Local Dependency-Enhanced Graph Convolutional Network for Aspect-Based Sentiment Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- We propose an aspect-aware mechanism based on multi-head interactive attention and multi-head self-attention to enhance the representation of aspect-related semantic features.
- We utilize SenticNet for graph construction to introduce external sentiment knowledge and enhance the focus on specific dependency relationships within the graph by building a specific set of dependencies.
- The LCW method is employed on the dependency-enhanced graph, which effectively diminishes attention on long-distance dependencies.
2. Related Works
2.1. Attention-Based models
2.2. Graph Neural Networks
2.3. Affective Knowledge
3. Proposed Approach/ Methodology
3.1. Task Definition
3.2. Embedding
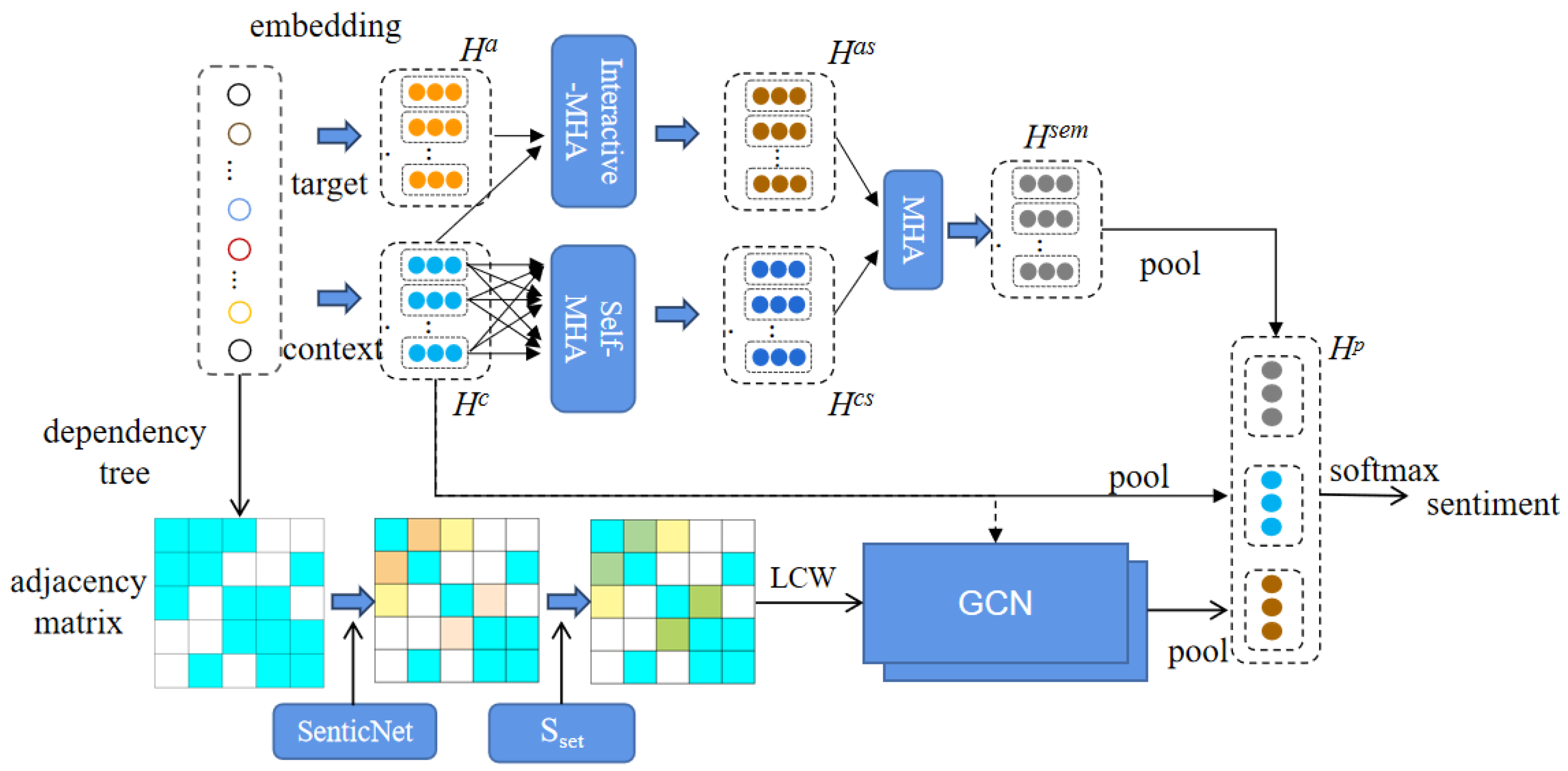
3.3. Semantic Feature Extraction
3.4. LDEGCN
3.4.1. Enhanced by Affective Knowledge
3.4.2. Enhanced by Aspect and Dependency Types
3.4.3. Local Context Weight
| Algorithm 1 The process of generating a dependency-enhanced matrix. |
Require: a sentence, ; aspect sequence, ; the dependency tree of the sentence, ; intensity scores from SenticNet; a specific dependency set, ; syntax distance,
|
3.4.4. Multilayer GCN
3.5. Feature Fusion
3.6. Sentiment Classifier
4. Experiment
4.1. Datasets and Experiment Setting
4.2. Comparative Models
4.3. Results and Analysis
4.4. Ablation Study
5. Discussion
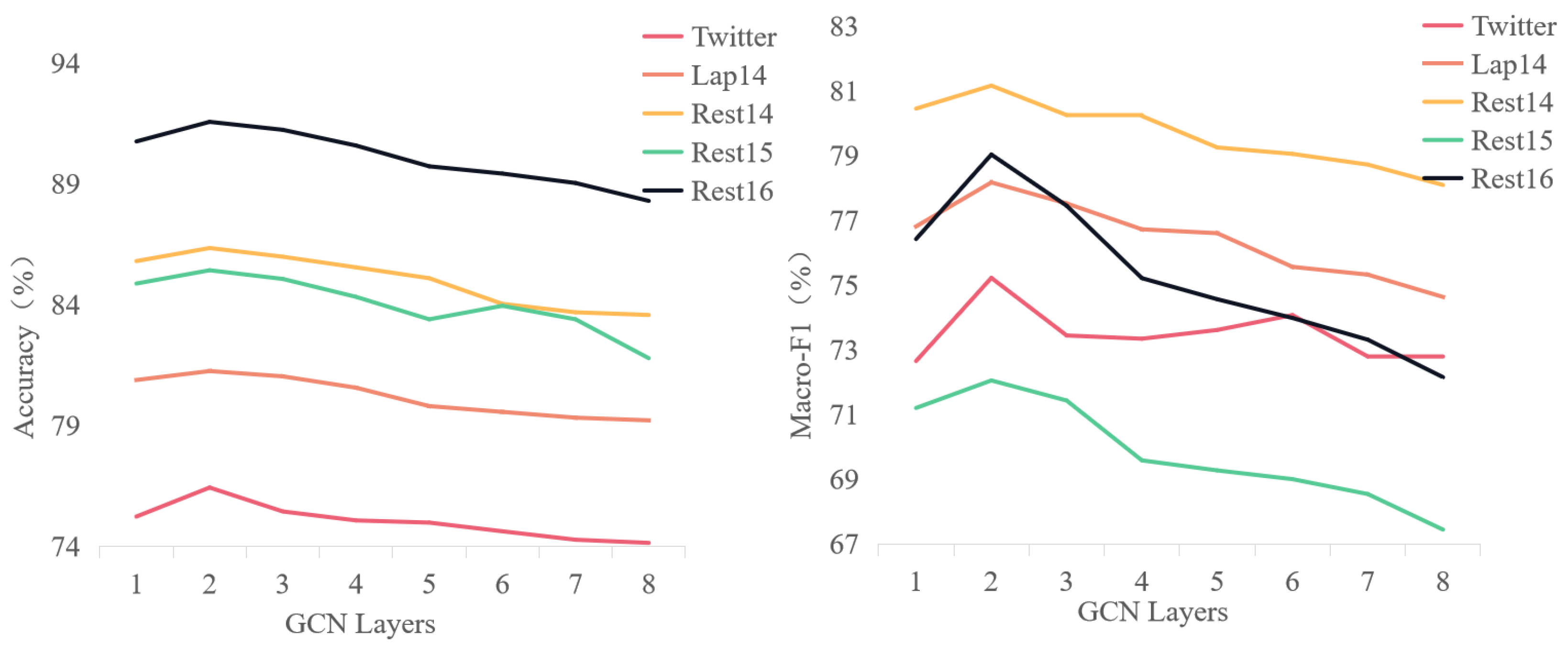
5.1. The Influence of the Number of Layers (L)
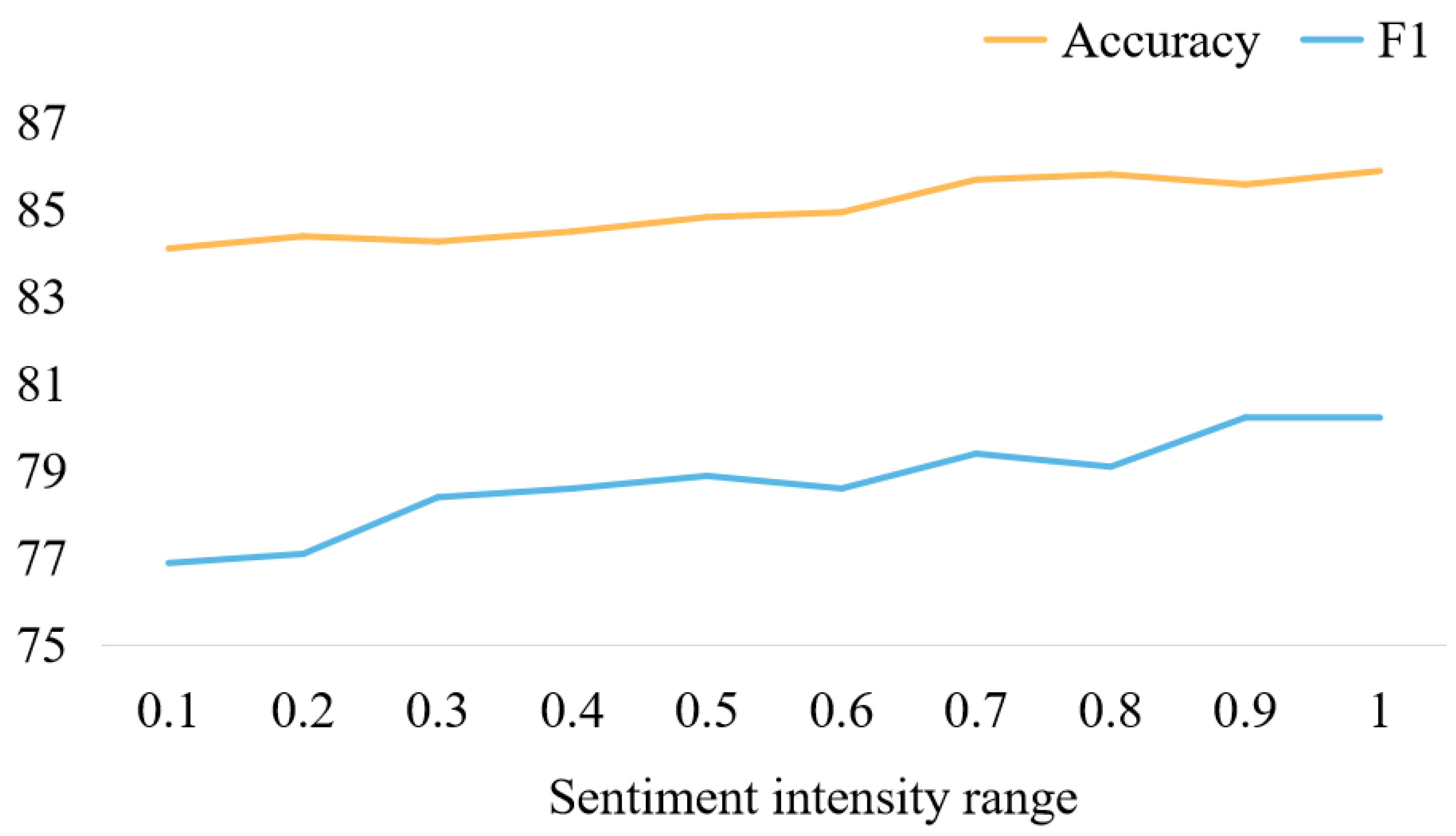
5.2. The Impact of Sentiment Words with Different Scores
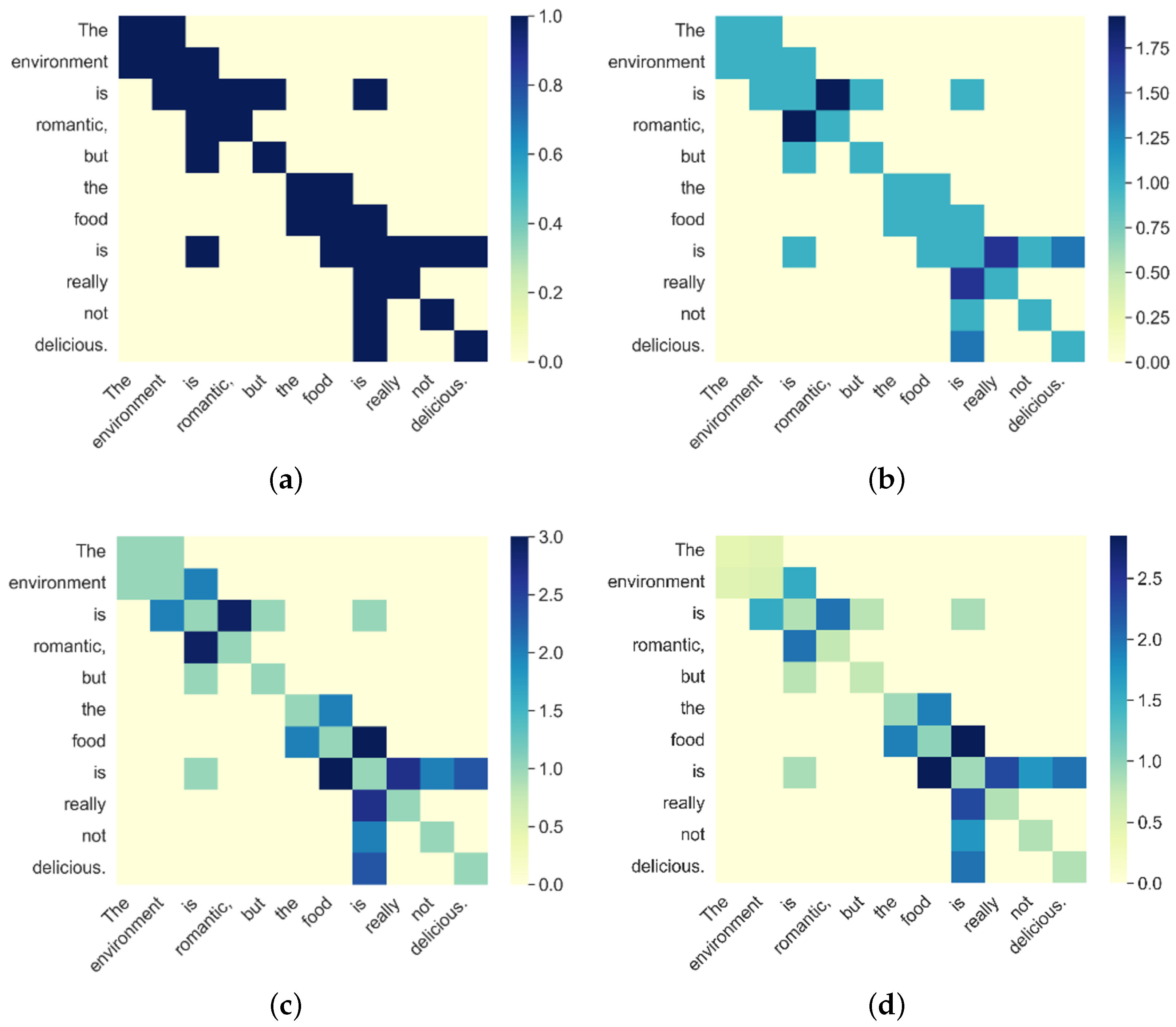
5.3. Visualization of LDEG
6. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, A.; Liu, D.; Bian, Y. Customer preferences extraction for air purifiers based on fine-grained sentiment analysis of online reviews. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2021, 228, 107259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hameed, Z.; Garcia-Zapirain, B. Sentiment classification using a single-layered BiLSTM model. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 73992–74001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Chatterjee, I.; Zhou, M.; Lu, X.S.; Abusorrah, A. Aspect-based sentiment analysis: A survey of deep learning methods. IEEE Trans. Comput. Soc. Syst. 2020, 7, 1358–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhu, J.; Wang, Z.; Bai, F.; Gong, J. Review of applications of natural language processing in text sentiment analysis. J. Comput. Appl. 2022, 42, 1011. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Dai, A.; Xue, Y.; Zeng, B.; Liu, X. Syntactically Enhanced Dependency-POS Weighted Graph Convolutional Network for Aspect-Based Sentiment Analysis. Mathematics 2022, 10, 3353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Huang, M.; Zhu, X.; Zhao, L. Attention-based LSTM for aspect-level sentiment classification. In Proceedings of the 2016 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Austin, TX, USA, 1–5 November 2016; pp. 606–615. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, P.; Sun, Z.; Bing, L.; Yang, W. Recurrent attention network on memory for aspect sentiment analysis. In Proceedings of the 2017 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Copenhagen, Denmark, 7–11 September 2017; pp. 452–461. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, D.; Li, S.; Zhang, X.; Wang, H. Interactive attention networks for aspect-level sentiment classification. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1709.00893. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, B.; Ou, Y.; Carley, K.M. Aspect level sentiment classification with attention-over-attention neural networks. In Proceedings 11, Proceedings of the Social, Cultural, and Behavioral Modeling: 11th International Conference, SBP-BRiMS 2018, Washington, DC, USA, 10–13 July 2018; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 197–206. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, F.; Feng, Y.; Zhao, D. Multi-grained attention network for aspect-level sentiment classification. In Proceedings of the 2018 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Brussels, Belgium, 31 October–4 November 2018; pp. 3433–3442. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Li, Q.; Song, D. Aspect-based sentiment classification with aspect-specific graph convolutional networks. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1909.03477. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, K.; Zhang, R.; Mensah, S.; Mao, Y.; Liu, X. Aspect-level sentiment analysis via convolution over dependency tree. In Proceedings of the 2019 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing and the 9th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing (EMNLP-IJCNLP), Hong Kong, China, 3–7 November 2019; pp. 5679–5688. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, B.; Yin, R.; Gui, L.; Du, J.; Xu, R. Jointly Learning Aspect-Focused and Inter-Aspect Relations with Graph Convolutional Networks for Aspect Sentiment Analysis. In Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Computational Linguistics, Barcelona, Spain, 8–13 December 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Shen, W.; Yang, Y.; Quan, X.; Wang, R. Relational graph attention network for aspect-based sentiment analysis. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.12362. [Google Scholar]
- Li, R.; Chen, H.; Feng, F.; Ma, Z.; Wang, X.; Hovy, E. Dual graph convolutional networks for aspect-based sentiment analysis. In Proceedings of the 59th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics and the 11th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing (Volume 1: Long Papers), Online, 1–6 August 2021; pp. 6319–6329. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, Y. SSEGCN: Syntactic and Semantic Enhanced Graph Convolutional Network for Aspect-based Sentiment Analysis. In Proceedings of the 2022 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, Seattle, DC, USA, 10–15 July 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Y.; Chen, G.; Song, Y. Aspect-based sentiment analysis with type-aware graph convolutional networks and layer ensemble. In Proceedings of the 2021 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, Online, 6–11 June 2021; pp. 2910–2922. [Google Scholar]
- Phan, M.H.; Ogunbona, P.O. Modelling context and syntactical features for aspect-based sentiment analysis. In Proceedings of the 58th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Online, 5–10 July 2020; pp. 3211–3220. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, P.; Li, L.; Luo, F.; Liu, T.; Sun, X. Enhancing topic-to-essay generation with external commonsense knowledge. In Proceedings of the 57th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Florence, Italy, 28 July–2 August 2019; pp. 2002–2012. [Google Scholar]
- Chaturvedi, I.; Satapathy, R.; Cavallari, S.; Cambria, E. Fuzzy commonsense reasoning for multimodal sentiment analysis. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2019, 125, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragoni, M.; Donadello, I.; Cambria, E. OntoSenticNet 2: Enhancing reasoning within sentiment analysis. IEEE Intell. Syst. 2022, 37, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Huang, J.X.; Hu, Q.V.; He, L. Sk-gcn: Modeling syntax and knowledge via graph convolutional network for aspect-level sentiment classification. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2020, 205, 106292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, F.Z.; Pallucchini, F.; Cambria, E. Cognitive-inspired domain adaptation of sentiment lexicons. Inf. Process. Manag. 2019, 56, 554–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, B.; Su, H.; Gui, L.; Cambria, E.; Xu, R. Aspect-based sentiment analysis via affective knowledge enhanced graph convolutional networks. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2022, 235, 107643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Wang, J.; Jiang, T.; Liu, Z.; Rao, Y. Targeted sentiment classification with attentional encoder network. In Artificial Neural Networks and Machine Learning–ICANN 2019: Text and Time Series, Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Artificial Neural Networks, Munich, Germany, 17–19 September 2019; Proceedings, Part IV 28; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 93–103. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, J.; Yan, H.; Sun, T.; Liu, P.; Qiu, X. Does syntax matter? A strong baseline for aspect-based sentiment analysis with roberta. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2104.04986. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, B.; Yang, H.; Xu, R.; Zhou, W.; Han, X. Lcf: A local context focus mechanism for aspect-based sentiment classification. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 3389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Wei, F.; Tan, C.; Tang, D.; Zhou, M.; Xu, K. Adaptive Recursive Neural Network for Target-dependent Twitter Sentiment Classification. In Proceedings of the 52nd Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Baltimore, MD, USA, 22–27 June 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Pontiki, M.; Galanis, D.; Pavlopoulos, J.; Papageorgiou, H.; Androutsopoulos, I.; Manandhar, S. SemEval-2014 Task 4: Aspect Based Sentiment Analysis. In Proceedings of the 8th International Workshop on Semantic Evaluation (SemEval 2014), Dublin, Ireland, 23–24 August 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Pontiki, M.; Galanis, D.; Papageorgiou, H.; Manandhar, S.; Androutsopoulos, I. Semeval-2015 task 12: Aspect based sentiment analysis. In Proceedings of the 9th International Workshop on Semantic Evaluation (SemEval 2015), Denver, CO, USA, 4–5 June 2015; pp. 486–495. [Google Scholar]
- Pontiki, M.; Galanis, D.; Papageorgiou, H.; Androutsopoulos, I.; Manandhar, S.; AL-Smadi, M.; Al-Ayyoub, M.; Zhao, Y.; Qin, B.; De Clercq, O.; et al. Semeval-2016 task 5: Aspect based sentiment analysis. In Proceedings of the ProWorkshop on Semantic Evaluation (SemEval-2016), San Diego, CA, USA, 16–17 June 2016; Association for Computational Linguistics: Cedarville, OH, USA, 2016; pp. 19–30. [Google Scholar]
- Devlin, J.; Chang, M.W.; Lee, K.; Toutanova, K. Bert: Pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1810.04805. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, H.; Ji, D.; Li, C.; Zhou, Q. Dependency Graph Enhanced Dual-transformer Structure for Aspect-based Sentiment Classification. In Proceedings of the 58th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Online, 5–10 July 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, Z.; Wu, J.; Chen, Q.; Deng, C. BERT4GCN: Using BERT intermediate layers to augment GCN for aspect-based sentiment classification. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2110.00171. [Google Scholar]
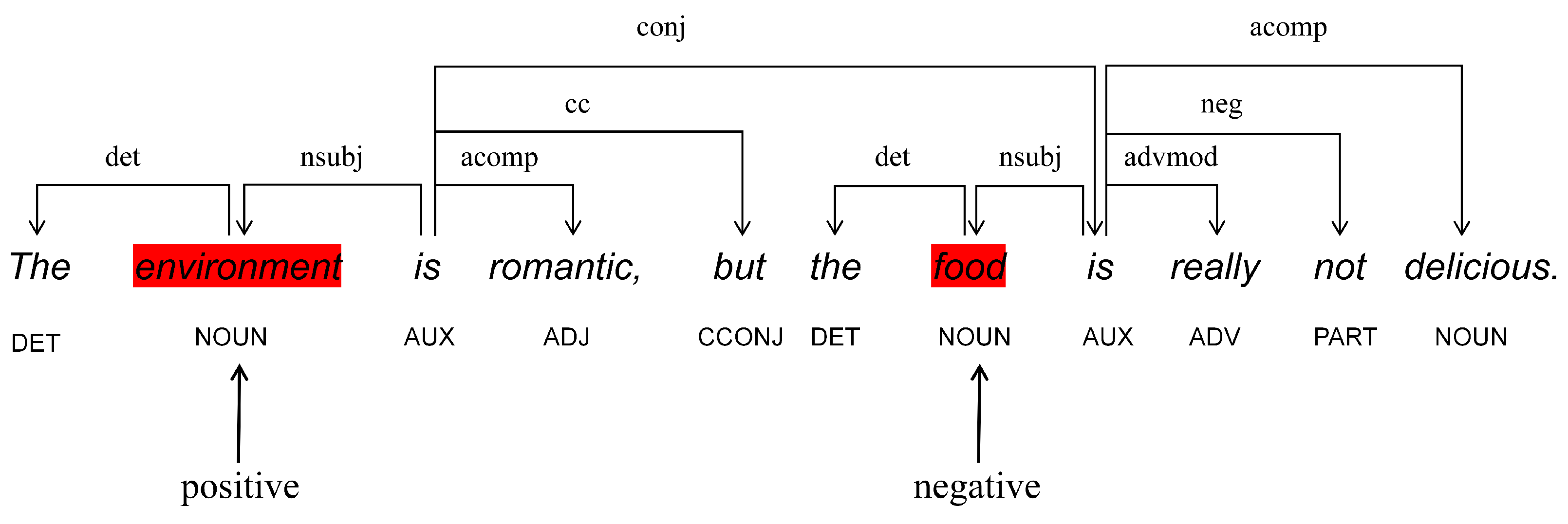
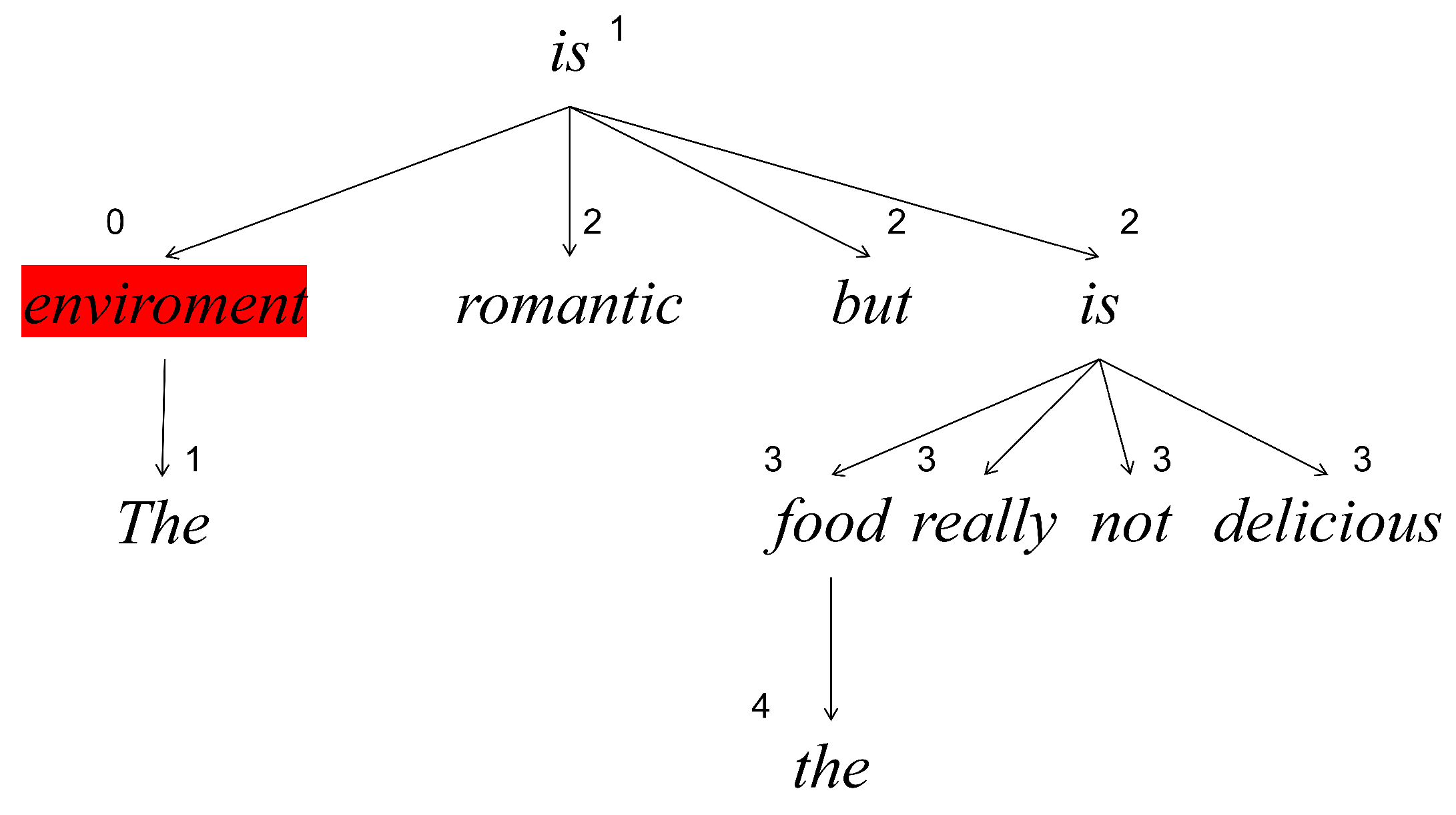
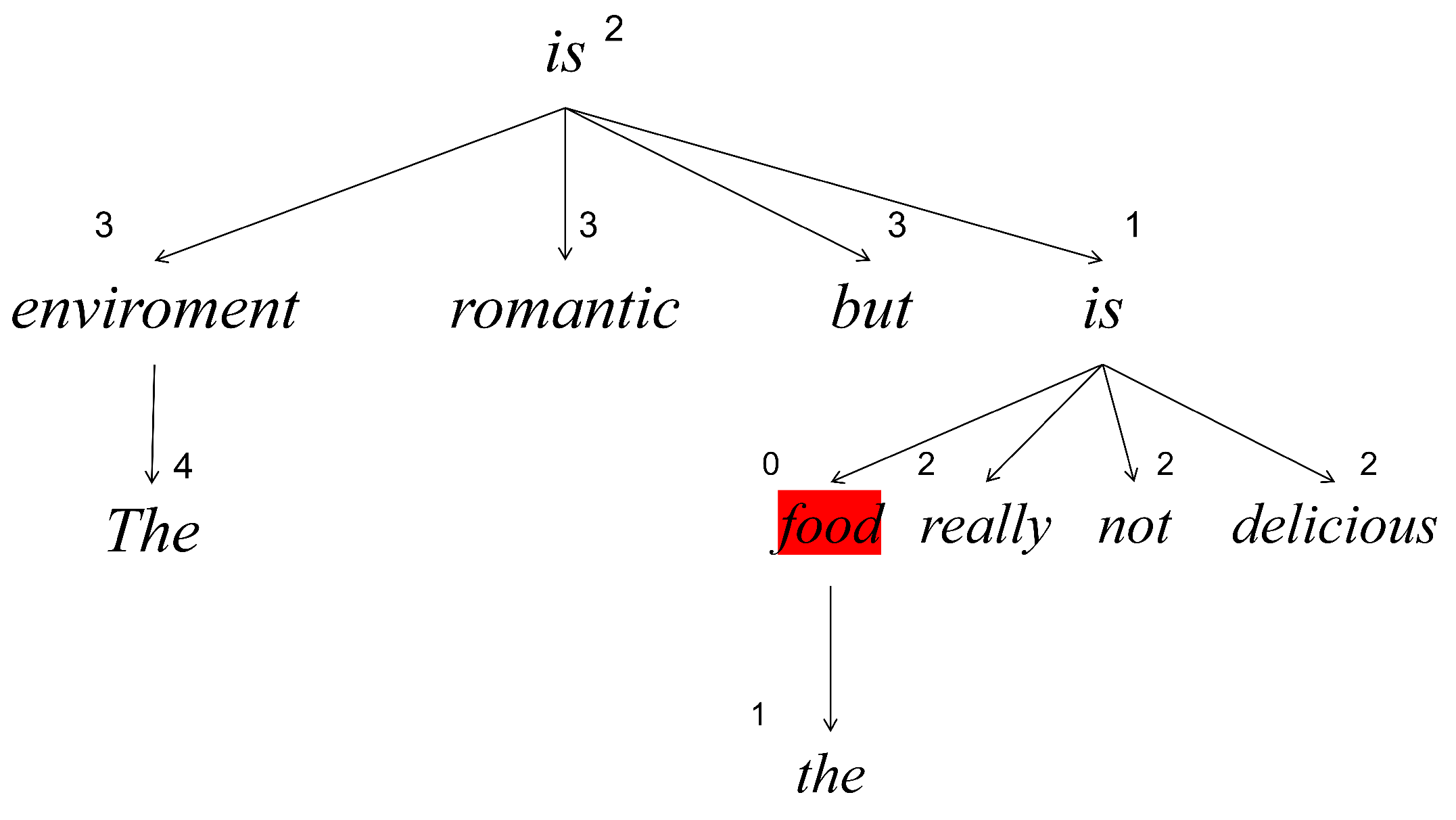
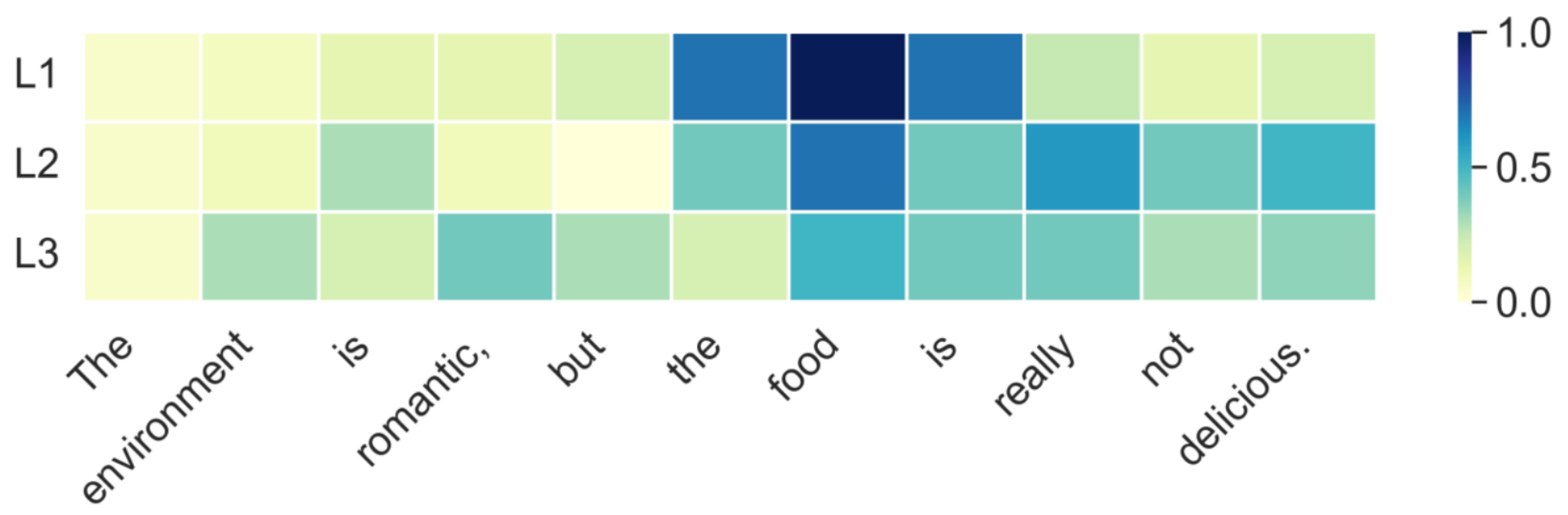
| Word | Intensity |
|---|---|
| Good | 0.659 |
| Excellent | 0.744 |
| Romantic | 0.851 |
| Reasonable | 0.170 |
| Bad | −0.659 |
| Horrible | −0.793 |
| Dataset | Type | Positive | Negative | Neural |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Train | 1561 | 3127 | 1560 | |
| Test | 174 | 346 | 173 | |
| Lap14 | Train | 994 | 464 | 870 |
| Test | 341 | 169 | 128 | |
| Rest14 | Train | 2164 | 637 | 807 |
| Test | 728 | 196 | 196 | |
| Rest15 | Train | 912 | 36 | 256 |
| Test | 326 | 34 | 182 | |
| Rest16 | Train | 1240 | 69 | 439 |
| Test | 469 | 30 | 117 |
| Model | Lap14 | Rest14 | Rest15 | Rest16 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acc | F1 | Acc | F1 | Acc | F1 | Acc | F1 | Acc | F1 | |
| IAN | 72.50 | 70.81 | 72.05 | 67.38 | 79.26 | 70.09 | 78.54 | 52.65 | 84.74 | 55.21 |
| AOA | 72.30 | 70.20 | 72.62 | 67.52 | 79.97 | 70.42 | 78.17 | 57.02 | 87.50 | 66.21 |
| BERT-SPC | 75.92 | 75.18 | 77.59 | 75.03 | 84.11 | 76.68 | 83.48 | 66.18 | 90.10 | 74.16 |
| AEN-BERT | 74.54 | 73.26 | 79.93 | 76.31 | 83.12 | 73.76 | 82.29 | 63.41 | 88.96 | 70.31 |
| ASGCN | 72.15 | 70.40 | 75.55 | 71.05 | 80.77 | 72.02 | 79.89 | 61.89 | 88.99 | 67.48 |
| DGEDT | 77.90 | 75.40 | 79.80 | 75.60 | 86.30 | 79.89 | 84.00 | 71.00 | 91.90 | 79.00 |
| BERT4GCN | 74.73 | 73.76 | 77.49 | 73.01 | 84.75 | 77.11 | - | - | - | - |
| T-GCN | 76.45 | 75.25 | 80.88 | 77.03 | 86.16 | 79.95 | 85.26 | 71.69 | 92.32 | 77.29 |
| DualGCN | 77.40 | 76.02 | 81.80 | 78.10 | 87.13 | 81.16 | - | - | - | - |
| SSEGCN | 77.40 | 76.02 | 81.01 | 77.96 | 87.31 | 81.09 | - | - | - | - |
| Our model | 76.43 | 75.22 | 81.25 | 78.17 | 86.34 | 81.16 | 85.42 | 72.05 | 91.56 | 79.45 |
| Model | Lap14 | Rest14 | Rest15 | Rest16 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acc | F1 | Acc | F1 | Acc | F1 | Acc | F1 | Acc | F1 | |
| W/o SEM | 75.73 | 74.10 | 80.13 | 76.81 | 85.62 | 80.07 | 84.87 | 71.42 | 90.8 | 77.65 |
| W/o SenticNet | 75.02 | 73.07 | 80.09 | 76.64 | 85.09 | 77.96 | 83.23 | 68.54 | 89.98 | 76.71 |
| W/o type | 75.43 | 74.22 | 80.88 | 77.52 | 85.26 | 78.74 | 84.56 | 70.88 | 90.59 | 77.45 |
| W/o LCW | 76.16 | 74.94 | 80.41 | 77.12 | 85.68 | 79.20 | 84.98 | 71.24 | 91.07 | 78.37 |
| W/o LDEGCN | 74.49 | 72.44 | 79.62 | 75.65 | 84.82 | 77.14 | 82.29 | 67.59 | 88.97 | 73.26 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, F.; Li, X. Local Dependency-Enhanced Graph Convolutional Network for Aspect-Based Sentiment Analysis. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 9669. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13179669
Wu F, Li X. Local Dependency-Enhanced Graph Convolutional Network for Aspect-Based Sentiment Analysis. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(17):9669. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13179669
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Fei, and Xinfu Li. 2023. "Local Dependency-Enhanced Graph Convolutional Network for Aspect-Based Sentiment Analysis" Applied Sciences 13, no. 17: 9669. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13179669
APA StyleWu, F., & Li, X. (2023). Local Dependency-Enhanced Graph Convolutional Network for Aspect-Based Sentiment Analysis. Applied Sciences, 13(17), 9669. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13179669






