Abstract
Molybdenum is an essential trace element, considered in recent work to be a promising 3D-printable biodegradable material for medical applications. Specifically, in our recent in vitro work, we were able to show that molybdenum is a material of high biocompatibility, sufficient stability, and uniform degradation. Thus, it seems to fulfill the optimal requirements for a resorbable osteosynthesis material. To confirm these results in a complex organism, we tested molybdenum against the gold standard titanium. For this purpose, we implanted either molybdenum or titanium implants into the nuchal folds of 48 Wistar rats. We examined all animals daily for clinical inflammatory parameters and euthanized one-third of the cohort after 12, 24, and 52 weeks, respectively. Subsequently, the tissues surrounding the samples, as well as the spleens, livers, and kidneys of all animals, were pathologically processed and examined. Subsequently, selected samples were examined metallographically. No significant increased inflammatory reaction of the material molybdenum versus titanium could be detected, either clinically or pathologically. The animals did not show any significant differences regarding their general condition or weight development. However, the introduced molybdenum platelets showed significantly less degradation than previously in the in vitro model. This is most likely due to the capsule formation, which has already been described for other implants.
1. Introduction
In oral and maxillofacial surgery, osteosynthesis materials are used for a wide variety of indications. Various plates, screws, and wires are mainly used for the treatment of midface and mandibular fractures or reconstructions, as well as in orthognathic surgery [1]. In addition, osteosynthesis systems are required for open cranial bone remodeling in craniosynostosis [2,3].
Modern osteosynthesis materials are subject to high standards of reliability and safety. In addition to excellent biocompatibility, sufficient long-term mechanical stability in relatively large dimensions is required, especially for plate and screw systems. The average mechanical forces acting on various osteosynthesis implants and the utility of titanium as a clinical gold standard are summarized in [4].
Titanium and stainless steel have been established and extensively tested for osteosynthesis systems for many decades [5]. For the most part, they demonstrate very good biocompatibility, high and sustained mechanical strength, and low release of metal ions into the organism, even in large-dimension systems.
Although they are generally considered the gold standard for osteosynthesis, various disadvantages, such as allergies, corrosion degradation, interference with imaging modalities, and immune reactions, have also been described for these systems [6,7]. Other problems with titanium implants are the temperature sensitivity and tactile sensation of plates and screws [8,9]. As a result of these and other problems, metal removal is often recommended or even necessary. In the case of a second necessary operation for metal removal, general anesthetic complications can occur in addition to local complications, such as bleeding or nerve damage. For these reasons, bioresorbable implants have been the subject of research for many decades. The aim is to use biocompatible implants that can be degraded once they have fulfilled their function and do not unnecessarily burden or hinder the patient in the long term. Various resorbable osteosynthesis materials have been developed over the past decades, and are now used for several indications in different specialties [10]. Two major groups of materials can be distinguished: metallic and non-metallic materials. Magnesium and different magnesium alloys are well-studied and well-established resorbable metallic materials as potential bases for osteosynthesis [11,12,13]. For example, the MAGNEZIX® CS screw (Syntellix AG, Hannover, Germany) made of magnesium alloy (MgYREZr) has been used in the field of orthopedics since 2013, and its successful use has already been described in several studies [14,15,16,17]. Magnesium alloys show excellent biocompatibility and good integration into bone tissue. Despite its successful use, however, the uneven degradation of magnesium due to pitting corrosion has also been repeatedly described [18]. This makes prediction of the time to failure of an implant under significant mechanical loads difficult, and creates uncertainty for clinical users. The much lower mechanical strength of magnesium alloys compared to stainless steel or titanium also leads to larger implant dimensions, restricting applications in, e.g., maxillofacial surgery. Magnesium-based implants are also difficult to distinguish in X-ray-based medical imaging because of the low atomic number and density of magnesium.
Another large group of bioresorbable implants are polymers made of polylactic acids and polyglycolic acid (PGA), as well as combinations of these. Plates, screws, and pins based on polymers have already been used for several years in the field of oral and maxillofacial surgery [19]. Their clinical applications were reported as early as the 1980s [20]. For example, the Resorb-X® system (KLS Martin, Tuttlingen, Germany) is an established osteosynthesis material for the surgical treatment in pediatric craniofacial surgery [21].
However, the systems developed so far based on polylactic acids have not provided completely satisfactory results. Due to the low mechanical strength, biodegradable polymers are unsuitable for implants that are subjected to high mechanical loads [4]. The use of polymers for such applications would lead to unacceptably large dimensions and introduce a high amount of degradable material into the body. In addition, possible foreign body reactions and long-term inflammation due to persistent degradation products have been described in various studies [22,23]. Radiopacity and consequently visibility in X-ray based imaging for biodegradable polymers is even lower than for magnesium implants.
Thus, despite the constant further development and increasing experience of surgeons with these osteosynthesis systems, disadvantages are still evident, even when using established systems. For these reasons, scientists continue to search for suitable materials that provide the required stability and biocompatibility for optimal bioresorbable osteosynthesis materials. In this context, molybdenum has proven to be a promising alternative. In the human body, it is found as a trace element and co-substrate of some specific enzymes [24]. The degradation products can be excreted renally [25]. In initial publications, molybdenum showed sufficient mechanical properties as a material for osteosynthesis [26,27].
In our latest work on molybdenum, we were able to show that, in addition to being a potential material for cardiac stents [27], it is also a very promising biocompatible material for osteosyntheses [28]. We were able to show that molybdenum has the necessary biocompatibility and excellent mechanical properties for use as an osteosynthesis material, even in the larger dimensions which are required. Specifically, we were able to demonstrate that molybdenum shows a very uniform degradation in vitro, with a complete loss of stability expected after 8–9 months. Furthermore, molybdenum of high purity showed no significant cytotoxicity in mouse or human fibroblasts, nor in human osteoblasts. Despite these positive results, testing the material in a complex organism is an imperative next step. Adverse effects such as renal damage, which has already been described due to overly high amounts of molybdenum intake [29,30], must be excluded.
The aim of our experiments was, therefore, to investigate the influence of molybdenum on the organism of a mammal—in this case, the rat. We investigated whether molybdenum samples produced by the selective laser melting process (SLM), also called laser powder bed fusion (LPBF), behave in a complex biological organism in a similarly biocompatible way as the gold standard titanium. We placed particular focus on ensuring that both titanium and molybdenum were manufactured in such a way that they could potentially serve as computer-aided and computer-manufactured (CAD-CAM) patient-specific implants (PSI).
For this purpose, a total of 96 rats were implanted with test specimens made of molybdenum and titanium subcutaneously (s.c.) in the fold of the neck. Local inflammation parameters, as described in Section 4, were recorded daily. Then, 12, 24, and 52 weeks later, the specimens from one-third of the total number of animals, respectively, were explanted, and the surrounding tissues were pathologically processed. The spleens, livers, and kidneys were also explanted and microscopically examined. To measure the degradation of the molybdenum samples, metallographic cross-sections of the samples were prepared and analyzed.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.1.1. Animal Model
A total of 96 male Wistar rats were obtained from Janvier Labs (Le Genest-Saint-Isle, France) and included in the experiment at 16 weeks of age. All of the rats were housed under standard conditions and maintained on normal rat chow. Only male rats were used for the experiments in order to exclude gender-specific influences as a confounding factor. The animals were kept exclusively in individual cages postoperatively. This was to prevent mutual manipulation of the wound surfaces.
All of the procedures were licensed and carried out according to the institutional animal care guidelines as regulated by the German federal law governing animal welfare (Recklinghausen, Germany; Aktenzeichen 81.02.04.2021).
2.1.2. Implants
Molybdenum Implants
The molybdenum implants were manufactured by KLS Martin (Tuttlingen, Germany) using the selective laser melting process, and had an overall size of 10 × 10 × 2 mm. Molybdenum powder, Mo-PDMPB, with a molybdenum content of >99.5% and a particle size smaller than 44 µm (obtained from H.C.—Starck, Goslar, Germany), was used. As a final step, the processed specimens were plasma-polished for 7 min using a nontoxic electrolyte developed and applied by H&E (Moritzburg, Germany) to obtain a surface roughness of Rzmax < 30 µm. The surface roughness of a molybdenum surface may influence the degradation rate, with rougher surfaces leading to higher degradation due to the larger real surface area. The polished state was chosen for the purpose of better comparison with earlier in vivo studies in which polished molybdenum wires were used.
Selective Laser Melting
Selective laser melting is an established process to generate additive manufactured geometries. For this purpose, a powder layer is applied to a building platform in a thin-film process, which is sintered, i.e., fused, by means of a laser. The platform is then lowered, and a new layer of material is applied and fused. This repeated process builds up the required design geometry layer by layer. When processing metallic materials with this technique, it is important that support structures are also built up, which then must be removed manually.
Titanium Implants
The titanium implants were produced by KLS Martin (Tuttlingen, Germany), also using the selective laser melting process, with dimensions of 10 × 10 × 2 mm. The processed powder, with a particle size of less than 63 µm, was Ti-6Al-4V (according to ASTM F136), which is the gold standard for the manufacturing of solid implant materials. The specimens were micro-glass pearl blasted and trovalized to gain a surface roughness of Rzmax < 30µm (standard process).
The specimens for both materials were produced on SLM 125 machines identical in build with the same vertical build-up strategy before being Gamma-sterilized at high doses (≥25 kGy) for the surgical application.
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Study Design
A total of 96 animals were randomly divided into 2 approximately equal cohorts: 49 animals (51.0%) received a molybdenum implant and 47 (49.0%) a titanium implant (Figure 1). Postoperative blinded examinations were performed daily based on a previously prepared examination form. A third of the total cohort was examined at 12, 24, and 52 weeks, and then euthanized. The platelets were explanted, and histopathological tissue samples were taken for further processing.
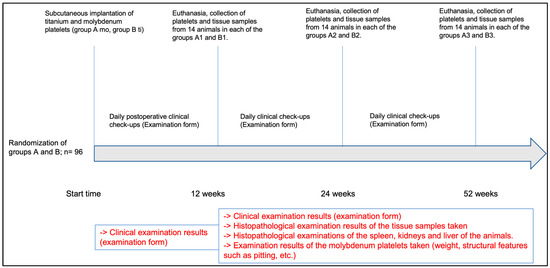
Figure 1.
Time course of the in vivo test series.
2.2.2. Surgical Implantation of the Molybdenum and Titanium Platelets
We operated on 96 male rats under general anesthesia. The animals were injected intraperitoneally with ketamine (Ketaset® Zoetis, NJ, USA), 100 mg/kg (individual weight-adapted administration), and xylazine (Rompun® Bayer AG, Leverkusen, Germany), 5 mg/kg (individual weight-adapted administration). This was followed by preoperative preparation. An eye ointment containing dexpanthenol (Bepanthen®) Bayer AG, Leverkusen, Germany) was applied to protect the eyes, and the surgical area (median skin incision in the area of the shoulder blades, skin incision approx. 1.0–1.5 cm long) was shorn with a mechanical shaver, “Favorita II” (Aesculap, Tuttlingen, Germany). The animals were then brought into the operating room, placed in prone position on a warming mat, and connected to the intraoperative monitoring system. The surgical field was cleaned and disinfected with an alcoholic iodine solution. In addition, meloxicam (Metacam® Boehringer Ingelheim, Ingelheim am Rhein, Deutschland), 1 mg/kg (individual weight-adapted administration), was injected s.c. preoperatively for analgesia. Before the start of surgery, a reflex test of the interphalangeal reflex was performed again for clinical control of the anesthesia. For the implantation of the molybdenum and titanium implants, first, a median skin incision (approx. 1.5 cm length) was made between the shoulder blades (Figure 2b). Then, a pocket was prepared in the area of the subcutaneous fat tissue using dissecting scissors and forceps (Figure 2c). Care was taken to ensure sufficient distance from the skin incision. The respective implant was inserted into the resulting subcutaneous pocket (Figure 2d).
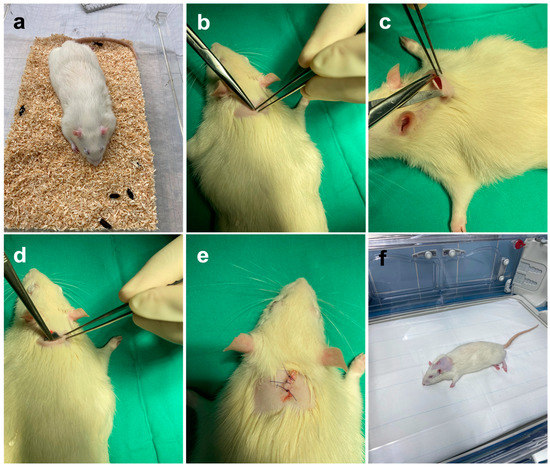
Figure 2.
Illustration of the perioperative procedure. (a) Wistar rats were anesthetized and treated with eye ointment. Until the onset of deep anesthesia, the rats were kept in the cage. (b) Skin incision; (c) preparation of the subcutaneous pocket; (d) insertion of the implant; (e) suture closure with absorbable suture material; (f) postoperative recovery phase in the incubator.
The implants, made of titanium (control group or molybdenum (comparison group)), were each 10 × 10 × 2 mm in size, and had rounded edges on all sides so that the peri-implant tissue was sufficiently protected. The sizes of the implants resulted from the limitations of the selective laser melting process. Thus, we used the smallest possible implants which could be manufactured from molybdenum in this way. For comparison purposes, the titanium implants had dimensions of the same size. After the implantation, the previously prepared skin pockets were closed with VicrylTM 5-0 (Ethicon, NJ, USA) after checking the position of the implant again. Finally, the skin was sutured using single-button sutures (Figure 2e) with VicrylTM 4-0 (Ethicon, NJ, USA) so that no suture removal was necessary in the later course. In total, we required an incision–suture time of between 10 and 15 min for the entire surgical procedure. At the end of the surgical procedure, the surgical wounds were disinfected and cleaned again. Finally, a spray dressing was applied. The animals were then placed in the prone position in incubators for the recovery phase (Figure 2f). After fully awakening from anesthesia, the animals were individually transferred to the cages and then to the animal rooms.
2.2.3. Postoperative Management
Animals were clinically assessed daily from the first examination, including documentation. A pre-determined scoring system decided whether clinical inflammation parameters were considered inflammation or not. If redness, swelling, purulent secretion, or hyperthermia were present together, or at least 2 of these 3 symptoms, it was considered a clinical inflammatory reaction. In this case, veterinarians were consulted daily for further co-management. The same applied to general abnormalities of the animals. In addition, the animals were weighed daily for the first seven days and then once a week to check their general condition. For postoperative analgesic therapy, the rats received meloxicam s.c. (Metacam® Boehringer Ingelheim, Ingelheim am Rhein, Germany) (1 mg/kg body weight, individual body weight-adjusted administration) once daily for the first three days after surgery.
2.2.4. Euthanasia and Removal of Implants and Organs
After the implantation of the platelets, 12 (group A1 and B1), 24 (group A2 and B2), and 52 weeks (group A3 and B3) passed before the animals underwent a final clinical examination and were subsequently sacrificed, in each case, by an intraperitoneal overdose of pentobarbital (Narcoren®) of 500 mg/kg body weight (28 animals in each case). The platelets were explanted (Figure 3) and examined metallographically for their weight and material composition.
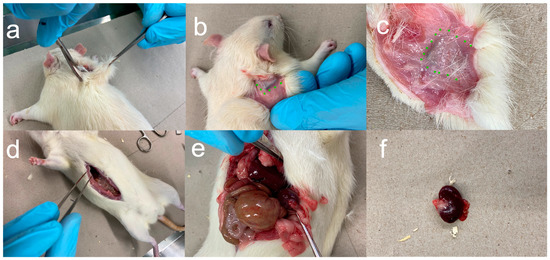
Figure 3.
Presentation of the procedure after euthanasia. (a) Skin incision for removal of the tissue, including platelets; (b) representation of the platelet with surrounding capsule; (c) tissue preparation with contained platelet (dotted green), where the capsule was left in place (dotted green); (d) medial abdominal incision for organ removal; (e) presentation of the situs before organ removal; (f) kidney removed.
2.2.5. Histopathological Processing and Examination
With the removal of the platelets, surrounding circulatory tissue was also obtained, which was subsequently processed and examined in cooperation with the histopathological institute of The University Clinic Düsseldorf (Düsseldorf, Germany).
For histological examinations, formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded (FFPE) samples were cut in sections 1.5 µm in thickness and stained with H&E. Slides were then digitized for further analysis (Aperio slide scanner, Leica Biosystems, Nussloch, Germany) using a 40× objective lens and a resolution of 0.2529 µm per pixel. Measurements, analyses, and picture captures for publication were carried out using the QuPath software (PMID: 29203879), version 0.4.1.
In particular, the features that indicated a chronic inflammatory reaction were examined. The focus was primarily on the infiltration of lymphocytic cells, increased angiogenesis, cell proliferation, and/or signs of fibrosis. To quantify and better compare the capsule formation around the implants and the inflammatory reactions, we used the synovitis score according to Krenn [31]. The spleens, livers, and kidneys of the animals were also processed and examined pathologically. The main aim was to compare these organs with the corresponding organs of the control group. Furthermore, we investigated whether deposits of molybdenum could be found in the corresponding organs.
2.2.6. Analysis of the Metallographic Cross Sections
We prepared samples from the 3-, 6-, and 12-month cohorts and compared them with each other. A sample that was not implanted also served as a control. The explanted molybdenum samples were cut by electrical discharge machining (EDM). The grain structures of the samples were made visible by metallographic preparation by grinding and polishing with alumina and diamond suspension. The surfaces of the samples were imaged by means of optical microscopy (Zeiss Axiocam 208 color, Oberkochen, Germany).
2.2.7. Statistics
The values obtained from the measurements and the clinical data were analyzed using Jamovi (version 1.6.9, (Computer Software). Retrieved from https://www.jamovi.org, accessed on 19 March 2022, Sydney, Australia). A p-value of 0.05 was set for the hypothesis test [32,33]. The Shapiro–Wilk test was performed to test the data for normal distribution, and the Mann–Whitney U test and Student’s t-test were used to compare the means of the two groups. A contingency table was constructed for the categorical variables. To test correlations between the categorical variables, the chi-square test was used. The weight progressions were calculated using Excel Microsoft 365 (2021).
3. Results
We enrolled 96 Wistar rats in the study and operated on them. The 96 animals were divided into 2 approximately equal cohorts: 49 animals (51.0%) received a molybdenum implant and 47 (49.0%) a titanium implant, as shown in Figure 4a. Both implant types were produced by the selective laser melting process. For the exact compositions of the plates, see Section 2.
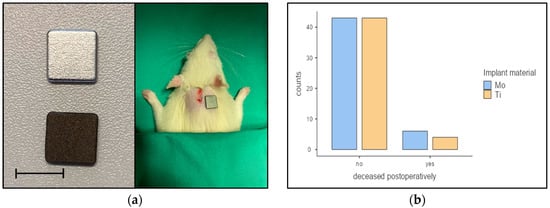
Figure 4.
(a) Wistar rats were implanted with either a molybdenum (above) or titanium implant (below); scale bar represents 10 mm; (b) 10 animals (10.4%) died immediately postoperatively (6 animals (60.0%) with molybdenum and 4 animals (40.0%) with titanium implants.
As shown in Figure 4b, 10 animals (10.4%) died immediately postoperatively (6 animals (60.0%) with molybdenum and 4 animals (40.0%) with titanium implants due to unspecific complications. Dissections of the animals performed immediately after death by a veterinarian did not reveal any pathological abnormalities. Another animal (with a titanium implant) died three days postoperatively from acute kidney failure. In the necropsy of the animal, the veterinarian could not establish a connection to the inserted titanium implant. The acute kidney failure was most likely a complication of the general anesthesia.
Figure 5 shows the clinical inflammatory reactions in the period immediately postoperatively and up to a maximum of postoperative week 12 (T1).
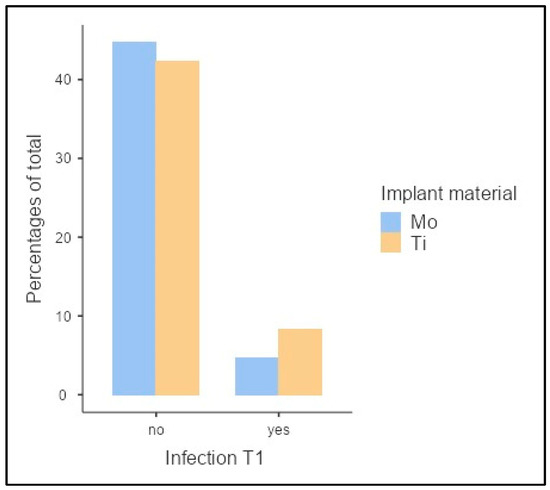
Figure 5.
Clinical inflammatory response within the first 12 weeks postoperatively (T1).
If an inflammatory reaction occurred in one of the animals during this time window, it was immediately recorded, and the animal was marked as positive for inflammation. Postoperative infections were present in 11 of 85 animals (12.9%). Within this subset, a molybdenum implant was implanted in 4 animals (36.4%) and a titanium implant in 7 animals (63.6%). No statistically significant dependence of the implanted material on the inflammatory response could be demonstrated (χ2(1) = 0.861, p = 0.354, Cramer’s V = 0.101).
According to clinical assessment, all local inflammatory reactions were scratch marks in response to the shaved area. One animal had to be euthanized for welfare reasons after the seventh postoperative week due to an excessively large sore area. This animal had been implanted with a titanium specimen.
Thus, from week 8 onwards, a total of 84 animals were included in the trial. Consequently, 28 animals were euthanized after 12 weeks (T2), 24 weeks (T3), or 52 weeks (T4).
After 12 weeks (T2), infection occurred in 4 of 84 animals (4.8%) (Figure 6). A molybdenum implant was used in 25.0% (n = 1) and a titanium implant in 75.0% (n = 3). With p = 0.329, no significant dependence of the implant choice on the inflammatory response was demonstrated (χ2(1) = 0.953, p = 0.329, Cramer’s V = 0.107).
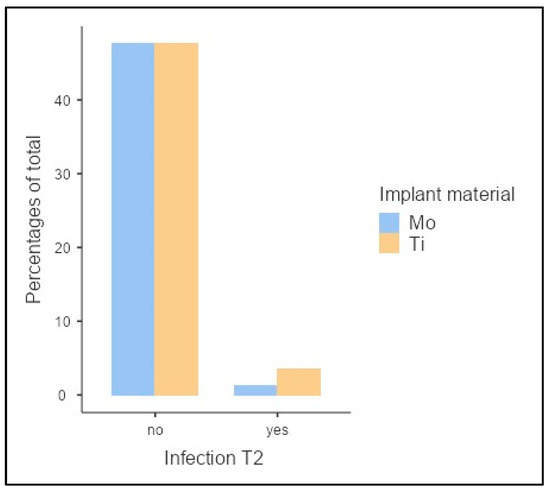
Figure 6.
Clinical inflammatory response 12 weeks postoperatively (T2).
No infections occurred from week 13 onward. At T3, the total collective consisted of a total of 55 animals, 45.5% (n = 25) of which had received molybdenum and 54.5% (n = 30) of which had received titanium implants. At T3, after 52 weeks, the distribution was as follows in n = 27 animals: 40.7% (n = 11) molybdenum and 59.3% (n = 16) titanium implants.
In summary, the molybdenum samples did not induce a significant inflammatory response at any time compared to titanium. Irrespective of the materials used, the infections that could be clinically detected were identified as scratch marks resulting from shaving and the reactions of the animals to the shaved areas (Supplementary Figure S1).
The animals had an average body weight at T1 of 457 ± 38.4 g (molybdenum implants) and 454 ± 39.2 g (titanium implants). During the course, the average weight was 554 ± 57.7 vs. 544 ± 55.0 (T2), 605 ± 40.7 vs. 604 ± 69.9 (T3), and 656 ± 51.6 vs. 689 ± 74.0 (T4). The differences between the two groups were not significant at any of the time points. Comparing the relative weight gain, there were no significant differences between the two groups nor between the different time points (Figure 7).
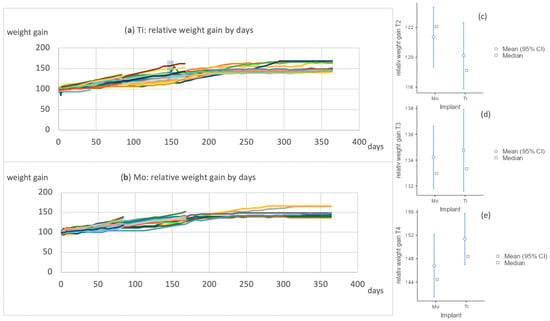
Figure 7.
The relative weight gain, by days, of the rats with either titanium implants (a) or molybdenum implants (b) is presented. (c–e) show the comparison of the weight development of the two groups, titanium and molybdenum, at the different time points (T2, T3, and T4).
After euthanasia, cutaneous, subcutaneous, and muscular tissue, including previously inserted samples, was collected and pathologically processed. We compared all preparations with those of the titanium platelets. There were moderate to mild inflammatory reactions around the platelets in each case, but no differences between the tissue around the molybdenum or titanium platelets. Tissue capsules were found to have formed around both types of implants (Figure 8). Within the capsules and in the adjacent tissue outside, slight metallic abrasion was seen in both groups. There was no difference regarding the implanted materials.
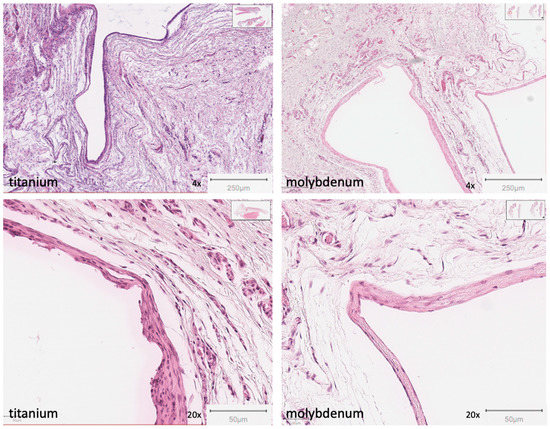
Figure 8.
Representative histological imaging of the tissue surrounding the platelet (left side: titanium at magnifications of 4× and 20×; right side: molybdenum at magnifications of 4× and 20×). The formation of the capsules is shown. H&E staining was performed.
To quantitatively characterize the capsule formation and the associated histopathological inflammatory reaction, we used the Krenn score as a guide. In the evaluation of the capsules according to Krenn et al., a sum score was formed from the individual scores of the synovial covering cell layer, the cell density of the synovial stroma, and the leucocytic infiltrates [31]. The score was used to describe either no synovitis, low-grade synovitis, or high-grade synovitis [31]. The capsules of 30 animals were evaluated, 17 titanium and 13 molybdenum (Table 1). The 30 pathological preparations showed scores of 0 (n = 2, 6.6%), 1 (n = 13, 43.3%), 2 (n = 9, 30.0%), and 3 (n = 6, 20.0%) for synovial covering of cell visibility. The cell density of the synovial stroma can be described with the following scores: 0 (n = 8, 26.7%), 1 (n = 17, 56.7%), 2 (n = 4, 13.3%), 3 (n = 1, 3.3%). Leukocytic infiltrates were calculated with a score of 0 (n = 3, 10.0%), 1 (n = 19, 63.3%), or 2 (n = 8, 26.7%).

Table 1.
Overview of the evaluation of the capsules according to Krenn et al. (synovial covering of the cell layer and the cell density of the synovial stroma and the leucocytic infiltrates).
In the capsule evaluation, according to Krenn, 3 cases (10.0%) showed no synovitis, 20 cases (66.7%) showed low-grade synovitis, and 7 cases (23.3%) showed high-grade synovitis.
Of the 30 evaluated specimens, 2 animals (6.7%) also showed an inflammatory reaction in the clinical assessment at time T1. One had received a titanium and the other a molybdenum implant. At the time of euthanasia at time T2, 1 animal had no synovitis (n = 1, 11.1%), 7 others had low-grade synovitis (n = 7, 77.7%), and 1 (n = 1, 11.1%) had high-grade synovitis. For time point T3 (n = 11), distributions of 0 (n = 2, 18.2%), 1 (n = 7, 63.6%), and 2 (n = 2, 18.2%) were found, and for T4 (n = 10), distributions of 1 (n = 6, 60.0%) and 2 (n = 4, 40.0%) were found.
No statistically significant correlation between capsular evaluation according to Krenn and the choice of implant could be demonstrated with χ2(2) = 1.77, p = 0.412, Cramer’s V = 0.243.
Regarding the duration of implantation in relation to the occurrence of synovitis, there was no statistically significant correlation with rs = 0.294 or p = 0.115 (Figure 9).
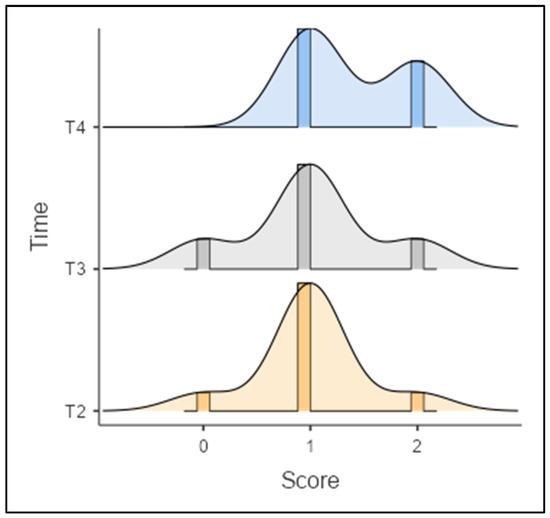
Figure 9.
Synovitis assessment according to Krenn at the time points of T2, T3, and T4.
We examined the spleens, kidneys, and livers of all 84 animals.
Two of the eighty-four kidneys showed slight abnormalities in the form of infarcted areas. One animal was from the titanium cohort and the other from the cohort with molybdenum, and both were euthanized after 52 weeks.
Otherwise, the kidneys were inconspicuous, and no deposits of molybdenum or titanium were found.
Neither the spleen nor the liver showed any organic changes, but 7 of 84 organs showed capsular necrosis, which, according to an investigation at the Institute of Pathology of the University clinic Düsseldorf, Germany, occurred post mortem due to cardiac arrest.
For all explanted molybdenum samples, surface colorations varying from yellow/golden to blue/violet were observed (Figure 10). Various colors were observed among the samples from each cohort, with no clear tendency towards a specific coloration within any of the cohorts. For molybdenum, the surface coloration was a first indication of the thickness of the degradation product layer on the surface. Yellow/golden coloration roughly corresponded to a thickness of around 50 nm, while blue/violet colorations corresponded to a thickness above 50 nm and below 100 nm. For a thickness higher than 0.8–1.0 µm, the degraded surface appeared black. The colorations of the explanted samples thus indicate that only a very thin layer of degradation products formed over 3–12 months. Correspondingly, only a very small amount of molybdenum would have dissolved, since the soluble product of the oxidation cascade of molybdenum, MoO3, was formed within the degradation layer and then was transferred into a solution in the form of MoO42− (molybdate ion).
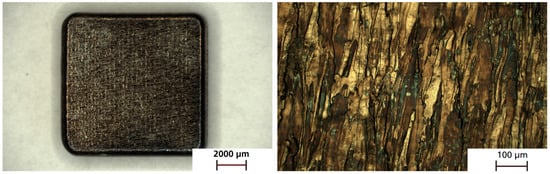
Figure 10.
Exemplary representation of the coloration of the specimens in plain view and in enlargement. Here, a sample of the 6-month cohort is shown.
The analysis of the metallographic cross-sections (Figure 11) of the explanted molybdenum samples confirmed that there were only miniscule degradation product layers, irrespective of the total duration of implantation. Due to the thickness of the degradation layers, far below 1 µm and likely in the range of 50–100 nm, it was not possible to distinguish the implanted samples from the samples in the as-manufactured state. The thin dark “layer” at the interface of Mo and the embedding resin was not the degradation product layer, but a small fissure that formed during embedding. This is supported by the fact that this fissure also appeared in the as-manufactured state. Five samples from each cohort were analyzed, with no marked differences either within a cohort or between cohorts.
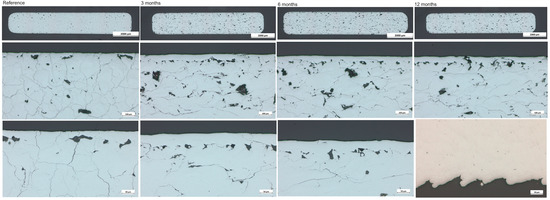
Figure 11.
Metallographic cross-sections of molybdenum samples. The analyses of the samples are shown from left to right in ascending order, from the reference to the 12-month sample. The upper line shows the cut sample, the middle line the 100× magnification, and the lower line the 200× magnification. Optical microscopy images are shown.
The cross-sections of all the as-manufactured samples and the samples explanted after 3 or 6 months showed internal cracks and pores. Since these defects were already observed in the as-manufactured samples, they were determined not to be related to exposure to the biological environment. Cracking and pore formation are known problems with SLM manufacturing of pure molybdenum [34]. Because of the highly uniform degradation of molybdenum, its release from a sample is directly proportional to the exposed surface area. However, since most cracks and pores are purely internal and not connected to the outer surface (see images with higher magnification in Figure 11), the additional internal surfaces are not exposed to body fluids and, therefore, do not contribute to the degradation of molybdenum or its release into the biological environment. In the samples implanted for 12 months, the regions close to the surface were mostly free from cracks and pores. However, in some regions of the surface, a “wave-like” roughness pattern appeared.
4. Discussion
The results must be considered from two different points of view—biocompatibility and degradation rates.
The overall aim of our experiment was to demonstrate the biocompatibility of molybdenum compared to the gold standard titanium in a complex organism.
We were able to clearly demonstrate, in a statistically sufficiently large cohort, that molybdenum plates do not cause a significant inflammatory reaction after insertion into the nuchal fold when compared with the gold standard titanium. This is based on evidence from daily clinical routine examination as well as histopathological diagnostics. Using the established Krenn histopathological synovitis score, we were able to quantify our observations of reactive capsule formation and compare both cohorts. There were no significant differences between the animals with either molybdenum or titanium implants. Furthermore, in addition to the inflammatory response, the general welfare of the animals was also examined daily. Both cohorts showed normal absolute weight, as well as adequate weight gain, without significant differences between the groups. These in vivo biocompatibility results are, therefore, in line with our previously conducted experiments, in which we were already able to demonstrate the biocompatibility of molybdenum in vitro [28].
The kidneys, livers, and spleens of the rats showed no macroscopic or pathological anomalies, and especially no differences in comparison between the examined cohorts. There were no measurable deposits of molybdenum. This is particularly noteworthy for the kidneys, because the excretion of molybdenum has, so far, mainly been described renally [35]. In addition, higher doses of molybdenum intake have been described as harmful to the kidneys of rats [29]. Bompart et al. showed that doses of 80 mg/kg/d lead to dysfunction of the tubules and glomeruli [30]. Sikora-Jasinska et al. also reported a qualitative pathological remodeling of Bowman’s capsule and glomeruli of the kidney, which could be related to Mo toxicity [27].
However, we must point out that, according to metallographic examination, very little Mo was dissolved, so it is not surprising that there were no changes. However, this is not evidence that Mo cannot theoretically cause damage.
So far, our biocompatibility results agree with those of Sikora-Jasinska et al. and Schaub et al. who also reported on the biocompatibility of molybdenum regarding the question of whether molybdenum is a potentially bioresorbable material for cardiac stents [27,36].
The very low degradation of the explanted molybdenum samples in this study is in marked contrast to the degradation rates observed in earlier in vivo studies of pure molybdenum. In the studies of molybdenum wires implanted into the aortic walls of Wistar rats [36] or mice [27], degradation product layers of more than 10 µm formed on the surfaces when the wires were integrated into the aortic wall. For the samples in the present study, the thickness of the degradation product layer was much lower than 1 µm. The thickness of the degradation product layer is a good indication of the total amount of dissolved molybdenum in a sample. Molybdenum does not dissolve from the metallic state, but undergoes several oxidation steps along a reaction cascade, leading to soluble-form MoO3 and, finally, dissolved-form Mo42− (molybdate) [37]. The rate-limiting step is the reaction of Mo2O5 (s) + H2O (l) ↔ Mo2O5OH (s) + H+ [38] + e− [39]. Therefore, the degradation proceeds by the formation of an oxide layer, the molybdenum content of which is reduced over time by the release of molybdate ions. The absence of an appreciable degradation product layer thus indicates minimal dissolution. The most likely explanation for the low degradation rate is the anatomical environment to which the samples are exposed. As described previously, the molybdenum samples in the fold of the neck were enclosed in tissue capsules, which was not observed in the studies of molybdenum wires implanted into the aortic wall. The capsule restricts the exchange of fluid with the rest of the body. Within the capsule, both the degradation of molybdenum (overall reaction equation: Mo + 4 H2O → MoO42− + 8H+ + 6e−) and the observed low-level inflammation may lead to more acidic conditions. Acidic conditions are known to slow the degradation of molybdenum [40]. The formation of the capsule may also inhibit the integration of the samples into the surrounding tissue. Based on results from earlier studies, tissue integration seems to be an important factor in determining the degradation rate, with less integrated samples degrading more slowly. For example, the degradation product layer thickness for a less integrated sample was reported to be only one-fifth of the layer thickness for a well-integrated sample in [34].
Bone healing, e.g., after a fracture, involves complex remodeling processes and depends, above all, on the body region. Complete ossification is usually observed after 6 weeks. Complete stability is normally assumed after about six months, especially in the field of maxillofacial surgery. A good guideline is that the implant should bear load for 3–6 months and then have fulfilled its function.
In our previous in vitro experiments, we were able to show that molybdenum sheets under physiological conditions exhibited a mass loss of approx. 20% after 6 months [28]. Thus, a relevant loss of stability occurred, which, in theory, would fit well with the time needed for bone stability to be regained. Furthermore, this rate of degradation indicates that there is a reasonable expectation that a molybdenum-based implant will degrade within a clinically relevant time frame, e.g., 1–2 years.
However, the degradation rates for encapsulated molybdenum are so low (<<1 µm/year) that degradation will not occur in humanly achievable time. Animal studies in other tissues (aortic wall) have shown degradation rates corresponding to a few tens of µm/year at most. Unless future experiments with other tissues show significantly higher rates, molybdenum implants should, therefore, not exceed structural sizes of 100 µm, or a maximum of 150 µm, to allow for degradation within a few years. The significant strength and stiffness of molybdenum are advantageous here, allowing for much thinner structure sizes than those of magnesium implants, for example.
The suitability of molybdenum as a resorbable biomaterial for osteosynthesis implants may, therefore, depend on the tissue reaction at the location of implantation. Direct contact with bone tissue in osteosynthesis would most likely lead to different degradation behavior. The degradation behavior in various tissues must be studied in more detail to determine the factors influencing the degradation. This may also result in strategies (such as surface functionalization) leading to the desired level of tissue integration and favorable conditions for moderate, uniform degradation in the range of several tens of µm per year.
5. Conclusions
Compared to the gold standard titanium, we did not detect any significant differences in inflammatory reactions associated with the implanted specimens or other influences on the health of the animals. This speaks to an excellent local biocompatibility of the molybdenum material.
The extensive histopathological studies showed capsule formation in the nuchal fold, which greatly slowed degradation compared to previous in vivo studies. Even after 12 months, degradation was minimal. Therefore, the deposition of molybdenum in the organs cannot be adequately and conclusively assessed.
The influence of tissue environment, tissue reaction, and tissue integration of the implants on molybdenum degradation needs to be investigated in more detail in further studies. If necessary, strategies should be developed to modify the implants in order to achieve more favorable degradation conditions. For this purpose, tests on larger animals in direct bone contact will be the touchstone for suitability as osteosynthesis materials.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/app13106312/s1, Figure S1: Scratch marks in response to the shaved area.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.T.; methodology, A.T., N.K., D.H., M.S., G.P., L.v.M. and H.M.; validation, A.T., H.M. and G.P.; data curation, A.T., H.M. and D.H.; writing—original draft preparation, A.T., H.M. and D.H.; writing—review and editing. A.T. and G.P.; visualization, A.T., H.M., G.P. and D.H.; supervision, M.R.; project administration, A.T. and M.R.; funding acquisition, M.R. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung (BMBF), Germany; Verbundprojekt: Resorbierbare patientenindividuelle Implantate für die pädiatrische Chirurgie (ResorbM); funding code: 13GW0303D.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The animal study protocol was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Landesamt für Natur, Umwelt und Verbraucherschutz Nordrhein-Westfalen, Germany (LANUV) (Aktenzeichen 81.02.04.2021, approved on 7 June 2021).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
For further information, please contact the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Haerle, F.; Champy, M. Atlas of Craniomaxillofacial Osteosynthesis: Microplates, Miniplates, and Screws; Thieme: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, H.; Abel, T.J.; Alotaibi, N.M.; Anderson, M.; Niazi, T.N.; Weil, A.G.; Fallah, A.; Phillips, J.H.; Forrest, C.R.; Kulkarni, A.V.; et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis of endoscopic versus open treatment of craniosynostosis. Part 1: The sagittal suture. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 2018, 22, 352–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, H.; Abel, T.J.; Alotaibi, N.M.; Anderson, M.; Niazi, T.N.; Weil, A.G.; Fallah, A.; Phillips, J.H.; Forrest, C.R.; Kulkarni, A.V.; et al. A systematic review of endoscopic versus open treatment of craniosynostosis. Part 2: The nonsagittal single sutures. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 2018, 22, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gareb, B.; Roossien, C.C.; van Bakelen, N.B.; Verkerke, G.J.; Vissink, A.; Bos, R.R.; van Minnen, B. Comparison of the mechanical properties of biodegradable and titanium osteosynthesis systems used in oral and maxillofacial surgery. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 18143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barber, C.C.; Burnham, M.; Ojameruaye, O.; McKee, M.D. A systematic review of the use of titanium versus stainless steel implants for fracture fixation. OTA Int. 2021, 4, e138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comino-Garayoa, R.; Cortés-Bretón Brinkmann, J.; Peláez, J.; López-Suárez, C.; Martínez-González, J.M.; Suárez, M.J. Allergies to Titanium Dental Implants: What Do We Really Know about Them? A Scoping Review. Biology 2020, 9, 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Case, C.; Langkamer, V.; James, C.; Palmer; Kemp, A.; Heap, P.; Solomon, L. Widespread dissemination of metal debris from implants. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 1994, 76-B, 701–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buijs, G.J.; Stegenga, B.; Bos, R. Efficacy and safety of biodegradable osteofixation devices in oral and maxillofacial surgery: A systematic review. J. Dent. Res. 2006, 85, 980–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gareb, B.; Van Bakelen, N.; Buijs, G.; Jansma, J.; De Visscher, J.; Hoppenreijs, T.J.; Bergsma, J.; van Minnen, B.; Stegenga, B.; Bos, R. Comparison of the long-term clinical performance of a biodegradable and a titanium fixation system in maxillofacial surgery: A multicenter randomized controlled trial. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0177152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanno, T.; Sukegawa, S.; Furuki, Y.; Nariai, Y.; Sekine, J. Overview of innovative advances in bioresorbable plate systems for oral and maxillofacial surgery. Jpn. Dent. Sci. Rev. 2018, 54, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdmann, N.; Bondarenko, A.; Hewicker-Trautwein, M.; Angrisani, N.; Reifenrath, J.; Lucas, A.; Meyer-Lindenberg, A. Evaluation of the soft tissue biocompatibility of MgCa0.8 and surgical steel 316L in vivo: A comparative study in rabbits. Biomed. Eng. Online 2010, 9, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waizy, H.; Diekmann, J.; Weizbauer, A.; Reifenrath, J.; Bartsch, I.; Neubert, V.; Schavan, R.; Windhagen, H. In vivo study of a biodegradable orthopedic screw (MgYREZr-alloy) in a rabbit model for up to 12 months. J. Biomater. Appl. 2014, 28, 667–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erdmann, N.; Angrisani, N.; Reifenrath, J.; Lucas, A.; Thorey, F.; Bormann, D.; Meyer-Lindenberg, A. Biomechanical testing and degradation analysis of MgCa0. 8 alloy screws: A comparative in vivo study in rabbits. Acta Biomater. 2011, 7, 1421–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- May, H.; Alper Kati, Y.; Gumussuyu, G.; Yunus Emre, T.; Unal, M.; Kose, O. Bioabsorbable magnesium screw versus conventional titanium screw fixation for medial malleolar fractures. J. Orthop. Traumatol. 2020, 21, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biber, R.; Pauser, J.; Brem, M.; Bail, H.J. Bioabsorbable metal screws in traumatology: A promising innovation. Trauma Case Rep. 2017, 8, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waizy, H.; Seitz, J.-M.; Reifenrath, J.; Weizbauer, A.; Bach, F.-W.; Meyer-Lindenberg, A.; Denkena, B.; Windhagen, H. Biodegradable magnesium implants for orthopedic applications. J. Mater. Sci. 2013, 48, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaass, C.; Ettinger, S.; Sonnow, L.; Koenneker, S.; Noll, Y.; Weizbauer, A.; Reifenrath, J.; Claassen, L.; Daniilidis, K.; Stukenborg-Colsman, C.; et al. Early results using a biodegradable magnesium screw for modified chevron osteotomies. J. Orthop. Res. 2016, 34, 2207–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.F.; Gu, X.N.; Witte, F. Biodegradable metals. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2014, 77, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eppley, B.L.; Morales, L.; Wood, R.; Pensler, J.; Goldstein, J.; Havlik, R.J.; Habal, M.; Losken, A.; Williams, J.K.; Burstein, F.; et al. Resorbable PLLA-PGA plate and screw fixation in pediatric craniofacial surgery: Clinical experience in 1883 patients. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2004, 114, 850–856; discussion 857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bos, R.R.; Boering, G.; Rozema, F.R.; Leenslag, J.W. Resorbable poly(L-lactide) plates and screws for the fixation of zygomatic fractures. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 1987, 45, 751–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, R.J.; Petronio, J.A.; Graupman, P.C.; Shell, C.D.; Gear, A.J.L. New Resorbable Plate and Screw System in Pediatric Craniofacial Surgery. J. Craniofacial Surg. 2012, 23, 845–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eppley, B.L. Zygomaticomaxillary fracture repair with resorbable plates and screws. J. Craniofacial Surg. 2000, 11, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergsma, J.E.; De Bruijn, W.; Rozema, F.; Bos, R.; Boering, G. Late degradation tissue response to poly(L-lactide) bone plates and screws. Biomaterials 1995, 16, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, G.; Mendel, R.R.; Ribbe, M.W. Molybdenum cofactors, enzymes and pathways. Nature 2009, 460, 839–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bojinov, M.; Betova, I.; Raicheff, R. A model for the transpassivity of molybdenum in acidic sulphate solutions based on ac impedance measurements. Electrochim. Acta 1996, 41, 1173–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redlich, C.; Quadbeck, P.; Thieme, M.; Kieback, B. Molybdenum—A biodegradable implant material for structural applications? Acta Biomater. 2020, 104, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikora-Jasinska, M.; Morath, L.M.; Kwesiga, M.P.; Plank, M.E.; Nelson, A.L.; Oliver, A.A.; Bocks, M.L.; Guillory, R.J.; Goldman, J. In-vivo evaluation of molybdenum as bioabsorbable stent candidate. Bioact. Mater. 2022, 14, 262–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toschka, A.; Pöhle, G.; Quadbeck, P.; Suschek, C.V.; Strauß, A.; Redlich, C.; Rana, M. Molybdenum as a Potential Biocompatible and Resorbable Material for Osteosynthesis in Craniomaxillofacial Surgery—An In Vitro Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15710. [Google Scholar]
- Murray, F.J.; Sullivan, F.M.; Tiwary, A.K.; Carey, S. 90-Day subchronic toxicity study of sodium molybdate dihydrate in rats. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2014, 70, 579–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bompart, G.; Pécher, C.; Prévot, D.; Girolami, J.P. Mild renal failure induced by subchronic exposure to molybdenum: Urinary kallikrein excretion as a marker of distal tubular effect. Toxicol. Lett. 1990, 52, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krenn, V.; Morawietz, L.; Burmester, G.R.; Kinne, R.W.; Mueller-Ladner, U.; Muller, B.; Haupl, T. Synovitis score: Discrimination between chronic low-grade and high-grade synovitis. Histopathology 2006, 49, 358–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, S. A dirty dozen: Twelve p-value misconceptions. Semin. Hematol. 2008, 45, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenland, S.; Senn, S.J.; Rothman, K.J.; Carlin, J.B.; Poole, C.; Goodman, S.N.; Altman, D.G. Statistical tests, P values, confidence intervals, and power: A guide to misinterpretations. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2016, 31, 337–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, J.; Kaserer, L.; Stajkovic, J.; Leitz, K.H.; Tabernig, B.; Singer, P.; Leibenguth, P.; Gspan, C.; Kestler, H.; Leichtfried, G. Molybdenum and tungsten manufactured by selective laser melting: Analysis of defect structure and solidification mechanisms. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2019, 84, 104999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turnlund, J.R.; Weaver, C.M.; Kim, S.K.; Keyes, W.R.; Gizaw, Y.; Thompson, K.H.; Peiffer, G.L. Molybdenum absorption and utilization in humans from soy and kale intrinsically labeled with stable isotopes of molybdenum. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1999, 69, 1217–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schauer, A.; Redlich, C.; Scheibler, J.; Poehle, G.; Barthel, P.; Maennel, A.; Adams, V.; Weissgaerber, T.; Linke, A.; Quadbeck, P. Biocompatibility and Degradation Behavior of Molybdenum in an In Vivo Rat Model. Materials 2021, 14, 7776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrova, M.; Bojinov, M.; Zanna, S.; Marcus, P. Mechanism of anodic oxidation of molybdenum in nearly-neutral electrolytes studied by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. Electrochim. Acta 2011, 56, 7899–7906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Hu, J.; Ma, D. Postoperative delirium: Perioperative assessment, risk reduction, and management. Br. J. Anaesth. 2020, 125, 492–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.W.; Chi, C.H.; Chen, C.K.; James, W.J. The Anodic Dissolution of Molybdenum. Corrosion 2013, 26, 338–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourbaix, M. Applications of electrochemistry in corrosion science and in practice. Corros. Sci. 1974, 14, 25–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).