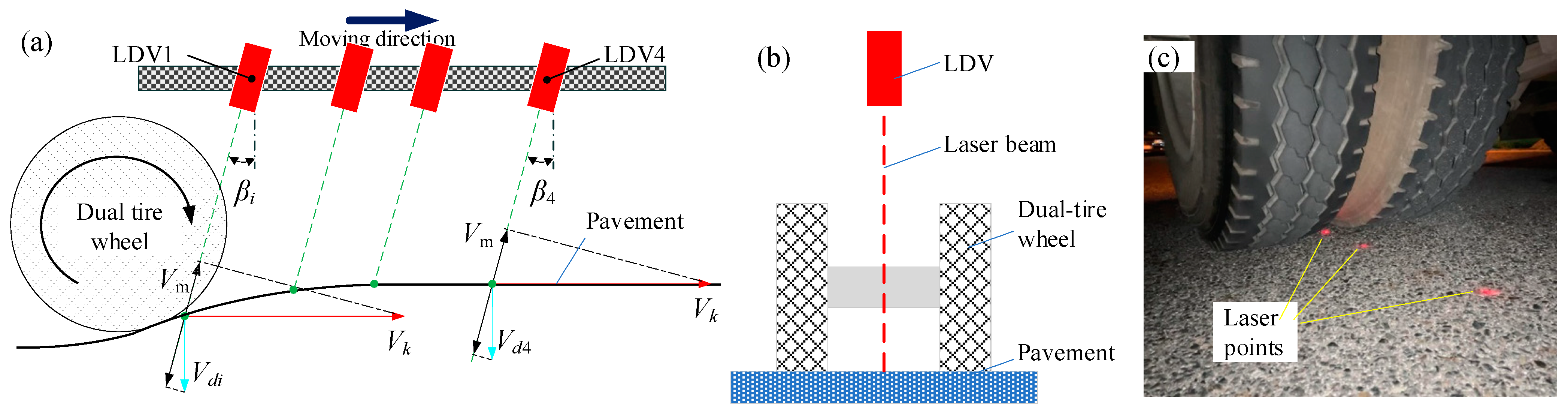
2.2. Measurement Principle of Pavement Deflection Velocity
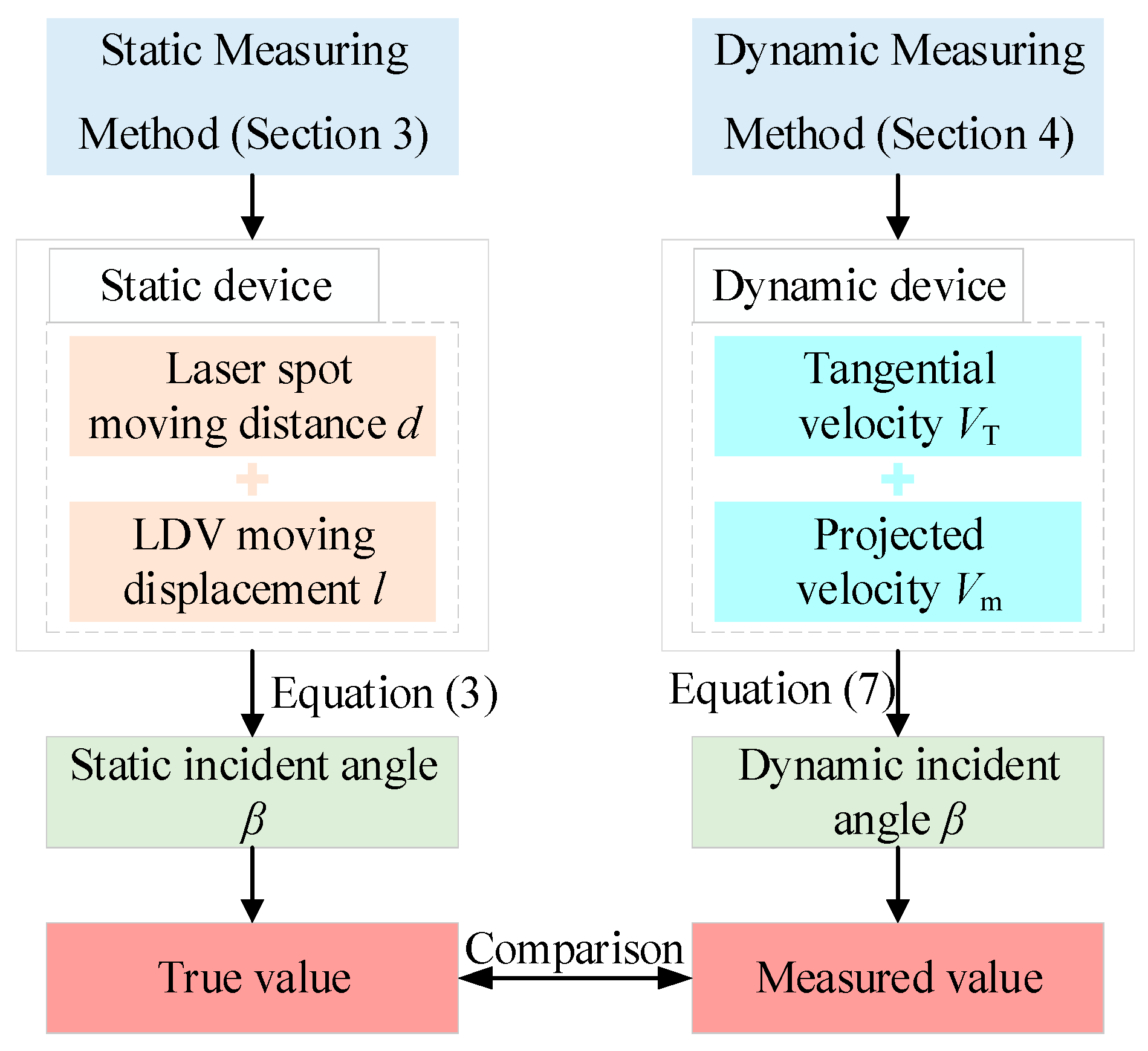
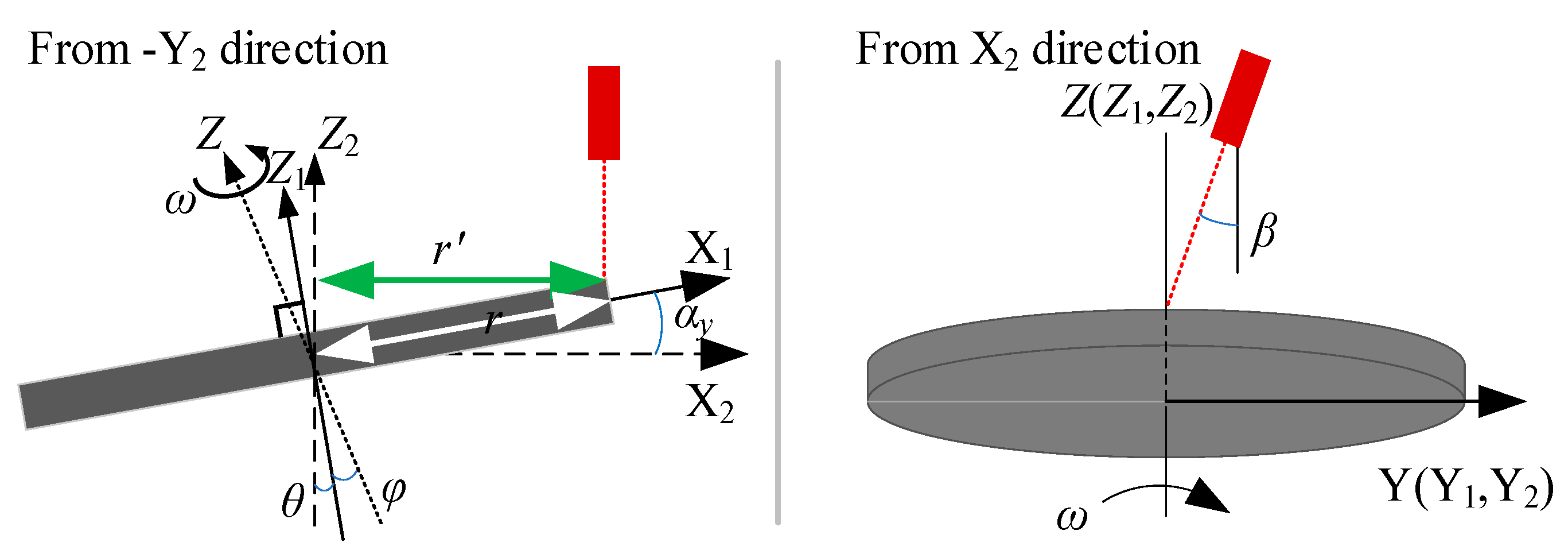
3. Static Measuring Method of Incident Angle
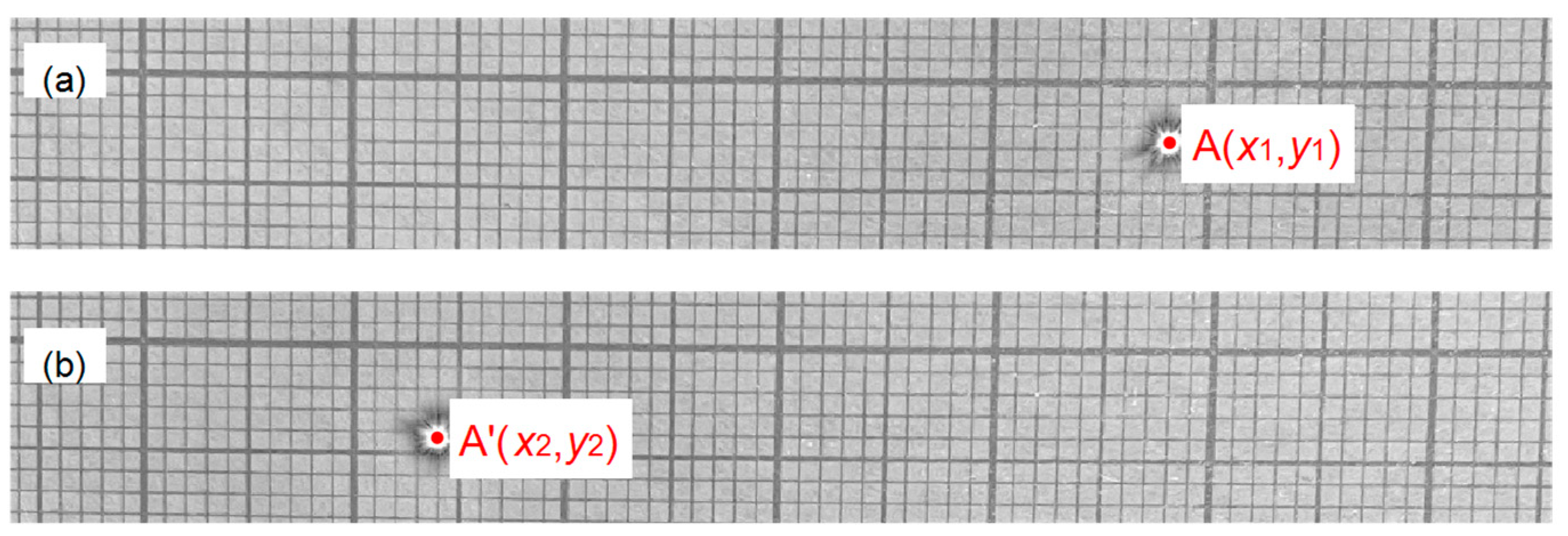
3.1. Principle of Static Measurement
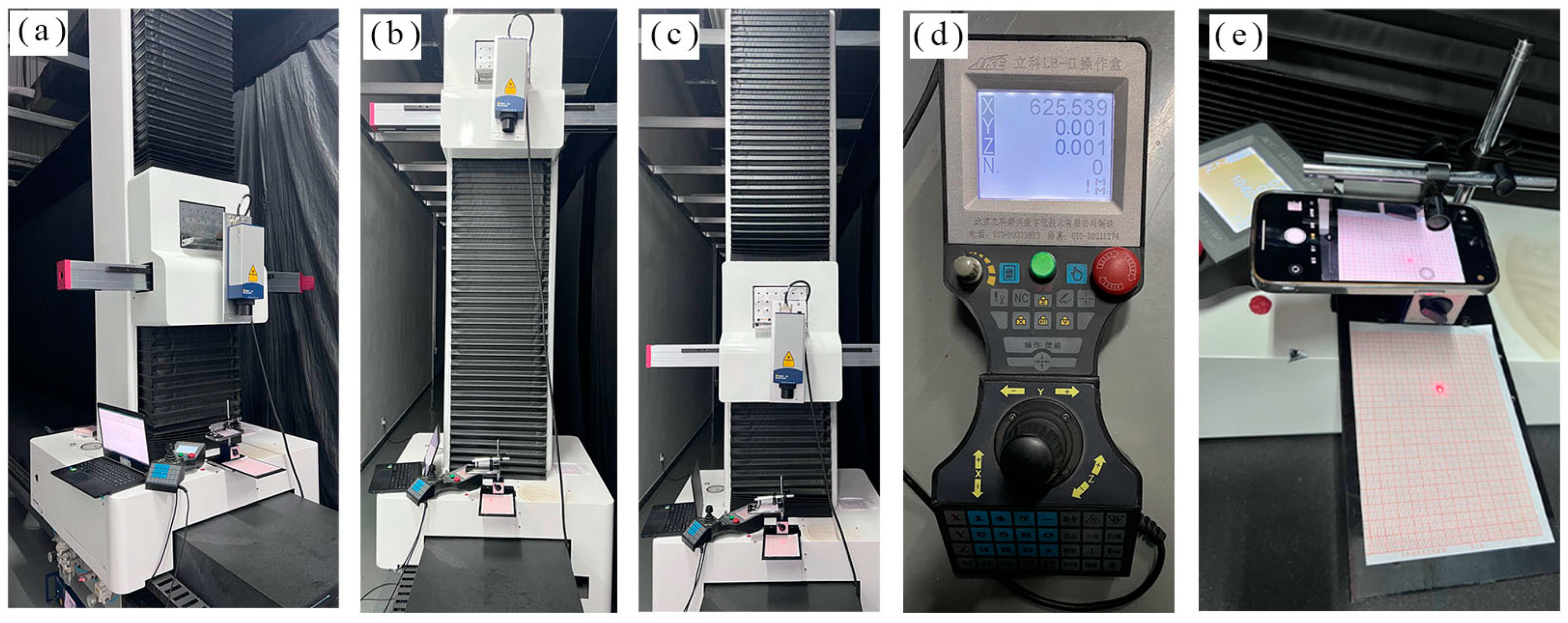
3.2. Static Measuring Device and Results
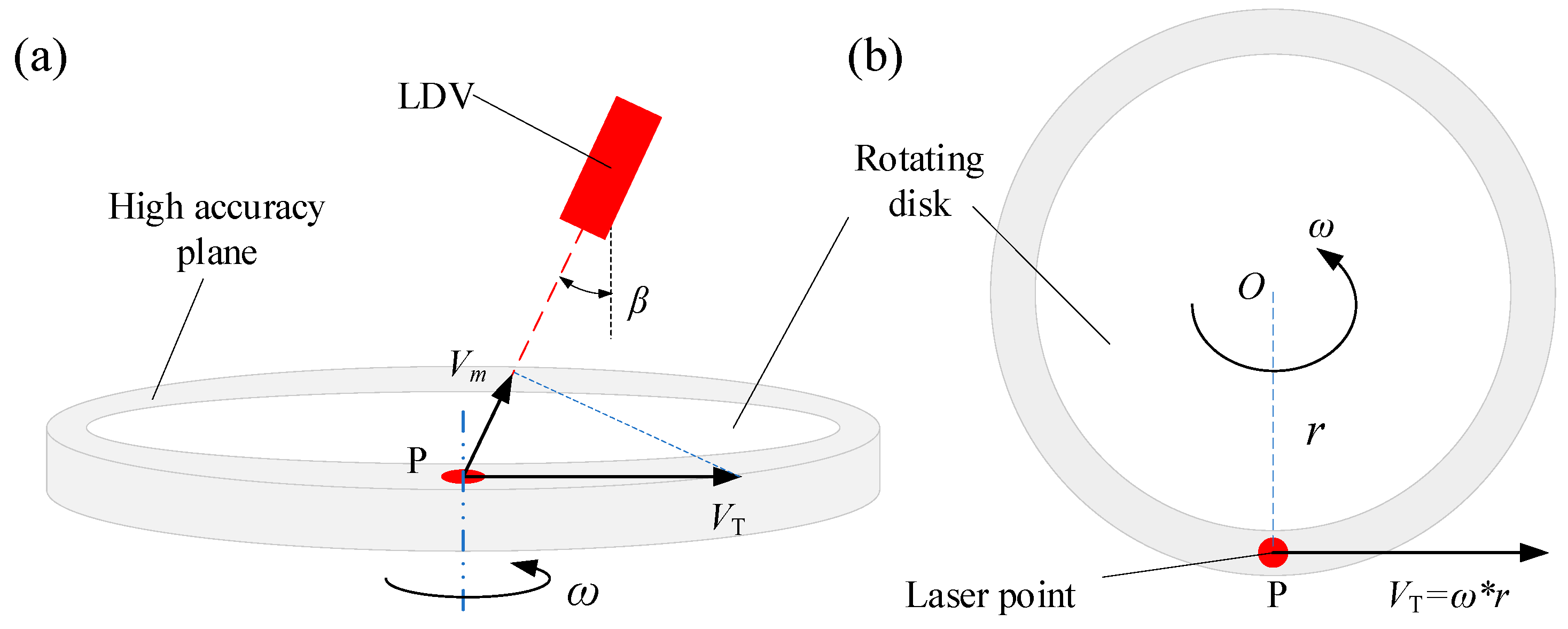
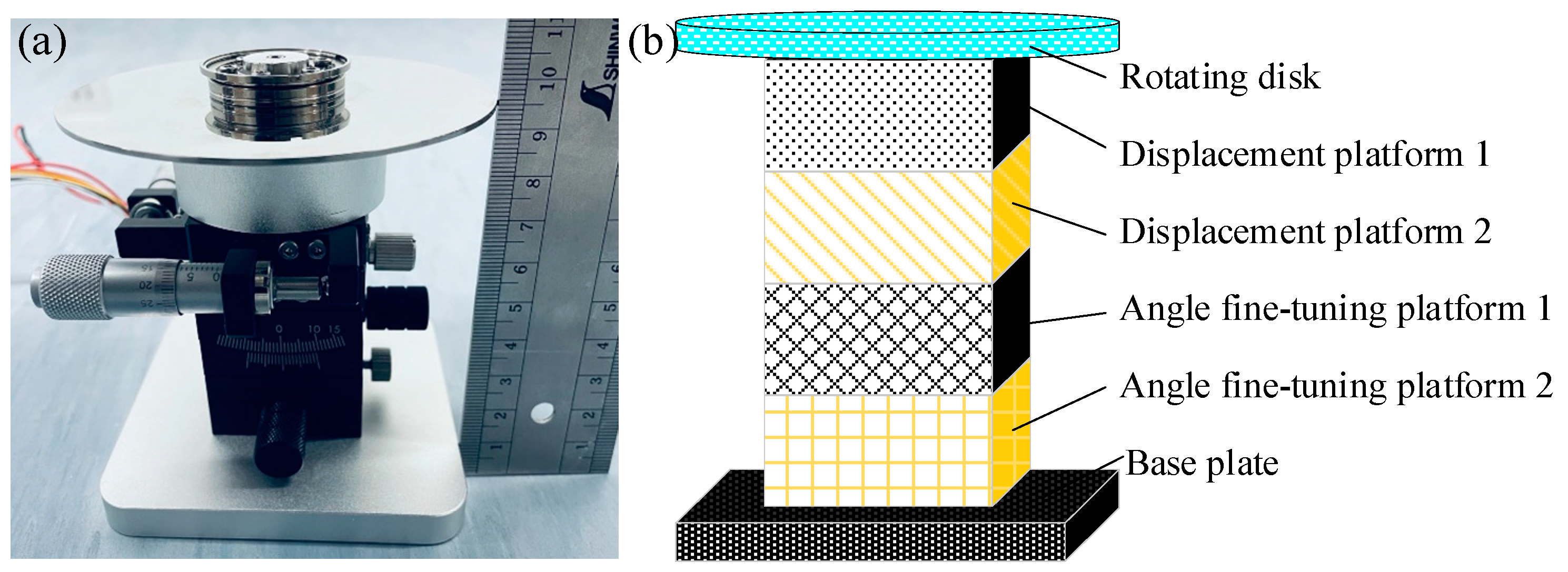
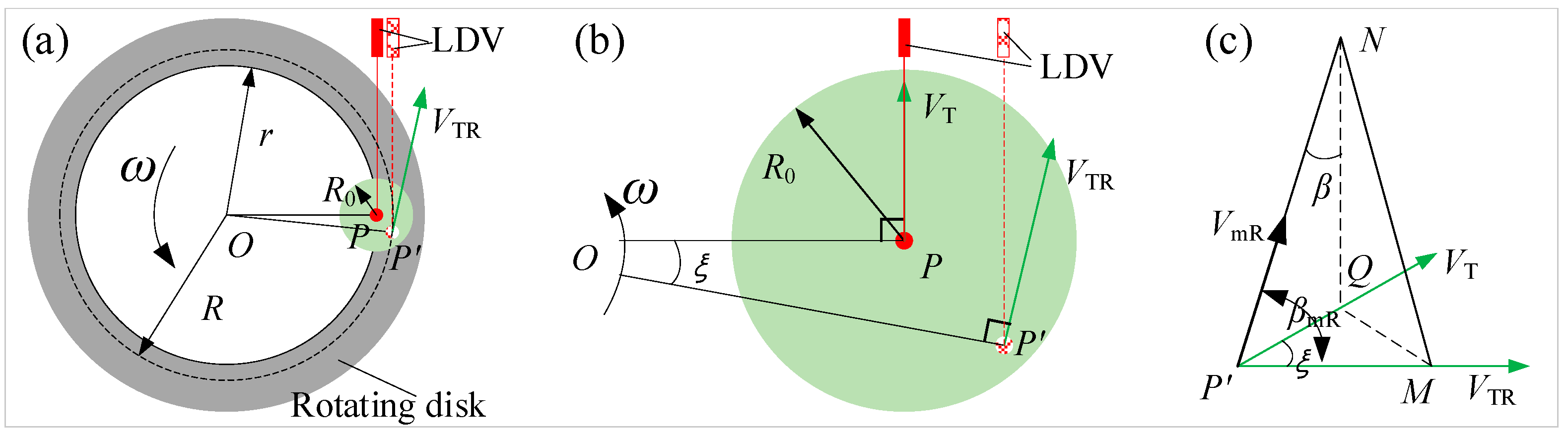
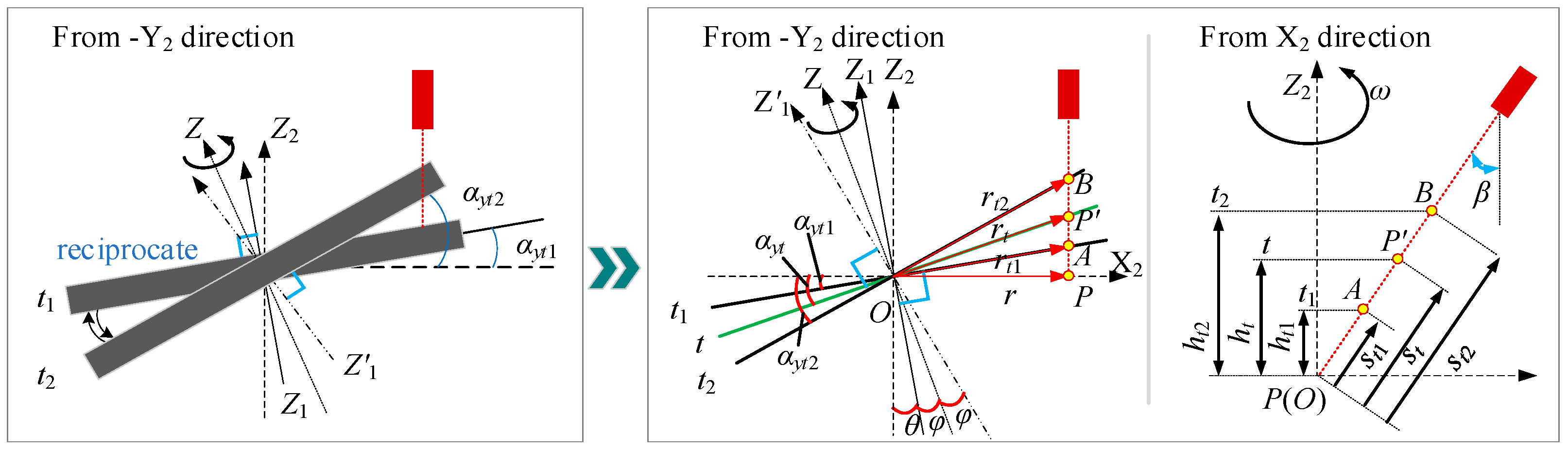
4. Dynamic Measuring Method of Incident Angle
4.1. Principle of Dynamic Measurement
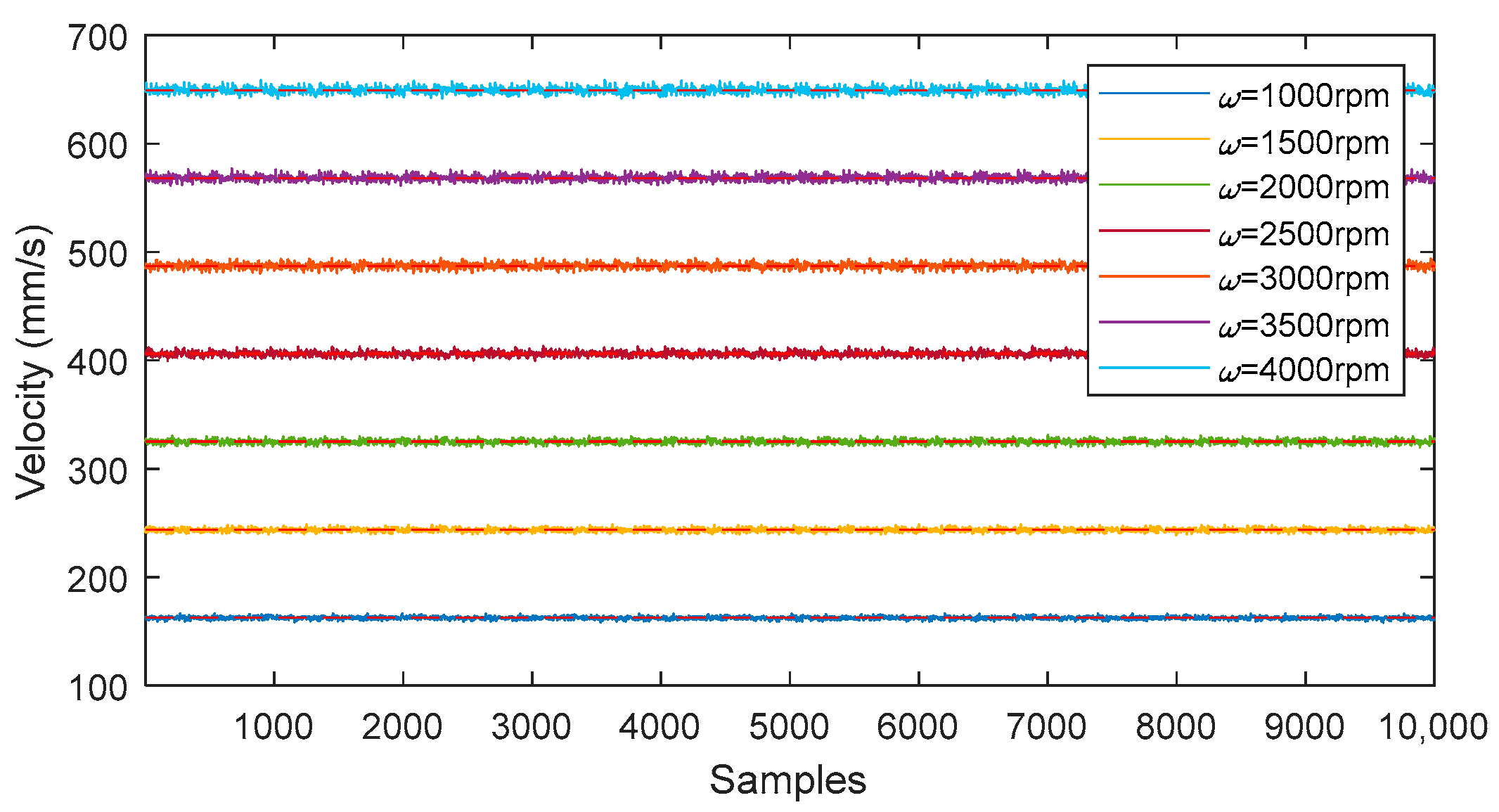
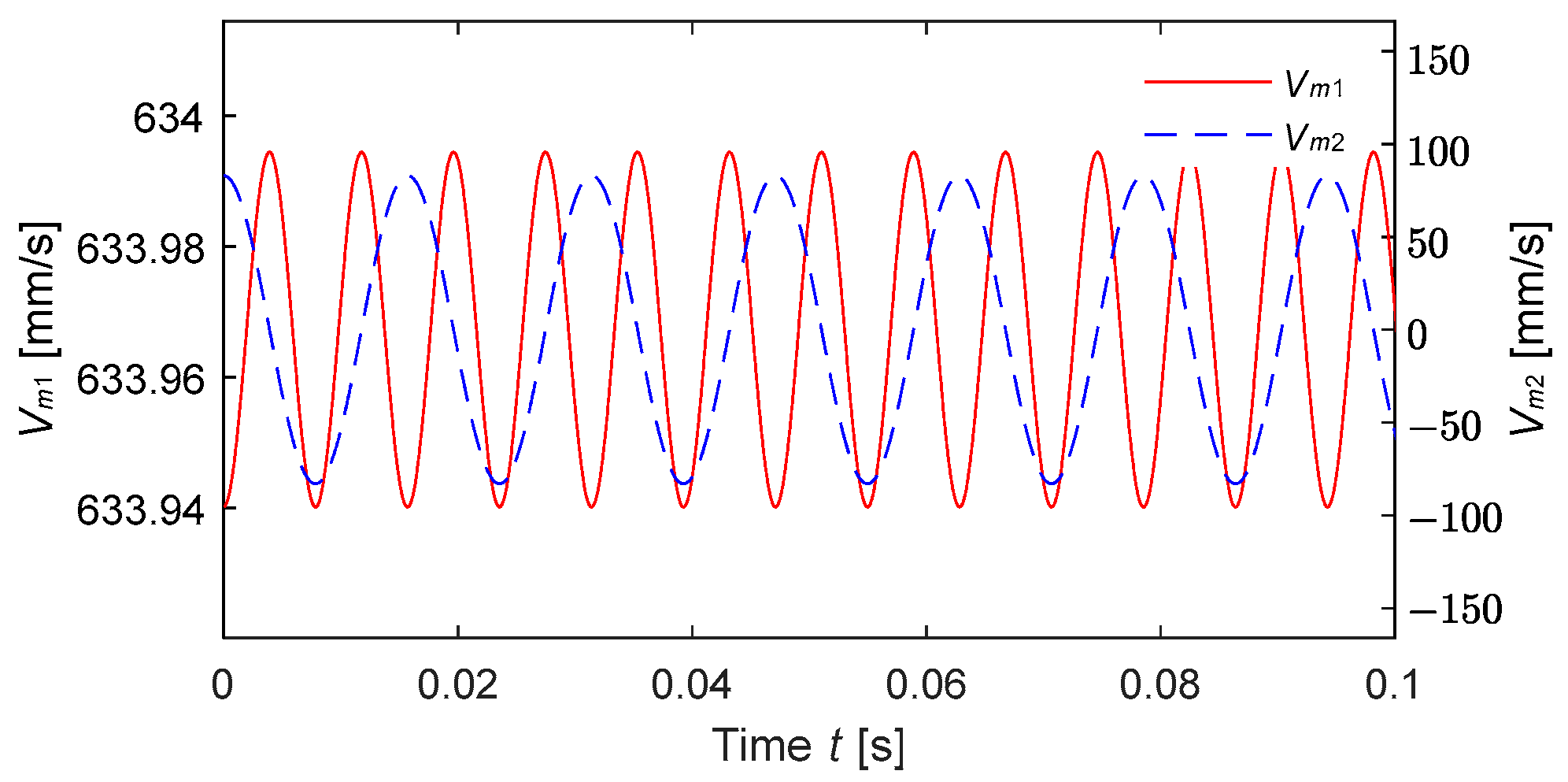
4.2. Dynamic Measuring Device and Results
5. Error Analysis and Discussion
5.1. Environmental Noise
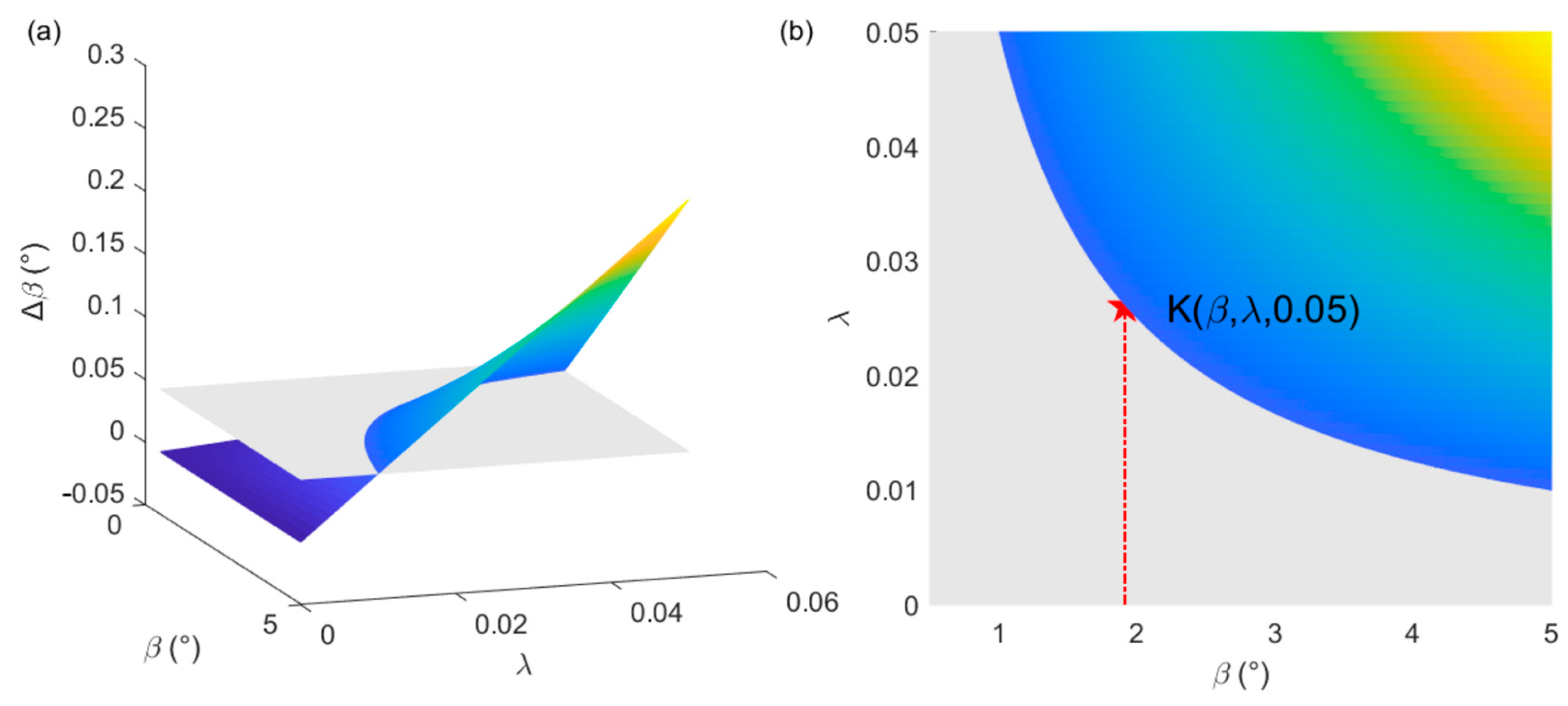
5.2. Laser Spot Position Error
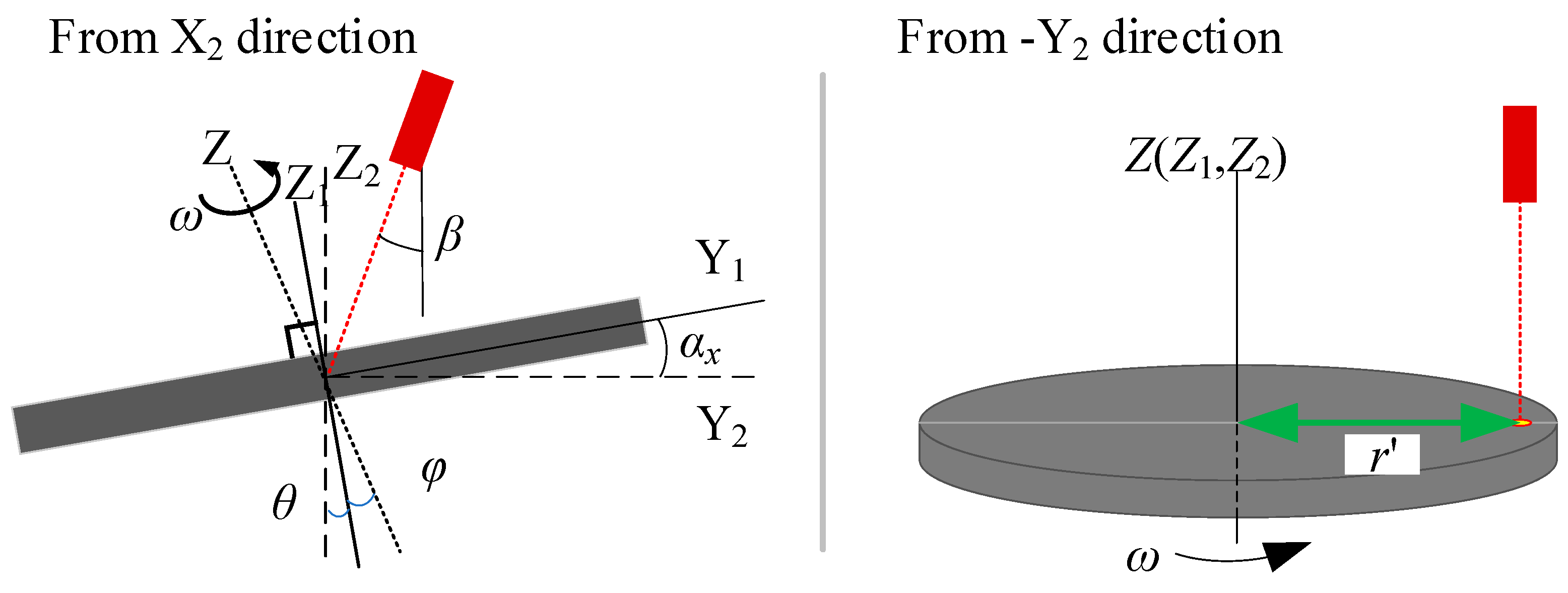
5.3. Rotating Disk System Error
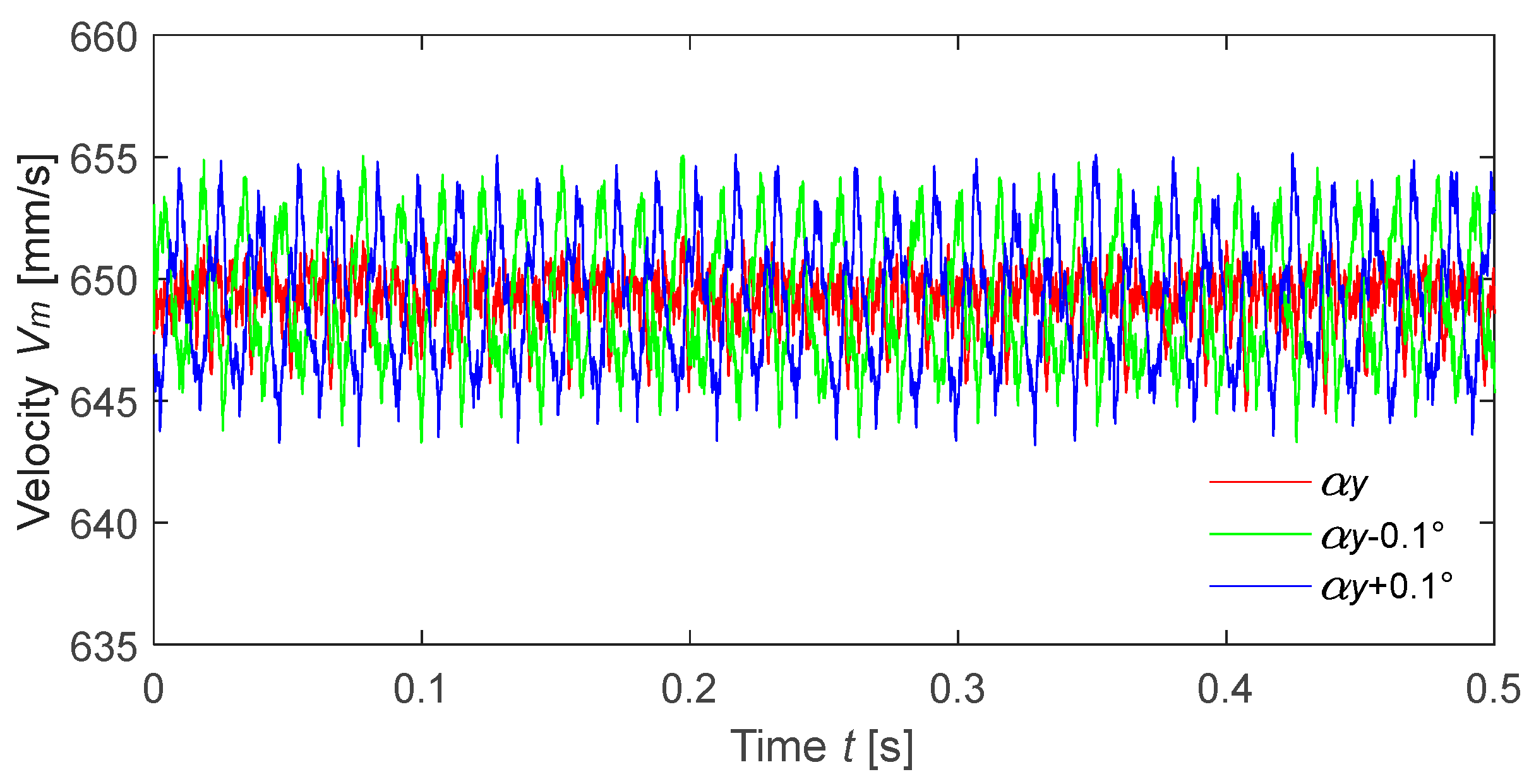
5.3.1. Roll Angle αy
5.3.2. Pitch Angle αx
5.3.3. Experimental Verification
5.4. Other Factors
6. Conclusions
- (1)
- The traditional method can measure and calibrate the incident angle of the LDV laser beam with high precision but requires an extensive spatial range. In contrast, the dynamic measuring method proposed in this paper utilizes the vibration measurement principle of LDV, overcomes the shortcomings of the traditional method to a large extent, and can also achieve a high precision measurement of the laser beam incident angle of the space-limited LDV;
- (2)
- Affected by many factors, the actual measured value of LDV is not constant but has a high signal-to-noise ratio. Using the average value instead of the actual measured value of LDV can reduce the measurement error caused by the environmental noise and the roll angle αy of the rotating disk;
- (3)
- The position error of the laser spot will significantly impact the measuring results of the incident angle. When the ratio of the error radius of the actual laser spot to the expected radius is less than or equal to 0.026, the error of the measuring result can be guaranteed to be less than 0.05°;
- (4)
- The pitch angle αx of the rotating disk directly determines the component of the circumferential velocity of the measuring point along the laser beam, and is the most critical factor affecting the measuring result of the incident angle. A high-precision inclinometer can be used to correct the measurement results, or an angle fine-tuning device can reduce the angle between the rotating disk and the horizontal plane to improve the dynamic measuring results.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| Symbols | |
| fD | Doppler frequency shift, Hz |
| fC | Laser’s frequency, Hz |
| C | Laser’s wavelength, m |
| Vm | LDV measurement, mm/s |
| Vk | Vehicle speed, mm/s |
| Vd | Pavement deformation velocity, mm/s |
| d | Moving distance of the laser spot, mm |
| l | Moving distance of LDV along the z-axis, mm |
| dpix | Pixel distance, mm/pix |
| VT | Tangential velocity, mm/s |
| ω | Angular velocity of rotating disk, rad/s |
| β | Angle between the laser beam and the vertical direction, known as the incident angle, ° |
| Mean value of Vm, mm/s | |
| Vmn | LDV values with noise, mm/s |
| n(t) | Environment noise, mm/s |
| Mean value of Vmn, mm/s | |
| ξ | ∠POP′ = ξ, ° |
| R0 | Radius of laser spot position error, mm |
| r | Distance of ideal laser spot P to rotation center O, mm |
| R | Distance of actual laser spot P′ to the rotation center O, mm |
| VTR | Tangential velocity of the actual laser spot P′, mm/s |
| VmR | LDV values measured from laser spot P′, mm/s |
| βmR | Actual angle β considering the laser spot position error, ° |
| ΔβmR | Measurement error caused by laser spot position error, ° |
| θ | Included angles between Z1 and Z in space, ° |
| φ | Included angles between Z1 and Z2 in space, ° |
| θx | Projection of the angle θ on the plane OY2Z2, ° |
| φx | Projection of the angle φ on the plane OY2Z2, ° |
| θy | Projection of the angle θ on the plane OX2Z2, ° |
| φy | Projection of the angle φ on the plane OX2Z2, ° |
| αy | Roll angle, ° |
| αx | Pitch angle, ° |
| rt | Distance from the laser spot P′ to the center O at time t |
| Vt | Circumferential velocity provided by point P′ at time t, mm/s |
| Vm1 | The first velocity component of LDV, mm/s |
| Am | Reciprocates amplitude between points A and B, mm/s |
| Vm2 | Velocity component generated by reciprocating motion, mm/s |
| Vmy | Actual measured velocity of the LDV considering the roll angle αy, mm/s |
| Mean value of coupling velocity Vmy, mm/s | |
| βmy | Incident angle considering the roll angel αy, ° |
| Vmx | Actual measured velocity of the LDV considering the pitch angle αx, mm/s |
| βmx | Incident angle considering the pitch angle αx, ° |
| Δβmx | Error due to pitch angle αx, ° |
References
- Rothberg, S.J.; Allen, M.S.; Castellini, P.; Di Maio, D.; Dirckx, J.J.J.; Ewins, D.J.; Halkon, B.J.; Muyshondt, P.; Paone, N.; Ryan, T.; et al. An international review of laser Doppler vibrometry: Making light work of vibration measurement. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2017, 99, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altmann, B.; Betker, T.; Pape, C.; Reithmeier, E. Alignment strategy for an optomechanical image derotator using a laser Doppler vibrometer. Appl. Opt. 2019, 58, 6555–6568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y.; Liu, H.; Xie, J. 100-m standoff detection of a QCL-induced photo-vibrational signal on explosives using a laser vibrometer. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2018, 107, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kim, K.; Sohn, H. In situ measurement of structural mass, stiffness, and damping using a reaction force actuator and a laser Doppler vibrometer. Smart Mater. Struct. 2013, 22, 85001–85004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Garg, P.; Fernando Moreu, M.A.; Ozdagli, A.; Mahmoud Reda Taha, M.A.; Mascareñas, D.; Mascareñas, A.D. Noncontact Dynamic Displacement Measurement of Structures Using a Moving Laser Doppler Vibrometer. J. Bridge Eng. 2019, 24, 4019089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Zhou, W.; Song, Y. Detecting oscillation amplitude and defects of hard disk rotating in high speed by laser Doppler technique. Measurement 2012, 45, 74–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Chaoping, Z. Damage Detection Using Modal Rotational Mode Shapes Obtained with a Uniform Rate CSLDV Measurement. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Cui, D.; Ying, Y. Nondestructive measurement of pear texture by acoustic vibration method. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2014, 96, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhang, D.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, C.; Che, S. Design of a high-precision and non-contact dynamic angular displacement measurement with dual-Laser Doppler Vibrometers. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 9094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sels, S.; Vanlanduit, S.; Bogaerts, B.; Penne, R. Three-dimensional full-field vibration measurements using a handheld single-point laser Doppler vibrometer. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2019, 126, 427–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhang, J.; Gong, H.; Jia, X.; Xiao, R.; Huang, H.; Huang, B. Numerical investigation of pavement responses under TSD and FWD loading. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 318, 126014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin Ahmed Zihan, Z.; Elseifi, M.A.; Gaspard, K.; Zhang, Z. Development of a structural capacity prediction model based on traffic speed deflectometer measurements. Transp. Res. Rec. J. Transp. Res. Board 2018, 2672, 315–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasimifar, M.; Kamalizadeh, R.; Heidary, B. The available approaches for using traffic speed Deflectometer data at network level pavement management system. Measurement 2022, 202, 111901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katicha, S.; Flintsch, G.; Diefenderfer, B. Ten Years of Traffic Speed Deflectometer Research in the United States: A Review. Transp. Res. Rec. J. Transp. Res. Board 2022, 2676, 152–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.; Lin, H.; Li, Q.; Zhang, D. A correction model for the continuous deflection measurement of pavements under dynamic loads. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 154770–154785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zou, Q.; Mao, Q.; Chen, X.; Li, B. Efficient calibration of a laser dynamic deflectometer. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2013, 62, 806–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Li, X.; Jing, G.; Guo, H.; Yin, Q.; Zhang, Y. Performance Evaluation of Traffic Speed Deflectometer Based on Virtual Standard Test Road. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 977–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, F.; Xiang, Q.; Hou, X.; Amirkhanian, S.N. Utilization of traffic speed deflectometer for pavement structural evaluations. Measurement 2021, 178, 109326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wix, R.; Murnane, C.; Moffatt, M. Experience gained investigating, acquiring and operating the first traffic speed deflectometer in Australia. Transp. Res. Procedia 2016, 14, 3060–3069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferne, B.W.; Langdale, P.; Round, N.; Fairclough, R. Development of a calibration procedure for the U.K. highways agency traffic-speed deflectometer. Transp. Res. Rec. J. Transp. Res. Board 2009, 2093, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonin, J.; Lièvre, D.; Rasmussen, S.; Hildebrand, G. Assessment of the Danish high speed deflectograph in France. In Proceedings of the International Conferences on the Bearing Capacity of Roads, Railways and Airfields, Trondheim, Norway, 25–27 June 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Flores-Fuentes, W.; Trujillo-Hernández, G.; Alba-Corpus, I.Y.; Rodríguez-Quiñonez, J.C.; Mirada-Vega, J.E.; Hernández-Balbuena, D.; Murrieta-Rico, F.N.; Sergiyenko, O. 3D spatial measurement for model reconstruction: A review. Measurement 2023, 207, 112321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, G. A vision measurement model of laser displacement sensor and its calibration method. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2013, 51, 1344–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Wu, B.; Sun, Z.; Wang, J. Calibration method of a laser beam based on discrete point interpolation for 3D precision measurement. Opt. Express 2020, 28, 27588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, C.; Liu, Y.; Fang, J.; Guo, X.; Lv, L.; Dong, P. Calibration of laser beam direction for optical coordinate measuring system. Measurement 2015, 73, 191–199. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, T.; Wang, Z.; Wu, Z.; Li, X.; Wang, L.; Liu, C. Calibration of Laser Beam Direction for Inner Diameter Measuring Device. Sensors 2017, 17, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhu, L. A robust and efficient calibration method for spot laser probe on CMM. Measurement 2020, 154, 107523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Lu, D.; Qian, W.; Gu, G.; Zhang, J.; Kong, X. Extrinsic calibration of a single-point laser rangefinder and single camera. Opt. Quantum Electron. 2019, 51, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Li, Y.; Li, N.; Zhao, B. Extrinsic Calibration of 2-D Laser Rangefinder and Camera from Single Shot Based on Minimal Solution. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2016, 65, 915–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Wang, L.; Cao, T.; Wang, J.; He, X.; Xiong, C. A large-scale laser plane calibration system. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2007, 18, 1768–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Chen, T.; Li, A. A High Precision Approach to Calibrate a Structured Light Vision Sensor in a Robot-Based Three-Dimensional Measurement System. Sensors 2016, 16, 1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirai, K.; Ishimura, S.; Kawanami, T.; Hirasawa, S. Development of a new velocity calibration method for laser velocimetry using multiple scattering points on a single slit aperture. Microsyst. Technol. 2016, 22, 1351–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terra, O.; Hussein, H.M. Simple and accurate calibration system for Laser Doppler Velocimeters. Optik 2019, 179, 733–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Nie, X.; Zhou, J. Laser Doppler velocimeter and its calibration system. Meas. J. Int. Meas. Confed. 2019, 134, 286–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Z.; Chen, B.; Hu, W.; Yan, K.; Miao, H.; Zhang, Q.; Yu, Q.; Fu, Y. LDV-induced stroboscopic digital image correlation for high spatial resolution vibration measurement. Opt. Express 2021, 29, 28134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Group | li (mm) | di (mm) | di′ (mm) | di″ (mm) | βi (°) | βi′ (°) | βi″ (°) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1029.994 | 34.327 | 34.427 | 34.227 | 1.9088 | 1.9144 | 1.9033 |
| 2 | 930.619 | 31.021 | 31.121 | 30.921 | 1.9092 | 1.9153 | 1.9030 |
| 3 | 1015.023 | 33.882 | 33.982 | 33.782 | 1.9118 | 1.9175 | 1.9062 |
| 4 | 976.006 | 32.552 | 32.652 | 32.452 | 1.9102 | 1.9161 | 1.9044 |
| 5 | 960.845 | 32.059 | 32.159 | 31.959 | 1.911 | 1.9169 | 1.9050 |
| 6 | 1011.97 | 33.835 | 33.935 | 33.735 | 1.915 | 1.9206 | 1.9093 |
| 7 | 919.53 | 30.709 | 30.809 | 30.609 | 1.9127 | 1.9190 | 1.9065 |
| 8 | 984.966 | 32.934 | 33.034 | 32.834 | 1.9151 | 1.9209 | 1.9093 |
| 9 | 956.842 | 31.986 | 32.086 | 31.886 | 1.9146 | 1.9206 | 1.9086 |
| 10 | 971.958 | 32.327 | 32.427 | 32.227 | 1.9088 | 1.9108 | 1.8990 |
| ω (rpm) | (mm/s) | β (°) |
|---|---|---|
| 1000 | 162.632 | 1.8736 |
| 1500 | 243.768 | 1.8722 |
| 2000 | 325.035 | 1.8723 |
| 2500 | 406.169 | 1.8717 |
| 3000 | 487.117 | 1.8705 |
| 3500 | 568.201 | 1.8703 |
| 4000 | 649.145 | 1.8696 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, Y.; An, H.; Li, X.; Jing, G. Dynamic Measuring Method of Laser Beam Incident Angle for Laser Doppler Vibrometer. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 10396. https://doi.org/10.3390/app131810396
Luo Y, An H, Li X, Jing G. Dynamic Measuring Method of Laser Beam Incident Angle for Laser Doppler Vibrometer. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(18):10396. https://doi.org/10.3390/app131810396
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Yingchao, Huazhen An, Xiaobing Li, and Genqiang Jing. 2023. "Dynamic Measuring Method of Laser Beam Incident Angle for Laser Doppler Vibrometer" Applied Sciences 13, no. 18: 10396. https://doi.org/10.3390/app131810396
APA StyleLuo, Y., An, H., Li, X., & Jing, G. (2023). Dynamic Measuring Method of Laser Beam Incident Angle for Laser Doppler Vibrometer. Applied Sciences, 13(18), 10396. https://doi.org/10.3390/app131810396






