Biomechanical Evaluation of a Novel Expandable Vertebral Augmentation System Using Human Cadaveric Vertebrae
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Specimen Preparation
2.2. Fracture Generation
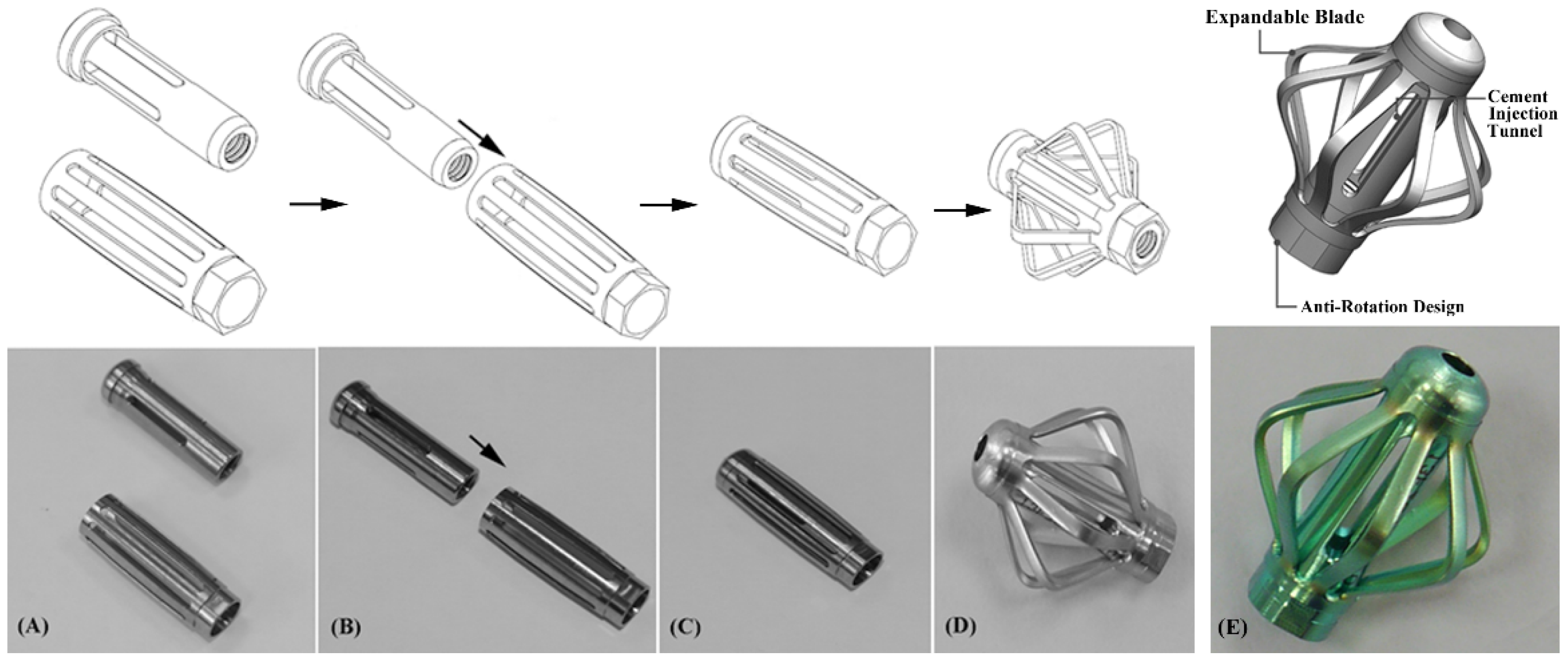
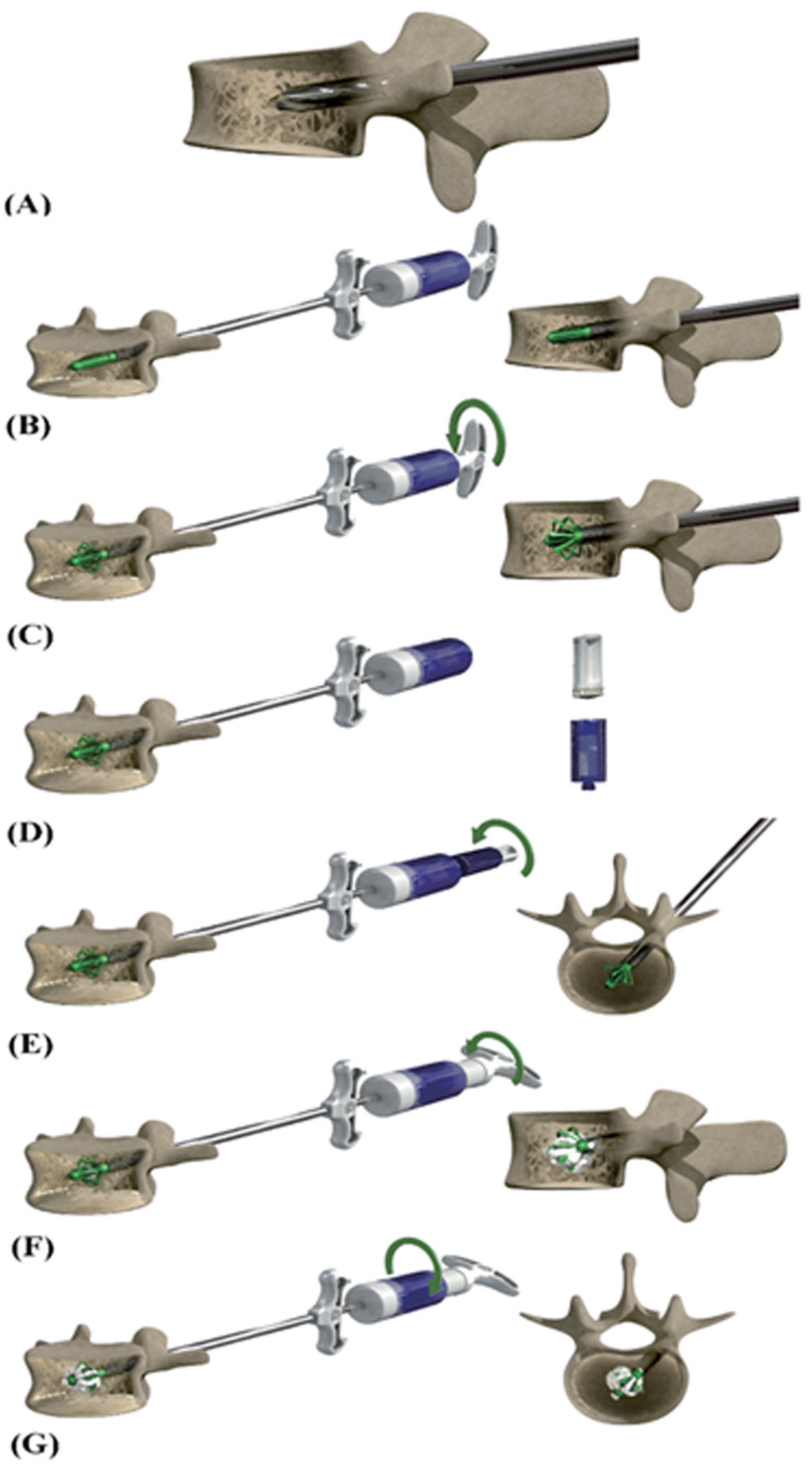
2.3. Implantation of EVA®
2.4. Implantation of OsseoFix®
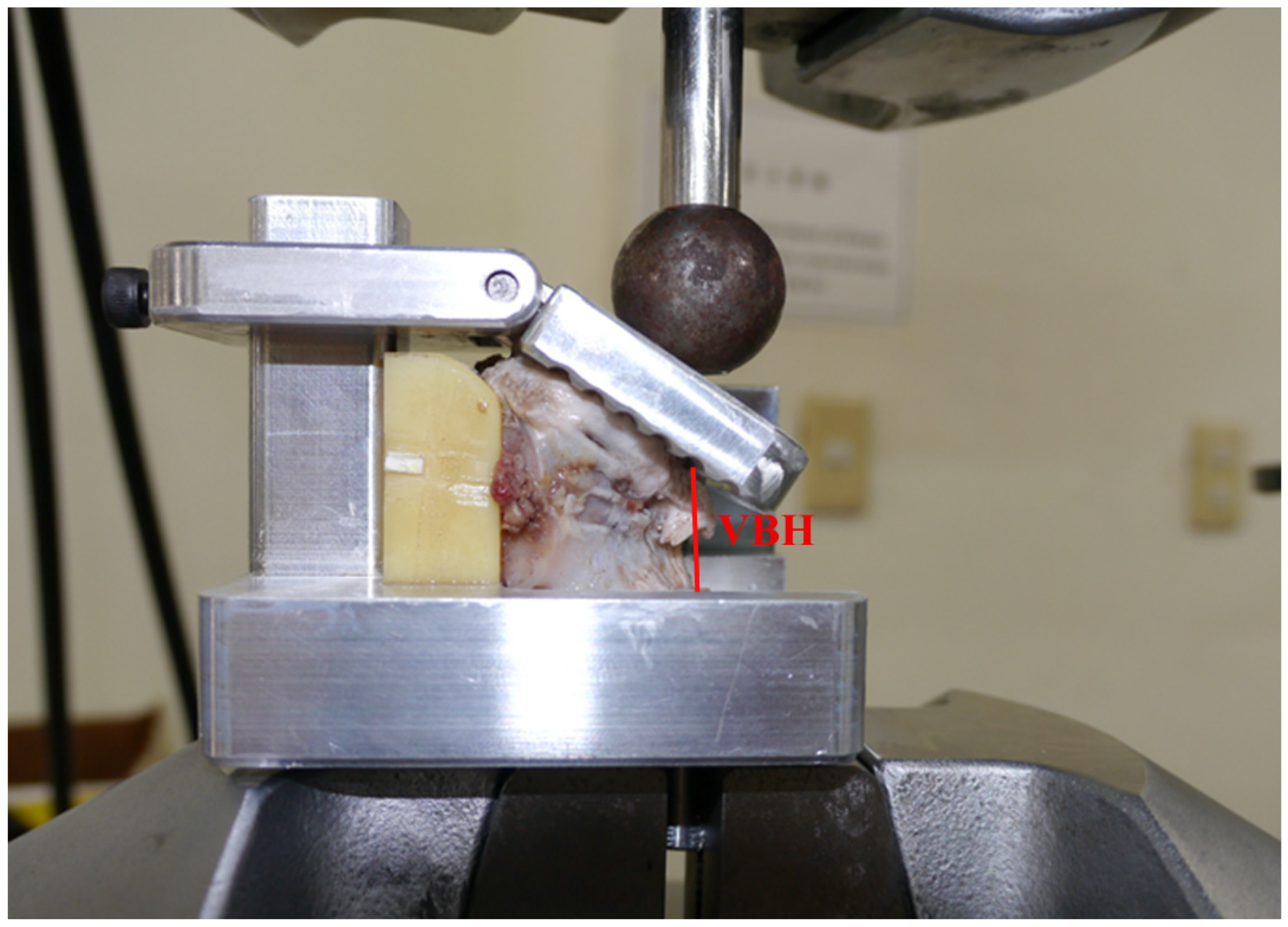
2.5. Biomechanical Testing
2.6. Statistical Analysis
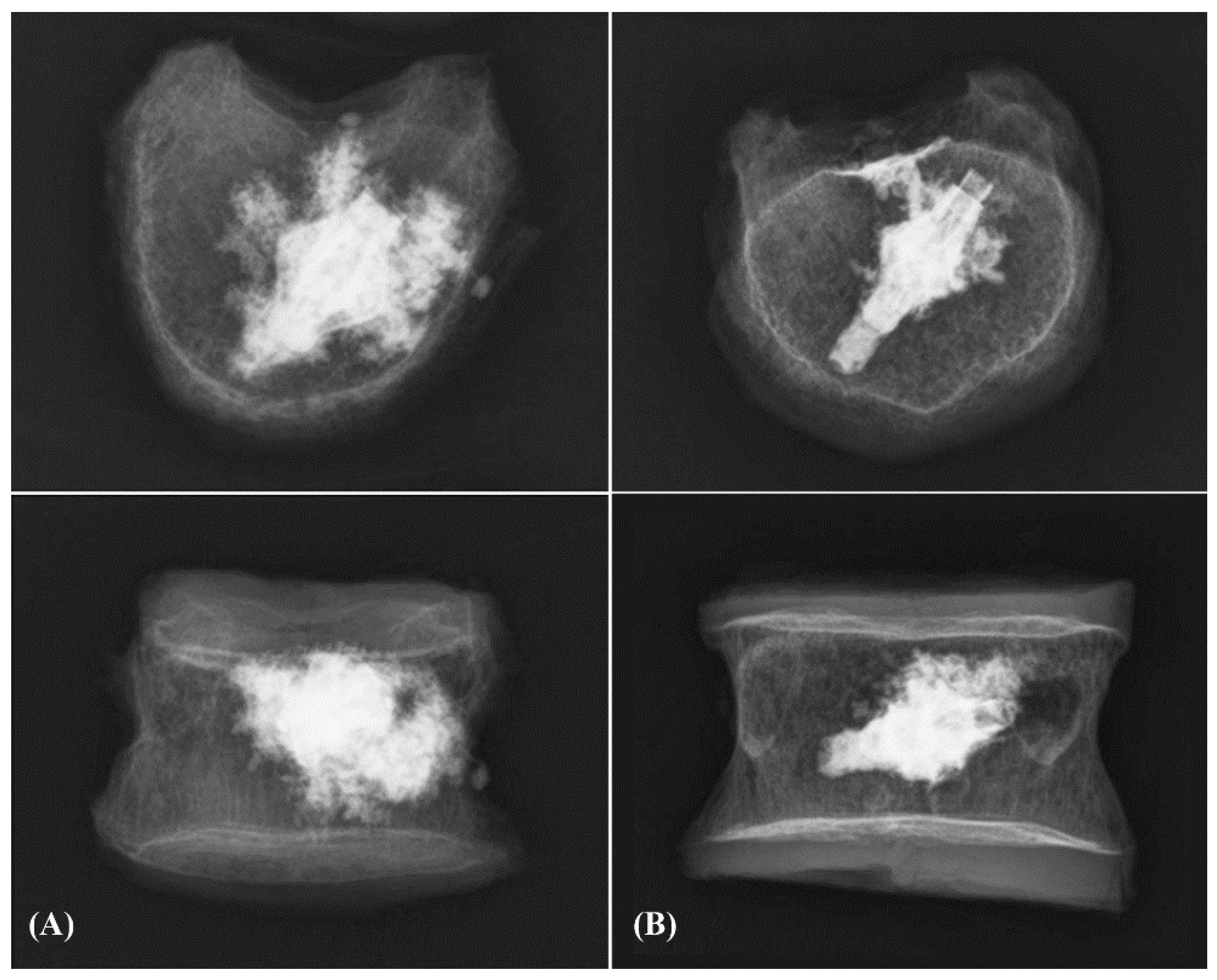
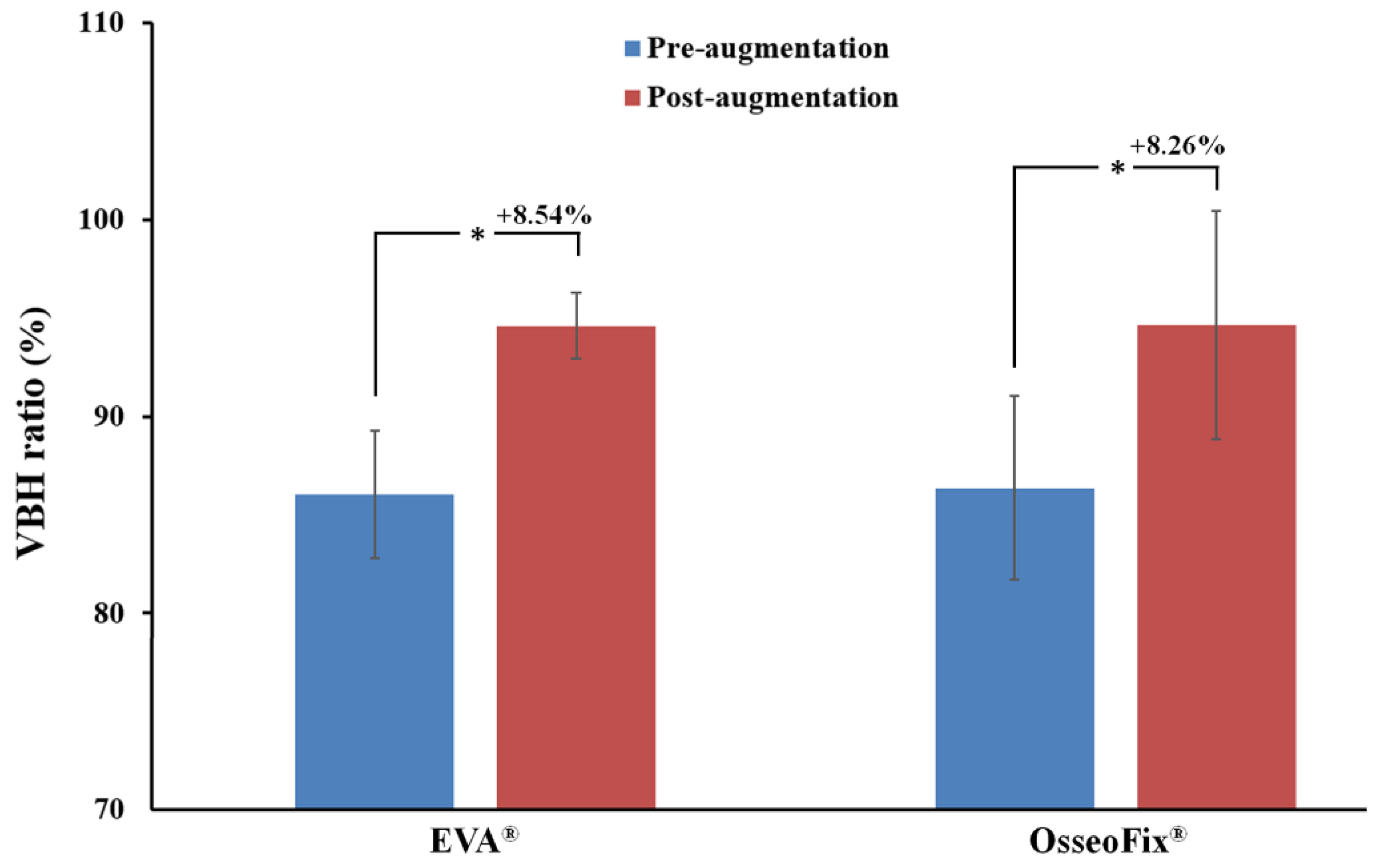
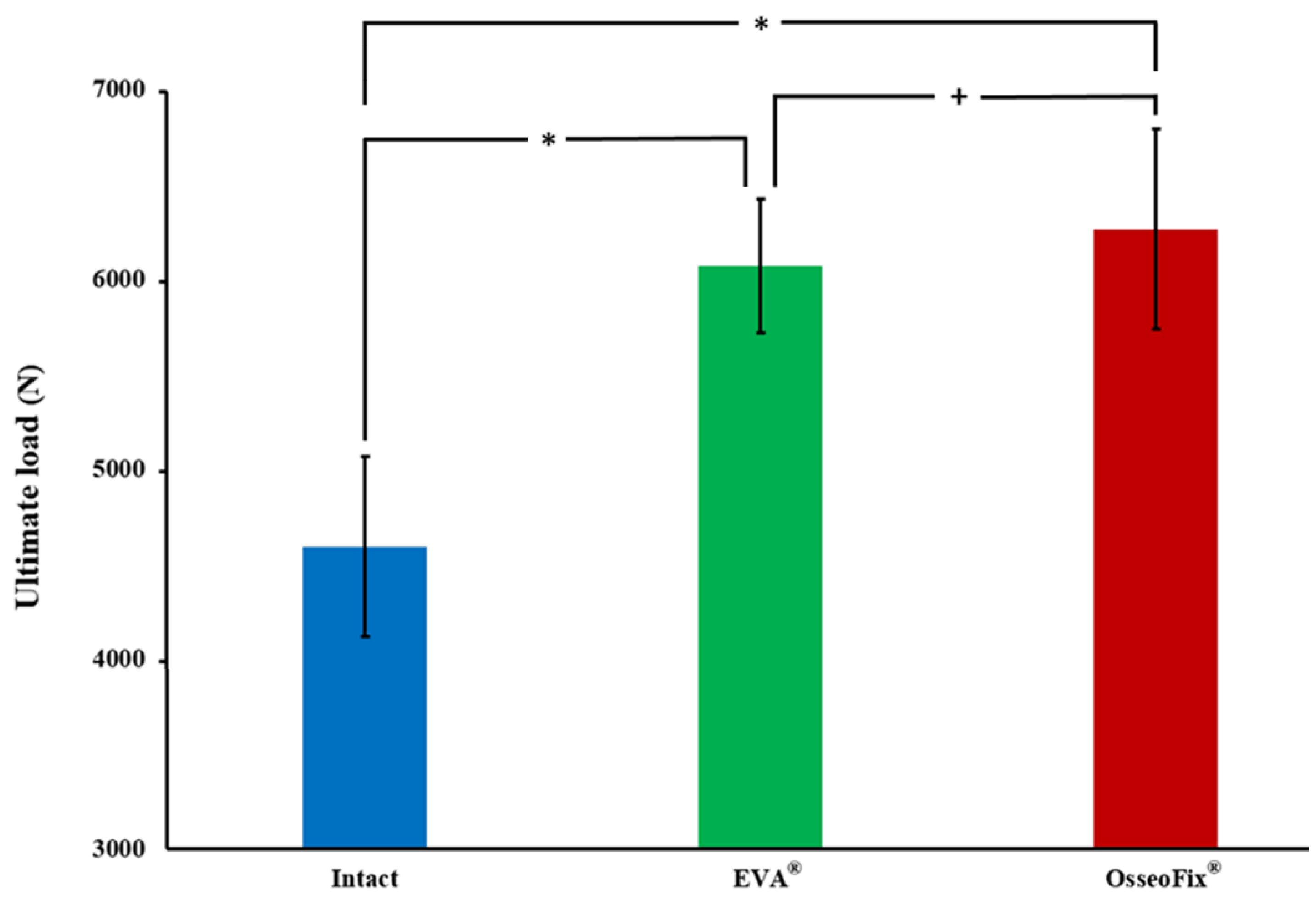
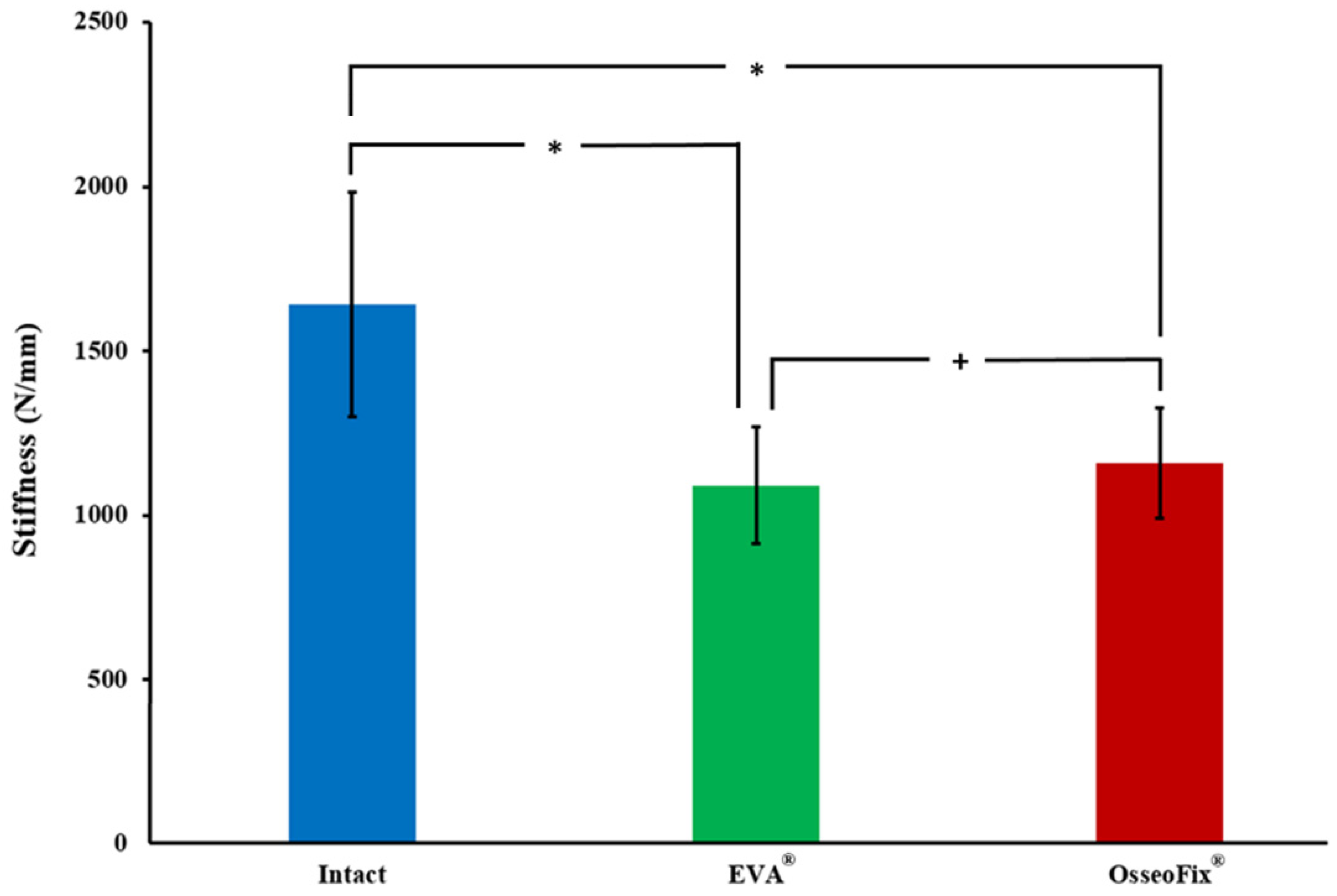
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Long, Y.; Yi, W.; Yang, D. Advances in Vertebral Augmentation Systems for Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures. Pain Res. Manag. 2020, 2020, 3947368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semaan, H.; Obri, T.; Bazerbashi, M.; Paull, D.; Liu, X.; Sarrouj, M.; Elgafy, H. Clinical outcome and subsequent sequelae of cement extravasation after percutaneous kyphoplasty and vertebroplasty: A comparative review. Acta Radiol. 2018, 59, 861–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldstein, C.L.; Chutkan, N.B.; Choma, T.J.; Orr, R.D. Management of the Elderly With Vertebral Compression Fractures. Neurosurgery 2015, 77, S33–S45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoyt, D.; Urits, I.; Orhurhu, V.; Orhurhu, M.S.; Callan, J.; Powell, J.; Manchikanti, L.; Kaye, A.D.; Kaye, R.J.; Viswanath, O. Current Concepts in the Management of Vertebral Compression Fractures. Curr. Pain Headache Rep. 2020, 24, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prost, S.; Pesenti, S.; Fuentes, S.; Tropiano, P.; Blondel, B. Treatment of osteoporotic vertebral fractures. Orthop. Traumatol. Surg. Res. 2020, 107, 102779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, R.; Maingard, J.; Asadi, H.; Slater, L.-A.; Mazwi, T.-L.; Marcia, S.; Barr, J.; Hirsch, J. Vertebroplasty and Kyphoplasty for Osteoporotic Vertebral Fractures: What Are the Latest Data? Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2018, 39, 798–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langner, S.; Henker, C. Vertebroplastie und Kyphoplastie. Der Radiol. 2020, 60, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boss, S.; Srivastava, V.; Anitescu, M. Vertebroplasty and Kyphoplasty. Phys. Med. Rehabilitation Clin. North Am. 2022, 33, 425–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, M.-K.; Kao, F.-C.; Chiu, P.-Y.; Chen, L.-H.; Yu, C.-W.; Niu, C.-C.; Lai, P.-L.; Tsai, T.-T. Risk factors of neurological deficit and pulmonary cement embolism after percutaneous vertebroplasty. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2019, 14, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Y.; Jiang, J.; Liao, H.; Tan, H.; Yang, K. Risk Factors for Cement Leakage After Vertebroplasty or Kyphoplasty: A Meta-Analysis of Published Evidence. World Neurosurg. 2017, 101, 633–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, I.-H.; Park, H.-Y.; Kim, K.-W.; Jang, T.-Y.; Lee, J.-S. Paraplegia due to intradural cement leakage after vertebroplasty: A case report and literature review. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2021, 22, 741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.C.; Tsai, S.H.L.; Goyal, A.; Fu, T.-S.; Lin, T.-Y.; Bydon, M. Comparison between vertebroplasty with high or low viscosity cement augmentation or kyphoplasty in cement leakage rate for patients with vertebral compression fracture: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Eur. Spine J. 2021, 30, 2680–2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arana-Guajardo, A.C.; Cavazos-Aranda, A.L. Embolismo pulmonar asintomático secundario a fuga de cemento tras vertebroplastia. Reumatol. Clínica 2021, 17, 302–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.-H.; Hsieh, M.-K.; Chen, W.-J.; Mk, H.; Lh, C.; Wj, C. Current concepts of percutaneous balloon kyphoplasty for the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: Evidence-based review. Biomed. J. 2013, 36, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippiadis, D.; Tutton, S.; Kelekis, A. Pain management: The rising role of interventional oncology. Diagn. Interv. Imaging 2017, 98, 627–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomas, C.; Jensen, A.; Ahmed, F.; Ho, C.K.; Jesse, M.K. Minding the Gap in Vertebroplasty: Vertebral Body Fracture Clefts and Cement Nonunion. Pain Physician 2021, 24, E221–E230. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kuo, Y.-R.; Cheng, T.-A.; Chou, P.-H.; Liu, Y.-F.; Chang, C.-J.; Chuang, C.-F.; Su, P.-F.; Lin, R.-M.; Lin, C.-L. Healing of Vertebral Compression Fractures in the Elderly after Percutaneous Vertebroplasty—An Analysis of New Bone Formation and Sagittal Alignment in a 3-Year Follow-Up. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, T.M.; Urban, R.M.; Singh, K.; Hall, D.J.; Renner, S.M.; Lim, T.-H.; Tomlinson, M.J.; An, H.S. Vertebroplasty comparing injectable calcium phosphate cement compared with polymethylmethacrylate in a unique canine vertebral body large defect model. Spine J. 2008, 8, 482–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wichlas, F.; Trzenschik, H.; Tsitsilonis, S.; Rohlmann, A.; Bail, H.-J. Biomechanical behavior of MRI-signal-inducing bone cements after vertebroplasty in osteoporotic vertebral bodies: An experimental cadaver study. Clin. Biomech. 2014, 29, 571–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ender, S.A.; Gradl, G.; Ender, M.; Langner, S.; Merk, H.R.; Kayser, R. Osseofix® System for Percutaneous Stabilization of Osteoporotic and Tumorous Vertebral Compression Fractures—Clinical and Radiological Results After 12 Months. In RöFo-Fortschritte auf dem Gebiet der Röntgenstrahlen und der bildgebenden Verfahren; © Georg Thieme Verlag KG: New York, NY, USA, 2013; Volume 186, pp. 380–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanni, D.; Galzio, R.; Kazakova, A.; Pantalone, A.; Grillea, G.; Bartolo, M.; Salini, V.; Magliani, V. Third-generation percutaneous vertebral augmentation systems. J. Spine Surg. 2016, 2, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, D.C.; Connolly, R.J.; Zhu, Q.; Emery, J.L.; Kingwell, S.P.; Kitchel, S.; Cripton, P.A.; Wilson, D.R. An ex vivo biomechanical comparison of a novel vertebral compression fracture treatment system to kyphoplasty. Clin. Biomech. 2012, 27, 346–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haddad, R.; Peltz, T.; Bertollo, N.; Walsh, W.R.; Nicklin, S. Looped suture properties: Implications for multistranded flexor tendon repair. J. Hand Surg. (Eur. Vol.) 2015, 40, 234–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krüger, A.; Oberkircher, L.; Figiel, J.; Floßdorf, F.; Bolzinger, F.; Noriega, D.C.; Ruchholtz, S. Height restoration of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures using different intravertebral reduction devices: A cadaveric study. Spine J. 2015, 15, 1092–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.; Mahar, A.; Perry, A.; Massie, J.; Lu, L.; Currier, B.; Yaszemski, M.J. Biomechanical Evaluation of an Injectable Radiopaque Polypropylene Fumarate Cement for Kyphoplasty in a Cadaveric Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fracture Model. J. Spinal Disord. Tech. 2007, 20, 604–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trost, M.; Schmoelz, W.; Wimmer, D.; Hörmann, R.; Frey, S.; Schulte, T.L. Local osteo-enhancement of osteoporotic vertebra with a triphasic bone implant material increases strength—A biomechanical study. Arch. Orthop. Trauma. Surg. 2020, 140, 1395–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ender, S.A.; Eschler, A.; Ender, M.; Merk, H.R.; Kayser, R. Fracture care using percutaneously applied titanium mesh cages (OsseoFix®) for unstable osteoporotic thoracolumbar burst fractures is able to reduce cement-associated complications—Results after 12 months. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2015, 10, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eschler, A.; Ender, S.A.; Ulmar, B.; Herlyn, P.; Mittlmeier, T.; Gradl, G. Cementless Fixation of Osteoporotic VCFs Using Titanium Mesh Implants (OsseoFix): Preliminary Results. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 853897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filippiadis, D.K.; Marcia, S.; Masala, S.; Deschamps, F.; Kelekis, A. Percutaneous Vertebroplasty and Kyphoplasty: Current Status, New Developments and Old Controversies. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2017, 40, 1815–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moura, D.L.; Gabriel, J.P. Expandable Intravertebral Implants: A Narrative Review on the Concept, Biomechanics, and Outcomes in Traumatology. Cureus 2021, 13, e17795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rotter, R.; Martin, H.; Fuerderer, S.; Gabl, M.; Roeder, C.; Heini, P.; Mittlmeier, T. Vertebral body stenting: A new method for vertebral augmentation versus kyphoplasty. Eur. Spine J. 2010, 19, 916–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Premat, K.; Perre, S.V.; Cormier, É.; Shotar, E.; Degos, V.; Morardet, L.; Fargeot, C.; Clarençon, F.; Chiras, J. Vertebral augmentation with the SpineJack® in chronic vertebral compression fractures with major kyphosis. Eur. Radiol. 2018, 28, 4985–4991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerschbaumer, G.; Gaulin, B.; Ruatti, S.; Tonetti, J.; Boudissa, M. Clinical and radiological outcomes in thoracolumbar fractures using the SpineJack device. A prospective study of seventy-four patients with a two point three year mean of follow-up. Int. Orthop. 2019, 43, 2773–2779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lofrese, G.; Ricciardi, L.; De Bonis, P.; Cultrera, F.; Cappuccio, M.; Scerrati, A.; Martucci, A.; Musio, A.; Tosatto, L.; De Iure, F. Use of the SpineJack direct reduction for treating type A2, A3 and A4 fractures of the thoracolumbar spine: A retrospective case series. J. NeuroInterventional Surg. 2022, 14, 931–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Zheng, Y.-H.; Zheng, T.; Sun, C.-H.; Lu, J.; Cao, P.; Zhou, J.-H. The implantation of a Nickel-Titanium shape memory alloy ameliorates vertebral body compression fractures: A cadaveric study. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 8, 16899–16906. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Seel, E.H.; Davies, E.M. A biomechanical comparison of kyphoplasty using a balloon bone tamp versus an expandable polymer bone tamp in a deer spine model. J. Bone Jt. Surgery. Br. Vol. 2007, 89, 253–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcia, S.; Piras, E.; Hirsch, J.A.; Mereu, A.; Marras, M.; Spinelli, A.; Saba, L. Efficacy of a Novel Vertebral Body Augmentation System in the Treatment of Patients with Symptomatic Vertebral Body Fractures. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2021, 44, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ender, S.A.; Wetterau, E.; Ender, M.; Kühn, J.-P.; Merk, H.R.; Kayser, R. Percutaneous Stabilization System Osseofix® for Treatment of Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures—Clinical and Radiological Results after 12 Months. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e65119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.-H.; Kuh, S.; Chin, D.K.; Jin, B.-H.; Kim, K.S.; Yoon, Y.-S.; Cho, Y.-E. Kyphoplasty Versus Vertebroplasty: Restoration of vertebral body height and correction of kyphotic deformity with special attention to the shape of the fractured vertebrae. J. Spinal Disord. Tech. 2012, 25, 338–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pumberger, M.; Schitz, F.; Bürger, J.; Schömig, F.; Putzier, M.; Palmowski, Y. Kyphoplasty Restores the Global Sagittal Balance of the Spine Independently from Pain Reduction. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 8894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, A.J.; Fink, H.A.; Mirigian, L.; Guañabens, N.; Eastell, R.; Akesson, K.; Bauer, U.C.; Ebeling, P.R. Pain, Quality of Life, and Safety Outcomes of Kyphoplasty for Vertebral Compression Fractures: Report of a Task Force of the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2017, 32, 1935–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T. Does Percutaneous Vertebroplasty or Balloon Kyphoplasty for Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures Increase the Incidence of New Vertebral Fractures? A Meta-Analysis. Pain Physician 2017, 20, E13–E28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, G.; Li, A.; Liu, B.; Lv, D.; Zhang, J.; Sheng, W.; Yang, G.; Gao, Y. A meta-analysis of the secondary fractures for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures after percutaneous vertebroplasty. Medicine 2021, 100, e25396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Movrin, I.; Vengust, R.; Komadina, R. Adjacent vertebral fractures after percutaneous vertebral augmentation of osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture: A comparison of balloon kyphoplasty and vertebroplasty. Arch. Orthop. Trauma. Surg. 2010, 130, 1157–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, L.; Sun, H.; Wang, H.; Cai, J.; Tao, Y.; Feng, X.; Wang, Y. Cement injection and postoperative vertebral fractures during vertebroplasty. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2019, 14, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, Y.-C.; Guo, W.; Xu, F.; Zhang, C.-C.; Liang, Z.-P.; Wu, L.; Chen, S.; Zeng, X.-W. Refracture of the cemented vertebrae after percutaneous vertebroplasty: Risk factors and imaging findings. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2021, 22, 459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.J.; Lindsey, D.P.; Hannibal, M.; Alamin, T.F. Vertebroplasty Versus Kyphoplasty: Biomechanical Behavior Under Repetitive Loading Conditions. Spine 2006, 31, 2079–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCann, H.; Lepine, M.; Glaser, J. Biomechanical Comparison of Augmentation Techniques for Insufficiency Fractures. Spine 2006, 31, E499–E502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cianfoni, A.; Distefano, D.; Pravatà, E.; Espeli, V.; Pesce, G.; Mordasini, P.; La Barbera, L.; Scarone, P.; Bonaldi, G. Vertebral body stent augmentation to reconstruct the anterior column in neoplastic extreme osteolysis. J. NeuroInterventional Surg. 2019, 11, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noriega, D.C.; Ramajo, R.H.; Lite, I.S.; Toribio, B.; Corredera, R.; Ardura, F.; Krüger, A. Safety and clinical performance of kyphoplasty and SpineJack® procedures in the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: A pilot, monocentric, investigator-initiated study. Osteoporos. Int. 2016, 276, 2047–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hsieh, M.-K.; Chen, W.-J.; Lee, M.S.; Lin, S.-Y.; Liu, M.-Y.; Lee, D.-M.; Tai, C.-L. Biomechanical Evaluation of a Novel Expandable Vertebral Augmentation System Using Human Cadaveric Vertebrae. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 10165. https://doi.org/10.3390/app121910165
Hsieh M-K, Chen W-J, Lee MS, Lin S-Y, Liu M-Y, Lee D-M, Tai C-L. Biomechanical Evaluation of a Novel Expandable Vertebral Augmentation System Using Human Cadaveric Vertebrae. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(19):10165. https://doi.org/10.3390/app121910165
Chicago/Turabian StyleHsieh, Ming-Kai, Wen-Jer Chen, Mel S. Lee, Sheng-Yu Lin, Mu-Yi Liu, De-Mei Lee, and Ching-Lung Tai. 2022. "Biomechanical Evaluation of a Novel Expandable Vertebral Augmentation System Using Human Cadaveric Vertebrae" Applied Sciences 12, no. 19: 10165. https://doi.org/10.3390/app121910165
APA StyleHsieh, M.-K., Chen, W.-J., Lee, M. S., Lin, S.-Y., Liu, M.-Y., Lee, D.-M., & Tai, C.-L. (2022). Biomechanical Evaluation of a Novel Expandable Vertebral Augmentation System Using Human Cadaveric Vertebrae. Applied Sciences, 12(19), 10165. https://doi.org/10.3390/app121910165





