Abstract
Temperature is one of the important factors affecting the mechanical properties of geotechnical soils, and its role in engineering construction in China cannot be underestimated. In order to study the effects of temperature and zinc contamination concentration on the mechanical properties of Guilin local red clay, a temperature-controlled triaxial shear test was conducted on Guilin red clay under three variables of temperature, zinc contamination concentration and surrounding pressure. The test findings revealed that there are significant differences in the effects of temperature, zinc contamination concentration and surrounding pressure on the mechanical properties of Guilin red clay. The stress–strain curves of the red clay at various temperatures, contamination concentrations and envelope pressures are of the strain-hardening type, and the deformation modulus showed a tendency to increase rapidly with increasing strain, then decrease rapidly, and finally, decrease slowly. With the increase of temperature, the cohesion of Zn-contaminated red clay increases, while the angle of internal friction increases and then decreases, both of which increase the shear strength of red clay. As the concentration of Zn contamination grows, the shear strength of the red clay increases, while the internal friction angle increases and then decreases, and the shear strength of the soil increases and then decreases. The shear strength of the Zn-contaminated red clay improved as the surrounding pressure increased.
1. Introduction
Red clay soil is a regional unique soil [1,2] that is relatively widespread in the southern region of China. In comparison to other soils, it has relatively obvious engineering properties, such as high pore ratio, high dispersion, low compressibility, obvious water loss and shrinkage, and soft and hard strata at the top and bottom of the strata [3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10]. These engineering properties have attracted extensive attention and research from many scholars. Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, commonly known as “the hometown of non-ferrous metals”, possesses a wealth of mineral resources, such as lead, zinc, tin, and sulfur iron ore, among which zinc and lead have the largest reserves. In the past, the local government’s model for economic development was a rough economy, and there were some industrial “three wastes” improperly treated in the process of producing and utilizing local mineral resources, which led to the deterioration of the ecosystem surrounding the mining area. For example, large amounts of heavy metal pollutants in high concentrations are discharged into the natural environment, resulting in severe soil and water pollution [11,12]. Excessive heavy metal pollutants in certain soils lead to a decrease in water quality in the associated watersheds, and some relevant indicators are exceeded, affecting the surrounding ecological environment posing a threat [13,14,15]. Li and Wang et al. [16,17] found that zinc contamination in the investigation and study of lead-zinc and zinc-manganese mining areas in Guangxi poses a threat to the natural environmental safety of the adjacent areas. The improper discharge of heavy metals from mines such as these, resulting in their infiltrating and migrating into the geotechnical body, causes soil contamination that poses many difficulties for engineering construction.
Since the beginning of the new century, governments and enterprises have paid increasing attention to environmental protection issues; consequently, countries have increased their investment in research and treatment of contaminated soil and water bodies to cope with the deteriorating environmental problems. In recent decades, domestic and international scholars have conducted a great deal of research and treatment on soils and contaminated soils under a variety of conditions. Some scholars have studied the variation pattern of shear strength and index of red clay under conventional physical independent variables [18], including dry density, water content, fracture degree, and other variables. Some scholars have studied the evolution pattern of mechanical strength of red clay under different engineering conditions [19,20,21], and explored the microstructural changes that accompany the mechanical evolution process under different engineering conditions [20]. In terms of soil improvement, researchers have improved the engineering properties of the original soil by incorporating various amendments into the soil [1,3,10,22,23,24], such as increasing the strength of the soil, altering the distribution of soil pores and volume, etc. In their investigation of contaminated soils, researchers have also achieved some research results. Currently, some researchers are concentrating on the properties of non-heavy metal contaminated soils [25,26], including shear strength and microstructure. As for the research on soils contaminated with heavy metals, the main focus is on the study and management of the properties of contaminated soils. Li J. M. et al. investigated the effects and mechanisms of zinc and chromium ions on the shear strength and structure of red clay [2,27,28]; Chen et al. [29] revealed the intrinsic link between shear strength and resistivity of copper ion-contaminated red clay through experimental studies; Yang Z. P. et al. [30] investigated the variation law of unconfined compressive strength of lead-contaminated soil after freeze-thawing. Chen et al. [31] (2019) explored the variation law of mineral composition and the microstructure trend in copper-contaminated red clay. Hazreek et al. [32] used the ERI technique to study the variation law of electrical resistance in heavy metal contaminated fields. All of these studies are about the physical and mechanical properties of various metal-contaminated soil types. In the treatment of soils polluted with heavy metals, some researchers have attempted to solidify heavy metal contaminated soils with various curing agents before studying their mechanical properties, mineral composition, and the evolution of the microstructure [4,33,34,35]. Dong et al. [36] examined the cementation mechanism of cadmium-contaminated clay cement by analyzing the properties such as the pore structure of the cement contaminants. In the study of soils under temperature conditions, Chang et al. [37] investigated the effects of drying temperature, moisture content, and dry density on the strength properties and fracture development of unsaturated red clay soils. In summary, the engineering conditions involved so far in the study of heavy metal contaminated soils primarily consist of dry and wet cycles, freeze–thaw cycles, etc., which all involve the influence of ambient temperature on contaminated soils, but none of them combine a single temperature with heavy metal contaminated soils to study their mechanical properties as well as microstructural changes, and the corresponding mechanisms.
As a significant factor in nature, temperature has a crucial impact on the mechanical properties of red clay. There are few results combining temperature and heavy metal contamination to study red clay, and the available literature is rather limited, so it is vital for us to research the mechanical properties of heavy metal contaminated red clay under temperature conditions.
In this paper, the mechanical property parameters of red clay soils of varying temperature, zinc contamination concentration, and surrounding pressure were tested by temperature-controlled triaxial tests under strictly controlled test temperature conditions, respectively. Based on the analysis of the mechanical parameters of the soils, the evolution of their mechanical properties is summarized, and the evolution mechanism of the Zn-contaminated soils under the temperature conditions is investigated. The research results of this paper improve the information of mechanical strength evolution of red clay soils in Guilin region under seasonal temperature variation. These findings provide reliable basic research for the management of heavy metal contaminated soils in Guilin and the subtropical region of southern China.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Test Soil
The test soil sample was taken from a building pit in Lingui District, Guilin City, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China. Within five meters of the surface was a Quaternary residual layer (Q3el) that is reddish brown. It contains kaolinite, illite, and montmorillonite as its primary clay minerals. It also contains quartz, acerulite, and a small amount of water. Its basic physical indices were obtained by the basic physical properties test in the room, as shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Basic physical indexes of red clay in Lingui area of Guilin.
2.2. Pollution Source of the Test Soil Sample
The contaminant utilized in the test was analytically pure zinc nitrate hexahydrate Zn(NO3)2∙6H2O produced by Xilong Technology Co., Ltd. (Shantou, China). It is colorless and transparent, crystallized easily, soluble in water, with a melting point of 36 °C, and a density of 2.065. Its technical conditions are shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
Technical conditions of zinc nitrate hexahydrate (Zn(NO3)2∙6H2O) (analytical purity) (unit: %).
2.3. Test Preparation
The red clay retrieved from a building pit in Lingui District was air-dried, removed from debris, crushed, and sieved through a 2 mm soil sieve to be utilized as a backup soil for the test. The amount of distilled water required for soil preparation was calculated by the water content of the original red clay, the target value of dry density of the contaminated red clay (1.4 g/cm3), the target water content (30%), and other parameters; then, the amount of distilled water required for soil preparation was calculated according to the doping of zinc ions of 0%, 0.05%, 0.1%, 0.2%, and 0.5% (the doping of zinc ions is the mass ratio of zinc ions to dry soil, and the doping amount in this test was determined by Zhou Xing et al. in the contaminated red clay). The required Zn(NO3)2·6H2O mass was calculated based on the desired Zn ion concentration [38,39] and the actual experimental results. Next, the proper amount of Zn(NO3)2∙6H2O solution was prepared according to the mass ratio needed for sample preparation (i.e., the mass ratio of Zn(NO3)2∙6H2O to distilled water), and finally, the Zn(NO3)2 solution was sprayed onto the red clay soil and stirred well. After mixing the soil sample, the zinc-contaminated wet soil was sealed in a constant temperature and humidity chamber for 24 h to make it evenly moist and fully react between the substances, then an appropriate amount of soil was taken for remeasurement of moisture content. When the desired moisture content of the test soil sample and the actual moisture content error are acceptable, the hydrostatic method is employed to generate an 80 mm × 39.1 mm triaxial specimen. When specimen preparation is completed, the prepared specimen must be promptly inserted into the triaxial specimen saturator. Then, it is placed in a vacuum saturation cylinder for at least 2 h, after which it is soaked in distilled water for 12 h to make the specimen completely saturated.
2.4. Test Method
The temperature-controlled SLB-1 type stress–strain controlled chamber triaxial shear penetration tester produced by Nanjing Soil Instrument Factory Co., Ltd. (Nanjing, China) was utilized for this test, as seen in Figure 1. Triaxial saturated specimens with various Zn ion concentrations were loaded onto the test bench of the triaxial apparatus at temperatures of 8.3 °C, 19.4 °C, 28.5 °C, and 40 °C (the temperature variables were selected from the local winter, year-round, and summer average temperatures in Guilin and a temperature from the local high temperature history records), the surrounding pressure of 100 kPa, 200 kPa, 300 kPa, and 400 kPa, and the shear rate of the solidification undrained shear test was carried out under the condition of 0.05 mm/min, and the test was stopped when the axial strain was 20%.

Figure 1.
Temperature-controlled SLB-1 type stress–strain controlled triaxial shear penetration tester.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Changes in Stress–Strain Curves of Red Clay with Different Concentrations of Zinc Contamination under Different Temperature Conditions
3.1.1. Effect of Temperature on Stress–Strain Curves of Zinc-Contaminated Red Clay
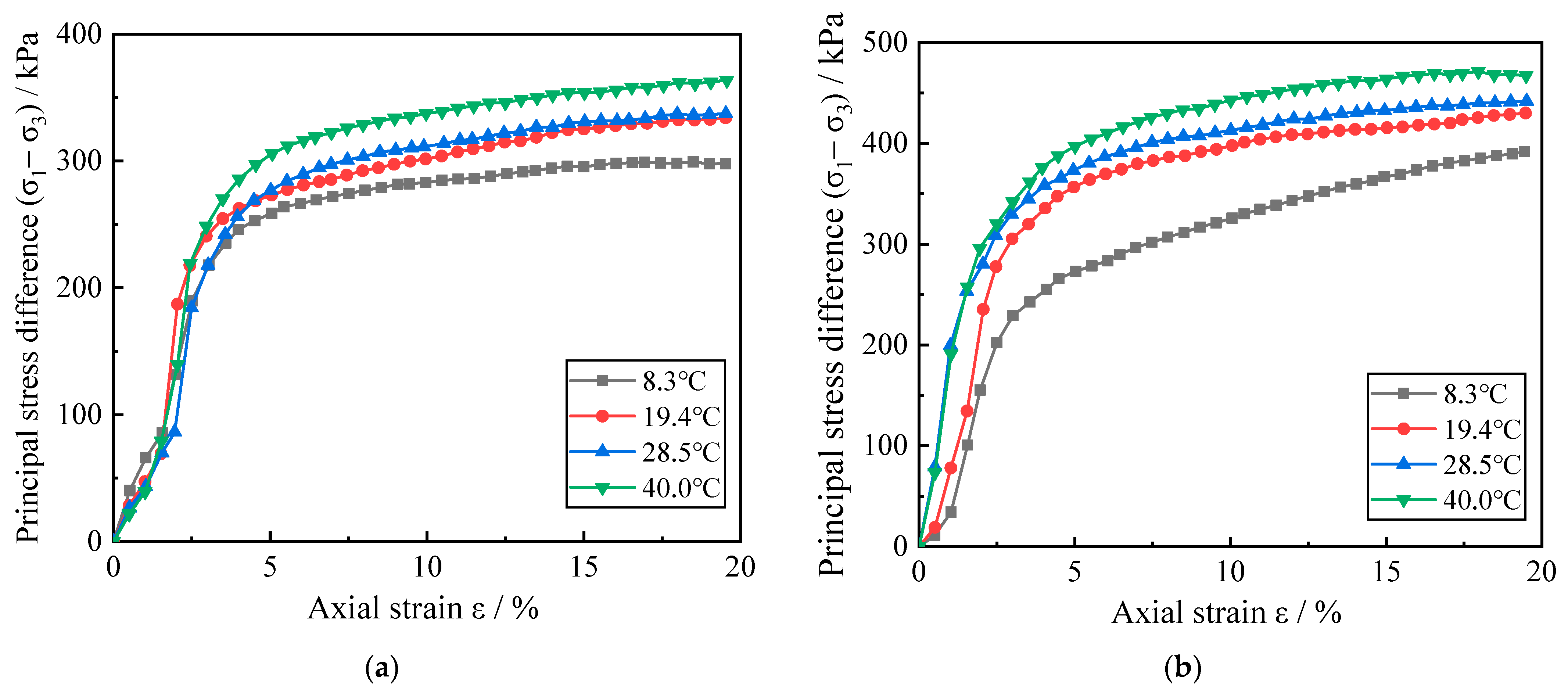
In order to study the deformation characteristics of soil environment temperature on zinc-contaminated red clay, four different temperature red clay stress–strain curves were selected under the conditions of zinc pollution concentration of 0% and 0.5% and confining pressure of 300 kPa and 400 kPa, as shown in Figure 2.
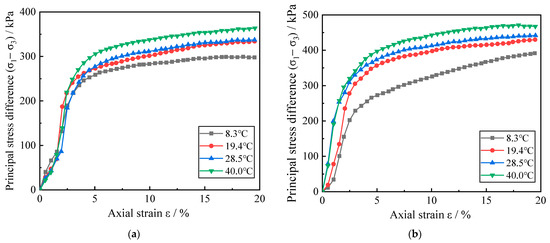
Figure 2.
Stress–strain curves of red clay under different temperature conditions. (a) The zinc ion concentration is 0% and the confining pressure is 300 kPa; (b) The zinc ion concentration is 0.5% and the confining pressure is 400 kPa.
According to the classification of mechanical properties of the soil stress–strain relationship, there are usually three types of strain hardening type, strain softening type, and ideal elastic-plastic type. As can be judged from the change of curves in Figure 2, the stress–strain relationship of red clay at different temperatures is of the strain-hardening type. As axial strain increases, the corresponding principal stress difference demonstrates a linear increase followed by a gradual increase. Initially, the deformation modulus of the red clay increases sharply; then, it decreases rapidly and then slowly with the increase of the axial strain. In Figure 2a, the elastic limits appear at ε = 2.5%, 2%, 2.5%, and 2.5% for the soils at each temperature condition with the increase of ambient temperature; and the elastic limits are 189.7 kPa, 187.1 kPa, 184.1 kPa, and 219.5 kPa, respectively. In Figure 2b, with the increase of ambient temperature, the elastic limits appear at ε = 2%, 2%, 1%, and 1% for the soils at each temperature condition, and the elastic limits are 155.2 kPa, 235.4 kPa, 253.4 kPa, and 257.3 kPa, respectively. This indicates that the ε corresponding to the elastic limit of uncontaminated red clay is basically constant with increasing temperature, while the ε corresponding to the elastic limit of zinc-contaminated red clay is gradually decreasing. Meanwhile, the elastic limit of uncontaminated red clay showed an overall decreasing trend with increasing temperature, while the elastic limit of zinc-contaminated red clay showed an overall increasing trend with increasing temperature. In Figure 2a, it can be seen that when ε = 15%, the stress in the uncontaminated red clay increases from 295.3 kPa to 353.8 kPa as the temperature increases from 8.3 °C to 40 °C, and the soil stresses at each temperature increase by 10.13%, 12.06%, and 19.81%, respectively; while in Figure 2b, the stress of red clay with 0.5% Zn ion concentration increased from 366.8 kPa to 463.7 kPa, and the soil stresses at each temperature increased by 13.25%, 17.91%, and 26.42%, respectively. It indicates that the principal stress difference corresponding to the same axial strain location basically increases with increasing temperature when the zinc ion concentration and the surrounding pressure in the red clay are the same. This suggests that temperature can greatly influence the mechanical strength of Zn-contaminated red clay. The reason is that as the ambient temperature of the soil rises, the red clay soil in the consolidation stage converts more bonded water into free water and discharges it from the soil due to thermal expansion and contraction. The contact between soil particles is closer, which enhances the ability of the soil to resist external shear damage. Meanwhile, the red clay soil in the undrained shear stage will make the movement of residual water more active due to thermal expansion and contraction. The moisture is more easily dispersed uniformly inside the soil body, and bears part of the external damage force through the super-pore water pressure.
3.1.2. Effect of Contamination Concentration on the Stress–Strain Relationship of Red Clay under Temperature Conditions
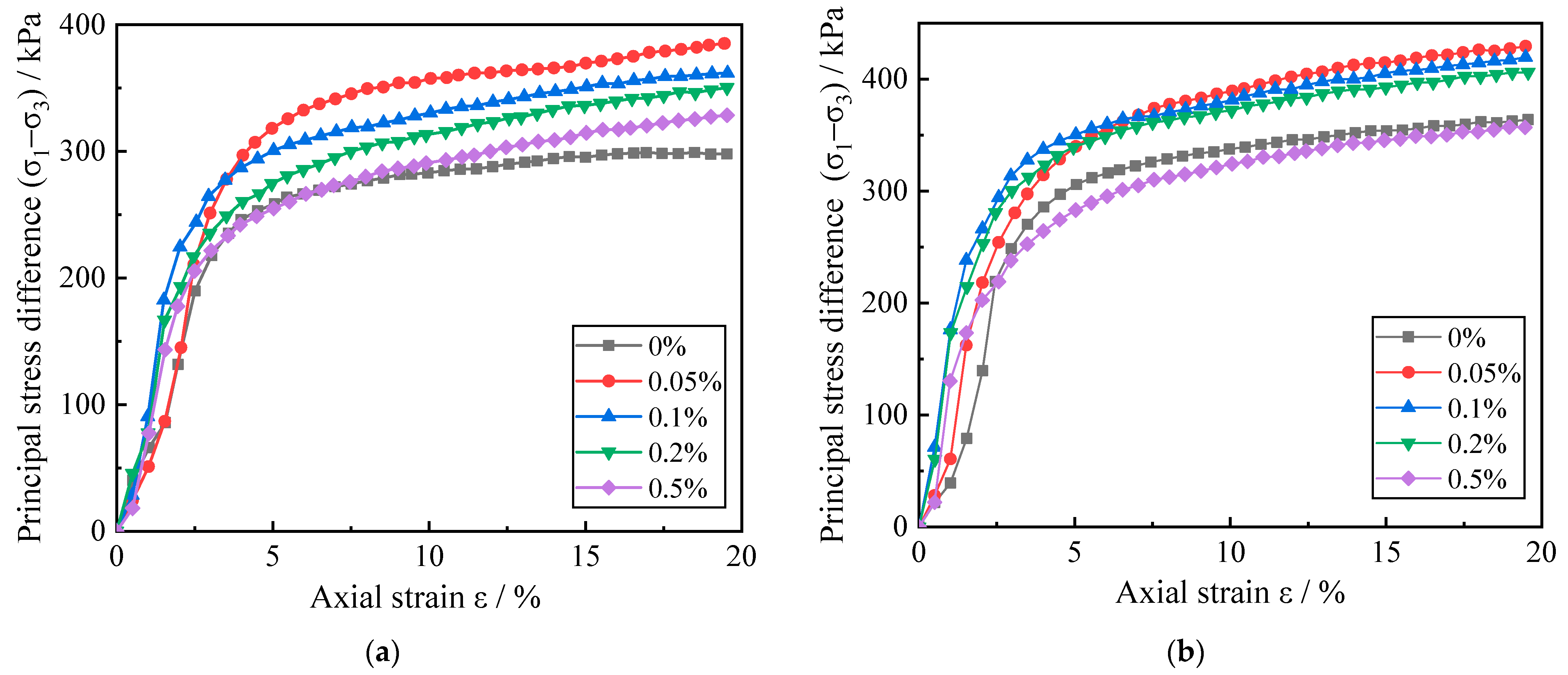
In order to study the deformation characteristics of red clay under the temperature conditions of pollution concentration, the stress–strain curves of red clay with five kinds of zinc pollution concentration under the ambient temperature of 8.3 °C, 40 °C, and the surrounding pressure are 300 kPa are selected, as shown in Figure 3.
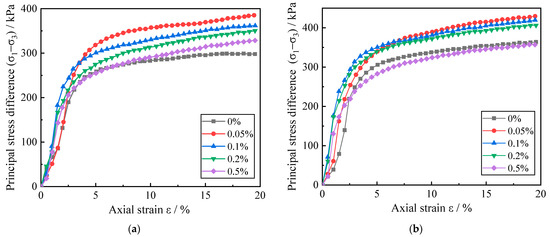
Figure 3.
Stress–strain curve of red clay with Zn pollution concentration. (a) The temperature is 8.3 °C and the confining pressure is 300 kPa; (b) The temperature is 40 °C and the confining pressure is 300 kPa.
Based on the type of soil stress–strain relationship and the change of stress–strain curve in Figure 3, it is possible to conclude that the stress–strain curve of red clay with varying contamination concentrations at the same ambient temperature exhibits strain hardening. During the shearing process, the primary stress difference exhibited a linear increase, followed by a slow increase, as the axial strain increase, while the deformation modulus also showed a trend of rapid increase and then a slow decrease. Comparing the curves in Figure 3, it was discovered that when the ambient temperature and the surrounding pressure of the soil were the same, the principal stress difference corresponding to the same axial strain of the red clay with Zn ion concentration from 0 to 0.05% exhibited an increasing trend, while the principal stress difference corresponding to the same axial strain of the red clay with Zn ion concentration from 0.05% to 0.5% exhibited a decreasing trend, and the degree of decrease was more obvious. In Figure 3a, it can be seen that when ε is 15%, the stress in the red clay at 8.3 °C increased from 295.3 kPa to 369.7 kPa, then decreased to 314.7 kPa as the concentration of zinc ions in the soil increased from 0 to 0.5%, and the stress in the soil at each concentration increased by 25.19%, 18.90%, 13.85%, and 10.66%, respectively. In Figure 3b, with the increase of zinc ion concentration in soil, the stress of red clay at 8.3 °C first increases from 353.8 kPa to 414.6 kPa and then decreases to 345.3 kPa, and the soil stress at each concentration increases by 17.18%, 14.47%, 10.96%, and −2.45% respectively. It indicates that the amount of Zn ions in red clay can influence its macroscopic strength via altering the red clay deformation. The reason is that when small amounts of zinc ions are present in red clay, crystalline water is present in the zinc salt produced by the reaction of zinc ions with soil particles. The crystalline water causes the surrounding soil particles to have a fitting effect, which in turn causes the local soil particles to aggregate. The denseness of the soil increases, making the soil more resistant to external destructive forces. When large amounts of zinc ions are present in the red clay, the zinc ions react with a large number of soil particles to produce more zinc salts. The bound water in zinc salts can attract to more soil particles and form larger agglomerates of soil particles, which destroys the overall structure of the soil body. At the same time, the reaction of zinc ions with soil particles destroys the cementing material between soil particles and also reduces the attraction between soil particles. Therefore, the macroscopic manifestation is that the ability of the soil body to resist external destructive forces is reduced.
3.1.3. Effect of Enclosure Pressure on Stress–Strain Curves of Zn-Contaminated Red Clay at Different Temperature Conditions
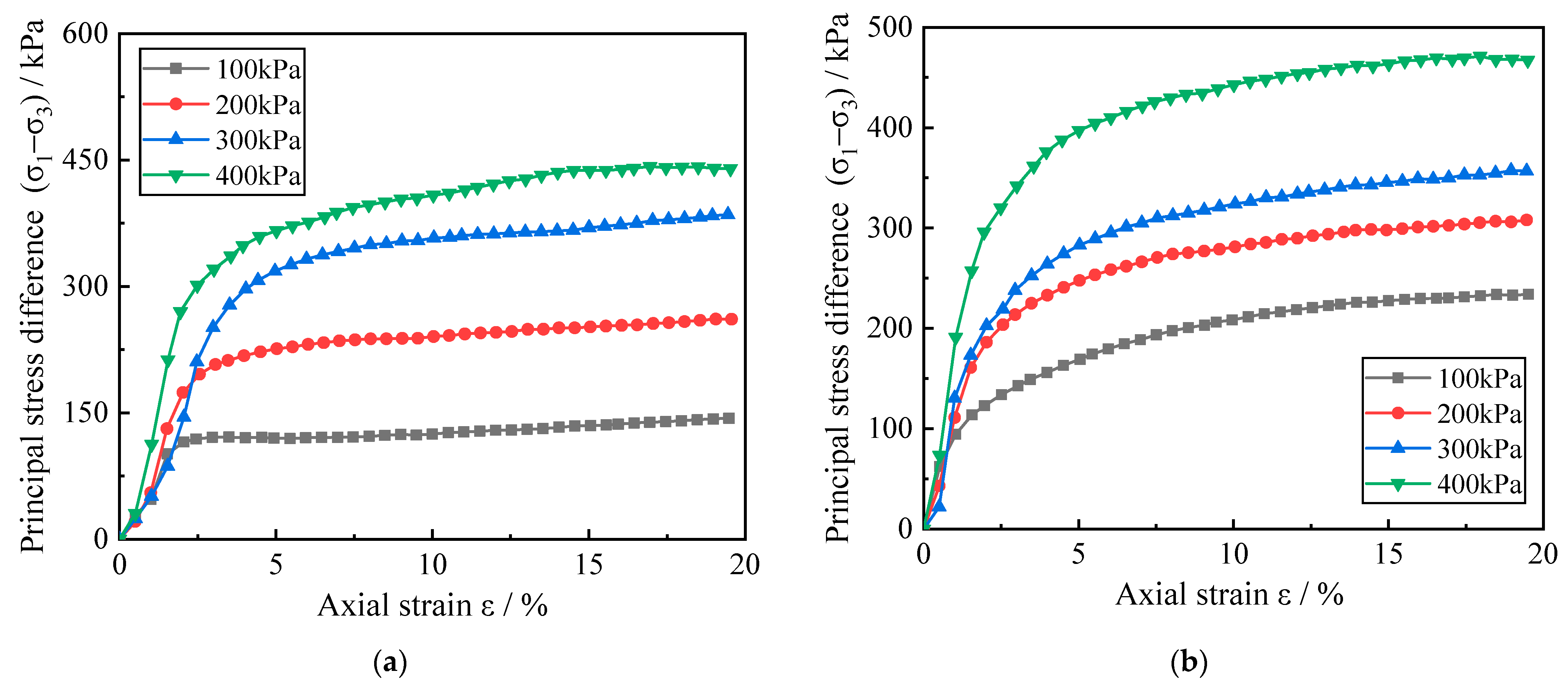
In order to study the deformation characteristics of Zn-contaminated red clay under different temperature conditions, the stress–strain curves of red clay with ambient temperatures of 8.3 °C and 40 °C and Zn-contaminated concentrations of 0.05% and 0.5% at different enclosure pressures were selected, as shown in Figure 4.
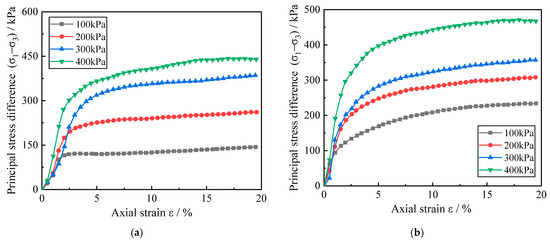
Figure 4.
Stress–strain curves of zinc-contaminated red clay under different confining pressures. (a) The temperature is 8.3 °C, and the zinc ion concentration is 0.05%; (b) The temperature is 40 °C, and the zinc ion concentration is 0.5%.
In addition to temperature and contamination concentration, the circumferential pressure to which the red clay is subjected also has an effect on its stress–strain relationship. From Figure 4, it can be judged that the stress–strain relationship of the Zn-contaminated red clay under different circumferential pressures also belongs to the strain-hardening type when the test temperature and the Zn contamination concentration of the red clay are the same. In Figure 4a, when ε is 15%, the stress of the red clay with 0.05% zinc ion concentration increases from 134.8 kPa to 437.3 kPa as the increase of the enclosing pressure from 100 kPa to 400 kPa. The stress of the soil at each enclosing pressure increases by 86.87%, 174.26%, and 224.41%, respectively. In Figure 4b, the stress of red clay with 0.5% Zn ion concentration increased from 227.5 kPa to 463.7 kPa with the increase of the enclosing pressure. The stress of the soil under each enclosing pressure increased by 13.25%, 17.91%, and 26.42%, respectively. In addition, the deformation modulus of the red clay increased linearly during the initial stage of shear; at a certain critical point, it began to fall rapidly and subsequently decreased gradually. At the same time, the principal stress difference of the red clay grows as the surrounding pressure becomes larger, and the phase of linear increase of the deformation modulus is extended. It indicates that the surrounding pressure can have a significant effect on the mechanical strength of zinc-contaminated red clay. This is due to the fact as the surrounding pressure applied to the soil increases, more water is removed from the red clay specimen during the consolidation stage, and it is known from the principle of effective stress of soil that with the discharge of pore water, the pore pressure decreases and the effective stress borne by the soil skeleton increases. In the undrained shear stage, the water in the soil is not completely discharged. The residual water in the soil can bear part of the shear stress with the increase of the surrounding pressure, so that the soil can resist the external damage ability.
3.2. Changes in Shear Strength of Zn-Contaminated Red Clay under Different Temperature Conditions
3.2.1. Effect of Temperature on the Shear Strength of Zinc-Contaminated Red Clay
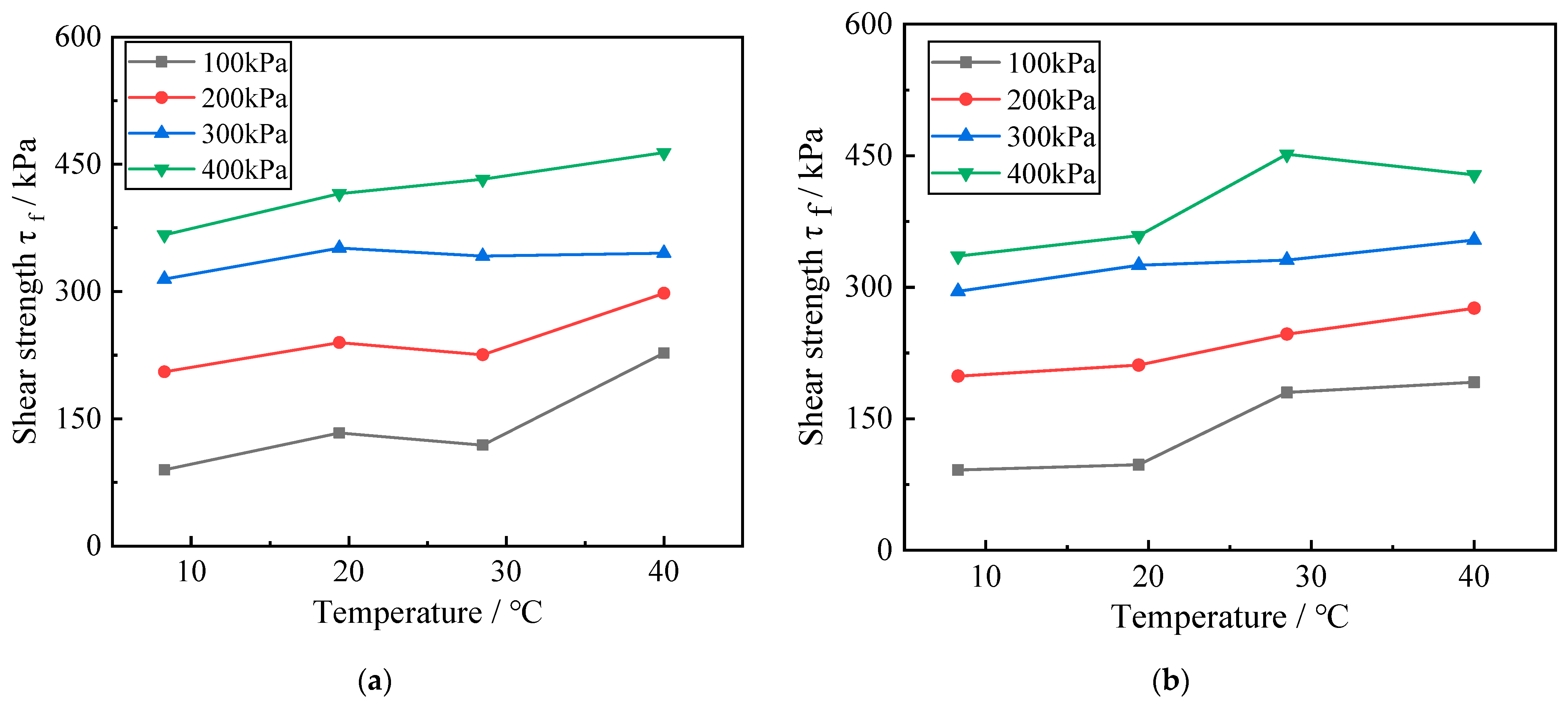
In order to better study the effect of temperature on the shear strength of Zn-contaminated red clay, the shear strength variation of red clay with contamination concentration of 0% and 0.5% under different temperature conditions were selected in this section. Figure 5 illustrates the shear strength variation curves of Zn-contaminated red clay at various ambient temperatures.
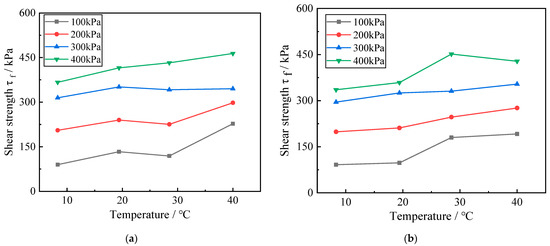
Figure 5.
Influence of temperature on the shear strength of red clay. (a) The zinc ion concentration is 0%; (b) The zinc ion concentration is 0.5%.
It can be seen in Figure 5 that the effect of temperature on the shear strength of red clay is relatively obvious, that with an increase in temperature, the shear strength of red clay under different contamination concentrations exhibits an upward trend, and that the relationship between the two is essentially linear. In addition, when the red clay is subjected to the same zinc contamination concentration is at the same temperature, its shear strength increases as the surrounding pressure rises, demonstrating a clear positive correlation.
This is because, when the ambient temperature of the red clay soil increases, the molecular movement inside the soil becomes more active, and the particles and pore water expand in volume due to the effect of thermal expansion and contraction. In the consolidation stage, due to the effect of the surrounding pressure, the expansion of both causes the pore water within the soil to leave the soil, the volume of the soil decreases, and the distance between the particles shrinks, bringing a specific soil particle into contact with more soil particles and increasing the effective stress of the soil. Therefore, the stress required to produce axial strain in red clay during shear likewise increases as ambient temperature rises, and the macroscopic expression is that the shear strength of zinc-contaminated red clay increases with the increase of ambient temperature.
3.2.2. Effect of Contamination Concentration on the Shear Strength of Zinc-Contaminated Red Clay
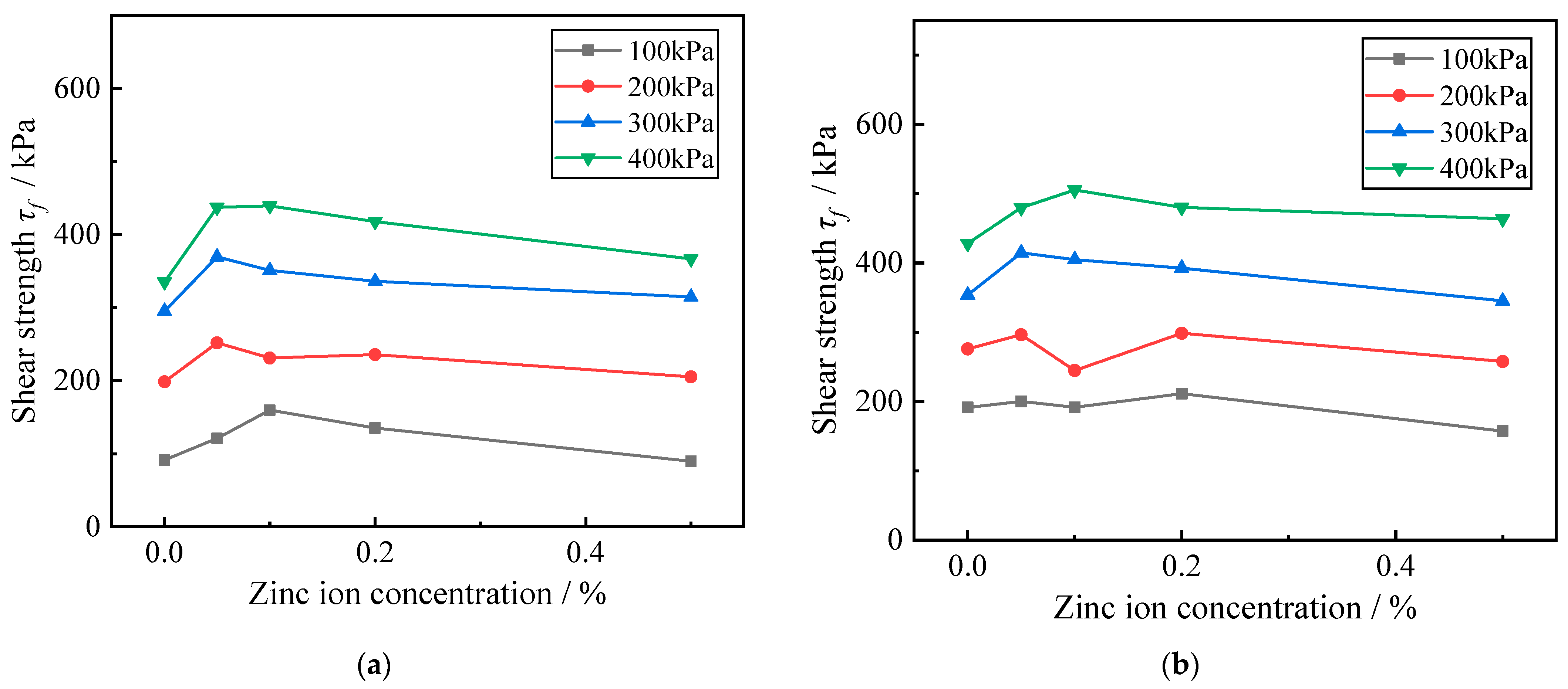
In order to better explore the influence of contamination concentration on the shear strength of Zn-contaminated red clay, the variation of the shear strength of Zn-contaminated red clay at temperatures of 8.3 °C and 40 °C, respectively, was selected. Figure 6 illustrates the shear strength variation curves of Zn-contaminated red clay with various contamination concentrations at the same ambient temperature conditions.
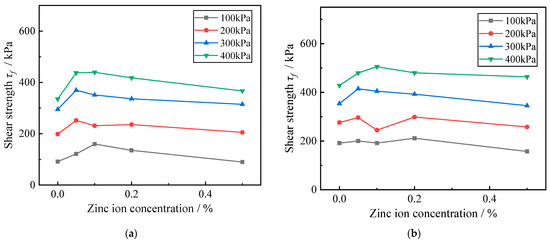
Figure 6.
Influence curve of contamination concentration on shear strength of zinc-contaminated red clay. (a) The temperature is 8.3 °C; (b) The temperature is 40 °C.
From Figure 6a, it can be seen that when the ambient temperature is 8.3 °C, the shear strength of red clay with different zinc contamination concentration changes very obviously; from Figure 6b, it can be seen that when the ambient temperature is 40 °C, the shear strength of red clay with different zinc contamination concentration changes more obviously; however, the changes of zinc ion concentration and soil shear strength in red clay under the two temperature conditions are not significantly different. At the same temperature, the shear strength of the red clay increased with the increase of zinc contamination concentration, then declined gradually. Comparing Figure 6a,b, we discovered that the shear strength of red clay first increased at the zinc ion content in red clay grew from zero to zero; after that, the shear strength of red clay basically showed a significant decreasing trend as the zinc ion content continued to increase. It demonstrates that the Zn ion content in the soil has a significant effect on the strength of the red clay, and a small amount of Zn ion can improve the shear strength of the red clay, whereas a large amount of Zn ion can significantly reduce the shear strength of the red clay, resulting in the deterioration of the engineering properties of the red clay and bringing adverse geological hazards to the construction. In addition, there is a positive association between the shear strength and the surrounding pressure of red clay soils under the same temperature settings and with the same concentration of zinc contamination also shows a positive correlation. That is, the greater the surrounding pressure of the red clay, the greater the shear strength of the red clay itself. This is because in the consolidation stage of the specimen, with the increase of the surrounding pressure, more pore water in the soil is eliminated; according to the principle of effective stress of soil, it is known that with the elimination of pore water in the soil, the pore pressure in the soil decreases, and the contact of soil particles becomes more compact, and the pressure borne by the soil skeleton is enhanced, leading to the enhancement of the effective stress of the soil, which is macroscopically expressed as the increase of the shear strength of the soil.
3.3. Changes of Shear Strength Index of Zinc-Contaminated Red Clay under Different Temperature Conditions
3.3.1. Effect of Temperature on the Shear Strength Index of Zinc-Contaminated Red Clay
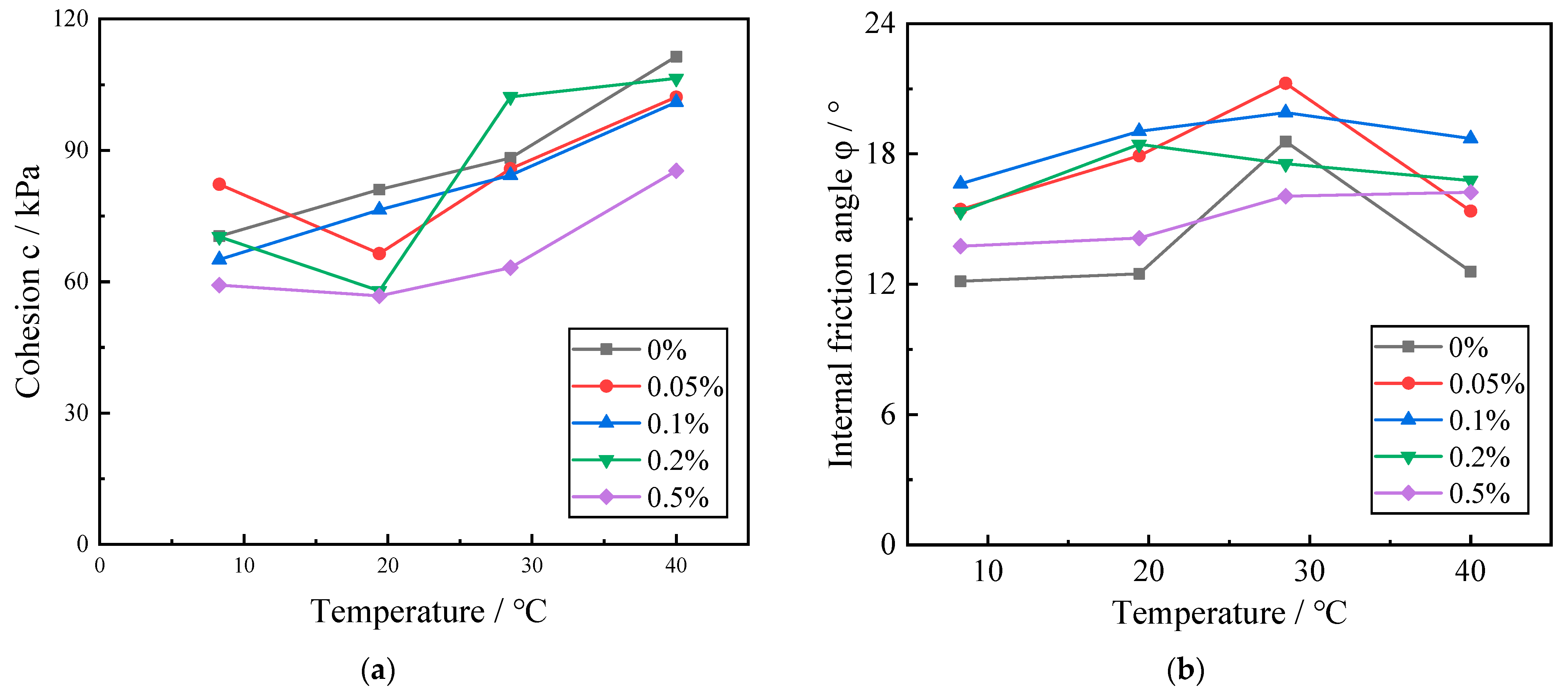
According to the data-processing method of the triaxial compression test in the Standard for Geotechnical Test Methods (GB/T 50123-2019), the values of the damage points in the test data are obtained, calculated, and processed in accordance with the relevant formulas, the total stress circle of damage under different circumferential pressure is drawn, and the common tangent is drawn, and finally, the values of cohesion and internal friction angle under each condition are obtained.
Figure 7 illustrates the variation curves of the shear strength index of Zn-contaminated red clay at various temperatures. In Figure 7, it can be seen that when the concentration of zinc contamination in the red clay remains constant, the cohesive force exhibits an overall increasing trend with the increase in temperature, whereas the internal friction angle exhibits a first increasing and then decreasing trend with the increase in temperature. Due to the thermal consolidation, as the ambient temperature rises, the volume of particles and pore water within the soil expands, the bound water between soil particles is converted into free water, the hydration film surrounding soil particles gradually decreases, the diffusion layer becomes thinner, and the hydrogel connection force between soil particles increases, resulting in a strengthening of the cohesion of red clay. Due to the confining effect of the surrounding pressure on the soil body during the heat consolidation stage, more pore water is discharged from the soil body, resulting in a decrease in pore pressure and an increase in pressure to be borne by the soil body, prompting the volume reduction of the soil body, the enhancement of the occlusion and friction between the soil particles, and a rise in the increase of the internal friction angle between the soil particles; after that, as the pore water continues to be discharged, the soil body deforms seriously, leading to the destruction of the occlusion point between the soil particles. Therefore, the internal friction angle of the red clay maintains the trend of first increasing and then decreasing with the increase of temperature.
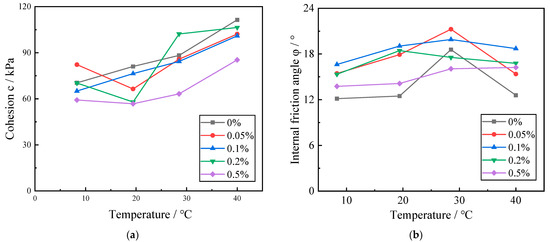
Figure 7.
Curve of influence of temperature on the shear strength index of red clay. (a) The graph of the change of cohesion force with temperature; (b) The graph of internal friction angle with temperature.
3.3.2. Effect of Pollution Concentration on the Shear Strength Index of Red Clay under the Same Temperature Condition
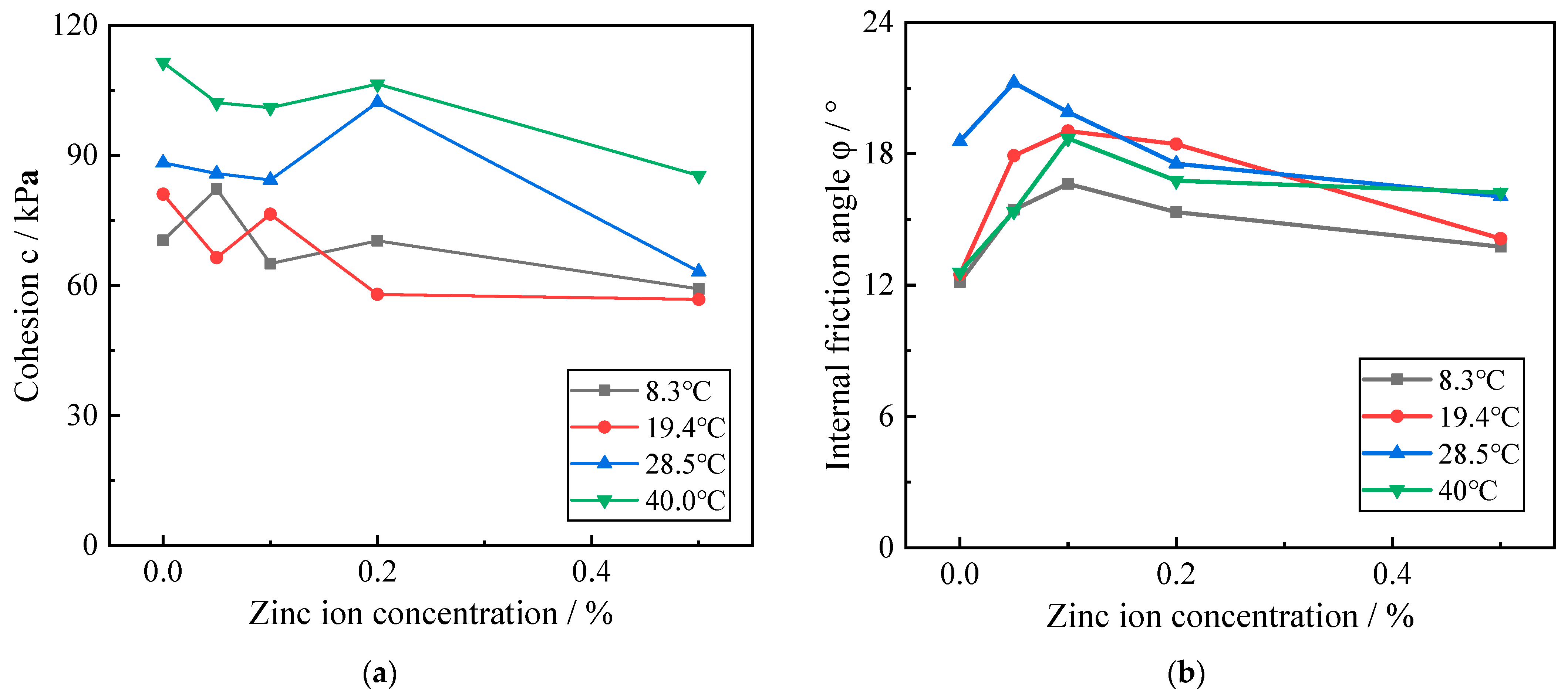
Figure 8 depicts the variation curves of shear strength index of red clay with different Zn contamination concentrations at the same temperature condition. From Figure 8, it can be shown that when the red clay is at the same ambient temperature, its cohesive force basically shows a decreasing trend with the increase of zinc contamination concentration, while its internal friction angle shows a trend of first increasing and then decreasing with the increase of zinc contamination concentration in the soil.
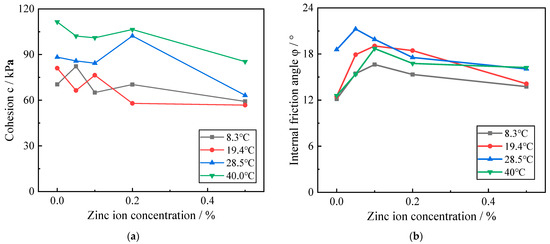
Figure 8.
Influence curve of zinc contamination concentration on shear strength index of red clay. (a) The variation of cohesion with zinc ion concentration; (b) The variation of internal friction angle with zinc ion concentration.
This is because, when the ambient temperature of the red clay remains constant, with the increase of Zn contamination concentration in the soil, more Zn ions react with the cemented material within the soil and destroy its structure, reducing the attraction between soil particles, and the macroscopic expression of the cohesion of the red clay gradually decreases with the increase in Zn contamination concentration. When zinc ions appear in the red clay, zinc ions react with the surrounding soil particles and produce zinc salts; after the crystalline water in zinc salts enters the pores of soil particles, it causes a kind of fitting effect on the surrounding soil particles, which then causes the present soil particles in the local area within the soil to gather, and the occlusal force and slip friction between them to increase, which is expressed as an increase in the internal friction angle of the soil body; when the content of zinc ions in the red clay continues to increase when the content of zinc ions in the red clay continues to increase, the number of zinc salts generated within the soil increases significantly, the number of agglomerates formed by the agglomerates of soil particles increases, the larger the volume of the agglomerates, the more the structure of the contaminated red clay is destroyed, followed by the formation of small particles of soil, an increase in the number of pores around them increases, and the friction between the soil particles around the pores decreases, and the macroscopic expression is that as the concentration of zinc contamination in the red clay increases, the angle of internal friction first increases and then decreases.
4. Conclusions
In this paper, red clay soil from a foundation pit in Guilin City, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region was used as the test soil, and the triaxial shear test of the red clay soil was conducted with temperature, zinc ion concentration, and surrounding pressure as variables to analyze the effects of these three variables on the deformation and strength of the local zinc-contaminated red clay soil in Guilin City. The following conclusions were obtained.
(1) The stress–strain relationship of red clay is strain-hardened at varying temperatures, different Zn ion concentrations, and different surrounding pressures, depending on which variable is altered. In the stress–strain relationship, the deformation modulus of the red clay tends to grow rapidly with an increase of axial strain before decreasing slowly.
(2) Temperature can change the strength of red clay. Under the same zinc contamination concentration and circumferential pressure, the red clay increases with the temperature, which boosts the thermal consolidation and changes the cohesion and internal friction angle of the red clay, resulting in a continuous increase in shear strength.
(3) The concentration of zinc contamination can also affect the shear strength of red clay. Under the same temperature and surrounding pressure, the shear strength of red clay tends to increase and subsequently drop as the concentration of zinc contamination rises.
(4) The surrounding pressure is also related to its shear strength. As the volume of red clay decreases in response to an increase of the surrounding pressure, the effective stress of the soil increases, hence increasing its shear strength.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.W. and Y.S.; methodology, J.W.; validation, Y.G., S.D. (Shuaishuai Dong) and S.D. (Song Ding); investigation, X.G.; writing—original draft preparation, J.W.; writing—review and editing, Y.S. and J.W.; supervision, X.G. and S.D. (Shuaishuai Dong); project administration, Y.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
(1) Guangxi Innovation-Driven Development Special Project “Research and Demonstration of Key Technologies for Water Resource Utilization and Synergistic Development of Water Ecological Industry in Typical Karst Wetlands in the Lijiang River Basin” (Guike AA20161004-1); (2) National key research and development program subject “R&D and experimental demonstration of key technologies for water resource regulation in Karst wetlands in the Lijiang River Basin” (2019YFC0507502); (3) The National Natural Science Foundation of China Project “Research on the Collapse Mechanism of Karst Water-soil Coupling in Guilin under Extreme Climate Conditions” (41967037).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Chen, L.J.; Chen, X.J.; Wang, H.; Huang, X.; Song, Y. Mechanical properties and microstructure of lime-treated red clay. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2021, 25, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Wang, J.Q.; Chen, X.J.; Yu, S.Z.; Ban, R.L.; Yang, X.; Zhang, X.C.; Han, Y. Study the effects of dry-wet cycles and cadmium pollution on the mechanical properties and microstructure of red clay. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 302, 119037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.J.; Chen, X.J.; Yang, X.; Bi, P.Y.; Ding, X.; Huang, X.; Wang, H. Effect of calcium carbonate on the mechanical properties and microstructure of red clay. Adv. Mate. Sci. Eng. 2020, 2020, 5298186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Li, H.; Gan, X.H.; Zhang, M.Z.; Xue, M.M.; Li, J. Comparative experimental study on calcium oxide, calcium hydroxide, and calcium carbonate solidified zinc-contaminated red clay. Geofluids 2022, 2022, 8428982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, K.M.; Kenichi, S. Fundamentals of Soil Behavior; John Wiley & Sons Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.F.; Liu, Z.K. Influence of different amount of red mud on shear strength of red clay. Yangtz. Riv. 2017, 48 (Suppl. S1), 264–267. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, H.B.; Ji, C.S.; Xie, C.; Zeng, Z.T.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Y.S. Effect of acids on physical and mechanical properties of Liuzhou lateritic soil. J. Guangxi Univ. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2017, 42, 1465–1471. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.Z.; Zuo, S.Y.; Ji, Y.X. Experimental Study on undisturbed and reconstituted mechanical properties of red clay. J. Undergr. Space Eng. 2017, 13, 1477–1482. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.Y.; Liu, Z.K. Strength change mechanism of undisturbed red clay and remolded red clay. J. Henan Univ. Sci. Technol. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2019, 27, 53–59. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.M.; Chen, X.J.; Yang, Y.; Huang, X.; Song, Y. Experiment of modified red clay by graphite nanoparticles. Henan Univ. Sci. Technol. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2019, 40, 69–73+80. [Google Scholar]
- Mukiza, E.; Zhang, L.L.; Liu, X.M.; Zhang, N. Utilization of red mud in road base and subgrade materials: A review. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 141, 187–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, W.S.; Feng, X.Z.; Wang, R.H.; Wei, W.F.; Luo, S.Y.; Zheng, R.J.; Yang, D.Z.; Mi, H.W.; Chen, H. High-efficiency core-shell magnetic heavy-metal absorbents derived from spent LiFePO4 battery. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 402, 123583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.B.; Wang, M.; Li, S.S.; Zhao, Z.Q.; E, W.D. Overview on current criteria for heavy metals and its hint for the revision of soil environmental quality standards in China. J. Integr. Agr. 2018, 17, 765–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Bharagava, R.N.; More, N.; Yadav, A.; Zainith, S.; Mani, S.; Chowdhary, P. Heavy metal contamination: An alarming threat to environment and human health. In Environmental Biotechnology: For Sustainable Future; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 103–125. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, T.R.; Ma, J.; Wu, X.; Ju, T.N.; Lin, X.L.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Li, X.H.; Gong, Y.W.; Hou, H.; Zhao, L.; et al. Inventories of heavy metal inputs and outputs to and from agricultural soils: A review. Ecotox. Environ. Safe. 2018, 164, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.C.; Yin, R.Z.; Luo, Y.P.; Lu, Y.L.; Zhang, L.D. Assessment of heavy metal contamination of soils in Daxin manganese mine Guangxi. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 33, 183–190. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.H.; Chen, X.J.; Zhao, Y.L.; Qi, S.H. Heavy metal pollution in soils and plant accumulation in a restored lead zinc mineland in Guangxi, South China. J. China Univ. Min. Technol. 2007, 36, 487–493. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.B.; Chen, X.J.; Qi, Y.L.; Huang, X.; Yu, S.Z.; Xiao, G.Y. Effects of dry density and moisture content on shear strength parameters of remolded red clay soil. J. Eng. Geol. 2019, 27, 1035–1040. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, X.P.; Tang, C.S.; Shi, B.; Wang, H.S.; Leng, T.; Tan, Y.Z.; Deng, Y.F. Evolution of soil microstructure during drying and wetting. J. Eng. Geol. 2019, 27, 775–793. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Y.H.; Zhang, B.H.; Liu, B.C.; Zeng, Z.T.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, Y. Shrinkage cracking and strength deterioration of red clay under cyclic drying and wetting. Alex. Eng. J. 2022, 61, 2574–2588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.; Yu, H.C.; Gao, Q.F.; Liu, J.; Liu, Z.H. Evolution of Tensile Properties of Compacted Red Clay under Wet and Dry Cycles. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2022, 26, 606–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.J.; Chen, L.J.; Song, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhou, X.; Li, J.M. Experimental study on improvement of red clay with lime. J. Eng. Geol. 2017, 25, 230–234. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.J.; Chen, L.J.; Song, Y.; Chen, H.B.; Wang, H. Experimental study on strength characteristics of red clay under different particle size of calcium carbonate. In International Symposium on Energy Geotechnics; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 236–242. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, Y.L.; Bai, M.Z.; Zhou, H.; Shi, H.; Li, P.X.; He, B.H. Study on the mechanical properties of red clay under drying-wetting cycles. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 2021, 8665167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, Q.; Yu, M.Y.; Wu, Z.H.; Gao, B.; Dong, J. Study on shear strength and microstructure characteristics of alkali contaminated red clay. J. Eng. Geol. 2018, 26, 1300–1310. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, K.; Ye, W.J.; Gao, H.J.; Dong, Q. Evolutionary law and microscopic mechanism of shear strength of acid-alkaline contaminated loess. Geotechnics 2022, 43 (Suppl. S1), 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.M.; Tang, S.B.; Chen, X.J. Analysis of the Mechanical properties and mechanism of zinc ion-contaminated red clay. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 2021, 6649691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Zhang, M.Z.; Li, H.; Yang, X.; Chen, X.J.; Li, J. Effect of chromium ion on the strength characteristics and damage law of red clay. Geofluids 2022, 2022, 8451476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.C.; Huang, X.; Chen, X.J.; Zhang, X.C.; Ban, R.L. Relationship between shear strength and electrical resistivity of cu2+ contaminated red clay. J. Yangtze Riv. Sci. Res. Inst. 2021, 38, 121–127+136. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.P.; Li, D.H.; Deng, R.F.; Tian, X.; Ren, S.P. An experimental study for influence of freeze thaw cycles on strength and pore characteristics of solidified lead contaminated soil. J. Eng. Geol. 2019, 27, 539–549. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.J.; Chen, Y.C.; Song, Y.; Li, J.M.; Yu, S.Z.; Chen, L.J. Analysis on variation of physical-mechanical properties of red clay contaminated by Cu2+. J. Eng. Geol. 2019, 27, 1010–1018. [Google Scholar]
- Hazreek, Z.A.M.; Azhar, A.T.S.; Rosli, S. Field miniature study on heavy metal detection using electrical resistivity imaging (ERI). Internat. J. Civ. Eng. Technol. 2018, 5, 284–292. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, H.L.; Shen, X.D.; Zhou, H.L.; Liu, X.H. Mechanical property and strength prediction of cement-solidified/stabilized zinc-contaminated red clay. Bullet. Chin. Ceram. Soci. 2016, 12, 3964–3971. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.H.; Sheng, X.D.; Fan, H.L.; Yuan, Q. Solidification rate and micro pore characteristics of cement stabilized zinc contaminated red clay. Environ. Eng. 2019, 37, 172–176. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Y.; Gan, X.H.; Li, H.; Zhang, M.Z.; Xue, M.M.; Gao, X.T.; Li, J. Curing effect and resistivity evolution of zinc-contaminated red clay cured by phosphate-based binder. Geofluids 2022, 2022, 8404620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.Q.; Lu, H.J.; Li, J.X. Ion release and micro structure of cd-polluted clay solidified by cement. Chin. J. Environ. Eng. 2015, 9, 4578–4584. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, L.C.; Wang, H.Y.; Xue, K.X. Study on thechanges of cracks and shear strength in unsaturated red clay under different drying temperature. J. Eng. Geol. 2021, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.M.; Chen, X.J.; Huang, X.; Cheng, Y.; Yu, S. Test on mechanical properties and microstructure of zinc-contaminated red clay. J. Henan Univ. Sci. Technol. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2020, 41, 99–104. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.J.; Zhou, X.; Song, Y.; Huang, Y.Y. Experimental study on the characteristics of zn2+ pollution on the strength damage of red clay under leaching conditions. J. Eng. Geol. 2017, 25, 1264–1269. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).