Electrically Conductive Nanocomposite Fibers for Flexible and Structural Electronics
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Composite Fibers Preparation
2.3. Composite Analysis and Testing
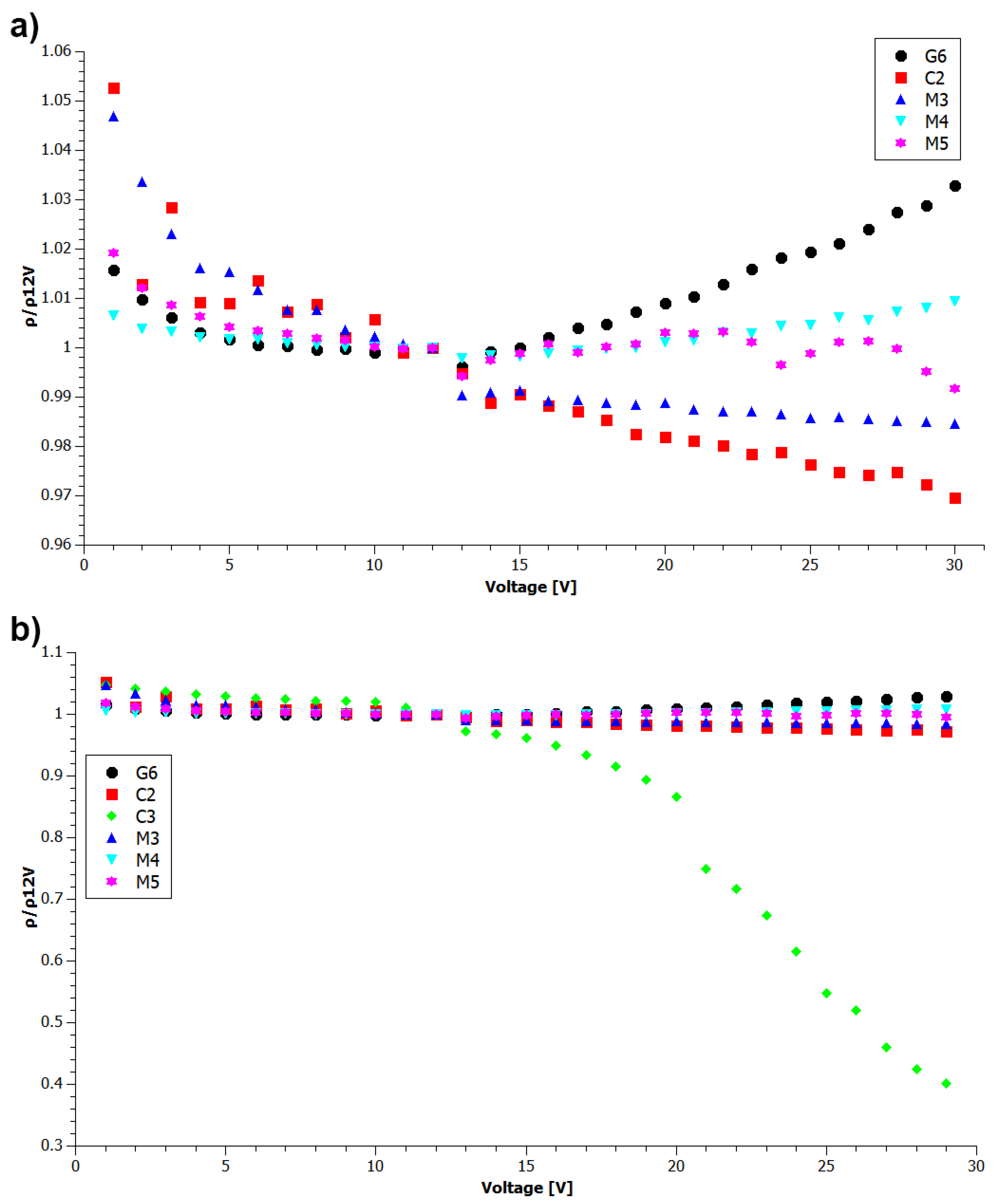
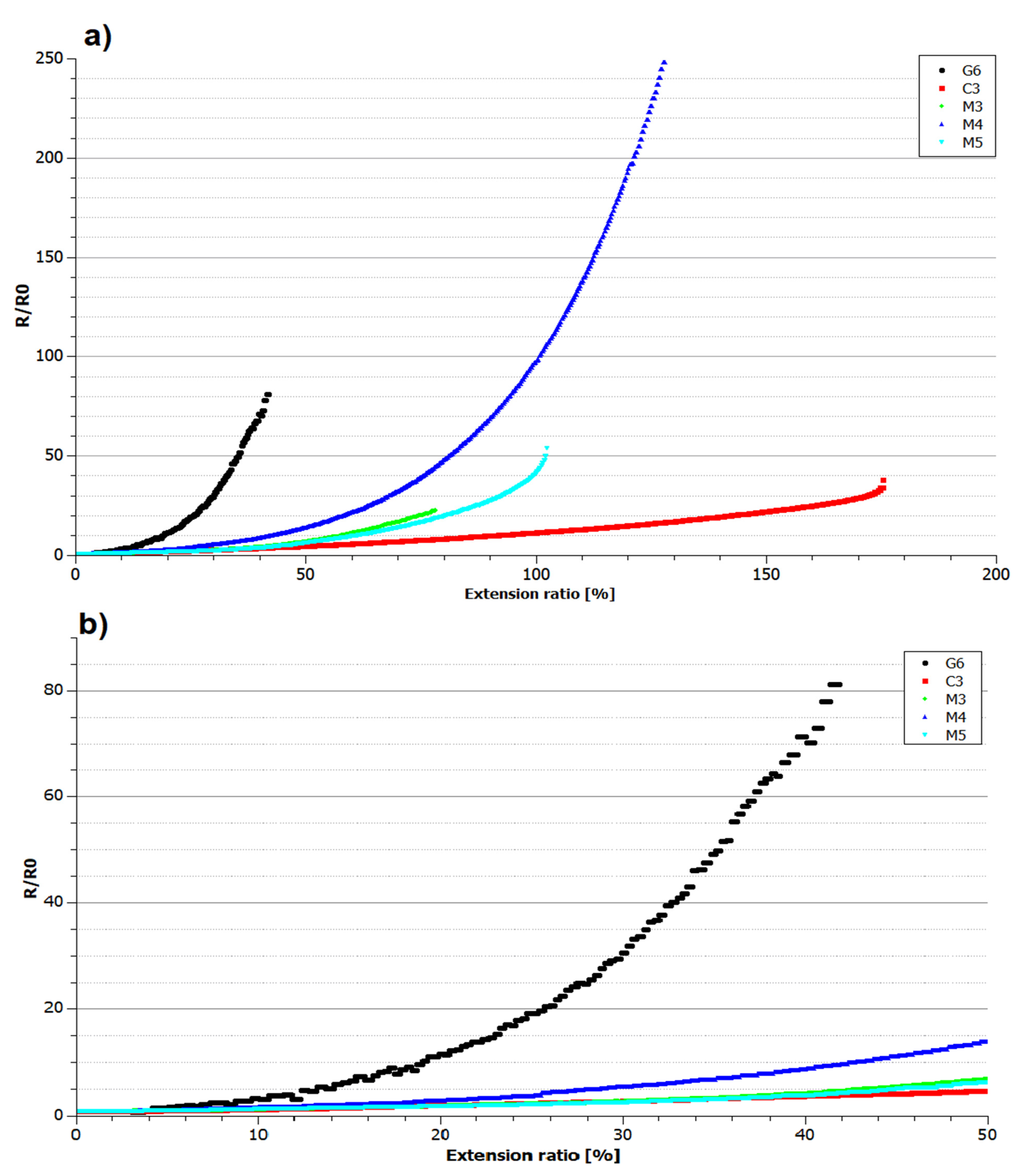
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Composite Fibres Content
3.2. Acceptance Criteria
3.3. Fabrication of Continous Fiber
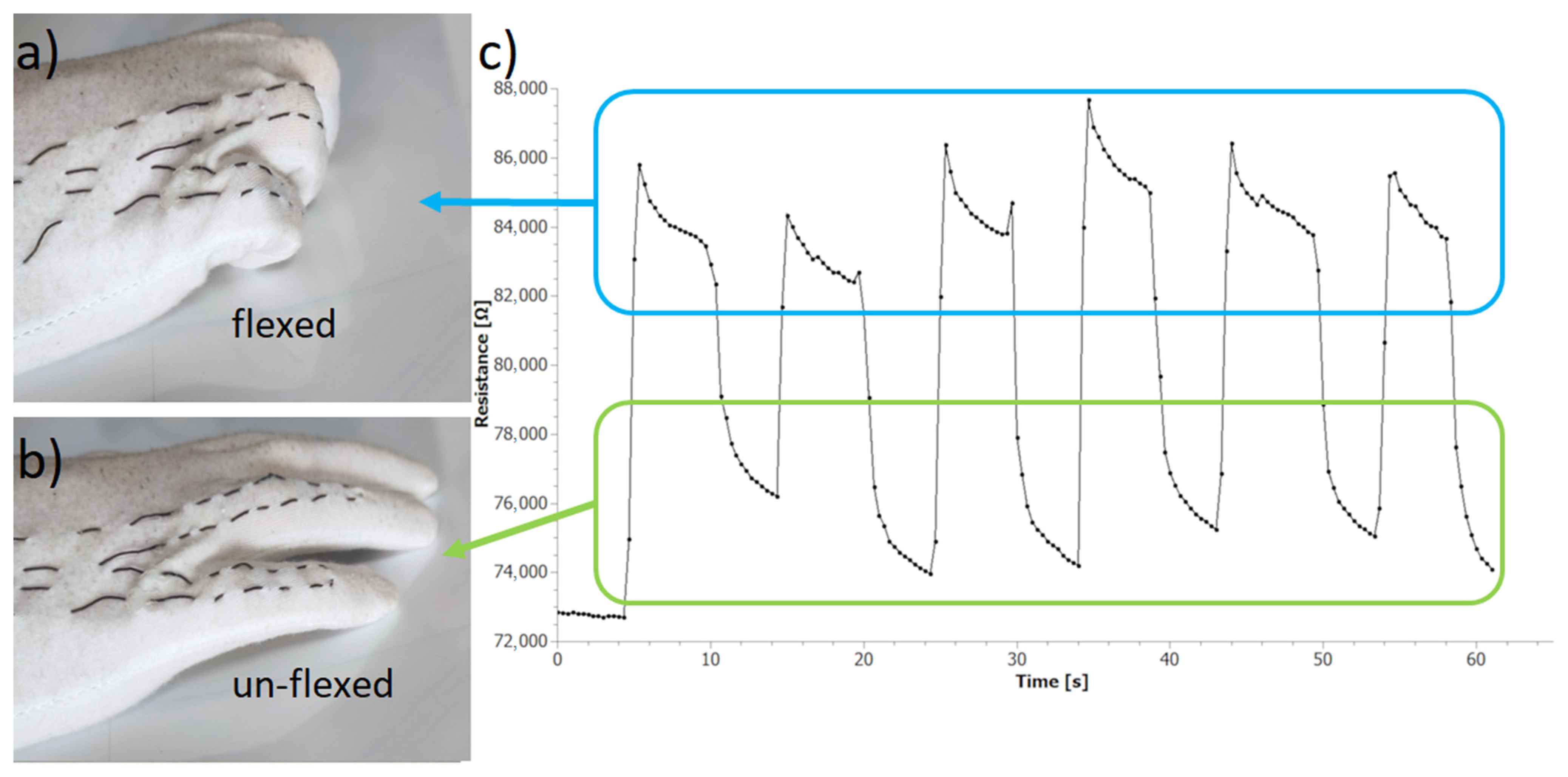
3.4. Electrical Properties
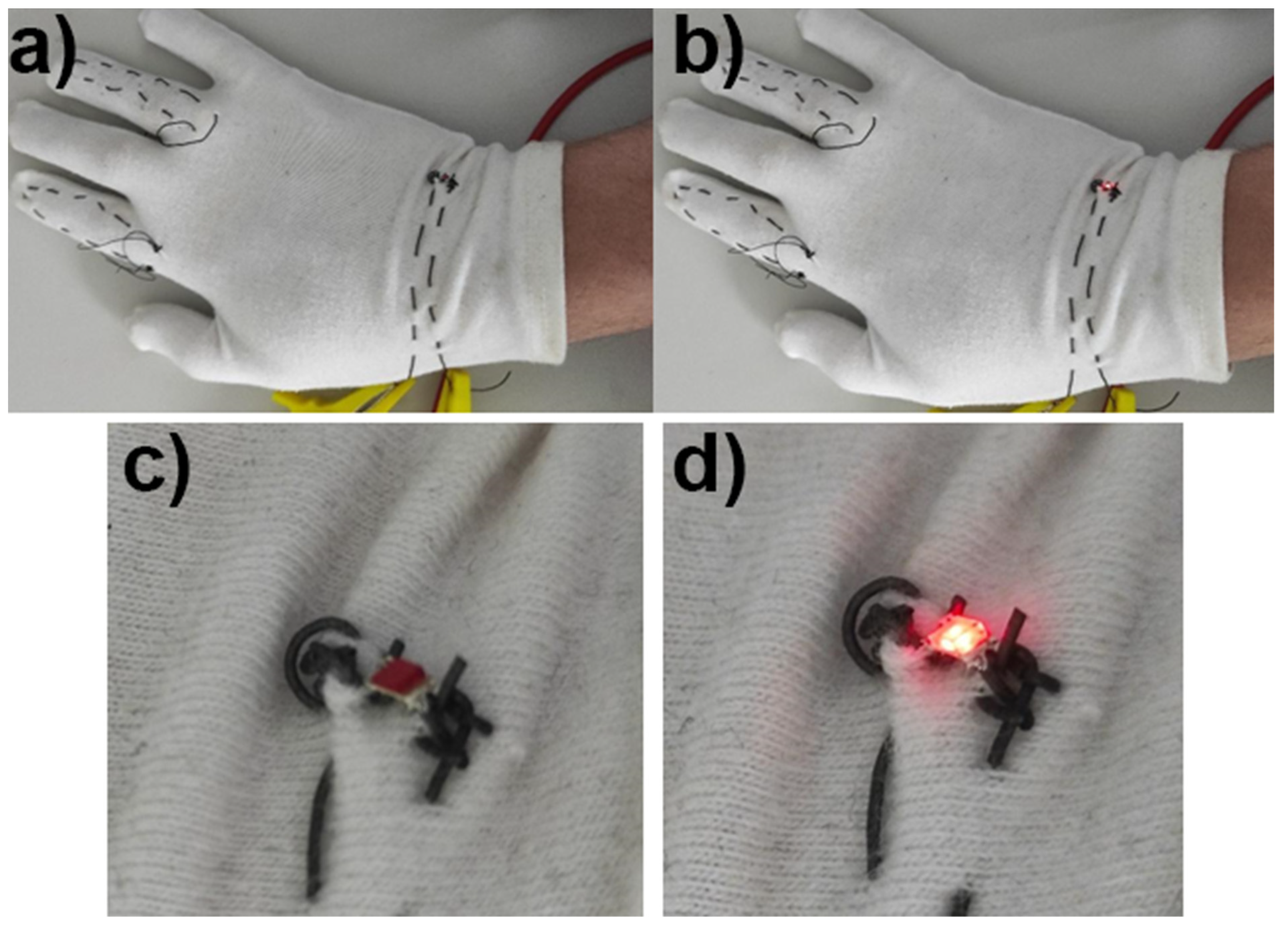
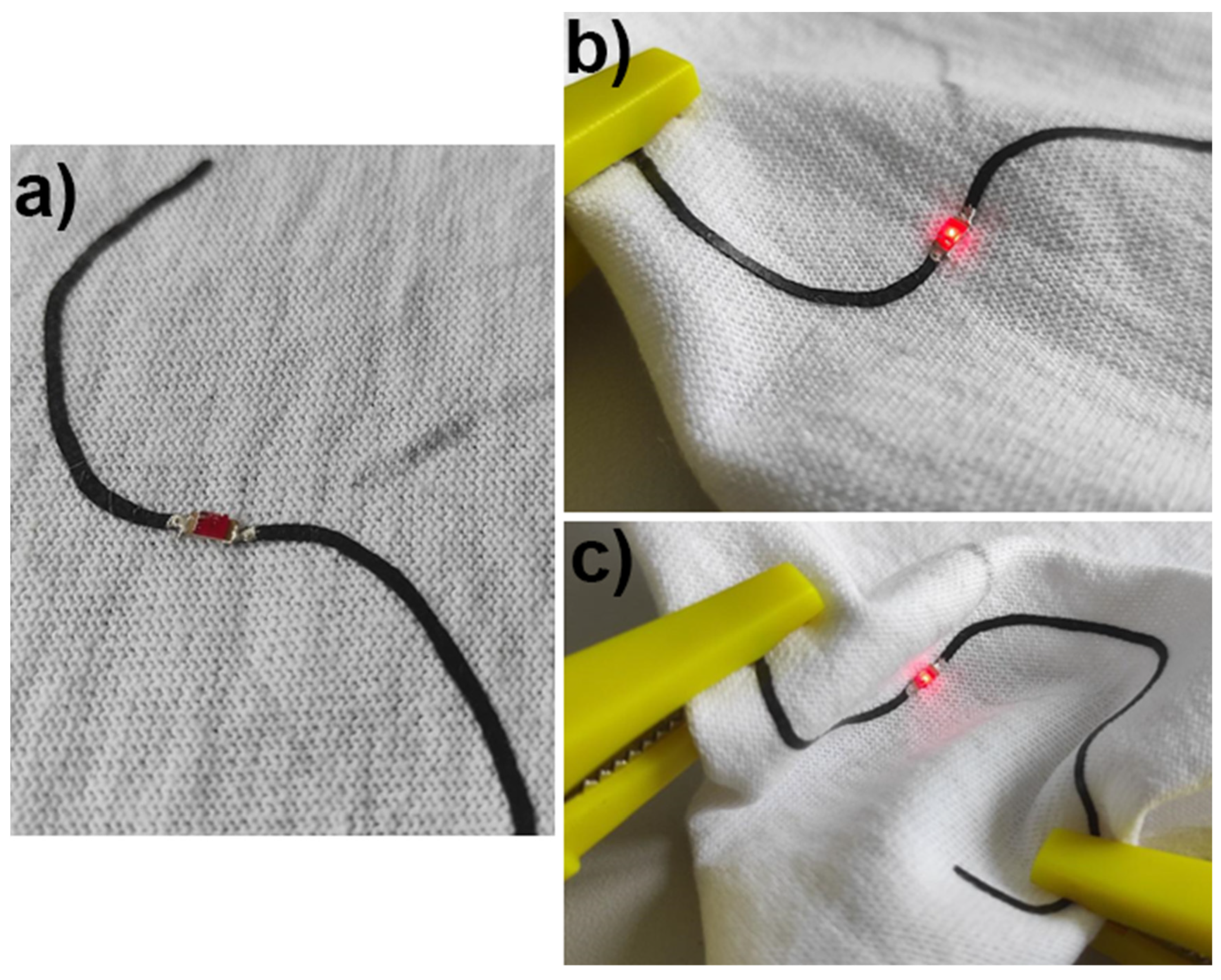
4. Applications
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Koncar, V. Introduction to Smart Textiles and Their Applications. In Smart Textiles and Their Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 1–8. ISBN 978-0-08-100574-3. [Google Scholar]
- Axisa, F.; Schmitt, P.M.; Gehin, C.; Delhomme, G.; McAdams, E.; Dittmar, A. Flexible Technologies and Smart Clothing for Citizen Medicine, Home Healthcare, and Disease Prevention. IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed. 2005, 9, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syduzzaman, M.; Patwary, S.; Farhana, K.; Ahmed, S. Smart Textiles and Nano-Technology: A General Overview. J. Text. Sci. Eng. 2015, 5, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Li, Y.; Bick, M.; Chen, J. Smart Textiles for Electricity Generation. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 3668–3720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coyle, S.; Wu, Y.; Lau, K.-T.; De Rossi, D.; Wallace, G.; Diamond, D. Smart Nanotextiles: A Review of Materials and Applications. MRS Bull. 2007, 32, 434–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cherenack, K.; van Pieterson, L. Smart Textiles: Challenges and Opportunities. J. Appl. Phys. 2012, 112, 091301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, L.; Pasta, M.; La Mantia, F.; Cui, L.; Jeong, S.; Deshazer, H.D.; Choi, J.W.; Han, S.M.; Cui, Y. Stretchable, Porous, and Conductive Energy Textiles. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 708–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Service, R.F. Electronic Textiles Charge Ahead. Science 2003, 301, 909–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaspar, P.; Sobola, D.; Částková, K.; Knápek, A.; Burda, D.; Orudzhev, F.; Dallaev, R.; Tofel, P.; Trčka, T.; Grmela, L.; et al. Characterization of Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF) Electrospun Fibers Doped by Carbon Flakes. Polymers 2020, 12, 2766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lepak-Kuc, S.; Podsiadły, B.; Skalski, A.; Janczak, D.; Jakubowska, M.; Lekawa-Raus, A. Highly Conductive Carbon Nanotube-Thermoplastic Polyurethane Nanocomposite for Smart Clothing Applications and Beyond. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, N.; Jain, P.K.; Tandon, P.; Pandey, P.M. Additive Manufacturing of Flexible Electrically Conductive Polymer Composites via CNC-Assisted Fused Layer Modeling Process. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 2018, 40, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aumnate, C.; Pongwisuthiruchte, A.; Pattananuwat, P.; Potiyaraj, P. Fabrication of ABS/Graphene Oxide Composite Filament for Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF) 3D Printing. Available online: https://www.hindawi.com/journals/amse/2018/2830437/ (accessed on 19 November 2018).
- Gnanasekaran, K.; Heijmans, T.; van Bennekom, S.; Woldhuis, H.; Wijnia, S.; de With, G.; Friedrich, H. 3D Printing of CNT- and Graphene-Based Conductive Polymer Nanocomposites by Fused Deposition Modeling. Appl. Mater. Today 2017, 9, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cravanzola, S.; Haznedar, G.; Scarano, D.; Zecchina, A.; Cesano, F. Carbon-Based Piezoresistive Polymer Composites: Structure and Electrical Properties. Carbon 2013, 62, 270–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushal, A.; Singh, V. Analysis of Mechanical, Thermal, Electrical and EMI Shielding Properties of Graphite/Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polypropylene Composites Prepared via a Twin Screw Extruder. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2022, 139, 51444. Available online: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/app.51444 (accessed on 6 October 2021). [CrossRef]
- Maurel, A.; Courty, M.; Fleutot, B.; Tortajada, H.; Prashantha, K.; Armand, M.; Grugeon, S.; Panier, S.; Dupont, L. Highly Loaded Graphite–Polylactic Acid Composite-Based Filaments for Lithium-Ion Battery Three-Dimensional Printing. Chem. Mater. 2018, 30, 7484–7493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, J.A.; Via, M.D.; Keith, J.M.; Morrison, F.A. Effects of Carbon Fillers on Rheology of Polypropylene-Based Resins. J. Compos. Mater. 2009, 43, 3073–3089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, E.; Rothstein, J.P. Control of the Sharkskin Instability in the Extrusion of Polymer Melts Using Induced Temperature Gradients. Rheol. Acta 2004, 44, 160–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koopmans, R.J.; Molenaar, J. The “Sharkskin Effect” in Polymer Extrusion. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1998, 38, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arda, D.R.; Mackley, M.R. The Effect of Die Exit Curvature, Die Surface Roughness and a Fluoropolymer Additive on Sharkskin Extrusion Instabilities in Polyethylene Processing. J. Non-Newton. Fluid Mech. 2005, 126, 47–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Difallah, B.; Kharrat, M.; Dammak, M.; Monteil, G. Mechanical and Tribological Response of ABS Polymer Matrix Filled with Graphite Powder. Mater. Des. 2012, 34, 782–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshavamurthy, R.; Tambrallimath, V.; Rajhi, A.A.; Patil, A.Y.; Khan, Y.; Makannavar, R. Influence of Solid Lubricant Addition on Friction and Wear Response of 3D Printed Polymer Composites. Polymers 2021, 13, 2905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Saleh, M.H.; Al-Anid, H.K.; Husain, Y.A.; El-Ghanem, H.M.; Jawad, S.A. Impedance Characteristics and Conductivity of CNT/ABS Nanocomposites. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2013, 46, 385305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchmutin, I.A.; Ponomarenko, A.T.; Krinichnaya, E.P.; Kozub, G.I.; Efimov, O.N. Electrical Properties of Composites Based on Conjugated Polymers and Conductive Fillers. Carbon 2003, 41, 1391–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, N.M.; Kamarudin, M.S.; Rus, A.Z.M.; Abdullah, M.F.L. Preparation of Conductive Polymer Graphite (PG) Composites. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 226, 012181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, R.; Ren, Z.; Bi, H.; Xu, M.; Cai, L. Electrical and Thermal Conductivity of Polylactic Acid (PLA)-Based Biocomposites by Incorporation of Nano-Graphite Fabricated with Fused Deposition Modeling. Polymers 2019, 11, 549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Yu, S.; Luo, S.; Chu, B.; Sun, R.; Wong, C.-P. Investigation of Nonlinear I–V Behavior of CNTs Filled Polymer Composites. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2016, 206, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramamurthy, P.C.; Malshe, A.M.; Harrell, W.R.; Gregory, R.V.; McGuire, K.; Rao, A.M. Polyaniline/Single-Walled Carbon Nanotube Composite Electronic Devices. Solid-State Electron. 2004, 48, 2019–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Z.-D.; Chen, T.; Li, Z.-M.; Bian, X.-C. Negative Temperature Coefficient of Resistivity in Lightweight Conductive Carbon Nanotube/Polymer Composites. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2009, 294, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohd Radzuan, N.A.; Sulong, A.B.; Hui, D.; Verma, A. Electrical Conductivity Performance of Predicted Modified Fibre Contact Model for Multi-Filler Polymer Composite. Polymers 2019, 11, 1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gau, C.; Kuo, C.-Y.; Ko, H.S. Electron Tunneling in Carbon Nanotube Composites. Nanotechnology 2009, 20, 395705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakaramontri, Y.; Kummerlöwe, C.; Vennemann, N.; Wisunthorn, S.; Pichaiyut, S.; Nakason, C. Electron Tunneling in Carbon Nanotubes and Carbon Black Hybrid Filler-Filled Natural Rubber Composites: Influence of Non-Rubber Components. Polym. Compos. 2018, 39, E1237–E1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zupin, Z.; Dimitrovski, K. Mechanical Properties of Fabrics Made from Cotton and Biodegradable Yarns Bamboo, SPF, PLA in Weft. In Woven Fabric Engineering; Dobnik, P., Ed.; Sciyo: London, UK, 2010; ISBN 978-953-307-194-7. [Google Scholar]
- Kaynak, H.K.; Babaarslan, O. Breaking Strength and Elongation Properties of Polyester Woven Fabrics on the Basis of Filament Fineness. J. Eng. Fibers Fabr. 2015, 10, 155892501501000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogulata, S.N.; Sahin, C.; Ogulata, R.T.; Balci, O. The Prediction of Elongation and Recovery of Woven Bi-Stretch Fabric Using Artificial Neural Network and Linear Regression Models. Fibres Text. East. Eur. 2006, 14, 56. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.; Kim, D.W.; Chun, S.; Song, J.H.; Yoo, E.S.; Kim, J.K.; Pang, C. Intrinsically Strain-Insensitive, Hyperelastic Temperature-Sensing Fiber with Compressed Micro-Wrinkles for Integrated Textronics. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2020, 5, 2000073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoppa, M.; Chiolerio, A. Wearable Electronics and Smart Textiles: A Critical Review. Sensors 2014, 14, 11957–11992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, Q.; Sun, J.; Hou, C.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, H. Advanced Functional Fiber and Smart Textile. Adv. Fiber Mater. 2019, 1, 3–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kolanowska, A.; Kuziel, A.W.; Herman, A.P.; Jędrysiak, R.G.; Giżewski, T.; Boncel, S. Electroconductive Textile Coatings from Pastes Based on Individualized Multi-Wall Carbon Nanotubes–Synergy of Surfactant and Nanotube Aspect Ratio. Prog. Org. Coat. 2019, 130, 260–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sloma, M.; Janczak, D.; Wroblewski, G.; Mlozniak, A.; Jakubowska, M. Electroluminescent Structures Printed on Paper and Textile Elastic Substrates. Circuit World 2014, 40, 13–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Bashir, T.; Bresky, E.; Persson, N.-K. Electroconductive Textiles. In Smart Textiles and Their Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 657–693. ISBN 978-0-08-100574-3. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, J.; Liu, S.; Zhang, L.; Yang, B.; Shu, L.; Yang, Y.; Ren, M.; Wang, Y.; Chen, J.; Chen, W.; et al. Smart Textile-Integrated Microelectronic Systems for Wearable Applications. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1901958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pulanthran, K.; Jizat, N.M.; Islam, M.S. A Low-Cost Textile Antenna Using Thermal-Transfer Printing. In Proceedings of the 2020 16th IEEE International Colloquium on Signal Processing & Its Applications (CSPA), Langkawi, Malaysia, 28–29 February 2020; pp. 162–165. [Google Scholar]
- Yamada, T.; Hayamizu, Y.; Yamamoto, Y.; Yomogida, Y.; Izadi-Najafabadi, A.; Futaba, D.N.; Hata, K. A Stretchable Carbon Nanotube Strain Sensor for Human-Motion Detection. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2011, 6, 296–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardoiwala, M.N.; Kaundal, B.; Choudhury, S.R. Toxic Impact of Nanomaterials on Microbes, Plants and Animals. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2018, 16, 147–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aschberger, K.; Johnston, H.J.; Stone, V.; Aitken, R.J.; Hankin, S.M.; Peters, S.A.K.; Tran, C.L.; Christensen, F.M. Review of Carbon Nanotubes Toxicity and Exposure—Appraisal of Human Health Risk Assessment Based on Open Literature. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2010, 40, 759–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirth, S.; Cena, L.; Cox, G.; Tomović, Ž.; Peters, T.; Wohlleben, W. Scenarios and Methods That Induce Protruding or Released CNTs after Degradation of Nanocomposite Materials. J. Nanopart. Res. 2013, 15, 1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ghiazza, M.; Vietti, G.; Fenoglio, I. 8-Carbon Nanotubes: Properties, Applications, and Toxicity. In Health and Environmental Safety of Nanomaterials; Njuguna, J., Pielichowski, K., Zhu, H., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2014; pp. 147–174. ISBN 978-0-85709-655-5. [Google Scholar]
- Schlagenhauf, L.; Nüesch, F.; Wang, J. Release of Carbon Nanotubes from Polymer Nanocomposites. Fibers 2014, 2, 108–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Material Amount [vol. %] | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SBS | Graphite | CNT | ||
| Composite symbol | G1 | 95 | 5 | 0 |
| G2 | 90 | 10 | 0 | |
| G3 | 80 | 20 | 0 | |
| G4 | 60 | 40 | 0 | |
| G5 | 55 | 45 | 0 | |
| G6 | 50 | 50 | 0 | |
| C1 | 98 | 0 | 2 | |
| C2 | 95 | 0 | 5 | |
| C3 | 90 | 0 | 10 | |
| M1 | 96 | 2 | 2 | |
| M2 | 93 | 2 | 5 | |
| M3 | 90 | 5 | 5 | |
| M4 | 85 | 10 | 5 | |
| M5 | 80 | 15 | 5 | |
| Resistivity [Ωm] | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nozzle Diameter [mm] | ||||
| 0.2 | 0.5 | 1 | ||
| Composite symbol | G1 | - | - | - |
| G2 | - | - | - | |
| G3 | - | 42.9 ± 8.5 | 11.8 ± 5.2 | |
| G4 | - | 0.384 ± 0.025 | 0.155 ± 0.008 | |
| G5 | 0.817 ± 0.007 | 0.252 ± 0.002 | 0.453 ± 0.008 | |
| G6 | 0.510 ± 0.006 | 0.0412 ± 0.0116 | 0.175 ± 0.011 | |
| C1 | - | - | - | |
| C2 | 1.45 ± 0.04 | 0.790 ± 0.019 | 0.367 ± 0.030 | |
| C3 | - * | 0.00212 ± 0.00056 | 0.0426 ± 0.0089 | |
| M1 | - | - | - | |
| M2 | 1.57 ± 0.06 | 0.479 ± 0.026 | 2.96 ± 0.02 | |
| M3 | 0.337 ± 0.015 | 0.271 ± 0.007 | 0.581 ± 0.029 | |
| M4 | 0.233 ± 0.004 | 0.0738 ± 0.0040 | 0.0263 ± 0.0031 | |
| M5 | 0.190 ± 0.006 | 0.0275 ± 0.0020 | 0.0153 ± 0.0015 | |
| Average Resistivity [Ωm] | Maximum Resistivity [Ωm] | Minimum Resistivity [Ωm] | Coefficient of Variation (V) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Composite symbol | G6 | 0.0412 | 0.0422 | 0.0407 | 0.0101 |
| C2 | 0.790 | 0.837 | 0.771 | 0.0186 | |
| C3 | 0.00213 | 0.00264 | 0.000975 | 0.265 | |
| M3 | 0.271 | 0.284 | 0.267 | 0.0157 | |
| M4 | 0.0738 | 0.0743 | 0.0735 | 0.00303 | |
| M5 | 0.0275 | 0.0280 | 0.0272 | 0.00509 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Podsiadły, B.; Walter, P.; Kamiński, M.; Skalski, A.; Słoma, M. Electrically Conductive Nanocomposite Fibers for Flexible and Structural Electronics. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 941. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12030941
Podsiadły B, Walter P, Kamiński M, Skalski A, Słoma M. Electrically Conductive Nanocomposite Fibers for Flexible and Structural Electronics. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(3):941. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12030941
Chicago/Turabian StylePodsiadły, Bartłomiej, Piotr Walter, Michał Kamiński, Andrzej Skalski, and Marcin Słoma. 2022. "Electrically Conductive Nanocomposite Fibers for Flexible and Structural Electronics" Applied Sciences 12, no. 3: 941. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12030941
APA StylePodsiadły, B., Walter, P., Kamiński, M., Skalski, A., & Słoma, M. (2022). Electrically Conductive Nanocomposite Fibers for Flexible and Structural Electronics. Applied Sciences, 12(3), 941. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12030941







