Physicochemical Characterization of a Cellulosic Film Modified with Two Room-Temperature Ionic Liquids
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Chemical Surface Characterization of the RC/IL Films
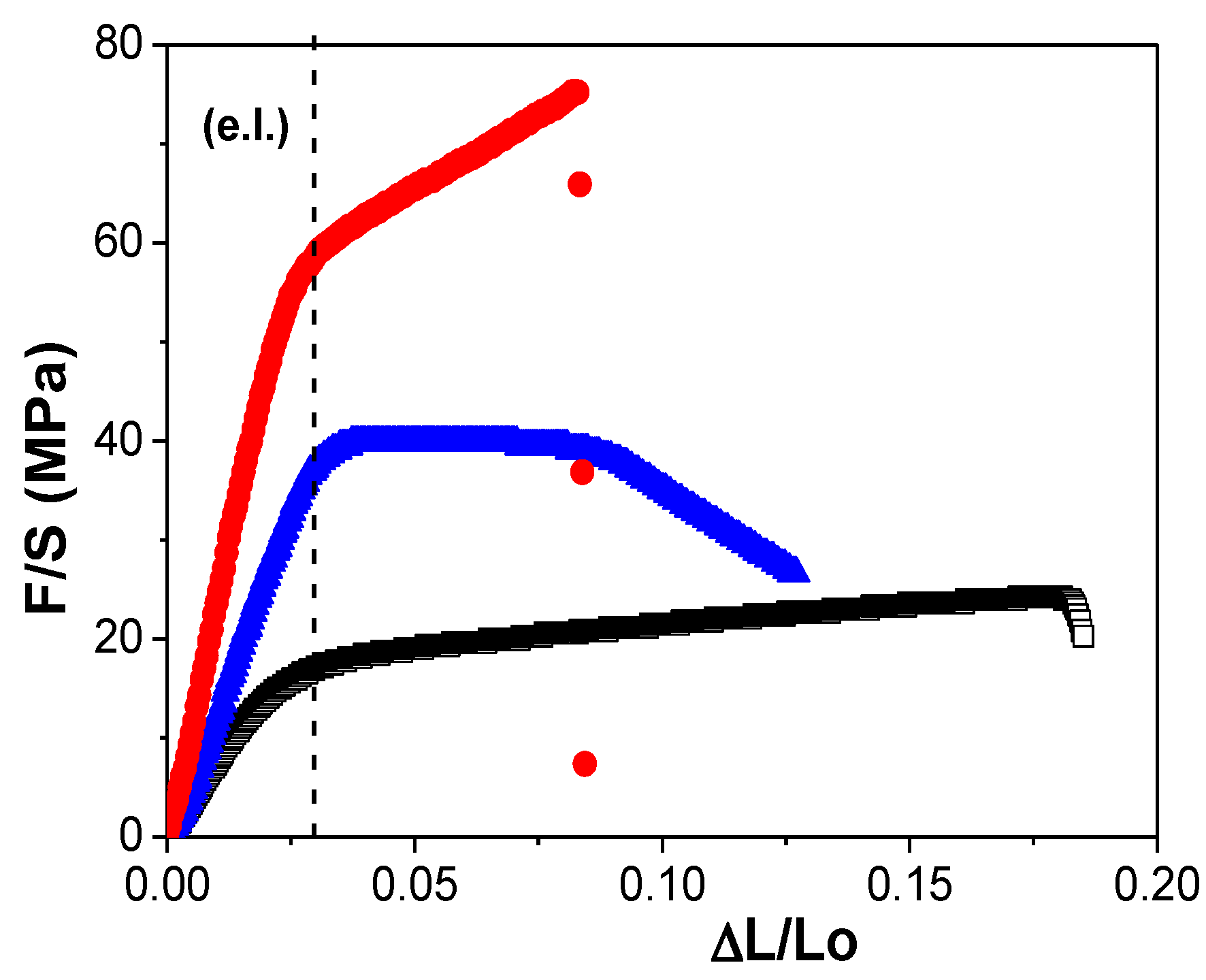
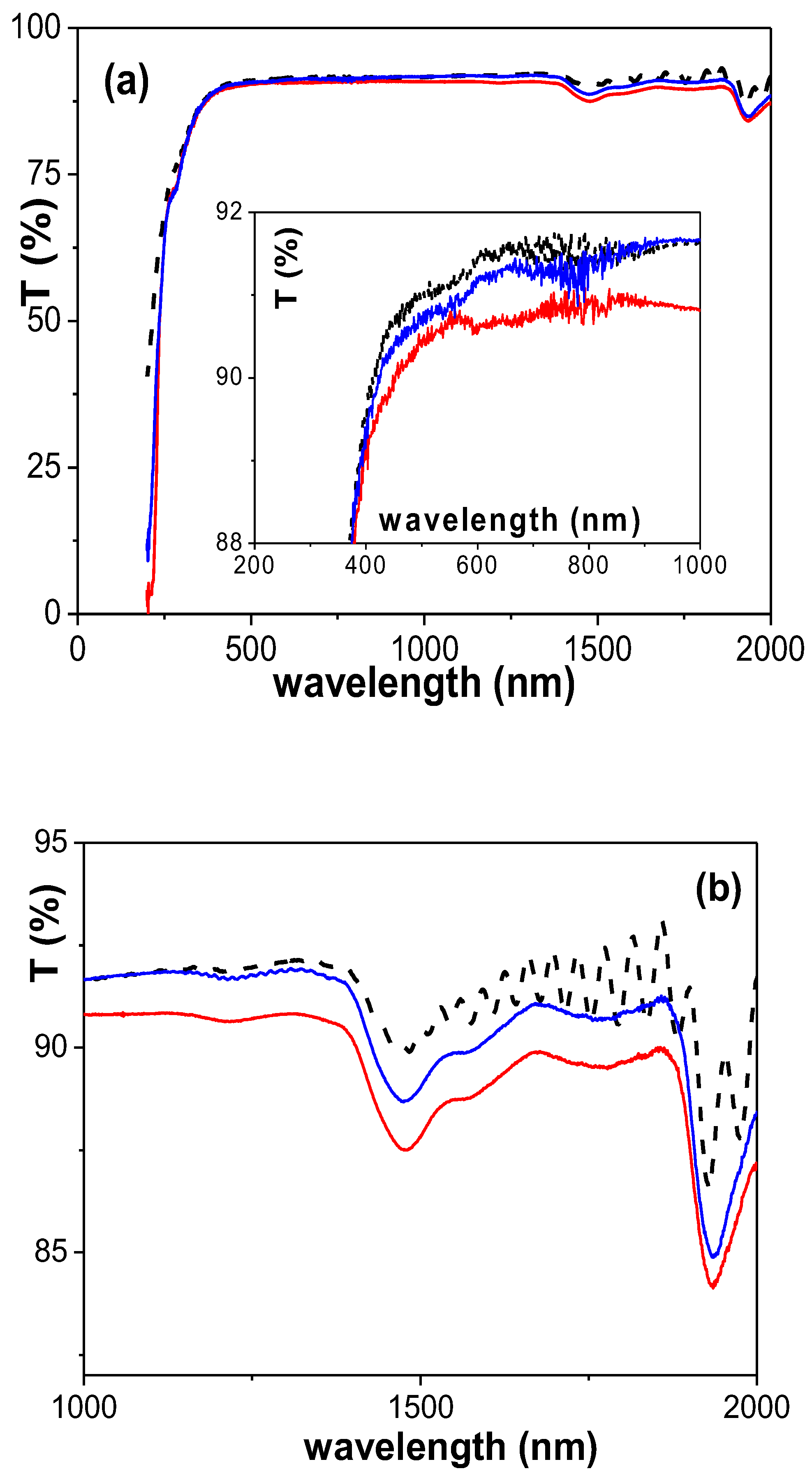
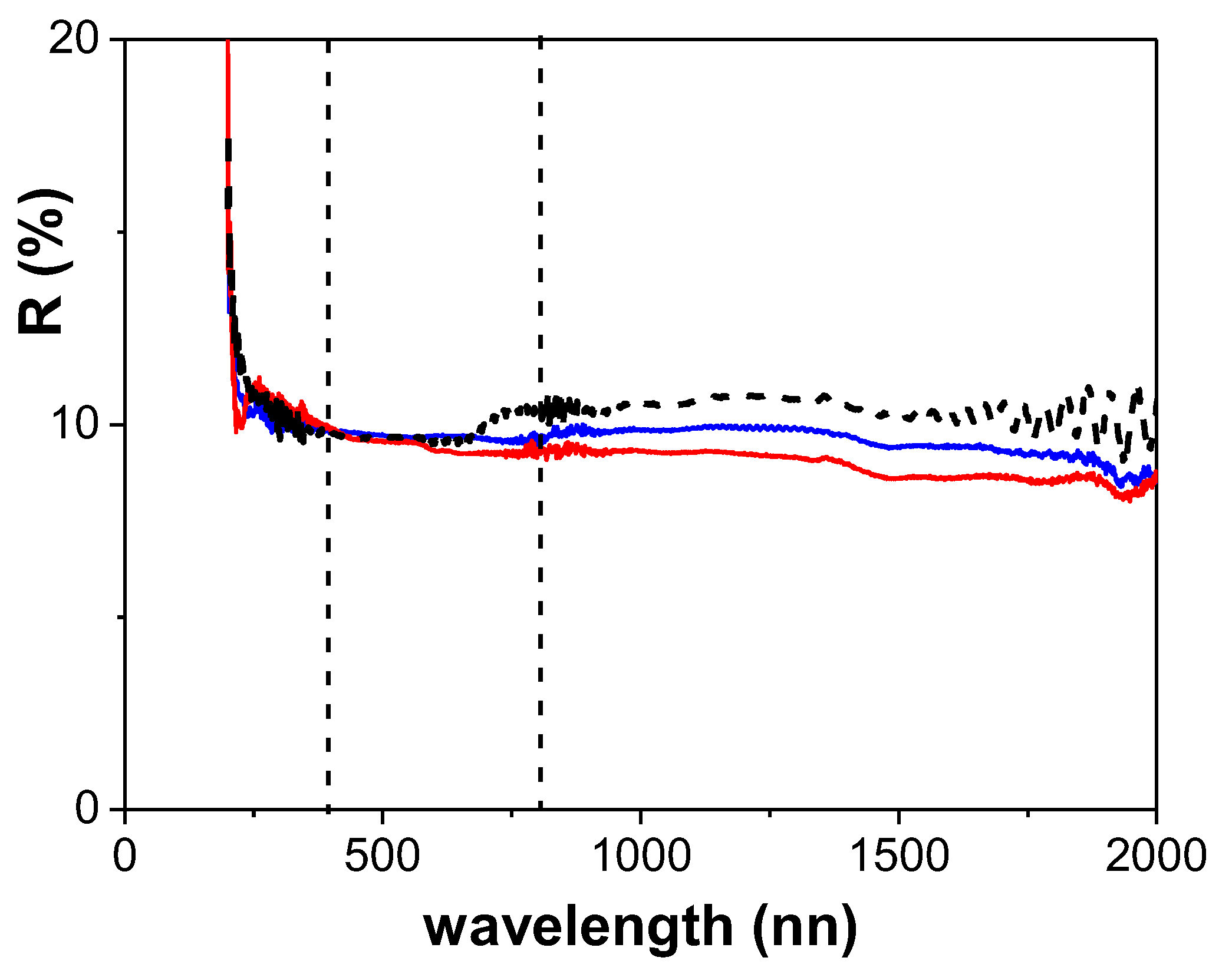
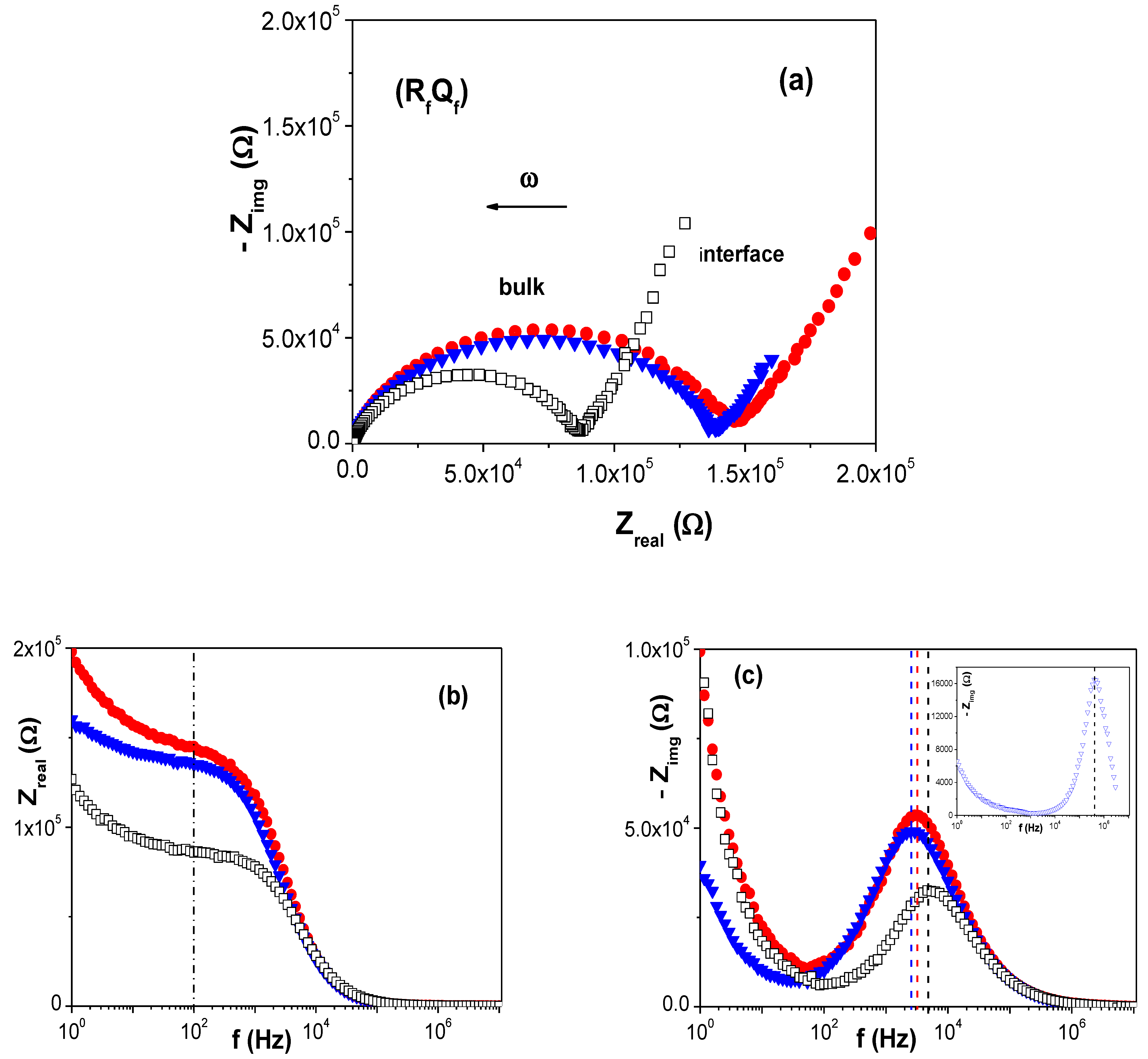
3.2. Physicochemical Characterization of the RC/IL Films
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Singh, S.K.; Savoy, A.W. Ionic liquids synthesis and applications: An overview. J. Mol. Liquids 2020, 297, 112038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welton, T. Room temperature ionic liquids. Solvent for synthesis and catalysis. Chem. Rev. 1999, 99, 2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abott, A.P.; McKenzie, K. Application of ionic liquids to the electrodeposition of metals. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2006, 8, 4265–4279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, H.; Sakaebe, H.; Tatsumi, K. Preparation of room temperature ionic liquids based on aliphatic onium cations and asymmetrc amide anions as a lithium battery electrode. J. Power Sources 2006, 160, 1308–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, A.; Mandal, P.K.; Samanta, A. On the optical properties of the imidazolium ionic liquids. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 109, 9148–9153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuyama, K.; Masuda, G.; Yoshida, H.; Sato, T. Ionic liquids containing the tetrafluoroborate anion have the best performance and stability for electric double layer capacitor applications. J. Power Sources 2006, 162, 1401–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armand, M.; Endres, F.; MacFarlane, D.R.; Ohno, H.; Scrosati, B. Ionic Liquids materials for the electrochemical changes of the future. Nat. Mater. 2009, 8, 621–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Bostrom, T. Application of Ionic Liquids in solar cells and batteries: A review. Curr. Org. Chem. 2015, 19, 556–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas, V.; Martínez, F.; Bernède, J.C.; Guenadez, L.C.; Efimov, A.; Lemmetyinen, H. Alkyl Thiophene Vinylene Electropolimerization in C8mimPF6, Potential Use in Solar Cells. Mater. Sci. Appl. 2017, 8, 405–417. [Google Scholar]
- Piatti, E.; Guglielmero, L.; Tofani, G.; Mezzetta, A.; Guazzelli, L.; D’Andrea, F.; Roddaro, S.; Pomelli, C.S. Ionic liquids for electrochemical applications: Correlation between molecular structure and electrochemical stability window. J. Mol. Liquids 2022, 364, 120001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Lv, S.; Jiang, K.; Zhou, G.; Liu, X. Recent development of ionic liquid-based electrolytes in lithium-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2022, 542, 231792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behera, K.; Pandey, S.; Kadyan, A.; Pandey, S. Ionic-liquid based optical and electrochemical carbon dioxide sensors. Sensors 2015, 15, 30487–30503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves, L.A.; Benavente, J.; Coelhoso, I.M.; Crespo, J.G. Design and characterization of Nafion membranes with incorporated ionic liquids cations. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 347, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikkola, J.-P.; Virtanen, P.; Sjöholm, R. Aliquat 336®-a versátil and afforable catión source for an entirely new family of hydrophobic ioni liquids. Green Chem. 2006, 8, 250–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontàs, C.; Vera, R.; Anticó, E.; Martínez de Yuso, M.V.; Rodríguez-Castellón, E.; Benavente, J. New Insights on the Effects of Water on Polymer Inclusion Membranes Containing Aliquat Derivatives as Carriers. Membranes 2022, 12, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correia, D.M.; Fernandes, L.C.; Fernandes, M.M.; Hermenegildo, M.; Meira, R.M.; Ribeiro, C.; Ribeiro, S.; Reguera, J.; Lanceros-Méndez, S. Ionic Liquid-Based Materials for Biomedical Applications. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortunato, R.; Branco, L.C.; Afonso, C.A.M.; Benavente, J.; Crespo, J. Electrical impedance spectroscopy characterization of supported ionic liquid membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 270, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueroa, J.D.; Fout, T.; Plasynki, S.; McIlvried, H.; Srivastava, R.D. Advances in CO2 capture technology-The U.S. Department of energy´s carbon sequestration program. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2008, 2, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salar-García, M.J.; Ortíz-Martínez, V.M.; de los Ríos, A.P.; Hernádez-Fernández, F.J. A method based on impedance spectroscopy for predicting the behaviour of novel ionic liquid-polymeric inclusion membranes in microbial cells. Energy 2015, 89, 648–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Bai, L.; Han, J.; Yang, B.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, X. Functionalized ionic liquid membranes for CO2 separation. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 12671–12685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves, L.A.; Crespo, J.G.; Coelhoso, I.M. Gas Permeation Studies in Supported Ionic Liquid Membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 357, 160–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, C.; Glück, T.; Schmidt-Naake, G. Modification of Nafion Membranes by Impregnation with Ionic Liquids. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2008, 31, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves, L.A.; Coelhoso, I.M.; Crespo, J.G. Methanol and gas crossover through modified nafion membranes by incorporation of ionic liquids cations. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 357, 160–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez de Yuso, M.V.; Neves, L.A.; Coelhoso, I.M.; Crespo, J.G.; Benavente, J.; Rodríguez-Castellón, E. A Study of Chemical Modifications of a Nafion Membrane by Incorporation of Different Room Temperature Ionic Liquids. Fuel Cells 2012, 12, 606–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez de Yuso, M.V.; Arango-Díaz, A.; Bijani, S.; Romero, V.; Benavente, J.; Rodríguez-Castellón, E. Chemical Surface, Thermal and Electrical Characterization of Nafion Membranes Doped with IL-Cations. Appl. Sci. 2014, 4, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Pandey, A.K.; Sharma, M.K.; Panicker, L.V.; Sodaye, S.; Suresh, G.; Ramagiri, S.V.; Bellare, J.R.; Goswami, A. Diffusional transport of ions in plasticized anion-exchange membranes. J. Phys. Chem. B 2011, 115, 5856–5867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, M.; Murakami, Y.; Minamidate, Y.; Kondo, K. Separation of lactic acid through polymer inclusión membranes containing ionic liquids. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2012, 47, 354–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez, M.I.; Romero, V.; Fontàs, C.; Anticó, E.; Benavente, J. Polymer inclusion membranes (PIMs) with the ionic liquid (IL) Aliquat 336 as extractant: Effect of base polymer nature and IL concentration on their physical-chemical and elastic characteristics. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 445, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gherasian, C.-V.; Borceanu, G.; Olariu, R.-I.; Arnese, C. A novel polymer inclusión membrane applied in chromium (VI) separation from aqueous solutions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 197, 244–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benavente, J.; Romero, V.; Vázquez, M.I.; Anticó, E.; Fontàs, C. Electrochemical Characterization of a Polymer Inclusion Membrane Made of Cellulose Triacetate and Aliquat 336 and Its Application to Sulfonamides Separation. Separations 2018, 5, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soheilmoghaddam, M.; Sharifzadeh, G.; Pour, R.H.; Wahit, M.U.; Whye, W.T.; Lee, X.Y. Regenerated cellulose/β-cyclodextrin scaffold prepared using ionic liquid. Mater. Lett. 2014, 135, 210–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benavente, J.; Vázquez, M.I.; Hierrezuelo, J.; Rico, R.; López-Romero, J.M.; López-Ramirez, M.R. Modification of a Regenerated Cellulose Membrane with Lipid Nanoparticles and Layers. Nanoparticle Preparation, Morphological and Physicochemical Characterization of Nanoparticles and Modified Membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 355, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Yan, L. Metal-free transparent luminescent cellulose films. Cellulose 2015, 22, 729–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez, M.I.; Algarra, M.; Benavente, J. Modification of regenerated cellulose membrane modified with thiol dendrimer. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 131, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuevas, A.; Campos, B.B.; Romero, R.; Algarra, M.; Vázquez, M.I.; Benavente, J. Eco-friendly modification of regenerated cellulose based film by silicon, carbon, and N-doped carbon quantum dots. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 206, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benavente, J.; García, M.E.; Urbano, N.; López-Romero, J.M.; Contreras-Cáceres, R.C.; Casado-Rodríguez, M.A.; Moscoso, A.; Hierrezuelo, J. Inclusion of silver nanoparticles for improving regenerated cellulose membrane performance and reduction of biofouling. Int. J. Biol. Macrom. 2017, 103, 758–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, Y.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Y.; Lei, B. Transparent sunlight conversion film based on carboxymethyl cellulose and carbon dots. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 151, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao Zou, M.; Chen, Y.; Chang, L.; Cheng, X.; Gao, L.; Guo, W.; Ren, Y.; Shupin, L.; Tang, Q. Toward 90 μm Superthin Transparent Wood Film Impregnated with Quantum Dots for Color-Converting Materials. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 2097–2106. [Google Scholar]
- Litaiem, Y.; Dhahbi, M. Physicochemical properties of an hydrophobic ionic liquid (Aliquat 336) in a polar protic solvent (formamide) at different temperatures. J. Disp. Sci. Technol. 2015, 36, 641–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benavente, J.; Rodríguez-Castellón, E. Application of electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) to the characterization of RTILs for electrochemical applications. In Ionic Liquids: Applications and Perspectives; Kokorin, A., Ed.; INTECH: Rijeka, Croatia, 2011; Chapter 27; pp. 607–626. [Google Scholar]
- Lockett, V.; Sedev, R.; Bassell, C.; Ralston, J. Angle-resolved X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy of the surface of imidazolium ionic liquids. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2008, 10, 1330–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukas, J.; Jezek, B. Inelastic mean free paths of photoelectrons from polymer surfaces determined by the XPS method. Collect. Czechoslov. Chem. Commun. 1983, 48, 2909–2913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Multitechnique ESCA. Software Reference Manual for the PC-ACCESS Software; Version 6.0.; Physical Electronics: Minneapolis, MI, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Moulder, J.F.; Stickle, W.F.; Sobol, P.E.; Bomben, K.D. Handbook of X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy; Chastain., J., Ed.; Perkin-Elmer Corporation: Minneapolis, MI, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Macdonald, J.R.; Johnson, W.B. Fundamentals of Impedance Spectroscopy. In Impedance Spectroscopy: Theory, Experiment, and Applications, 3rd ed.; Barsoukov, E., Ed.; Wiley Online Library: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benavente, J. Use of Impedance Spectroscopy for characterization of modified membranes. In Membrane Modification: Technology and Applications. Hilal, N., Kayet, M., Wright, C.J., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2012; ISBN 9781439866368. [Google Scholar]
- Brigg, D.; Seah, M.P. Practical Surface Analysis: Auger and X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 1995; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Simon, M.; Fulchiron, R.; Gouanvé, F. Water Sorption and Mechanical Properties of Cellulosic Derivative Fibers. Polymers 2022, 14, 2836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vázquez, M.I.; De Lara, R.; Benavente, J. Transport and elastic parameters of regenerated cellulose membranes: Temperature effect. Desalination 2009, 245, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saedi, S.; Garcia, C.V.; Kim, J.T.; Shin, G.H. Physical and chemical modifications of cellulose fibers for food packaging applications. Cellulose 2021, 28, 8877–8897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, R.; Pandiaraj, S.; Muthusamy, S.; Panchal, H.; Alsoufi, M.S.; Ibrahim, A.M.M.; Elsheikh, A. Biodegradable magnesium metal matrix composites for biomedical implants: Synthesis, mechanical performance, and corrosion behavior—A review. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 20, 650–670. [Google Scholar]
- Ramos, J.D.; Milano, C.; Romero, V.; Escalera, S.; Alba, M.C.; Vázquez, M.I.; Benavente, J. Water effect on physical-chemical and elastic parameters for a dense cellulose regenerated membrane. Transport of different aqueous electrolyte solutions. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 352, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, K.O.; Maheswari, C.U.; Dhlamini, M.S.; Mothudi, B.M.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; Nagarajan, R.; Rajulu, A.V. Preparation and characterization of regenerated cellulose films using borassus fruit fibers and an ionic liquid. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 160, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuevas, A.L.; Martínez de Yuso, M.V.; Vega, V.; González, A.S.; Prida, V.M.; Benavente, J. Influence of ALD coating layers on optical properties of nanoporous alumina-based structures. Coatings 2019, 9, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelde, L.; Cuevas, A.L.; Benavente, J. Influence of Pore-Size/Porosity on Ion Transport and Static BSA Fouling for TiO2-Covered Nanoporous Alumina Membranes. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 5687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algarra, M.; Cuevas, A.L.; Valle Martínez de Yuso, M.V.; Romero, R.; Alonso, B.; Casado, C.M.; Benavente, J. Optical and Physicochemical Characterizations of a Cellulosic/CdSe-QDs@S-DAB5. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vera, R.; Gelde, L.; Anticó, E.; Martínez de Yuso, M.V.; Benavente, J.; Fontàs, C. Tuning physicochemical, electrochemical and transport characteristics of polymer inclusion membrane by varying the counter-anion of the ionic liquid Aliquat 336. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 529, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, A.S.; Vega, V.; Cuevas, A.L.; Martínez de Yuso, M.V.; Prida, V.M.; Benavente, J. Surface Modification of Nanoporous Anodic Alumina during Self-Catalytic Atomic Layer Deposition of Silicon Dioxide from (3-Aminopropyl)Triethoxysilane. Materials 2021, 14, 5052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, L.; Zhang, C.; Du, Y.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, Q.; Zhu, S. Improving Dielectric Constant of Polymers through Liquid Electrolyte Inclusion. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2007863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

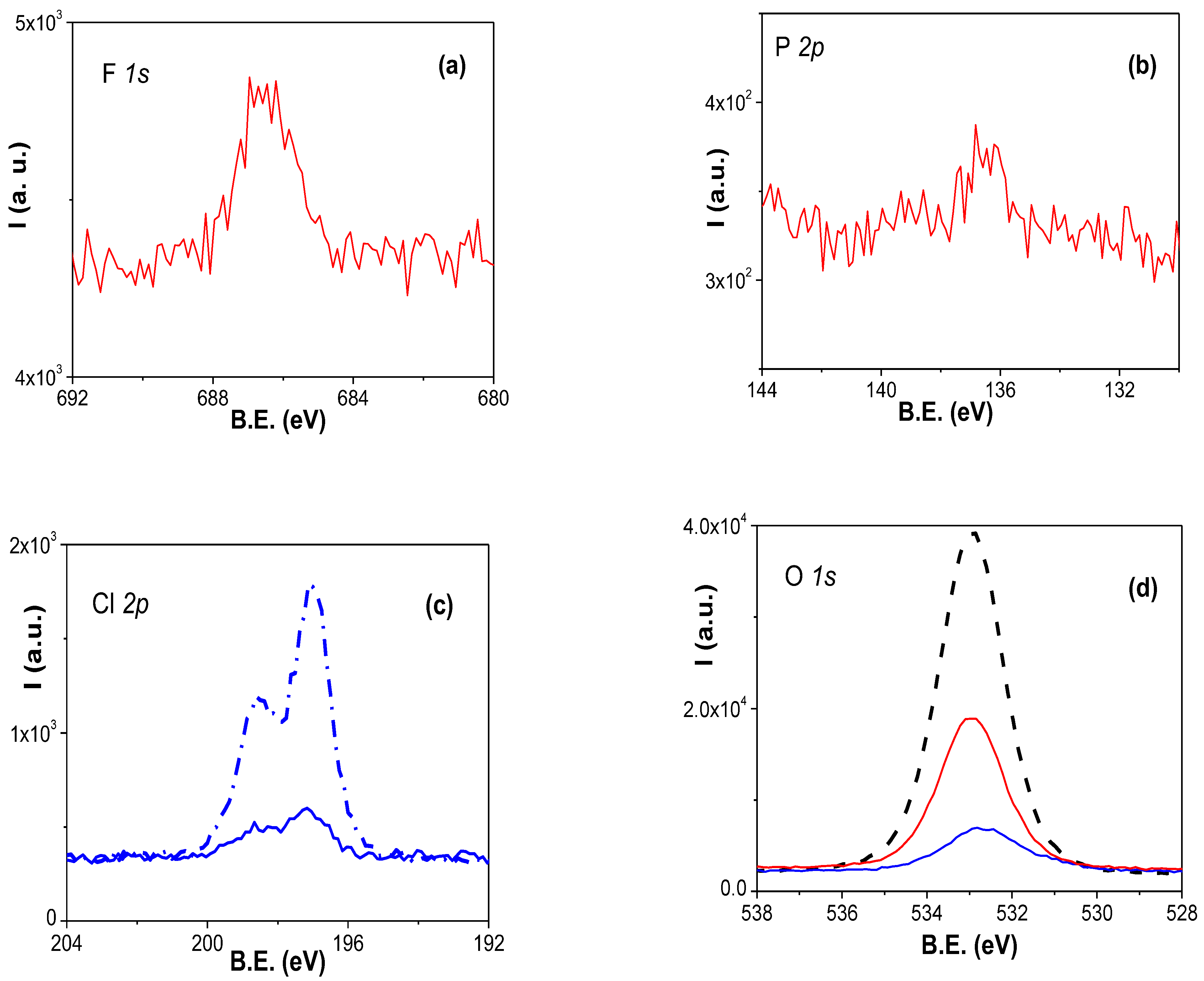

| RC/IL Film | C (%) | N (%) | F (%) | P (%) | Cl (%) | O (%) | Si (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RC/AliquatCl | 83.2 | 2.7 | --- | --- | 0.6 | 12.6 | 0.3 |
| RC/BMIMPF6 | 68.4 | 1.4 | 5.1 | 1.0 | --- | 21. 21.5 | 1.4 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yuso, M.d.V.M.d.; Cuevas, A.L.; Benavente, J. Physicochemical Characterization of a Cellulosic Film Modified with Two Room-Temperature Ionic Liquids. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 10290. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122010290
Yuso MdVMd, Cuevas AL, Benavente J. Physicochemical Characterization of a Cellulosic Film Modified with Two Room-Temperature Ionic Liquids. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(20):10290. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122010290
Chicago/Turabian StyleYuso, Maria del Valle Martinez de, Ana Laura Cuevas, and Juana Benavente. 2022. "Physicochemical Characterization of a Cellulosic Film Modified with Two Room-Temperature Ionic Liquids" Applied Sciences 12, no. 20: 10290. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122010290
APA StyleYuso, M. d. V. M. d., Cuevas, A. L., & Benavente, J. (2022). Physicochemical Characterization of a Cellulosic Film Modified with Two Room-Temperature Ionic Liquids. Applied Sciences, 12(20), 10290. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122010290







