CBMDB: A Database for Accessing, Analyzing, and Mining CBM Information
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
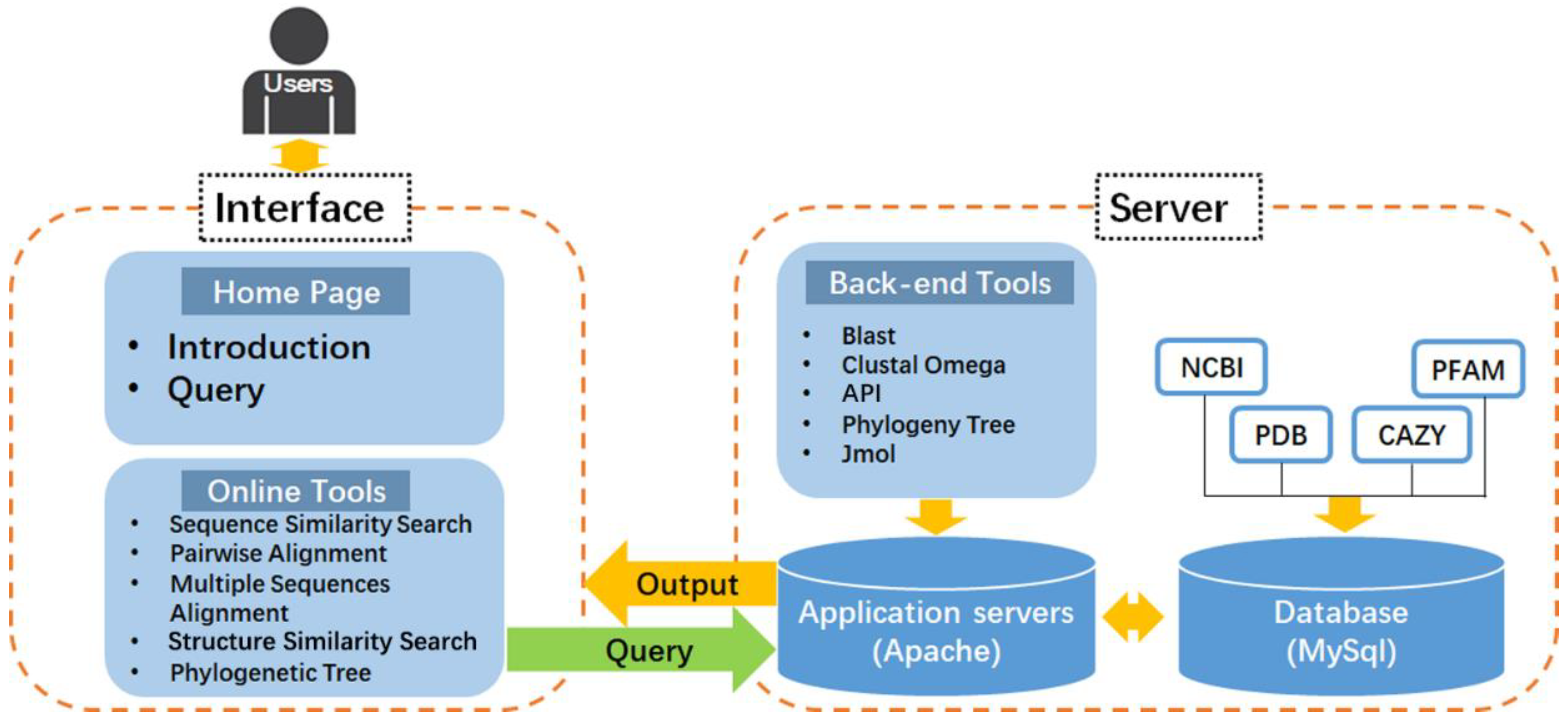
2.1. Database Architecture and Web Interface
2.2. Data Acquisition and Compilation
2.3. Data Organization
2.4. Integration of Web Tools
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Data Statistics
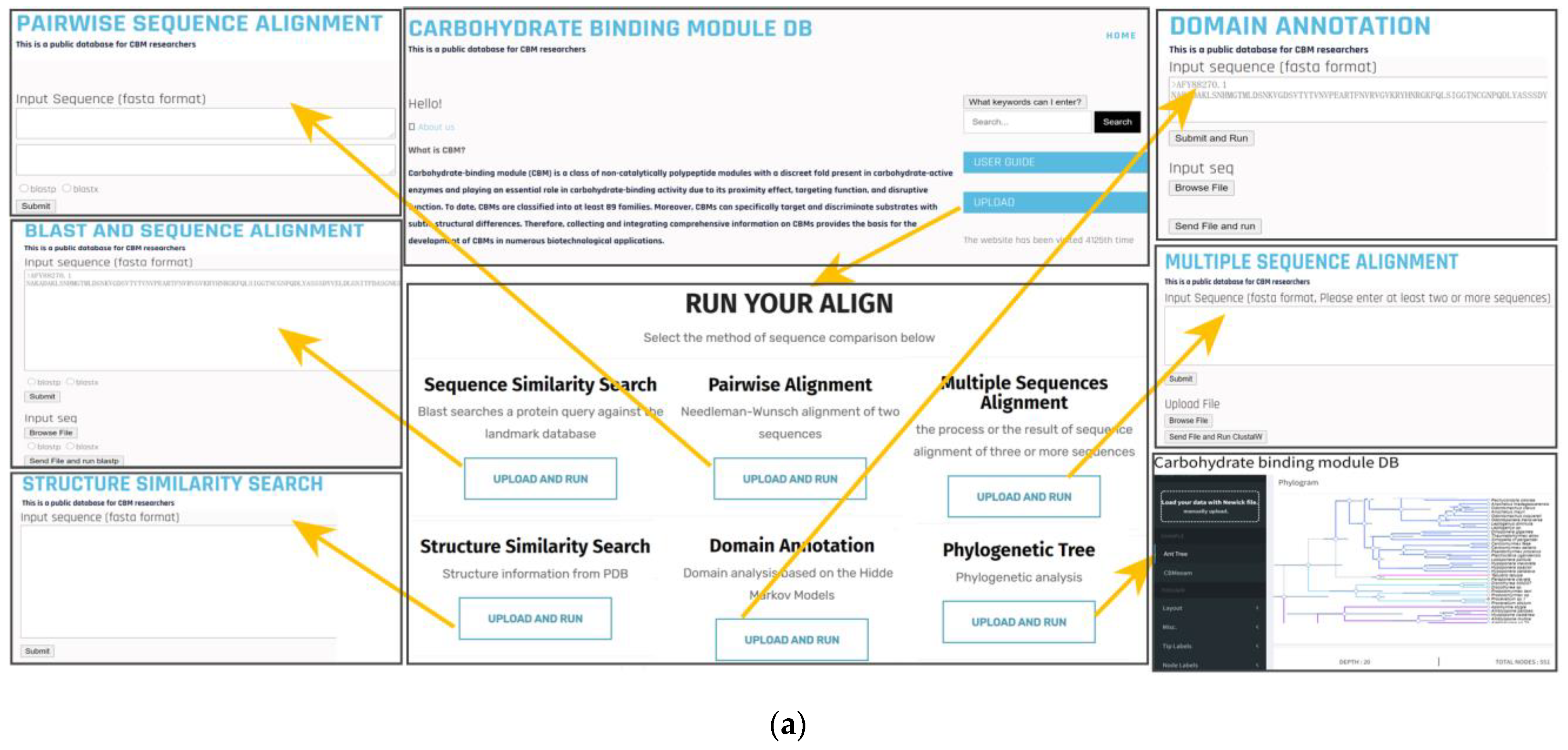
3.2. Web Interface: Data Query and Analysis Tool
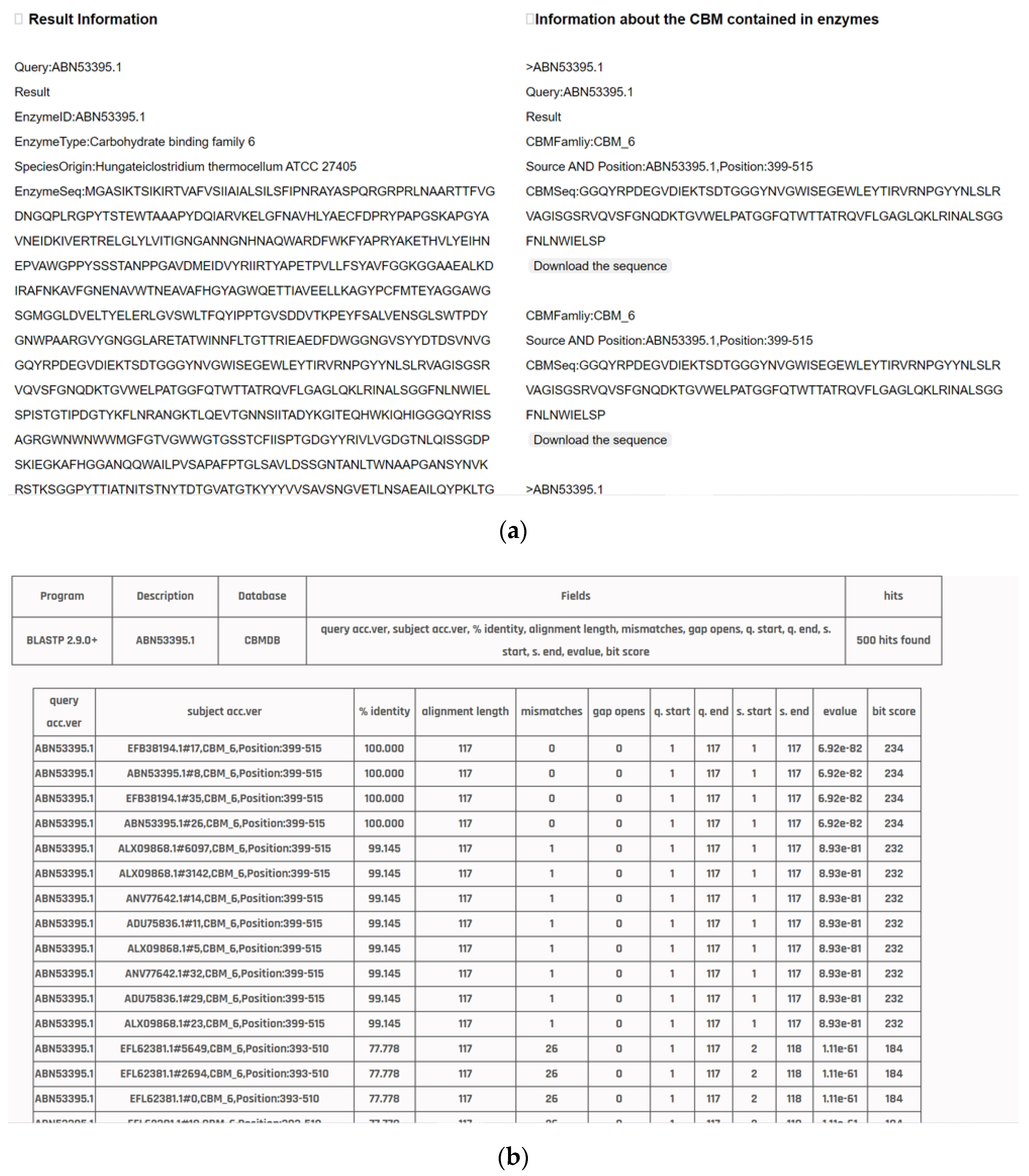
3.3. Data Query
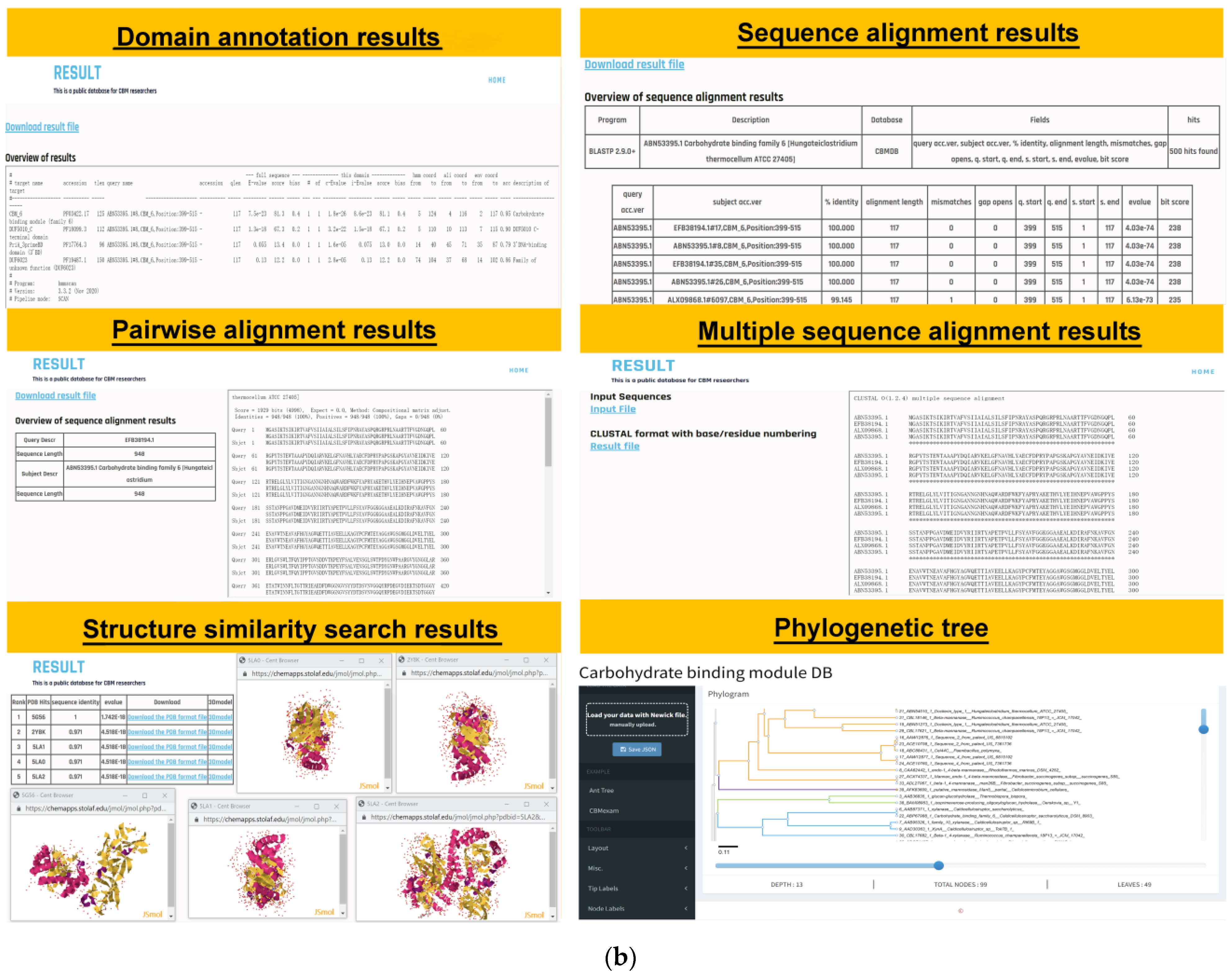
3.4. Analysis Tools
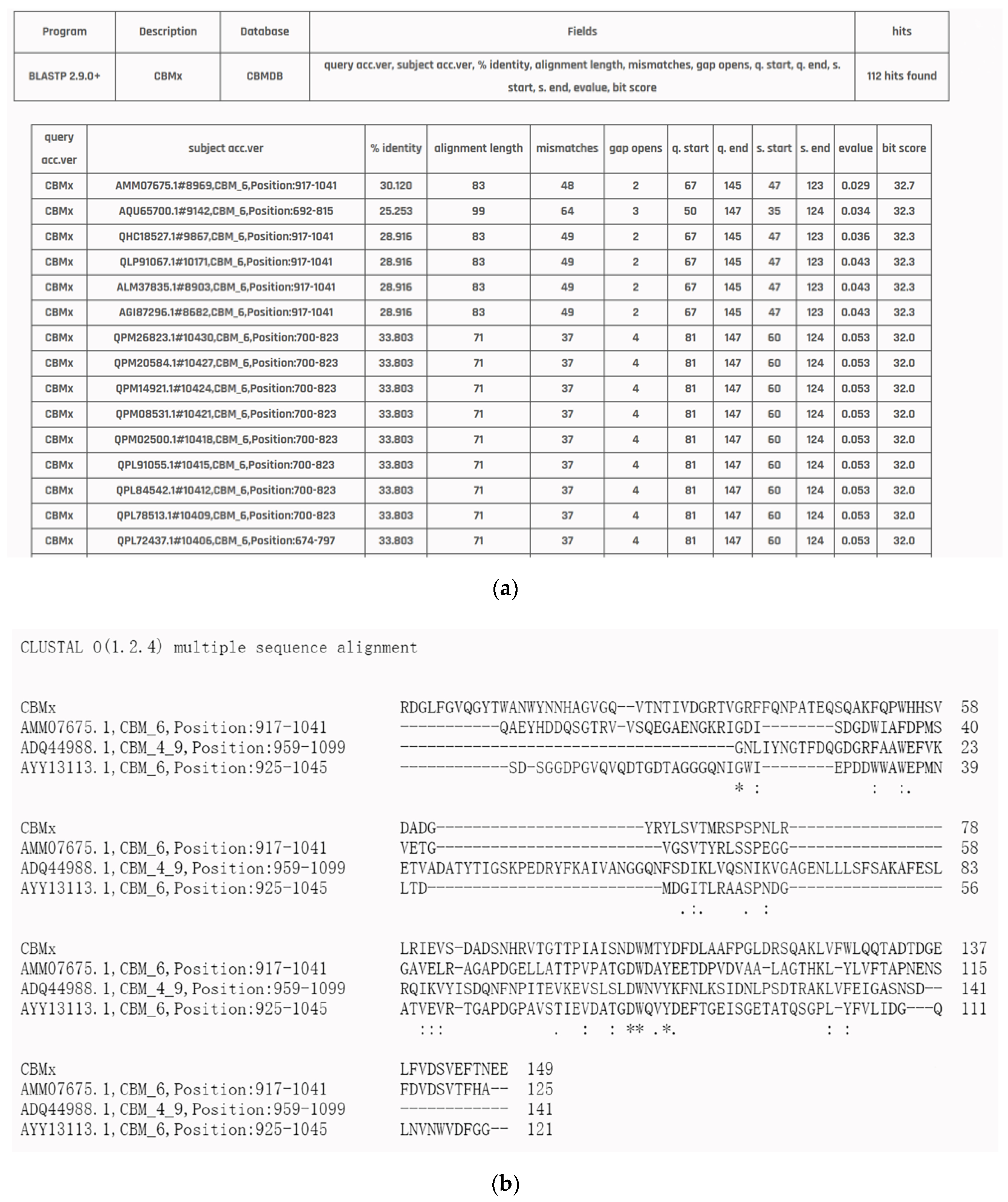
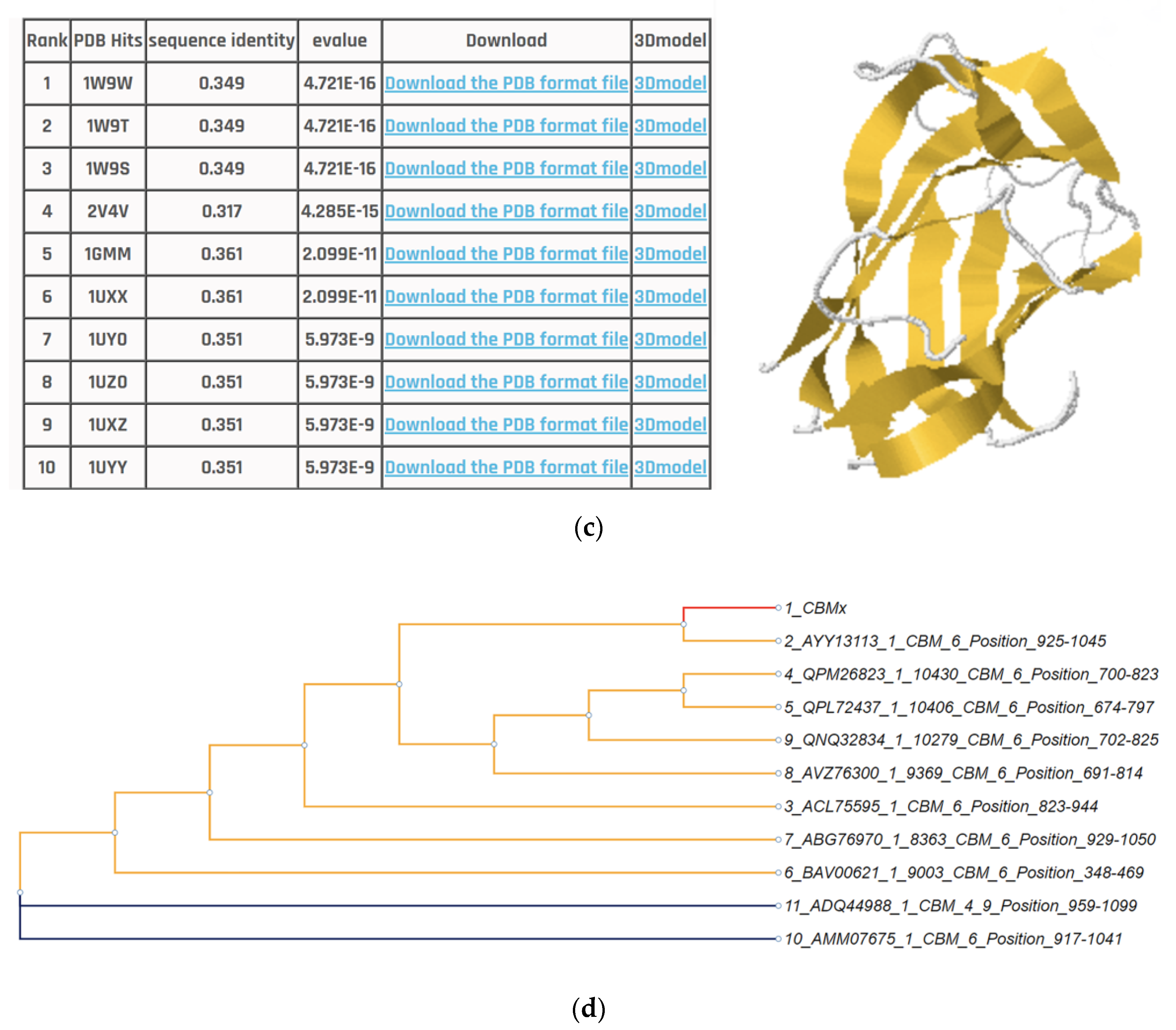
3.5. Application
3.6. Comparison to Other Databases
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sidar, A.; Albuquerque, E.D.; Voshol, G.P.; Ram, A.F.J.; Vijgenboom, E.; Punt, P.J. Carbohydrate Binding Modules: Diversity of Domain Architecture in Amylases and Cellulases From Filamentous Microorganisms. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boraston, A.B.; Bolam, D.N.; Gilbert, H.J.; Davies, G.J. Carbohydrate-Binding Modules: Fine-Tuning Polysaccharide Recognition. Biochem. J. 2004, 382, 769–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guillén, D.; Sánchez, S.; Rodríguez-Sanoja, R. Carbohydrate-Binding Domains: Multiplicity of Biological Roles. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 85, 1241–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levy, I.; Shoseyov, O. Cellulose-Binding Domains: Biotechnological Applications. Biotechnol. Adv. 2002, 20, 191–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoseyov, O.; Shani, Z.; Levy, I. Carbohydrate Binding Modules: Biochemical Properties and Novel Applications. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2006, 70, 283–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Linder, M.; Teeri, T.T. The Roles and Function of Cellulose-Binding Domains. J. Biotechnol. 1997, 57, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Stuckey, J.A.; Wishart, M.J.; Dixon, J.E. A Unique Carbohydrate Binding Domain Targets the Lafora Disease Phosphatase to Glycogen. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 2377–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McCartney, L.; Gilbert, H.; Bolam, D.; Boraston, A.; Knox, P. Glycoside Hydrolase Carbohydrate-Binding Modules as Molecular Probes for the Analysis of Plant Cell Wall Polymers. Anal. Biochem. 2004, 326, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barral, P.; Suárez, C.; Batanero, E.; Alfonso, C.; Alché, J.D.D.; Rodríguez-García, M.I.; Villalba, M.; Rivas, G.; Rodríguez, R. An Olive Pollen Protein with Allergenic Activity, Ole e 10, Defines a Novel Family of Carbohydrate-Binding Modules and Is Potentially Implicated in Pollen Germination. Biochem. J. 2005, 390, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, P.-J.; Chen, G.-J.; Wang, T.-H.; Zhang, Y.-S.; Liu, J. Non-Hydrolytic Disruption of Crystalline Structure of Cellulose by Cellulose Binding Domain and Linker Sequence of Cellobiohydrolase I from Penicillium Janthinellum. Sheng Wu Hua Xue Yu Sheng Wu Wu Li Xue Bao Acta Biochim. Et Biophys. Sin. 2001, 33, 13–18. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, P. A Novel Function for the Cellulose Binding Module of Cellobiohydrolase I. Sci. China C Life Sci. 2008, 51, 620–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, J. Entrez Direct: E-Utilities on the Unix Command Line. In Entrez Program. Util. Help. [Internet]; National Center for Biotechnology Information: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Hmmer.org. Available online: http://hmmer.org/ (accessed on 1 June 2022).
- Camacho, C.; Coulouris, G.; Avagyan, V.; Ma, N.; Papadopoulos, J.; Bealer, K.; Madden, T.L. BLAST+: Architecture and Applications. BMC Bioinform. 2009, 10, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sievers, F.; Higgins, D.G. Clustal Omega for Making Accurate Alignments of Many Protein Sequences: Clustal Omega for Many Protein Sequences. Protein Sci. 2018, 27, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jovanovic, N.; Mikheyev, A.S. Interactive Web-Based Visualization and Sharing of Phylogenetic Trees Using Phylogeny.IO. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W266–W269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dotsika, F. Semantic APIs: Scaling up towards the Semantic Web. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2010, 30, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, R.M. Jmol–A Paradigm Shift in Crystallographic Visualization. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2010, 43, 1250–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Needleman, S.B.; Wunsch, C.D. A General Method Applicable to the Search for Similarities in the Amino Acid Sequence of Two Proteins. J. Mol. Biol. 1970, 48, 443–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackshields, G.; Sievers, F.; Shi, W.; Wilm, A.; Higgins, D.G. Sequence Embedding for Fast Construction of Guide Trees for Multiple Sequence Alignment. Algorithms Mol. Biol. 2010, 5, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sievers, F. Fast, Scalable Generation of Highquality Protein Multiple Sequence Alignments Using Clustal Omega. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2011, 7, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eddy, S.R. What Is a Hidden Markov Model? Nat. Biotechnol. 2004, 22, 1315–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abbott, D.W.; van Bueren, A.L. Using Structure to Inform Carbohydrate Binding Module Function. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2014, 28, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Li, H.; Sun, J.; Guo, X.; Zhang, X.; Tao, M.; Chen, X.; Li, X. Novel Endotype Xanthanase from Xanthan-Degrading Microbacterium Sp. Strain XT11. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 85, e01800–e01818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cantarel, B.L.; Coutinho, P.M.; Rancurel, C.; Bernard, T.; Lombard, V.; Henrissat, B. The Carbohydrate-Active EnZymes Database (CAZy): An Expert Resource for Glycogenomics. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, D233–D238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yohe, T.; Huang, L.; Entwistle, S.; Wu, P.; Yang, Z.; Busk, P.K.; Xu, Y.; Yin, Y. DbCAN2: A Meta Server for Automated Carbohydrate-Active Enzyme Annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W95–W101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, X.; Xie, X.; Wang, X.; Yu, Z.; Chen, X.; Yang, F. CBMDB: A Database for Accessing, Analyzing, and Mining CBM Information. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 7842. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12157842
Lin X, Xie X, Wang X, Yu Z, Chen X, Yang F. CBMDB: A Database for Accessing, Analyzing, and Mining CBM Information. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(15):7842. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12157842
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Xu, Xiaoqi Xie, Xueyan Wang, Zhimin Yu, Xiaoyi Chen, and Fan Yang. 2022. "CBMDB: A Database for Accessing, Analyzing, and Mining CBM Information" Applied Sciences 12, no. 15: 7842. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12157842
APA StyleLin, X., Xie, X., Wang, X., Yu, Z., Chen, X., & Yang, F. (2022). CBMDB: A Database for Accessing, Analyzing, and Mining CBM Information. Applied Sciences, 12(15), 7842. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12157842





