Energy Dissipation and Stress Equilibrium Behavior of Granite under Dynamic Impact
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Material
2.2. SHPB System
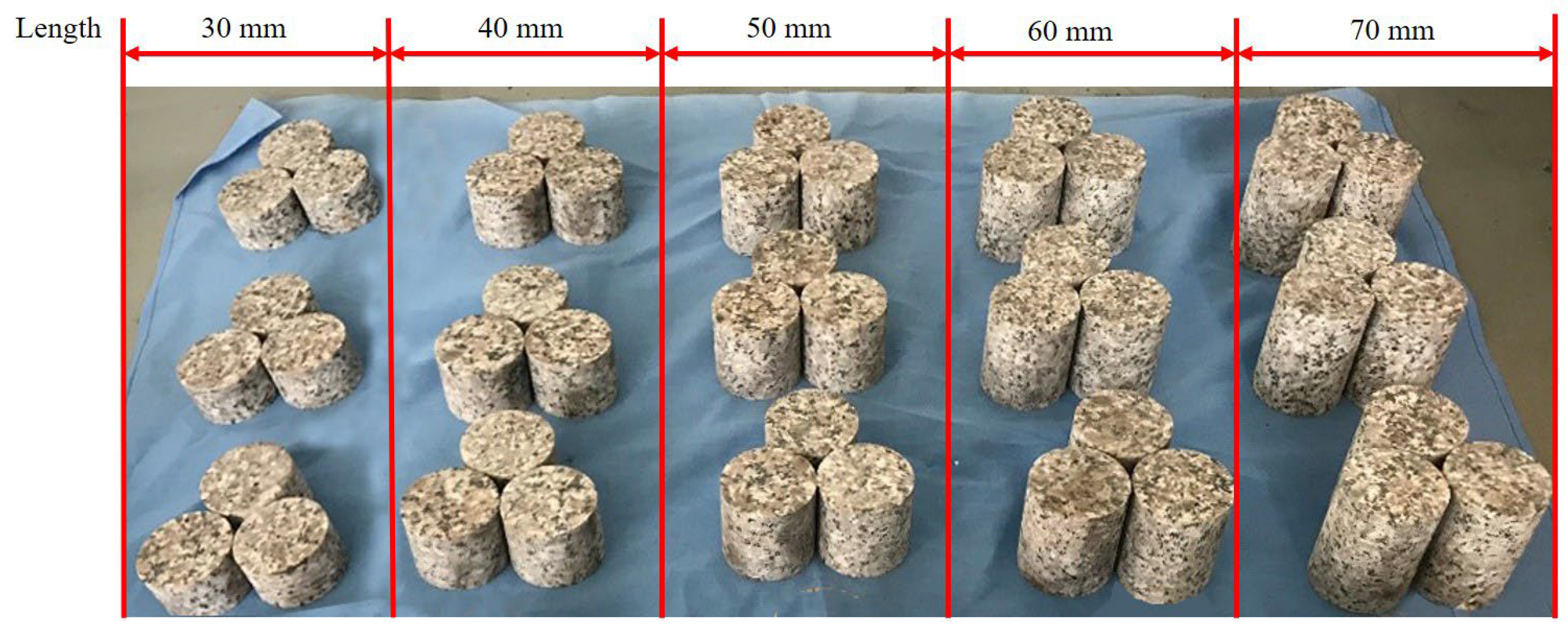
2.3. Test Preparation
- (1)
- Option of length–diameter ratio
- (2)
- Option of strain rate
- (3)
- Option of data range
- (4)
- Analysis methods
3. Energy Dissipation and Stress Equilibrium Time
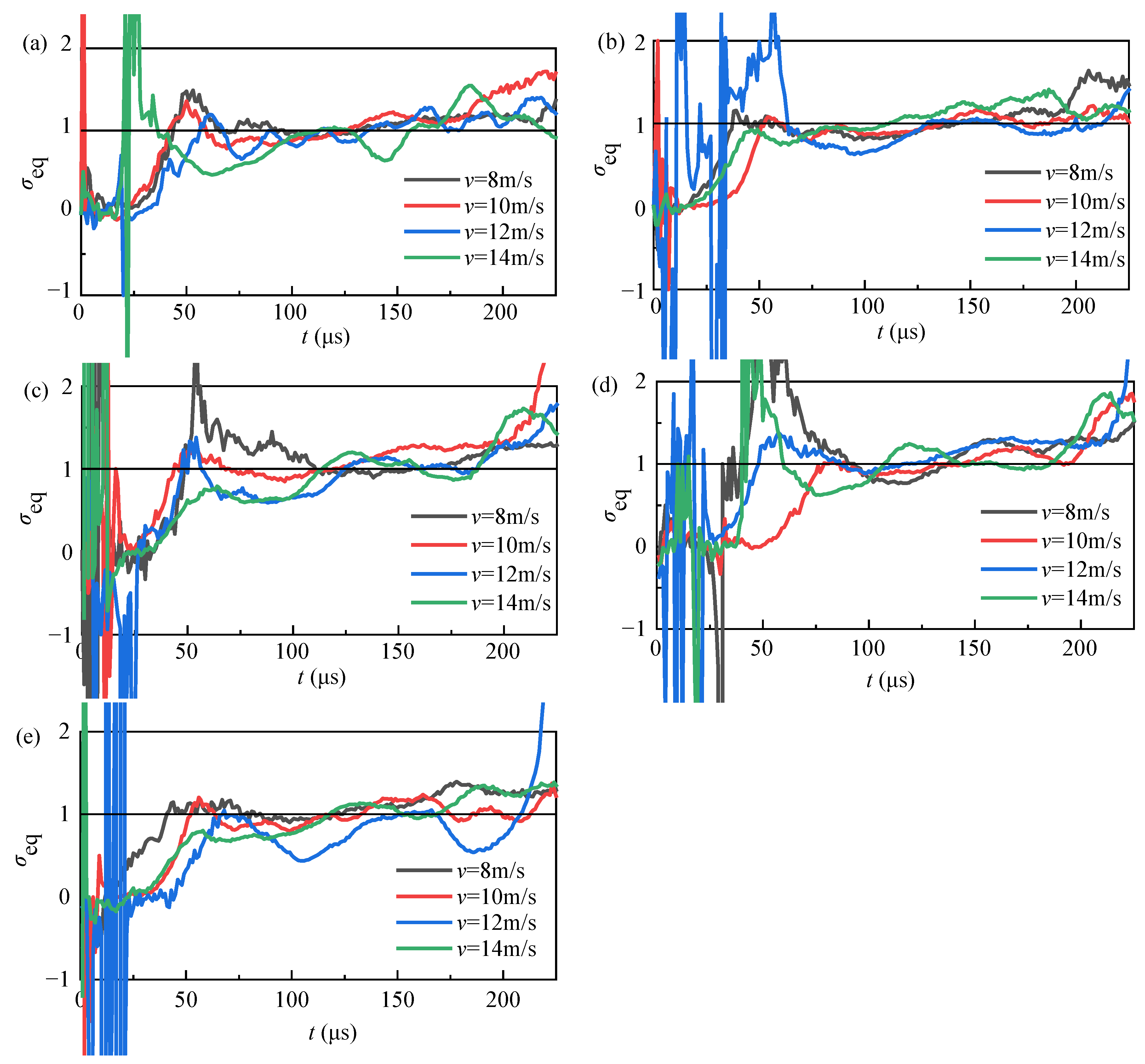
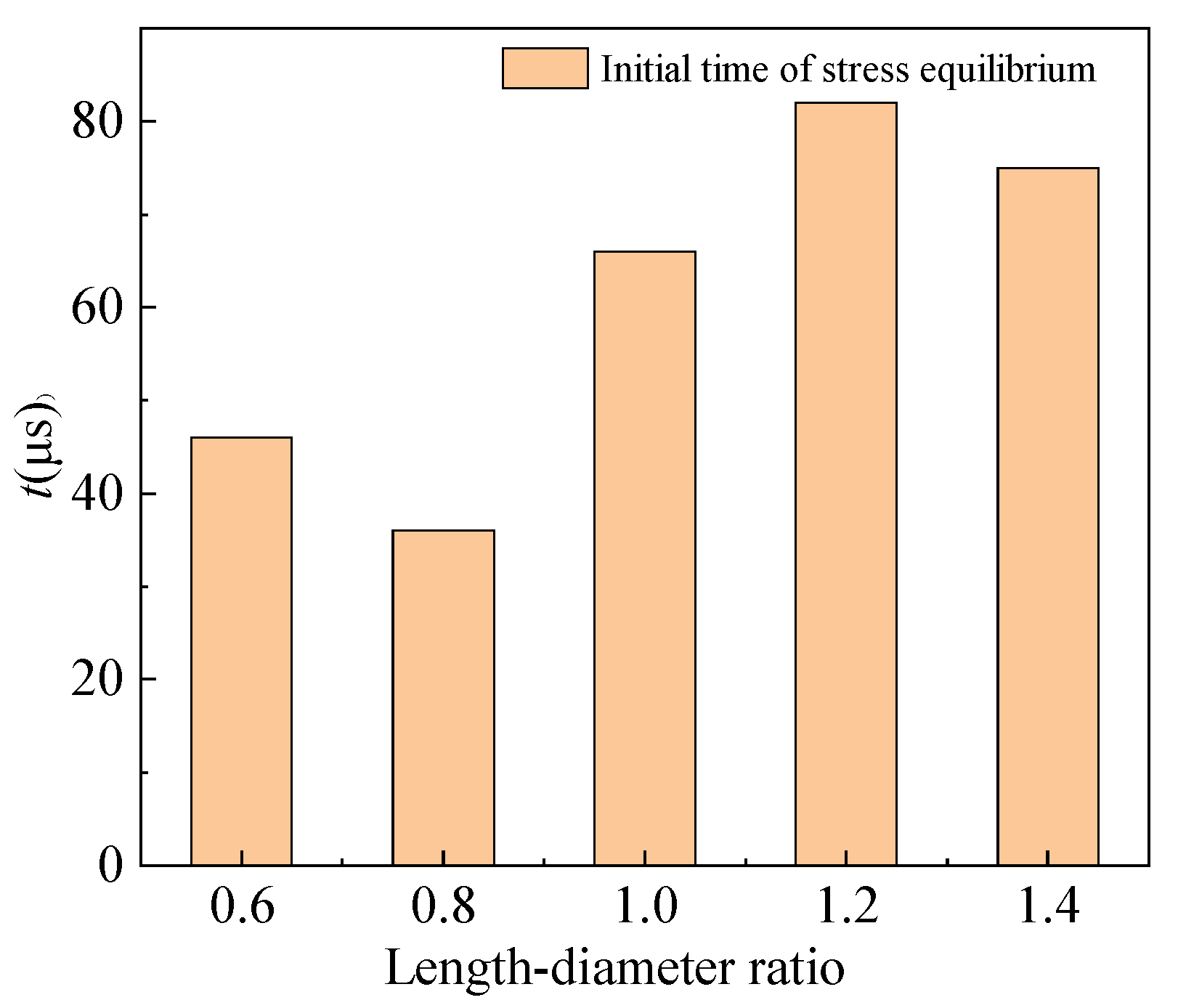
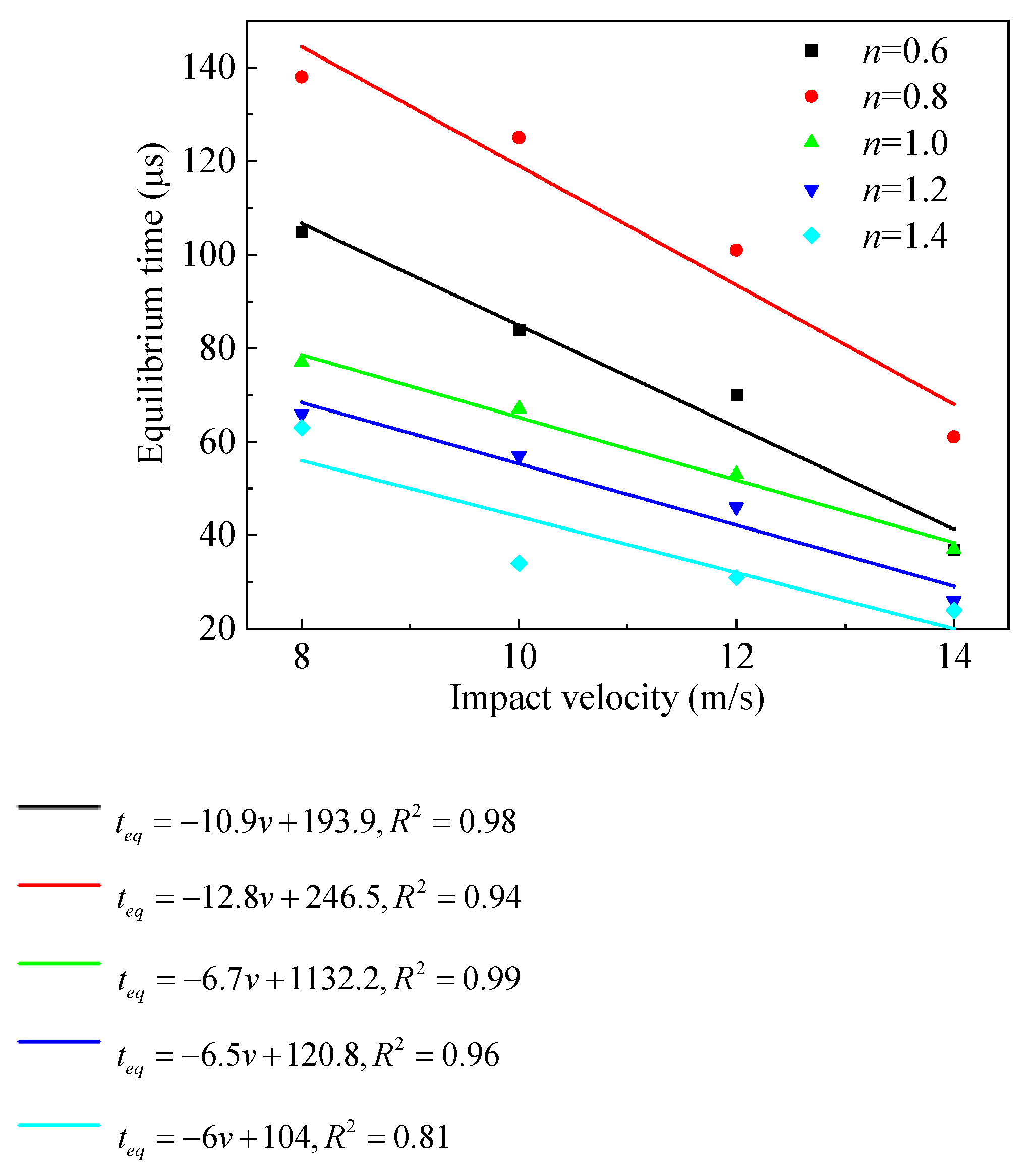
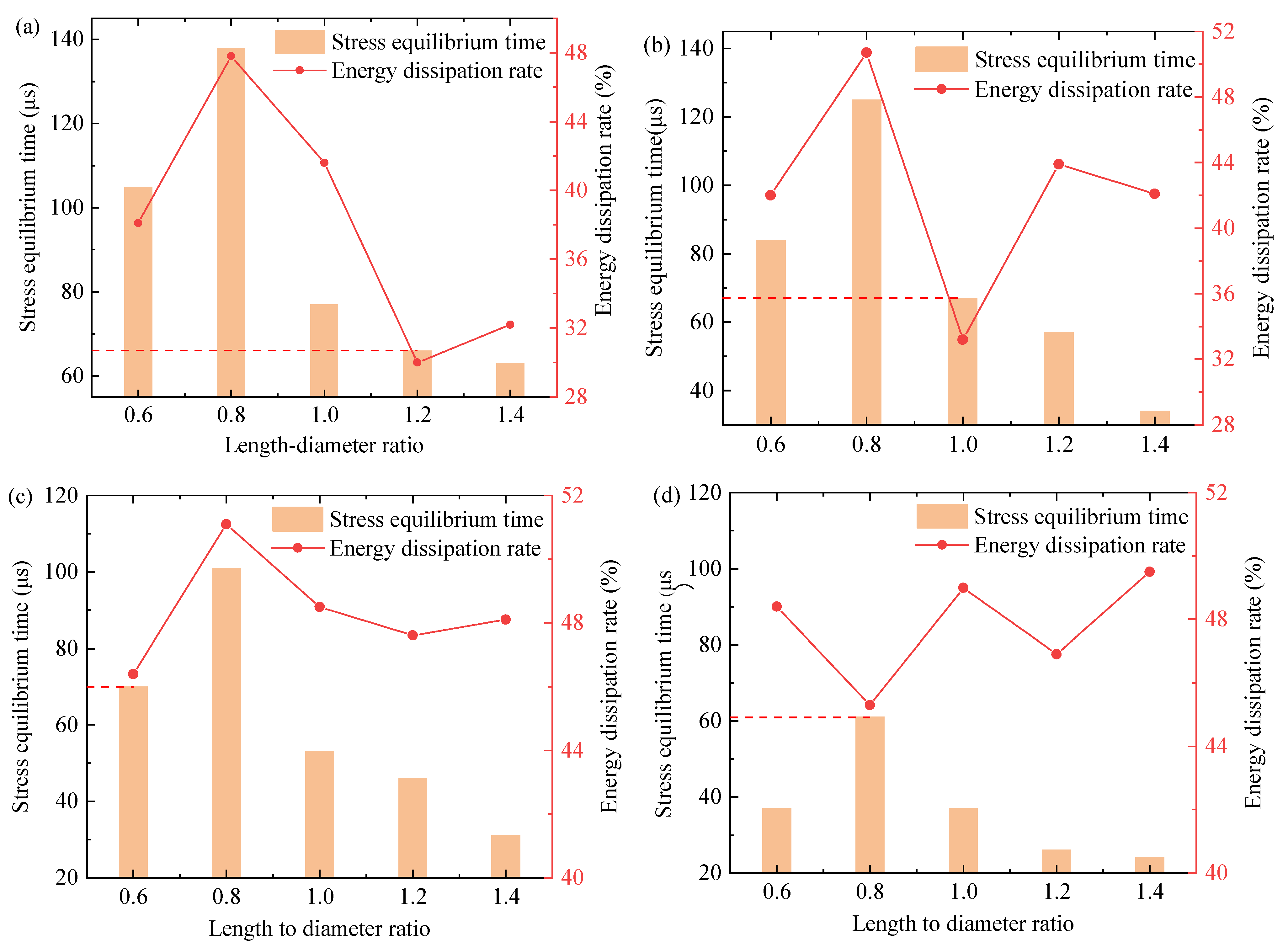
3.1. Stress Equilibrium Time
3.1.1. Equilibrium Factor
3.1.2. Stress Equilibrium Factor Curve
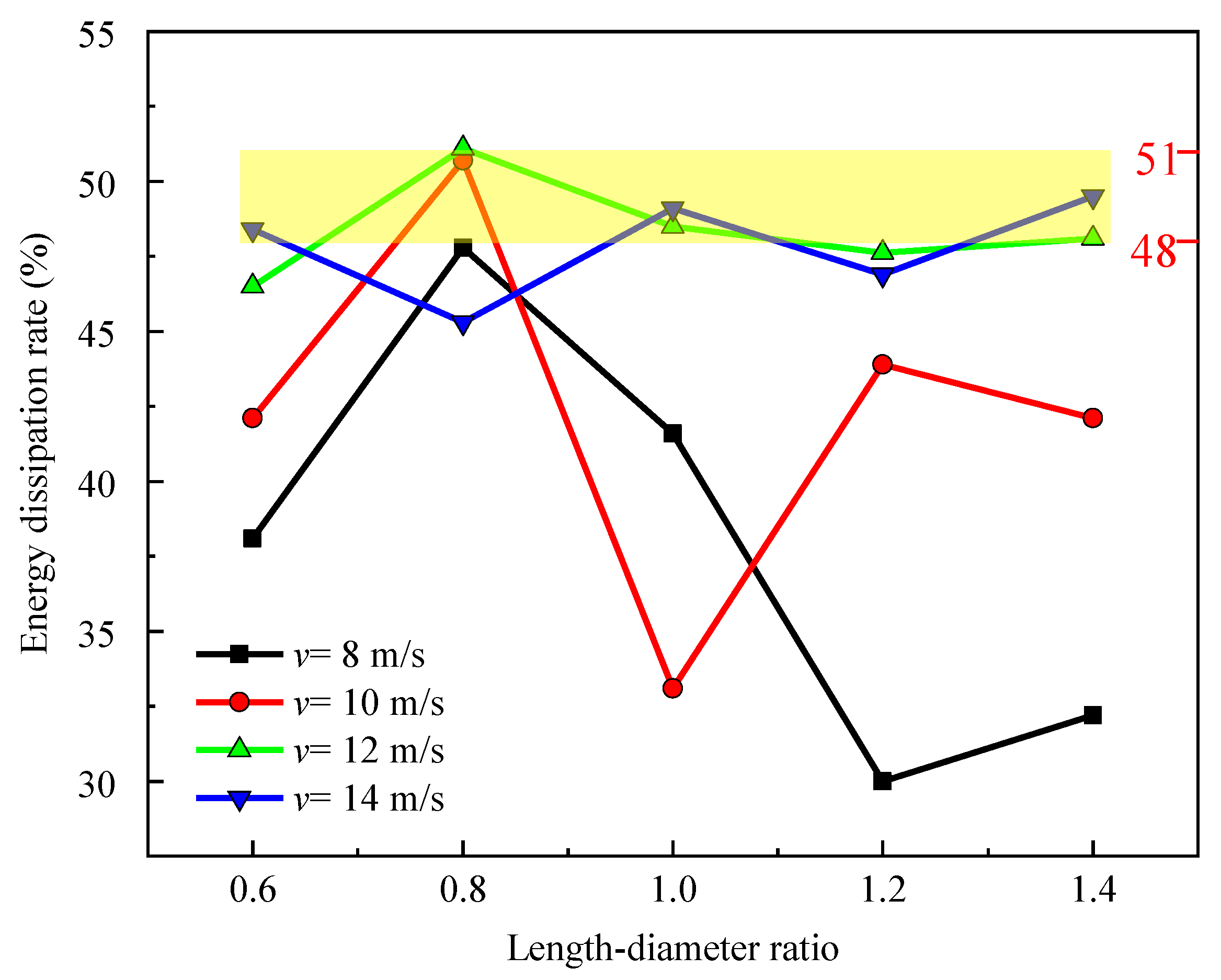
3.2. Energy Calculation
3.3. Energy Dissipation Rate
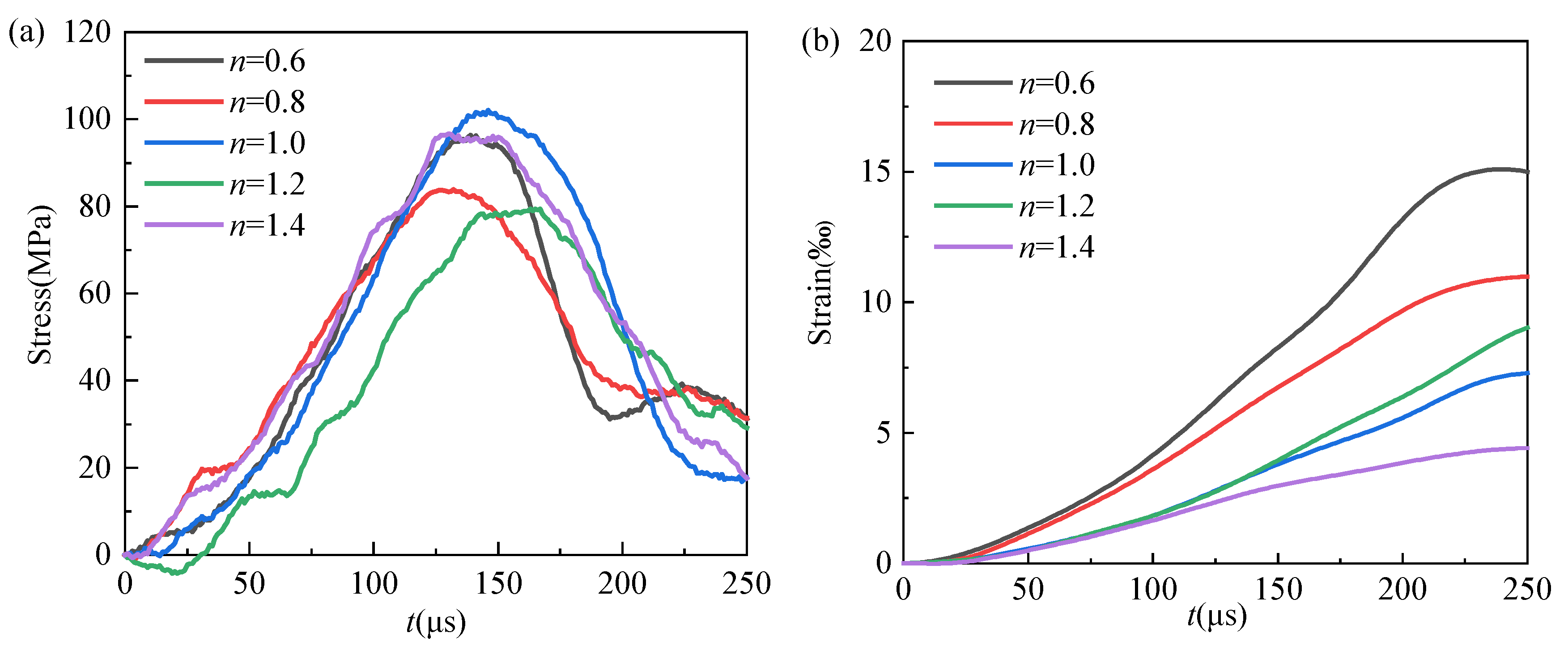
3.4. Effect on Impact Loading
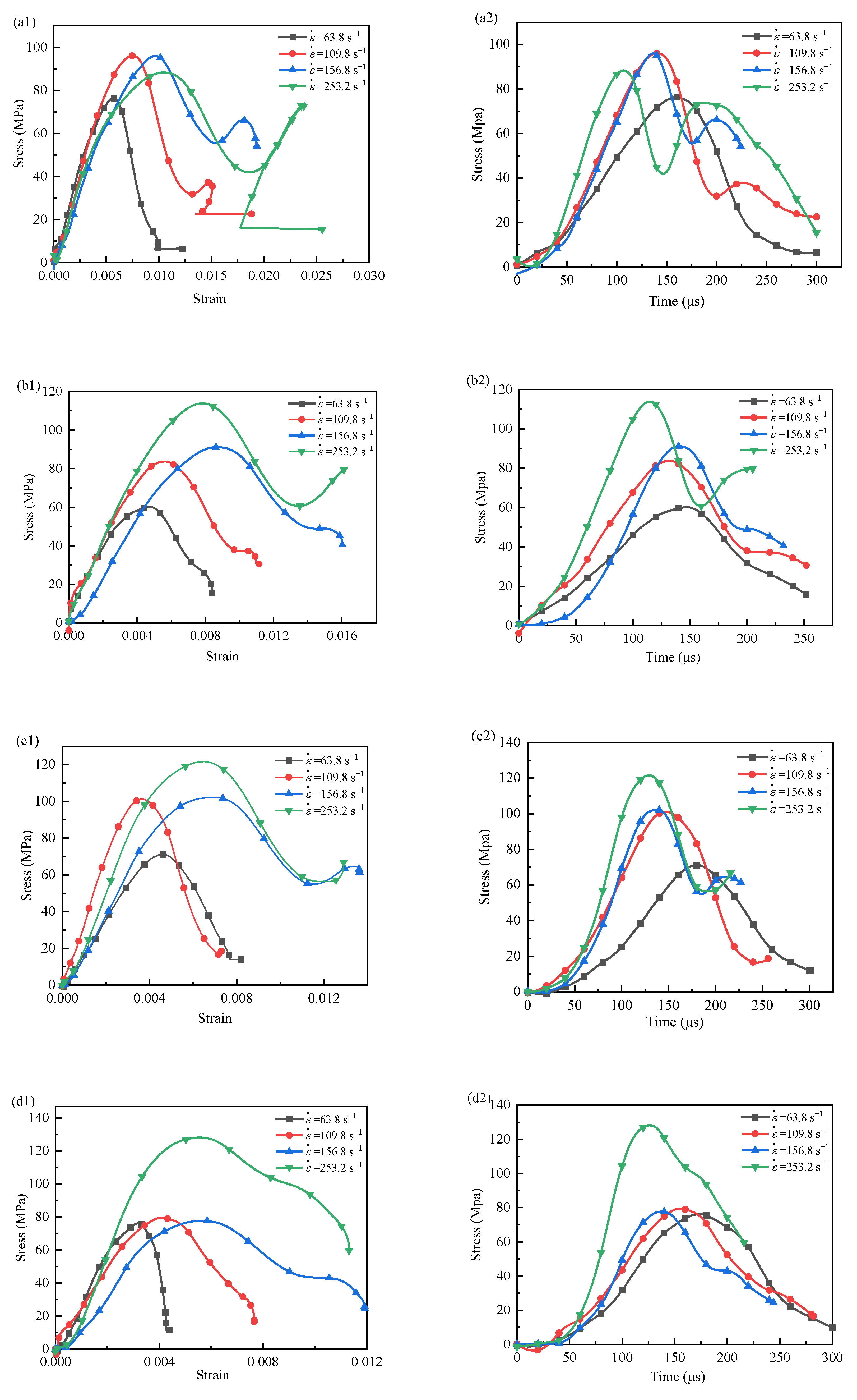
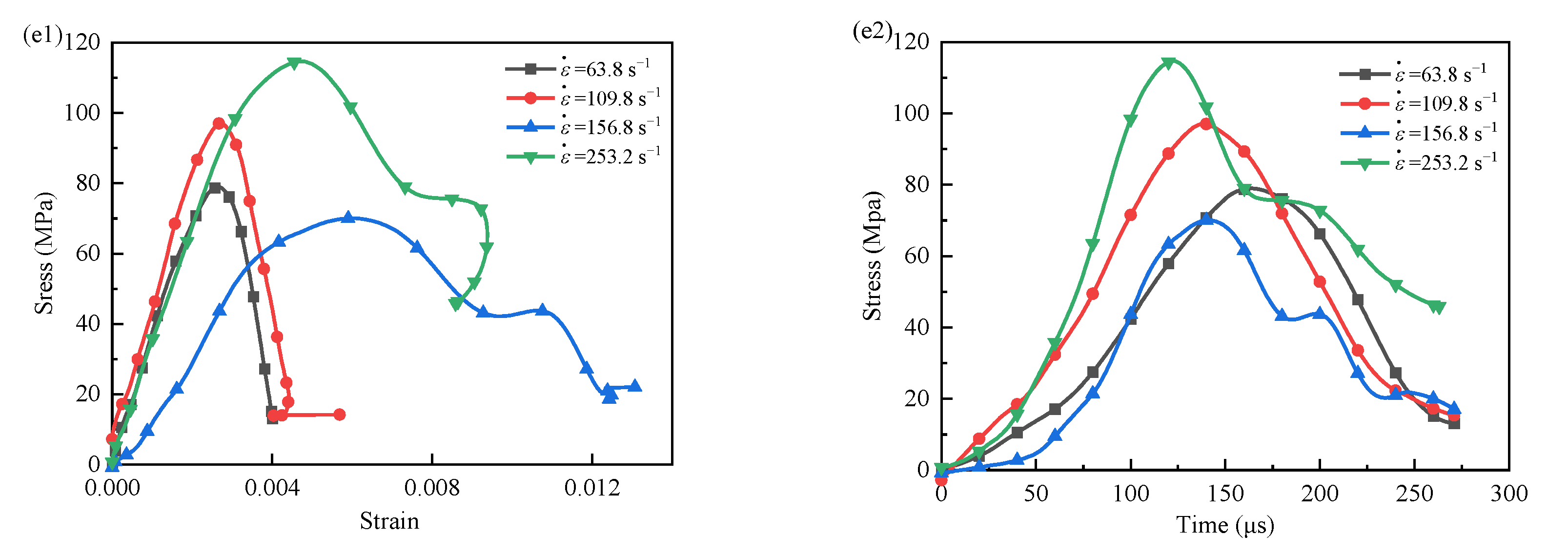
4. Dynamic Behavior
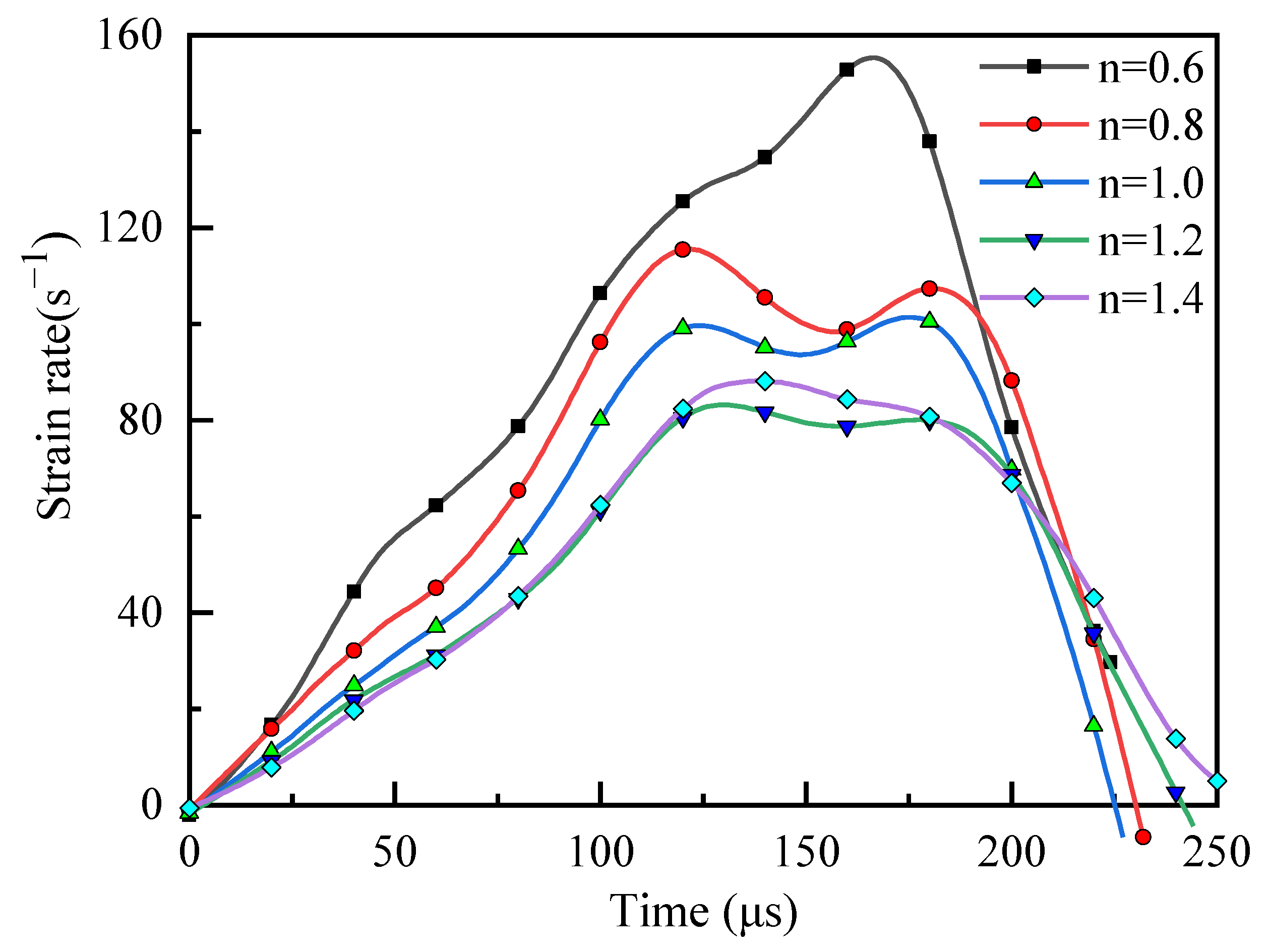
4.1. Strain Character
4.2. Peak Strength
4.3. Elastic Modulus
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, Q.B.; Zhao, J. A Review of Dynamic Experimental Techniques and Mechanical Behaviour of Rock Materials. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2014, 47, 1411–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dai, F.; Huang, S.; Xia, K.; Tan, Z. Some Fundamental Issues in Dynamic Compression and Tension Tests of Rocks Using Split Hopkinson Pressure Bar. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2010, 43, 657–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daryadel, S.S.; Mantena, P.R.; Kim, K.; Stoddard, D.; Rajendran, A.M. Dynamic response of glass under low-velocity impact and high strain-rate SHPB compression loading. J. Non Cryst. Solids 2016, 432, 432–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.; Wille, K. Experimental impact analysis on ultra-high performance concrete (UHPC) for achieving stress equilibrium (SE) and constant strain rate (CSR) in Split Hopkinson pressure bar (SHPB) using pulse shaping technique. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 144, 747–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q.; Xie, Y.; Long, G.; Niu, D.; Song, H.; Liu, X. Impact characterization and modelling of cement and asphalt mortar based on SHPB experiments. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2017, 106, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, F.Q.; Si, X.F.; Li, X.B.; Wang, S.Y. Dynamic triaxial compression tests on sandstone at high strain rates and low confining pressures with split Hopkinson pressure bar. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2019, 113, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, B.; Demartino, C.; Xiao, Y. High-strain rate compressive behavior of CFRP confined concrete: Large diameter SHPB tests. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 201, 484–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Q.; Xie, G.; Wang, L.; Jiao, Z.; Zou, P.; Liu, H.; Khan, N.M. Experimental Study on Stress Uniformity and Deformation Behavior of Coals with Different Length-to-Diameter Ratios under Dynamic Compression. Shock Vib. 2021, 2021, 6675200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Hao, H.; Cui, J.; Hao, Y.F. Numerical investigation of the failure mechanism of cubic concrete specimens in SHPB tests. Def. Technol. 2022, 18, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Chen, M.; Jin, Y.; Zou, D. Theoretical analysis and experimental research on the energy dissipation of rock crushing based on fractal theory. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2016, 33, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Zou, Y.; Zhou, Z. Numerical Simulation of the Rock SHPB Test with a Special Shape Striker Based on the Discrete Element Method. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2014, 47, 1693–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ma, L.; Zhao, F.; Lv, B.; Gong, W.; He, M.; Liu, P. Dynamic Strain Field for Granite Specimen under SHPB Impact Tests Based on Stress Wave Propagation. Undergr. Space 2022, 2467–9674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, K.; Wang, S.; Xu, Y.; Chen, R.; Wu, B. Advances in experimental studies for deep rock dynamics. Chin. J. Rock Mech. Eng. 2021, 40, 448–474. [Google Scholar]
- Song, L.; Hu, S.S. Two-Wave and Three-Wave Method in SHPB Data Processing; Explosion & Shock Waves: Beijing, China, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.X.; Xia, K.W.; Li, X.B.; Li, H.B.; Ma, G.W.; Zhao, J.; Zhou, Z.L.; Dai, F. Suggested methods for determining the dynamic strength parameters and mode-I fracture toughness of rock materials. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2011, 49, 35–44. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Fan, L.; Gong, J.; Yang, M.; Sun, L. Strain rate effect and energy dissipation characteristics of sandstone in coal measures under impact loading. J. China Coal Soc. 2021, 46, 2281–2293. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Meng, X.; Liu, C.; Liu, Z.; Xu, W.; Cheng, X. Study on the Rock Size Effect of Quasistatic and Dynamic Compression Characteristics. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 2021, 9974606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Wang, H.; Zong, Q. Experimental study on energy dissipation of mudstone in coal mine under im-pact loading. J. China Coal Soc. 2019, 6, 1716–1725. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Hao, J.; Gan, D.; Liu, Z. Energy dissipation characteristic of magnetite ore crushing under impact load. Harbin Inst. Technol. 2020, 52, 150–159. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Guo, L.J.; Zhang, D.N. Experimental study for stress uniformity of rock specimen in SHPB test. Eng. Blasting 2016, 22, 24–27. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Jiang, F.; Wang, Z.; Yuan, D.; Gao, G.; Guo, C. Mechanical behavior and microstructural evolution of a bainite-based quenching-partitioning (BQ&P) steel under high strain rates. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2021, 818, 141414. [Google Scholar]






| Loading Condition | Range |
|---|---|
| Loading strain rate | 50 s−1~300 s−1 |
| Impact strength | 0.12 MPa~0.25 MPa |
| Impact velocity | 8 m/s~14 m/s |
| Length–Diameter Ratio | Strain Rate (s−1) | Initial Time (μs) | End Time (μs) | Duration (μs) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.6 | 63.8 | 46 | 151 | 105 |
| 109.8 | 55 | 139 | 84 | |
| 156.8 | 86 | 156 | 70 | |
| 253.2 | 96 | 133 | 37 | |
| 0.8 | 63.8 | 36 | 174 | 138 |
| 109.8 | 50 | 175 | 125 | |
| 156.8 | 69 | 170 | 101 | |
| 253.2 | 73 | 134 | 61 | |
| 1.0 | 63.8 | 108 | 185 | 77 |
| 109.8 | 66 | 133 | 67 | |
| 156.8 | 122 | 175 | 53 | |
| 253.2 | 136 | 173 | 37 | |
| 1.2 | 63.8 | 82 | 148 | 66 |
| 109.8 | 79 | 136 | 57 | |
| 156.8 | 85 | 131 | 46 | |
| 253.2 | 136 | 162 | 26 | |
| 1.4 | 63.8 | 75 | 138 | 63 |
| 109.8 | 106 | 140 | 34 | |
| 156.8 | 141 | 172 | 31 | |
| 253.2 | 150 | 174 | 24 |
| Length–Diameter Ratio | σmax-time | σmax (MPa) | Length–Diameter Ratio | σmax-time | σmax (MPa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.6 | 160 | 76.33 | 1.2 | 175 | 76.17 |
| 139 | 96.05 | 156 | 79.42 | ||
| 136 | 95.99 | 135 | 77.56 | ||
| 106 | 88.33 | 125 | 128.08 | ||
| 0.8 | 146 | 60.21 | 1.4 | 163 | 78.95 |
| 130 | 83.64 | 143 | 97.88 | ||
| 139 | 91.09 | 139 | 70.23 | ||
| 114 | 113.82 | 121 | 114.6 | ||
| 1.0 | 179 | 71.15 | |||
| 145 | 101.13 | ||||
| 136 | 102.18 | ||||
| 129 | 121.56 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, Z.; Wu, Y.; Liu, X.; Guo, L.; Hu, Z. Energy Dissipation and Stress Equilibrium Behavior of Granite under Dynamic Impact. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 6107. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12126107
Xu Z, Wu Y, Liu X, Guo L, Hu Z. Energy Dissipation and Stress Equilibrium Behavior of Granite under Dynamic Impact. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(12):6107. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12126107
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Zhenyang, Yixuan Wu, Xin Liu, Lianjun Guo, and Zhihang Hu. 2022. "Energy Dissipation and Stress Equilibrium Behavior of Granite under Dynamic Impact" Applied Sciences 12, no. 12: 6107. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12126107
APA StyleXu, Z., Wu, Y., Liu, X., Guo, L., & Hu, Z. (2022). Energy Dissipation and Stress Equilibrium Behavior of Granite under Dynamic Impact. Applied Sciences, 12(12), 6107. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12126107






