The Interplay of Exogenous and Endogenous Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S) in Maintaining Redox Homeostasis in Individuals with Low Ferritin Levels
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Ferritin Levels and the Frequency of Spring Visits
2.2. Sulfide and Thiol Measurement in Plasma
2.3. Lipid Peroxidation and Total Oxidative Stress Measurement
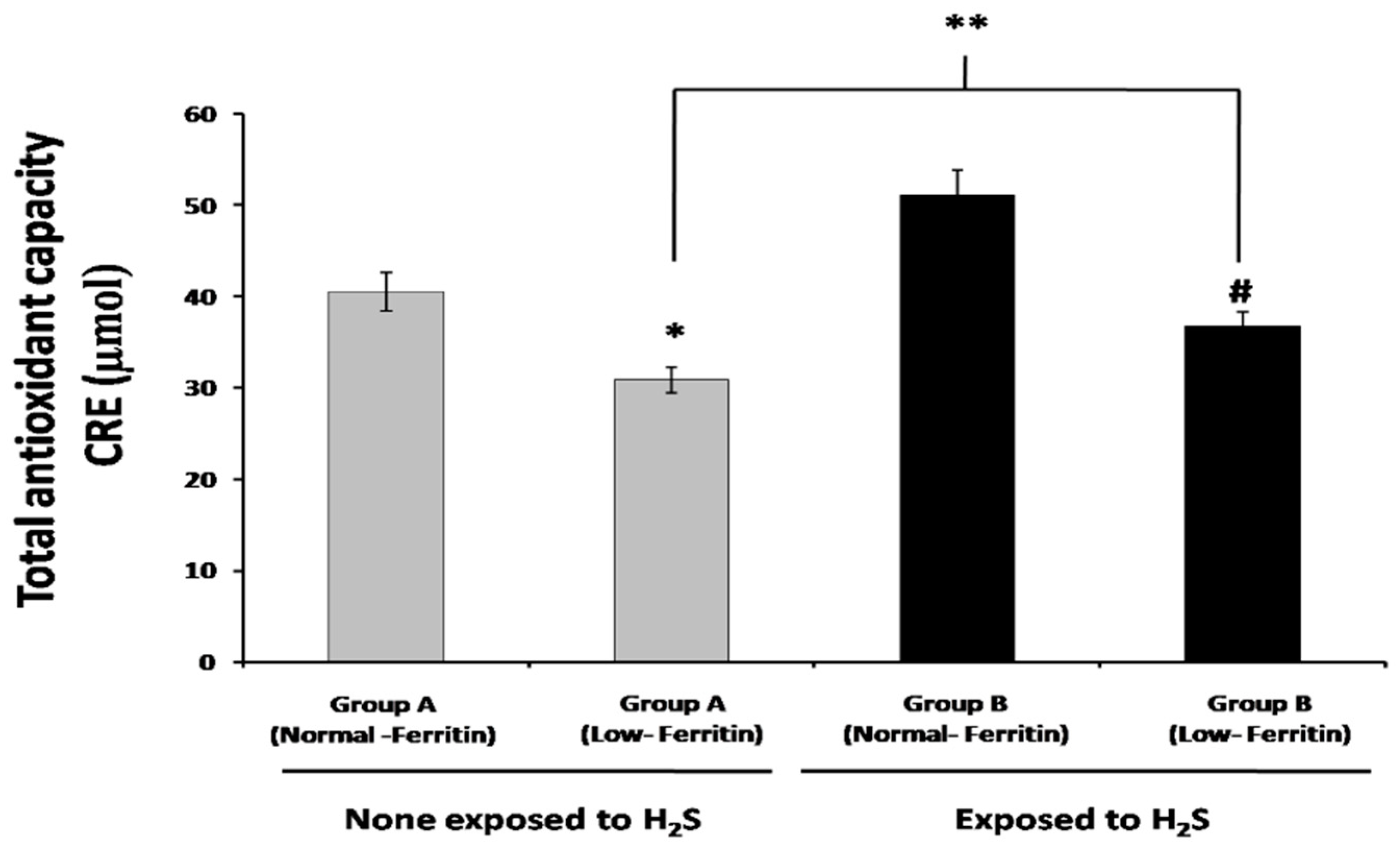
2.4. Total Antioxidant Capacity
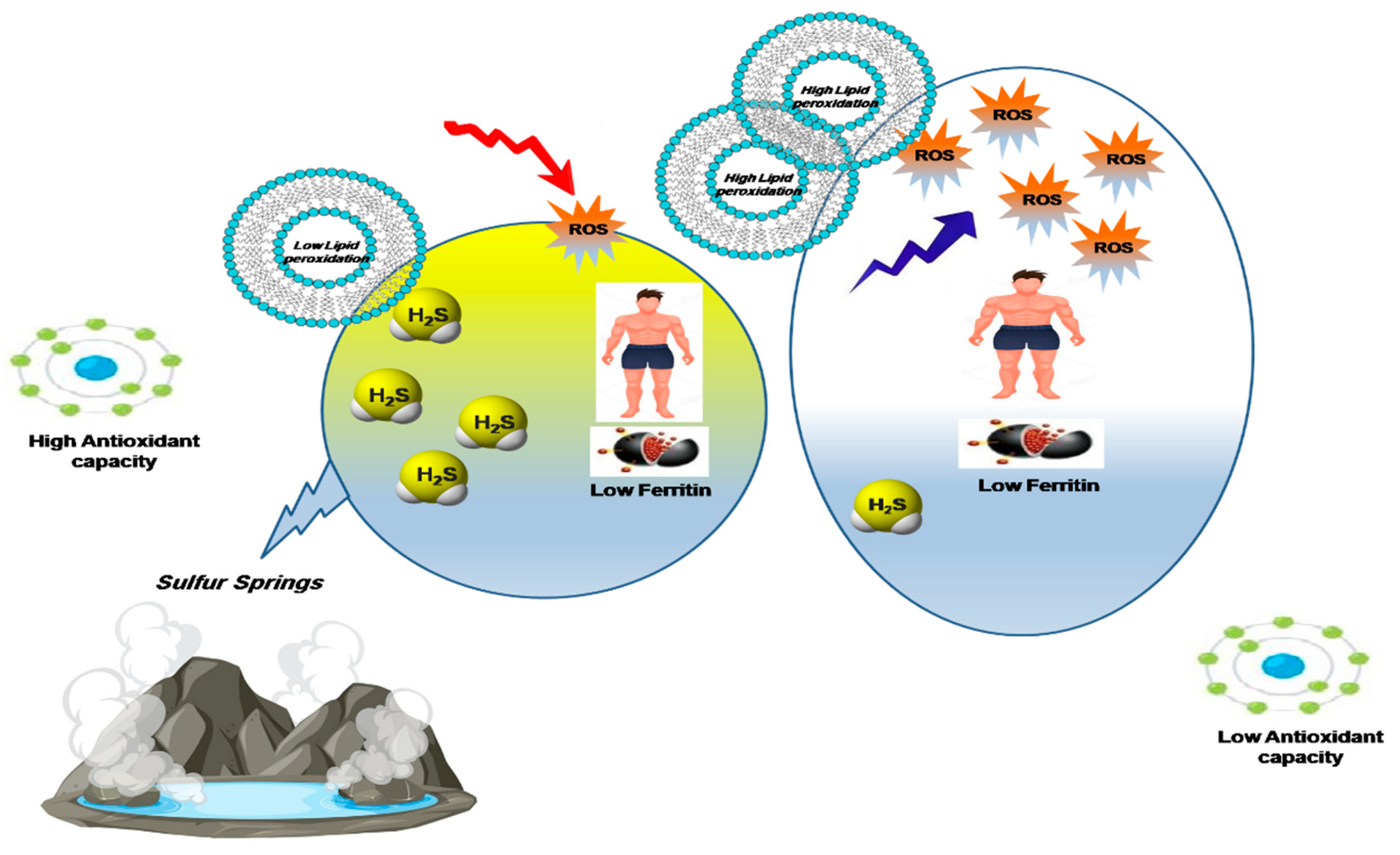
3. Discussion
Limitation and Perspective of the Study
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Participants
4.2. Plasma H2S-Sulphide Measurement
4.3. Antioxidant Capacity Total Oxidative Stress Measurement
4.4. Total Sulfhydryl Group/Total Thiol (-SH) Measurement
4.5. Lipid Peroxidation Determination
4.6. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, R.U.I. Two’s company, three’s a crowd: Can H2S be the third endogenous gaseous transmitter? FASEB J. 2002, 16, 1792–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altaany, Z.; Moccia, F.; Munaron, L.; Mancardi, D.; Wang, R. Hydrogen sulfide and endothelial dysfunction: Relationship with nitric oxide. Curr. Med. Chem. 2014, 21, 3646–3661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R. Physiological implications of hydrogen sulfide: A whiff exploration that blossomed. Physiol. Rev. 2012, 92, 791–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altaany, Z.; Yang, G.; Wang, R. Crosstalk between hydrogen sulfide and nitric oxide in endothelial cells. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2013, 17, 879–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, H. Signaling molecules: Hydrogen sulfide and polysulfide. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2015, 22, 362–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubright, S.L.M.; Pearce, L.L.; Peterson, J. Environmental toxicology of hydrogen sulfide. Nitric Oxide 2017, 71, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.Z.; Liu, Y.; Bian, J.S. Hydrogen Sulfide and Cellular Redox Homeostasis. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 6043038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendran, P.; Nandakumar, N.; Rengarajan, T.; Palaniswami, R.; Gnanadhas, E.N.; Lakshminarasaiah, U.; Gopas, J.; Nishigaki, I. Antioxidants and human diseases. Clin. Chim. Acta 2014, 436, 332–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouayed, J.; Bohn, T. Exogenous antioxidants—Double-edged swords in cellular redox state: Health beneficial effects at physiologic doses versus deleterious effects at high doses. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2010, 3, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Q.; Ying, J.; Xiang, L.; Zhang, C. The biologic effect of hydrogen sulfide and its function in various diseases. Medicine 2018, 97, e13065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corsello, T.; Komaravelli, N.; Casola, A. Role of Hydrogen Sulfide in NRF2- and Sirtuin-Dependent Maintenance of Cellular Redox Balance. Antioxidants 2018, 7, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asif, M.; Manzoor, Z.; Farooq, M.S.; Munawar, S.H.; Aziz, A.; Khan, I.A. Status of oxidant, antioxidantand serum enzymes in thalassaemic children receiving multiple blood transfusions. J. Pak. Med. Assoc. 2015, 65, 838–843. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Aust, S.D.; Morehouse, L.A.; Thomas, C.E. Role of metals in oxygen radical reactions. J. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 1985, 1, 3–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Ceci, P.; Ilari, A.; Giangiacomo, L.; Laue, T.M.; Chiancone, E.; Chasteen, N.D. Iron and hydrogen peroxide detoxification properties of DNA-binding protein from starved cells. A ferritin-like DNA-binding protein of Escherichia coli. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 27689–27696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theil, E.C.; Matzapetakis, M.; Liu, X. Ferritins: Iron/oxygen biominerals in protein nanocages. J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2006, 11, 803–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aisen, P.; Listowsky, I. Iron transport and storage proteins. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1980, 49, 357–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rockey, D.C.; Cello, J.P. Evaluation of the gastrointestinal tract in patients with iron-deficiency anemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 1993, 329, 1691–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaka-Ur-Rab, Z. Effect of Oral Iron on Markers of Oxidative Stress and Antioxidant Status in Children with Iron Deficiency Anaemia. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2016, 10, sc13–sc19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isler, M.; Delibas, N.; Guclu, M.; Gultekin, F.; Sutcu, R.; Bahceci, M.; Kosar, A. Superoxide dismutase and glutathione peroxidase in erythrocytes of patients with iron deficiency anemia: Effects of different treatment modalities. Croat. Med. J. 2002, 43, 16–19. [Google Scholar]
- Kurtoğlu, E.; Ugur, A.; Baltaci, A.K.; Undar, L. Effect of iron supplementation on oxidative stress and antioxidant status in iron-deficiency anemia. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2003, 96, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiteman, M.; Cheung, N.S.; Zhu, Y.Z.; Chu, S.H.; Siau, J.L.; Wong, B.S.; Armstrong, J.S.; Moore, P.K. Hydrogen sulphide: A novel inhibitor of hypochlorous acid-mediated oxidative damage in the brain? Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 326, 794–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, V.K.; Bandyopadhyay, P.; Singh, A. Hydrogen sulfide in physiology and pathogenesis of bacteria and viruses. IUBMB Life 2018, 70, 393–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wedmann, R.; Onderka, C.; Wei, S.; Szijártó, I.A.; Miljkovic, J.L.; Mitrovic, A.; Lange, M.; Savitsky, S.; Yadav, P.K.; Torregrossa, R.; et al. Improved tag-switch method reveals that thioredoxin acts as depersulfidase and controls the intracellular levels of protein persulfidation. Chem. Sci. 2016, 7, 3414–3426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halliwell, B.; Gutteridge, J.M. Role of iron in oxygen radical reactions. Methods Enzymol. 1984, 105, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Imam, M.U.; Zhang, S.; Ma, J.; Wang, H.; Wang, F. Antioxidants Mediate Both Iron Homeostasis and Oxidative Stress. Nutrients 2017, 9, 671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sies, H. Oxidative stress: A concept in redox biology and medicine. Redox Biol. 2015, 4, 180–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, H. Hydrogen sulfide: Its production and functions. Exp. Physiol. 2011, 96, 833–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, K.; Kimura, H. The possible role of hydrogen sulfide as an endogenous neuromodulator. J. Neurosci. 1996, 16, 1066–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valko, M.; Leibfritz, D.; Moncol, J.; Cronin, M.T.D.; Mazur, M.; Telser, J. Free radicals and antioxidants in normal physiological functions and human disease. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2007, 39, 44–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, A.; Aponte-Mellado, A.; Premkumar, B.J.; Shaman, A.; Gupta, S. The effects of oxidative stress on female reproduction: A review. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2012, 10, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabo, C.; Papapetropoulos, A. International Union. of Basic. and Clinical Pharmacology. CII: Pharmacological Modulation of H2S Levels: H2S Donors and H2S Biosynthesis Inhibitors. Pharmacol. Rev. 2017, 69, 497–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, E.; Mbowe, O.; Lee, A.S.W.; Davis, J. Effect of environmental exposure to hydrogen sulfide on central nervous system and respiratory function: A systematic review of human studies. Int. J. Occup. Environ. Health 2016, 22, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olas, B.; Kontek, B. Hydrogen sulfide decreases the plasma lipid peroxidation induced by homocysteine and its thiolactone. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2015, 404, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papapetropoulos, A.; Pyriochou, A.; Altaany, Z.; Yang, G.; Marazioti, A.; Zhou, Z.; Jeschke, M.G.; Branski, L.K.; Herndon, D.N.; Wang, R.; et al. Hydrogen sulfide is an endogenous stimulator of angiogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 21972–21977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marutani, E.; Ichinose, F. Emerging pharmacological tools to control hydrogen sulfide signaling in critical illness. Intensive Care Med. Exp. 2020, 8, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powell, C.R.; Dillon, K.M.; Matson, J.B. A review of hydrogen sulfide (H2S) donors: Chemistry and potential therapeutic applications. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2018, 149, 110–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, S.S.; Dahiru, M.; Abdullahi, B.; Abdullahi, S.B.; Maigari, U.M.; Uba, A.I. Status of malondialdehyde, catalase and superoxide dismutase levels/activities in schoolchildren with iron deficiency and iron-deficiency anemia of Kashere and its environs in Gombe State, Nigeria. Heliyon 2019, 5, e02214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumerova, A.; Lece, A.; Skesters, A.; Silova, A.; Petuhovs, V. Anaemia and antioxidant defence of the red blood cells. Mater. Med. Pol. 1998, 30, 12–15. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, J.H.; Kim, D.K.; Kim, H.W.; Park, S.Y.; Yoo, T.-H.; Kim, B.S.; Kang, S.-W.; Choi, K.H.; Han, D.-S.; Jeong, H.J.; et al. Changing prevalence of glomerular diseases in Korean adults: A review of 20 years of experience. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2009, 24, 2406–2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohkawa, H.; Ohishi, N.; Yagi, K. Assay for lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal. Biochem. 1979, 95, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Group A (Control Area) | Group B (Exposed to H2S Area) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 37 | 38 | 40 | 40 |
| Gender | Female: 89 Male: 11 | Female: 81 Male: 19 | Female: 77 Male: 23 | Female: 86 Male: 14 |
| Ferritin levels (ng/mL) | 6.57 ± 0.22 | 87.51 ± 4.99 | 6.18 ± 0.32 | 91.65 ± 0.22 |
| Number of visits (times/year) * | ~2–3 | ~2–3 | ~10–12 | ~10–12 |
| Duration of each visit (hrs) * | ~2–3 | ~2–3 | ~2–3 | ~2–3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Altaany, Z.; Alkaraki, A.; Abo Alrob, O.; Taani, O.; Khatatbeh, M. The Interplay of Exogenous and Endogenous Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S) in Maintaining Redox Homeostasis in Individuals with Low Ferritin Levels. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 6621. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13116621
Altaany Z, Alkaraki A, Abo Alrob O, Taani O, Khatatbeh M. The Interplay of Exogenous and Endogenous Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S) in Maintaining Redox Homeostasis in Individuals with Low Ferritin Levels. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(11):6621. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13116621
Chicago/Turabian StyleAltaany, Zaid, Almuthanna Alkaraki, Osama Abo Alrob, Omar Taani, and Moawiah Khatatbeh. 2023. "The Interplay of Exogenous and Endogenous Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S) in Maintaining Redox Homeostasis in Individuals with Low Ferritin Levels" Applied Sciences 13, no. 11: 6621. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13116621
APA StyleAltaany, Z., Alkaraki, A., Abo Alrob, O., Taani, O., & Khatatbeh, M. (2023). The Interplay of Exogenous and Endogenous Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S) in Maintaining Redox Homeostasis in Individuals with Low Ferritin Levels. Applied Sciences, 13(11), 6621. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13116621






