Abstract
Metal contamination, especially in river floodplain soils, can have detrimental effects on human health. Much research has been conducted to describe the distribution patterns of metals and the factors involved in these patterns. However, most studies focus on the distribution of individual metals in soils, not on the co-occurrence of metals, and on a selection of metals associated with anthropogenic sources known to have especially severe effects; this had led to a lack of knowledge about many other metals with potentially harmful effects. Therefore, this study aimed to identify the multi-metal distribution patterns of 38 metals in the Sacramento River floodplain and find their controlling factors. We found 484 significant correlations between metal distributions. Less commonly studied metals, such as gallium, lanthanum, scandium, and vanadium, had more than 25 correlations each. In total, 13 individual metal patterns described the spatial distribution of 22 metals. Three multi-metal patterns were extracted, explaining 86.9% of the spatial variation of the individual patterns. The most important factors were the distance to specific streams due to emission and transport processes in their watersheds, and local soil properties. We conclude that multi-metal distribution patterns hold more information than individual metal patterns, contributing to the gathering of information about less commonly sampled metals and allowing more specific source identification.
1. Introduction
Floodplains are intermediary areas between a river and the surrounding landscape. They are formed and dominated by fluvial processes and have been the preferred setting for human settlement and development since ancient times. Floodplains can also function as sinks for materials transported into and through them by different processes. In particular, soils in the floodplains can store matter, such as carbon, salts, or metals [1,2]. Since many floodplains are used for food production [3,4], metal contamination of soils can be detrimental to human health [5,6]. Studies on metals such as cadmium (Cd), chromium (Cr), nickel (Ni), lead (Pb) and zinc (Zn) have shown that they affect soil biota and can accumulate in plants growing in the soils, potentially entering the human food chain [7,8,9]. Once metals enter the soil, they may migrate along the soil column and into the groundwater, thus affecting the environment [10,11]. Furthermore, soils in floodplains that have functioned as sinks for long periods can become sources of metals when conditions (such as pH) or processes (such as erosion and deposition) change [12,13,14]. Under these changed conditions, significant amounts of metals may be released back into the streams and cause adverse effects to aquatic and connected terrestrial ecosystems [15]. Therefore, understanding the distribution of metals in floodplain soils and their controlling factors is essential.
Metals in floodplain soils are not distributed homogeneously, but rather show spatial patterns in their distribution [16,17]. These spatial patterns result from transport, deposition, and accumulation processes that depend on environmental factors [18,19]. Factors that affect metal concentrations in soils are geology, land cover, hydrology, terrain, and emission sources [20,21,22]. As these factors are not homogeneously distributed along a floodplain but vary with location, so do their effects on metal accumulation in floodplain soils [23,24,25,26]. Knowledge of these patterns can be used to identify areas for specific use cases, remediation measures, or scientific studies on the effects of metal concentrations.
Much research has been undertaken to find and describe the patterns of metal accumulation and the factors that cause them. For example, bank morphology affected heavy metal accumulation in soils along rivers [27]. The spatial distribution patterns of metals in floodplain soils were found to depend on flooding and sedimentation frequency [28]. This accumulation in the floodplain soils was controlled by the emission from the parent material of soil formation [29,30] and affected by human activity and land cover patterns [31,32]. While these studies researched metal patterns and the processes that lead to them, they focused on the distribution patterns of individual metals in soils, not or only seldom on the co-occurrence of different metals in soils, i.e., multi-metal distribution patterns. Depending on the processes that lead to these metals’ release, transport, and accumulation, the spatial distribution of several metals may show similar patterns. Finding these similarities between different metals and linking them with the underlying processes may allow for several improvements, such as inferring information about less commonly sampled metals from more commonly sampled metals or from existing datasets, or increasing the efficiency of combined soil quality improvement measures. Additionally, identifying the specific combination of metals in certain locations may improve the association of the metals with their most probable sources, as different combinations of metals may point to different emission and transport pathways.
Furthermore, most of the existing studies focus on a relatively small selection of metals; these are commonly a subset of Cd, copper (Cu), iron (Fe), Pb, magnesium (Mg), manganese (Mn), Ni, or Zn. This is due to the abundance of these metals, the role of anthropogenic factors in their release into the environment, and their known potential toxicity to ecosystems and humans. Nevertheless, many more metals come from different sources that can accumulate in soils, have toxic effects, or are suspected of having toxic effects, such as barium (Ba), gallium (Ga), lanthanum (La), scandium (Sc) or vanadium (V) [33,34,35]. These metals often receive less attention, or have only recently become a research topic as climate and industrial processes change and environmental awareness develops [36,37,38].
Therefore, this study focuses on the multi-metal distribution patterns of a large number of different metals in the soils of the Sacramento River floodplain in California, USA, to identify individual metal patterns to represent groups of metals, multi-metal distribution patterns, and the controlling features that explain the spatial variability of these patterns. This study site is especially suitable for this research since it has a very high density of existing data sets from soil samples and a wide range of measured soil metal concentrations [39,40]. This richness of data makes this floodplain well suited for a fundamental investigation of multi-metal distribution patterns. In the first step, groupings of individual metal distribution patterns were identified. Then, a principal component analysis was conducted to reduce the complexity of the metal concentration data and identify multi-metal distribution patterns. Finally, the environmental factors best describing the spatial variance of these patterns were identified using variable importance in spatial Random Forest models. In selecting the factors, the focus was on those assumed to be stable over long periods, such as soil, vegetation, and terrain.
2. Materials and Methods
The research area is located in the northern part of the Central Valley in California, USA. This part of the Central Valley, also called the Sacramento Valley, is dominated by the Sacramento River (Figure 1). In addition, several smaller streams that have their catchments in the surrounding mountain ranges discharge into the Sacramento River. The largest part of the study area in the Sacramento Valley is covered by agricultural land, with several larger cities in the floodplain, such as Sacramento, east of the Sacramento River.
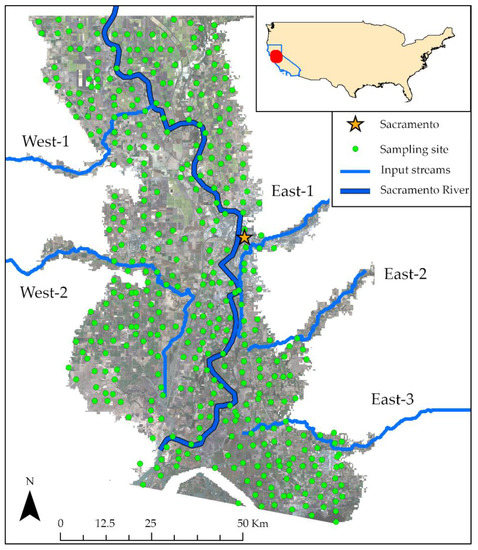
Figure 1.
Overview of the research area in the Sacramento River floodplain in California, USA. Indicated are the soil sample sites, traffic routes, and rivers.
Multiple datasets were combined to form the basis for the analysis. First, the soil chemical concentration data were obtained from the National Geochemical Database (NGDB) soil database [41]. All samples were taken from the topsoil (0–25 cm depth) at various locations. From the available samples, only those located in the floodplain defined by the GFPLAIN250m dataset [42] were selected for this study. The mean distance between the resulting 411 sample sites was 2904.4 m. The geochemical data described the concentration of 38 different metals in the soil samples.
For the location of each soil sample, environmental features data was collected. The resulting variables were grouped into five groups. Group terrain: elevation, slope, and Topographic Wetness Index (TWI) were extracted or calculated from SRTM 30 m data [43,44,45,46]. TWI is an index that expresses the terrain-controlled wetness of any given grid cell in a digital elevation model. Group input streams: the SRTM dataset was also used to delineate the five streams that enter the floodplain from the neighbouring mountainous areas. For brevity, they were called west-1 (Cache Creek), west-2 (Putah Creek), east-1 (American River), east-2 (Cosumnes River), and east-3 (Mokelumne River), as indicated in Figure 1. Raster grids containing the proximity to each of the five streams were created based on inverse Euclidean distance. The Euclidean distance grids and density grids of the Sacramento River (Group Sacramento River) were created based on vector data [47]. Group soil: additional soil data, such as sand, silt, and clay percentages of the fine soil fraction, were obtained from a database based on the STATSGO2 soil database, pre-processed for use in the Soil And Water Assessment Tool (SWAT) model [48]. This database was chosen because it contains derived parameters expected to affect soil metal concentrations. The selected features were soil bulk density (g/cm3), the available water capacity (AWC), measuring the soil volume that can be filled with water (mm/mm), hydraulic conductivity K (mm/h), the carbon, rock, sand, silt and clay content (%), the soil albedo (%), and the Universal Soil Loss Equation (USLE) factor K, measuring erodibility. Group vegetation: the vegetation indices Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) and Enhanced Vegetation Index (EVI) were calculated based on Landsat-5 imagery captured in September 1986 (Landsat-5 image courtesy of the U.S. Geological Survey). NDVI and EVI are based on the near-infrared reflectance of the Earth’s surface and are indicators of land cover type and vegetation health status [49]. Table 1 shows a summary statistic of the environmental features used in this study. Maps of the factors for the study area can be found in the Supplementary Figures S1–S3.

Table 1.
The 22 environmental features used in the respective RF models.
The input data pre-processing, raster arithmetic, and sampling for each soil sample location were performed in ArcGIS (version 10.4, Esri, Redlands, CA, USA), QGIS (version 3.16.4, QGIS Association, Gruet, Switzerland), and SAGA GIS (version 2.3.2, SAGA User Group Association, Hamburg, Germany). The data analysis was performed in the R statistical programming language (version 4.0.5, R Core Team, Vienna, Austria) in the RStudio development environment (version 2022.02.3+492, RStudio, Boston, MA, USA).
One of the core methods of the analysis was the machine learning algorithm Random Forest (RF), for which the spatialRF package in R was used [50]. This package is based on the ranger RF package [51]. RF is a popular algorithm since it can find linear and non-linear relationships and patterns in large datasets that contain many features. RF is a large collection of decision trees, individually trained on a random subset of the full training dataset, and tested against the remaining data. This process is called out-of-bag training (OOB) and makes the algorithm robust against overfitting [52]. RF has been used in numerous scientific studies on soil research [53,54] and metal concentrations specifically [55,56,57,58]. The target variables and features were tested for spatial autocorrelation in the present study. Autocorrelation can lead to errors in the prediction, and spatialRF incorporates spatial predictors into the model to overcome these issues.
Figure 2 gives an overview of the workflow of this study. There were two phases of complexity reduction in the methodology. The first step was to create a model with each of the 38 metal concentrations as the dependent variable and all other metal concentrations as independent features to identify relationships between the distributions of metals.
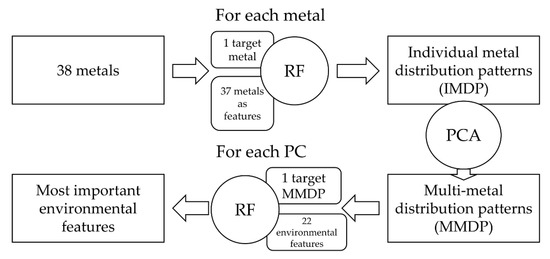
Figure 2.
Overview of the research process, detailing the different steps and input data.
All models that achieved an OOB R2 of >0.7 were selected for further study. The most important variable, i.e., the metal with the closest relationship to the target metal of the respective model, was recorded. This step resulted in 13 individual metal distribution patterns (IMDP). The 13 IMDP were then treated with a Principal Component Analysis (PCA) to reduce complexity further and describe multi-metal distribution patterns (MMDP). The variability of the MMDP was then explained with another set of RF models. In these models, 22 environmental features were included as independent variables. The importance of the variables in these models was used to rank the factors affecting the MMDP.
3. Results
A correlation between all 38 metals was performed to understand the relationships between the different metals. As shown in Figure 3, of the 722 possible unique correlations, 484 (67%) were significant (p < 0.05), consisting of 364 positive correlations and 120 negative correlations. Tungsten (W), Ga, and thallium (Tl) had more than 28 positive correlations each, while 21 metals had 20 or more positive correlations (Figure 3). The least positive correlations were found for sodium (Na) and tin (Sn), which had eight positive correlations, and Cd, which only had seven. Na had the most significant negative correlations, totalling 20. Ni, strontium (Sr), Cr, calcium (Ca), Co, Mg, niobium (Nb), potassium (K), and lithium (Li) had more than ten negative correlations. Three metals, i.e., Ba, Cd, and Sn, had no significant negative correlations. Additionally, these three metals also had relatively few positive correlations. The results of the correlation study showed that there are moderate to strong relationships between the individual metals in the Sacramento River floodplain.
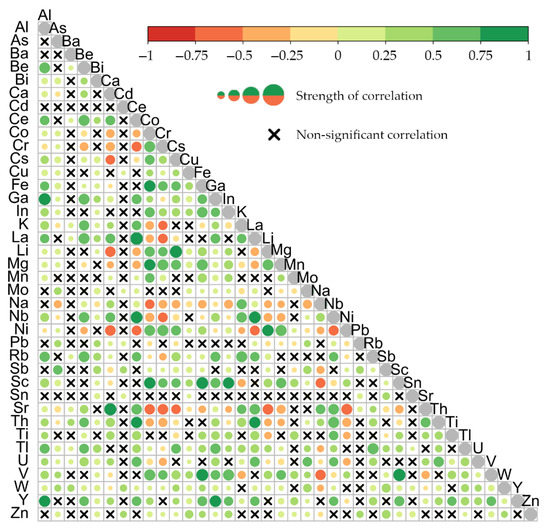
Figure 3.
Correlation matrix of the 38 metals studied in the soil samples of the research area. The size and colour of the circles indicate the direction and strength of the correlation (larger indicating stronger correlations, red indicating negative, and green indicating positive correlations). Non-significant correlations are marked with an ×.
Due to a large number of significant correlations, we next aimed to find a more condensed representation of the relationships between the metals and describe more generalized distribution patterns. In this first step of complexity reduction, the RF model analysis for each of the 38 metals resulted in 13 IMDPs, each named after the individual metal best describing the distribution pattern (Table 2). Model results were only considered when the OOB R2 reached 0.7, and 22 models remained. The IMDP “Ni”, defined by the distribution pattern of nickel, best described the distribution of four metals (Ni, Co, Cr, and Mg). V was IMDP for three other metals, while Ga, La, Li, rubidium (Rb), and Sc were IMDP for two metals each. Aluminium (Al), Ca, cerium (Ce), caesium (Cs), K, and Sr were each IMDP for a single other metal. The correlation values between the IMDP and the metals were all medium to very strong (correlation coefficients 0.61 to 0.98) and positive. The only negative IMDP relationship with metal was between the IMDP V and the metal Na.

Table 2.
The 22 metals for which the RF model performance exceeded an R2 of 0.7.
The IMDP showed clear spatial patterns, as shown in the kriging maps in Figure 4. The IMDP Ca, Ce, K, La, and Sr showed similar patterns, with the highest concentrations in the southeast of the floodplain. Al, Ga, and Rb had similarly high concentrations in the south and central region and differing higher concentrations in the north. Cs, Li, Ni, Sc, and V had very low concentrations in the southeast. Sc and V had an almost identical distribution along the north–south axis of the research area. Cs, Li, and Ni had higher concentrations in the areas along the floodplain’s western side.
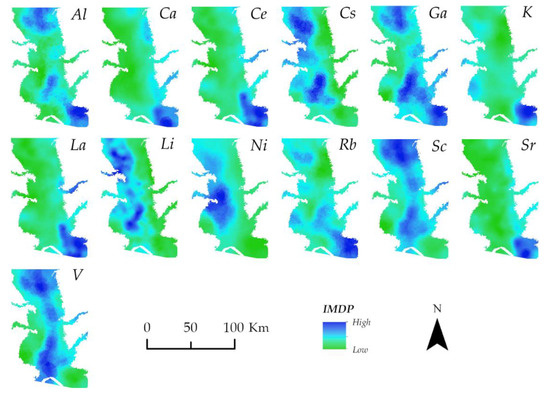
Figure 4.
The 13 individual metal distribution patterns are named after the respective metal concentrations in the topsoil of the Sacramento River floodplain.
Next, using PCA, multi-metal distribution patterns were created to extract comprehensive spatial patterns that describe most of the metal distributions in the Sacramento River floodplain. After performing the PCA, three principal components (PC) with an eigenvalue (the square of the standard deviation) over 1.0 were considered for further study (Table 3). PC1 described 41% of the variation in the input data, PC2 described 31%, and PC3 described 13%. Together, all three PC reflected 86.9% of the variation in the data. The relationship between the respective IMDP and the three PC is shown in the Supplementary Figures S4–S16.

Table 3.
Results of the principal component analysis with information about the three utilized principal components.
The respective spatial distribution patterns of the rotated values of the PC, i.e., the multi-metal distribution patterns (MMDP), are shown in Figure 5. The higher values of MMDP1 were concentrated in the western regions of the floodplain, while the eastern side showed very low values. MMDP2 showed a northern region of high values and a southern region of higher values focused on the floodplain’s central areas. MMDP3 was similar to the distribution of MMDP1, but the band of low values in the east was broader, the western region with high values did not stretch south as far, and there was a patch of high values in the southeast of the floodplain.
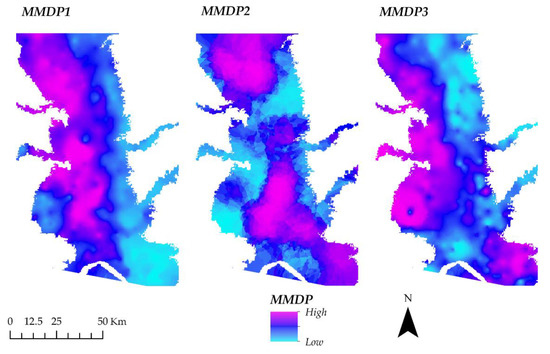
Figure 5.
The three resulting multi-metal distribution patterns describe the generalized metal accumulation in the Sacramento River floodplain.
Another correlation was performed to identify the relationship between the three MMPD and the respective metal distributions in the soil. Figure 6 shows the correlation coefficients between the three MMDP and the 13 IMDP. MMPD1 showed strong negative correlations with the IMDP Ca, Ce, La, and Sr, and relatively strong positive correlations with Ni, Li, and Cs. MMDP2 had positive correlations with the metal concentrations, except for a very weak negative correlation with Sr. The correlations with Al and Ga were very strong, followed by Cs, Rb, Sc, and V. The correlations between MMDP3 and the IMDP were generally weaker than those of MMDP1 and MMDP2; the strongest positive correlation was with K, and the strongest negative correlations were with Sc and V.
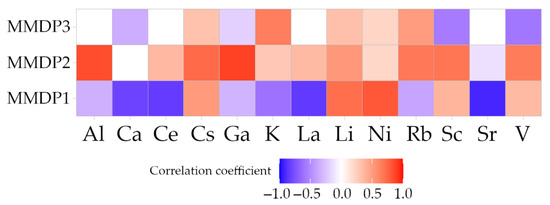
Figure 6.
Correlation of the three MMDP with the 13 IMDP. Non-significant correlations are displayed in white.
After defining the multi-metal spatial patterns of soil metal concentrations in the Sacramento River floodplain, the goal was to identify the environmental factors of these patterns. To achieve this, three RF models were used. Where necessary, spatial predictors were included to overcome the effects of spatial autocorrelation (Supplementary Figure S17). The R2 values of the RF model for MMDP1, MMDP2, and MMDP3 were 0.87, 0.36, and 0.72, respectively. Figure 7 shows the respective six most important variables of the three RF models. Changes in these variables had the highest effect on the prediction power of the model. The most important feature in the MMDP1 RF model was the proximity to stream west-1, followed by the proximity to stream east-3. The next most important variables all belonged to the Soil category, especially soil hydraulic conductivity and soil rock and sand percentages. Three categories, Input streams, Sacramento River, and Soil, were present in the most important features in the MMDP2 model. The most important feature was the proximity to stream west-1, followed by river distance (the distance to the Sacramento River). Soil hydraulic conductivity was the third most important feature. The most important feature in the MMDP3 model was river distance, followed by river density and proximity to streams west-1, west-2, and east-3.
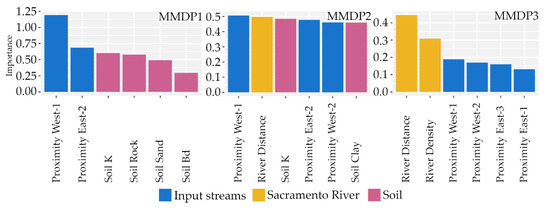
Figure 7.
The six most important variables for each of the three MMDP RF models. The colours of the bars indicate the group to which each variable belongs.
4. Discussion
We found many significant correlations between the initial set of 38 metals, most of which were positive. No significant correlation between Cu and Pb was found in our study. In contrast, a significant positive correlation between Cu and Pb was found in four other studies [27,29,32,59], and one study found a significant negative correlation [60]. Deposit and accumulation processes are site-specific, and Cu and Pb may primarily stem from different sources in the research area [61,62]. We found a significant positive correlation between Cu and Zn, which agrees with the six studies’ results [27,29,32,59,60,63]. Similarly, our study found a significant positive correlation between Pb and Zn, as did four other studies [27,29,32,59]. Na was found to have a very large number of significant negative correlations (with 20 metals), and most of the higher Na values are concentrated in the southeast of the floodplain where most other metals have low values. It is possible that there is a natural or anthropogenic Na source in that region of the study area [64,65]. Similarly, Ba, Cd, and Sn were generally found to have only a few significant correlations in our study; this is probably caused by their relatively homogeneous distribution over the study area, without a clear concentration pattern. The high number of significant correlations highlighted the fact that close relationships exist between many metals, which potentially hold valuable information about their distributions. Additionally, the high number of significant correlations for less commonly studied metals such as Ga (31), La (25), Sc (27), and V (28) showed that the research of these metals can be supported by studying metal relationships.
The underlying reasons for correlations and relationships in any direction are similarities in the source and the processes of transport and accumulation of the metals. The results show the need for a reduction in complexity. In our study, RF was used as a first step in identifying 13 individual metal distribution patterns named after the respective metal describing them. These IMDP were the most important variables for describing the distribution of 1 or more of the remaining 22 metals. Here, the IMDP may not necessarily be that of the metal with the strongest correlation in earlier results, as seen in Figure 3, since the relationship between the IMDP and the respective metal may be non-linear. Model variable importance can be a powerful tool in finding relationships between variables, especially if these relationships may be non-linear [66,67]. The IMDP Ni and V described the distribution of three metals each. Ga, La, Li, Rb, and Sc described that of two metals each. This means that the IMDP are representative of several metals’ distribution. There are several sources of Ni in the environment. Among the natural sources is the release from the weathering of rocks and minerals and volcanic activities. Anthropogenic sources include fuel combustion, mining and smelting, industrial and domestic wastewater, and effluent from landfills [40,68,69,70]. The origin of V is similar. It can be released from natural sources, such as the weathering of rocks, but also by human activities, such as from metal-related industries, fuel combustion, and due to its use as a catalyst in different production techniques [71,72]. Generally, the sources of Ga, La, Li, Rb, and Sc sources are also similar. They are either released from weathering minerals and rocks, as by-products in industrial processes, or from waste products [73,74,75,76]. The results of our study reflect the same close relationship between these metals. The allocation to each of the sources is site-specific, and similar patterns are formed for different metals.
To reduce the complexity of the IMDP and to study comprehensive underlying patterns, the 13 IMDP were combined using PCA, resulting in three multi-metal distribution patterns. PCA was used in other studies and was an adequate tool to describe the underlying complexity of soil metal concentrations and their factors [77,78]. However, the explicit interpretation of PCA rotated values as spatial patterns indicative of soil metal concentrations, as achieved in our study, appears to be a novel approach. Three MMDPs were found to describe a large proportion of the variation in the IMDP. Two models (those for MMDP1 and MMDP3) performed reasonably well, with OOB R2 values of 0.87 and 0.72, respectively, while the model for MMDP2 had an R2 of 0.36. The high portion of the distribution variance explained by the three MMDP shows that these multi-metal distribution patterns may hold information that exceeds that of individual distribution patterns.
One of the study’s main goals was to identify the environmental factors that determine the distribution of metals in floodplain soils. The most important variables of the respective models showed that the spatial patterns of MMDP1, MMDP2, and MMDP3 depend on different environmental factors. In the MMDP1 model, the proximity to the streams west-1 and east-3 was the most important, i.e., changes in these variables affected the model result the most strongly. The rock and soil chemistry in the western mountain ranges is affected by volcanic activity, and the metal-rich matter is transported into the floodplain [39,40]. The results of our study support the idea that this transportation of matter from the mountains has this effect on the floodplain soils. Other important variables came from the group of soil parameters, especially soil hydraulic conductivity, and rock, and sand content. These soil features have been found to affect the metal concentrations in soils in other studies [79,80]. The effects of the different groups in the MMDP2 model were not as distinctive. Most of the variables were of similar importance. In the MMDP3 model, the most important variables were the distance to the Sacramento River and the density of the main river network. As another route by which metals are input and transported into the floodplain, the Sacramento River may play a major role in metal accumulation [81,82]. The proximity to the west and east streams played a role, while soil properties were the least important for the variance of MMDP3. Vegetation, in the form of NDVI and EVI, did not play a major role in the RF models, even though it has been found to affect metal concentrations in other studies [83,84]. This is probably caused by the relative homogeneity of the vegetation in the research area. Most of the Sacramento Valley is covered by agriculture. The results showed that each metal had a relationship with each of the MMDPs, therefore, a relationship with spatially varying factors.
The importance of the MMDP RF model features, in combination with the correlation results in Figure 6, revealed further interesting connections. MMDP1 was negatively correlated with 8 of the 13 IMDP, i.e., Al, Ca, Ce, Ga, K, La, Rb, and Sr. This result highlights that the distribution of these metals is negatively affected by the specific environmental features that affect the distribution of MMDP1. These environmental features are attributes belonging to the groups Input streams and Soil. The five other IMDP, Cs, Li, Ni, Sc, and V, were positively correlated with the distribution of MMDP1. This means that the relationship with the same factors of Input streams and Soil affecting MMDP1 is inverted for these metals, when compared to the metals with a negative correlation. MMDP2 was positively correlated to almost all IMDP, except Sr, which had a weak negative correlation. MMDP3 was positively correlated with five IMDPs and negatively correlated with four IMDPs. Of the aforementioned, less commonly studied metals, Ga, Sc, and V were significantly negatively correlated with MMDP3. This shows the importance of the distance to the Sacramento River and to the input streams for these metals. The relationship hints at higher metal concentrations closer to the Sacramento River and further away from the eastern input streams. There was an overlap between MMDP3 and MMDP1, i.e., some IMDP (Ca, Cs, Ga, Li and Ni) showed the same correlation for MMDP1 and MMDP3. Other IMDPs (K, Rb, Sc and V) had opposite relationships with MMDP1 and MMDP3. The factors from Input streams were important for explaining the variance in both patterns, while Soils was only important for MMDP1. This shows that the metals are affected by distinctive features and potentially by interactions between features. The effect of specific features is not the same over the whole study area but also has a spatial characteristic, as has been shown elsewhere [85]. This spatial variance in the effects of the controlling factors was visible in other studies, as well [67,86].
While our study’s chosen methodology and datasets have been demonstrated to be suitable, the application has certain potential issues. The predictive power of the MMDP2 RF model was not very high, which means that another feature may play a role in metal distribution that has not been included in the study. Among other features explaining the distribution of MMDP2 may be long-term stable factors belonging to vegetation, terrain, or soil properties, but also factors that change more rapidly, such as emissions sources. Future work identifying descriptive parameters for PC2 may be the basis for further research. Furthermore, selecting the variables is important in studies involving Random Forest and other methodologies. A certain knowledge of the local conditions and especially of the potential effects of environmental features is necessary. Finally, although we performed this study for the Sacramento River floodplain, the focus on stable, physical environmental factors may improve the transferability of the results to other areas with a similar setup.
5. Conclusions
This study found clear spatial patterns in the distribution of 38 metals in the topsoil of the Sacramento River floodplain. We found 484 significant correlations between the metal patterns, and a high number of significant correlations for less commonly studied metals, such as Ga, La, Sc and V, were observed. We found 13 individual patterns which described the distribution of 22 metals. In addition, three multi-metal distribution patterns described most of the variability in these thirteen patterns. The spatial variance of these patterns was explained by the distance to the Sacramento River, different input streams, and soil properties. Multi-metal distribution patterns hold information exceeding that contained in individual metal patterns. This information can contribute to inferring information about less commonly sampled metals. For example, depending on local conditions, existing Ni and K screenings and mapping data may be used to identify potential sampling sites for Ga or Rb. In addition, the relationship between different metals may allow for more specific source identification based on the presence and absence of different metals in the samples. Furthermore, these results can be used to identify areas for specific use cases or the exclusion of use cases, such as food production, remediation measures, or scientific studies on the effects of metal concentrations.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/app12178462/s1, Figure S1: Maps of the environmental features in the study area—Land cover, elevation, slope, terrain wetness index, NDVI and EVI; Figure S2: Maps of the environmental features in the study area—River distance, river density, proximity to streams west-1, west-2, east-1, east-2, east-3; Figure S3: Maps of the environmental features in the study area—Sand, silt, clay, rock, bulk density, available water capacity, hydraulic conductivity, carbon content, USLE K, soil albedo; Figure S4: The normalized Al values in relation to the three principal components; Figure S5: The normalized Ca values in relation to the three principal components; Figure S6: The normalized Ce values in relation to the three principal components; Figure S7: The normalized Cs values in relation to the three principal components; Figure S8: The normalized Ga values in relation to the three principal components; Figure S9: The normalized K values in relation to the three principal components; Figure S10: The normalized La values in relation to the three principal components; Figure S11: The normalized Li values in relation to the three principal components; Figure S12: The normalized Ni values in relation to the three principal components; Figure S13: The normalized Rb values in relation to the three principal components; Figure S14: The normalized Sc values in relation to the three principal components; Figure S15: The normalized Sr values in relation to the three principal components; Figure S16: The normalized V values in relation to the three principal components; Figure S17: Spatial autoregression in the random forest models.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, T.L.; methodology, T.L.; software, T.L.; validation, T.L.; formal analysis, T.L., S.S., and C.O.; investigation, T.L.; resources, T.L., S.S., and C.O.; data curation, T.L.; writing—original draft preparation, T.L., S.S., and C.O.; writing—review and editing, T.L., S.S., and C.O.; visualization, T.L.; supervision, T.L.; project administration, T.L.; funding acquisition, T.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the scientific research start-up fund for high-level talents of Jinling Institute of Technology: jit-b-202139.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Kelly, T.J.; Hamilton, E.M.; Watts, M.J.; Ponting, J.; Sizmur, T. The Effect of Flooding and Drainage Duration on the Release of Trace Elements from Floodplain Soils. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2020, 39, 2124–2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebed’-Sharlevich, Y.I.; Kulachkova, S.A.; Mozharova, N. Generation, sink, and emission of greenhouse gases by urban soils at different stages of the floodplain development in Moscow. J. Soils Sediments 2019, 19, 3204–3216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brémond, P.; Grelot, F.; Agenais, A.-L. Review Article: Economic evaluation of flood damage to agriculture—Review and analysis of existing methods. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 13, 2493–2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levesque, A.-B.; Dupras, J.; Bissonnette, J.F. The pitchfork or the fishhook: A multi-stakeholder perspective towards intensive farming in floodplains. J. Environ. Plan. Manag. 2019, 63, 1987–2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Yuan, Y.; Li, C.; Sun, W.-L.; Yang, M.; Wang, X.-R. Environmental Health and Ecological Risk Assessment of Soil Heavy Metal Pollution in the Coastal Cities of Estuarine Bay—A Case Study of Hangzhou Bay, China. Toxics 2020, 8, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.; Malik, D.; Patel, S.l.; Gupta, V.K. Human health risk assessment and mitigation of heavy metal pollution in agriculture and environment. Contam. Agric. Environ. Health Risks Remediat. 2019, 1, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pusz, A.; Wiśniewska, M.; Rogalski, D. Assessment of the Accumulation Ability of Festuca rubra L. and Alyssum saxatile L. Tested on Soils Contaminated with Zn, Cd, Ni, Pb, Cr, and Cu. Resources 2021, 5, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meena, V.; Dotaniya, M.L.; Saha, J.K.; Das, H.; Patra, A.K. Impact of Lead Contamination on Agroecosystem and Human Health. In Radionuclides and Heavy Metals in the Environment; Gupta, D., Chatterjee, S., Walther, C., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Saha, J.K.; Selladurai, R.; Coumar, M.V.; Dotaniya, M.L.; Kundu, S.; Patra, A.K. Assessment of Heavy Metals Contamination in Soil. In Soil Pollution—An Emerging Threat to Agriculture; Saha, J.K., Selladurai, R., Coumar, M.V., Dotaniya, M.L., Kundu, S., Patra, A.K., Eds.; Environmental Chemistry for a Sustainable World; Springer: Singapore, 2017; pp. 155–191. [Google Scholar]
- Chandrasekar, T.; Keesari, T.; Gopalakrishnan, G.; Karuppannan, S.; Senapathi, V.; Sabarathinam, C.; Viswanathan, P.M. Occurrence of Heavy Metals in Groundwater Along the Lithological Interface of K/T Boundary, Peninsular India: A Special Focus on Source, Geochemical Mobility and Health Risk. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2021, 80, 183–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciszewski, D.; Aleksander-Kwaterczak, U. Metal Mobility in a Mine-Affected Floodplain. Minerals 2020, 10, 814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matys Grygar, T.; Elznicová, J.; Kiss, T.; Smith, H.G. Using sedimentary archives to reconstruct pollution history and sediment provenance: The Ohře River, Czech Republic. Catena 2016, 144, 109–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beier, T.; Opp, C.; Hahn, J.; Zitzer, N. Sink and Source Functions for Metal(loid)s in Sediments and Soils of Two Water Reservoirs of the Ore Mountains, Saxony, Germany. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 6354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, A.; Wilcke, W.; Zech, W.; Styk, J. Heavy Metal Release from Soils in Batch pHstat Experiments. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1999, 63, 290–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Bai, J.; Xiao, R.; Zhao, Q.; Jia, J.; Cui, B.; Liu, X. Heavy metal fractions and ecological risk assessment in sediments from urban, rural and reclamation-affected rivers of the Pearl River Estuary, China. Chemosphere 2017, 184, 278–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tota, O.; Huqi, B.; Skuraj, E.; Sallaku, F.; Moisiu, A. An investigation of the spatial variability of heavy metal concentrations in floodplain sediments around the metallurgical combine of Elbasani, Albania. Res. J. Agric. Sci. 2010, 42, 340–346. [Google Scholar]
- Zimmer, D.; Kiersch, K.; Baum, C.; Meissner, R.; Müller, R.; Jandl, G.; Leinweber, P. Scale-Dependent Variability of As and Heavy Metals in a River Elbe Floodplain. Clean-Soil Air Water 2011, 39, 328–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adimalla, N.; Qian, H.; Wang, H. Assessment of heavy metal (HM) contamination in agricultural soil lands in northern Telangana, India: An approach of spatial distribution and multivariate statistical analysis. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.; Zhou, S.; Su, Q.; Yi, H.; Wang, J. Comparison Study on the Estimation of the Spatial Distribution of Regional Soil Metal(loid)s Pollution Based on Kriging Interpolation and BP Neural Network. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 15, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotz, T.; Opp, C. Ranking of Basin-Scale Factors Affecting Metal Concentrations in River Sediment. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 2805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, A.; Haghnia, G.H.; Ayoubi, S.; Safari, T. Impacts of geology and land use on magnetic susceptibility and selected heavy metals in surface soils of Mashhad plain, northeastern Iran. J. Appl. Geophys. 2017, 138, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Rehman, S.; Zeb Khan, A.; Amjad Khan, M.; Tahir Shah, M. Soil and vegetables enrichment with heavy metals from geological sources in Gilgit, northern Pakistan. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2010, 73, 1820–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, S.; Cox, S.F.; McKinley, J.M.; Ofterdinger, U. Soil-geochemical factors controlling the distribution and oral bioaccessibility of nickel, vanadium and chromium in soil. Appl. Geochem. 2014, 51, 255–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, X.; Li, Y.; Li, F.; Feng, J.-Y.; Shen, J.; Shi, Z. Impacts of Land Use and Landscape Patterns on Heavy Metal Accumulation in Soil. Huan Jing Ke Xue Huanjing Kexue 2019, 40, 2471–2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Xiao, J.; Wang, L.; Liang, T.; Guo, Q.; Guan, Y.; Rinklebe, J. Elucidating the differentiation of soil heavy metals under different land uses with geographically weighted regression and self-organizing map. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 260, 114065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, S.; Jian, H.; Yang, F.; Liu, Q.; Yao, Q. Impact of water-sediment regulation on the concentration and transport of dissolved heavy metals in the middle and lower reaches of the Yellow River. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 150535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szabó, Z.; Buró, B.; Szabó, J.; Tóth, C.A.; Baranyai, E.; Herman, P.; Prokisch, J.; Tomor, T.; Szabó, S. Geomorphology as a Driver of Heavy Metal Accumulation Patterns in a Floodplain. Water 2020, 12, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middelkoop, H. Heavy-metal pollution of the river Rhine and Meuse floodplains in the Netherlands. Neth. J. Geosci.-Geol. En Mijnb. 2016, 79, 411–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, K.; Ye, Z.; Zhang, L.; Dong, J.; Shao, Y.; Zhang, C.; Fu, W. Spatial Patterns of Potentially Hazardous Metals in Soils of Lin’an City, Southeastern China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, J.; Bui, T.-K.L.; Kessler, M.; Weber, C.J.; Beier, T.H.; Mildenberger, A.; Traub, M.; Opp, C. Catchment Soil Properties Affect Metal(loid) Enrichment in Reservoir Sediments of German Low Mountain Regions. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrugo-Negrete, J.; Pinedo-Hernández, J.; Combatt, E.M.; Bravo, A.G.; Díez, S. Flood-induced metal contamination in the topsoil of floodplain agricultural soils: A case-study in Colombia. Land Degrad. Dev. 2019, 30, 2139–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobierski, M. Evaluation of the Content of Heavy Metals in Fluvisols of Floodplain Area Depending on the Type of Land Use. J. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 16, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lamb, D.T.; Matanitobua, V.; Palanisami, T.; Megharaj, M.; Naidu, R. Bioavailability of barium to plants and invertebrates in soils contaminated by barite. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 4670–4676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syu, C.H.; Chen, L.; Lee, D.-Y. The growth and uptake of gallium (Ga) and indium (In) of wheat seedlings in Ga- and In-contaminated soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 759, 143943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, W.-H.; Wang, G.; Zhang, S.; Li, T.-x.; Xu, X.; Deng, O.; Luo, L.; He, Y.; Zhou, W. Physiochemical responses of earthworms (Eisenia fetida) under exposure to lanthanum and cerium alone or in combination in artificial and contaminated soils. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 296, 118766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paltseva, A.A.; Neaman, A. An Emerging Frontier: Metal(loid) Soil Pollution Threat Under Global Climate Change. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2020, 39, 1653–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Zhang, D.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, S.; Chang, L.-L.; Qi, Y.; Li, X.-H.; Liu, J.-G.; Guo, W.; Zhao, J.J.; et al. Comparative insights into influences of co-contamination by rare-earth elements and heavy metals on soil bacterial and fungal communities. J. Soils Sediments 2022, 22, 2499–2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwenzi, W.; Mangori, L.; Danha, C.; Chaukura, N.; Dunjana, N.; Sanganyado, E. Sources, behaviour, and environmental and human health risks of high-technology rare earth elements as emerging contaminants. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 636, 299–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, J.M.; Goldhaber, M.B.; Mills, C.T.; Breit, G.N.; Hooper, R.L.; Holloway, J.M.; Diehl, S.F.; Ranville, J.F. Weathering and transport of chromium and nickel from serpentinite in the Coast Range ophiolite to the Sacramento Valley, California, USA. Appl. Geochem. 2015, 61, 72–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, J.M.; Goldhaber, M.B.; Lee, L.; Holloway, J.M.; Wanty, R.B.; Wolf, R.E.; Ranville, J.F. A regional-scale study of chromium and nickel in soils of northern California, USA. Appl. Geochem. 2009, 24, 1500–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USGS. National Geochemical Database: Soil; USGS: Reston, VA, USA, 2016.
- Nardi, F.; Annis, A.; Di Baldassarre, G.; Vivoni, E.R.; Grimaldi, S. GFPLAIN250m, a global high-resolution dataset of Earth’s floodplains. Sci. Data 2019, 6, 180309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farr, T.; Rosen, P.; Caro, E.; Crippen, R.; Duren, R.; Hensley, S.; Kobrick, M.; Paller, M.; Rodriguez, E.; Roth, L.; et al. The Shuttle Radar Topography Mission. Rev. Geophys. 2007, 45, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farr, T.G.; Kobrick, M. Shuttle radar topography mission produces a wealth of data. Eos Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 2011, 81, 583–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NASA. NASA Shuttle Radar Topography Mission Global 1 Arc Second [Data Set]; NASA: Washington, DA, USA, 2013. [CrossRef]
- Rosen, P.A.; Hensley, S.; Joughin, I.R.; Li, F.K.; Madsen, S.N.; Rodriguez, E.; Goldstein, R.M. Synthetic aperture radar interferometry. Proc. IEEE 2000, 88, 333–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naturalearthdata. Free Vector and Raster Map Data at 1:10m, 1:50m, and 1:110m Scales. Available online: https://www.naturalearthdata.com/ (accessed on 5 October 2021).
- Arnold, J.G.; Moriasi, D.N.; Gassman, P.W.; Abbaspour, K.C.; White, M.J.; Srinivasan, R.; Santhi, C.; Harmel, R.D.; van Griensven, A.; Van Liew, M.W.; et al. Swat Model Use, Calibration, and Validation. Trans. ASABE 2012, 55, 1491–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Didan, K. MOD13A1 MODIS/Terra Vegetation Indices 16-Day L3 Global 500m SIN Grid V006 [Data set]; LAADS: Greenbelt, MD, USA, 2015. [CrossRef]
- Benito, B. BlasBenito/spatialRF: SpatialRF: Easy Spatial Regression with Random Forest. Zenodo 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, M.N.; Ziegler, A. ranger: A Fast Implementation of Random Forests for High Dimensional Data in C++ and R. J. Stat. Softw. 2017, 77, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Liu, G.; Chen, S.; Rasmussen, C.; Liu, B. Assessing soil thickness in a black soil watershed in northeast China using random forest and field observations. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2021, 9, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dharumarajan, S.; Hegde, R. Digital mapping of soil texture classes using Random Forest classification algorithm. Soil Use Manag. 2020, 38, 135–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Geng, T.; Shen, W.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, Y. Quantifying the influencing factors and multi-factor interactions affecting cadmium accumulation in limestone-derived agricultural soil using random forest (RF) approach. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 209, 111773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, K.; Ma, W.; Wu, F.; Du, Q. Random forest–based estimation of heavy metal concentration in agricultural soils with hyperspectral sensor data. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yilihamu, Q.; Yuan, M.; Bai, H.; Xu, H.; Wu, J. Prediction models of soil heavy metal(loid)s concentration for agricultural land in Dongli: A comparison of regression and random forest. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 119, 106801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Shi, H.; Fei, Y.; Wang, C.; Mo, L.; Shu, M. Identification of Soil Heavy Metal Sources in a Large-Scale Area Affected by Industry. Sustainability 2021, 13, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafezi Moghaddas, N.; Hajizadeh Namaghi, H.; Ghorbani, H.; Dahrazma, B. The effects of agricultural practice and land-use on the distribution and origin of some potentially toxic metals in the soils of Golestan province, Iran. Environ. Earth Sci. 2012, 68, 487–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ennaji, W.; Barakat, A.; El Baghdadi, M.; Rais, J. Heavy metal contamination in agricultural soil and ecological risk assessment in the northeast area of Tadla plain, Morocco. J. Sediment. Environ. 2020, 5, 307–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Liu, J.; Hu, L.; Liu, M.; Wang, L.; Zhang, X.; Fan, D. Spatio-temporal distribution and sources of Pb identified by stable isotopic ratios in sediments from the Yangtze River Estuary and adjacent areas. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 580, 936–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raj, D.; Maiti, S.K. Sources, bioaccumulation, health risks and remediation of potentially toxic metal(loid)s (As, Cd, Cr, Pb and Hg): An epitomised review. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, M.M.; Akther, S.M.; Hossain, M.F.; Parveen, Z. Spatial distribution and ecological risk assessment of potentially toxic metals in the Sundarbans mangrove soils of Bangladesh. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 10422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassani, A.; Azapagic, A.; Shokri, N. Global predictions of primary soil salinization under changing climate in the 21st century. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 6663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Rusuli, Y. Assessment of Soil Salinization Risk by Remote Sensing-Based Ecological Index (RSEI) in the Bosten Lake Watershed, Xinjiang in Northwest China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 7118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, K.; Xiao, L.; Li, M.; Tian, Y.; Wu, F. Assessment of Anthropogenic Sources of Potentially Toxic Elements in Soil from Arable Land Using Multivariate Statistical Analysis and Random Forest Analysis. Sustainability 2020, 12, 8538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaheen, A.; Iqbal, J. Spatial Distribution and Mobility Assessment of Carcinogenic Heavy Metals in Soil Profiles Using Geostatistics and Random Forest, Boruta Algorithm. Sustainability 2018, 10, 799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begum, W.; Rai, S.; Banerjee, S.; Bhattacharjee, S.; Mondal, M.H.; Bhattarai, A.; Saha, B. A comprehensive review on the sources, essentiality and toxicological profile of nickel. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 9139–9153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Naggar, A.; Ahmed, N.; Mosa, A.; Niazi, N.K.; Yousaf, B.; Sharma, A.; Sarkar, B.; Cai, Y.; Chang, S.X. Nickel in soil and water: Sources, biogeochemistry, and remediation using biochar. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 419, 126421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poznanović Spahić, M.M.; Sakan, S.; Glavaš-Trbić, B.M.; Tančić, P.; Škrivanj, S.; Kovacevic, J.; Manojlović, D.D. Natural and anthropogenic sources of chromium, nickel and cobalt in soils impacted by agricultural and industrial activity (Vojvodina, Serbia). J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2019, 54, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappuyns, V.; Slabbinck, E. Occurrence of Vanadium in Belgian and European Alluvial Soils. Appl. Environ. Soil Sci. 2012, 2012, 979501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guagliardi, I.; Cicchella, D.; Rosa, R.D.; Ricca, N.; Buttafuoco, G. Geochemical sources of vanadium in soils: Evidences in a southern Italy area. J. Geochem. Explor. 2018, 184, 358–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.S.; Liao, W.T. Gallium: Environmental Pollution and Health Effects. In Encyclopedia of Environmental Health; Nriagu, J.O., Ed.; Elsevier: Burlington, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 829–833. [Google Scholar]
- Kolawole, T.O.; Olatunji, O.S.; Ajibade, O.M.; Oyelami, C.A. Sources and Level of Rare Earth Element Contamination of Atmospheric Dust in Nigeria. J. Health Pollut. 2021, 11, 210611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anke, M.K.; Angelov, L. Rubidium. In Elements and Their Compounds in the Environment; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2004; pp. 547–563. [Google Scholar]
- Pyrzyńska, K.; Kilian, K.; Pęgier, M. Separation and purification of scandium: From industry to medicine. Sep. Purif. Rev. 2019, 48, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Li, Y.; Yan, M.; Yang, L.; Lei, J.; Liu, H. Surface soil metal elements variability affected by environmental and soil properties. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0254928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-l.; Tian, X.; Liu, R.; Liu, S.; Zuza, A.V. Key driving factors of selenium-enriched soil in the low-Se geological belt: A case study in Red Beds of Sichuan Basin, China. Catena 2021, 196, 104926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Yuan, Z.; Li, D.; Zheng, M.; Nie, X.; Liao, Y. Effects of soil particle size on the adsorption, distribution, and migration behaviors of heavy metal(loid)s in soil: A review. Environ. Sci. Processes Impacts 2020, 22, 1596–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sungur, A.; Soylak, M.; Yılmaz, E.; Yilmaz, S.; Ozcan, H. Characterization of Heavy Metal Fractions in Agricultural Soils by Sequential Extraction Procedure: The Relationship Between Soil Properties and Heavy Metal Fractions. Soil Sediment Contam. Int. J. 2015, 24, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alpers, C.N.; Antweiler, R.C.; Taylor, H.E.; Dileanis, P.D.; Domagalski, J.L. Metals transport in the Sacramento River, California, 1996–1997; Volume 2, Interpretation of metal loads. Water-Resour. Investig. Rep. 2000, 2, 1–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cain, D.J.; Carter, J.L.; Fend, S.V.; Luoma, S.N.; Alpers, C.N.; Taylor, H.E. Metal exposure in a benthic macroinvertebrate, Hydropsyche californica, related to mine drainage in the Sacramento River. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2000, 57, 380–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Yang, L.; Chen, L.; Zhao, F.; Sun, L. Spatial distribution of heavy metal concentrations in peri-urban soils in eastern China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 26, 1615–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Yang, S.; Zheng, M.; Han, F.X.; Ma, Y. Effects of Vegetable Fields on the Spatial Distribution Patterns of Metal(loid)s in Soils Based on GIS and Moran’s I. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 4095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allafta, H.; Opp, C. Spatio-temporal variability and pollution sources identification of the surface sediments of Shatt Al-Arab River, Southern Iraq. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 6979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Shao, G.; Wang, L.; Tang, L. Spatial Distribution and Potential Sources of Five Heavy Metals and One Metalloid in the Soils of Xiamen City, China. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2019, 103, 308–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).