Abstract
More than 7000 synthetic compounds known as per- and poly-fluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) are applied to food packaging and other materials to provide fat, fire, and/or water resistance properties. These compounds have exceptional environmental stability and persistence due to the strong C-F chemical bond, earning them the moniker “forever chemicals”. Emission of PFAS from industrial waste leads to water, air, and soil contamination. Due to this ubiquitous nature, combined with the fact that PFAS in humans are known to have carcinogenic and reprotoxic effects and to cause vaccine resistance and depression of the immunity system, PFAS may constitute a major threat to human health. For this reason, the attention of the scientific community and of control bodies is increasing and as a consequence legislation and the scientific literature on PFAS are constantly evolving. This review aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the state of the art about current legislation addressing PFAS; targeted and screening method for identification, detection and quantification of PFAS; toxicity of PFAS; and contamination of environmental and food matrices and from food contact matrices. A comprehensive review of the latest scientific research and recent developments in the legislation of PFAS will provide insights into the current understanding of PFAS and its health implications. Moreover, it will serve as a valuable reference for further studies related to PFAS and could help in informing future policy decisions.
1. Introduction
The broad category of hundreds of synthetic chemicals known as per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) is widely utilized for a wide range of applications, from Gore-Tex materials and anti-adherent pans to firefighting foams. They are, however, more frequently identified as environmental contaminants, and some of them have been connected to harmful effects on human health [1]. The PFAS backbone is constituted by single-bonded carbon atoms with fluorine atoms covalently bonded to the alkyl chain, one of the strongest in chemistry, and therefore PFAS do not break down easily in the environment [2]. In addition, PFASs can be classified in different families [3]: perfluoroalkyl substances and polyfluoroalkyl substances for the non-polymers group; and fluoropolymers, perfluoropolyethers, and side-chain fluorinated polymers for the polymers group. The chemical structures of the different classes are depicted in Figure 1.
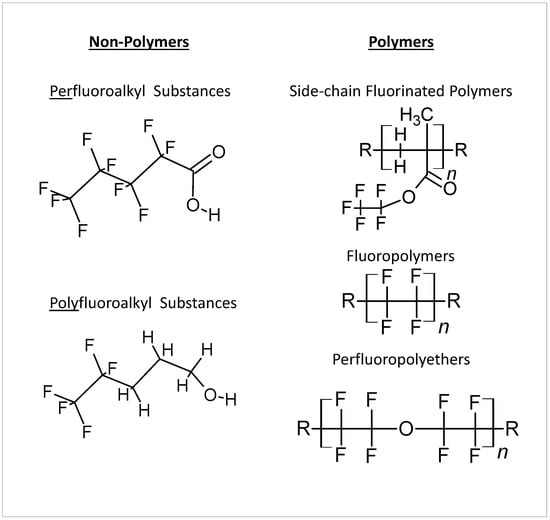
Figure 1.
Classification of PFASs major groups.
PFAS are known to be ubiquitous forever chemicals that can come in contact with humans through contaminated environmental and food matrices such as drinking waters and eggs [4,5,6] and therefore the attention is constantly increasing at the scientific level and also outside the scientific community. For instance, companies are starting to use the “PFAS free” label on their products to demonstrate safety to consumers. The results of a search on Google Trends, Figure 2 [7], show the increasing interest around PFAS over time on the net, where searches in the last two decades (from January 2004 to the current year) have exponentially grown.
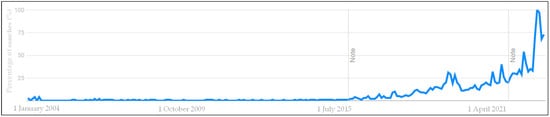
Figure 2.
Interest over time of the word “PFAS” in Google searches since 2004. Data source: Google Trends (https://trends.google.com/trends/explore?date=all&q=PFAS (accessed on 12 May 2023)) [7].
As depicted in Figure 3, the attention of the scientific community to this topic has also largely increased in the last 15 years. By exploring the Web of ScienceTM platform [8], by searching the scientific papers published per year that include the terms “PFAS” and “per” to avoid false responses based on PFAS acronyms that are not unique, a clear visualization of the increasing number of scientific papers published on the PFAS topic in the last decade is obtained, and from 2017 to 2022 a tenfold increase has occurred.
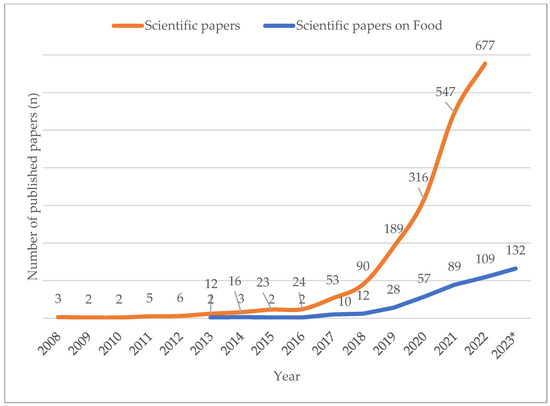
Figure 3.
Chart for scientific papers and scientific papers on food published with the words “PFAS”, “per” and “food” collecting data from Web of ScienceTM site since 2008 (2023* data were estimated).
Like other chemical, PFAS are potentially capable to have an adverse effect on human health [9] and, in parallel to the discovery of the accumulation of different type of PFAS in the environment and in food, authorities have begun looking into the toxicity of PFAS and in estimating the human uptake. Regarding toxicity, Velez et al. [10] found that perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) and perfluorohexane sulfonic acid (PFHxS), even at lower levels than previously reported [11,12,13,14], may diminish fecundability.
Grandjean et al. [15] underlined the possible need for a specific protection for infants and children, in particular in relation to their immune system. Abraham et al. [16] demonstrated that the transdermal absorption of PFOA (and consequently other PFASs) from cosmetic products can significantly contribute to the total exposure to PFAS for costumers. Blomberg et al. [17] demonstrated changes in PFAS levels in human milk during breastfeeding depending on the level of exposure (from almost zero to elevated levels). In particular, PFOS levels increased over time, from colostrum to milk matured, while PFOA ones were observed to decrease. The level of exposure for children depends on both the specific mix of PFAS and the source of exposure.
In a final determination published in March 2021 “Regulatory Determinations for Contaminants on the Fourth Contaminant Candidate List”, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) states that two of the so-called “legacy PFAS”, PFOA and perfluorooctane sulfonic acid (PFOS), need to be regulated in drinking water due to their already known contamination and toxicity. On 14 March 2023, the EPA proposed a national drinking water regulation for PFOA and PFOS. Along with taking this step, the EPA is also addressing additional PFAS and specific measures for defined PFAS groups. By the end of 2023, the EPA expects to have the regulation in its final form [18]. In addition, according to the FDA’s (Food and Drug Administration of US) testing of foods grown or produced in regions with documented environmental PFAS contamination in the soil, water, or air can be absorbed by plants and animals, resulting in contaminated foods [19]. In addition, the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) published a scientific opinion on their journal on 2020 stating that fish meat, fruit and fruit products, and eggs and egg products were the top contributing categories for the combined exposure to PFOA, perfluorononanoic acid (PFNA), PFHxS, and PFOS for all demographic groups. For the majority of people, diet is the main way they are exposed to PFAS, although other factors such as breathing in indoor air and ingesting dust may also play a big part. This focus on food requires EFSA researchers to establish a Tolerable Weekly Intake (TWI) of 4.4 ng/kg(body weight)/week based on the intake of the sum of PFOA, PFNA, PFHxS, and PFOS [20]. In 2022, the European Union Reference Laboratory for Persistent Organic Pollutants (EURL-POPs) published the “Guidance Document on Analytical Parameters for the Determination of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) in Food and Feed,” which established a path for analytical laboratories around the world to follow in developing and validating robust and reliable methods for the discovery and quantification of PFAS, as well as implementing a lower limit of quantification in food and feed to assess the level of contamination [21].
2. Legislation
States and countries around the world are managing PFAS in multiple ways: limiting or removing their usage in common source material, establishing testing and reporting requirements, and directing and funding repair.
In this paragraph, an overview of the legislation on PFAS is given for each continent. The timeline of the legislation is depicted as a visual representation in Figure 4.
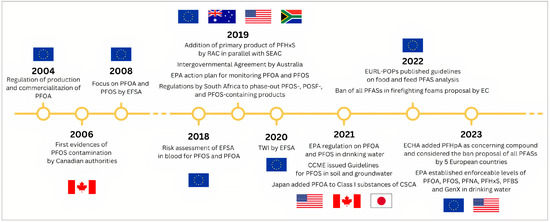
Figure 4.
Timeline of PFAS legislation.
The current legislation is lacking in regulating PFAS levels in drinking water and food, especially outside Europe. An overview of the current regulations is described in Table 1, Table 2 and Table 3 [22,23,24,25,26,27].

Table 1.
PFAS levels (μg/L) permitted in drinking water.

Table 2.
PFAS levels (μg/kg) permitted in Eggs.

Table 3.
PFAS levels (μg/kg) permitted in Fish meat.
2.1. Europe—European Unions’ Countries
At the European level, major authorities took the first step toward monitoring PFAS contamination in 2004. In fact, this year the European Union published a regulation of the production and commercialization of PFOS that was valid until 2019 [28]. That legal document was replaced by the “Regulation (EU) 2019/1021 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 20 June 2019 on persistent organic pollutants” [29], where the manufacturing, use, and placing on the market of substances listed in Annex I, such as PFOS and its derivatives C8F17SO2X (X = OH, metal salt (O-M+), halide, amide, and other derivatives including polymers, in mixtures or in articles, shall be prohibited with some exemptions. In 2008, a scientific opinion of the panel on pollutants in the food chain was issued by EFSA., focusing on PFOA, PFOS, and their salts, which are the byproducts of the breakdown of PFAS in polymers. The conclusion of the opinion was that the relative contribution of such precursors to the PFOS and PFOA environmental contamination is not yet understood [30]. Later, in 2018, prior to the TWI declaration, EFSA published the risk assessment on human health linked to the presence of PFOS and PFOA in food, underlying that “PFOS and PFOA were detected in blood samples of almost all individuals assessed, demonstrating ubiquitous exposure”. This already suggested illo tempore the need for novel analytical methods and legislation developments [31]. In the same opinion, the state-of-the-art analytical techniques were listed.
The Norwegian Environment Agency, in 2019, submitted a proposal to list PFHxS (with its salts) and PFHxS-related compounds in Annexes A, B, and/or C to the Stockholm Convention on POPs. In parallel, the Committee for Risk Assessment (RAC) contributed with the Dossier Submitter’s suggested scope, which covers roughly 150 chemicals that potentially degrade to PFHxS. In parallel, the Committee for Socio-economic Analysis (SEAC) agreed that a more thorough strategy is required to address the dangers associated with products and mixes containing PFHxS, its salts, and related compounds rather than relying solely on national rules [32,33]. Due to the advances in technologies that allow it to reach a lower level of detection and the increasing levels of contamination, on 23 February 2022, the European Commission proposed a ban on all PFASs in firefighting foams throughout the entire European Union. Such a restriction aims to counter soil and groundwater contamination as well as threats to the environment and human health. The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) assessed the benefits and drawbacks of five possible strategies for reducing the risks posed by PFAS in firefighting foams [34]. According to “ANNEX XV RESTRICTION REPORT for Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in firefighting foams” published in March 2022, the proposal aims to prohibit the marketing, use, and formulation of all PFAS in post-use fire-fighting foams or industry-specific transition periods [35]. After the proposals for banning PFOA, PFOS, and PFHxS on 17 January 2023, the ECHA added perfluoropentanoic acid (PFHpA) to the candidate list of compounds of very high concern due to its dangerous characteristics. Although this compound is not REACH-registered, its inclusion on the list can be seen as a preventive action for avoiding its use ad a PFAS substitute that can be in the substitutions in the future [36].
Denmark, Germany, the Netherlands, Norway, and Sweden took the most significant step in the fight against per- and polyfluoroalkyl substance contamination in Europe when they submitted a proposal to ECHA to prohibit PFAS under REACH. The five authorities found risks related to the manufacture, marketing, and use of the contaminants that are not properly controlled and need to be addressed by the EU and EEA (European Economic Area). ECHA published the detailed proposal, one of the broadest in the EU’s history, on 7 February 2023. RAC and SEAC of ECHA will determine if the proposal satisfies REACH’s legislative requirements during their meetings in March 2023. If so, the committees will begin conducting a scientific evaluation of the proposal. A six-month consultation is set to start on 22 March 2023 [37].
2.2. America
2.2.1. United States
In the United States, state legislatures and the federal government are taking actions in order to protect the environment (water, soils) and public health [38].
The US EPA, after the publication in 2016 of a nonenforceable health advisory on PFOA and PFOS, unveiled a formal PFAS Action Plan in 2019, then updated it in February 2020.
In the plan, the following points are addressed: maximum contaminant level for states and local water utilities; listing PFOA and PFOS as hazardous substances under the CERLCA; and developing more accurate and innovative techniques to identify contaminants in drinking water, soil, and groundwater.
In October 2021, EPA announced the Agency’s PFAS Strategic Roadmap [39], which represents an important and meaningful step to safeguard communities from PFAS contamination, providing a more enduring and protective solution.
In March 2023, the EPA moved forward with the development of a national drinking water regulation to establish maximum contaminant levels (MCLs) for 6 PFAS: PFOA, PFOS, PFNA, GenX compounds, PFHxS, and perfluorobutane sulfonic acid (PFBS).
States will be forced to establish their requirements at least to those levels when the final regulations take effect.
In parallel, state policymakers have targeted PFAS substances and have enacted laws restricting PFAS in firefighting foam; regulating the presence of PFAS in drinking water, food packaging and consumer products; and allocating funds for clean-up and remediation.
From 2018 to 2021, lawmakers enacted more than 250 PFAS-related bills to regulate their use in several materials and setting maximum levels of contamination. More than 200 measures with PFAS-related terminology were discussed by legislators in 2022, and approximately 50 bills on PFAS in food packaging, firefighter personal protective equipment, and environmental remediation were passed in at least 18 states. The issue of PFAS in consumer items such as apparel, children’s goods, cookware, furniture, cosmetics, and ski wax were also brought up by lawmakers in their legislation.
After Maine became the first US state in 2021 to ban the sale of products containing intentionally added PFAS, several states took the lead to regulate PFAS.
2.2.2. Canada
In Canada, starting from 2006, authorities took steps to deal with PFAS in the environment [40]. That year, the federal government concluded that PFOS, its salts, and other compounds could enter the environment resulting in harmful effect on the environment or its biological diversity, but the human health assessment concluded that concentrations of PFOS exposure were below levels that might affect human health. By 2012, the government included the chemicals spotlighted in 2006 in Canada’s Prohibition of Certain Toxic Chemicals Regulations.
In 2016, Health Canada (HC) included seven other PFAS, to PFOA and PFOS, for the drinking water monitoring. A year later, HC published a similar regulation for soil screening.
HC added two additional PFAS in drinking water and soil monitoring from 2018 to 2021 and also issued drinking water quality guidelines for PFOS and PFOA.
In 2021, the Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment (CCME) issued soil and groundwater guidelines for PFOS.
Lastly, in spring 2021, Canada proclaimed the intention to consider PFAS as a class, rather than individual compounds.
2.2.3. Brazil
Concerning other American countries, in Brazil an action plan was developed for PFOS in the NIP-Brazil-2015. However, some proposed activities are yet to be finished or have not yet started [41,42]. The implementation of a specific tracking code for foreign trade data of PFOS and related compounds is the most notable achievement, and its importance is highlighted in the face of the infeasibility of tracking foreign trade data for PFOA. The Brazilian Agricultural Research Corporation (EMBRAPA) is currently working on the diagnosis of environmental contamination by PFOS from sulfluramid application in Brazilian soils. However, general challenges such as raising stakeholder commitment and expanding and enhancing collected information were not overcome yet.
For both PFOS and PFOA, a draft legislation should be developed, establishing restrictions and guidelines for the environmental licensing of listed PFAS applications within the scope of specific exemptions and acceptable purposes under the Stockholm Convention. The Brazilian National Council for the Environment (CONAMA) resolutions dealing with water and soil quality should be reviewed for inclusion of listed PFAS in environmental quality parameters.
2.3. Asia
In a similar course, Asian nations are attempting to tighten their laws [43].
2.3.1. Japan
In Japan, in April 2021, PFOA was added to the list of Class I Specified Chemical Substances under the CSCA, while the PFOA-related substances were not.
2.3.2. China
In China, in November 2020, 18 compounds, PFOA included, were put on the list of Priority Control Chemicals, and this is a starting point for the laws and legislation to take measures on the environmental risk control. On 11 October 2021, China’s Ministry of Ecology and Environment released a draft planning to manage new pollutants including PFOA more effectively.
2.3.3. Taiwan
In Taiwan, the government amended the regulation on toxic chemical substances in September 2020, changing the handling volume by grade and toxicity classification of PFOA [44].
2.3.4. Singapore
In Singapore, the addition of PFOA as a regulated substance was introduced in 2019.
2.3.5. Indonesia
In Indonesia, since October 2019, the amount of PFOA in some products, including textiles, bedclothes, and blankets, is regulated.
2.3.6. Thailand
In Thailand, in May 2021, eight molecules, including PFOA, were proposed as Class 4 prohibited substances. On 9 February 2022, the Department of Industrial Works, Ministry of Industry of Thailand opened a new draft on PFOA regulations, on 21 December 2022 adding PFOA, its salts, and PFOA-related compounds into the hazardous substances list.
2.3.7. Vietnam
In Vietnam, for the first time, the Law on Environmental Protection of 2020 specifically mentions the Stockholm Convention. One of its subordinate laws, the draft decree, lists PFOA as a substance to be regulated. Later, in November 2021, the Law on Environmental Protection set allowable limits of POPs including PFOA. On 18 October 2022, Vietnam’s government issued the Decree No. 82/2022/ND-CP that listed PFOA in the ANNEX II of Decree 113/2017/ND-CP.
2.4. Africa
In Africa, although many countries endorsed the Stockholm Convention and developed national implementation plans (NIPs), efforts taken to minimize PFAS exposure vary [45]. The NIPs were often developed before 2009, that is, before the listing of PFAS in the Convention, and many have not been updated since [46]. Therefore, PFAS are often not included in these NIPs. However, some countries are updating their regulations concerning PFAS.
South Africa
For example, in South Africa, regulations require that PFOS-, POSF-, and PFOS-containing products be phased out by December 2021 (South African Government Gazette, 2019). Studies of PFAS in Africa have only recently started [40]. From an African viewpoint, most nations have trouble incorporating this new class of pollutants into existing environmental management frameworks. Although countries such as South Africa have environmental legislation that is well-structured for the regulation of hazardous substances, chemical-specific management nevertheless necessitates the creation of environmental quality criteria for such compounds [47,48].
2.5. Oceania
Australia
In Australia, on February 2019, an Intergovernmental Agreement came into effect to face PFAS contamination [49]. The agreement supports consistent responses to PFAS contamination protecting the environment and human health, keeping in mind that initiatives must be feasible, risk-appropriate, and supportive of economic stability aiming to support Australian governments to face PFAS contamination.
2.6. Discussion
Legislatures around the world are responding to the concerns related to risks that PFAS pose to public health and to the environment by enacting measures to control PFASs both nationally and across borders. In Europe and the US, authorities and lawmakers have recently proposed a range of legislation in an effort to reduce or eliminate the use of PFAS chemicals in consumer products. In parallel, Asian countries such as China, Japan, and South Korea have begun to take steps towards stricter legislation on PFAS-containing products in order to protect their citizens’ health. Due to increasing public awareness, many emerging countries are beginning to recognize the need for legislation to regulate PFAS and protect public health.
It is encouraging to see that governments are actively working to reduce the presence of PFAS in the environment and in food. The restrictions on the production, use, and disposal of PFAS products should help to reduce the overall risk posed by these chemicals.
3. Toxicity/Toxicological Effects
3.1. Toxic Effects of PFAS in Organisms
In recent decades, major studies on the toxicological effects of perfluoroalkyl substances have focused on two of the first legacy compounds discovered, PFOS and PFOA, that are the most representative molecules for perfluoroalkyl sulfonic acids (PFSAs) and perfluoroalkyl carboxylic acids (PFCAs), respectively [50,51,52,53,54]. Laine et al. [55] addressed, beside PFOA, PFHxA as a potential ecotoxicological compound for the freshwater microbial community. Statistical analysis showed that both PFOA and PFHxA at elevated doses considerably modified the composition of the microbial community. Moreover, statistical analysis demonstrated the more intense toxicity of PFOA, although unexpected outcomes were also found when PFHxA treatments were contrasted. PFOA reduced the biovolume of the bacteria, but it was unable to show that they reduced activity by monitoring cell respiration.
An important factor to consider is the trophic transfer and bioaccumulation of PFAS. The study made by Cara et al. [56] examined many locations in the Belgian portion of the Western Scheldt Estuary and the North Sea, sampling various fish and crustacean species. All matrices included only long-chain PFAS; fish muscle and liver tissue had seven chemicals, whereas crustaceans contained five. Regardless of the kind of fish or the location, liver tissue exhibited considerably higher PFAS levels than muscle tissue overall. The fact that the current study’s PFOS concentrations in fish (P. platessa) and crustaceans (C. crangon and crab sp.) are lower than those of previous studies is a noteworthy finding. The most likely cause is the PFOS and PFOA phase-out performed by 3M in 2000 [57]. Several studies demonstrate a steady decline in PFOS levels throughout the biota.
Li et al. [58] combined targeted and untargeted approaches to predict toxicity using LC-HRMS, LC-MS, and GC-MS. The study results in a strong positive relationship between body weight and liver damage for 13 PFASs. Eick et al. [59] investigated dietary predictors of prenatal PFAS exposure and discovered seven of them in approximately 65% of subjects. The ingestion of dairy products at least once a week was modestly related to higher levels of PFNA and perfluorodecanoic acid (PFDeA). For dairy milk and cheese, the relationships were shown with PFDeA and PFNA, respectively. The level of PFOA, PFDeA, PFNA, and PFOS were found to correlate with the consumption of fish, chicken, and red meat at least once a week. The work of Liu et al. [60] contributes to a better understanding of children’s exposure to PFAS. In particular, 107 raw milk samples and 70 cow feed samples from nine Chinese provinces were analyzed in order to investigate the correlation between the level of PFAS of milk and the contamination of PFASs in milk and feed. The findings showed that children are more vulnerable to the risk of PFAS intake from milk than adults.
The findings of the scientific community aim to assist institutions in defining limits and maximum levels of contamination and/or exposure that can be tolerated. The PFOS-induced transcriptional dose-response data were first collected by Chen et al. [61] in both in vitro and in vivo human and animal studies. After the application of statistical models that were demonstrated to be feasible and reliable to perform a human health risk assessment, it was shown that the reference doses for the most sensitive diseases and pathways were below the EPA reference dose, but similar to the tolerable doses settled by EFSA. Cytotoxic effects in humans were also addressed by recent studies. Amstutz et al. [62] investigated the correlation between structure-activity of linear PFASs and their toxicity, with a focus on their impact on hepatotoxicity in HepG2 cells. The data clearly demonstrate a relationship between the chemical structure of PFAS and their Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) production and cytotoxic activities in HepG2 cells.
The analysis of the impact takes into account both the exposure period and the chemical structure. Solan et al. [63] showed that appropriate data on the impact on health of short-chain PFAS may be obtained using the same strategies used for in vitro human cellular models. Human cell lines from six distinct tissues were exposed to five short-chain PFASs and two legacy PFASs: colon (CaCo-2), brain (HMC-3), kidney (HEK293), lung (MRC-5), liver (HepaRG), and muscle (RMS-13). RMS-13 showed the highest decline in viability after being exposed to PFBS for 48 h, whereas HepaRG appeared to be the most susceptible to hexafluoropropylene oxide-dimer acid (HFPO-DA) exposure. For the long-chain PFAS cytotoxicity, Caco-2 and MRC-5 were less vulnerable to PFOA exposure, whereas PFOA had the largest impact on viability in HepaRG, HMC-3, and RMS-13 comparable to 6:2 FTOH for the short-chain group. An independent t-test was used to compare these data, but no differences were found. Batzella et al. [64] studied the relationship between high PFASs exposure and cardiovascular diseases and cardiometabolic outcomes. Blood samples of 232 male ex-workers in Europe’s most important PFAS manufacturing factory between 1968 and 2018 were tested, and four out of twelve PFASs were found in at least half of the samples. The combination of four PFASs combined were positively correlated with TC, LDL-C, and SBP (markers of cardiovascular diseases). Lin et al. [65] showed for the first time a link between PFAS concentrations in serum and thrombograms of a panel of young and middle-aged persons in Asia, particularly in Taiwan. Moreover, for PFOS and PFOA, concentrations were higher than the 50th percentile, while the average number of platelets was at its lowest.
3.2. Discussion
The Toxicology studies on PFAS are incredibly important, as these compounds have been linked with serious health effects such as cancer, liver damage, and reproductive issues. Further studies in this area are needed to i. provide valuable additional information about the potential effects of exposure to different levels of PFAS; ii. support authorities to take informed decisions on how best to protect public health; and iii. develop informed policies aimed at regulating the levels of PFAS in the environment and consumer products, in an effort to protect people from unwanted exposure.
4. Contamination in Environment and Food
Due to the risks posed to human health by the exposure to PFASs, reliable data about the level of contamination of the environment and food matrices are required and several studies are already available [66,67,68,69,70,71,72]. An updated overview is given in this section and then summarized in Table 4 (environmental matrices) and Table 5 (food and FCMs).

Table 4.
Summary of relevant data from the literature for contamination of PFAS in environment.

Table 5.
Summary of relevant data from the literature for contamination of PFAS in food and from FCMs.
4.1. Environmental Contamination
In order to estimate the risk posed by PFAS to human health, it is important to monitor the possible source to which humans can be exposed. In this respect, wastewater is known to play a significant role and several studies [73,74] have studied the level of contamination of sludge from wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs) in Europe. In particular, Fredriksson et al. [75] detected novel perfluoroalkyl sulfonamide-based (FASA) copolymers in WWTPs in Sweden. The study demonstrated that these copolymers come from both domestic and industrial sources. In New Zealand, Lenka et al. [76] detected, in addition to 20 PFASs, ultrashort-chain perfluoropropionic acid (PFPrA) in urban waters, coming from two urban WWTPs.
A step forward is understanding the contribution of groundwaters. Several studies carried out in Europe and US addressed this point and showed high levels of contamination. In particular, 12 out of 29 PFASs were found in Sweden [77] and 14 out of 24 in the Eastern United States [78]. Given the large number of PFAS documented in commercial use and the environment, the PFASs examined here might not reflect the entire PFAS inventory in groundwater.
Also, crude oil, according to EPA [79], needs to be tested due to its presence in the interface between soil and groundwater. Yao et al. [80] proved that crude oil may be a significant source of PFAS contamination in the environment because they are applied in oil exploitation activity. PFCAs (27%) and p-perfluorousnonenoxybenzene sulphonate (OBS) (31%) made up the majority of the crude oil sample, while PFSAs (16%), ether-substituted polyfluoroalkyl (linear) sulphonic acids (OPFLSAs) (10%), 6:2 fluorotelomer sulfonamidoalkyl betaine (6:2 FTAB) (7%) and hydrogen-substituted polyfluoroalkyl (linear) carboxylic acids (HPFLCAs) (5%) made the rest of the samples. Their findings showed that certain new PFASs appeared in crude oil as a result of the use of chemical oil additives during the oil drilling process.
Ng et al. [81] focused their study on rivers, another important possible source of contamination, looking for the occurrence of PFAS in the Danube River Basin. The researchers used both target and suspect screening (non-targeted) approaches that allowed them to detect a total of 82 PFAS, 72 of which were detected only by suspect screening. PFOS was the only compound found in all of the water and biota matrices studied. Five PFAS were detected only in influent wastewater samples and not in effluent wastewater samples, indicating that they were successfully removed during wastewater treatment.
Another approach for assessing contamination coming from the terrestrial environment is to use wild animals as indicators to monitor PFAS. Moretti et al. [82] determined legacy and emerging poly- and per-fluoropolyethers in 28 wild boars using an HPLC-HRMS method. Boars were chosen because they are already confirmed to be suitable models to monitor PFAS contamination in the terrestrial environment [83,84]. The boars come from Italy and the analysis was carried out by sampling the boars’ livers. The chloropolyfluoropolyeters carboxylates and their related dechlorinated congeners, HPFPECAs, were discovered for the first time in pooled liver from Italian wild boars. These PFASs might be used as an indicator for terrestrial food chains. This preliminary data shows that the panel of PFAS with toxicological significance should be expanded.
4.2. Contamination of Food and from Food Contact Materials
Global concern is spreading fast due to the high levels of PFAS detected in blood serum [85,86,87,88]. The FDA’s Total Diet Study was one of the first studies monitoring PFAS in food in the United States. Genualdi et al. [89] found out that three out of 167 samples were detected positive, but no foods had concentrations of PFAS above 150 ng/kg.
In this paragraph, an updated overview of the scientific research around PFAS contamination in relevant food and food related matrices is reported.
In the last decades many studies addressed the level of PFAS in drinking water [90,91,92].
Liu et al. [93] collected data on a total of 18 PFASs in 526 samples of drinking water from 66 Chinese cities. Cities that produce PTFE have significantly greater levels of PFOA in their drinking water than cities that do not (with significance explained by a p < 0.05). The study showed that most Chinese cities have PFAS levels in drinking water that are higher than strict international guidelines and higher than Chinese health advisories.
Domingo et al. [94] collected 30 samples at different stages of drinking water treatment in Catalonia and found relevant concentration of PFOS and PFOA.
Scher et al. [95] analyzed the occurrence of PFAS in garden produce at homes to discover if soils with a history of contaminated drinking water could determine contamination for fruits and vegetables. The detection of PFBA and, with lower occurrence, PFPeA demonstrated the uptake of short-chained PFASs from soil to plants and confirmed that PFBA and PFPeA had the highest “foliage to root concentration factor” (defined as the concentration in foliage/concentration in the root). It was also established that PFBA concentrations strongly depended on the type of vegetable and on the water loading.
Babayev et al. [96] aimed to understand the levels of PFAS in drinking water and blood serum for people in the southeast Alaska community. This pilot research confirmed that water samples nearby airport operations and fire training sites are strongly contaminated and found a positive correlation between PFAS concentrations in serum and well water. The most prevalent substances were PFOS, PFOA, PFHxS, and PFHxA.
Gloria B. Post [97] published a mini-review on the Environmental Health Perspectives (EHP) about the PFAS levels in breast milk in the US and Canada populations. The researcher confirmed that it will be necessary to take preventive actions to protect breastfeeding mothers from exposure to PFAS in order to reduce their quantities in breast milk in the general population. Han et al. [98] looked for 30 PFAS in 100 pooled human breast milk samples during the 2017–2020 National Human Milk Survey to characterize the exposure risks of legacy and emerging PFAS in perinatal women and their children in China. The findings showed that L-PFOA, L-PFOS, and 6:2 Cl-PFESA were the three most common PFAS found in Chinese human milk.
Giari et al. [99] studied PFAS levels in fish species providing a significant information on the level of contamination of fish in the Po River, Italy. Prevalently were detected PFOS, PFDA and PFUnDA, while GenX and C6O4 were not detected. For the first time this study focused on the PFAS partitioning in a parasite-fish system obtaining that the infection state did not significantly alter the accumulation of PFAS in fish.
More than 500 samples of fish filets were characterized by Barbo et al. [100] in the US from 2013 to 2015 as part of the US EPA’s monitoring programs. The study demonstrated that almost all fish in American rivers, streams, and the Great Lakes were contaminated by significant levels of PFAS, primarily PFOS, whereas seafood purchased at grocery stores has significantly lower levels of PFAS. Other studies, such as Kumar et al. [101], made progress in detecting PFAS contamination by looking for fluorinated compounds in fish samples in the Baltic Sea and Finnish lakes, and PFOS was found in all the 1134 fishes analyzed, and also long-chain PFCAs were frequently detected. The monitoring of PFOS levels over the last decades do not show any decrease, so this demonstrates that no effective actions have been taken. In the Czech Republic, Semerád et al. [102] confirmed contamination in freshwater fishes. In particular, long-chain PFASs were detected at a relevant concentration, with short-chain PFASs and GenX measured at relatively low levels. A study focused on fish filet samples [103] showed that from 2014 and 2019 a decrease of PFAS occurred, while PFOS increased. Hoa et al. [104] deepened the study on fish by investigating distribution of PFAS contamination in the different tissues. The fish blood samples were found to be contaminated by 17 PFAS, with concentrations from 5.2 ng/mL to 29 ng/mL. In addition, the concentrations were substantially higher in liver samples than in muscle samples. In general, the study demonstrated that PFAS have unique distribution profiles depending on the species, tissue, and location. Rüdel et al. [105] derived a filet-to-whole fish conversion factor to assess potential risks posed by the consumption of fish filet.
PFAS contamination in eggs has been studied as well due to their greasy nature [106,107]. Miller et al. [108] investigating temporal trends of PFAS in eggs of different species. Among all PFAS, PFOS was found to be present in the highest concentration, even if with a decreasing trend over time probably due their industrial phase out in the last decades. On the contrary, long chain PFAS such as perfluorotridecanoic acid (PFTrDA) and perfluoroundecanoic acid (PFUdA) were found to increase. These results were confirmed by Glória Pereira et al. [109], during a monitoring over 35 years in eggs of the northern gannet in UK.
Investigations by Granby et al. [110] of the Technical University of Denmark (DTU) National Food Institute unequivocally show that the PFAS entered the eggs through fish meal in the chicken diet. Hence, substituting a non-contaminated feed component might substantially lower the amount of PFAS in the eggs within a few weeks.
Androulakakis et al. [111] studied freshwater and terrestrial top predators from Northern Europe. The majority of apex predators (AP) and their prey were found to be contaminated, and, in particular the three perfluoroalkylphosphinic acids were detected in all the samples. The study demonstrated a strong correlation between the geographic origin of the specimens and the quantities of PFAS in AP, with samples taken from urban and agricultural regions being significantly more polluted than those taken from pristine or semi-pristine places.
The migration of PFAS from Food Contact Materials (FCMs) is considered to be a relevant source of contamination. According to Galbiati et al. [112], some substances in the group of PFASs used in the FCM production have been classified as endocrine-disrupting chemicals (EDCs), therefore it is important to investigate their possible migration into foods. Lerch et al. [113] conducted migration tests on paper FCMs treated with PFAS for understanding their behavior at high temperature applications, and it was found that PFAS migration to real foods contributes significantly to tolerable weekly intake. Minet et al. [114] studied the use and release of PFASs in FCMs in Canada and the US and showed that FCM containing minimal concentration of PFAS can nonetheless contaminate the entire waste stream. In Canada, Schwartz-Narbonne et al. [115] tested fast food packaging for PFAS contamination by comparing compostable bowls to single-use plastic bowls. Despite the fact that compostable bowls are promoted as “green” alternatives to plastic bowls, they have been positively tested for PFAS contamination sources and therefore appear to be a regrettable alternative to single-use bowls.
Testing food simulants and leakage of non-intentionally added substances (NIAS) by FCMs is not the only way to estimate the level of contamination of PFAS related to food packaging migration. It is also important to investigate the exposure of consumers [116,117,118,119,120]. Susmann et al. [121], for example, studied the dietary habits of the US population, monitoring the exposure to PFASs also through food packaging. The results showed that popcorn consumption is associated with significantly higher levels of PFOA, PFNA, PFDA, and PFOS in serum. This correlation was not detected in other types of foods, e.g., pizza. That outcome could be accounted for as an effect of the migration from microwave popcorn packaging.
The fact that PFAS can contaminate humans is demonstrated by studies addressing the measurement of PFAS levels in blood serum. The work of Richterová et al. [122] was the first research to use standardized, consistent, and quality-controlled PFAS exposure data from Europe. This research was carried out as a European Human Biomonitoring Initiative (HBM4EU) aligned study. A total of 1957 children and teenagers from Sweden, Norway, Slovakia, Spain, Slovenia, Greece, France, Germany, and Belgium were tested. Almost all subjects tested positive for PFOS, PFOA, PFNA, and PFHxS. Teenagers in the North and West of Europe have much higher PFAS values than those in the South and East. The eating of fish and shellfish was linked to greater PFAS concentrations, while consuming eggs was linked to increased concentrations of PFOS and PFNA. These findings offer details on possible PFAS exposure sources for focused PFAS in food monitoring.
4.3. Discussion
Monitoring PFAS in food and environment is critical to understanding and managing potential health and environmental impacts. Accurate and reliable measurements of levels of PFAS in our soils, water, and foods will ensure the development of effective action in preventing and/or mitigating the possible risk related to PFAS.
According to recent studies, several food matrices, including those intended for infants and children, have been found to be positive to PFAS contamination at levels that are strongly dependent on the geographical area (e.g., proximity to industrial areas). In addition, it is concerning to see how high PFAS levels are in food contact materials. We need to take steps to reduce our exposure by using materials that are free from this contaminant. The health risks associated with the long-term consumption of PFAS are still not fully understood, so it is important to take proactive steps to reduce our exposure whenever possible, as phasing out PFAS from production of FCM.
5. Analytical Techniques for Detection and Quantification of PFAS
The established methods for performing PFAS analysis are based on Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS). Both the sample preparation and the development of the chromatographic set-up are crucial steps for reliable, precise, and accurate measurements. According to the literature, the conventional reverse phase separation stationary phase column is the most widely utilized [123,124,125,126] approach. To improve the chromatographic performance, columns equipped with polar functionalized C18 alkyl chains were introduced [127]. The adoption of columns with polar groups on the surface of the stationary phase permits them to better retain the more polar compounds, in particular the shortest one at the first minutes of elution. In addition, the implementation of an isocratic elution method [128] enabled the thorough investigation of C2, C3, C4, C6, C8, and alternative PFAS by using a special hybrid HILIC/ion-exchange column. In this way, it was possible to quickly and easily analyze legacy, alternative, and ultrashort-chain PFAS in water samples.
The development of novel analytical methods is a crucial step because the legal limits are changing rapidly so that the actual techniques can become rapidly obsolete. Decreasing the limit of quantification is the biggest challenge for the ultra-trace search for PFAS in environmental and food matrices.
An overview of the analytical technique strategy is depicted in Table 6.

Table 6.
Scheme of analytical techniques strategy.
5.1. Sampling and Storage
The first step to improve the level of detection and quantification in complex matrices, in particular from the environment (air, water, soil), is the sampling. For analyzing 26 PFASs in drinking water treatment plant (DWTP) Gobelius et al. [129] used two approaches, based on hydrophilic-lipophilic balance (HLB) and weak anion exchange (WAX) of polar organic chemical integrative samplers (POCIS) which were calibrated and used in the investigation. The average PFAS concentration was measured to be rather stable over the course of the days, demonstrating the suitability of the calibration method used for the passive samplers POCIS-WAX and POCIS-HLB. In general, there were no appreciable differences in the detection of individual PFAS contents in drinking water between POCIS-WAX, POCIS-HLB, and composite water samples (collected in aliquots during periods). It is noteworthy that POCIS-HLB had low absorption rates, which may account for the fact that perfluorobutanoic acid (PFBA) was only found using POCIS-WAX and composite water sampling. New microporous polyethylene (PE) diffusion passive sampler was also tested for PFAS groundwater monitoring [130]. Using this design, the linear absorption phase of PFASs was successfully extended and a mean t1/2 of 240 days was estimated.
For testing the best condition for storing the samples, Woudneh et al. [131] measured the stability of 29 PFAS in different types of water stored at different temperatures. PFAS were spiked in different water samples that were then kept in HDPE containers for up to 180 days at +20, +4, and −20 °C. The study showed that keeping the samples below 0 °C is the only way to ensure the stability of PFAS over time because the effects of the analyte interconversions were noticeable within 7 days of storage at 4 °C, which is the temperature that is normally used to stock aqueous samples for analysis of PFAS.
In case of air samples, to overcome the issue of sampling air including the particulate matter and the gaseous phase for the discovery of unknown novel PFASs, the study of Yu et al. [132] showed the use of a cryogenic air sampler (CAS) to simultaneously collect atmospheric gaseous phase and particulate matter comprehensively. Five groups of chlorinated perfluoropolyethers were reported for the first time in this study.
Simon et al. [133] studied a fast and simple extraction method for PFAS contaminated soil. The samples of soil were freeze-dried or air-dried before analysis and were also collected from different locations. Johnson [134] analyzed soils samples collected at different depth levels. It was the first known study of this type and the results showed that this sort of sampling provides insightful information about the type, source and the consequence of the contamination.
5.2. Extraction and Clean-Up
As contaminants, in real matrices PFASs are usually present in very low concentration (trace levels) so it is necessary to extract them prior to the analysis. As a first step, the methods needed to be validated in water samples, and in 2019 the ISO 21675:2019 “Water quality—Determination of perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in water—Method using solid phase extraction and liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS)” was published. To validate the method an inter-laboratory trial (ILT) was conducted by Taniyasu et al. [135], involving 27 labs in total. The results suggested that the storage at 28 °C of water samples is preferred for those that are not analyzed within four weeks of collection, and it is also recommended to rinse the container wall with methanol prior to the elution step in order to improve recovery and achieve repeatable results for long-chain PFAS. More complex matrices have been already addressed, such as plant-based materials with the aim of developing and testing a straightforward extraction and clean-up approach for the measurement of five PFAS classes in various plant tissues [136]. The method demonstrated to be suitable for PFAS analysis, and adequate validation parameters were achieved for the majority of analytes. Addressing other matrices than water, Drábová et al. [137] studied the clean-up methods for fatty matrices, which is a critical step for PFAS analysis. Four different sorbents’ lipid clean-up capabilities were assessed in samples of fatty fish following extraction using Quick Easy Cheap Effective Rugged Safe (QuEChERS) or the ethyl acetate technique. The sorbents tested were silica, Z-Sep, C18, and EMR-lipid. The most efficient dispersive-Solid Phase Extraction (dSPE) sorbent was the EMR-lipid one performed after a QuEChERS extraction.
The QuEChERSER (more than QuEChERS) method validated by Taylor et al. [138] increases the polarity range of QuEChERS. The technique is essentially performed by an ACN/H2O extraction followed by an ultra-centrifugation to obtain the fraction for LC. In addition, from the acetonitrile layer derived by the further addition of QuEChERS salts in the remaining initial extract it was possible to obtain, due to the salting-out effect into the Instrument Top Sample Preparation (ITSP) clean-up, a fraction for Gas Chromatography (GC). The method demonstrated advancement in clean-up efficiency, matrix effect, and recoveries compared to other PFAS analysis methods in food stuff previously used by US federal agencies. The ITSP proved to be a faster and automated approach to evaluate clean-up efficiency compared to the dSPE one.
Gallocchio et al. [139] demonstrated the effectiveness of a QuEChERS extraction/clean-up method shortening the time required per analysis of environmental and food matrices, also increasing the efficiency and resulting in approximately 30 samples being ready for LC-MS/MS analysis in one working day. Based on these results, Askeland et al. [140] proposed a novel method based on a multistep sorption of PFASs for high volume direct injection of aqueous samples, which involves sorbent addition with biochar, centrifugation of samples, methanol addition, and a filtration with a 0.22 μm syringe filter of cellulose prior to direct injection in a triple quadrupole LC-MS. The innovation of this method is the provision of high sample throughput due to the exclusion of instrument preparation and determination of equilibrium time.
5.3. Analytical Detection Techniques
Mass spectrometry in all of its forms is the elite technique for the identification and quantification of PFAS, and there are numerous examples [141,142,143,144,145].
Wu et al. [146], aiming to speed up the analysis of PFAS, developed and applied a hyphenated nano-electrospray ionization to HRMS (Nano-ESI-HRMS) to analyze wastewater and aqueous film-forming foams (AFFFs) samples collected from three local wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs). Nano-ESI-HRMS enables detection of various PFAS with the inclusion of the ultra-short chain and other very polar molecules which are often underestimated in LC. This approach has the advantages of saving time (lower than two minutes per sample) without compromising accuracy and sensitivity. Taking a step forward in the rapid identification of PFAS, Dodds et al. [147] devised a quick and efficient method for separating isobar molecules such as 6:2 FTS and Hydro-EVE that differs only for 0.023 m/z. Even with HRMS instruments, mass separation of these precursors is extremely difficult. Collision cross section (CCS) is the phenomenon that underpins ion mobility separation; whereas other LC techniques separate molecules based on their interaction with the stationary phase of the column (polarity) over time, the additional step of this analysis allows for separation based on atom spatial distribution (molecular size).
The scientific community is also working to develop new approaches to fight PFAS contamination through various techniques that may be more rapid or “in situ”.
Jackson et al. [148] studied albumin as the main protein involved as a carrier for some PFAS compounds in human serum, aiming to use this affinity to rapidly characterize the contaminants. Albumin has numerous nonspecific sites that selectively bind hormones, fatty acids, drugs, and several xenobiotics, particularly PFASs. Prior to the development of the current technology, the methods for determining this affinity, such as surface plasmon resonance or titration chemistry, required too much time because of the large number of distinct PFAS that needed to be examined. Differential Scanning Fluorimetry (DSF) is a quick, high-throughput technique for determining ligand-binding interactions, and it is most frequently used to assess the stability of proteins under various circumstances. The findings showed that DSF can specify protein binding affinities and pinpoint the physicochemical factors that contribute to protein binding for a significant number of PFAS. A different approach to perform a rapid and in situ analysis was found by Park et al. [149] who discovered the aptamer binding to PFOA (KD = 5.5 μM) phenomenon for the first time, owing to the alkyl length, which is important in the physicochemical event. To investigate this behavior, a fluorescence-based aptasensor was created, which allows for easy and rapid monitoring of PFAS and other emerging pollutants in situ. The results obtained utilizing a multimode plate reader were compared to traditional LC-MS detection methods. NMR spectroscopy and circular dichroism analysis were performed to compare the binding strengths of the aptamer with and without the addition of PFOA, and the results show that the aptamer can bind long alkyl chains with specificity.
In parallel to routine quantification of legacy PFAS, in order to monitor the global contamination levels, it is also necessary to detect all possible fluorinated substances, which may be toxic as well. The untargeted approach is the only way to discover all the organic fluorinated compounds, and it is usually performed with high-resolution mass spectrometry [150,151,152,153].
Xiao et al. [154] developed for the first time a non-targeted method using fluorine extraction using fluoro-cotton fibers put in SPE cartridges. The interaction F-F aids in the extraction and, as a result, enhancement of organic fluorine compounds. In this study, rice samples were grown in artificially contaminated soils with perfluoroalkyl substance soils to validate the method. This method improved the use of extraction methods to aid in untargeted characterization, but it is also possible to improve chromatographic conditions for the purpose. A novel analytical method for the non-targeted detection of total PFAS was developed by Renai et al. [155] for the analysis of fire-fighting AFFFs. The researchers performed the untargeted identification due to a LCxLC chromatography system coupled to a high-resolution mass spectrometer. The peak capacity of chromatographic systems was increased by using the 2D-LC method and this was essential to map the chemical space of complicated mixtures such as AFFFs.
For screening all possible PFAS on AFFFs, Young et al. [156] tested a method based on the Fourier-transform (FT) ion cyclotron resonance (ICR) MS. One of the purposes of this study was to show the effectiveness of FT-ICR MS direct infusion for suspect and non-target detection of PFAS in a complex mixture of AFFFs. Molecular structure cannot be determined definitively by direct infusion MS (or any mass analyzer) by detecting the molecular ion alone, but the study shows that the list of known PFASs can be expanded during subsequent analyses using accepted structural identification standards. Another alternative approach for untargeted analysis of perfluorinated compounds is the inductively-coupled plasma (ICP) MS. This method allows Jamari et al. [157] to identify all fluorinated compounds whether or not they are ionized under electro spray conditions, and a fluorinated standard is available. This non-targeted approach is well adapted to assist in identifying a large proportion of organofluorines not detected.
5.4. Discussion
Analytical techniques for the detection of PFAS have come a long way and continue to develop. Currently, modern PFAS analysis can use various methods, including the combination of various hyphenated chromatography techniques such as liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS) and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS). These techniques allow for accurate and sensitive detection of individual PFAS and sometimes even identifying specific PFAS precursors. So far, the main innovations rely on in situ and high throughput techniques which are necessary to answer the monitoring requests. In parallel, the implementation of non-targeted screening methods will allow the understanding of the novel classes of PFAS introduced in the industry products and, also, the characterization of their presence in environment and food. The development of even more accurate and sensitive in situ and screening techniques will constitute the main strategy to fight PFAS contamination and to provide reliable inputs to regulatory bodies and lawmakers.
6. Future Perspectives
PFAS and PFAS contamination are nowadays a “hot-topic” that interest all levels of society, from scientific communities to citizens. Worldwide, authorities are actively and constantly working on legislation to reduce the release of PFASs into the environment, while waiting for expert opinions from the scientific community on the levels of actual contamination. Researchers are addressing this topic from different points of view, including toxicological studies and advances in analytical methods for detection of PFAS traces in real matrices. Groundwater and food are already known to be the most common sources of contamination for humans, and drinking water and plant-based foods are currently under deeper investigation. Improving untargeted analysis of perfluorinated compounds is an important step toward an exhaustive comprehension of the possible risk posed by PFAS to the environment and to human health. To this end, screening methods based on high-resolution mass spectrometry can constitute a powerful tool to discover new PFAS analytes at every stage of the food chain. It is also of paramount importance to monitor the PFAS levels in biological samples from animals and humans in order to evaluate the correlation between food and environmental contamination and the PFAS intake and accumulation in human bodies.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.S. and C.P.; investigation, C.S. and C.P.; resources, C.S. and C.P.; writing—original draft preparation, C.S. and C.P.; writing—review and editing, C.S. and C.P.; visualization, C.S. and C.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The present work has been supported by the project “20NET02 Food-MetNet”, which has received funding from the EURAMET EMPIR programme co-financed by the Participating States and from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
| 2D-LC | 2 dimensions Liquid Chromatography |
| ACN | Acetonitrile |
| AFFFs | Aqueous Film-Forming Foams |
| AP | Apex Predator |
| CAS | Cryogenic Air Sampler |
| CCME | Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment |
| CCS | Collision Cross Section |
| CERLCA | Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation and Liability Act |
| Cl-PFESA | Chlorinated polyfluorinated ether sulfonic acids |
| CONAMA | Brazilian National Council for the Environment |
| CSCA | China Standard Conformity Assessment |
| dSPE | dispersive Solid Phase Extraction |
| DSF | Differential Scanning Fluorimetry |
| DWTP | Drinking Water Treatment Plant |
| ECHA | European Chemicals Agency |
| EDCs | Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals |
| EEA | European Economic Area |
| EFSA | European Food Safety Authority |
| EHP | Environmental Health Perspectives |
| EMBRAPA | Brazilian Agricultural Research Corporation |
| EPA | Environmental Protection Agency |
| ESI | Electronspray Ionization |
| EU | European Union |
| EURL | European Union Reference Laboratory |
| FASA | Perfluoroalkane sulfonamide |
| FCMs | Food Contact Materials |
| FDA | Food and Drug Administration |
| FTAB | Fluorotelomer sulfonamidoalkyl betaine |
| FTOH | Fluorotelomer alcohol |
| FTS | Fluorotelomer sulfonate |
| FT-ICR | Fourier-Transform Ion Cyclotron Resonance |
| GC MS | Gas Chromatography Mass Spectrometry |
| GenX | same as HFPO-DA |
| HC | Health Canada |
| HDPE | High Density PolyEthylene |
| HFPO-DA | Hexafluoropropylene oxide-dimer acid or GenX |
| HILIC | Hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography |
| HLB | Hydrophilic-lipophilic balance |
| HPLC | High Performance Liquid Chromatography |
| HPFPECAs | Hydro- perfluoroether carboxylic acid |
| HPFLCAs | Hydrogen-substituted polyfluoroalkyl (linear) carboxylic acids |
| HRMS | High-resolution mass spectrometry |
| Hydro-EVE | 2,2,3,3-Tetrafluoro-3-{[1,1,1,2,3,3-hexafluoro-3-(1,2,2,2-tetrafluoroethoxy)propan-2-yl]oxy}propanoic acid |
| ICP-MS | Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry |
| ILT | Inter-laboratory trial |
| ISO | International Organization for Standardization |
| ITSP | Instrument Top Sample Preparation |
| LC-MS/MS | Liquid Chromatography coupled to tandem Mass Spectrometry |
| L-PFOA | Linear perfluorooctanoic acid |
| L-PFOS | Linear perfluorooctane sulfonic acid |
| MCLs | Maximum contaminant levels |
| NIAS | Non-intentionally added substances |
| NMR | Nuclear Magnetic Resonance |
| OBS | p-perfluorousnonenoxybenzene sulphonate |
| PE | Polyethylene |
| PFAAs | Long-chain perfluoroalkyl acids |
| PFAS | Perfluoroalkyl substances |
| PFBA | Perfluorobutanoic acid |
| PFBS | Perfluorobutane sulfonic acid |
| PFCAs | Perfluoroalkyl carboxylic acids |
| PFDA | Perfluorodecanoic acid |
| PFTrDA | Perfluorotridecanoic acid |
| PFUdA | Perfluoroundecanoic acid |
| PFHpA | Perfluoroheptanoic acid |
| PFHxA | Perfluorohexanoic acid |
| PFHxS | Perfluorohexane sulfonic acid |
| PFNA | Perfluorononanoic acid |
| PFOA | Perfluorooctanoic acid |
| PFOS | Perfluorooctane sulfonic acid |
| PFPeA | Perfluoropentanoic acid |
| PFPrA | Perfluoropropionic acid |
| PFSAs | Perfluoroalkyl sulfonic acids |
| POCIS | Polar Organic Chemical Integrative Samplers |
| POPs | Persistent Organic Pollutants |
| POSF | Perfluorooctane sulfonyl fluoride |
| PTFE | Polytetrafluoroethylene |
| QuEChERS | Quick Easy Cheap Effective Rugged and Safe |
| RAC | Committee for Risk Assessment |
| REACH | European Chemicals Regulation |
| ROS | Reactive Oxygen species |
| SEAC | Committee for Socio-economic Analysis |
| SPE | Solid Phase Extraction |
| TOF | Time-of-flight |
| TWI | Tolerable Weekly Intake |
| WAX | Weak anion exchange |
| WWTPs | Wastewater treatment plants |
| US | United States |
References
- Available online: https://echa.europa.eu/it/hot-topics/perfluoroalkyl-chemicals-pfas (accessed on 12 May 2023).
- Available online: https://www.niehs.nih.gov/health/topics/agents/pfc/index.cfm (accessed on 12 May 2023).
- Buck, R.C.; Franklin, J.; Berger, U.; Conder, J.M.; Cousins, I.T.; De Voogt, P.; Jensen, A.A.; Kannan, K.; Mabury, S.A.; van Leeuwen, S.P.J. Perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances in the environment: Terminology, classification, and origins. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2011, 7, 513–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, E.R.; Chan, B.P.; Talbot, E.A.; Nassif, J.; Bean, C.; Cavallo, S.J.; Metcalf, E.; Simone, K.; Woolf, A.D. Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substance (PFAS) exposure assessment in a community exposed to contaminated drinking water, New Hampshire, 2015. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2018, 221, 569–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurikova, M.; Dvorakova, D.; Pulkrabova, J. The occurrence of perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in drinking water in the Czech Republic: A pilot study. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 60341–60353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazzotti, T.; Sirri, F.; Ghelli, E.; Zironi, E.; Zampiga, M.; Pagliuca, G. Perfluoroalkyl contaminants in eggs from backyard chickens reared in Italy. Food Chem. 2021, 362, 130178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://trends.google.com/trends/explore?date=all&q=PFAS (accessed on 12 May 2023).
- Available online: https://www.webofscience.com/wos/woscc/basic-search (accessed on 12 May 2023).
- Fenton, S.E.; Ducatman, A.; Boobis, A.; DeWitt, J.C.; Lau, C.; Ng, C.; Smith, J.S.; Roberts, S.M. Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substance Toxicity and Human Health Review: Current State of Knowledge and Strategies for Informing Future Research. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2021, 40, 606–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vélez, M.P.; Arbuckle, T.E.; Fraser, W.D. Maternal exposure to perfluorinated chemicals and reduced fecundity: The MIREC study. Hum. Reprod. 2015, 30, 701–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, C.; McLaughlin, J.K.; Lipworth, L.; Olsen, J. Maternal levels of perfluorinated chemicals and subfecundity. Hum. Reprod. 2009, 24, 1200–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitworth, K.W.; Haug, L.S.; Baird, D.D.; Becher, G.; Hoppin, J.A.; Skjaerven, R.; Thomsen, C.; Eggesbo, M.; Travlos, G.; Wilson, R.; et al. Perfluorinated compounds and subfecundity in pregnant women. Epidemiology 2012, 23, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vestergaard, S.; Nielsen, F.; Andersson, A.M.; Hjøllund, N.H.; Grandjean, P.; Andersen, H.R.; Jensen, T.K. Association between perfluorinated compounds and time to pregnancy in a prospective cohort of Danish couples attempting to conceive. Hum. Reprod. 2012, 27, 873–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buck Louis, G.M.; Sundaram, R.; Schisterman, E.F.; Sweeney, A.M.; Lynch, C.D.; Gore-Langton, R.E.; Maisog, J.; Kim, S.; Chen, Z.; Barr, D.B. Persistent environmental pollutants and couple fecundity: The LIFE study. Environ. Health Perspect. 2013, 121, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grandjean, P.; Heilmann, C.; Weihe, P.; Nielsen, F.; Mogensen, U.B.; Timmermann, A.; Budtz-Jørgensen, E. Estimated exposures to perfluorinated compounds in infancy predict attenuated vaccine antibody concentrations at age 5-years. J. Immunotoxicol. 2017, 14, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, K.; Monien, B.H. Transdermal absorption of 13C4-perfluorooctanoic acid (13C4-PFOA) from a sunscreen in a male volunteer—What could be the contribution of cosmetics to the internal exposure of perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS)? Environ. Int. 2022, 169, 107549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blomberg, A.J.; Haug, L.S.; Lindh, C.; Sabaredzovic, A.; Pineda, D.; Jakobsson, K.; Nielsen, C. Changes in perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) concentrations in human milk over the course of lactation: A study in Ronneby mother-child cohort. Environ. Res. 2023, 219, 115096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sdwa/and-polyfluoroalkyl-substances-pfas#:~:text=EPA%20is%20developing%20a%20proposed,by%20the%20end%20of%202023. (accessed on 12 May 2023).
- Available online: https://www.fda.gov/food/environmental-contaminants-food/and-polyfluoroalkyl-substances-pfas (accessed on 12 May 2023).
- Schrenk, D.; Bignami, M.; Bodin, L.; Chipman, J.K.; del Mazo, J.; Grasl-Kraupp, B.; Hogstrand, C.; Hoogenboom, L.; Leblanc, J.C.; Nebbia, C.S.; et al. Risk to human health related to the presence of perfluoroalkyl substances in food. EFSA J. 2020, 18, e06223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahnke, A.; Marchand, P. Guidance Document on Analytical Parameters for the Determination of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) in Food and Feed; EURL POPs: Freiburg, Germany, 2022; pp. 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX:32020L2184&from=EN (accessed on 25 May 2023).
- Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sdwa/and-polyfluoroalkyl-substances-pfas (accessed on 25 May 2023).
- National Health and Medical Research Council (Australia); Natural Resource Management Ministerial Council (Australia). Australian Drinking Water Guidelines Version 3.8; National Health and Medical Research Council: Canberra, Australia, 2022; ISBN 1864965118.
- Available online: https://www.canada.ca/en/health-canada/services/environmental-workplace-health/reports-publications/water-quality/water-talk-per-polyfluoroalkyl-substances-drinking-water.html (accessed on 25 May 2023).
- Wang, X.; Zhang, H.; He, X.; Liu, J.; Yao, Z.; Zhao, H.; Yu, D.; Liu, B.; Liu, T.; Zhao, W. Contamination of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in the water source from a typical agricultural area in North China. Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 10, 2545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/reg/2022/2388/oj (accessed on 25 May 2023).
- Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/ALL/?uri=celex:32004R0850 (accessed on 12 May 2023).
- Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/en/TXT/?uri=CELEX%3A32019R1021 (accessed on 12 May 2023).
- Alexander, J.; Auðunsson, G.A.; Benford, D.; Cockburn, A.; Cravedi, J.-P.; Di Domenico, A.; Fernández-Cruz, M.L.; Fink-Gremmels, J.; Fürst, P.; Galli, C.; et al. Opinion of the Scientific Panel on Contaminants in the Food chain on Perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS), perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) and their salts. EFSA J. 2008, 653, 1–131. [Google Scholar]
- Knutsen, H.K.; Alexander, J.; Barregård, L.; Bignami, M.; Brüschweiler, B.; Ceccatelli, S.; Cottrill, B.; Dinovi, M.; Edler, L.; Grasl-Kraupp, B.; et al. Risk to human health related to the presence of perfluorooctane sulfonic acid and perfluorooctanoic acid in food. EFSA J. 2018, 16, e05194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://echa.europa.eu/it/registry-of-restriction-intentions/-/dislist/details/0b0236e1827f87da (accessed on 12 May 2023).
- Available online: https://echa.europa.eu/documents/10162/fdaed5b0-b6e4-9a21-b45d-ca607c05f845 (accessed on 12 May 2023).
- Available online: https://echa.europa.eu/-/proposal-to-ban-forever-chemicals-in-firefighting-foams-throughout-the-eu (accessed on 12 May 2023).
- Available online: https://echa.europa.eu/documents/10162/4524f49c-ae14-b01b-71d2-ac3fa916c4e9 (accessed on 12 May 2023).
- Available online: https://echa.europa.eu/-/echa-adds-nine-hazardous-chemicals-to-candidate-list (accessed on 12 May 2023).
- Available online: https://echa.europa.eu/-/echa-receives-pfass-restriction-proposal-from-five-national-authorities (accessed on 12 May 2023).
- Available online: https://www.ncsl.org/environment-and-natural-resources/per-and-polyfluoroalkyl-substances (accessed on 12 May 2023).
- Available online: https://www.epa.gov/pfas/pfas-strategic-roadmap-epas-commitments-action-2021-2024 (accessed on 12 May 2023).
- Available online: https://www.stantec.com/en/ideas/topic/covid-19/pfas-in-canadian-provinces-where-are-the-regulations#:~:text=federal%20government%20doing%3F-,On%20a%20federal%20level%2C%20Canada%20took%20steps%20to%20deal%20with,environment%20or%20its%20biological%20diversity (accessed on 12 May 2023).
- Barbosa Machado Torres, F.; Guida, Y.; Weber, R.; Machado Torres, J.P. Brazilian overview of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances listed as persistent organic pollutants in the stockholm convention. Chemosphere 2022, 291, 132674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of the Environment. National Implementation Plan Brazil: Convention Stockholm/Ministry of the Environment; MMA, Brazilian Institute of Environment and Natural Renewable Resources: Brasilia, Brazil, 2015; p. 178.
- Available online: https://enviliance.com/regions/others/asia-pfoa (accessed on 12 May 2023).
- Available online: https://www.tcsb.gov.tw/fp-288-5776-06543-2.html (accessed on 12 May 2023).
- Groffen, T.; Nkuba, B.; Wepener, V.; Bervoets, L. Risks posed by per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) on the African continent, emphasizing aquatic ecosystems. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2021, 17, 726–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ssebugere, P.; Sillanpää, M.; Matovu, H.; Wang, Z.; Schramm, K.W.; Omwoma, S.; Wanasolo, W.; Ngeno, E.C.; Odongo, S. Environmental levels and human body burdens of per- and poly-fluoroalkyl substances in Africa: A critical review. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 739, 139913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, T.; Roos, C. Regulation and management of hazardous chemical substances in South Africa. In Fundamentals of Ecotoxicology: The Science of Pollution, 4th ed.; Newman, M., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015; pp. 463–469. [Google Scholar]
- Claassen, M.; Dabrowski, J.M.; Nepfumbada, T.; van der Laan, M.; Shadung, J.; Thwala, M. Incorporating Environmental Fate Models into Risk Assessment for Pesticide Registration in South Africa; Water Research Commission: Pretoria, South Africa, 2020; ISBN 9780639201351. [Google Scholar]
- Available online: https://federation.gov.au/about/agreements/intergovernmental-agreement-national-framework-responding-pfas-contamination (accessed on 12 May 2023).
- Briels, N.; Ciesielski, T.M.; Herzke, D.; Jaspers, V.L.B. Developmental Toxicity of Perfluorooctanesulfonate (PFOS) and Its Chlorinated Polyfluoroalkyl Ether Sulfonate Alternative F-53B in the Domestic Chicken. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 12859–12867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bursian, S.J.; Link, J.E.; McCarty, M.; Simcik, M.F. The Subacute Toxicity of Perfluorooctane Sulfonate and/or Perfluorooctanoic Acid and Legacy Aqueous Film-Forming Foams to Japanese Quail (Coturnix japonica) Chicks. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2021, 40, 695–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartlett, A.J.; De Silva, A.O.; Schissler, D.M.; Hedges, A.M.; Brown, L.R.; Shires, K.; Miller, J.; Sullivan, C.; Spencer, C.; Parrott, J.L. Lethal and sublethal toxicity of perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) in chronic tests with Hyalella azteca (amphipod) and early-life stage tests with Pimephales promelas (Fathead minnow). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 207, 111250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Niu, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Sun, D. Evaluating the sub-lethal toxicity of PFOS and PFOA using rotifer Brachionus calyciflorus. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 180, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, X.; Du, Y.; Lam, P.K.S.; Wu, R.S.S.; Zhou, B. Developmental toxicity and alteration of gene expression in zebrafish embryos exposed to PFOS. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2008, 230, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laine, M.B.; Vesamäki, J.S.; Puupponen, V.M.; Tiirola, M.; Taipale, S.J. Comparing the Ecotoxicological Effects of Perfluorooctanoic Acid (PFOA) and Perfluorohexanoic Acid (PFHxA) on Freshwater Microbial Community. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cara, B.; Lies, T.; Thimo, G.; Robin, L.; Lieven, B. Bioaccumulation and trophic transfer of perfluorinated alkyl substances (PFAS) in marine biota from the Belgian North Sea: Distribution and human health risk implications. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 311, 119907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations Industrial Development Organization (UNIDO). Preparing for HCFC Phase-Out: Fundamentals of Uses, Alternatives, Implications and Funding for Article 5 Countries; UNIDO: Vienna, Austria, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Yu, N.; Wang, X.; Shi, W.; Liu, H.; Zhang, X.; Yang, L.; Pan, B.; Yu, H.; Wei, S. Comprehensive Exposure Studies of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in the General Population: Target, Nontarget Screening, and Toxicity Prediction. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 14617–14626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eick, S.M.; Goin, D.E.; Trowbridge, J.; Cushing, L.; Smith, S.C.; Park, J.S.; DeMicco, E.; Padula, A.M.; Woodruff, T.J.; Morello-Frosch, R. Dietary predictors of prenatal per- and poly-fluoroalkyl substances exposure. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2023, 33, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Li, Y.; Hao, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, L.; Wang, P.; Yin, Y.; Zhang, S.; Li, T.; et al. Occurrence of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in raw milk and feed from nine Chinese provinces and human exposure risk assessment. Chemosphere 2022, 300, 134521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Chou, W.C.; Lin, Z. Integration of Toxicogenomics and Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Modeling in Human Health Risk Assessment of Perfluorooctane Sulfonate. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 3623–3633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amstutz, V.H.; Cengo, A.; Gehres, F.; Sijm, D.T.H.M.; Vrolijk, M.F. Investigating the cytotoxicity of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in HepG2 cells: A structure-activity relationship approach. Toxicology 2022, 480, 153312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solan, M.E.; Senthilkumar, S.; Aquino, G.V.; Bruce, E.D.; Lavado, R. Comparative cytotoxicity of seven per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in six human cell lines. Toxicology 2022, 477, 153281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batzella, E.; Girardi, P.; Russo, F.; Pitter, G.; Da Re, F.; Fletcher, T.; Canova, C. Perfluoroalkyl substance mixtures and cardio-metabolic outcomes in highly exposed male workers in the Veneto Region: A mixture-based approach. Environ. Res. 2022, 212, 113225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.Y.; Wang, C.; Sung, F.C.; Su, T.C. Association between serum per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances and thrombograms in young and middle-aged Taiwanese populations. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 236, 113457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.canada.ca/en/health-canada/services/environmental-workplace-health/reports-publications/environmental-contaminants/human-biomonitoring-resources/per-polyfluoroalkyl-substances-canadians.html (accessed on 25 May 2023).
- Boone, J.S.; Vigo, C.; Boone, T.; Byrne, C.; Ferrario, J.; Benson, R.; Donohue, J.; Simmons, J.E.; Kolpin, D.W.; Furlong, E.T.; et al. Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in source and treated drinking waters of the United States. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 653, 359–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaefer, C.E.; Hooper, J.L.; Strom, L.E.; Abusallout, I.; Dickenson, E.R.V.; Thompson, K.A.; Mohan, G.R.; Drennan, D.; Wu, K.; Guelfo, J.L. Occurrence of quantifiable and semi-quantifiable poly- and perfluoroalkyl substances in united states wastewater treatment plants. Water Res. 2023, 233, 119724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Cai, Y.; Ma, L.; Lin, X.; Li, Q.; Li, Y.; Wang, X. Perfluoroalkyl substances in water, sediment, and fish from a subtropical river of China: Environmental behaviors and potential risk. Chemosphere 2022, 288, 132513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.; Choo, G.; Kim, H.; Oh, J.E. Evaluation of the current contamination status of PFASs and OPFRs in South Korean tap water associated with its origin. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 634, 1505–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Y.; Chen, C.E.; Zhang, D.; Tang, J. Emerging and legacy per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances in the rivers of a typical industrialized province of China: Spatiotemporal variations, mass discharges and ecological risks. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalonde, B.; Garron, C. Perfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs) in the Canadian Freshwater Environment. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2022, 82, 581–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semerád, J.; Hatasová, N.; Grasserová, A.; Černá, T.; Filipová, A.; Hanč, A.; Innemanová, P.; Pivokonský, M.; Cajthaml, T. Screening for 32 per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) including GenX in sludges from 43 WWTPs located in the Czech Republic—Evaluation of potential accumulation in vegetables after application of biosolids. Chemosphere 2020, 261, 128018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aro, R.; Eriksson, U.; Kärrman, A.; Chen, F.; Wang, T.; Yeung, L.W.Y. Fluorine Mass Balance Analysis of Effluent and Sludge from Nordic Countries. ACS ES&T Water 2021, 1, 2087–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredriksson, F.; Eriksson, U.; Kärrman, A.; Yeung, L.W.Y. Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in sludge from wastewater treatment plants in Sweden—First findings of novel fluorinated copolymers in Europe including temporal analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 846, 157406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenka, S.P.; Kah, M.; Padhye, L.P. Occurrence and fate of poly- and perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in urban waters of New Zealand. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 428, 128257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mussabek, D.; Söderman, A.; Imura, T.; Persson, K.M.; Nakagawa, K.; Ahrens, L.; Berndtsson, R. PFAS in the Drinking Water Source: Analysis of the Contamination Levels, Origin and Emission Rates. Water 2023, 15, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMahon, P.B.; Tokranov, A.K.; Bexfield, L.M.; Lindsey, B.D.; Johnson, T.D.; Lombard, M.A.; Watson, E. Perfluoroalkyl and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in Groundwater Used as a Source of Drinking Water in the Eastern United States. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 2279–2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www3.epa.gov/carbon-footprint-calculator/tool/definitions/crude-oil.html#:~:text=Crude%20oil%20means%20a%20mixture,passing%20through%20surface%20separating%20facilities (accessed on 12 May 2023).
- Yao, Y.; Meng, Y.; Chen, H.; Zhu, L.; Sun, H. Non-target discovery of emerging PFAS homologues in Dagang Oilfield: Multimedia distribution and profiles in crude oil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 437, 129300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, K.; Alygizakis, N.; Androulakakis, A.; Galani, A.; Aalizadeh, R.; Thomaidis, N.S.; Slobodnik, J. Target and suspect screening of 4777 per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in river water, wastewater, groundwater and biota samples in the Danube River Basin. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 436, 129276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moretti, S.; Barola, C.; Giusepponi, D.; Paoletti, F.; Piersanti, A.; Tcheremenskaia, O.; Brambilla, G.; Galarini, R. Target determination and suspect screening of legacy and emerging per- and poly-fluoro poly-ethers in wild boar liver, in Italy. Chemosphere 2023, 312, 137214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arioli, F.; Ceriani, F.; Nobile, M.; Vigano’, R.; Besozzi, M.; Panseri, S.; Chiesa, L.M. Presence of organic halogenated compounds, organophosphorus insecticides and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in meat of different game animal species from an Italian subalpine area. Food Addit. Contam. Part A Chem. Anal. Control Expo. Risk Assess. 2019, 36, 1244–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rupp, J.; Guckert, M.; Berger, U.; Drost, W.; Mader, A.; Nödler, K.; Nürenberg, G.; Schulze, J.; Söhlmann, R.; Reemtsma, T. Comprehensive target analysis and TOP assay of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in wild boar livers indicate contamination hot-spots in the environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 871, 162028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitter, G.; Da Re, F.; Canova, C.; Barbieri, G.; Jeddi, M.Z.; Daprà, F.; Manea, F.; Zolin, R.; Bettega, A.M.; Stopazzolo, G.; et al. Serum levels of perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in adolescents and young adults exposed to contaminated drinking water in the Veneto region, Italy: A cross-sectional study based on a health surveillance program. Environ. Health Perspect. 2020, 128, 027007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nilsson, S.; Smurthwaite, K.; Aylward, L.L.; Kay, M.; Toms, L.M.; King, L.; Marrington, S.; Barnes, C.; Kirk, M.D.; Mueller, J.F.; et al. Serum concentration trends and apparent half-lives of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in Australian firefighters. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2022, 246, 114040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotlarz, N.; McCord, J.; Collier, D.; Suzanne Lea, C.; Strynar, M.; Lindstrom, A.B.; Wilkie, A.A.; Islam, J.Y.; Matney, K.; Tarte, P.; et al. Measurement of novel, drinking water-associated pfas in blood from adults and children in Wilmington, North Carolina. Environ. Health Perspect. 2020, 128, 077005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graber, J.M.; Alexander, C.; Laumbach, R.J.; Black, K.; Strickland, P.O.; Georgopoulos, P.G.; Marshall, E.G.; Shendell, D.G.; Alderson, D.; Mi, Z.; et al. Per and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) blood levels after contamination of a community water supply and comparison with 2013–2014 NHANES. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2019, 29, 172–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genualdi, S.; Beekman, J.; Carlos, K.; Fisher, C.M.; Young, W.; DeJager, L.; Begley, T. Analysis of per- and poly-fluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in processed foods from FDA’s Total Diet Study. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2022, 414, 1189–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, B.M.; Bharat, G.K.; Tayal, S.; Larssen, T.; Bečanová, J.; Karásková, P.; Whitehead, P.G.; Futter, M.N.; Butterfield, D.; Nizzetto, L. Perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in river and ground/drinking water of the Ganges River basin: Emissions and implications for human exposure. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 208, 704–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reade, A.; Quinn, T.; Schreiber, J.S. PFAS in Drinking Water 2019: Scientific and Policy Assessment for Addressing Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) in Drinking Water; Natural Resources Defense Council: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 1–102. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, K.; Kim, S.; Kho, Y.; Sakong, J.; Paek, D.; Choi, K. Major perfluoroalkyl acid (PFAA) concentrations and influence of food consumption among the general population of Daegu, Korea. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 438, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Qu, Y.; Huang, J.; Weber, R. Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in Chinese drinking water: Risk assessment and geographical distribution. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2021, 33, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingo, J.L.; Ericson-Jogsten, I.; Perelló, G.; Nadal, M.; Van Bavel, B.; Kärrman, A. Human exposure to perfluorinated compounds in Catalonia, Spain: Contribution of drinking water and fish and shellfish. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 4408–4415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scher, D.P.; Kelly, J.E.; Huset, C.A.; Barry, K.M.; Hoffbeck, R.W.; Yingling, V.L.; Messing, R.B. Occurrence of perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in garden produce at homes with a history of PFAS-contaminated drinking water. Chemosphere 2018, 196, 548–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babayev, M.; Capozzi, S.L.; Miller, P.; McLaughlin, K.R.; Medina, S.S.; Byrne, S.; Zheng, G.; Salamova, A. PFAS in drinking water and serum of the people of a southeast Alaska community: A pilot study. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 305, 119246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Post, G.B. Invited Perspective: Current Breast Milk PFAS Levels in the United States and Canada Indicate Need for Additional Monitoring and Actions to Reduce Maternal Exposures. Environ. Health Perspect. 2022, 130, 2021–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, F.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Lyu, B.; Liu, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, Y. Occurrences of legacy and emerging per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in human milk in China: Results of the third National Human Milk Survey (2017–2020). J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 443, 130163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giari, L.; Guerranti, C.; Perra, G.; Cincinelli, A.; Gavioli, A.; Lanzoni, M.; Castaldelli, G. PFAS levels in fish species in the Po River (Italy): New generation PFAS, fish ecological traits and parasitism in the foreground. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 876, 162828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbo, N.; Stoiber, T.; Naidenko, O.V.; Andrews, D.Q. Locally caught freshwater fish across the United States are likely a significant source of exposure to PFOS and other perfluorinated compounds. Environ. Res. 2023, 220, 115165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, E.; Koponen, J.; Rantakokko, P.; Airaksinen, R.; Ruokojärvi, P.; Kiviranta, H.; Vuorinen, P.J.; Myllylä, T.; Keinänen, M.; Raitaniemi, J.; et al. Distribution of perfluoroalkyl acids in fish species from the Baltic Sea and freshwaters in Finland. Chemosphere 2022, 291, 132688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semerád, J.; Horká, P.; Filipová, A.; Kukla, J.; Holubová, K.; Musilová, Z.; Jandová, K.; Frouz, J.; Cajthaml, T. The driving factors of per- and polyfluorinated alkyl substance (PFAS) accumulation in selected fish species: The influence of position in river continuum, fish feed composition, and pollutant properties. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 816, 151662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stahl, L.L.; Snyder, B.D.; McCarty, H.B.; Kincaid, T.M.; Olsen, A.R.; Cohen, T.R.; Healey, J.C. Contaminants in fish from U.S. rivers: Probability-based national assessments. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 861, 160557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoa, N.T.Q.; Lieu, T.T.; Anh, H.Q.; Huong, N.T.A.; Nghia, N.T.; Chuc, N.T.; Quang, P.D.; Vi, P.T.; Tuyen, L.H. Perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in freshwater fish from urban lakes in Hanoi, Vietnam: Concentrations, tissue distribution, and implication for risk assessment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 52057–52069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rüdel, H.; Radermacher, G.; Fliedner, A.; Lohmann, N.; Koschorreck, J.; Duffek, A. Tissue concentrations of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in German freshwater fish: Derivation of fillet-to-whole fish conversion factors and assessment of potential risks. Chemosphere 2022, 292, 133483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Schyff, V.; Kwet Yive, N.S.C.; Polder, A.; Cole, N.C.; Bouwman, H. Perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in tern eggs from St. Brandon’s Atoll, Indian Ocean. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 154, 111061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikolajczyk, S.; Pajurek, M.; Warenik-Bany, M. Perfluoroalkyl substances in hen eggs from different types of husbandry. Chemosphere 2022, 303, 134950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, A.; Elliott, J.E.; Elliott, K.H.; Lee, S.; Cyr, F. Temporal trends of perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in eggs of coastal and offshore birds: Increasing PFAS levels associated with offshore bird species breeding on the Pacific coast of Canada and wintering near Asia. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2015, 34, 1799–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, M.G.; Lacorte, S.; Walker, L.A.; Shore, R.F. Contrasting long term temporal trends in perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in eggs of the northern gannet (Morus bassanus) from two UK colonies. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 754, 141900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.food.dtu.dk/english/news/pfas-found-in-organic-eggs-in-denmark?id=789f9ba1-bdfc-4a7d-908b-fc6cccff4742 (accessed on 12 May 2023).
- Androulakakis, A.; Alygizakis, N.; Gkotsis, G.; Nika, M.C.; Nikolopoulou, V.; Bizani, E.; Chadwick, E.; Cincinelli, A.; Claßen, D.; Danielsson, S.; et al. Determination of 56 per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in top predators and their prey from Northern Europe by LC-MS/MS. Chemosphere 2022, 287, 131775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galbiati, E.; Tietz, T.; Zellmer, S.; Merkel, S. Risk Assessment of Food Contact Materials II. EFSA J. 2022, 20, e200408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerch, M.; Nguyen, K.H.; Granby, K. Is the use of paper food contact materials treated with per- and polyfluorinated alkyl substances safe for high-temperature applications?—Migration study in real food and food simulants. Food Chem. 2022, 393, 133375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minet, L.; Wang, Z.; Shalin, A.; Bruton, T.A.; Blum, A.; Peaslee, G.F.; Schwartz-Narbonne, H.; Venier, M.; Whitehead, H.; Wu, Y.; et al. Use and release of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in consumer food packaging in U.S. and Canada. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2022, 24, 2032–2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz-Narbonne, H.; Xia, C.; Shalin, A.; Whitehead, H.D.; Yang, D.; Peaslee, G.F.; Wang, Z.; Wu, Y.; Peng, H.; Blum, A.; et al. Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in Canadian Fast Food Packaging. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2023, 10, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.C.; Dassuncao, C.; Zhang, X.; Grandjean, P.; Weihe, P.; Webster, G.M.; Nielsen, F.; Sunderland, E.M. Can profiles of poly- and Perfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in human serum provide information on major exposure sources? Environ. Health A Glob. Access Sci. Source 2018, 17, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Eon, J.C.; Mabury, S.A. Is indirect exposure a significant contributor to the burden of perfluorinated acids observed in humans? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 7974–7984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boronow, K.E.; Brody, J.G.; Schaider, L.A.; Peaslee, G.F.; Havas, L.; Cohn, B.A. Serum concentrations of PFASs and exposure-related behaviors in African American and non-Hispanic white women. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2019, 29, 206–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tittlemier, S.A.; Pepper, K.; Seymour, C.; Moisey, J.; Bronson, R.; Cao, X.L.; Dabeka, R.W. Dietary exposure of Canadians to perfluorinated carboxylates and perfluorooctane sulfonate via consumption of meat, fish, fast foods, and food items prepared in their packaging. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 3203–3210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaider, L.A.; Balan, S.A.; Blum, A.; Andrews, D.Q.; Strynar, M.J.; Dickinson, M.E.; Lunderberg, D.M.; Lang, J.R.; Peaslee, G.F. Fluorinated Compounds in U.S. Fast Food Packaging. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2017, 4, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susmann, H.P.; Schaider, L.A.; Rodgers, K.M.; Rudel, R.A. Dietary habits related to food packaging and population exposure to PFASs. Environ. Health Perspect. 2019, 127, 107003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richterová, D.; Govarts, E.; Fábelová, L.; Rausová, K.; Rodriguez Martin, L.; Gilles, L.; Remy, S.; Colles, A.; Rambaud, L.; Riou, M.; et al. PFAS levels and determinants of variability in exposure in European teenagers—Results from the HBM4EU aligned studies (2014–2021). Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2023, 247, 114057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zacs, D.; Bartkevics, V. Trace determination of perfluorooctane sulfonate and perfluorooctanoic acid in environmental samples (surface water, wastewater, biota, sediments, and sewage sludge) using liquid chromatography—Orbitrap mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1473, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, F.; Golovko, S.A.; Golovko, M.Y. Identification of novel non-ionic, cationic, zwitterionic, and anionic polyfluoroalkyl substances using UPLC–TOF–MS E high-resolution parent ion search. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 988, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, Z.Y.; Kim, K.Y.; Oh, J.E. The occurrence and distributions of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in groundwater after a PFAS leakage incident in 2018. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 268, 115395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janda, J.; Nödler, K.; Brauch, H.J.; Zwiener, C.; Lange, F.T. Robust trace analysis of polar (C2–C8) perfluorinated carboxylic acids by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry: Method development and application to surface water, groundwater and drinking water. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 7326–7336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Available online: https://phenomenex.blob.core.windows.net/documents/7dc5a613-2fbf-4664-bed6-d0dc4f8ca05c.pdf (accessed on 12 May 2023).
- Available online: https://www.restek.com/globalassets/pdfs/literature/EVAN3220A-UNV.pdf (accessed on 12 May 2023).
- Gobelius, L.; Persson, C.; Wiberg, K.; Ahrens, L. Calibration and application of passive sampling for per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in a drinking water treatment plant. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 362, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaserzon, S.L.; Vijayasarathy, S.; Bräunig, J.; Mueller, L.; Hawker, D.W.; Thomas, K.V.; Mueller, J.F. Calibration and validation of a novel passive sampling device for the time integrative monitoring of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) and precursors in contaminated groundwater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 366, 423–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woudneh, M.B.; Chandramouli, B.; Hamilton, C.; Grace, R. Effect of Sample Storage on the Quantitative Determination of 29 PFAS: Observation of Analyte Interconversions during Storage. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 12576–12585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, N.; Wen, H.; Wang, X.; Yamazaki, E.; Taniyasu, S.; Yamashita, N.; Yu, H.; Wei, S. Nontarget Discovery of Per- And Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in Atmospheric Particulate Matter and Gaseous Phase Using Cryogenic Air Sampler. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 3103–3113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, F.; Gehrenkemper, L.; von der Au, M.; Wittwer, P.; Roesch, P.; Pfeifer, J.; Cossmer, A.; Meermann, B. A fast and simple PFAS extraction method utilizing HR–CS–GFMAS for soil samples. Chemosphere 2022, 295, 133922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, G.R. PFAS in soil and groundwater following historical land application of biosolids. Water Res. 2022, 211, 118035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniyasu, S.; Yeung, L.W.Y.; Lin, H.; Yamazaki, E.; Eun, H.; Lam, P.K.S.; Yamashita, N. Quality assurance and quality control of solid phase extraction for PFAS in water and novel analytical techniques for PFAS analysis. Chemosphere 2022, 288, 132440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassazzi, W.; Lai, F.Y.; Ahrens, L. A novel method for extraction, clean-up and analysis of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in different plant matrices using LC-MS/MS. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2022, 1212, 123514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drábová, L.; Dvořáková, D.; Urbancová, K.; Gramblička, T.; Hajšlová, J.; Pulkrabová, J. Critical Assessment of Clean-Up Techniques Employed in Simultaneous Analysis of Persistent Organic Pollutants and Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Fatty Samples. Toxics 2022, 10, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, R.B.; Sapozhnikova, Y. Comparison and validation of the QuEChERSER mega-method for determination of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in foods by liquid chromatography with high-resolution and triple quadrupole mass spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2022, 1230, 340400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallocchio, F.; Moressa, A.; Zonta, G.; Angeletti, R.; Lega, F. Fast and Sensitive Analysis of Short- and Long-Chain Perfluoroalkyl Substances in Foods of Animal Origin. Molecules 2022, 27, 7899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askeland, M.; Clarke, B.; Paz-Ferreiro, J. A serial PFASs sorption technique coupled with adapted high volume direct aqueous injection LCMS method. MethodsX 2020, 7, 100886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piva, E.; Fais, P.; Cecchetto, G.; Montisci, M.; Viel, G.; Pascali, J.P. Determination of perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in human hair by liquid chromatography-high accurate mass spectrometry (LC-QTOF). J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2021, 1172, 122651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, U.; Haukås, M. Validation of a screening method based on liquid chromatography coupled to high-resolution mass spectrometry for analysis of perfluoroalkylated substances in biota. J. Chromatogr. A 2005, 1081, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Getzinger, G.J.; Higgins, C.P.; Ferguson, P.L. Structure Database and in Silico Spectral Library for Comprehensive Suspect Screening of Per- And Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs) in Environmental Media by High-resolution Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 2820–2827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, P.; Yue, Z.; Zheng, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Li, W.; Zhao, F.; Xiao, C.; Bai, R.; Lin, W. Determination of perfluoroalkyl acids in lamb liver by high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry combined with dispersive solid phase extraction. Chin. J. Chromatogr. 2015, 33, 494–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mottaleb, M.A.; Ding, Q.X.; Pennell, K.G.; Haynes, E.N.; Morris, A.J. Direct injection analysis of per and polyfluoroalkyl substances in surface and drinking water by sample filtration and liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2021, 1653, 462426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Wang, Q.; Chen, H.; Li, M. Rapid quantitative analysis and suspect screening of per-and polyfluorinated alkyl substances (PFASs) in aqueous film-forming foams (AFFFs) and municipal wastewater samples by Nano-ESI-HRMS. Water Res. 2022, 219, 118542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodds, J.N.; Hopkins, Z.R.; Knappe, D.R.U.; Baker, E.S. Rapid Characterization of Per- And Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) by Ion Mobility Spectrometry-Mass Spectrometry (IMS-MS). Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 4427–4435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, T.W.; Scheibly, C.M.; Polera, M.E.; Belcher, S.M. Rapid Characterization of Human Serum Albumin Binding for Per- And Polyfluoroalkyl Substances Using Differential Scanning Fluorimetry. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 12291–12301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.; Yang, K.A.; Choi, Y.; Choe, J.K. Novel ssDNA aptamer-based fluorescence sensor for perfluorooctanoic acid detection in water. Environ. Int. 2022, 158, 107000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Cui, D.; Ng, B.; Ogunbiyi, O.D.; De Navarro, M.G.; Gardinali, P.; Quinete, N. Non-targeted Analysis for the Screening and Semi-quantitative Estimates of Per-and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in Water Samples From South Florida Environments. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 452, 131224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickman, R.A.; Aga, D.S. Efficient workflow for suspect screening analysis to characterize novel and legacy per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in biosolids. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2022, 414, 4497–4507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunzelmann, M.; Winter, M.; Åberg, M.; Hellenäs, K.E.; Rosén, J. Non-targeted analysis of unexpected food contaminants using LC-HRMS. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 5593–5602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Pike, K.A.; Gray, R.; Sprankle, J.W.; Faust, J.A.; Edmiston, P.L. Non-targeted identification and semi-quantitation of emerging per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in US rainwater. In Environmental Science: Processes & Impacts; The Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2023; pp. 2050–7887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.M.; Zhao, S.; Hussain, D.; Chen, J.L.; Luo, D.; Wei, F.; Wang, X. Fluoro-cotton assisted non-targeted screening of organic fluorine compounds from rice (Oryza sativa L.) grown in perfluoroalkyl substance polluted soil. Environ. Res. 2023, 216, 114801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renai, L.; Del Bubba, M.; Samanipour, S.; Stafford, R.; Gargano, A.F.G. Development of a comprehensive two-dimensional liquid chromatographic mass spectrometric method for the non-targeted identification of poly- and perfluoroalkyl substances in aqueous film-forming foams. Anal. Chim. Acta 2022, 1232, 340485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, R.B.; Pica, N.E.; Sharifan, H.; Chen, H.; Roth, H.K.; Blakney, G.T.; Borch, T.; Higgins, C.P.; Kornuc, J.J.; McKenna, A.M.; et al. PFAS Analysis with Ultrahigh Resolution 21T FT-ICR MS: Suspect and Nontargeted Screening with Unrivaled Mass Resolving Power and Accuracy. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 2455–2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamari, N.L.A.; Dohmann, J.F.; Raab, A.; Krupp, E.M.; Feldmann, J. Novel non-targeted analysis of perfluorinated compounds using fluorine-specific detection regardless of their ionisability (HPLC-ICPMS/MS-ESI-MS). Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1053, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).