Post-Authorship Attribution Using Regularized Deep Neural Network
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- The development of regularized deep neural-network method for improving the performance of a PAA system.
- The introduction of an interactive system to visualize the results of the PAA method, which could be useful in the process of an evidence-based forensic investigation.
- The demonstration of the performance of the proposed PAA method through experimental comparison with existing prominent methods.
2. Related Works
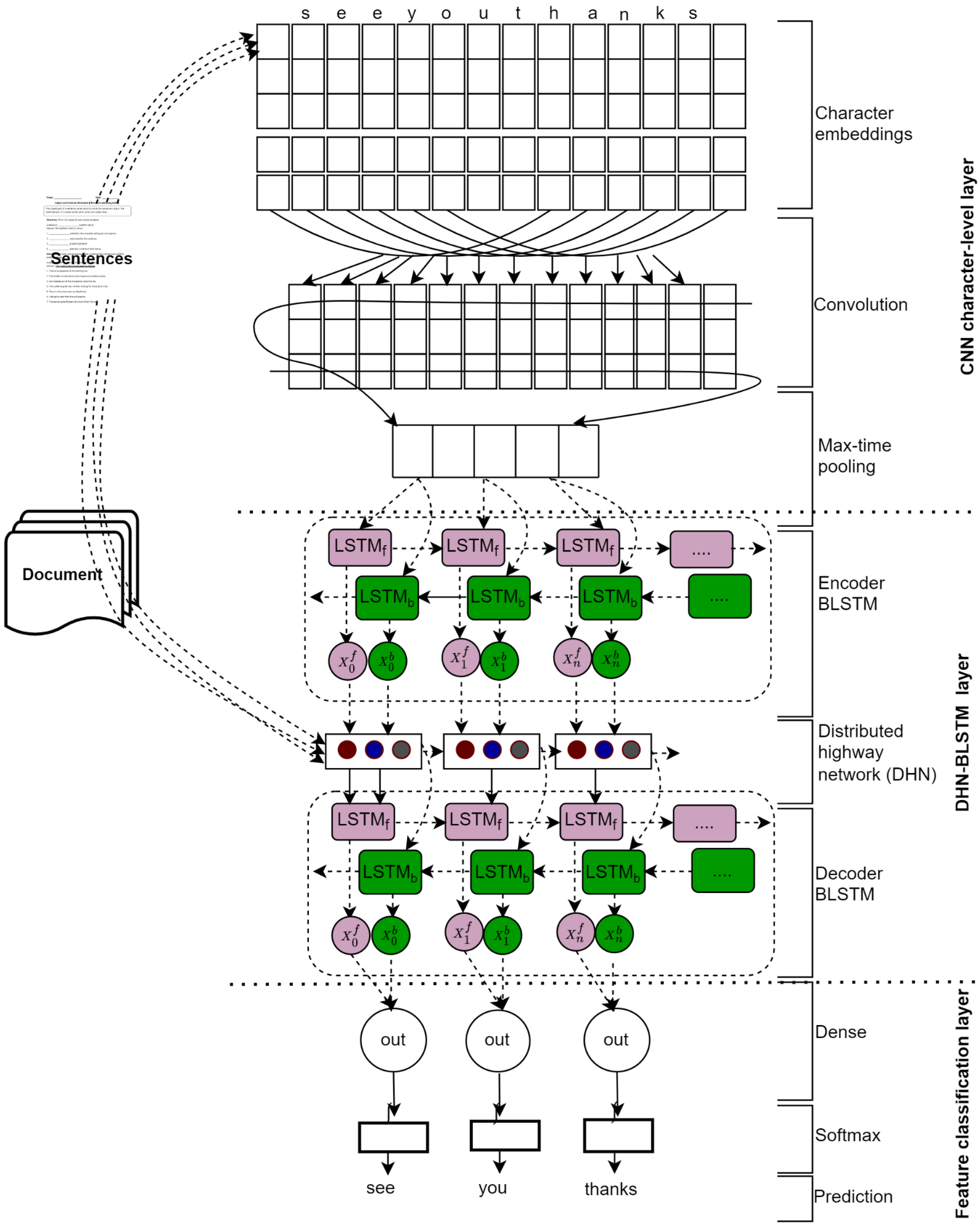
3. Proposed Method
3.1. CNN Character-Level Layer
3.2. Distributed Highway Network with Bidirectional Long Short-Term Memory
3.2.1. Distributed Highway Network
3.2.2. Bidirectional Long Short-Term Memory
3.3. Feature-Classification Layer
4. Experimental Results
4.1. Datasets
4.2. Parameter Settings
4.3. Results
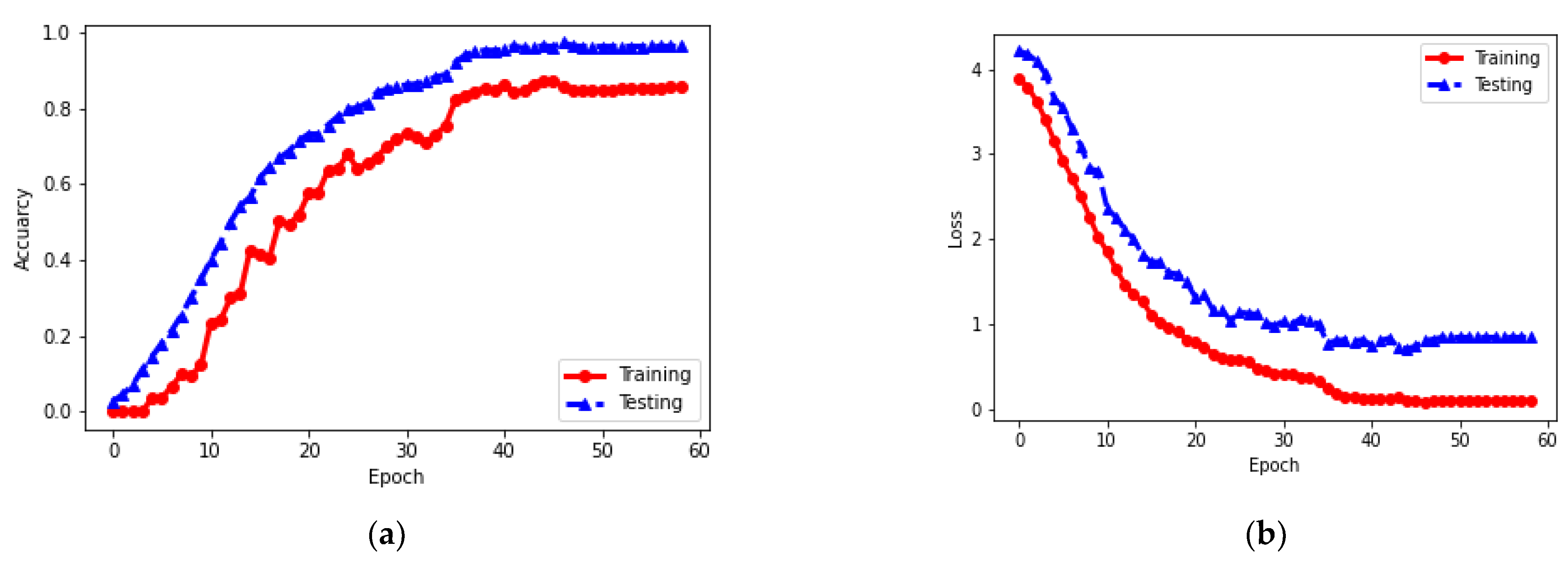
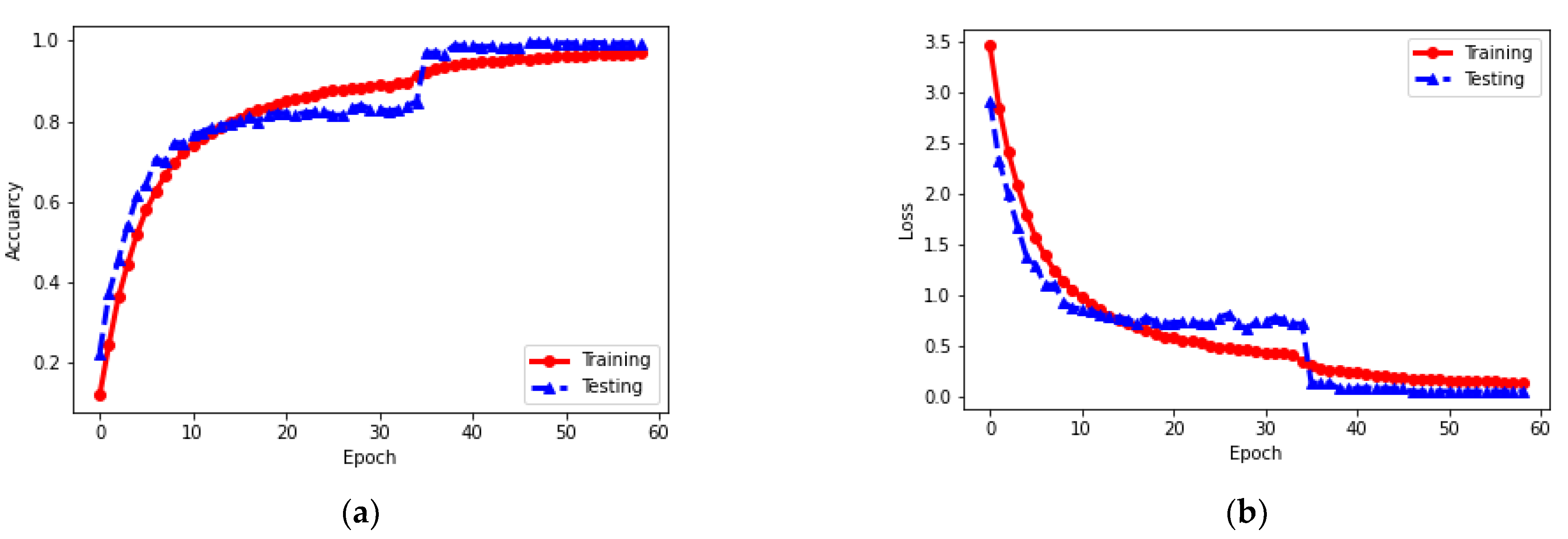
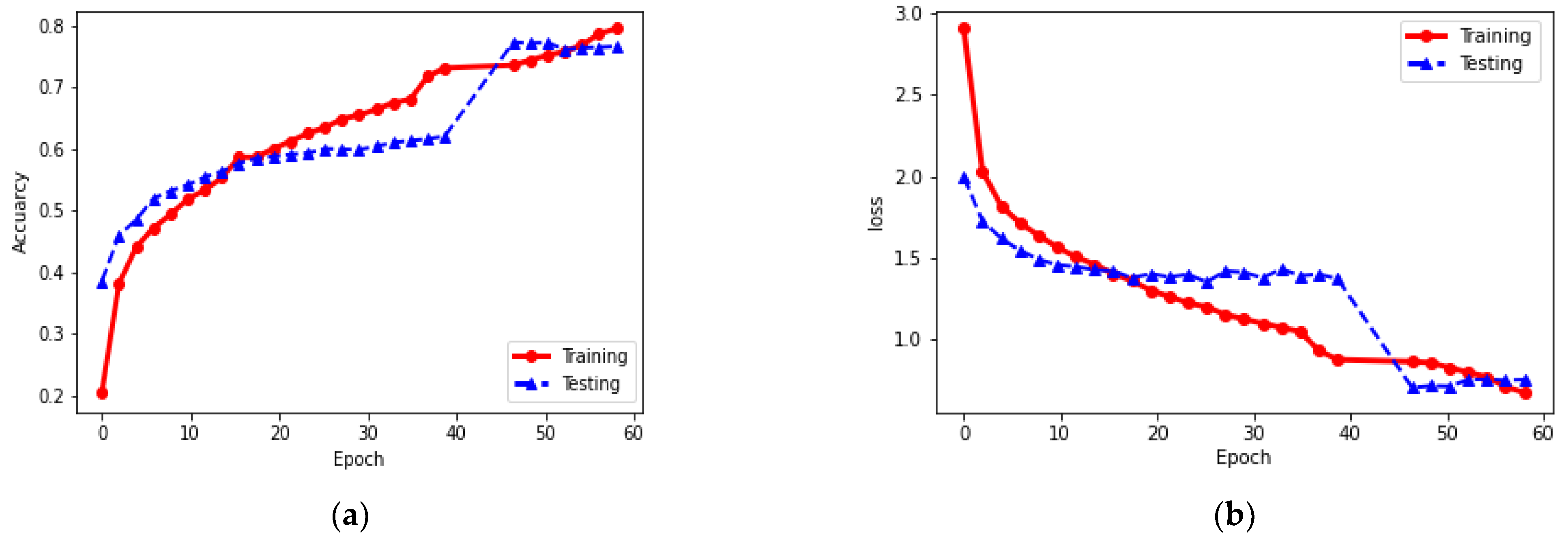
4.3.1. Quantitative Results
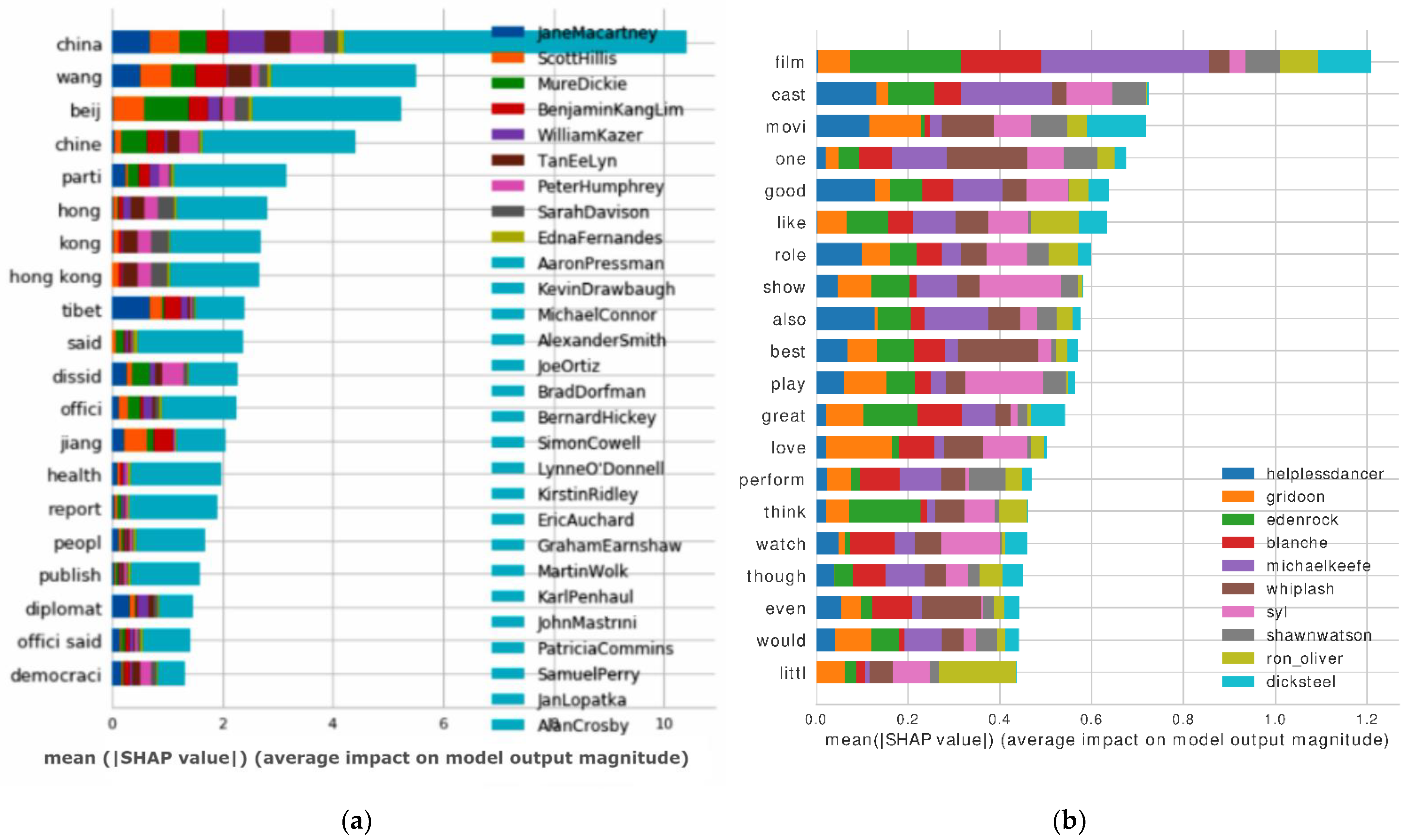
4.3.2. Result Visualization
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ding, S.H.H.; Fung, B.C.M.; Iqbal, F.; Cheung, W.K. Learning stylometric representations for authorship analysis. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2017, 49, 107–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Lv, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, L.; Wang, F.-Y. Detecting traffic information from social media texts with deep learning approaches. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2018, 20, 3049–3058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Java, A.; Song, X.; Finin, T.; Tseng, B. Why We Twitter: An Analysis of a Microblogging Community. In International Workshop on Social Network Mining and Analysis; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 118–138. [Google Scholar]
- Wikipedia. Twitter—Wikipedia. 2022. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Twitter (accessed on 14 June 2022).
- Mishne, G. Applied Text Analytics for Blogs. Universiteit van Amsterdam. 2007. Available online: http://brenocon.com/gilad_mishne_phd_thesis_ch6.pdf (accessed on 14 June 2022).
- Lin, Y. 10 Blogging Statistics You Need to Know in 2021 [Infographic]. 2021. Available online: https://www.oberlo.com/blog/blogging-statistics (accessed on 14 June 2022).
- Zheng, R.; Li, J.; Chen, H.; Huang, Z. A framework for authorship identification of online messages: Writing-style features and classification techniques. J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 2006, 57, 378–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abiodun, M.; Olugbara, O.O.; Ojo, S.O. Identifying Advanced Fee Fraud Activities on Internet Using Machine Learning Algorithms. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Computational Intelligence and Industrial Application, Wuhan, China, 6–7 November 2010; Volume 5. [Google Scholar]
- Afroz, S.; Brennan, M.; Greenstadt, R. Detecting Hoaxes, Frauds, and Deception in Writing Style Online. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy, San Francisco, CA, USA, 20–23 May 2012; pp. 461–475. [Google Scholar]
- Diale, M.; van der Walt, C.; Celik, T.; Modupe, A. Feature Selection and Support Vector Machine Hyper-Parameter Optimi-sation for Spam Detection. In Proceedings of the 2016 Pattern Recognition Association of South Africa and Robotics and Mechatronics International Conference (PRASA-RobMech), Stellenbosch, South Africa, 30 November–2 December 2016; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Gianfredi, V.; Bragazzi, N.L.; Nucci, D.; Martini, M.; Rosselli, R.; Minelli, L.; Moretti, M. Harnessing Big Data for Communicable Tropical and Sub-Tropical Disorders: Implications from a Systematic Review of the Literature. Front. Public Health 2018, 6, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonso-Fernandez, F.; Belvisi, N.M.S.; Hernandez-Diaz, K.; Muhammad, N.; Bigun, J. Writer identification using microblog-ging texts for social media forensics. IEEE Trans. Biom. Behav. Identity Sci. 2021, 3, 405–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, A.; Baron, A.; Rayson, P.; May-Chahal, C.; Greenwood, P.; Walkerdine, J. Who am I? Analyzing digital personas in cy-bercrime investigations. Computer 2013, 46, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobicev, V.; Sokolova, M.; el Emam, K.; Jafer, Y.; Dewar, B.; Jonker, E.; Matwin, S. Can anonymous posters on medical forums be reidentified? J. Med. Internet Res. 2013, 15, e2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wängqvist, M.; Frisén, A. Who am I online? Understanding the meaning of online contexts for identity development. Adolesc. Res. Rev. 2016, 1, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennan, M.; Afroz, S.; Greenstadt, R. Adversarial stylometry: Circumventing authorship recognition to preserve privacy and anonymity. ACM Trans. Inf. Syst. Secur. 2012, 15, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afroz, S.; Islam, A.C.; Stolerman, A.; Greenstadt, R.; McCoy, D. Doppelgänger Finder: Taking Stylometry to the Underground. In Proceedings of the IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy, San Jose, CA, USA, 18–21 May 2014; pp. 212–226. [Google Scholar]
- Altakrori, M.H.; Iqbal, F.; Fung, B.C.M.; Ding, S.H.H.; Tubaishat, A. Arabic Authorship Attribution: An Extensive Study on Twitter Posts. ACM Trans. Asian Low Resour. Lang. Inf. Process. 2018, 18, 1–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, A.; Scheirer, W.J.; Forstall, C.W.; Cavalcante, T.; Theophilo, A.; Shen, B.; Carvalho, A.R.B.; Stamatatos, E. Authorship attribution for social media forensics. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2016, 12, 5–33. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, C.; Ginsberg, A. Social Networking without Sacrificing Privacy. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on System Science and Engineering (ICSSE), New Taipei City, Taiwan, 28–30 June 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Stamatatos, E. A survey of modern authorship attribution methods. J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 2009, 60, 538–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koppel, M.; Schler, J.; Argamon, S. Computational methods in authorship attribution. J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 2009, 60, 9–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neal, T.; Sundararajan, K.; Fatima, A.; Yan, Y.; Xiang, Y.; Woodard, D. Surveying stylometry techniques and applications. ACM Comput. Surv. 2017, 50, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalgutkar, V.; Kaur, R.; Gonzalez, H.; Stakhanova, N.; Matyukhina, A. Code authorship attribution: Methods and challenges. ACM Comput. Surv. 2019, 52, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcu, D. The rhetorical parsing of unrestricted texts: A surface-based approach. Comput. Linguist. 2000, 26, 395–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarwar, R.; Yu, C.; Tungare, N.; Chitavisutthivong, K.; Sriratanawilai, S.; Xu, Y.; Chow, D.; Rakthanmanon, T.; Nutanong, S. An effective and scalable framework for authorship attribution query processing. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 50030–50048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, F.; Hadjidj, R.; Fung, B.C.M.; Debbabi, M. A novel approach of mining write-prints for authorship attribution in e-mail forensics. Digit. Investig. 2008, 5, S42–S51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanisz, T.; Kwapień, J.; Drożdż, S. Linguistic data mining with complex networks: A stylometric-oriented approach. Inf. Sci. 2019, 482, 301–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modupe, A.; Olugbara, O.O.; Ojo, S.O. Exploring Support Vector Machines and Random Forests to Detect Advanced Fee Fraud Activities on Internet. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE 11th International Conference on Data Mining Workshops, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 11 December 2011; pp. 331–335. [Google Scholar]
- Modupe, A.; Olugbara, O.O.; Ojo, S.O. Comparing Supervised Learning Classifiers to Detect Advanced Fee Fraud Activities on Internet. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Science and Information Technology, Bangalore, India, 2–4 January 2012; pp. 87–100. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, S.H.H.; Fung, B.C.M.; Debbabi, M. A visualizable evidence-driven approach for authorship attribution. ACM Trans. Inf. Syst. Secur. 2015, 17, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kešelj, V.; Peng, F.; Cercone, N.; Thomas, C. N-gram-based author profiles for authorship attribution. In Proceedings of the Conference Pacific Association for Computational Linguistics, Halifax, NS, Canada, 22–25 August 2003; Volume 3, pp. 255–264. [Google Scholar]
- Stamatatos, E.; Koppel, M. Plagiarism and authorship analysis: Introduction to the special issue. Lang. Resour. Eval. 2011, 45, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramnial, H.; Panchoo, S.; Pudaruth, S. Authorship attribution using stylometry and machine learning techniques. In Intelligent Systems Technologies and Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 113–125. [Google Scholar]
- Fabien, M.; Villatoro-Tello, E.; Motlicek, P.; Parida, S. BertAA: BERT fine-tuning for authorship attribution. In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Natural Language Processing (ICON), Bihar, India, 18–21 December 2020; pp. 127–137. [Google Scholar]
- Pennacchiotti, M.; Popescu, A.-M. A Machine Learning Approach to Twitter user Classification. In Proceedings of the Inter-national AAAI Conference on Web and Social Media, Barcelona, Spain, 17–21 July 2011; Volume 5. [Google Scholar]
- Weren, R.D.; Kauer, A.U.; Mizusaki, L.; Moreira, V.P.; de Oliveira, J.P.M.; Wives, L.K. Examining multiple features for author profiling. J. Inf. Data Manag. 2014, 5, 266. [Google Scholar]
- Golbeck, J.; Hansen, D. Computing political preference among Twitter followers. In Proceedings of the SIGCHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 7–12 May 2011; pp. 1105–1108. [Google Scholar]
- Golbeck, J.; Hansen, D. A method for computing political preference among Twitter followers. Soc. Netw. 2014, 36, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conover, M.; Ratkiewicz, J.; Francisco, M.; Gonçalves, B.; Menczer, F.; Flammini, A. Political polarization on Twitter. In Proceedings of the International AAAI Conference on Web and Social Media, Barcelona, Spain, 17–21 July 2011; Volume 5, pp. 89–96. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, W.; Liu, R.; Wang, L.; Vosoughi, S. Towards improved model design for authorship identification: A survey on writing style understanding: A survey on writing style understanding. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2009.14445. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Zobel, J. Searching with style: Authorship attribution in classic literature. In ACM International Conference Proceeding Series; Australian Computer Society, Inc.: Sydney, Australia, 2007; Volume 244, pp. 59–68. [Google Scholar]
- Hirst, G.; Feiguina, O. Bigrams of syntactic labels for authorship discrimination of short texts. Lit. Linguist. Comput. 2007, 22, 405–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frantzeskou, G.; Stamatatos, E.; Gritzalis, S.; Katsikas, S. Effective Identification of Source Code Authors Using Byte-Level Information. In Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Software Engineering, Shanghai, China, 20–28 May 2006; pp. 893–896. [Google Scholar]
- Frantzeskou, G.; Stamatatos, E.; Gritzalis, S.; Katsikas, S. Source Code Author Identification Based on N-Gram Author Profiles. In IFIP International Conference on Artificial Intelligence Applications and Innovations; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2006; pp. 508–515. [Google Scholar]
- Frantzeskou, G.; Stamatatos, E.; Gritzalis, S.; Chaski, C.E.; Howald, B.S. Identifying Authorship by Byte-Level n-Grams: The Source Code Author Profile (Scap) Method. Int. J. Digit. Evid. 2007, 6, 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Escalante, J.; Solorio, T.; Montes, M. Local Histograms of Character N-grams for Authorship Attribution. In Proceedings of the 49th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, Portland, OR, USA, 19–24 June 2011; pp. 288–298. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, D.D.; Yang, Y.; Russell-Rose, T.; Li, F. Rcv1: A new benchmark collection for text categorization research. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2004, 5, 361–397. [Google Scholar]
- Koppel, M.; Schler, J.; Argamon, S.; Messeri, E. Authorship Attribution with Thousands of Candidate Authors. In Proceedings of the 29th Annual International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, Seattle, WA, USA, 6–11 August 2006; pp. 659–660. [Google Scholar]
- Koppel, M.; Schler, J.; Argamon, S. Authorship attribution in the wild. Lang. Resour. Eval. 2011, 45, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapkota, U.; Bethard, S.; Montes, M.; Solorio, T. Not all character n-grams are created equal: A study in authorship attribution. In Proceedings of the 2015 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, Denver, CO, USA, 31 May–5 June 2015; pp. 93–102. [Google Scholar]
- Plakias, S.; Stamatatos, E. Tensor space models for authorship identification. In Proceedings of the Hellenic Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Syros, Greece, 2–4 October 2008; pp. 239–249. [Google Scholar]
- Muttenthaler, L.; Lucas, G.; Amann, J. Authorship Attribution in Fan-Fictional Texts Given Variable Length Character and Word N-grams. Notebook for PAN at CLEF 2019. Available online: http://ceur-ws.org/Vol-2380/paper_49.pdf (accessed on 20 January 2022).
- PAN. Cross-Domain Authorship Attribution 2019. Available online: https://pan.webis.de/clef19/pan19-web/authorship-attribution.html (accessed on 20 January 2022).
- Markov, I.; Stamatatos, E.; Sidorov, G. Improving Cross-Topic Authorship Attribution: The Role of Pre-Processing. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computational Linguistics and Intelligent Text Processing, Budapest, Hungary, 17–23 April 2017; pp. 289–302. [Google Scholar]
- Seroussi, Y.; Zukerman, I.; Bohnert, F. Authorship attribution with topic models. Comput. Linguist. 2014, 40, 269–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen-Zvi, M.; Griffiths, T.; Steyvers, M.; Smyth, P. The Author-Topic Model for Authors and Documents. In Proceedings of the 20th Conference on Uncertainty in Artificial Intelligence, Banff, AB, Canada, 7–11 July 2004; pp. 487–494. [Google Scholar]
- Blei, D.M.; Ng, A.Y.; Jordan, M.I. Latent Dirichlet allocation. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2003, 3, 993–1022. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.; Zhou, Y.; Sun, W. Character-level text classification via convolutional neural network and gated recurrent unit. Int. J. Mach. Learn. Cybern. 2020, 11, 1939–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sari, Y.; Vlachos, A.; Stevenson, M. Continuous n-gram representations for authorship attribution. In Proceedings of the 15th Conference of the European Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Valencia, Spain, 3–7 April 2017; Volume 2, pp. 267–273. [Google Scholar]
- Ullah, F.; Wang, J.; Jabbar, S.; Al-Turjman, F.; Alazab, M. Source Code Authorship Attribution Using Hybrid Approach of Program Dependence Graph and Deep Learning Model. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 141987–141999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alrabaee, S.; Shirani, P.; Debbabi, M.; Wang, L. On the Feasibility of Malware Authorship Attribution. In International Symposium on Foundations and Practice of Security; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 256–272. [Google Scholar]
- Burrows, S.; Tahaghoghi, S.M.M. Source Code Authorship Attribution Using N-grams. In Proceedings of the Twelth Australasian Document Computing Symposium, Melbourne, Australia, 10 December 2007; pp. 32–39. [Google Scholar]
- Bandara, U.; Wijayarathna, G. Source Code Author Identification with Unsupervised Feature Learning. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2013, 34, 330–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsulami, B.; Dauber, E.; Harang, R.; Mancoridis, S.; Greenstadt, R. Source Code Authorship Attribution Using Long Short-Term Memory Based Networks. In European Symposium on Research in Computer Security; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 65–82. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, S.; Wu, J.; Niu, Z. Authorship Identification of Source Codes. In Asia-Pacific Web (APWeb) and Web-Age Information Management (WAIM) Joint Conference on Web and Big Data; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 282–296. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, B.; Park, J.; Suh, J. Transparency and accountability in AI decision support: Explaining and visualizing convolutional neural networks for text information. Decis. Support Syst. 2020, 134, 113302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Layton, R.; McCombie, S.; Watters, P. Authorship attribution of IRC messages using inverse author frequency. In Proceedings of the 2012 Third Cybercrime and Trustworthy Computing Workshop, Ballarat, Australia, 29–30 October 2012; pp. 7–13. [Google Scholar]
- Juola, P. Authorship Attribution; Now Publishers Inc.: Norwell, MA, USA, 2008; Volume 3. [Google Scholar]
- Layton, R.; Watters, P.; Dazeley, R. Recentred local profiles for authorship attribution. Nat. Lang. Eng. 2012, 18, 293–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, R.; Tsur, O.; Rappoport, A.; Koppel, M. Authorship attribution of micro-messages. In Proceedings of the 2013 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Seattle, WA, USA, 18–21 October 2013; pp. 1880–1891. [Google Scholar]
- Donais, J.A.; Frost, R.A.; Peelar, S.M.; Roddy, R.A. A system for the automated author attribution of text and instant messages. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE/ACM International Conference on Advances in Social Networks Analysis and Mining, Niagara, ON, Canada, 25–28 August 2013; pp. 1484–1485. [Google Scholar]
- Okuno, S.; Asai, H.; Yamana, H. A challenge of authorship identification for ten-thousand-scale microblog users. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Big Data (Big Data), Washington, DC, USA, 27–30 October 2014; pp. 52–54. [Google Scholar]
- Bhargava, M.; Mehndiratta, P.; Asawa, K. Stylometric analysis for authorship attribution on Twitter. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Big Data Analytics, Silicon Valley, CA, USA, 6–9 October 2013; pp. 37–47. [Google Scholar]
- Ruder, S.; Ghaffari, P.; Breslin, J.G. Character-level and multi-channel convolutional neural networks for large-scale authorship attribution. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1609.06686. [Google Scholar]
- Shrestha, P.; Sierra, S.; González, F.A.; Montes-y-Gómez, M.; Rosso, P.; Solorio, T. Convolutional neural networks for au-thorship attribution of short texts. In Proceedings of the 15th Conference of the European Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics EACL, Valencia, Spain, 3–7 April 2017; pp. 669–674. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R.; Hu, Z.; Guo, H.; Mao, Y. Syntax encoding with application in authorship attribution. In Proceedings of the 2018 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Brussels, Belgium, 31 October–4 November 2018; pp. 2742–2753. [Google Scholar]
- Jafariakinabad, F.; Hua, K.A. Style-Aware Neural Model with Application in Authorship Attribution. In Proceedings of the 2019 18th IEEE International Conference on Machine Learning and Applications (ICMLA), Boca Raton, FL, USA, 16–19 December 2019; pp. 325–328. [Google Scholar]
- Jafariakinabad, F.; Tarnpradab, S.; Hua, K.A. Syntactic neural model for authorship attribution. In Proceedings of the Thirty-Third International Flairs Conference, Miami, FL, USA, 17–18 May 2020; pp. 234–239. [Google Scholar]
- Seroussi, Y.; Zukerman, I.; Bohnert, F. Authorship attribution with latent Dirichlet allocation. In Proceedings of the Fifteenth Conference on Computational Natural Language Learning, Portland, OR, USA, 23–24 June 2011; pp. 181–189. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y. Convolutional neural networks for sentence classification. In Proceedings of the 2014 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), Doha, Qatar, 25–29 October 2014; pp. 1746–1751. [Google Scholar]
- al Zamal, F.; Liu, W.; Ruths, D. Homophily and latent attribute inference: Inferring latent attributes of Twitter users from neighbors. In Proceedings of the International AAAI Conference on Web and Social Media, Dublin, Ireland, 4–7 June 2012; Volume 6, pp. 387–390. [Google Scholar]
- Hitschler, J.; van den Berg, E.; Rehbein, I. Authorship attribution with convolutional neural networks and POS-Eliding. In Proceedings of the Workshop on Stylistic Variation, Copenhagen, Denmark, 8 September 2017; pp. 53–58. [Google Scholar]
- Bird, S.; Dale, R.; Dorr, B.J.; Gibson, B.; Joseph, M.T.; Kan, M.; Lee, D.; Powley, B.; Radev, D.R.; Tan, Y.F. The ACL anthology reference corpus: A reference dataset for bibliographic research in computational linguistics. In Proceedings of the Sixth In-ternational Conference on Language Resources and Evaluation (LREC’08), Marrakech, Morocco, 28–30 May 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Z.; Lee, R.K.-W.; Wang, L.; Lim, E.; Dai, B. Deepstyle: User style embedding for authorship attribution of short texts. In Proceedings of the Asia-Pacific Web (APWeb) and Web-Age Information Management (WAIM) Joint International Conference on Web and Big Data, Tianjin, China, 12–14 August 2020; pp. 221–229. [Google Scholar]
- Schler, J.; Koppel, M.; Argamon, S.; Pennebaker, J.W. Effects of age and gender on blogging. In Proceedings of the AAAI Spring Symposium: Computational Approaches to Analyzing Weblogs, Stanford, CA, USA, 27–29 March 2006; Volume 6, pp. 199–205. [Google Scholar]
- Murauer, B.; Specht, G. Developing a benchmark for reducing data bias in authorship attribution. In Proceedings of the 2nd Workshop on Evaluation and Comparison of NLP Systems, Punta Cana, Dominican Republic, 10–11 November 2021; pp. 179–188. [Google Scholar]
- Devlin, J.; Chang, M.-W.; Lee, K.; Toutanova, K. Bert: Pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language under-standing. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1810.04805. [Google Scholar]
- Sanh, V.; Debut, L.; Chaumond, J.; Wolf, T. DistilBERT, a distilled version of BERT: Smaller, faster, cheaper and lighter. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1910.01108. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Ott, M.; Goyal, N.; Du, J.; Joshi, M.; Chen, D.; Levy, O.; Lewis, M.; Zettlemoyer, L.; Stoyanov, V. Roberta: A robustly optimized Bert pretraining approach. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1907.11692. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, Q. Exploring Syntactic and Semantic Features for Authorship Attribution. Appl. Soft Comput. 2021, 111, 107815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Jernite, Y.; Sontag, D.; Rush, A.M. Character-aware neural language models. In Proceedings of the Thirtieth AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Phoenix, AZ, USA, 12–17 February 2016; pp. 2741–2749. [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava, R.K.; Greff, K.; Schmidhuber, J. Training very deep networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2015, 28, 2377–2385. [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro, T.; Singh, S.; Guestrin, C. ‘Why should I trust you?’ Explaining the predictions of any classifier. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–17 August 2016; pp. 1135–1144. [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg, S.M.; Lee, S.-I. A unified approach to interpreting model predictions. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2017, 30, 4768–4777. [Google Scholar]
- Mikolov, T.; Sutskever, I.; Chen, K.; Corrado, G.; Dean, J. Distributed representations of words and phrases and their compo-sitionality. In Proceedings of the 26th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Lake Tahoe, NV, USA, 5–10 December 2013; Volume 2, pp. 3111–3119. [Google Scholar]
- Le, Q.; Mikolov, T. Distributed representations of sentences and documents. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Beijing, China, 21–26 June 2014; pp. 1188–1196. [Google Scholar]
- Loshchilov, I.; Hutter, F. Fixing Weight Decay Regularization in Adam. 2018. Available online: https://openreview.net/pdf?id=rk6qdGgCZ (accessed on 16 August 2021).
- Seroussi, Y.; Zukerman, I.; Bohnert, F. Collaborative inference of sentiments from texts. In Proceedings of the International Conference on User Modeling, Adaptation, and Personalization, Manoa, HI, USA, 20–14 June 2010; pp. 195–206. [Google Scholar]
- Glorot, X.; Bengio, Y. Understanding the difficulty of training deep feedforward neural networks. In Proceedings of the Thirteenth International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics, Sardinia, Italy, 13–15 May 2010; pp. 249–256. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. A method for stochastic optimization. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.6980. [Google Scholar]
- Vilar, D.; Federico, M. A statistical extension of byte-pair encoding. In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Spoken Language Translation (IWSLT 2021), Bangkok, Thailand, 5–6 August 2021; pp. 263–275. [Google Scholar]
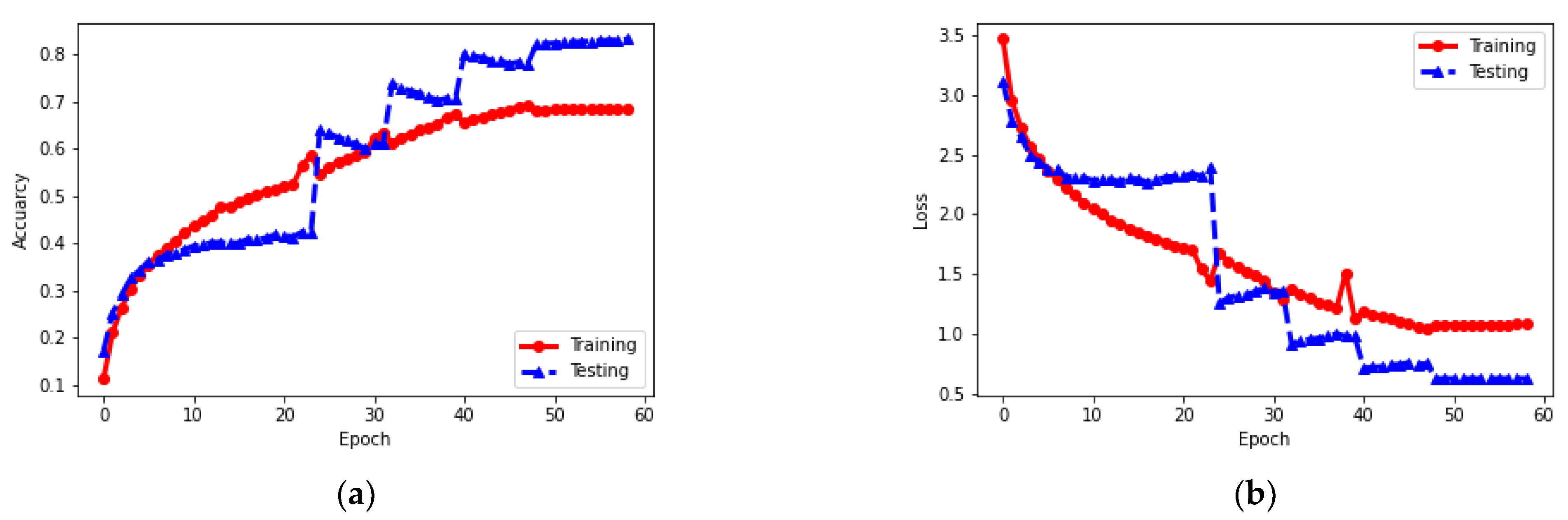
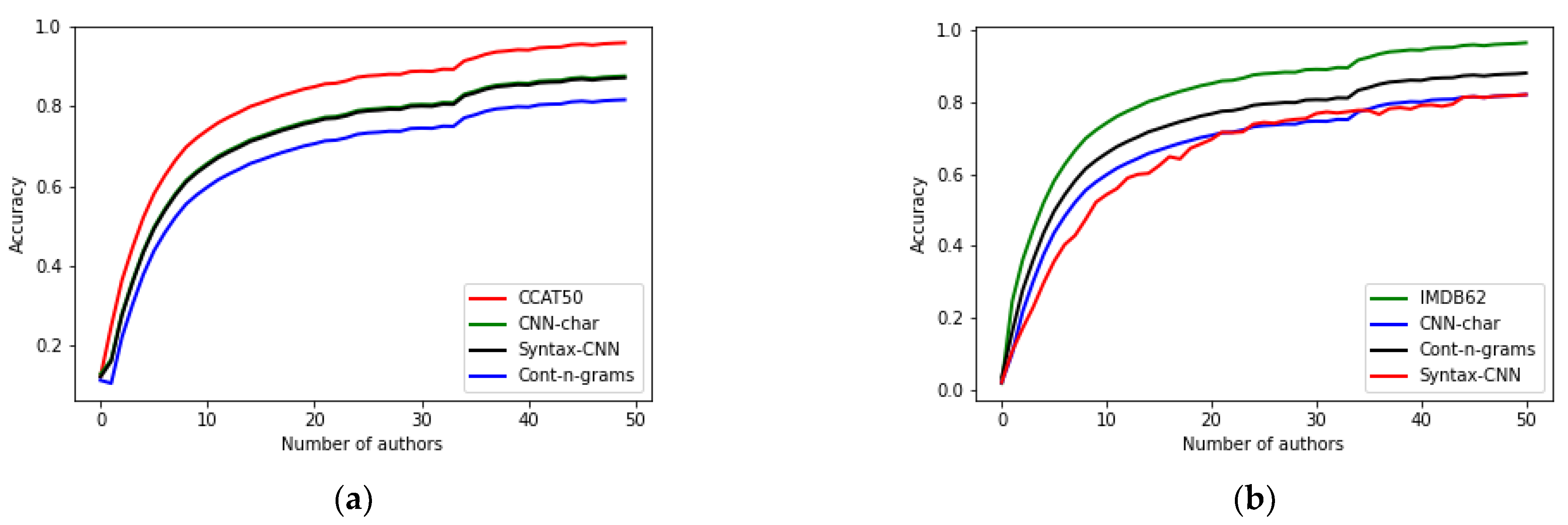
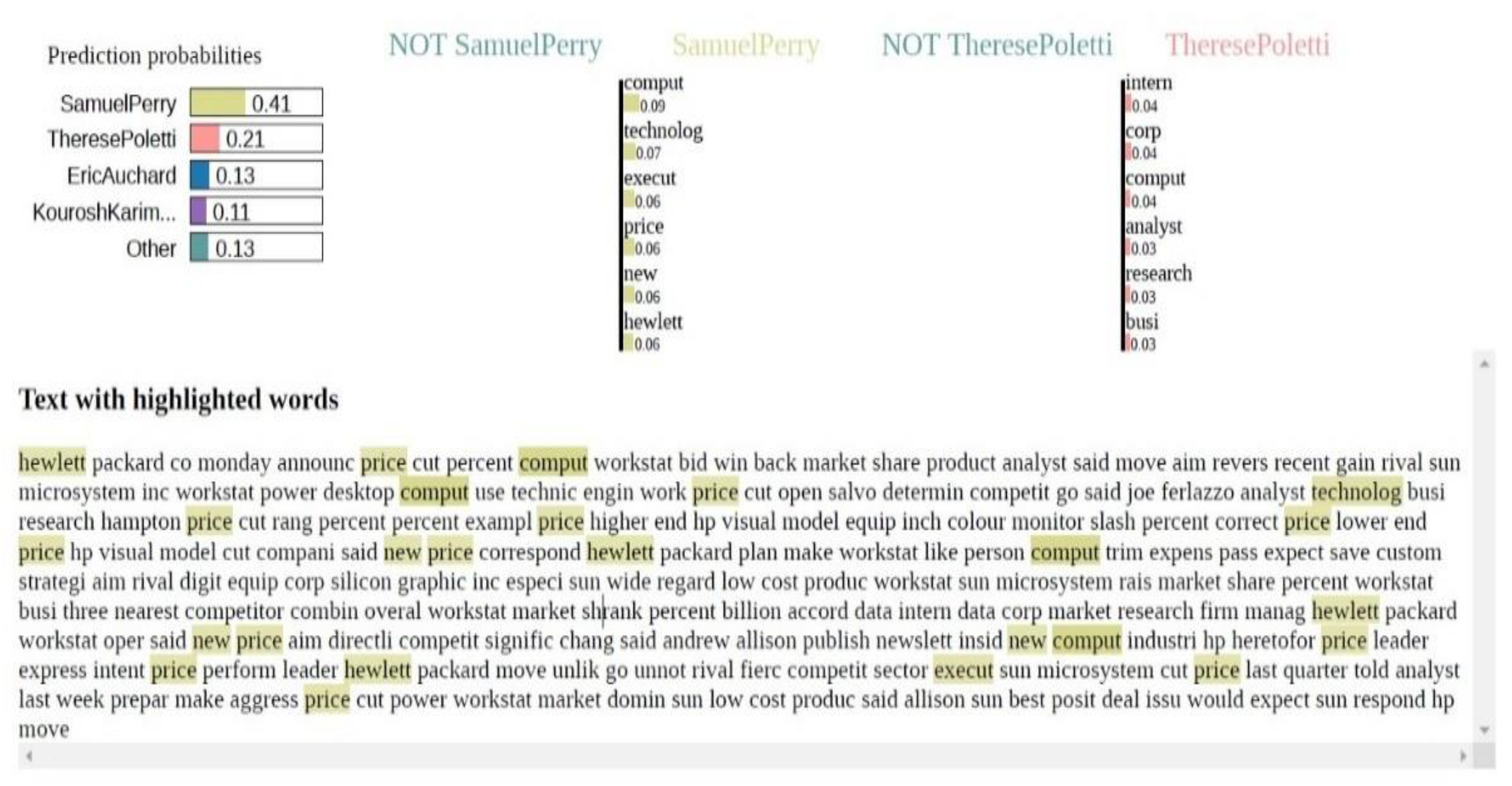

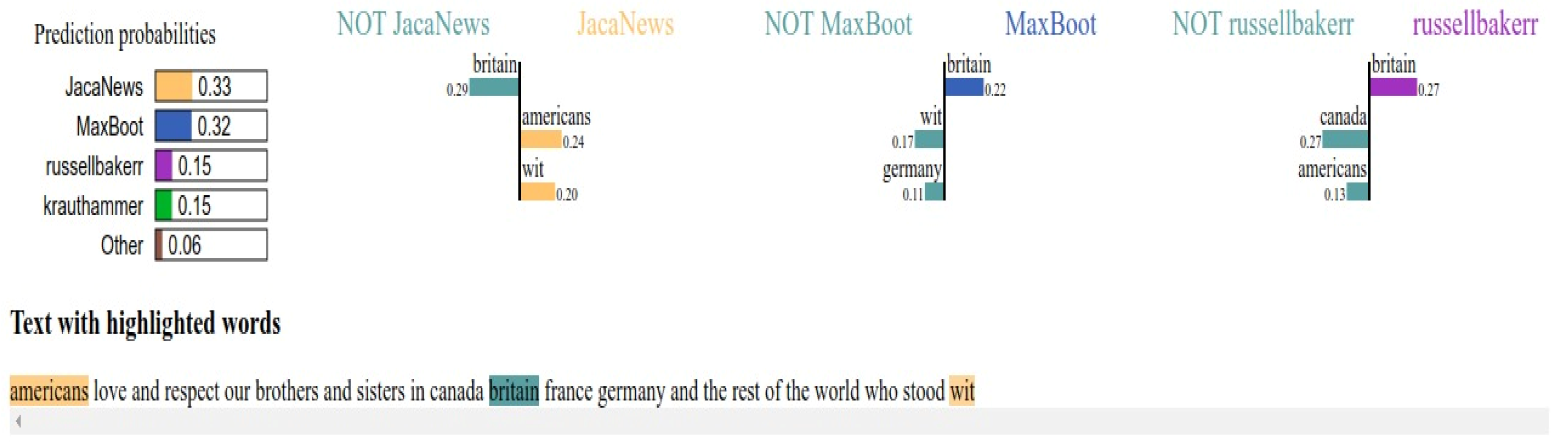


| Reference | Features | Representation | Classification Method | Visualization | Data |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [1] | Lexical, syntactic, and topical | Word2Vec, and Doc2Vec | Shallow NN and SoftMax | No | |
| [19] | Lexical, syntactic, and structural | BOW over n-grams | SVM, RF, and SCAP | No | |
| [22] | Stylometric | Character n-grams and word | SVM and Bayesian | No | Literature corpus, email, and blog posts |
| [32] | Lexical | Byte-level n-grams | Dissimilarity measure | No | English and Chinese |
| [35] | Lexical and syntactic | BERT | Dense, SoftMax | No | Email, IMDB, and blog posts |
| [78] | Lexical, syntactic, and structural | CNN, LSTM, and attention | SoftMax | No | CCAT10, CCAT50, Blogs10, and Blogs50 |
| [45] | Lexical | Byte-level n-grams | Dissimilarity Measure | No | Source code |
| [46] | Lexical | Character-level n-grams | SVM | No | CCAT10 |
| [49] | Lexical and syntactic | TF-IDF over word, character | SVM | No | English blog posts |
| [50] | Lexical and syntactic | Character-level n-grams | Similarity-based methods | No | Blog posts |
| [51] | Lexical and syntactic | Character-level n-grams, affix punctuation 3-g | SVM | No | CCAT10, and CCAT50 |
| [52] | Lexical and syntactic | Frequent 3-g | SVM | No | CCAT10, and CCAT50 |
| [53] | Lexical and syntactic | TF-IDF over n-grams | Soft voting ensemble | No | PAN 2019 |
| [55] | Lexical and syntactic | Punctuation marks, name entity, and character n-grams | SVM | No | CCAT10 |
| [61,62,63] | Lexical syntactic, and structural | LDA, AT, and DADT | Probabilistic Model | No | Judgment, email, and IMDB |
| [60] | Lexical, syntactic, and structural | Character, word, and FastText | SoftMax | No | Judgment, IMDB62, and CCAT50 |
| [68] | Lexical | Weighting n-gram | CNG, SCAP, and RLP | No | IRC, and |
| [71] | Lexical and syntactic | Character, Word n-gram, and K-signature | Linear SVM | No | |
| [72] | Lexical | ChatSafe | NB | No | SMS |
| [73] | Lexical and syntactic | POS tag combine n-grams | Cosine Similarity | No | |
| [74] | Lexical, syntactic, and structural | NLTP | SVM | No | |
| [75] | Lexical and syntactic | Character and word-level n-grams | Word embedding, CNN, and SoftMax | No | Email, Blogs, Redditt, and Twitter |
| [77] | Lexical and syntactic | Syntax Parse Tree | CNN, SoftMax | No | CCAT10, CCAT50, IMDB, and Blogs |
| [83] | Lexical and syntactic | POS tag and word embedding | CNN, SoftMax | No | ARC |
| [85] | Lexical, syntactic, and structural | Character, word, n-gram, and POS tags | CNN, SoftMax | No | Twitter and Weibo |
| [87] | Lexical, syntactic, and structural | BERT, RoBERT, and DistilBERT | SoftMax | No | CCAT10, IMDB, and Reddit |
| RDNN | Lexical, syntactic, and structural | Character-level CNN and DHN-BLSTM | Dense and SoftMax | Yes | CCAT50, IMDB62, Blogs50, and Twitter50 |
| Datasets | Classes | Word Size | Character Size | Average per Author | Total Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CCAT50 | 50 | 584 | 3010 | 100 | 5000 |
| IMDB62 | 62 | 345 | 1742 | 542 | 62,985 |
| Blogs50 | 50 | 117 | 542 | 682 | 681,288 |
| Twitter50 | 50 | 36 | 119 | 270 | 1,109,964 |
| Layers | Parameters | CCAT50 | IMDB62 | Blogs50 | Twitter50 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CNN Character-level | d | 30 | 70 | 70 | 70 |
| f | ReLU | ReLU | ReLU | RELU | |
| 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | ||
| 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | ||
| BLSTM | m | 128 | 128 | 256 | 512 |
| FCL | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | |
| 0.7 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | ||
| m | 512 | 512 | 128 | 128 | |
| SoftMax | SoftMax | SoftMax | SoftMax |
| Methods | CCAT50 | IMDB62 | Blogs50 | Twitter50 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | F1-Score | Accuracy | F1-Score | Accuracy | F1-Score | Accuracy | F1-Score | |
| Lexical and Topical [1] | 97.72 | 97.72 | 85.04 | |||||
| PMSVM [19] | 70.00 | |||||||
| BertAA [35] | 93.00 | 59.70 | 56.70 | |||||
| SRNN [45] | 90.58 | 94.10 | 61.19 | |||||
| SCAP [45] | 94.80 | 94.80 | 41.60 | 41.60 | 82.50 | 82.50 | ||
| Imposters [50] | 49.90 | 76.90 | 22.60 | 52.50 | ||||
| SVM Affix-punctuation 3-g [51] | 69.30 | |||||||
| SVM with frequent 3-g [52] | 67.00 | 70.30 | 81.40 | |||||
| Continuous n-gram (2,3,4) [60] | 72.60 | 94.80 | ||||||
| SCAP n = 5 and L = 100 [68] | 31.83 | |||||||
| IAF, RLP with n = 4, L = 100 [68] | 51.05 | |||||||
| Character n-grams and Word n-grams [71] | 55.50 | |||||||
| Character n-grams [71] | 60.00 | |||||||
| n-gram and POS-tag [72] | 53.20 | |||||||
| IAF, RLP with n = 4, L = 1000 [74] | 64.54 | 77.13 | ||||||
| CNN word [75] | 84.30 | 84.30 | 65.70 | 43.00 | 80.50 | 80.50 | ||
| CNN character [75] | 91.70 | 91.70 | 49.40 | 48.10 | 73.20 | 86.80 | ||
| n-gram CNN [76] | 76.50 | 91.21 | 53.09 | |||||
| Syntax-tree CNN [77] | 81.00 | 96.16 | 56.73 | |||||
| DeepStyle [85] | 80.45 | 90.51 | 64.80 | |||||
| BRET [87] | 66.20 | 97.90 | 33.50 | |||||
| LDAH-S with the topic [80] | 72.00 | 72.00 | 18.30 | 18.30 | 38.30 | |||
| RDNN Method | 93.20 | 92.20 | 96.50 | 95.75 | 63.40 | 76.69 | 86.48 | 84.80 |
| Metrics | Trial Number | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
| Accuracy (%) | 63.39 | 63.35 | 63.44 | 63.38 | 63.46 |
| Mean ± SD | 63.40 ± 0.045 | ||||
| Metrics | Trial Number | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
| Accuracy (%) | 86.42 | 86.50 | 86.24 | 86.42 | 86.55 |
| Mean ± SD | 86.48 ± 0.051 | ||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Modupe, A.; Celik, T.; Marivate, V.; Olugbara, O.O. Post-Authorship Attribution Using Regularized Deep Neural Network. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 7518. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12157518
Modupe A, Celik T, Marivate V, Olugbara OO. Post-Authorship Attribution Using Regularized Deep Neural Network. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(15):7518. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12157518
Chicago/Turabian StyleModupe, Abiodun, Turgay Celik, Vukosi Marivate, and Oludayo O. Olugbara. 2022. "Post-Authorship Attribution Using Regularized Deep Neural Network" Applied Sciences 12, no. 15: 7518. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12157518
APA StyleModupe, A., Celik, T., Marivate, V., & Olugbara, O. O. (2022). Post-Authorship Attribution Using Regularized Deep Neural Network. Applied Sciences, 12(15), 7518. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12157518








