Antioxidant and Hypoglycemic Activity of Sacha Inchi Meal Protein Hydrolysate
Abstract
Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Protein Extraction
2.3. Enzymatic Hydrolysis
2.4. Molecular Weight Distribution
2.5. Antioxidant Activity
2.6. Inhibitory Activity of α-Amylase
2.7. Inhibitory Activity of Dipeptidyl Peptidase (DPP-IV)
2.8. Inhibitory Type of Hydrolysates on DPP-IV
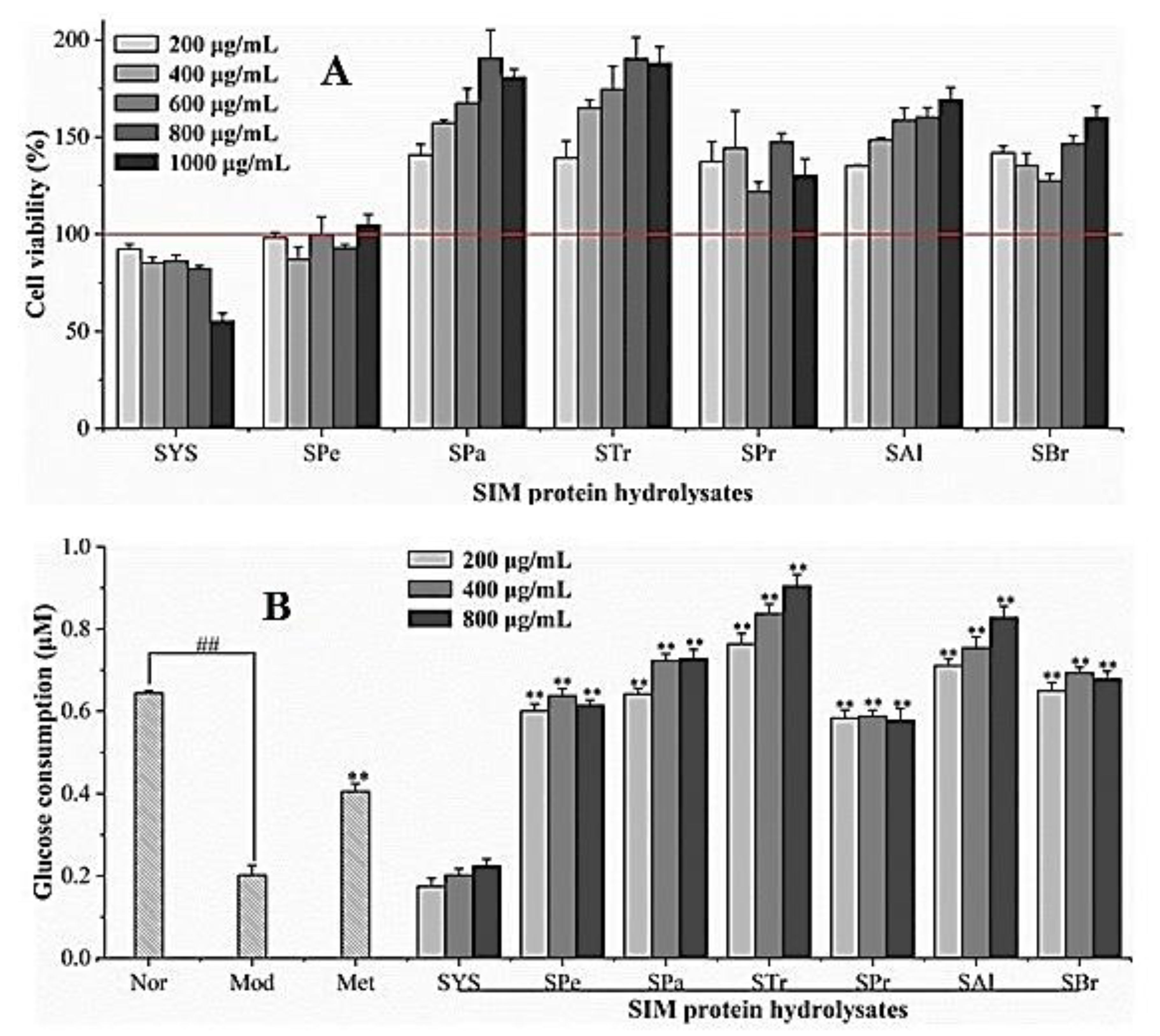
2.9. Cell Viability and Hypoglycemic Activity
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
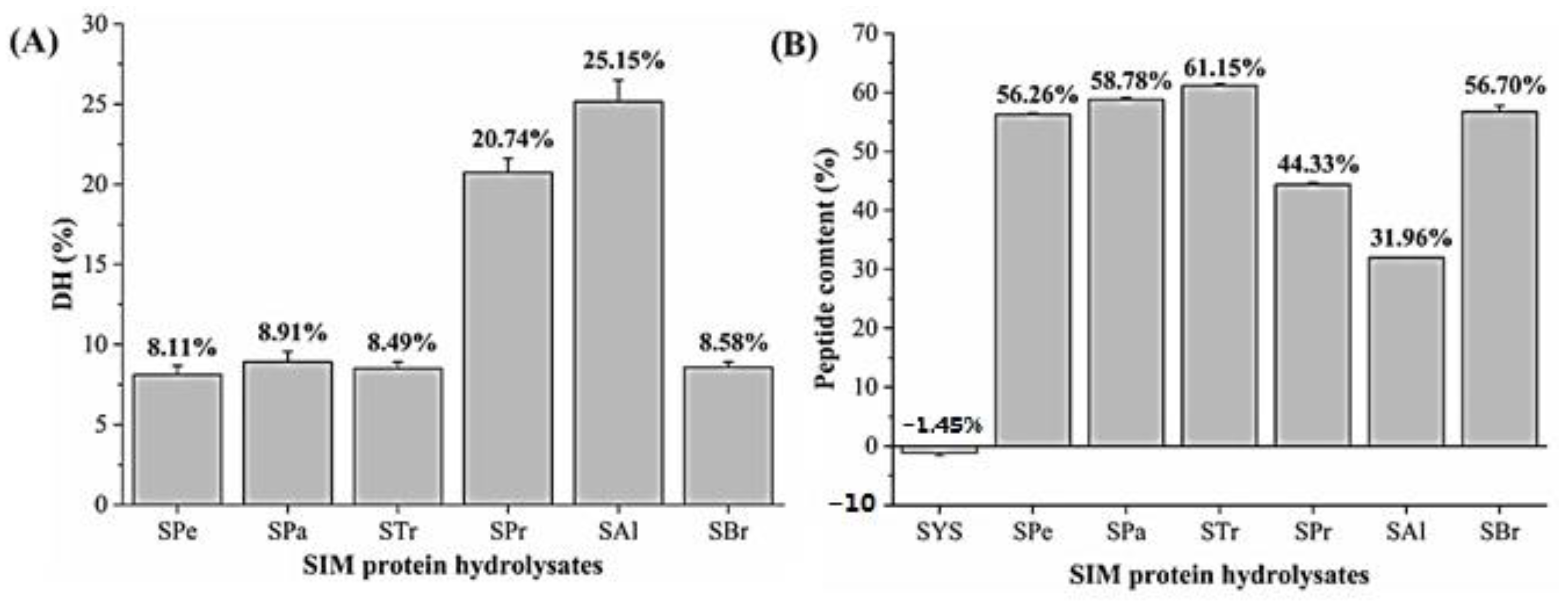
3.1. Hydrolysis of SIM Protein
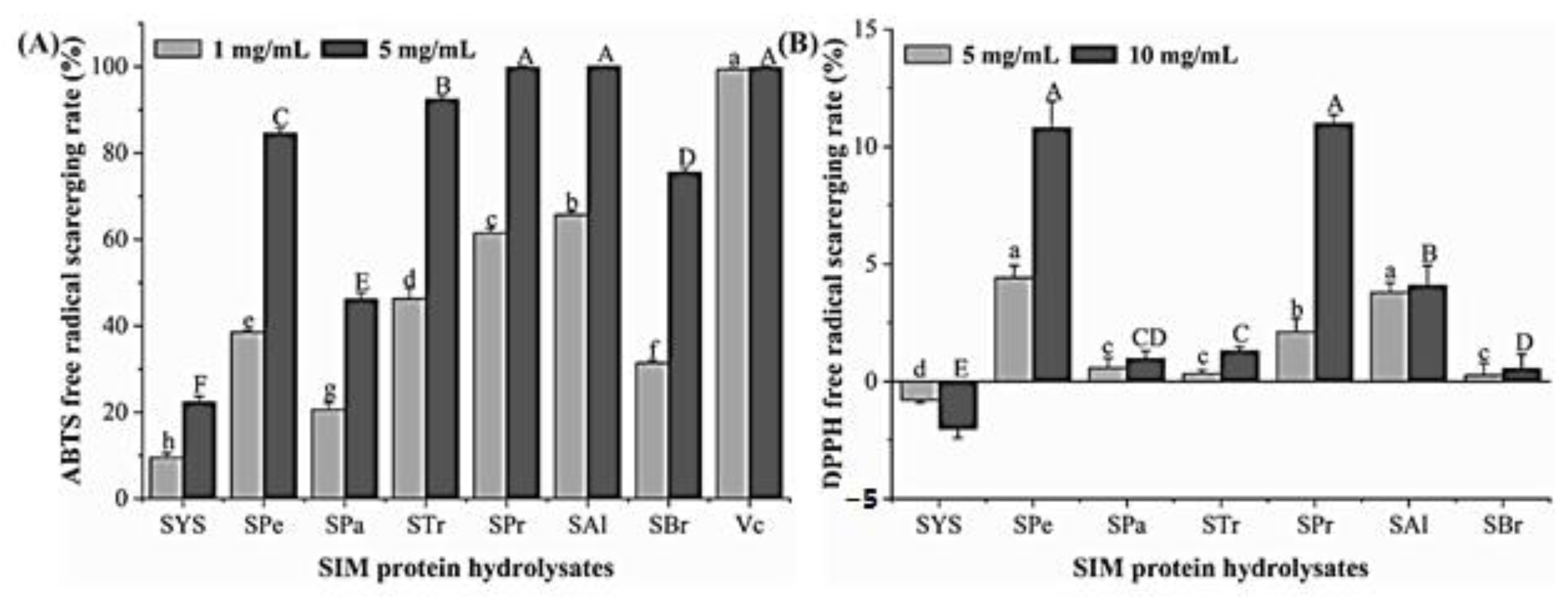
3.2. Antioxidant Activity
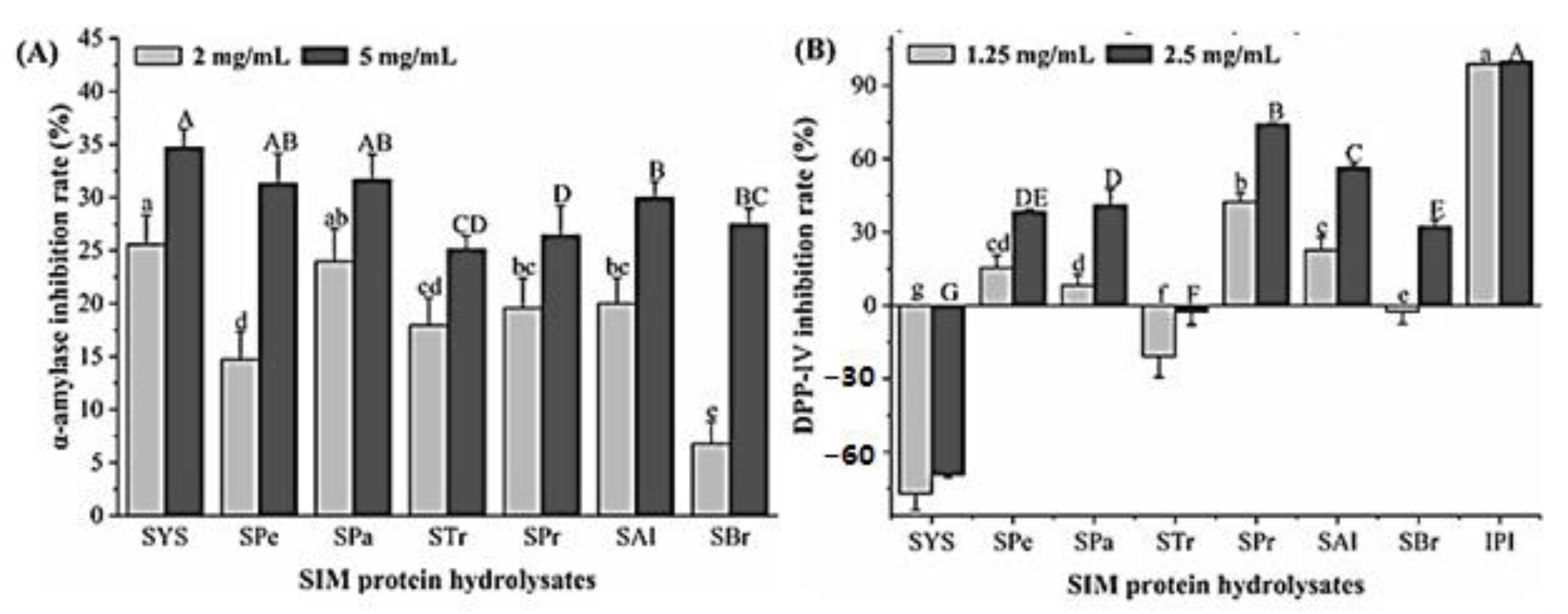
3.3. Inhibitory Activity on α-Amylase
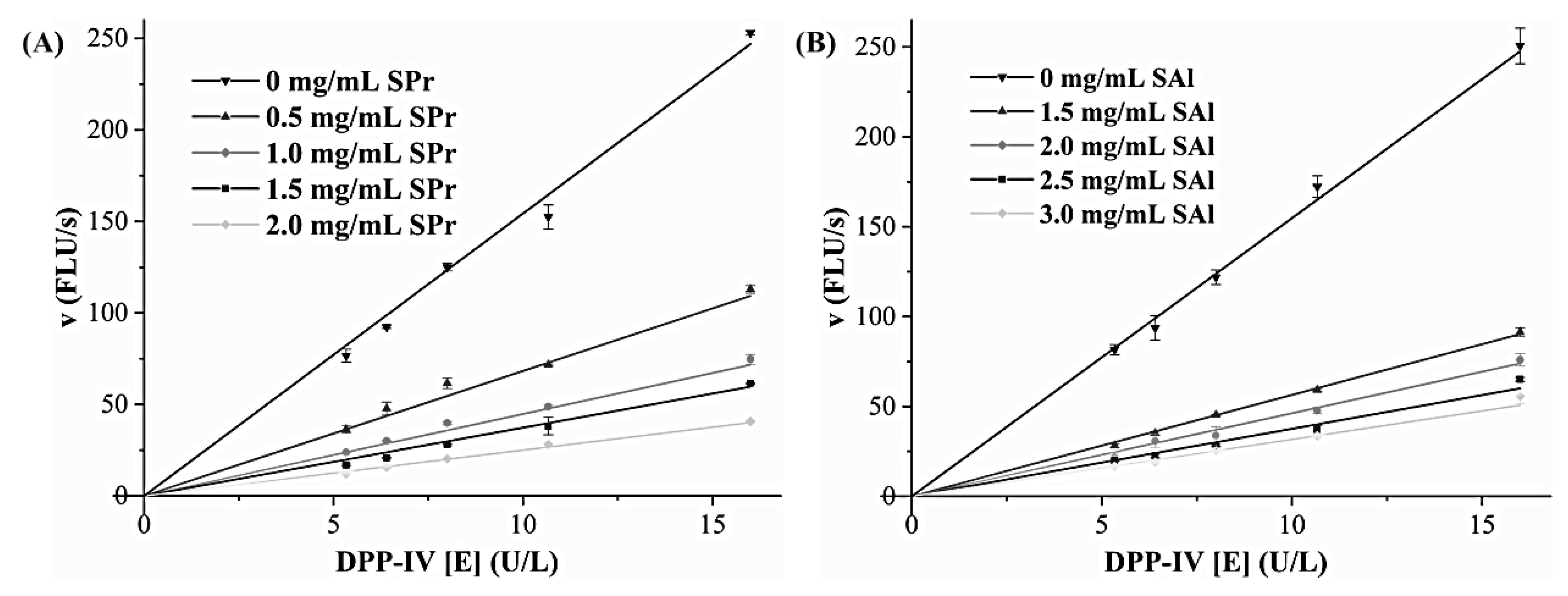
3.4. Inhibitory Activity and Inhibition Type on DPP-IV
3.5. Effects of the Hydrolysates on Glucose Uptake
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cai, Z.Q. Shade delayed flowering and decreased photosynthesis, growth and yield of Sacha Inchi (Plukenetia volubilis) plants. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2011, 34, 1235–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhu, F.; Kakuda, Y. Sacha inchi (Plukenetia volubilis L.): Nutritional composition, biological activity, and uses. Food Chem. 2018, 265, 316–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawdkuen, S.; D’Amico, S.; Schoenlechner, R. Physicochemical, Functional, and In Vitro Digestibility of Protein Isolates from Thai and Peru Sacha Inchi (Plukenetia volubilis L.) Oil Press-Cakes. Foods 2022, 11, 1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, F.; Boye, J.I.; Simpson, B.K. Bioactive proteins and peptides in pulse crops: Pea, chickpea and lentil. Food Res. Int. 2010, 43, 432–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Yao, Y.S.; Ibrahim, M.A.A.; El Halawany, A.M.; Yang, L.; Zhang, X.W. Production of Dual Inhibitory Hydrolysate by Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Squid Processing By-product. Mar. Biotechnol. 2022, 24, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.F.; Fan, X.D.; Qi, P.; Zhang, X.W. Identification of anti-diabetes peptides from Spirulina platensis. J. Funct. Foods 2019, 56, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alashi, A.M.; Blanchard, C.L.; Mailer, J.R.; Agboola, S.; Mawson, J.A.; He, R.; Girgih, A.; Aluko, R.E. Antioxidant properties of Australian canola meal protein hydrolysates. Food Chem. 2014, 146, 500–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onuh, J.O.; Girgih, A.T.; Aluko, R.E.; Aliani, M. Inhibitions of renin and angiotensin converting enzyme activities by enzymatic chicken skin protein hydrolysates. Food Res. Int. 2014, 53, 260–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.X.; Gao, Y.H.; Sun, J.X.; Li, C.Q.; Yue, X.Q.; Shao, J.H. Influence of ultrasonic treatment on functional properties and structure of tussah pupa protein isolate. J. Insects Food Feed 2022, 8, 1133–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.D.; Hu, S.F.; Wang, K.; Yang, R.F.; Zhang, X.W. Coupling of ultrasound and subcritical water for peptides production from Spirulina platensis. Food Prod. Process. 2020, 121, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evangelho, J.A.; Berrios, J.J.; Pinto, V.Z.; Antunes, M.D.; Vanier, N.L.; Zavareze, E.R. Antioxidant activity of black bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) protein hydrolysates. Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 36 (Suppl. 1), 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khositanon, P.; Panya, N.; Roytrakul, S.; Krobthong, S.; Chanroj, S.; Choksawangkarn, W. Effects of fermentation periods on antioxidant and angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory activities of peptides from fish sauce by-products. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 135, 110122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, R.; Girgih, A.T.; Malomo, S.A.; Ju, X.; Aluko, R.E. Antioxidant activities of enzymatic rapeseed protein hydrolysates and the membrane ultrafiltration fractions. J. Funct. Foods 2013, 5, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasir, N.A.M.; Sarbon, N.M. Angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE), antioxidant activity and functional properties of shortfin scad (Decapterus macrosoma) muscle protein hydrolysate at different molecular weight variations. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2019, 20, 101254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, A.; Azizi, M.H.; Ahmadi Gavlighi, H. Fractionation of hydrolysate from corn germ protein by ultrafiltration: In vitro antidiabetic and antioxidant activity. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 8, 2395–2405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.S.K. Investigation of jumbo squid (Dosidicus gigas) skin gelatin peptides for their in vitro antioxidant effects. Life Sci. 2005, 77, 2166–2178. [Google Scholar]
- Sampath Kumar, N.S.; Nazeer, R.A.; Jaiganesh, R. Purification and identification of antioxidant peptides from the skin protein hydrolysate of two marine fishes, horse mackerel (Magalaspis cordyla) and croaker (Otolithes ruber). Amino Acids 2012, 42, 1641–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngoh, Y.-Y.; Tye, G.J.; Gan, C.-Y. The investigation of alpha-amylase inhibitory activity of selected Pinto bean peptides via preclinical study using AR42J cell. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 35, 641–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngoh, Y.-Y.; Gan, C.-Y. Enzyme-assisted extraction and identification of antioxidative and alpha-amylase inhibitory peptides from Pinto beans (Phaseolus vulgaris cv. Pinto). Food Chem. 2016, 190, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza Rocha, T.; Hernandez, L.M.R.; Chang, Y.K.; de Mejía, E.G. Impact of germination and enzymatic hydrolysis of cowpea bean (Vigna unguiculata) on the generation of peptides capable of inhibiting dipeptidyl peptidase IV. Food Res Int. 2014, 64, 799–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, R.; Hernández Álvarez, A.J.; Maycock, J.; Murray, B.S.; Boesch, C. Comparison of alcalase- and pepsin-treated oilseed protein hydrolysates—Experimental validation of predicted antioxidant, antihypertensive and antidiabetic properties. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2021, 4, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, X.; Zhang, L.; Song, W.; Zhang, C.; Hua, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, X. Separation, identification and molecular binding mechanism of dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitory peptides derived from walnut (Juglans regia L.) protein. Food Chem. 2021, 347, 129062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.; Cheng, J.; Wu, H. Discovery of Food-Derived Dipeptidyl Peptidase IV Inhibitory Peptides: A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tkaczewska, J.; Bukowski, M.; Mak, P. Identification of antioxidant peptides in enzymatic hydrolysates of carp (Cyprinus Carpio) skin gelatin. Molecules 2019, 24, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Hydrolysates | Various Components (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| >10 kD | 5–10 kD | 3–5 kD | 1–3 kD | 0.5–1 kD | <0.5 kD | |
| SPe | 4.08 ± 0.09 a | 5.32 ± 0.16 a | 5.89 ± 0.11 a | 18.38 ± 0.31 a | 15.38 ± 0.26 a | 50.95 ± 0.79 a |
| SPa | 4.70 ± 0.06 a | 5.22 ± 0.02 a | 5.70 ± 0.01 a | 17.87 ± 0.04 a | 15.45 ± 0.03 a | 51.05 ± 0.16 a |
| STr | 3.02 ± 0.23 a | 3.36 ± 0.02 a | 4.35 ± 0.02 a | 19.66 ± 0.06 a | 19.85 ± 0.05 a | 49.76 ± 0.13 a |
| SPr | 1.51 ± 0.03 b | 1.60 ± 0.03 b | 1.88 ± 0.03 b | 10.82 ± 0.04 b | 14.92 ± 0.02 a | 69.28 ± 0.11 b |
| SAl | 0.05 ± 0.00 c | 0.20 ± 0.01 b | 0.50 ± 0.00 b | 5.98 ± 0.02 c | 13.30 ± 0.06 a | 79.97 ± 0.07 b |
| SBr | 4.81 ± 0.07 a | 4.98 ± 0.00 a | 5.85 ± 0.05 a | 20.37 ± 0.16 a | 16.45 ± 0.07 a | 47.55 ± 0.22 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shu, T.; Wang, K.; Zhang, X. Antioxidant and Hypoglycemic Activity of Sacha Inchi Meal Protein Hydrolysate. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 6528. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13116528
Shu T, Wang K, Zhang X. Antioxidant and Hypoglycemic Activity of Sacha Inchi Meal Protein Hydrolysate. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(11):6528. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13116528
Chicago/Turabian StyleShu, Tianyu, Kai Wang, and Xuewu Zhang. 2023. "Antioxidant and Hypoglycemic Activity of Sacha Inchi Meal Protein Hydrolysate" Applied Sciences 13, no. 11: 6528. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13116528
APA StyleShu, T., Wang, K., & Zhang, X. (2023). Antioxidant and Hypoglycemic Activity of Sacha Inchi Meal Protein Hydrolysate. Applied Sciences, 13(11), 6528. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13116528







