Radio Signal Modulation Recognition Method Based on Deep Learning Model Pruning
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
3. Problem Definition
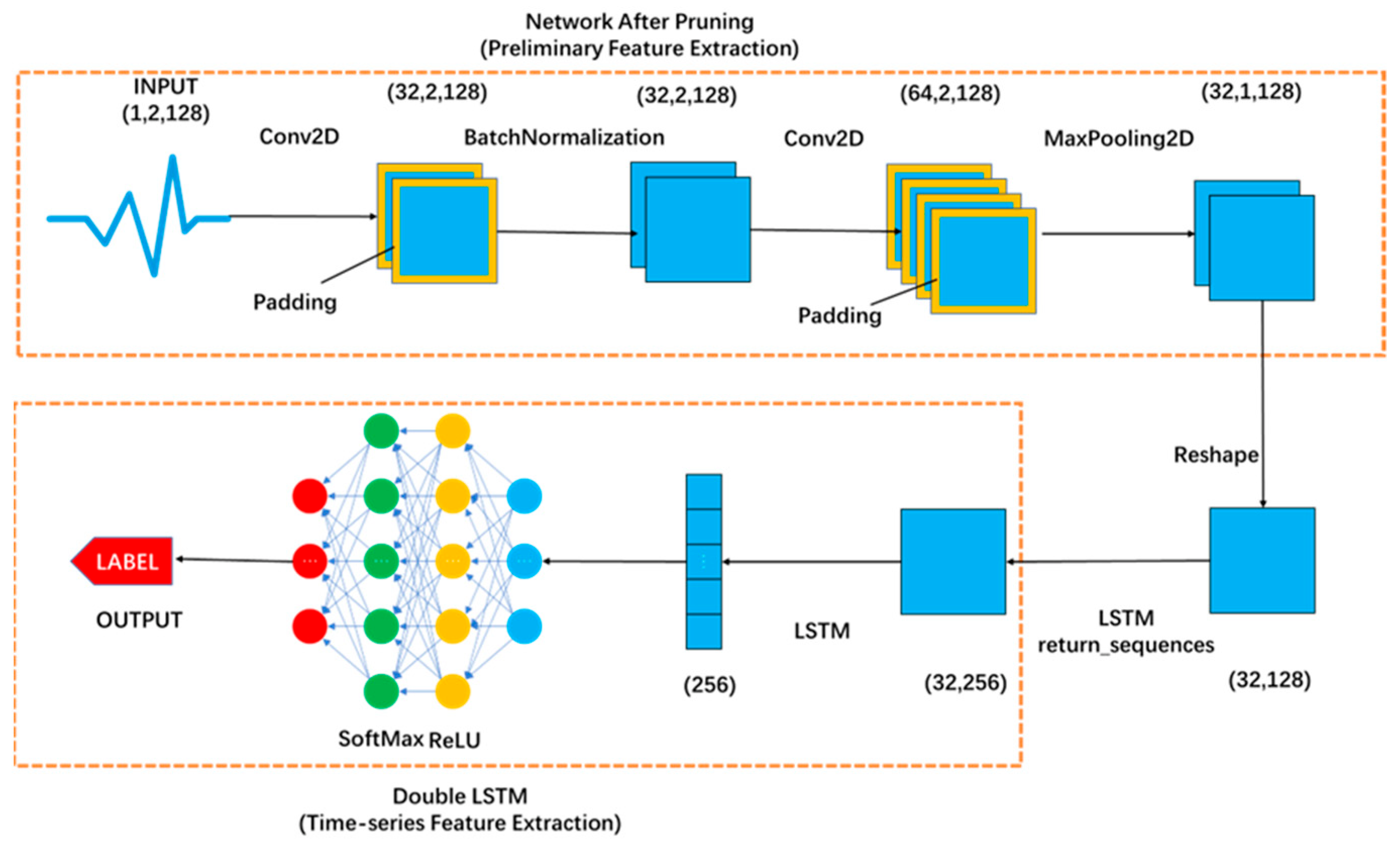
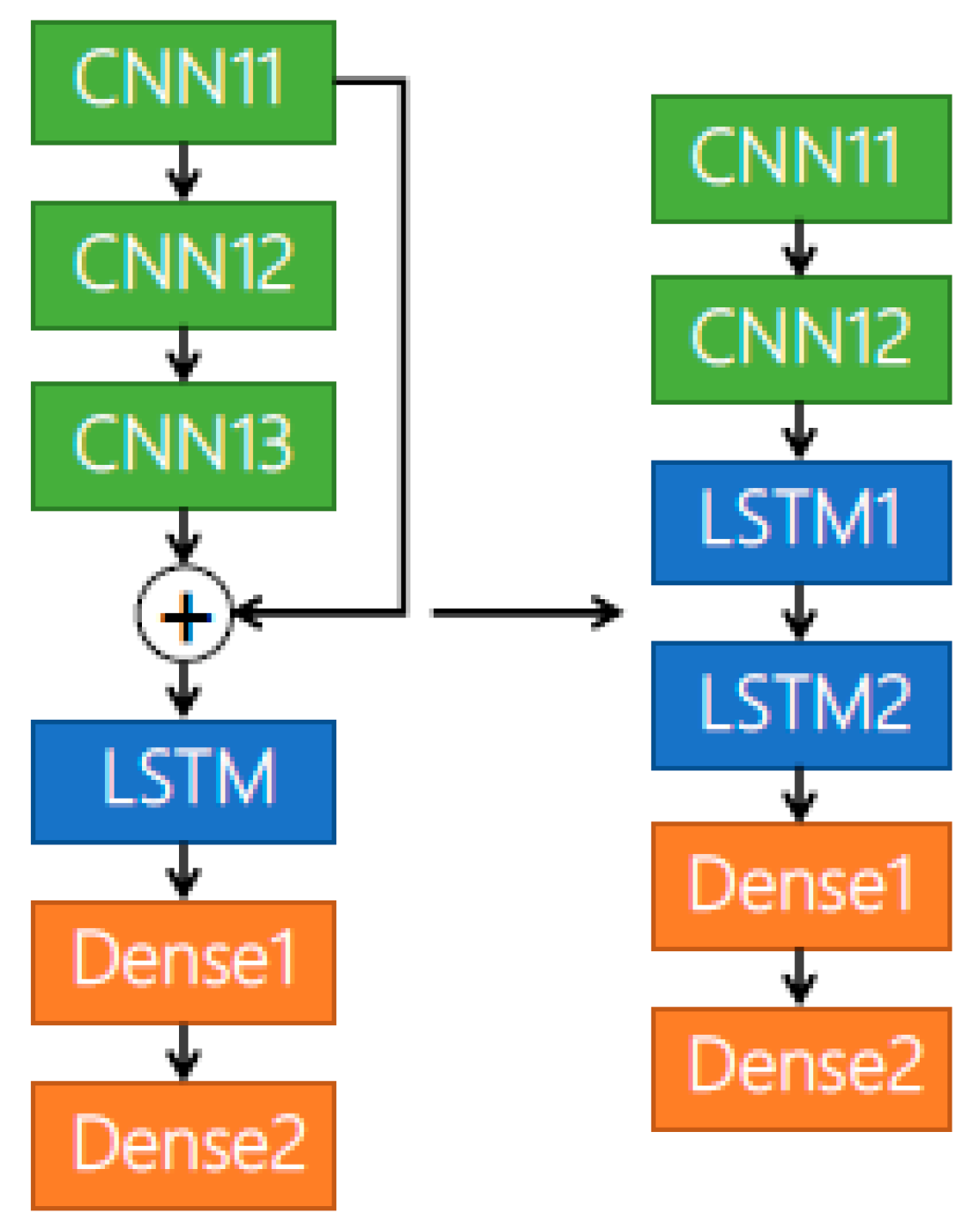
4. The Proposed Approach
5. Experimental Analysis
5.1. The Effect of CNN Kernel Size
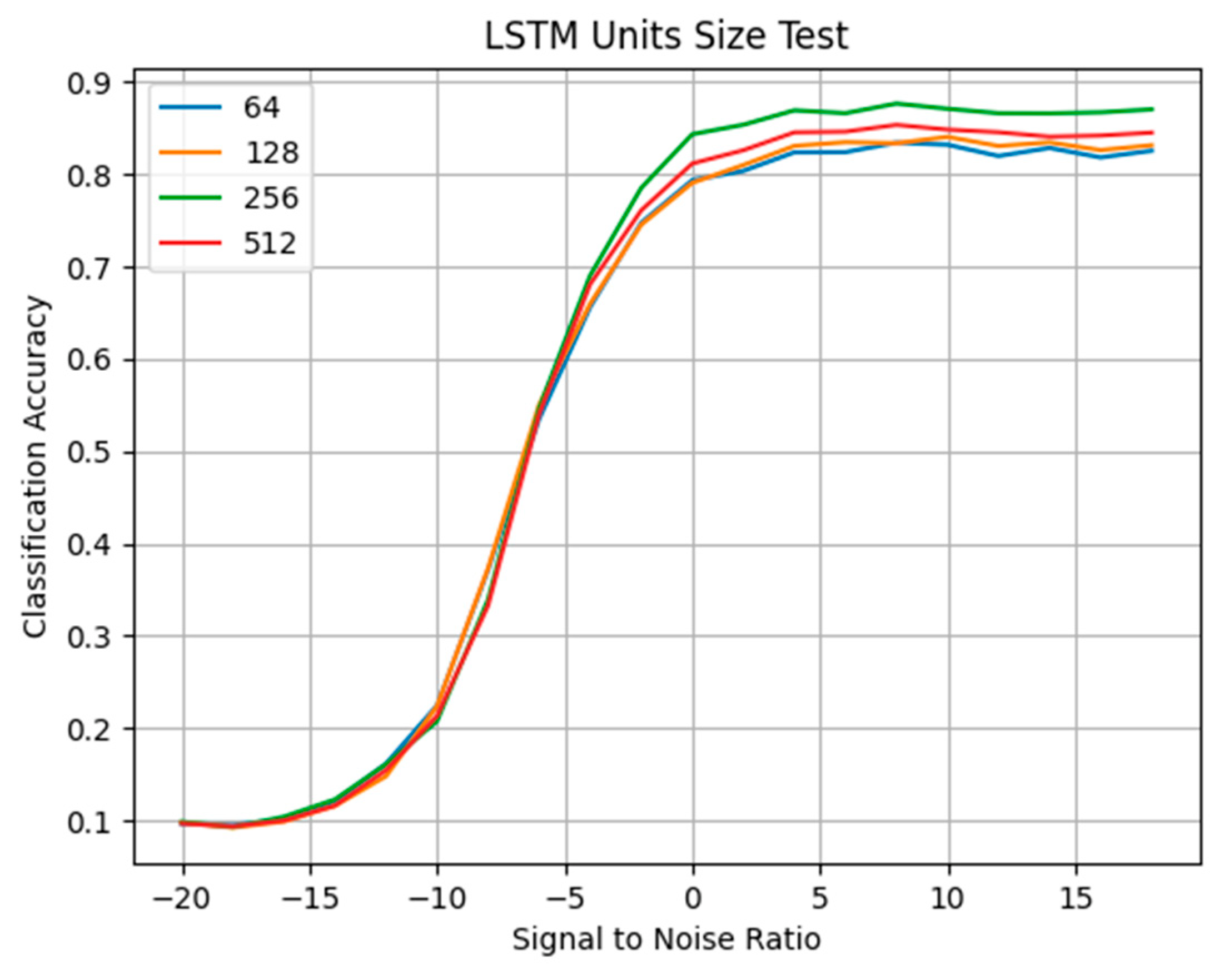
5.2. The Effect of LSTM Unit Size
5.3. The Effect of LSTM Layer Number
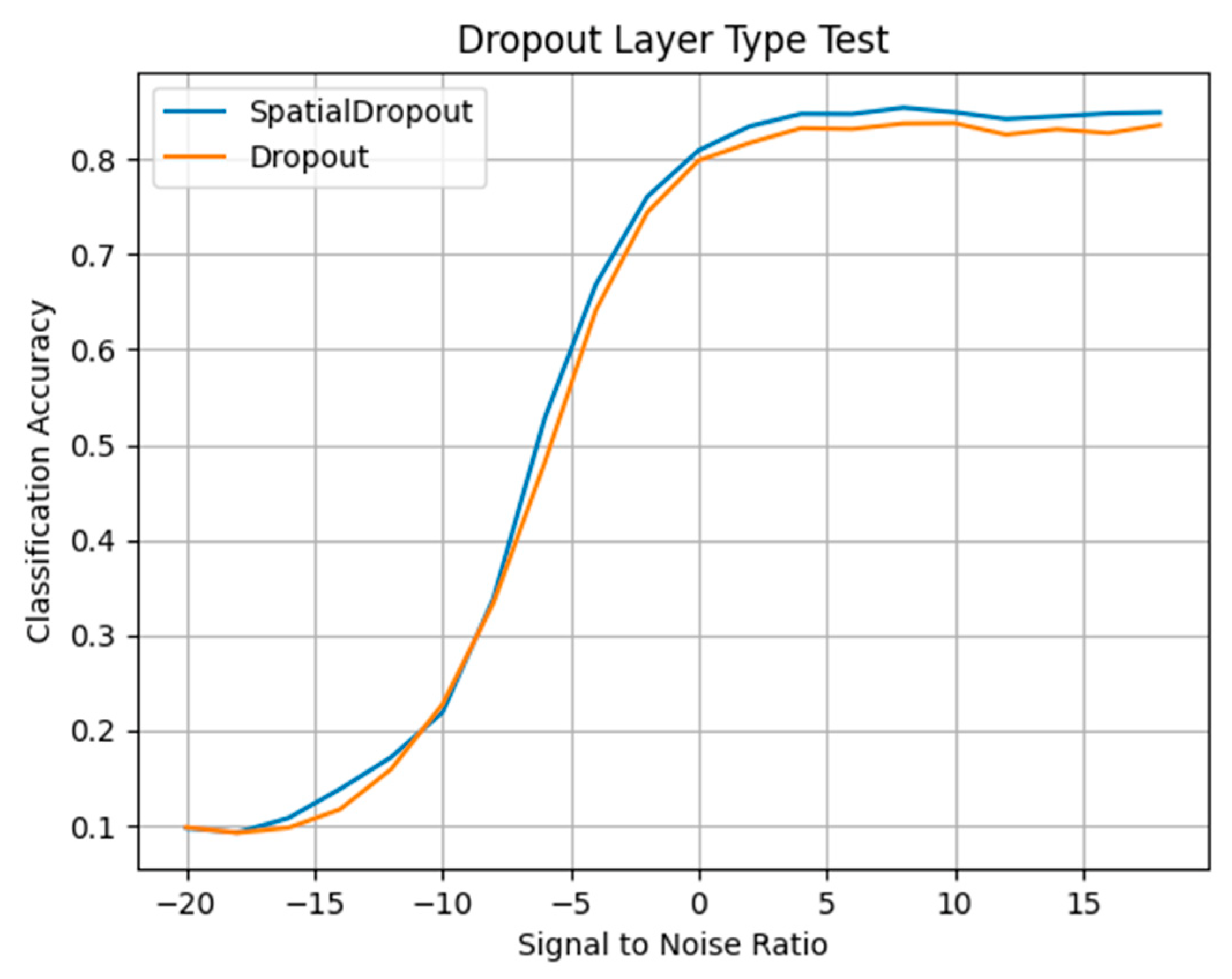
5.4. The Effect of Dropout Layer Type
5.5. The Effect of Batch Size
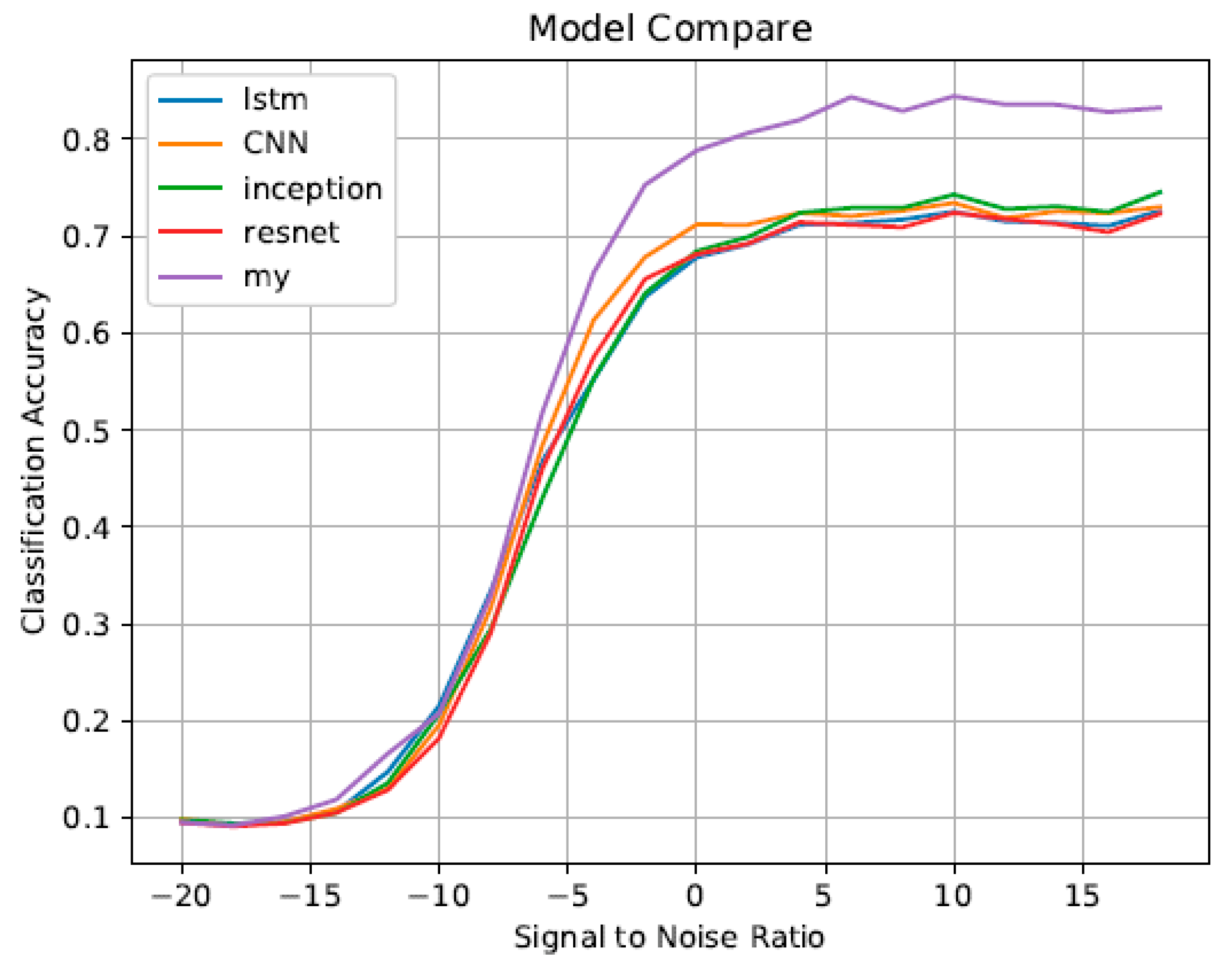
5.6. Comparison with Existing Models
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dobre, O.A.; Abdi, A.; Bar-Ness, Y.; Su, W. The classification of joint analog and digital modulations. In Proceedings of the MILCOM 2005—2005 IEEE Military Communications Conference, Atlantic City, NJ, USA, 17–20 October 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazza, A.; Shoaib, M.; Alshebeili, S.A.; Fahad, A. An overview of feature-based methods for digital modulation classification. In Proceedings of the 2013 1st International Conference on Communications, Signal Processing and their Applications (ICCSPA), Sharjah, United Arab Emirates, 12–14 February 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Shi, Y.Q.; Su, W. M-ary frequency shift keying signal classification based-on discrete Fourier transform. In Proceedings of the IEEE Military Communications Conference, Boston, MA, USA, 13–16 October 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sills, J.A. Maximum-likelihood modulation classification for PSK/QAM. In Proceedings of the MILCOM 1999 IEEE Military Communications Conference Proceedings, Atlantic City, MA, USA, 31 October—3 November 1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.C.; Kuo, C. Sequential modulation classification of dependent samples. In Proceedings of the 1996 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing Conference Proceedings, Atlanta, GA, USA, 9 May 1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhang, Y.; He, Z.; Nie, J.; Zhang, W. A novel attention cooperative framework for automatic modulation recognition. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 15673–15686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, J.; Liu, M.; Gui, G. LightAMC: Lightweight automatic modulation classification via deep learning and compressive sensing. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2020, 69, 3491–3495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, N.E.; O’Shea, T.J. Deep architectures for modulation recognition. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Symposium on Dynamic Spectrum Access Networks (DySPAN), Baltimore, MA, USA, 6–9 March 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Shea, T.J.; Corgan, J.; Clancy, T.C. Convolutional radio modulation recognition networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Engineering Applications of Neural Networks, Aberdeen, UK, 19 August 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh-The, T.; Hua, C.H.; Pham, Q.V.; Kim, D.S. MCNet: An efficient CNN architecture for robust automatic modulation classification. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2020, 24, 811–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Luo, H.; Wang, C.; Gan, C.; Xiang, Y. Automatic modulation classification using CNN-LSTM based dual-stream structure. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2020, 69, 13521–13531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yuan, L.; Wu, G.; Zhou, F.; Wu, Q. Automatic modulation classification using involution enabled residual networks. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2021, 10, 2417–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramjee, S.; Ju, S.; Yang, D.; Liu, X.; Gamal, A.E.; Eldar, Y.C. Fast deep learning for automatic modulation classification. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1901.05850. https://arxiv.org/abs/1901.05850. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, X.; Li, D.; Wang, Z.; Guo, Q.; Wei, X. A deep learning method based on convolutional neural network for automatic modulation classification of wireless signals. Wirel. Netw. 2019, 25, 3735–3746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, M.; Peng, C.; Wu, L.; Wang, X. Automatic modulation classification: A deep learning enabled approach. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2018, 67, 10760–10772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Ding, W.; Zhang, B.; Xie, C.; Li, H. Automatic modulation classification based on deep learning for unmanned aerial vehicles. Sensors 2018, 18, 924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L.; Gao, Z.; Zhu, Z. Blind Modulation Classification via Accelerated Deep Learning. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 5th International Conference on Computer and Communications (ICCC), Chengdu, China, 6–9 December 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, M.H.; Dang, X. Low-complexity deep learning and rbfn architectures for modulation classification of space-time block-code (stbc)-mimo systems. Digit. Signal Process. 2020, 99, 102656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Jiang, H.; Wang, H.; Alwageed, H.; Yao, Y.D. Modulation classification based on signal constellation diagrams and deep learning. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2018, 99, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Zhang, H.; Xu, J.; Chen, Z. Pattern Recognition of Wireless Modulation Signals Based on Deep Learning. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 6th International Symposium on Electromagnetic Compatibility (ISEMC), Nanjing, China, 1–4 November 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Lin, L.; Xie, J. Recognition of Signal Modulation Mode Based on Gaussian Filter and Deep Learning. In Proceedings of the 2018 3rd International Conference on Computer Science and Information Engineering (ICCSIE 2018), Xian, China, 21 September 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Lin, Q.; Yun, L. Research on modulation identification of digital signals based on deep learning. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Electronic Information and Communication Technology (ICEICT), Harbin, China, 20–22 August 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Tu, Y. A Pruning Neural Network for Automatic Modulation Classification. In Proceedings of the 2021 8th International Conference on Dependable Systems and Their Applications (DSA), Yinchuan, China, 5–6 August 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Kernel Size | Loss |
|---|---|
| 1 × 2 | 1.2986183166503906 |
| 1 × 3 | 1.2517382701237996 |
| 1 × 4 | 1.2592326800028484 |
| 1 × 5 | 1.1835391124089558 |
| 2 × 2 | 1.1842063665390015 |
| 2 × 3 | 1.1451027790705364 |
| 2 × 4 | 1.1322169701258342 |
| 2 × 5 | 1.1263486941655476 |
| 3 × 3 | 1.1229949394861858 |
| 4 × 4 | 1.1136138439178467 |
| Batch Size | Loss | Time Per Epoch (s) |
|---|---|---|
| 64 | 1.153881827990214 | 26 |
| 128 | 1.1463038523991902 | 17 |
| 256 | 1.119464596112569 | 13 |
| 512 | 1.1418431202570598 | 11 |
| 1024 | 1.1403136253356934 | 9 |
| 2048 | 1.1303218603134155 | 8 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hao, X.; Xia, Z.; Jiang, M.; Ye, Q.; Yang, G. Radio Signal Modulation Recognition Method Based on Deep Learning Model Pruning. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 9894. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12199894
Hao X, Xia Z, Jiang M, Ye Q, Yang G. Radio Signal Modulation Recognition Method Based on Deep Learning Model Pruning. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(19):9894. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12199894
Chicago/Turabian StyleHao, Xinyu, Zhang Xia, Mengxi Jiang, Qiubo Ye, and Guangsong Yang. 2022. "Radio Signal Modulation Recognition Method Based on Deep Learning Model Pruning" Applied Sciences 12, no. 19: 9894. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12199894
APA StyleHao, X., Xia, Z., Jiang, M., Ye, Q., & Yang, G. (2022). Radio Signal Modulation Recognition Method Based on Deep Learning Model Pruning. Applied Sciences, 12(19), 9894. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12199894









