Evolution of Qualitative and Quantitative Lipid Profiles of High-Pressure-Processed Serra da Estrela Cheese throughout Storage
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cheese Manufacture and High-Pressure Processing
2.2. Chemicals
2.3. Lipid Extraction
2.4. Triglycerides Determination
2.5. Methyl Esters Fatty Acids Preparation
2.6. Fatty Acids Identification and Quantification
2.7. Nutritional Quality Indices of Lipids
2.8. Conjugated Linoleic Acid Determination
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
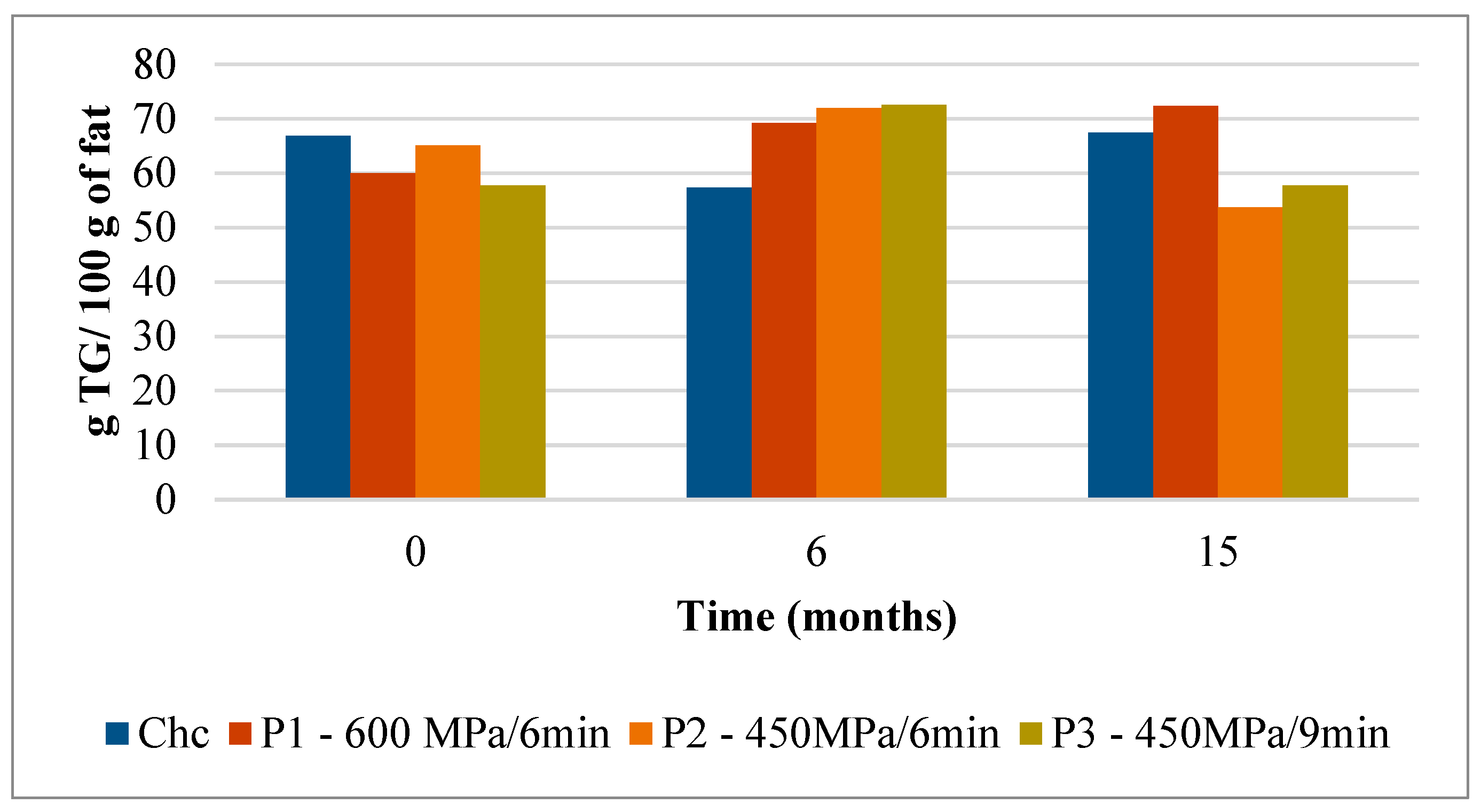
Triglycerides Composition of Serra da Estrela Cheese
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Macedo, A.C.; Malcata, F.X.; Oliveira, J.C. The technology, chemistry, and microbiology of Serra cheese: A review. J. Dairy Sci. 1993, 76, 1725–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khattab, A.R.; Guirguis, H.A.; Tawfik, S.M.; Farag, M.A. Cheese ripening: A review on modern technologies towards flavor enhancement, process acceleration and improved quality assessment. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 88, 343–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McSweeney, P.L.H. Biochemistry of Cheese Ripening: Introduction and Overview; Elsevier: London, UK, 2004; pp. 347–360. [Google Scholar]
- Partidário, A.M.; Barbosa, M.; Vilas Boas, L. Free fatty acids, triglycerides and volatile compounds in Serra da Estrela cheese—Changes throughout ripening. Int. Dairy J. 1998, 8, 873–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macedo, A.C.; Tavares, G.; Malcata, F.X. Esterase activities of intracellular extracts of wild strains of lactic acid bacteria isolated from Serra da Estrela cheese. Food Chem. 2003, 81, 379–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macedo, A.C.; Malcata, F.X. Role of adventitious microflora in proteolysis and lipolysis of Serra cheese: Preliminary screening. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 1997, 205, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macedo, A.C.; Costa, M.L.; Malcata, F.X. Assessment of proteolysis and lipolysis in Serra cheese: Effects of axial cheese location, ripening time and lactation season. Lait 1996, 76, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis Lima, M.J.; Fontes, L.; Bahri, H.; Veloso, A.C.A.; Teixeira-Lemos, E.; Peres, A.M. Fatty acids profile of Serra da Estrela PDO cheeses and respective atherogenic and thrombogenic indices. Nutr. Food Sci. 2019, 50, 417–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhineshkumar, V.; Ramasamy, D.; Siddharth, M. High pressure processing technology in dairy processing: A review. Asian J. Dairy Food Res. 2016, 35, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inácio, R.S. Effect of High-Pressure as a Non-Thermal Pasteurisation Technology for Raw Ewes’ Milk and Cheese Safety and Quality: Case Study on Serra da Estrela Cheese. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidade Católica Portuguesa, Porto, Portugal, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Inácio, R.S.; Monteiro, M.J.P.; Lopes-da-silva, J.A.; Gomes, A.M.P.; Saraiva, J.A. Comparing different packaging conditions on quality stability of high-pressure treated Serra da Estrela cheeses during cold storage. Foods 2023, 12, 1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juan, B.; Ferragut, V.; Guamis, B.; Trujillo, A.J. The effect of high-pressure treatment at 300 MPa on ripening of ewes’ milk cheese. Int. Dairy J. 2008, 18, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juan, B.; Ferragut, V.; Buffa, M.; Guamis, B.; Trujillo, A.J. Effects of high-pressure treatment on free fatty acids release during ripening of ewes’ milk cheese. J. Dairy Res. 2007, 74, 438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rynne, N.M.; Beresford, T.P.; Guinee, T.P.; Sheehan, E.; Delahunty, C.M.; Kelly, A.L. Effect of high-pressure treatment of 1 day-old full-fat Cheddar cheese on subsequent quality and ripening. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2008, 9, 429–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ávila, M.; Calzada, J.; Garde, S.; Nuñez, M. Effect of a bacteriocin-producing Lactococcus lactis strain and high-pressure treatment on the esterase activity and free fatty acids in Hispánico cheese. Int. Dairy J. 2007, 17, 1415–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saldo, J.; Fernández, A.; Sendra, E.; Butz, P.; Tauscher, B.; Guamis, B. High pressure treatment decelerates the lipolysis in a caprine cheese. Food Res. Int. 2003, 36, 1061–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calzada, J.; Del Olmo, A.; Picon, A.; Gaya, P.; Nuñez, M. High-Pressure Processing for the Control of Lipolysis, Volatile Compounds and Off-odours in Raw Milk Cheese. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2014, 7, 2207–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Pinilla, J.; Márquez, G.; Tabla, R.; Ramírez, R.; Delgado, F.J. Microbiological and lipolytic changes in high-pressure-treated raw milk cheeses during refrigerated storage. Dairy Sci. Technol. 2015, 95, 425–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calzada, J.; Del Olmo, A.; Picon, A.; Nuñez, M. Effect of High Pressure Processing on the Lipolysis, Volatile Compounds, Odour and Colour of Cheese Made from Unpasteurized Milk. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2015, 8, 1076–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matyash, V.; Liebisch, G.; Kurzchalia, T.V.; Shevchenko, A.; Schwudke, D. Lipid extraction by methyl-tert-butyl ether for high-throughput lipidomics. J. Lipid Res. 2008, 49, 1137–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Gómez, M.P.; Holgado, F.; Rodríguez-Alcalá, L.M.; Montero, O.; Fontecha, J. Comprehensive Study of the Lipid Classes of Krill Oil by Fractionation and Identification of Triacylglycerols, Diacylglycerols, and Phospholipid Molecular Species by Using UPLC/QToF-MS. Food Anal. Methods 2015, 8, 2568–2580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimentel, L.L.; Fontes, A.L.; Gomes, A.M.P.; Rodríguez-Alcalá, L.M. Considerations about the in situ derivatization and fractionation of EFA and NEFA in biological and food samples. MethodsX 2015, 2, 475–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulbricht, T.L.V.; Southgate, D.A.T. Coronary heart disease: Seven dietary factors. Lancet 1991, 338, 985–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Alcalá, L.M.; Alonso, L.; Fontecha, J. Stability of fatty acid composition after thermal, high pressure, and microwave processing of cow milk as affected by polyunsaturated fatty acid concentration. J. Dairy Sci. 2014, 97, 7307–7315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Alcalá, L.M.; Castro-Gómez, P.; Felipe, X.; Noriega, L.; Fontecha, J. Effect of processing of cow milk by high pressures under conditions up to 900 MPa on the composition of neutral, polar lipids and fatty acids. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 62, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carocho, M.; Barreira, J.C.M.; Antonio, A.L.; Bento, A.; Morales, P.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R. The incorporation of plant materials in “Serra da Estrela” cheese improves antioxidant activity without changing the fatty acid profile and visual appearance. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2015, 117, 1607–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naydenova, N.; Kaishev, I.; Iliev, T.; Mihaylova, G. Fatty acids profile, atherogenic and thrombogenic health indices of white brined cheese made from buffalo milk. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2014, 6, 352–355. [Google Scholar]
- Kris-Etherton, P.M.; Pearson, T.A.; Wan, Y.; Hargrove, R.L.; Moriarty, K.; Fishell, V.; Etherton, T.D. High–monounsaturated fatty acid diets lower both plasma cholesterol and triacylglycerol concentrations. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1999, 70, 1009–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prandini, A.; Sigolo, S.; Piva, G. A comparative study of fatty acid composition and CLA concentration in commercial cheeses. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2011, 24, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Alcalá, L.M.; Fontecha, J. Hot Topic: Fatty Acid and Conjugated Linoleic Acid (CLA) Isomer Composition of Commercial CLA-Fortified Dairy Products: Evaluation after Processing and Storage. J. Dairy Sci. 2007, 90, 2083–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhamid, A.S.; Martin, N.; Bridges, C.; Brainard, J.S.; Wang, X.; Brown, T.J.; Hanson, S.; Jimoh, O.F.; Ajabnoor, S.M.; Deane, K.H.; et al. Polyunsaturated fatty acids for the primary and secondary prevention of cardiovascular disease. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2018, 2018, CD012345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addis, M.; Cabiddu, A.; Pinna, G.; Decandia, M.; Piredda, G.; Pirisi, A.; Molle, G. Milk and Cheese Fatty Acid Composition in Sheep Fed Mediterranean Forages with Reference to Conjugated Linoleic Acid cis-9,trans-11. J. Dairy Sci. 2005, 88, 3443–3454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, F.J.; González-Crespo, J.; Ladero, L.; Cava, R.; Ramírez, R. Free fatty acids and oxidative changes of a Spanish soft cheese (PDO ‘Torta del Casar’) during ripening. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2009, 44, 1721–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| ChC | P1 600 MPa/6 min | P2 450 MPa/6 min | P3 450 MPa/9 min | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Storage Time (Months) | 0 | 6 | 15 | 0 | 6 | 15 | 0 | 6 | 15 | 0 | 6 | 15 |
| IA | 2.36 | 2.35 | 2.37 | 2.36 | 2.33 | 2.40 | 2.37 | 2.37 | 2.38 | 2.32 | 2.33 | 2.38 |
| IT | 2.60 | 2.55 | 2.60 | 2.58 | 2.56 | 2.64 | 2.62 | 2.59 | 2.61 | 2.55 | 2.56 | 2.61 |
| Omega 6/Omega 3 | 12.47 | 10.59 | 11.51 | 11.21 | 11.97 | 11.78 | 12.89 | 11.29 | 11.68 | 11.57 | 11.96 | 11.57 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Inácio, R.S.; Rodríguez-Alcalá, L.M.; Pimentel, L.L.; Saraiva, J.A.; Gomes, A.M.P. Evolution of Qualitative and Quantitative Lipid Profiles of High-Pressure-Processed Serra da Estrela Cheese throughout Storage. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 5927. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13105927
Inácio RS, Rodríguez-Alcalá LM, Pimentel LL, Saraiva JA, Gomes AMP. Evolution of Qualitative and Quantitative Lipid Profiles of High-Pressure-Processed Serra da Estrela Cheese throughout Storage. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(10):5927. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13105927
Chicago/Turabian StyleInácio, Rita S., Luís M. Rodríguez-Alcalá, Lígia L. Pimentel, Jorge A. Saraiva, and Ana M. P. Gomes. 2023. "Evolution of Qualitative and Quantitative Lipid Profiles of High-Pressure-Processed Serra da Estrela Cheese throughout Storage" Applied Sciences 13, no. 10: 5927. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13105927
APA StyleInácio, R. S., Rodríguez-Alcalá, L. M., Pimentel, L. L., Saraiva, J. A., & Gomes, A. M. P. (2023). Evolution of Qualitative and Quantitative Lipid Profiles of High-Pressure-Processed Serra da Estrela Cheese throughout Storage. Applied Sciences, 13(10), 5927. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13105927









