Steganalysis of Context-Aware Image Steganography Techniques Using Convolutional Neural Network
Abstract
1. Introduction
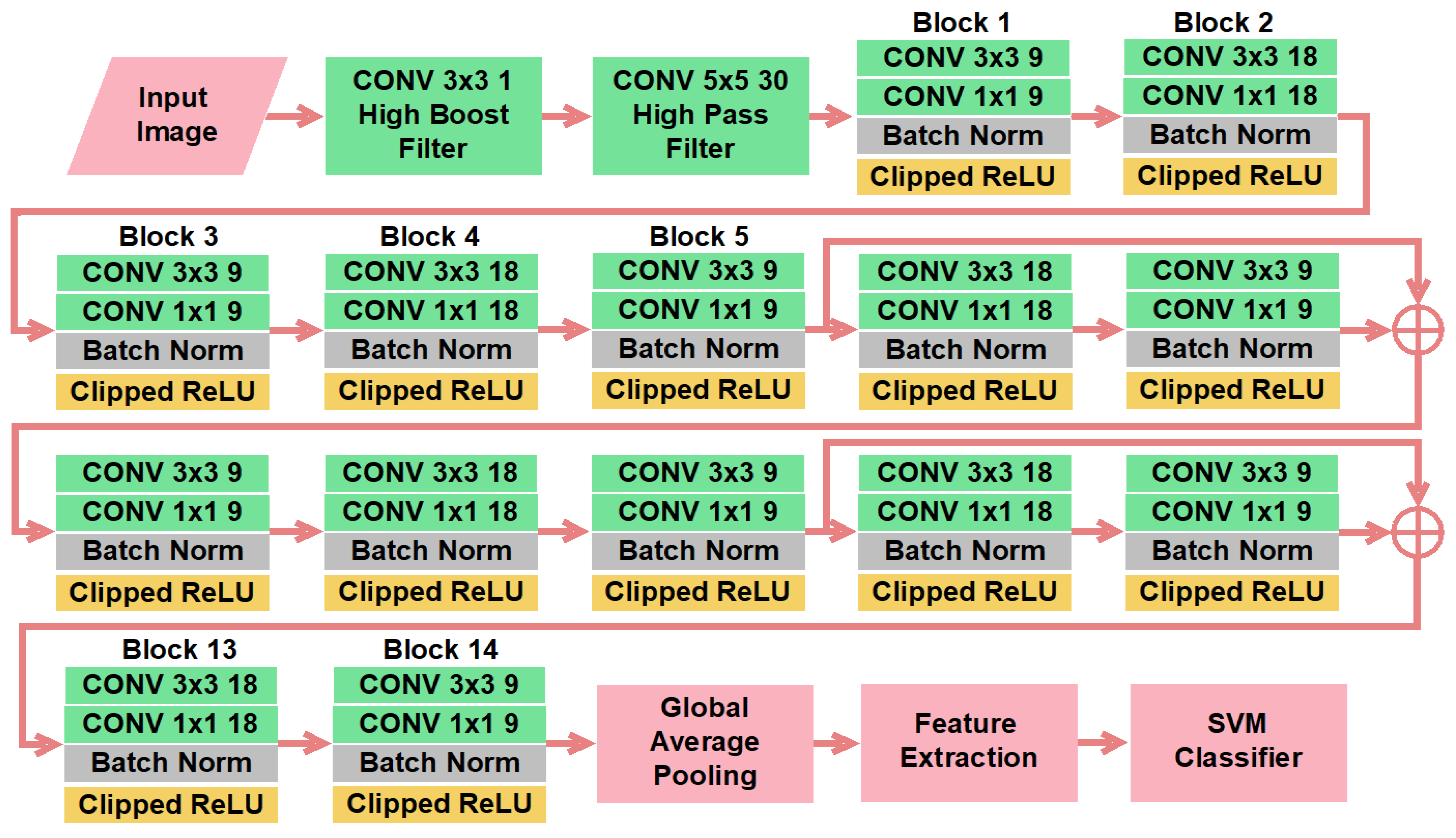
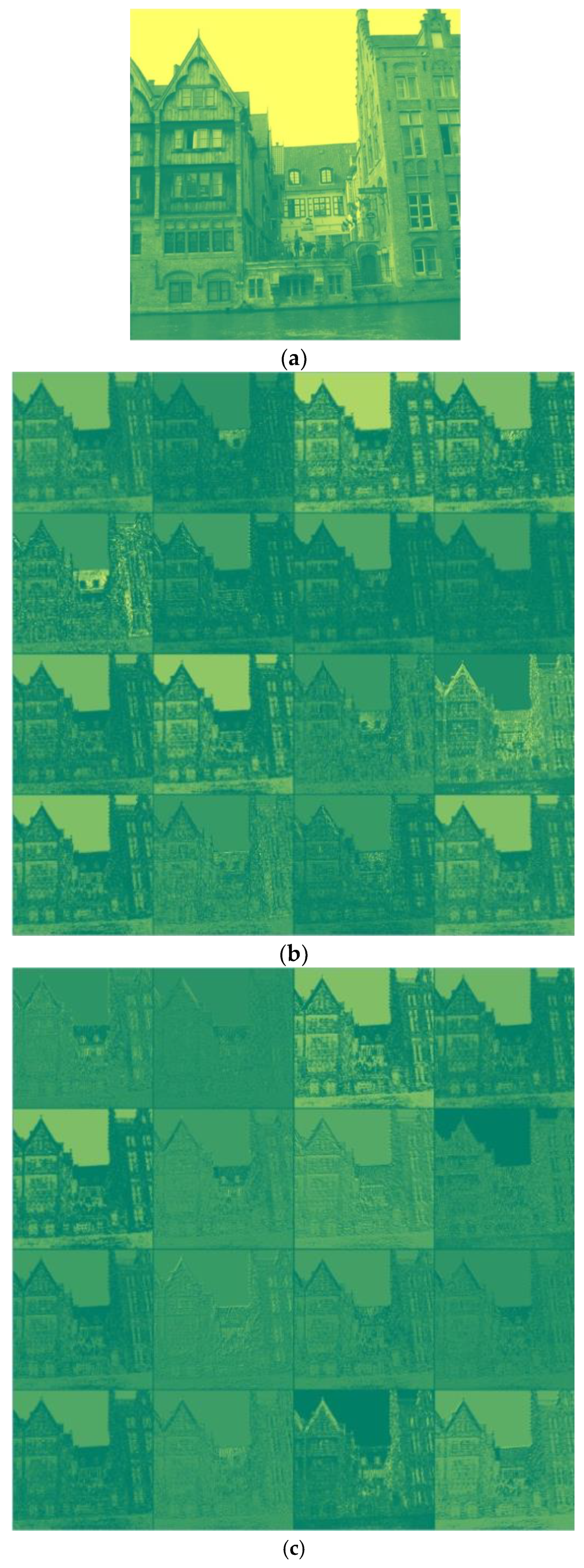
- The proposed technique highlights the high-frequency elements using a high-boost filter in the first non-trainable convolutional layer. It improves the detection accuracy by more than one percent.
- Thirty high-pass filtered images were generated using SRM filters in the second non-trainable convolutional layer to give prominence to the noise of the stego-image effectively.
- A single pooling layer in the last part of the CNN was used to sustain the complete statistical traces from each layer.
- A clipped ReLU layer was introduced for customized thresholding to obtain more statistical information.
- The SVM classifier was utilized instead of the softmax classifier to increase the detection performance. The SVM classifier outperforms in many applications.
- Experimental results of the proposed technique were compared with SRNet, Ye-Net, Yedroudj-Net, and Zhu-Net. The experimental results are displayed for the HILL, S-UNIWARD, and WOW steganography algorithms with payloads of 0.2, 0.3, and 0.4 bits per pixel.
- In the detailed experimental analysis, the proposed technique was proven to be better than the existing techniques with a higher detection accuracy.
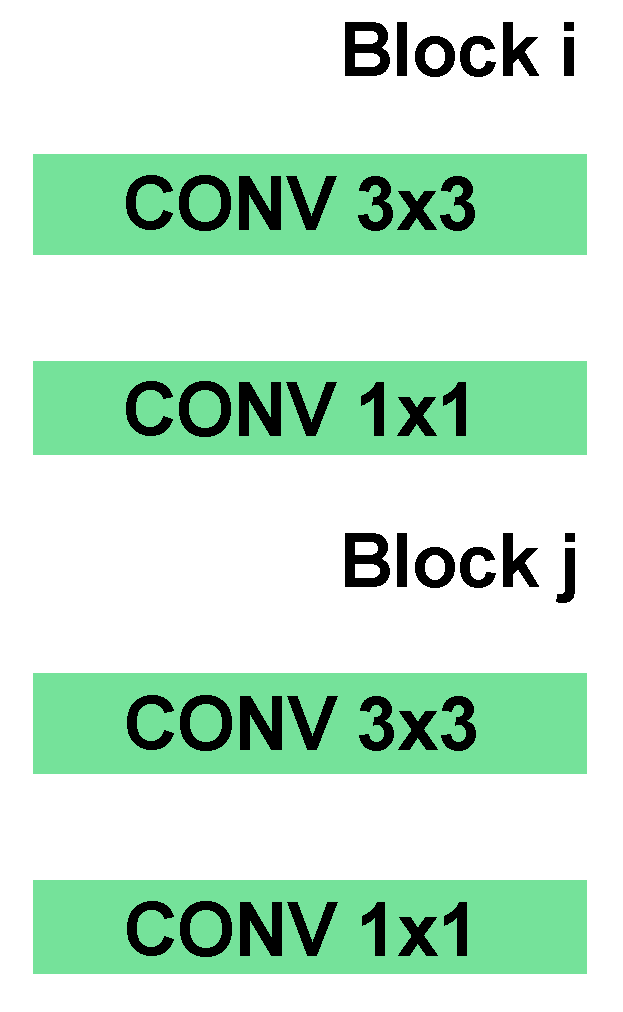
2. The Proposed Scheme
3. Experimental Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, B.; Wang, M.; Huang, J.; Li, X. A New Cost Function for Spatial Image Steganography. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, Paris, France, 27–30 October 2014; pp. 4206–4210. [Google Scholar]
- Holub, V.; Fridrich, J.; Denemark, T. Universal distortion function for steganography in an arbitrary domain. EURASIP J. Inf. Secur. 2014, 2014, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holub, V.; Fridrich, J. Designing Steganographic Distortion Using Directional Filters. In Proceedings of the WIFS 2012—Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Workshop on Information Forensics and Security, Costa Adeje, Spain, 2–5 December 2012; pp. 234–239. [Google Scholar]
- Lyu, S.; Farid, H. Steganalysis Using Higher-Order Image Statistics. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2006, 1, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provos, N.; Honeyman, P. Detecting Steganographic Content on the Internet. USA Today 2001, 1001, 48103-4943. [Google Scholar]
- Westfeld, A. F5—A Steganographic Algorithm. In International Workshop on Information Hiding; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2001; pp. 289–302. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Huang, J.; Shi, Y.Q. Textural Features Based Universal Steganalysis. In Proceedings of the Security, Forensics, Steganography, and Watermarking of Multimedia Contents X, San Jose, CA, USA, 14 February 2008; p. 681912. [Google Scholar]
- Pevný, T.; Filler, T.; Bas, P. Using High-Dimensional Image Models to Perform Highly Undetectable Steganography. In Lecture Notes in Computer Science (including subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics); Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; Volume 6387, pp. 161–177. ISBN 364216434X. [Google Scholar]
- Pevny, T.; Bas, P.; Fridrich, J. Steganalysis by Subtractive Pixel Adjacency Matrix. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2010, 5, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, G.; Ping, X.; Zhang, T.; Hou, X. Image textural features for steganalysis of spatial domain steganography. J. Electron. Imaging 2012, 21, 033015-1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fridrich, J.; Kodovsky, J. Rich Models for Steganalysis of Digital Images. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2012, 7, 868–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Li, H.; Luo, W.; Huang, J. Adaptive Steganalysis against WOW Embedding Algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2nd ACM Workshop on Information Hiding and Multimedia Security—IH&MMSec ’14; ACM Press: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 91–96. [Google Scholar]
- Denemark, T.; Sedighi, V.; Holub, V.; Cogranne, R.; Fridrich, J. Selection-Channel-Aware Rich Model for Steganalysis of Digital Images. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Workshop on Information Forensics and Security, Atlanta, GA, USA, 3–5 December 2014; pp. 48–53. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.; Dong, J.; Wang, W.; Tan, T. Local Correlation Pattern for Image Steganalysis. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE China Summit and International Conference on Signal and Information Processing (ChinaSIP), Chengdu, China, 12 July 2015; pp. 468–472. [Google Scholar]
- Mielikainen, J. LSB matching revisited. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2006, 13, 285–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Zhang, X.; Cheng, H.; Yu, J. Digital image steganalysis based on local textural features and double dimensionality reduction. Secur. Commun. Netw. 2014, 9, 729–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Li, Z.; Zhou, S.; Tan, S.; Zhang, X. New Steganalytic Features for Spatial Image Steganography Based on Derivative Filters and Threshold LBP Operator. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2017, 13, 1242–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Wang, M.; Li, X.; Tan, S.; Huang, J. A Strategy of Clustering Modification Directions in Spatial Image Steganography. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2015, 10, 1905–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedighi, V.; Cogranne, R.; Fridrich, J. Content-Adaptive Steganography by Minimizing Statistical Detectability. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2015, 11, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Liu, F.; Yang, C. Towards feature representation for steganalysis of spatial steganography. Signal Process. 2019, 169, 107422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, H.; Hu, D.; Xu, H.; Li, M.; Zheng, S. New Steganalytic Features for Spatial Image Steganography Based on Non-Negative Matrix Factorization. In Lecture Notes in Computer Science (Including Subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics); Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; Volume 12022, pp. 337–351. ISBN 9783030435745. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, Y.; Dong, J.; Wang, W.; Tan, T. Deep Learning for Steganalysis via Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the Media Watermarking, Security, and Forensics 2015, San Francisco, CA, USA, 9–11 February 2015; p. 94090J. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, Y.; Dong, J.; Wang, W.; Tan, T. Learning and transferring representations for image steganalysis using convolutional neural network. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Phoenix, AZ, USA, 25–28 September 2016; pp. 2752–2756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Wu, H.-Z.; Shi, Y.-Q. Structural Design of Convolutional Neural Networks for Steganalysis. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2016, 23, 708–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Zhong, S.H.; Liu, Y. Steganalysis via Deep Residual Network. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE 22nd International Conference on Parallel and Distributed Systems—ICPADS, Wuhan, China, 13–16 December 2016; pp. 1233–1236. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S.; Zhong, S.; Liu, Y. Deep residual learning for image steganalysis. Multimedia Tools Appl. 2017, 77, 10437–10453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Ni, J.; Yi, Y. Deep Learning Hierarchical Representations for Image Steganalysis. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2017, 12, 2545–2557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boroumand, M.; Chen, M.; Fridrich, J. Deep Residual Network for Steganalysis of Digital Images. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2018, 14, 1181–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Ni, J.; Shi, Y.Q. Uniform Embedding for Efficient JPEG Steganography. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2014, 9, 814–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yedroudj, M.; Comby, F.; Chaumont, M. Yedroudj-Net: An Efficient CNN for Spatial Steganalysis. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Calgary, AB, Canada, 15–20 April 2018; Volume 2018-April, pp. 2092–2096. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S.; Zhong, S.-H.; Liu, Y. A Novel Convolutional Neural Network for Image Steganalysis With Shared Normalization. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2019, 22, 256–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Zhu, F.; Liu, J.; Liu, G. Depth-Wise Separable Convolutions and Multi-Level Pooling for an Efficient Spatial CNN-Based Steganalysis. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2019, 15, 1138–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Z.; Sang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Cai, B.; Xia, X.; Wu, W. A New Convolutional Neural Network-Based Steganalysis Method for Content-Adaptive Image Steganography in the Spatial Domain. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 47013–47020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, M.; Yang, Y.; Lei, M.; Dong, Z. Joint multi-domain feature learning for image steganalysis based on CNN. EURASIP J. Image Video Process. 2020, 2020, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Wei, Y.; Yao, H.; Pan, D.; Xiao, G. High-Boost-Based Multiscale Local Contrast Measure for Infrared Small Target Detection. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2017, 15, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oszust, M.; Piórkowski, A.; Obuchowicz, R. No-reference Image Quality Assessment of Magnetic Resonance Images with High-boost Filtering and Local Features. Magn. Reson. Med. 2020, 84, 1648–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bas, P.; Furon, T. Break Our Watermarking System. Available online: http//bows2.ec-lille.fr/ (accessed on 21 January 2021).
- Xavier Glorot, Y.B. Understanding the Difficulty of Training Deep Feedforward Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the thirteenth international conference on artificial intelligence and statistics, Sardinia, Italy, 13–15 May 2010; pp. 249–256. [Google Scholar]
- Hannun, A.; Case, C.; Casper, J.; Catanzaro, B.; Diamos, G.; Elsen, E.; Prenger, R.; Satheesh, S.; Sengupta, S.; Coates, A.; et al. Deep Speech: Scaling up End-to-End Speech Recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.5567. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, G. Deep Convolutional Neural Network to Detect J-UNIWARD. In Proceedings of the IH and MMSec 2017—Proceedings of the 2017 ACM Workshop on Information Hiding and Multimedia Security, New York, NY, USA, 20–22 June 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, R.E.; Chen, P.H.; Lin, C.J. Working Set Selection Using Second Order Information for Training Support Vector Machines. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2005, 6, 1889–1918. [Google Scholar]
- Bas, P.; Filler, T.; Pevný, T. “Break Our Steganographic System”: The Ins and Outs of Organizing BOSS. In Lecture Notes in Computer Science (Including Subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics); Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; Volume 6958, pp. 59–70. ISBN 9783642241772. [Google Scholar]

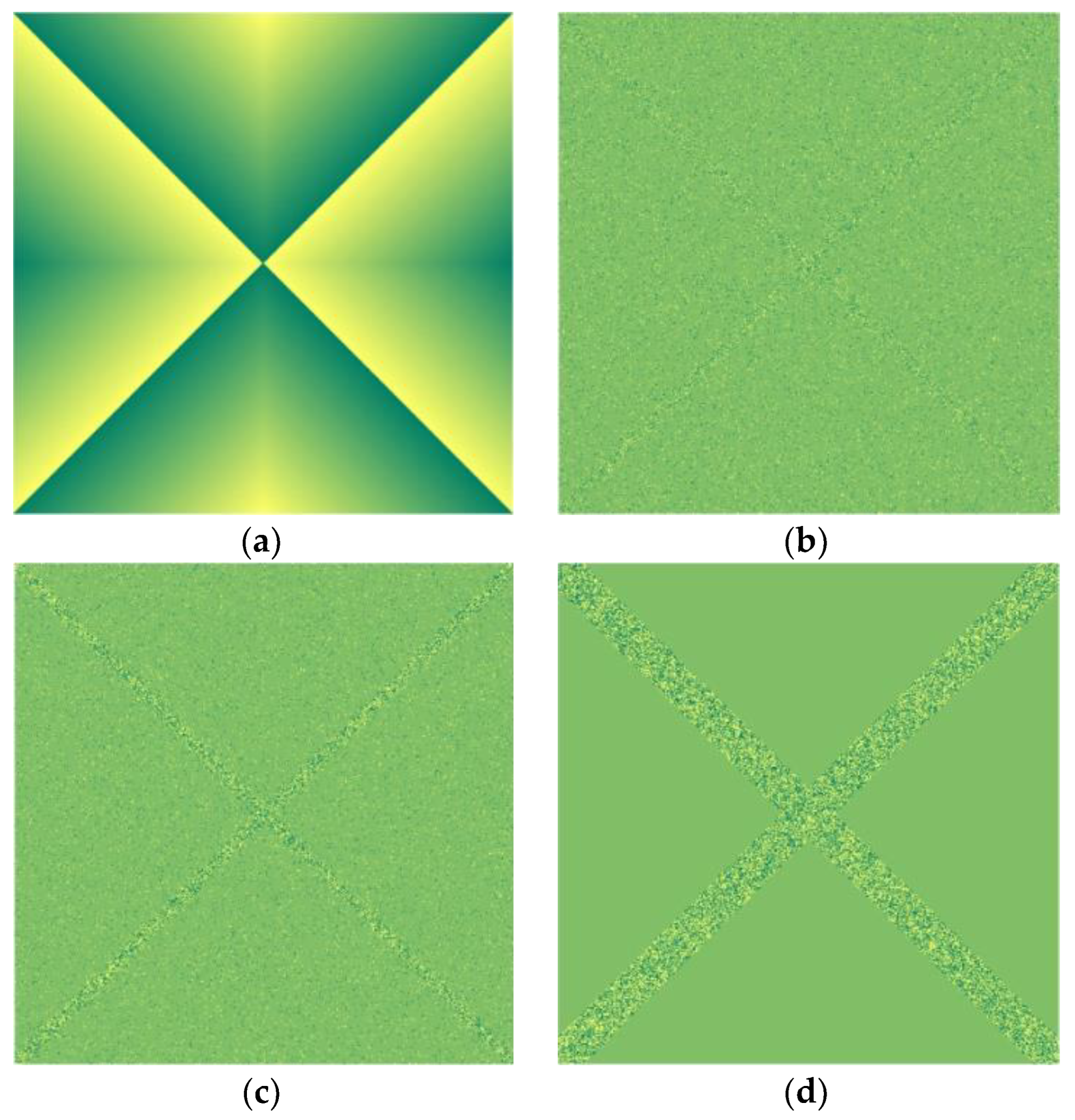
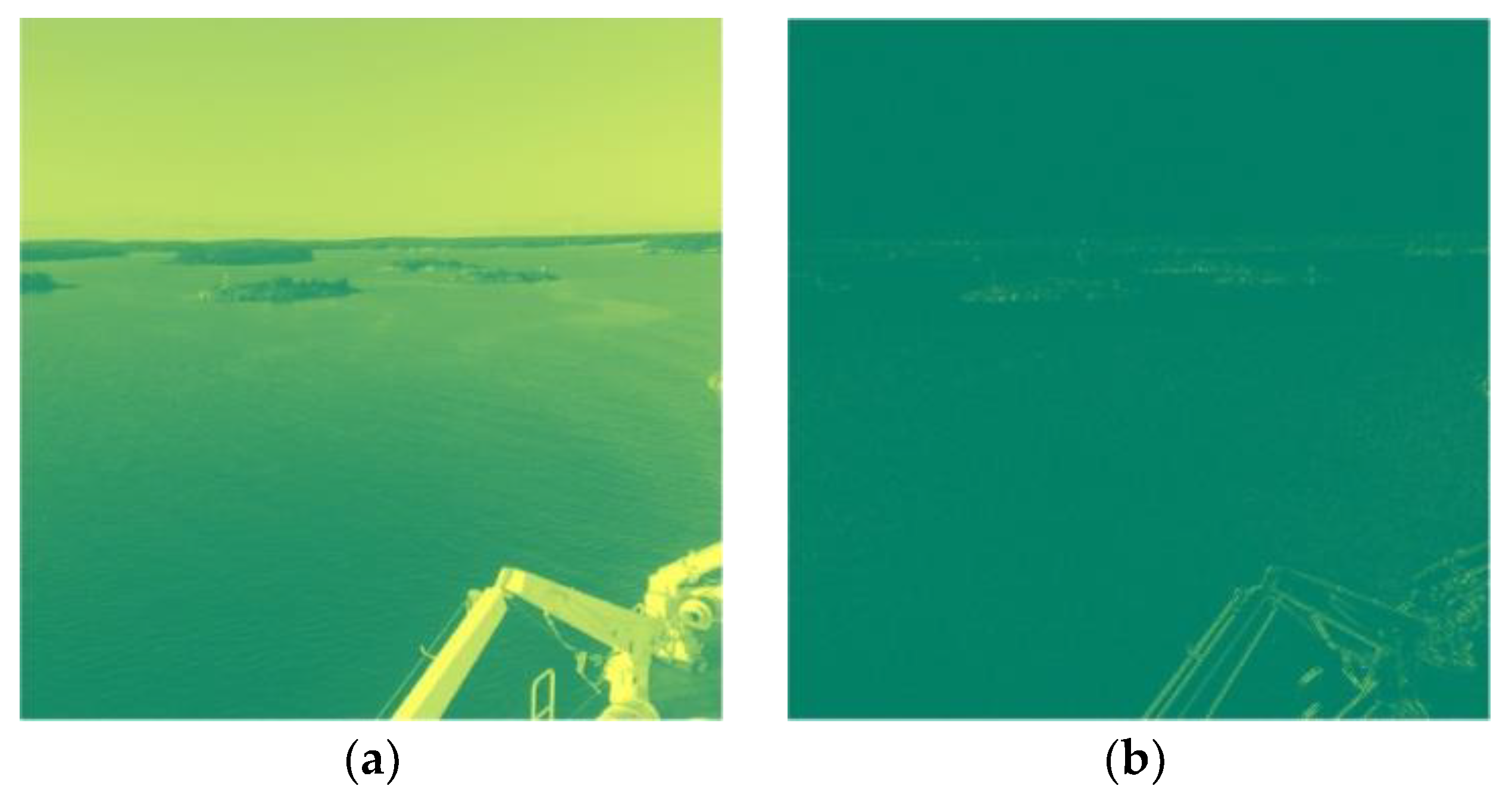


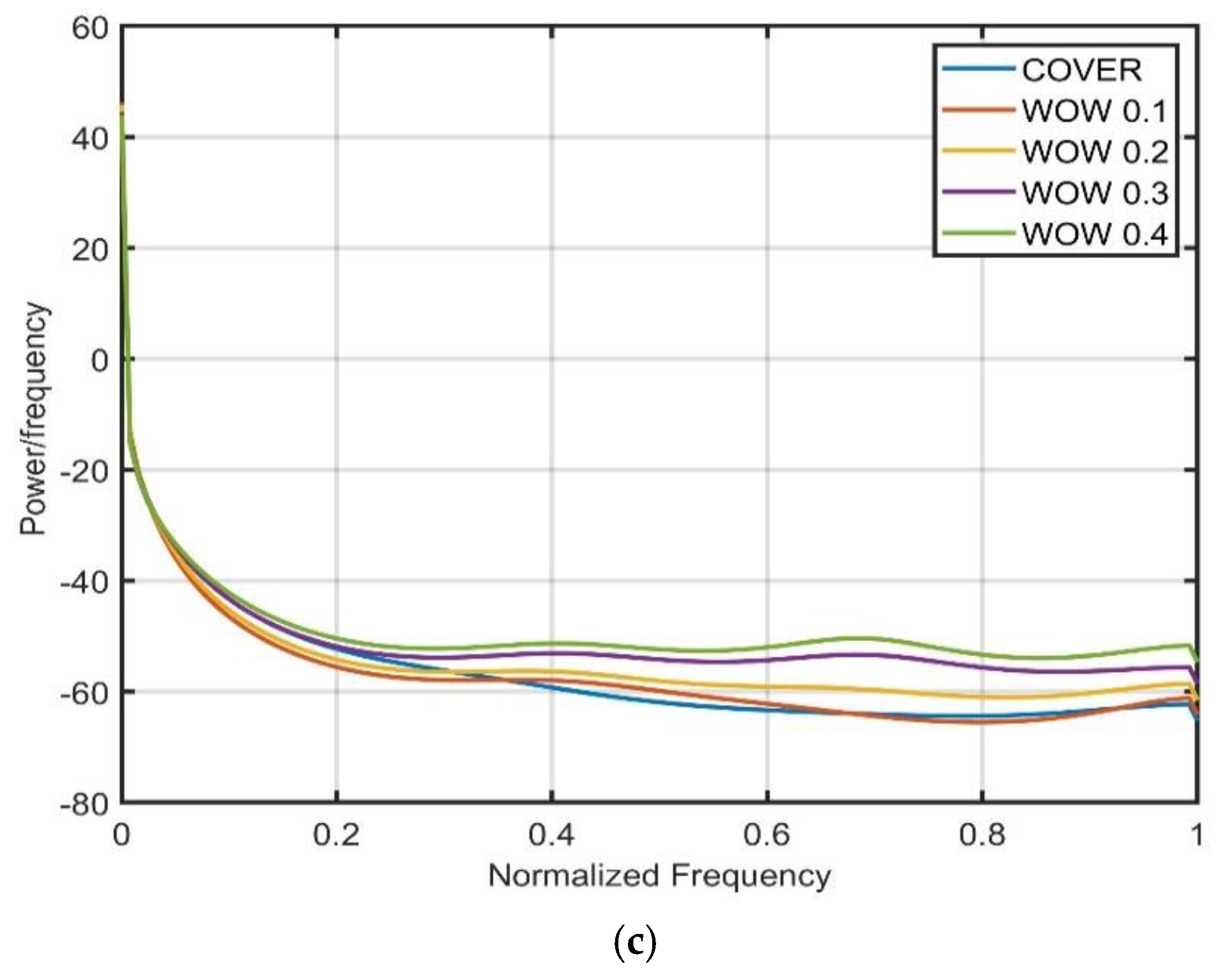
| Payload (bpp) | HILL | S-UNIWARD | WOW |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.2 | 45.43 | 40.58 | 53.33 |
| 0.3 | 46.95 | 39.87 | 53.79 |
| 0.4 | 48.61 | 41.27 | 54.49 |
| S. No. | Steganography Technique/ Payload (bpp) | HILL | S-UNIWARD | WOW | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.4 | ||
| 1 | SRM + ReLU | 60.33 | 67.09 | 69.69 | 68.05 | 76.27 | 82.35 | 73.46 | 80.48 | 84.75 |
| 2 | SRM + CReLU | 61.24 | 67.90 | 70.82 | 69.02 | 77.04 | 81.61 | 74.13 | 81.79 | 85.43 |
| 3 | HB + SRM + ReLU | 61.93 | 69.14 | 71.68 | 69.51 | 77.97 | 82.85 | 75.03 | 82.45 | 86.38 |
| 4 | HB + SRM + CReLU | 62.49 | 68.59 | 72.26 | 70.00 | 78.68 | 84.11 | 76.02 | 83.36 | 87.74 |
| S. No. | Steganography Technique/ Payload (bpp) | HILL | S-UNIWARD | WOW | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.4 | ||
| 1 | Softmax Classifier | 62.49 | 68.59 | 72.26 | 70.00 | 78.68 | 84.11 | 76.02 | 83.36 | 87.74 |
| 2 | SVM classifier | 63.25 | 69.91 | 73.07 | 69.54 | 79.88 | 84.79 | 77.02 | 83.95 | 87.26 |
| Steganography Technique/ Payload (bpp) | HILL | S-UNIWARD | WOW | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.4 | |
| SRNet | 55.51 | 63.64 | 67.62 | 64.97 | 73.88 | 79.34 | 72.52 | 79.41 | 83.59 |
| Ye-Net | 54.31 | 59.40 | 63.85 | 60.20 | 68.01 | 74.83 | 69.39 | 72.97 | 78.65 |
| Yedroudj-Net | 54.09 | 58.72 | 67.98 | 59.74 | 69.29 | 74.97 | 69.96 | 75.52 | 81.07 |
| Zhu-Net | 61.74 | 66.61 | 74.56 | 70.23 | 78.12 | 82.81 | 74.37 | 78.41 | 86.23 |
| Proposed Method | 63.25 | 69.91 | 73.07 | 69.54 | 79.88 | 84.79 | 77.02 | 83.95 | 87.26 |
| Steganography Technique/ Payload (bpp) | HILL | S-UNIWARD | WOW | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.4 | |
| SRNet | 60.85 | 67.10 | 68.79 | 67.17 | 76.18 | 79.06 | 77.40 | 83.97 | 88.49 |
| Ye-Net | 53.79 | 61.60 | 65.61 | 62.32 | 70.60 | 74.98 | 70.42 | 78.81 | 82.37 |
| Yedroudj-Net | 57.28 | 64.14 | 66.91 | 63.51 | 71.28 | 74.15 | 73.49 | 81.93 | 85.46 |
| Zhu-Net | 63.81 | 69.85 | 77.27 | 73.40 | 79.89 | 83.40 | 79.51 | 87.55 | 92.66 |
| Proposed Method | 64.49 | 74.10 | 77.13 | 75.06 | 83.64 | 86.85 | 81.50 | 88.81 | 91.78 |
| Steganography Technique/ Payload (bpp) | HILL | S-UNIWARD | WOW | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.4 | |
| SRNet | 64.44 | 70.03 | 72.92 | 74.31 | 81.29 | 84.66 | 78.28 | 84.37 | 87.97 |
| Ye-Net | 59.62 | 64.84 | 69.81 | 65.72 | 74.08 | 82.25 | 72.46 | 77.50 | 83.66 |
| Yedroudj-Net | 60.94 | 66.93 | 70.17 | 67.03 | 75.40 | 80.02 | 74.25 | 82.66 | 86.85 |
| Zhu-Net | 66.82 | 72.45 | 78.97 | 80.57 | 85.28 | 88.45 | 81.86 | 90.37 | 92.31 |
| Proposed Method | 72.24 | 76.92 | 82.28 | 82.16 | 87.23 | 91.37 | 83.32 | 89.27 | 93.16 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Agarwal, S.; Kim, C.; Jung, K.-H. Steganalysis of Context-Aware Image Steganography Techniques Using Convolutional Neural Network. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 10793. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122110793
Agarwal S, Kim C, Jung K-H. Steganalysis of Context-Aware Image Steganography Techniques Using Convolutional Neural Network. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(21):10793. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122110793
Chicago/Turabian StyleAgarwal, Saurabh, Cheonshik Kim, and Ki-Hyun Jung. 2022. "Steganalysis of Context-Aware Image Steganography Techniques Using Convolutional Neural Network" Applied Sciences 12, no. 21: 10793. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122110793
APA StyleAgarwal, S., Kim, C., & Jung, K.-H. (2022). Steganalysis of Context-Aware Image Steganography Techniques Using Convolutional Neural Network. Applied Sciences, 12(21), 10793. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122110793







