Abstract
The rapid expansion of the Internet and communication technologies is leading to significant changes in both society and the economy. This development is driving the evolution of smart cities, which utilize cutting-edge technologies and data analysis to optimize efficiency and reduce waste in their infrastructure and services. As the number of mobile devices and embedded computers grows, new technologies, such as fifth-generation (5G) cellular broadband networks and the Internet of Things (IoT), are emerging to extend wireless network connectivity. These cities are often referred to as unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), highlighting their innovative approach to utilizing technology. To address the challenges posed by continuously varying perturbations, such as unknown states, gyroscopic disturbance torque, and parametric uncertainties, an adaptive recursive sliding mode control (ARSMC) has been developed. The high computational cost and high-order nonlinear behavior of UAVs make them difficult to control. The controller design is divided into two steps. First, a confined stability analysis is performed using controllability and observability to estimate the system’s stability calculation. Second, a Lyapunov-based controller design analysis is systematically tackled using a recursive design procedure. The strategy design aims to enhance robustness through Lyapunov stability-based mathematical analysis in the presence of considered perturbations. The ARSMC introduces new variables that depend on state variables, controlling parameters, and stabilizing functions to minimize unwanted signals and compensate for nonlinearities in the system. The paper’s significant contribution is to improve the controlled output’s rise time and stability time while ensuring efficient robustness.
1. Introduction
Unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) path learning for optimizing age and power consumption in Internet of Things (IoT) applications with UAV battery recharge is an important task for future smart cities [1]. It is important to optimize UAVs’ flight paths to minimize their age and power consumption while ensuring full data coverage. There are challenges and opportunities of using UAVs for environmental monitoring, such as the ability to collect data over remote or inaccessible areas. The effectiveness of UAV systems is demonstrated through several case studies in [2]. Helicopters (UAVs) are lifted and propelled by one or more rotors, making them suitable for operation in congested or remote areas where fixed-wing aircraft cannot operate. The key advantage of a helicopter is that its lift and direction can be controlled by adjusting the speed of its rotors through motors. As a result, helicopters are often used in areas where takeoff or landing is difficult. The importance of real-time applications for air vehicles has increased over time [3,4,5]. In order for a closed-loop system to exhibit the desired response, the controlling variables must be manipulated accordingly. To study this phenomenon, an experimental setup of a twin-rotor MIMO system (TRMS), a type of UAV with significant coupling effects, is developed and modeled in [6]. The setup for the UAV is a highly nonlinear system with limited degrees of freedom. It consists of two basic parts: a mechanical part and an electrical part. The objective involves addressing the challenges posed by the controller task, which include: (i) dealing with the dynamic changes of the UAV; (ii) handling the changing dynamics of the system, including mismatched disturbances and varying parametric dynamics; and (iii) managing the absence of the time-varying parameter variations states of the system. A comprehensive review of the literature will help enable us to understand the trajectory for robust optimization.
A linear controller with all of its properties was utilized to regulate the TRMS and its coupling effect, whereby the main rotor, through its pitch angle, governs movement along the vertical axis, while the tail rotor, through its yaw angle, governs movement along the horizontal axis [7,8,9]. The use of PID control in different scenarios has been explored in several studies. In [10], PID control is discussed as a fractional controller based on the degree of freedom, while [11] explains its application for UAVs with a degree of freedom. In [12,13], estimation control with nonlinear control is used for highly nonlinear systems. Additionally, [14] presents a decoupled system optimized via swarm optimization based on the PID control strategy. The efficiency of classical control is confirmed in [15,16] through its effective output response of the TRMS. Hybrid control as classical and nonlinear control is presented in [17,18]. The authors of [19] analyze the performance of a twin-rotor MIMO system using a linear quadratic regulator (LQR) and LQG control techniques and discuss the differences in the response of pitch and yaw angle control inputs. In [20], a comparative analysis is presented of different control techniques for a twin-rotor MIMO system and the reasons why pitch angle control input may show more variations compared to yaw angle control input are discussed. The authors of [21] undertook a comparative study of PID and fuzzy logic controllers for a twin-rotor MIMO system and considered the differences in the response of pitch and yaw angle control inputs. To eliminate the coupling effect, a decoupling method was employed, either through static decoupling or dynamic decoupling. Furthermore, a classical control strategy, specifically optimal control, was implemented to gain insights into the behavior of the system [22,23]. An adaptive model for predictive control based on a tube was proposed in [24]. Nonlinear model identification with adaptive model predictive control using neural networks was considered in [25] and neural network observer-based control for a twin-rotor MIMO system was investigated in [26]. Learning-based fast nonlinear model predictive control to address issues of parametric uncertainty was reported in [27,28]. One approach to address parameter uncertainty is to use a modified extended Kalman filter (EKF) to perform joint state and parameter estimation. Another method is to use the multiple model second level adaptation (MALSA) scheme [29,30]. A discrete-time intelligent control strategy was implemented in [31], which was designed to match the behavior of the prototype. To address the nonlinear response of states following system decoupling, a robust control strategy was developed in [32]. Two types of robust control, sliding mode control (SMC) and integral SMC, were designed to overcome these nonlinearities [33,34]. A fuzzy and LQR controller designed for decoupled systems was used to control the pitch and yaw angle over desired values based on the model. Additionally, a real-time adaptive model inversion technique utilizing an artificial neural network was proposed to control the cross-coupled dynamics of nonlinear systems in [35]. Rapid and sudden changes in rotor speeds are the primary cause of cross-coupling between pitch and yaw dynamics. However, because some states of the system cannot be measured, mathematical modeling of the system can become challenging, as the system is no longer flat. In previous research, robust generalized dynamic inversion (RGDI)-based control theory and mixed-optimization control were applied in [36,37] to a UAV, and its performance was characterized through an experimental test of the prototype.
In order to fulfill the objective, the first step involves inverting the motion equations. To simplify the model, a controller design utilizing nonlinear dynamic inversion (NDI) was implemented. To ensure system stability, calculations of controllability and observability matrices were performed, resulting in full rank matrices of order 6 × 10 and 10 × 6, respectively. In previous research, a real-time robust generalized dynamic inversion-based optimization was applied to the UAV, and its efficiency was evaluated through experimental testing. The issue of chattering, which can occur in higher-order complex systems with fast switching control inputs, was also addressed. The adaptive recursive sliding mode control (ARSMC) method was developed directly from the mathematical model of the system under study by introducing new variables that depend on the state variables, controlling parameters, and stabilizing functions. The stabilizing functions are used to compensate for nonlinearities in the system that can affect its operational stability. In the future of smart cities, optimizing the age and power consumption of UAVs through path learning will be crucial within the realm of Internet of Things (IoT) applications, especially for achieving efficient UAV optimization. The main objective is to design an adaptive recursive technique that incorporates adaptation laws and a recursive fast terminal sliding surface. This technique is specifically tailored for highly nonlinear and cross-coupled multiple input multiple output (MIMO) systems. The innovative approach is tested on a UAV to ensure accurate flight path tracking and stabilization. The remaining paper is organized into the mathematical modeling in two sections and the UAV stability analysis is discussed in Section 3. The recursive control design is elaborated in Section 4 and the adaptive recursive sliding mode control is explained with adaptation laws in Section 5. In Section 6, the performance of controllers is elaborated via figures. The final section provides conclusions based on a comparison of the simulation’s response.
2. Mathematical Model
Suitable and reasonable assumptions must be made in order to model a higher-order nonlinear system [6]. In this section, we describe a highly nonlinear system with a finite degree of freedom and discuss its important parameters in Table 1. We use mathematical state equations to describe an experimental prototype represented in Figure 1 with both main and tail rotors, as follows:
where is the pitch angle of the main rotor. The variable is the inertia of the main rotor.
where is the yaw angle of the tail rotor. The variable is the inertia of the main rotor. The variable represents the inertia of the tail rotor. The equation for the main motor of the TRMS (UAV),
where represents the momentum of the main rotor. The equation for the tail motor of the TRMS (UAV),
where represents the momentum of the tail rotor.

Table 1.
Parameters of TRMS (UAV).
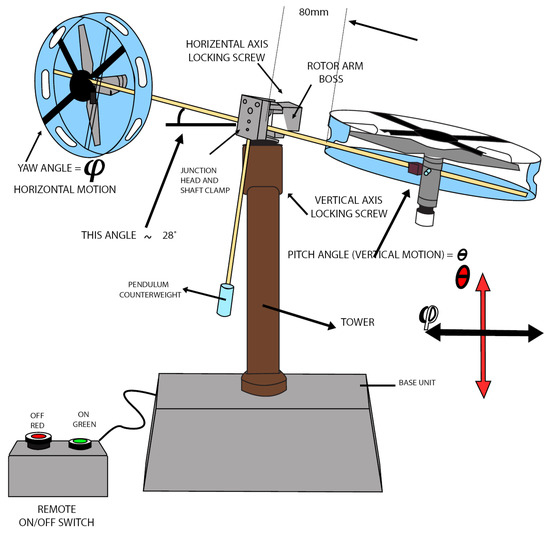
Figure 1.
Basic schematic sketch of TRMS [6].
In order to model a system, some suitable assumptions need to be made. An experimental prototype consisting of both main and tail rotors can be described through mathematical state equations, which are then converted into linear state equations. This means that there are no terms with a degree higher than one in the resulting equations. The process of obtaining linear equations with some compromising assumptions is called linearization. The linearized model is more amenable to analysis and controller design.
where and show real numbers and input value, while is considered as the output of the system. Dynamic states as state vectors are given as:
where is the elevation position, is the azimuth position, is the main rotor momentum and represents the tail rotor momentum. The dynamic states at origin, ,
The simplified matrices can be obtained at origin as,
Figure 2 shows a block diagram of a UAV with a representation of the coupling effect. The diagram includes two output states, which are the pitch angle and the yaw angle. The coupling effect is also depicted in the diagram.
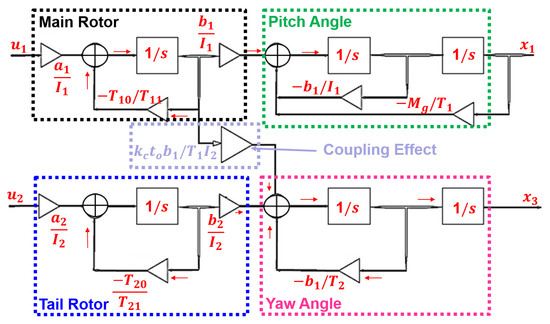
Figure 2.
Block Diagram of System.
The system under consideration is checked by a well-known calculation process with respect to controllability and observability. The controllability property of the system, coupling within the state, and the input involves the system matrices. The matrix is a linear system said to be in controllable form if it is possible to find some input, and this input will transform the state’s x(to) to the origin at a finite time. If there exists some input which gives , admitted for all initial times and states, then it is verified for the controller [38]. The full rank of the controllability matrix further validates that the system is indeed controllable.
The full rank property of the system is validated by the matrix shown above, which is a positive sign of controllability. The observability matrix has been calculated and is provided below. The full rank property of the matrix confirms the observability of the system.
3. Design Procedure of Robust Sliding Mode Control
Based on variable structure systems (VSS) control theory, sliding mode control (SMC) maintains sliding mode system states by continuously changing the controller structure in response to fluctuations in the state variables. By using high-frequency switching control, SMC alters the system dynamics [12]. There are two parts to the controller design. The sliding surface is chosen in the first segment according to the sequence of the system under consideration.
The designed sliding surface can be expressed as:
where is known as the selected manifold as the sliding surface and is the measured tracked output with the new state as a state variable. It is vital to pay emphasis to the control rule that forces the control factors to their set point while choosing the sliding surface. The control law can be formulated mathematically as:
while
where represents the equivalent controller, is a sign function that creates a discontinuous control input resulting from a limited switching around the sliding surface and is a constant. The trajectory of the controlled system moves along the manifold during the application of SMC as a result of the actions of several structures and follows the switch condition known as the chattering phenomenon displayed in Figure 3. It has been suggested that switching functions [36], denoted by x, that may be a scalar or a vector, define the system structure during SMC. In the phase plane, the switching surface can be seen as a line with the symbol .
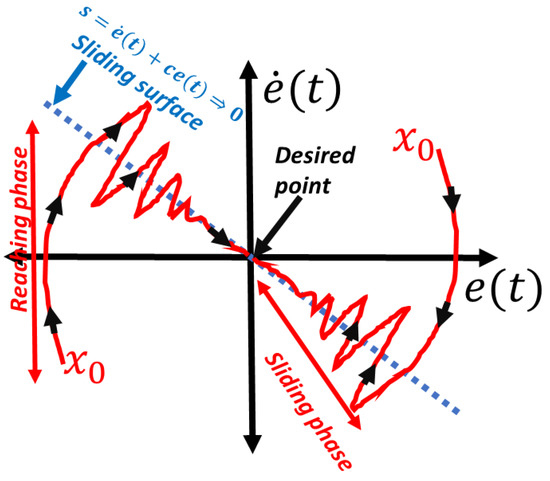
Figure 3.
Chattering phenomena.
A strategy that is frequently used to evaluate the stability of nonlinear systems based on ODE theory is the use of a Lyapunov function. The Lyapunov function should be determined in order to verify the system’s stability according to ODE class theory, it must be negative definite. This requirement is adequate to ensure the nonlinear system’s asymptotic stability. However, creating a suitable Lyapunov function for ODEs can be challenging. It has been noted that the sliding motion in the context of sliding mode control (SMC) happens close to the sliding surface, much like the frequency switching phenomenon. In SMC, the system’s nonlinear behavior may attempt to move away from the sliding surface, but the controller will compel the system to follow the line until it reaches the origin, referred to as the boundary layer. SMC simulations have demonstrated satisfactory convergence for pitch and yaw angles. However, the SMC chattering pattern for these systems is unsuitable as it can pose a risk to the actuators. Figure 4 shows the rapid and sudden changes in voltage patterns that require highly optimized power suppliers. The TRMS output requires smooth convergence with a regular voltage pattern that can be optimized using an optimization method.
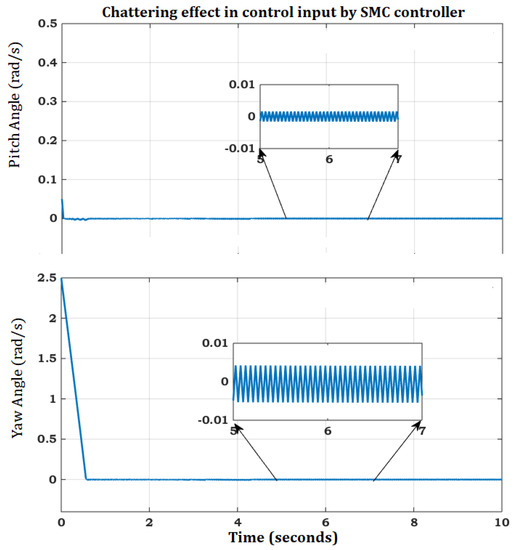
Figure 4.
Chattering in Control Input for Pitch and Yaw Angle.
4. Recursive Control Design
After that, we continue working on the controller’s recursive section to create additional states as new state variables. When the final control phase is reached, nonlinearities are removed using the backstepping control design method [39]. Comparing this form of controller to earlier TRMS research, it offers a more accurate and efficient response. Control theory has advanced significantly as a result of the simulation response and experimental confirmation. To identify the new state variables, execute the following controller design steps:
where are state variables and is the control input are nonlinear differentiable functions up to the order with
The first error dynamics of the system are:
where is the desired output to be tracked by the actual output of the system. The rest of the error dynamics of the transformed system can be found as:
where are the stabilizing functions.
Step 01: The error dynamics are arranged to design the virtual controller, also known as the stabilization function, , for the first subsystem.
The stabilizing function to stabilize the first error state.
The resultant error dynamics of can be obtained as:
Step 02: The error dynamics are arranged as:
The stabilizing function to stabilize the second error state.
The resultant error dynamics of can be obtained as:
Step i: The error dynamics are arranged as:
The stabilizing function to stabilize the error state.
The resultant error dynamics of can be obtained as:
Step n: At the final iteration, a control law is designed that ensures the asymptotic stability of the system and, hence, we can also write this as for
The control law u ensures the asymptotic stability of the system.
The resultant error dynamics of can be obtained as:
Stability Analysis of Recursive Backstepping: The error dynamics of the closed-loop system in coordinate can be written as:
The above matrix demonstrates that the off-diagonal elements possess skew-symmetric properties. To evaluate the stability of the transformed system, a Lyapunov candidate function can be utilized. Lyapunov functions are scalar functions used to establish the equilibrium stability of an ordinary differential equation (ODE). These functions are essential to stability and control theory and are named after the Russian mathematician Aleksandr Mikhailovich Lyapunov. For several classes of ODEs, the presence of the Lyapunov function is a necessary and sufficient condition for stability. Although constructing a Lyapunov function for ODEs is not a general technique, it is known for many specific cases. In essence, a Lyapunov function is a function that has positive values everywhere except at the equilibrium and decreases (or remains non-increasing) along every trajectory of the ODE. The primary advantage of Lyapunov-function-based stability analysis of ODEs is that the exact solution of the ODE is not required, whether analytical or numerical [40]. The candidate function for the considered system is here:
Adaptive Recursive Sliding Mode Control Strategy
In summary, adaptive recursive sliding mode control (ARSMC) combines three different control techniques—adaptive control [39], recursive control [40], and sliding mode control [36]—to achieve robust and adaptive control of complex nonlinear systems with uncertain dynamics. The sliding mode control provides robustness to disturbances and uncertainties, while the adaptive control adjusts the controller parameters in real-time based on estimation of the system states and model parameters. The recursive control updates the controller parameters based on the current state of the system, allowing it to track changes in the system dynamics and adapt to them in real-time. The ARSMC has been successfully applied to a wide range of complex nonlinear systems, including robotics, aerospace, and power systems. Its effectiveness and robustness have been demonstrated through simulation and experimental studies, making it a promising approach for advanced control of complex nonlinear systems.
ARSMC is an advanced control strategy that combines adaptive control, recursive control, and sliding mode control (SMC) techniques to improve the control performance of complex nonlinear systems. In ARSMC, the system model is not required to be known exactly and the controller adapts to the changes in the system dynamics to achieve better control performance. The controller is designed recursively, which means that the current state of the system is used to update the controller parameters for the next control action. This allows the controller to track the changes in the system dynamics and adapt to them in real-time. The sliding mode control technique is used to force the system states to converge to a sliding surface that is defined based on the system model and the desired control objectives. The sliding mode provides robustness to the system against disturbances and uncertainties. The adaptive control technique is used to adjust the controller parameters in real time based on estimation of the system states and model parameters. Overall, the ARSMC strategy, represented in Figure 5, provides better control performance, robustness, and adaptability to complex nonlinear systems compared to traditional control strategies. It has been applied in various fields, such as robotics, aerospace, and industrial automation. This section implements an adaptive backstepping for position trajectory tracking control, taking the output vector for the UAV position as . The variables used in the design procedure for the MIMO system are:
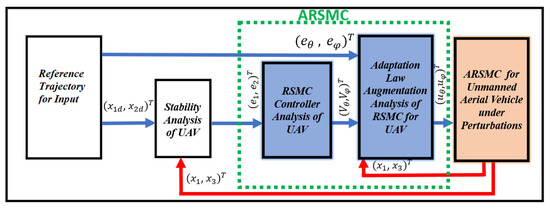
Figure 5.
Block diagram of UAV for ARSMC.
Defining the position tracking errors as:
The required condition for the Lyapunov function to fulfill the asymptotic stability as:
The arbitrary control laws for the pitch and yaw position are formulated as follows:
where are the estimates of and , respectively.
Theorem 1.
In [39], it was reported that if the TRMS position system is controlled using Equation (54) along with the adaptation law Equation (49), the convergence is guaranteed. In addition, the adaptation laws for parametric stability are provided as follows:
where , and are positive constants. The Barbalat’s Lemma is used to evaluate the worth of the considered theorem. The above lemma requires:
Lemma 1.
In [39,40], if the function is a uniform function and validated, then must be converged at zero (origin) asymptotically.
Proof.
To provide confined convergence of the system with explanation of and as the parameters of a system, the Lyapunov stability analysis is applied. For , the candidate function is introduced for the considered subsystem.
where shows the error. The time derivative of Equation (57) is
In Equation (57), the mentioned term will be equal to zero. By taking a positive constant, the derivative of can be expressed as . Now the candidate function is elaborated in Equation (56), which will be:
Thus, the stability condition is satisfied through Equation (58). To guarantee the stability of the positioning system, the Lyapunov candidate function for the system’s position is chosen: The time derivative of the Lyapunov position is
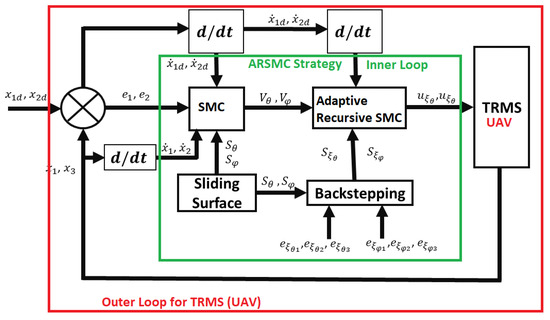
where , and are the parameters of both angles. The basic variables representation for the control of TRMS can be characterized from Figure 6. This section explains how an adaptive recursive method for trajectory tracking in a specific system was developed. Equations (59) and (60) allow the system to follow the specified flight trajectory and guarantee the stability of the system. The suggested control’s second parameter is calculated using the adaptive recursive technique using adaptive laws. A recursive method is used to update this parameter continually, which improves the system’s ability to monitor the trajectory. The system can adjust to changes in the environment and still maintain stability while following the planned flying trajectory using adaptive rules. As a result, the system is strengthened and better suited for use in practical applications. □

Figure 6.
Controller design procedure for UAV.
5. Discussion: Simulation Response of Control Strategies
The novel ARSMC strategy effectively addresses key issues, such as finite-time convergence, robustness for parametric perturbations, and singularity. To verify its effectiveness, we conducted a comparison study and evaluated the performance of the controller in terms of the vertical stability (pitch angle) and horizontal stability (yaw angle). Additionally, the controller was tested in the presence of disturbances, such as external disturbances, parametric uncertainties, coupling effects, and noise signals. The simulation response of TRMS under different control strategies provides key ideas on how the augmentation of a recursive strategy in SMC with adaptive laws performs better. The convergence time of pitch and yaw angles in Figure 7 and Figure 8 represents the brief response with their convergence time in subplots. The figure that shows the square input for both the pitch angle and yaw angle of the TRMS illustrates that the pitch angle has a faster convergence time than the yaw angle. This delay is because the main rotor must be stabilized first in order to counteract the disturbance generated by the tail rotor, such as the gyroscopic torque effect and the coupling effect. As a result, the convergence time of the tail rotor cannot be faster than that of the main rotor.
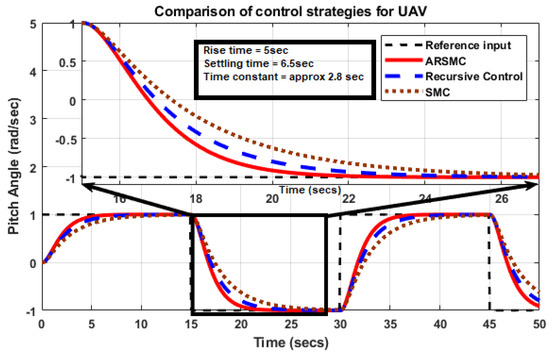
Figure 7.
Pitch angle of UAV for ARSMC.
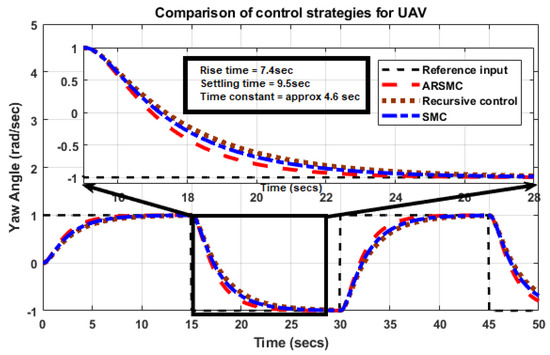
Figure 8.
Yaw angle of UAV for ARSMC.
The step input tracking response in the simulation confirms that the control theory regarding the convergence time of the angles, specifically the pitch and yaw angles, is logical and results in a sharp stability response. According to the effectiveness of the proposed controller, the control actions response for both angles can be characterized on the basis of minimum voltage variations. A subplot also shows the attenuation due to the applied noise signal and the range of disturbance being tackled by an efficient controller. Other subplots verify how the controller can manage the considered disturbance over time. The system response becomes more stable over time, which represents a remarkable difference with respect to other applied control methods to date. The convergence time and effect of attenuation are greater in the yaw angle. The reason behind this change is that the coupling effect due to the disturbance torque is greater due to the weighted rotor as well as the blades of the main rotor. A slight sharp variation in yaw angle is generated by different factors created by the main rotor. The time constant values are also provided in the subplots of both figures, which refer to the characteristic timescales associated with the system’s response to changes or disturbances. The specific time constants depend on the nature and complexity of the mechanical system under consideration. The control actions of both angles are elaborated via Figure 9 and Figure 10. The control action for the pitch angle shows slightly more variations compared to the control input of the yaw angle. There are several reasons for this. As we know, the pitch angle and yaw angle are both important angles that need to be controlled in a twin-rotor MIMO (multiple-input multiple-output) system. However, the response of the pitch angle control input may show more variations compared to the yaw angle control input due to several factors. The first reason is that the twin-rotor MIMO system is inherently unstable and highly nonlinear. This means that even small changes in the input or the system’s parameters can result in significant variations in the output. The pitch angle control input may be more sensitive to changes in the system’s dynamics, leading to more variations in the response. The second reason is that the pitch angle control input may require more precise control than the yaw angle control input. Pitch angle control is essential for maintaining the altitude and stability of the system, which requires very precise control. On the other hand, the yaw angle control input is more straightforward and less sensitive to variations as it primarily controls the heading of the system. The third reason is the coupling effect due to the gyroscopic torque of the main rotor. The variations in the response of the pitch angle control input in a twin-rotor MIMO system are due to the system’s inherent instability and nonlinearity, as well as the need for more precise control to maintain the system’s altitude and stability.
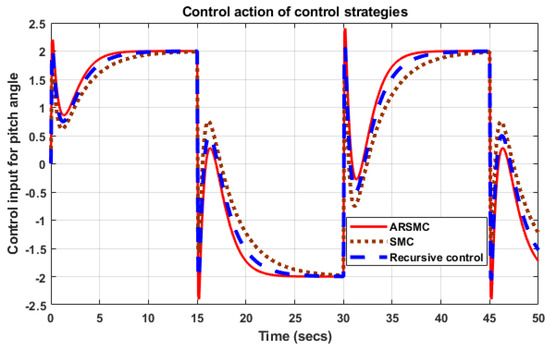
Figure 9.
Control input of pitch angle for ARSMC.
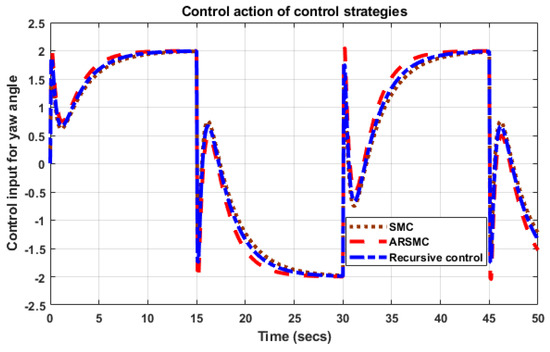
Figure 10.
Control input of yaw angle for ARSMC.
6. Conclusions
We present a novel dynamic control strategy that is highly efficient and results in improved convergence time, achieved through the use of a Lyapunov stability mathematical operator. The novel dynamic recursive structure of the controller developed based on the mathematical model of the system highlights its excellent resistance against the considered varying perturbations. The effectiveness of the dynamic approach was demonstrated through worst scenario conditions, including simultaneous noise and parametric variation provided to both rotors with disturbance torque. In the future of smart cities, the optimization of UAV’s age and power consumption through path learning will be a critical endeavor in the realm of Internet of Things (IoT) applications, particularly in achieving efficient UAV optimization. The primary objective of this study is to design an adaptive recursive technique, incorporating adaptation laws and a recursive fast terminal sliding surface, specifically tailored for highly nonlinear and cross-coupled multiple input multiple outputs (MIMO) systems. This innovative approach is put to the test on a UAV to ensure accurate flight path tracking and stabilization. Additionally, it is utilized to devise robust controllers that can effectively handle uncertainties in the UAV’s operating environment. The control strategy implemented in this study comprised two distinct phases. The first phase involved comprehending the system’s behavior, which proved to be challenging due to the presence of high coupling and disturbance torque. To address this, time-varying dynamic constraints were designed. To provide a simplified model of the TRMS, NDI is employed. However, the limitations of NDI and singularity issues were taken into account during this phase. In the second phase of the control strategy, reference trajectories were used to track the output states. To ensure robustness and stability validation against the nonlinear characteristics of the coupled system with uncertainties, sinusoidal reference tracking of states was employed. This approach aimed to address the nonlinear behavior and uncertainties within the system, thereby validating the effectiveness and reliability of the control strategy.
The inclusion of a robust term in previous research controllers was developed to increase robustness against external perturbations and unmodeled states. The ARSMC method is based on the mathematical model of the TRMS system which addresses varying parametric uncertainties and loss of thrust anomalies. The controller uses an adaptive law to track the desired trajectory of the vehicle in both vertical and horizontal angles (positions). This control approach offers finite-time convergence, reduces the problem, and provides a parameter-tuning law to eliminate external perturbations. A novel reaching law based on an adaptive recursive approach with a finite-time convergence technique was used to generate a control law for stabilizing the nonlinear system. The hybrid controller was designed for full system trajectory tracking and stability in a closed-loop system and produced using hybrid Lyapunov analysis. The adaptive law was used to estimate the controller coefficients and the global stability of the closed-loop system was proved using Lyapunov analysis. Accurate fast-tracking and error convergence performance in all cases of perturbations (noise matrix, parametric disturbance) revealed the effectiveness of the applied controller. Numerical simulation was conducted to evaluate the performance of the developed control system. Based on the simulation validation, some important suggestions are provided below for control engineers to aid their understanding of the nature of control design and system behavior.
- The presence of significant inherent uncertainties in the physical parameters can cause nonlinear behavior that must be addressed by precise application of recursive adaption law.
- The high amplitude noise signal causes severe contamination for the input actuators and high-voltage range.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, N.A.; Methodology, N.A.; Software, N.A. and Z.A.; Validation, N.A. and X.L.; Formal analysis, Z.A.; Investigation, N.A. and X.L.; Data curation, N.A., Z.A. and X.L.; Writing—original draft, N.A.; Writing—review & editing, Z.A.; Supervision, X.L.; Project administration, X.L.; Funding acquisition, X.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research work is funded by Omega Aviation Ltd., UK, and the National Key R and D Program of China under Grant No. 2018YFB1702200.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in the published article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Eldeeb, E.; de Souza Sant’Ana, J.M.; Pérez, D.E.; Shehab, M.; Mahmood, N.H.; Alves, H. Multi-UAV Path Learning for Age and Power Optimization in IoT with UAV Battery Recharge. IEEE Trans.-Hicular Technol. 2022, 72, 5356–5360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, V.; Chan, Y.K.; Vetharatnam, G.; Chua, M.Y.; Lim, C.H.; Lim, C.S.; Thum, C.C.; Lim, T.S.; Ahmad, Z.B.; Mahmood, K.A.; et al. A new un-manned aerial vehicle synthetic aperture radar for environmental monitoring. Prog. Electromagn. Res. 2012, 122, 245–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, A.; Vu, T.X.; Khan, W.U.; Chatzinotas, S.; Ottersten, B. Optimizing Computational and Com-munication Resources for MEC Network Empowered UAV-RIS Communication. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE Globecom Workshops (GC Wkshps), Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 4–8 December 2022; pp. 974–979. [Google Scholar]
- Bucolo, M.; Buscarino, A.; Fortuna, L.; Gagliano, S. Bifurcation scenarios for pilot induced oscillations. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2020, 106, 106194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orozco, R.G. Mixed sensitivity control: A non-iterative approach. Syst. Sci. Control. Eng. 2020, 8, 441–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twin Rotor, Multiple Input Multiple Output (MIMO). System Control Experiments 33-949S; User Manual; Feedback Instruments Ltd.: East Sussex, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Ramalakshmi, A.P.S.; Manoharan, P.S. Non-linear modeling and PID control of twin rotor MIMO system. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Conference on Advanced Communication Control and Computing Technologies (ICACCCT), Ramanathapuram, India, 23–25 August 2012; pp. 366–369. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, U.; Anjum, W.; Bukhari, S.M.A. H2 and H∞ controller design of twin rotor system (TRS). Sci. Res. 2013, 4, 27843. [Google Scholar]
- John, L.; Mija, S.J. Robust H∞ control algorithm for twin rotor MIMO system. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Advanced Communications, Control and Computing Technologies, Ramanathapuram, India, 8–10 May 2014; pp. 168–173. [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhary, S.; Kumar, A. Control of twin rotor mimo system using 1-degree-of-freedom PID, 2-degree-of-freedom PID and fractional order PID controller. In Proceedings of the 2019 3rd International Conference on Electronics, Communication and Aerospace Technology (ICECA), Coimbatore, India, 12–14 June 2019; pp. 746–751. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, P.; Li, Y. Twin rotor system modeling, de-coupling and optimal control. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Mechatronics and Automation, Beijing, China, 7–10 August 2011; pp. 1839–1842. [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez, B.; Steven, O.H.; Angelo, M.L.; Giraldo, E. Rls estimation and sliding mode control with integral action for a twin rotor mimo system. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 4th Colombian Conference on Automatic Control (CCAC), Medellin, Colombia, 15–18 October 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Song, D.; Li, X.; Peng, Z. Mixed sensitivity H-infinity control of an adaptive optics system. Opt. Eng. 2016, 55, 094106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, P.; Maiti, R.; Kolay, A.; Sharma, K.D.; Sarkar, G. PSO based PID controller design for twin rotor MIMO system. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference on Control, Instrumentation, Energy and Communication (CIEC), Calcutta, India, 31 January–2 February 2014; pp. 56–60. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, V.S.; George, V.I.; Kamath, S.; Shreesha, C. Comparison of lqg controller with reliable h infinity con-troller designed for trms. Int. J. Control. Theory Appl. 2015, 8, 1171–1179. [Google Scholar]
- Dube, D.Y.; Patel, H.G. Suppressing the noise in measured signals for the control of helicopters. Fluct. Noise Lett. 2019, 18, 1950002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, J.; Ullah, M.; Khan, S.G.; Khelifa, B.; Ćuković, S. Nonlinear control systems—A brief overview of historical and recent advances. Nonlinear Eng. 2017, 6, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.H.; Khan, S.G.; ul Haq, I.; Shah, K.; Abid, A. Compliance control of robotic walk assist device via integral sliding mode control. In Proceedings of the 2019 16th International Bhurban Conference on Applied Sciences and Technology (Ibcast), Islamabad, Pakistan, 8–12 January 2019; pp. 515–520. [Google Scholar]
- Iftikhar SKhan, S.U.; Mahmood, A. A comparative analysis of twin rotor MIMO system with different control schemes. ISA Trans. 2018, 82, 148–158. [Google Scholar]
- Nazir, A.; Malik, S.A.; Iqbal, S. Comparative analysis of different control techniques for a twin rotor MIMO system. Int. J. Control Autom. Syst. 2019, 17, 1225–1237. [Google Scholar]
- Rahim, M.; Aras, S.M.; Zainudin, S. Comparative study of PID and fuzzy logic controllers for twin rotor MIMO system. Int. J. Adv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 29, 1423–1430. [Google Scholar]
- Cajo, R.; Agila, W. Evaluation of algorithms for linear and nonlinear PID control for Twin Rotor MIMO System. In Proceedings of the 2015 Asia-Pacific Conference on Computer Aided System Engineering, Quito, Ecuador, 14–16 July 2015; pp. 214–219. [Google Scholar]
- Rahideh, A.; Shaheed, M.H. Robust model predictive control of a twin rotor MIMO system. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE International Conference on Mechatronics, Malaga, Spain, 14–17 April 2009; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Köhler, J.; Kötting, P.; Soloperto, R.; Allgöwer, F.; Müller, M.A. A robust adaptive model predictive control framework for nonlinear uncertain systems. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear Control 2021, 31, 8725–8749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akpan, V.A.; Hassapis, G.D. Nonlinear model identification and adaptive model predictive control using neural networks. ISA Trans. 2011, 50, 177–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratap, B.; Purwar, S. Neural network observer for twin rotor MIMO system: An LMI based approach. In Proceedings of the 2010 International Conference on Modelling, Identification and Control, Okayama, Japan, 17–19 July 2010; pp. 539–544. [Google Scholar]
- Mehndiratta, M.; Kayacan, E.; Patel, S.; Kayacan, E.; Chowdhary, G. Learning-based fast nonlinear model predictive control for custom-made 3D printed ground and aerial robots. In Handbook of Model Predictive Control; Birkhauser: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 581–605. [Google Scholar]
- Bouffard, P.; Aswani, A.; Tomlin, C. Learning-based model predictive control on a quadrotor: Onboard implementation and experimental results. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Saint Paul, MN, USA, 14–18 May 2012; pp. 279–284. [Google Scholar]
- Pandey, V.K.; Kar, I.; Mahanta, C. Controller design for a class of nonlinear MIMO coupled system using multiple models and second level adaptation. ISA Trans. 2017, 69, 256–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, V.K.; Kar, I.; Mahanta, C. Adaptive Controller Design for Nonlinear Uncertain Systems Using Multiple Model based Two Level Adaptation Technique. Ph.D. Dissertation, Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati, India, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Hashim, H.A.; Abido, M.A. Fuzzy controller design using evolutionary techniques for twin rotor MIMO system: A comparative study. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2015, 2015, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, C.W.; Taur, J.S.; Chen, Y.C. Design of a parallel distributed fuzzy LQR controller for the twin rotor multi-input multi-output system. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 2010, 161, 2081–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saroj, D.K.; Kar, I.; Pandey, V.K. Sliding mode controller design for Twin Rotor MIMO system with a nonlinear state observer. In Proceedings of the 2013 International Mutli-Conference on Automation, Computing, Communication, Control and Compressed Sensing (iMac4s), Kottayam, India, 22–23 March 2013; pp. 668–673. [Google Scholar]
- Ilyas, M.; Abbas, N.; UbaidUllah, M.; Imtiaz, W.A.; Shah, M.A.Q.; Mahmood, K. Control law design for twin rotor MIMO system with nonlinear control strategy. Discret. Dyn. Nat. Soc. 2016, 2016, 2952738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahideh, A.; Bajodah, A.H.; Shaheed, M.H. Real time adaptive nonlinear model inversion control of a twin rotor MIMO system using neural networks. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2012, 25, 1289–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, N.; Pan, X.; Raheem, A.; Shakoor, R.; Arfeen, Z.A.; Rashid, M.; Umer, F.; Safdar, N.; Liu, X. Real-time robust generalized dynamic inversion based optimization control for coupled twin rotor MIMO system. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 17852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, N.; Liu, X. A mixed dynamic optimization with µ-synthesis (DK iterations) via gain scheduling for varying dynamics of decoupled twin-rotor MIMO system based on the method of inequality (MOI). Con. Eng. App. Inf. 2022, 24, 13–23. [Google Scholar]
- Brogan, W.L. Modern Control Theory; Pearson Education: Chennai, India, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Labbadi, M.; Mohamed, C. Robust adaptive backstepping fast terminal sliding mode controller for un-certain quadrotor UAV. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2019, 93, 105306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, M.; Wang, Q.; Hou, D.; Dong, C. Backstepping design of missile guidance and control based on adaptive fuzzy sliding mode control. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2014, 27, 634–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).