Lightweight YOLOv5s Human Ear Recognition Based on MobileNetV3 and Ghostnet
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Related Works
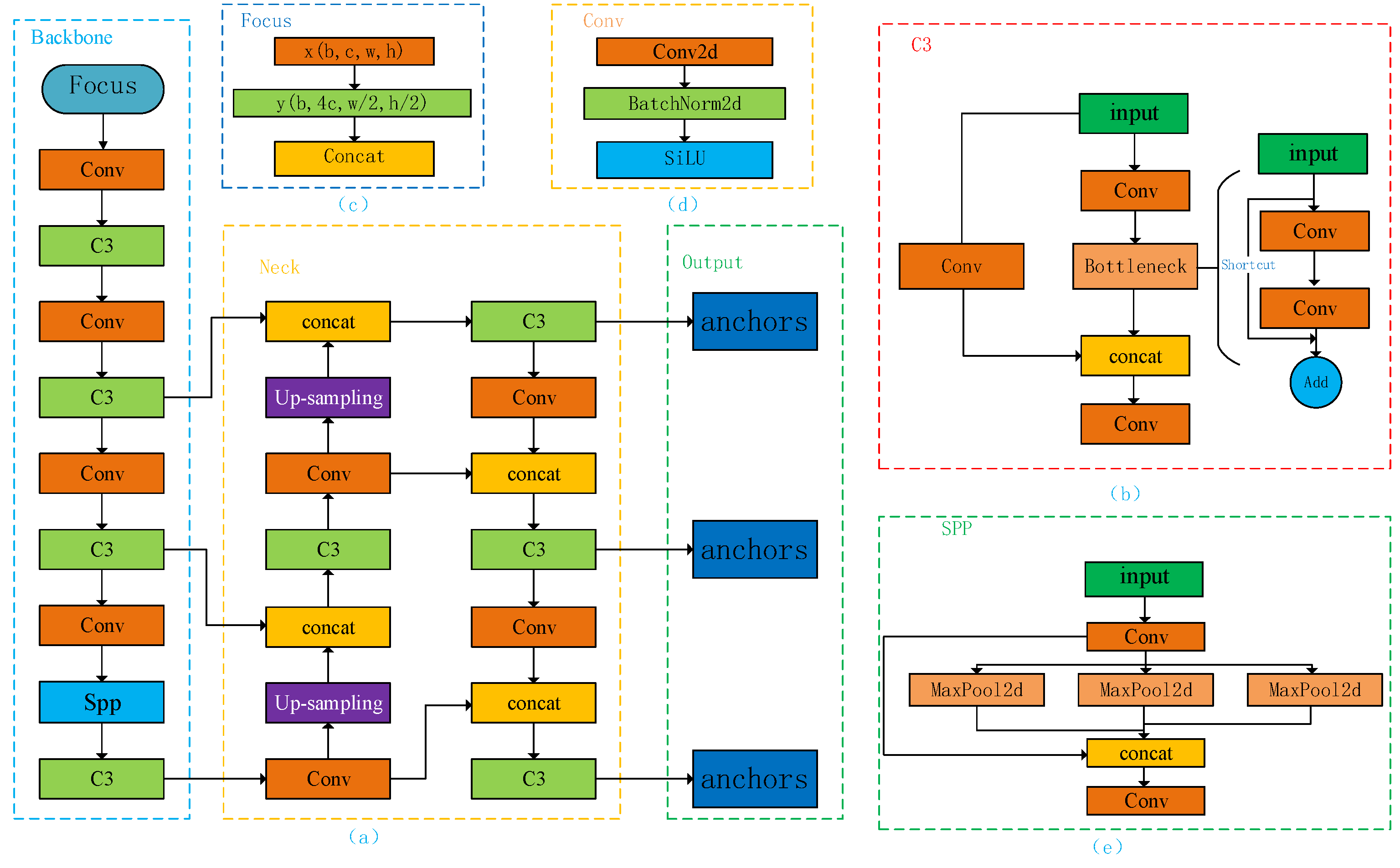
2.1. YOLOv5s
2.2. Lightweight Network
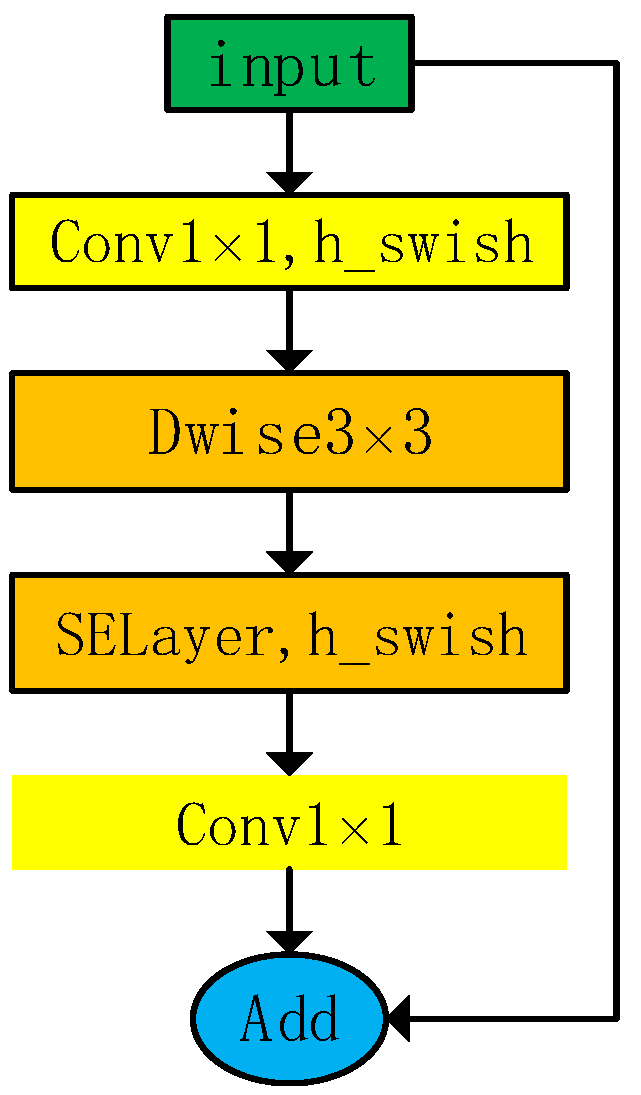
2.2.1. MobileNetV3
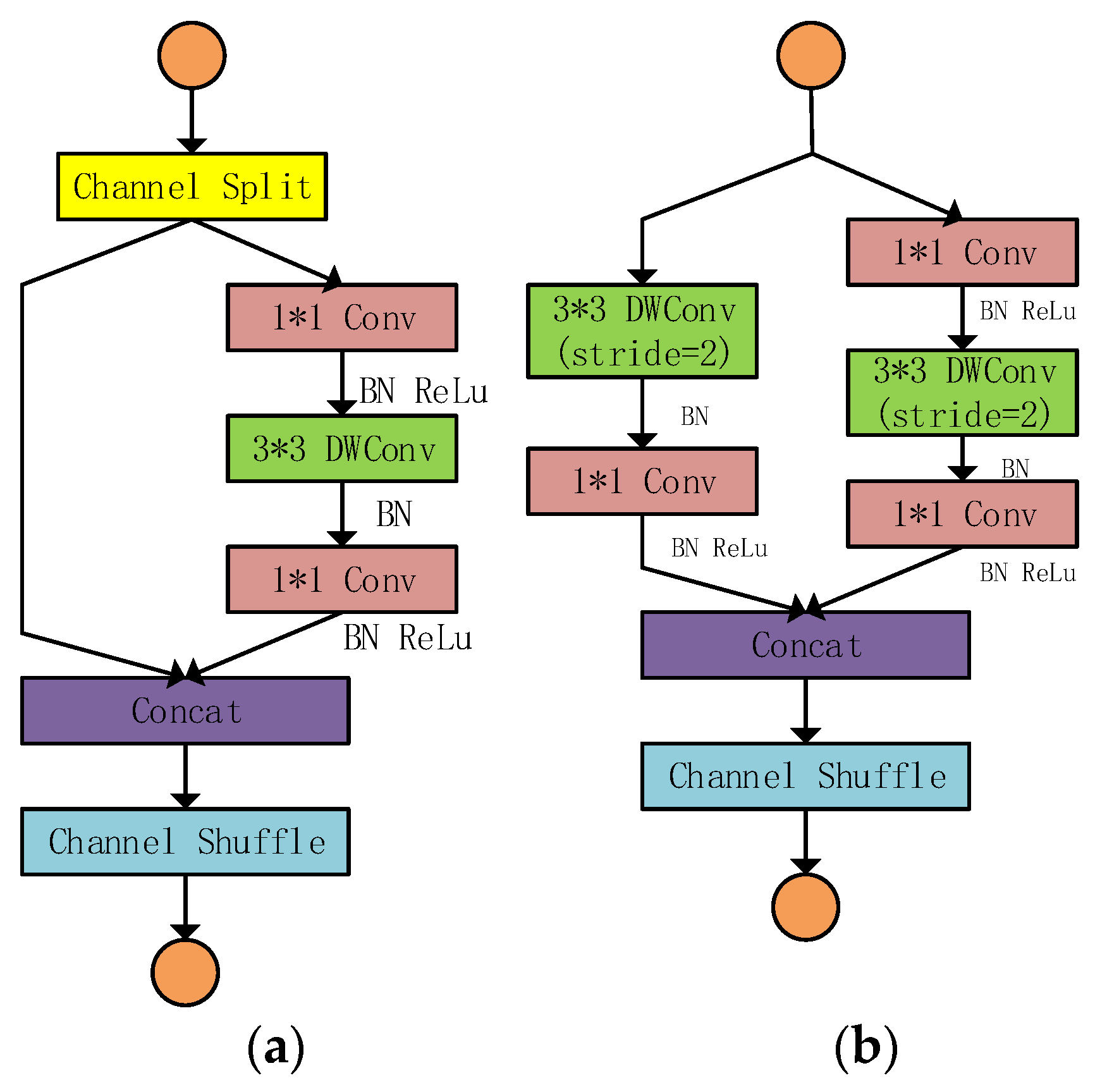
2.2.2. ShuffleNetv2
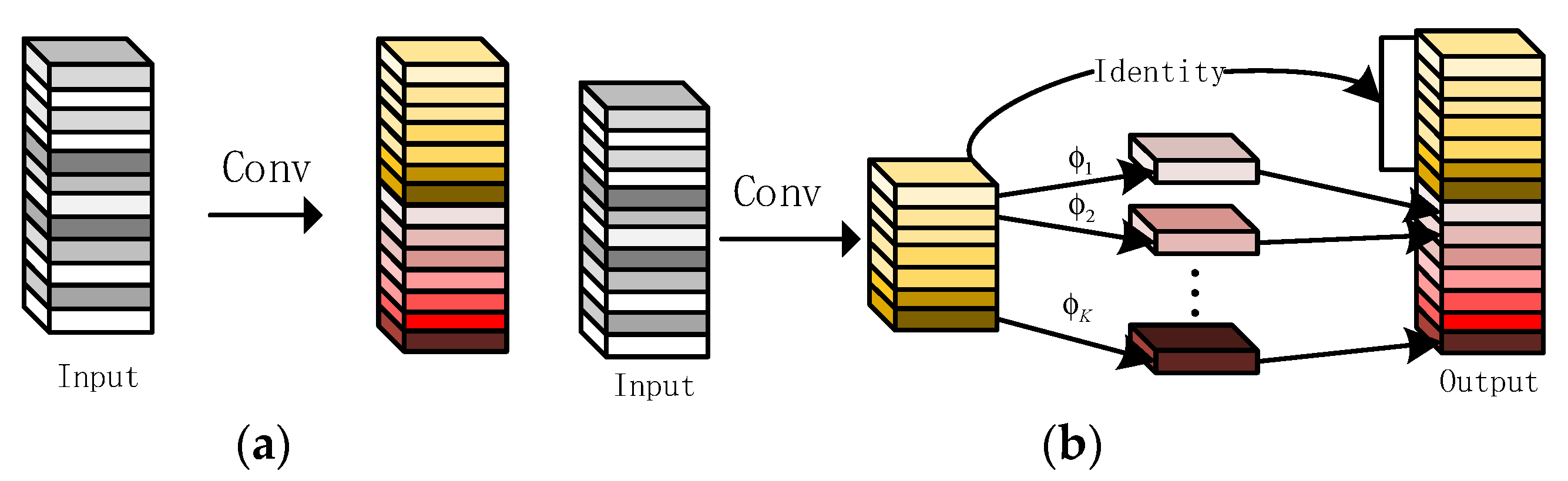
2.2.3. GhostNet
3. Proposed Method
3.1. Lightweight of YOLOv5s Backbone Network Based on MobileNetV3
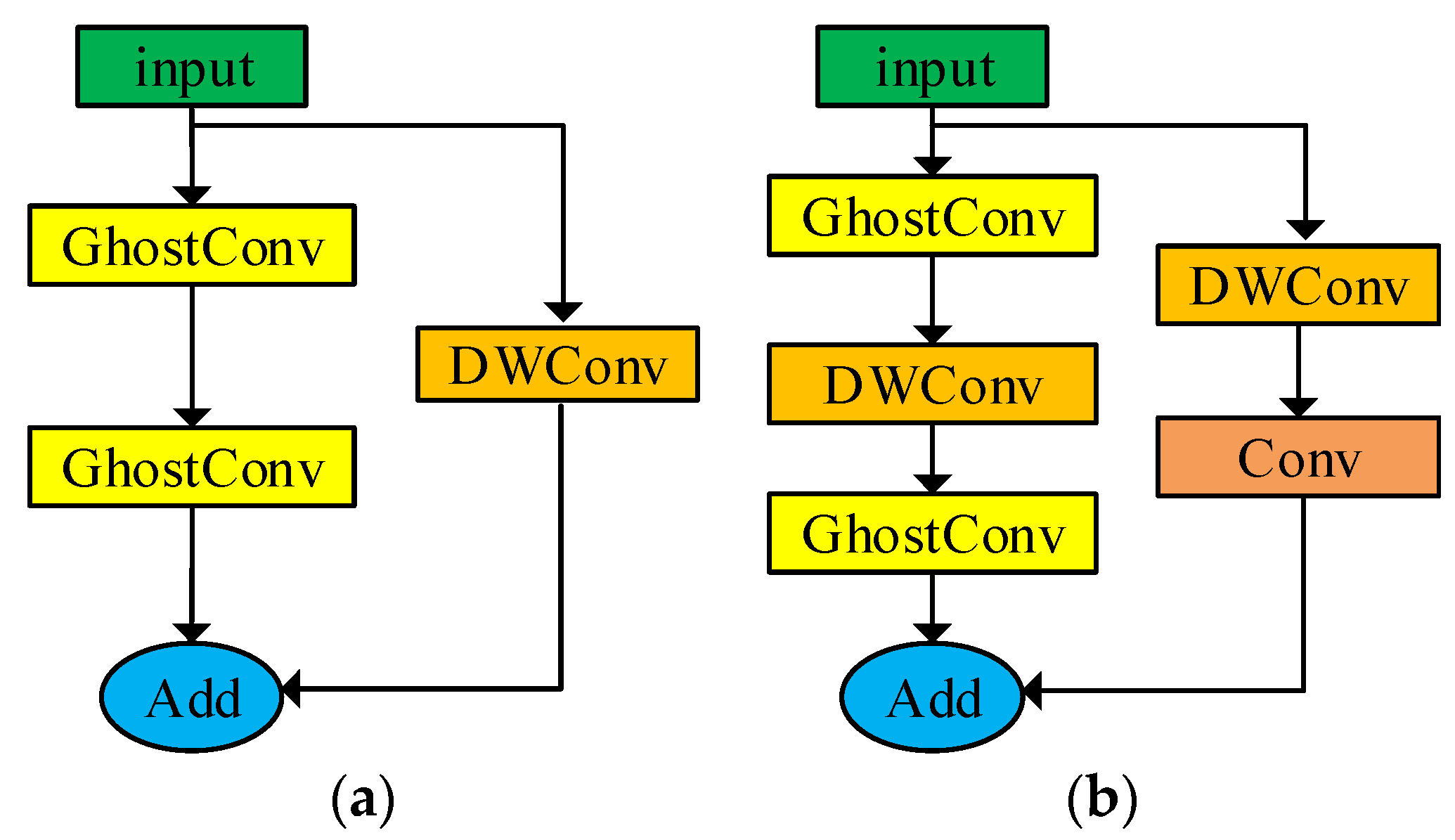
3.2. Lightweight of YOLOv5s Neck Network Based on Ghostnet
4. Experimental Results
4.1. Human Ear Datasets
4.1.1. CCU-DE
4.1.2. USTB
4.1.3. EarVN1.0
4.2. Experimental Setting
4.3. Evaluation Indicators
4.3.1. mAP
- Classification target division result;
- 2.
- Precision and Recall;
- 3.
- Average precision (AP) and mean average precision (mAP);
4.3.2. Model Parameter Quantity (Params/M)
4.3.3. Amount of Calculation (GFLOPS/G)
4.3.4. Model Size (MB)
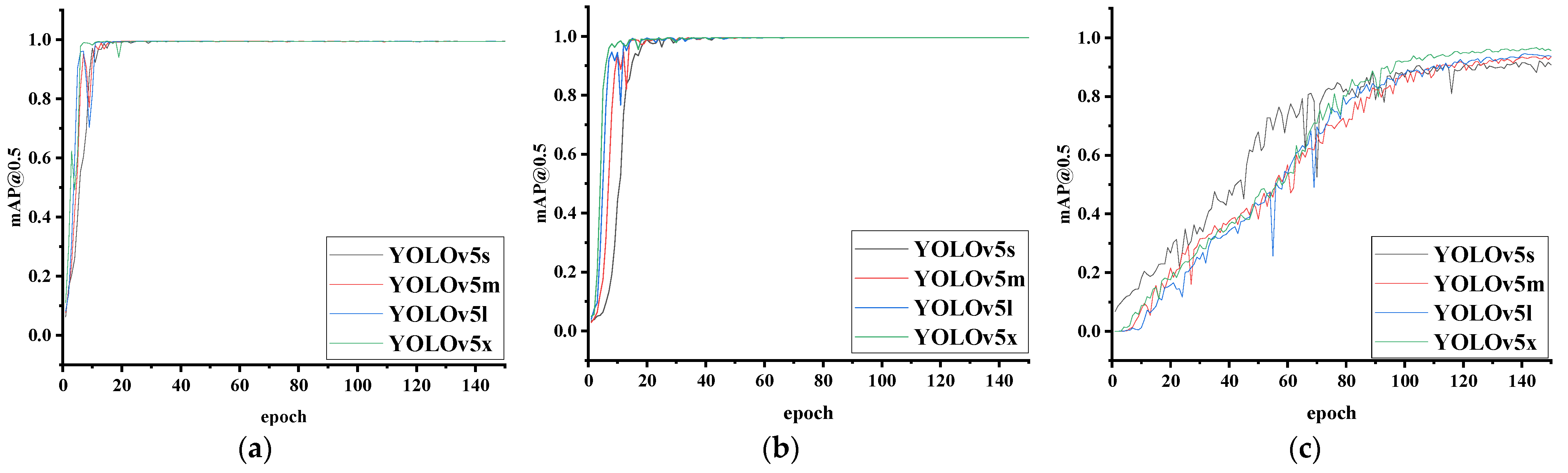
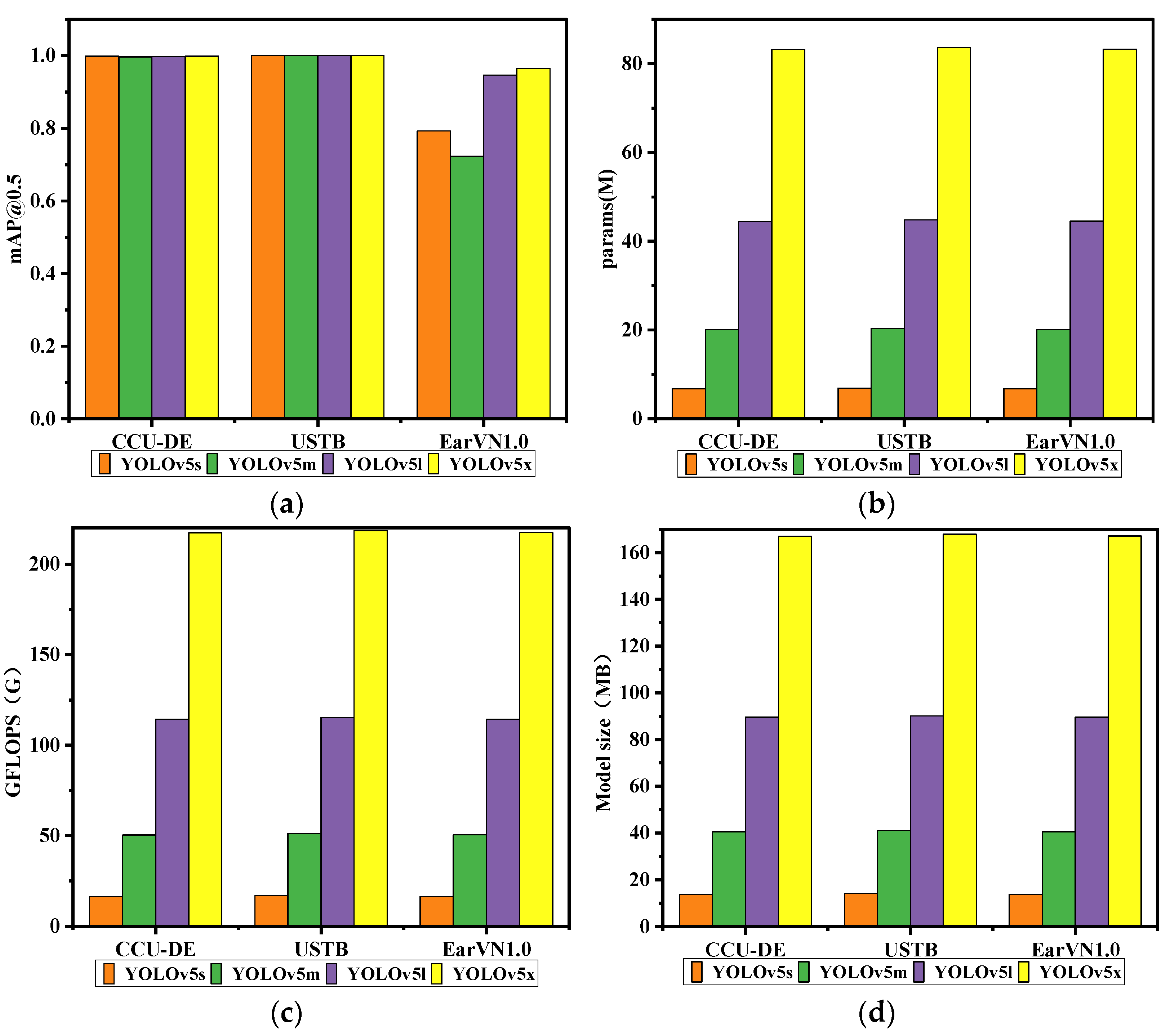
4.4. Ear Recognition Experiments of Four YOLOv5 Models on Three Datasets
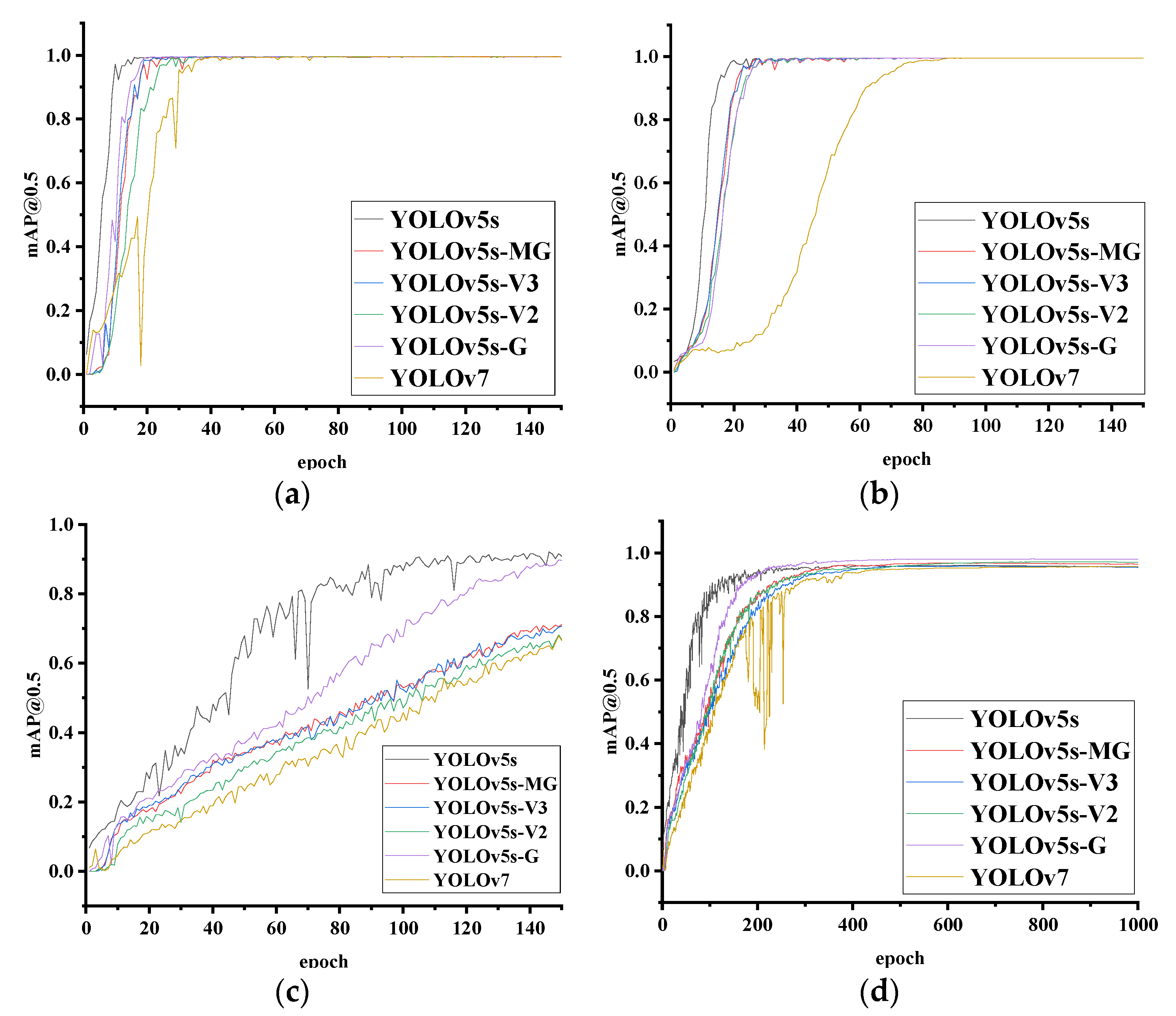
4.5. Ear Recognition Experiments of the Improved YOLOv5s-MG on Three Datasets
4.6. The Computational Complexity Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jain, A.K.; Pankanti, S.; Prabhakar, S.; Lin, H.; Ross, A. Biometrics: A grand challenge. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Pattern Recognition, Cambridge, UK, 26 August 2004; Volume 2, pp. 935–942. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.N. Research on Ear Recognition Based on Deep Learning. Master’s Thesis, University of Science and Technology Liaoning, Anshan, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, Y.M. Research on Ear Recognition Based on Improved Sparse Representation. Master’s Thesis, Harbin University of Science and Technology, Harbin, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.P.; Su, G.D. Summary of Face Recognition Technology. J. Image Graph. 2000, 11, 7–16. [Google Scholar]
- Sakthimohan, M.; Rani, G.E.; Navaneethkrihnan, M.; Janani, K.; Nithva, V.; Pranav, R. Detection and Recognition of Face Using Deep Learning. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Intelligent Systems for Communication, IoT and Security (ICISCoIS), Coimbatore, India, 9–11 February 2023; pp. 72–76. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, S.D. Research on the Fingerprint Identification Technology and Attendance System Application. Master’s Thesis, Nanjing University of Posts and Telecommunications, Nanjing, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, M. Overview of Fingerprint Identification Technology Development. China Sci. Technol. Inf. 2011, 13, 70. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.L.; Wang, H.B.; Tao, L. Multi-feature recognition of palm vein and palm print in single near-infrared palm image. Comput. Eng. Appl. 2018, 54, 156–164+236. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.H. Research and Implementation of Iris Recognition Key Problems. Master’s Thesis, Jilin University, Changchun, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Jiao, X.H. Research and Implementation of Iris Authentication Technology Based on Embedded. Master’s Thesis, Heilongjiang University, Harbin, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y. Ear Detection and Recognition under Uncontrolled Conditions Based on Deep Learning Algorithm. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Science and Technology Beijing, Beijing, China, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, A.; Zhang, D. Ear authentication using log-Gabor wavelets. Biometric Technology for Human Identification IV. Int. Soc. Opt. Photonics 2007, 6539, 65390A. [Google Scholar]
- AsmaaSabet, A.; Kareem Kamal A, G.; Hesham, E. Human Ear Recognition Using SIFT Features. In Proceedings of the 2015 Third World Conference on Complex Systems (WCCS), Marrakech, Morocco, 23–25 November 2015; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Nosrati, M.S.; Faez, K.; Faradji, F. Using 2D wavelet and principal component analysis for personal identification based on 2D ear structure. In Proceedings of the 2007 International Conference on Intelligent and Advanced Systems, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 25–28 November 2007; pp. 616–620. [Google Scholar]
- Omara, I.; Li, X.M.; Xiao, G.; Adil, K.; Zuo, W. Discriminative local feature fusion for ear recognition problem. In Proceedings of the 2018 8th International Conference on Bioscience, Biochemistry and Bioinformatics (ICBBB 2018), Association for Computing Machinery, New York, NY, USA, 18–21 January 2018; pp. 139–145. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, C.X.; Mu, Z.C.; Xie, J.J. Multi-pose ear recognition based on LLE. J. Intell. Syst. 2008, 4, 321–327. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, Y.L.; Gai, S.Y.; Zheng, D.L. Fast 3D ear recognition based on local and global information. J. Instrum. 2019, 40, 99–106. [Google Scholar]
- Susan, E. Ear Detection in the Wild using Faster R-CNN. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/ACM International Conference on Advances in Social Networks Analysis and Mining (ASONAM), Barcelona, Spain, 28–31 August 2018; pp. 1124–1130. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, Y.M.; Du, B.W.; Qian, J.R.; Feng, Z.B. Research on Ear Recognition Based on SSD_MobileNet_v1 Network. In Proceedings of the 2020 Chinese Automation Congress (CAC), Shanghai, China, 6–8 November 2020; pp. 4371–4376. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, J.R. Research on Dynamic Human Ear Recognition Method Based on Deep Learning. Master’s Thesis, Chang Chun University, Changchun, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, J. Research on Target Identification Method Based on Human Ear Detection Technology. Master’s Thesis, ChangChun University, Changchun, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Redmon, J.; Divvala, S.; Girshick, R.; Farhadi, A. You only look once: Unified real-time object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 779–788. [Google Scholar]
- Redmon, J.; Farhadi, A. YOLO9000: Better, Faster, Stronger. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 6517–6525. [Google Scholar]
- Redmon, J.; Farhadi, A. YOLOv3: An Incremental Improvement. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.02767. [Google Scholar]
- Bochkovskiy, A.; Wang, C.Y.; Liao, H.Y.M. YOLOv4: Optimal Speed and Accuracy of Object Detection. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.10934. [Google Scholar]
- Jirarat, I.; Surapon, N.C.; Suchart, Y. Deep Learning-based Face Mask Detection Using YoloV5. In Proceedings of the 2021 9th International Electrical Engineering Congress, Pattaya, Thailand, 10–12 March 2021; pp. 428–431. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Li, L.; Jiang, H.; Weng, K.; Geng, Y.; Li, L.; Ke, Z.; Li, Q.; Cheng, M.; Nie, W.; et al. YOLOv6: A single-stage object detection framework for industrial applications. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2209.02976. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.Y.; Bochkovskiy, A.; Liao, H.Y.M. YOLOv7: Trainable bag-of-freebies sets new state-of-the-art for real-time object detectors. arXiv 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, R.Y.; Cai, W.M. Fracture Detection in Pediatric Wrist Trauma X-ray Images Using YOLOv8 Algorithm; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Howard, A.; Sandler, M.; Chu, G.; Chen, L.C.; Chen, B.; Tan, M.X.; Wang, W.J.; Zhu, Y.K.; Pang, R.M.; Vasudevan, V. Searching for MobileNetV3. International Conference on Computer Vision. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 1314–1324. [Google Scholar]
- Han, K.; Wang, Y.; Tian, Q.; Guo, J.; Xu, C.; Xu, C. GhostNet: More Features from Cheap Operations. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 1577–1586. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, N.N.; Zhang, X.Y.; Zheng, H.-T.; Sun, J. ShuffleNet V2: Practical Guidelines for Efficient CNN Architecture Design. Comput. Vis. ECCV 2018, 2018, 122–138. [Google Scholar]
- Howard, A.G.; Zhu, M.; Chen, B.; Kalenichenko, D.; Wang, W.; Weyand, T.; Andreetto, M.; Adam, H. MobileNets: Efficient Convolutional Neural Networks for Mobile Vision Applications. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1704.04861. [Google Scholar]
- Sandler, M.; Howard, A.; Zhu, M. MobileNetV2: Inverted Residuals and Linear Bottlenecks. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 4510–4520. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Zhou, X.; Lin, M. ShuffleNet: An Extremely Efficient Convolutional Neural Network for Mobile Devices. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 6848–6856. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, Y.; Qian, J.; Pan, D.; Xu, T. Research on Small Sample Dynamic Human Ear Recognition Based on Deep Learning. Sensors 2022, 22, 1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: http://www1.ustb.edu.cn/resb/visit/visit.htm (accessed on 30 December 2021).
- Hoang, V.T. EarVN1.0: A new large-scale ear images dataset in the wild. Sci. Direct 2019, 27, 104630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.H.; Pan, L.H.; Yang, F.; Zhang, R. Improved YOLOv5 lightweight mask detection algorithm. Comput. Eng. Appl. 2023, 59, 232–241. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, K.; Liu, X.; Ja, L.J.; Fang, Y.L.; Zhao, C.X. Insulator Defect Detection Based on Lightweight Network and Enhanced Multi-scale Feature. High Volt. Eng. 2023, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, P.; Yang, K.J.; Liang, C. Improved YOLOv5 algorithm for real-time detection of irregular driving behavior. Comput. Eng. Appl. 2023, 1–9. Available online: http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.2127.TP.20230206.1311.003.html (accessed on 6 February 2023).


| Version | YOLOv5s | YOLOv5m | YOLOv5l | YOLOv5x |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| depth multiple (DM) | 0.33 | 0.67 | 1.0 | 1.33 |
| width multiple (WM) | 0.50 | 0.75 | 1.0 | 1.25 |
| No. | Version | YOLOv5s | YOLOv5m | YOLOv5l | YOLOv5x | Version | YOLOv5s | YOLOv5m | YOLOv5l | YOLOv5x |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st | C3-3 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | Focus (Conv-64) | 32 | 48 | 64 | 80 |
| 2nd | C3-9 | 3 | 6 | 9 | 12 | Conv-128 | 64 | 96 | 128 | 160 |
| 3rd | C3-9 | 3 | 6 | 9 | 12 | Conv-256 | 128 | 192 | 256 | 320 |
| 4th | C3-3 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | Conv-512 | 256 | 384 | 512 | 640 |
| 5th | C3-3 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | Conv-1024 | 512 | 768 | 1024 | 1280 |
| 6th | C3-3 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | Conv-256 | 128 | 192 | 256 | 320 |
| 7th | C3-3 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | Conv-512 | 256 | 384 | 512 | 640 |
| 8th | C3-3 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | Conv-256 | 128 | 192 | 256 | 320 |
| Layers | Operator | Exp Size | SE | NL | S | Layers | Operator | Exp Size | SE | NL | S |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Conv2d | 16 | - | HS | 2 | 11 | Bneck, 3 × 3 | 184 | - | HS | 1 |
| 2 | Bneck, 3 × 3 | 16 | - | RE | 1 | 12 | Bneck, 3 × 3 | 480 | √ | HS | 1 |
| 3 | Bneck, 3 × 3 | 64 | - | RE | 2 | 13 | Bneck, 3 × 3 | 672 | √ | HS | 1 |
| 4 | Bneck, 3 × 3 | 72 | - | RE | 1 | 14 | Bneck, 5 × 5 | 672 | √ | HS | 2 |
| 5 | Bneck, 5 × 5 | 72 | √ | RE | 2 | 15 | Bneck, 5 × 5 | 960 | √ | HS | 1 |
| 6 | Bneck, 5 × 5 | 120 | √ | RE | 1 | 16 | Bneck, 5 × 5 | 960 | √ | HS | 1 |
| 7 | Bneck, 5 × 5 | 120 | √ | RE | 1 | 17 | conv2d, 1 × 1 | - | - | HS | 1 |
| 8 | Bneck, 3 × 3 | 240 | - | HS | 2 | 18 | Pool, 7 × 7 | - | - | HS | 1 |
| 9 | Bneck, 3 × 3 | 200 | - | HS | 1 | 19 | conv2d 1 × 1, NBN | - | - | - | 1 |
| 10 | Bneck, 3 × 3 | 184 | - | RE | 1 | 20 | conv2d 1 × 1, NBN | - | - | HS | 1 |
| Layers | Operator | Exp Size | SE | NL | S | Layers | Operator | Exp Size | SE | NL | S |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Conv2d, 3 × 3 | 16 | - | HS | 2 | 9 | Bneck, 5 × 5 | 48 | √ | HS | 1 |
| 2 | Bneck, 3 × 3 | 16 | √ | RE | 2 | 10 | Bneck, 5 × 5 | 96 | √ | HS | 2 |
| 3 | Bneck, 3 × 3 | 24 | - | RE | 2 | 11 | Bneck, 5 × 5 | 96 | √ | HS | 1 |
| 4 | Bneck, 3 × 3 | 24 | - | RE | 1 | 12 | Bneck, 5 × 5 | 96 | √ | HS | 1 |
| 5 | Bneck, 5 × 5 | 40 | √ | HS | 2 | 13 | conv2d, 1 × 1 | 576 | √ | HS | 1 |
| 6 | Bneck, 5 × 5 | 40 | √ | HS | 1 | 14 | Pool, 7 × 7 | - | - | HS | 1 |
| 7 | Bneck, 5 × 5 | 40 | √ | HS | 1 | 15 | conv2d 1 × 1, NBN | 1024 | - | HS | 1 |
| 8 | Bneck, 5 × 5 | 48 | √ | HS | 1 | 16 | conv2d 1 × 1, NBN | K | - | HS | 1 |
| Database | Shooting Situation |
|---|---|
| Eardata1 | Static human ear fixed-point shooting |
| Eardata2 | Video of human ears moving in translation with the human body when the human body is walking normally at different angles |
| Eardata3 | Video of the photographed standing in the shooting center doing a 90° uniform rotation motion |
| Eardata4 | Video of the photographed standing in the shooting center doing a 180° uniform rotation motion |
| Eardata5 | Dynamic human ear video with interference information |
| Database | Category | Left Ear (NF) | Right Ear (NF) | Total (NF) | Size of the Picture |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eardata4 | ear1 | 153 | 135 | 288 | 1280 × 720 |
| Eardata3 | ear25 | 111 | 139 | 250 | |
| Eardata3 | ear26 | 112 | 154 | 266 | |
| Eardata4 | ear27 | 249 | 156 | 405 | |
| Eardata4 | ear28 | 96 | 106 | 202 | |
| Eardata4 | ear29 | 163 | 188 | 351 | |
| Eardata4 | ear30 | 156 | 124 | 280 | |
| Eardata4 | ear31 | 203 | 186 | 389 | |
| Eardata4 | ear32 | 175 | 182 | 357 | |
| Eardata4 | ear33 | 235 | 251 | 486 | |
| total | 1653 | 1621 | 3274 |
| Category | Attitude Change | Size | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 70 | 0° | 5° | −5° | 10° | −10° | 20° | −20° | flip left and right | enhancement | 768 × 576 | ||
| contrast | brightness | color | ||||||||||
| Human Ear Dataset | Data Size | Attitude Change | Resolution | Category | Status | Gender |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CCU-DE | 3274 | richest | highest | 10 | dynamic | female and male |
| USTB | 7700 | richer | higher | 70 | static | female and male |
| EarVN1.0 | 3201 | richest | uneven | 15 | static | female and male |
| Name | Configuration |
|---|---|
| CPU | IntelI CoreIi5-10400F CPU@2.90GHZ |
| Memory | 16 GB |
| GPU | NVIDIA GeFORCE RTX 3060 |
| GPU-accelerated library | CUDA11.1.134, CUDNN8.0.5 |
| Operating system | Windows10(64bit) |
| Software environment | pytorch1.8, python3.8 |
| Dataset partitioning | Training set:validation set:test set = 3:1:1 |
| Name | Configuration |
|---|---|
| Initial learning rate | 0.01 |
| Learning rate reduction coefficient | 0.2 |
| Weight attenuation coefficient | 0.0005 |
| Momentum coefficient | 0.937 |
| Optimizer | SGD with momentum |
| Batch size | 16 |
| Human Ear Dataset | Model | Params (M) | GFLOPS(G) | Model Size (MB) | mAP@0.5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CCU-DE (epoch = 150) | YOLOv5s | 6.75 | 16.4 | 13.7 | 0.999 |
| YOLOv5m | 20.1 | 50.4 | 40.55 | 0.997 | |
| YOLOv5l | 44.49 | 114.2 | 89.5 | 0.998 | |
| YOLOv5x | 83.22 | 217.3 | 167 | 0.999 | |
| USTB (epoch = 150) | YOLOv5s | 6.9 | 16.9 | 14.07 | 1 |
| YOLOv5m | 20.32 | 51.2 | 41.03 | 1 | |
| YOLOv5l | 44.79 | 115.3 | 90.09 | 1 | |
| YOLOv5x | 83.60 | 218.6 | 167.85 | 1 | |
| EarVN1.0 (epoch = 150) | YOLOv5s | 6.76 | 16.4 | 13.7 | 0.793 |
| YOLOv5m | 20.12 | 50.5 | 40.5 | 0.723 | |
| YOLOv5l | 44.51 | 114.3 | 89.5 | 0.947 | |
| YOLOv5x | 83.25 | 217.4 | 167.1 | 0.965 |
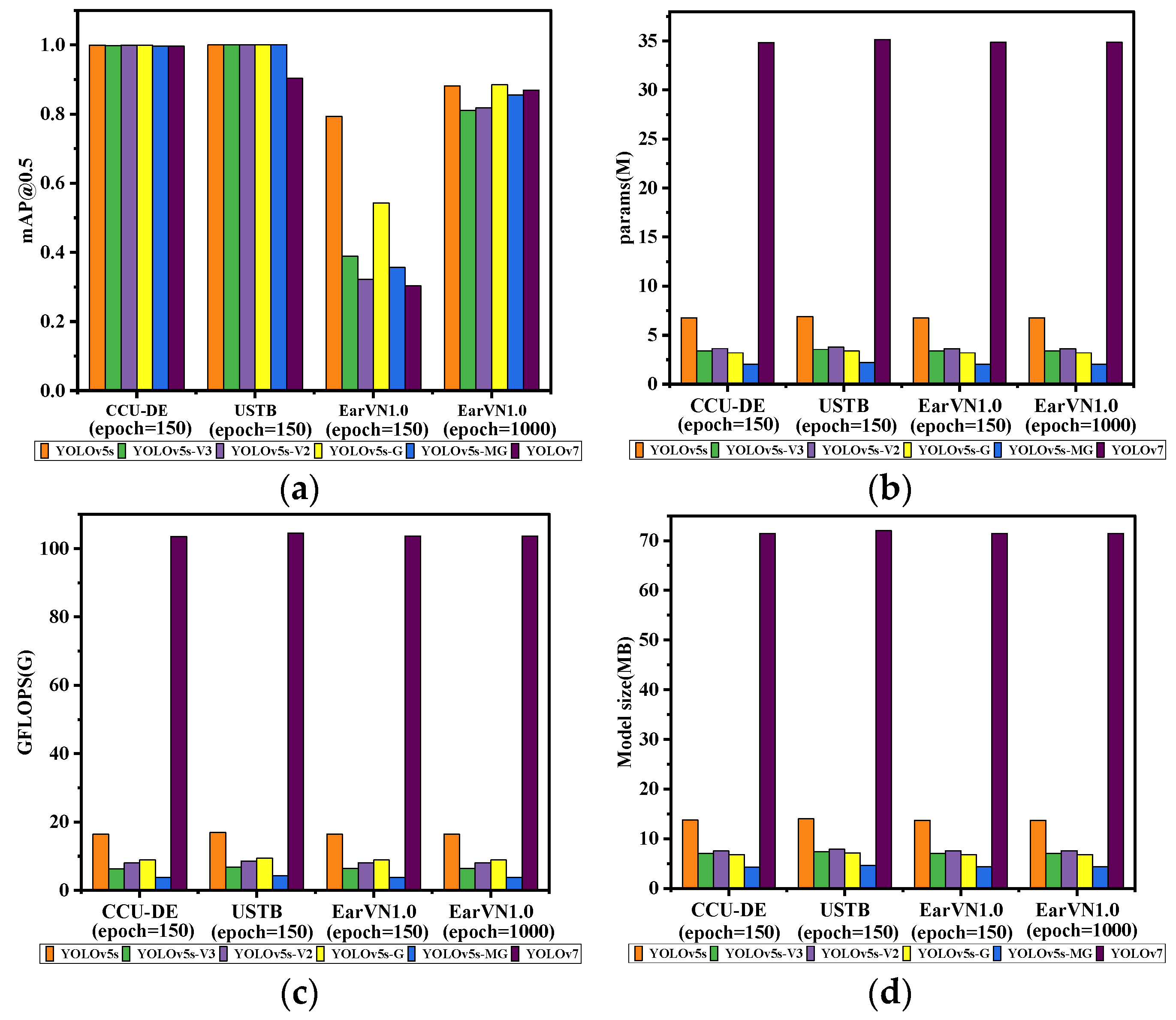
| Human Ear Dataset | Model | Params (M) | GFLOPS (G) | Model Size (MB) | mAP@0.5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CCU-DE (epoch = 150) | YOLOv5s | 6.75 | 16.4 | 13.7 | 0.999 |
| YOLOv5s-V3 [39] | 3.39 | 6.3 | 7.04 | 0.998 | |
| YOLOv5s-V2 [40] | 3.63 | 8 | 7.56 | 0.999 | |
| YOLOv5s-G [41] | 3.2 | 8.9 | 6.8 | 0.999 | |
| YOLOv5s-MG | 2.05 | 3.7 | 4.3 | 0.997 | |
| YOLOv7 | 34.84 | 103.5 | 71.41 | 0.993 | |
| USTB (epoch = 150) | YOLOv5s | 6.9 | 16.9 | 14.07 | 1 |
| YOLOv5s-V3 [39] | 3.55 | 6.8 | 7.37 | 1 | |
| YOLOv5s-V2 [40] | 3.79 | 8.5 | 7.88 | 1 | |
| YOLOv5s-G [41] | 3.4 | 9.4 | 7.14 | 1 | |
| YOLOv5s-MG | 2.2 | 4.2 | 4.6 | 1 | |
| YOLOv7 | 35.14 | 104.5 | 72.04 | 0.904 | |
| EarVN1.0 (epoch = 150) | YOLOv5s | 6.76 | 16.4 | 13.7 | 0.793 |
| YOLOv5s-V3 [39] | 3.4 | 6.4 | 7.05 | 0.389 | |
| YOLOv5s-V2 [40] | 3.6 | 8 | 7.57 | 0.322 | |
| YOLOv5s-G [41] | 3.2 | 8.9 | 6.82 | 0.543 | |
| YOLOv5s-MG | 2.06 | 3.7 | 4.34 | 0.356 | |
| YOLOv7 | 34.86 | 103.6 | 71.45 | 0.303 | |
| EarVN1.0 (epoch = 1000) | YOLOv5s | 6.76 | 16.4 | 13.7 | 0.882 |
| YOLOv5s-V3 [39] | 3.4 | 6.4 | 7.05 | 0.811 | |
| YOLOv5s-V2 [40] | 3.6 | 8 | 7.57 | 0.818 | |
| YOLOv5s-G [41] | 3.2 | 8.9 | 6.82 | 0.885 | |
| YOLOv5s-MG | 2.06 | 3.7 | 4.34 | 0.855 | |
| YOLOv7 | 34.86 | 103.6 | 71.45 | 0.869 |
| Human Ear Dataset | Model | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv5s | YOLOv5s-V3 | YOLOv5s-V2 | YOLOv5s-G | YOLOv5s-MG | YOLOv7 | |
| CCU-DE (epoch = 150) | 6.7 | 12 | 10.5 | 8 | 14.5 | 1 |
| USTB (epoch = 150) | 4.6 | 7.5 | 6.2 | 5.5 | 8.5 | 1.3 |
| EarVN1.0 (epoch = 150) | 5.7 | 9.6 | 8.1 | 6.7 | 11.2 | 1.1 |
| EarVN1.0 (epoch = 1000) | 5.8 | 9.7 | 8.3 | 6.8 | 11.4 | 1.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lei, Y.; Pan, D.; Feng, Z.; Qian, J. Lightweight YOLOv5s Human Ear Recognition Based on MobileNetV3 and Ghostnet. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 6667. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13116667
Lei Y, Pan D, Feng Z, Qian J. Lightweight YOLOv5s Human Ear Recognition Based on MobileNetV3 and Ghostnet. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(11):6667. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13116667
Chicago/Turabian StyleLei, Yanmin, Dong Pan, Zhibin Feng, and Junru Qian. 2023. "Lightweight YOLOv5s Human Ear Recognition Based on MobileNetV3 and Ghostnet" Applied Sciences 13, no. 11: 6667. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13116667
APA StyleLei, Y., Pan, D., Feng, Z., & Qian, J. (2023). Lightweight YOLOv5s Human Ear Recognition Based on MobileNetV3 and Ghostnet. Applied Sciences, 13(11), 6667. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13116667







