A Clustered PD-NOMA in an Ultra-Dense Heterogeneous Network with Improved System Capacity and Throughput
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Prior Work
1.2. Challenges of PD-NOMA
1.3. Motivation
1.4. Contribution
1.5. Organization
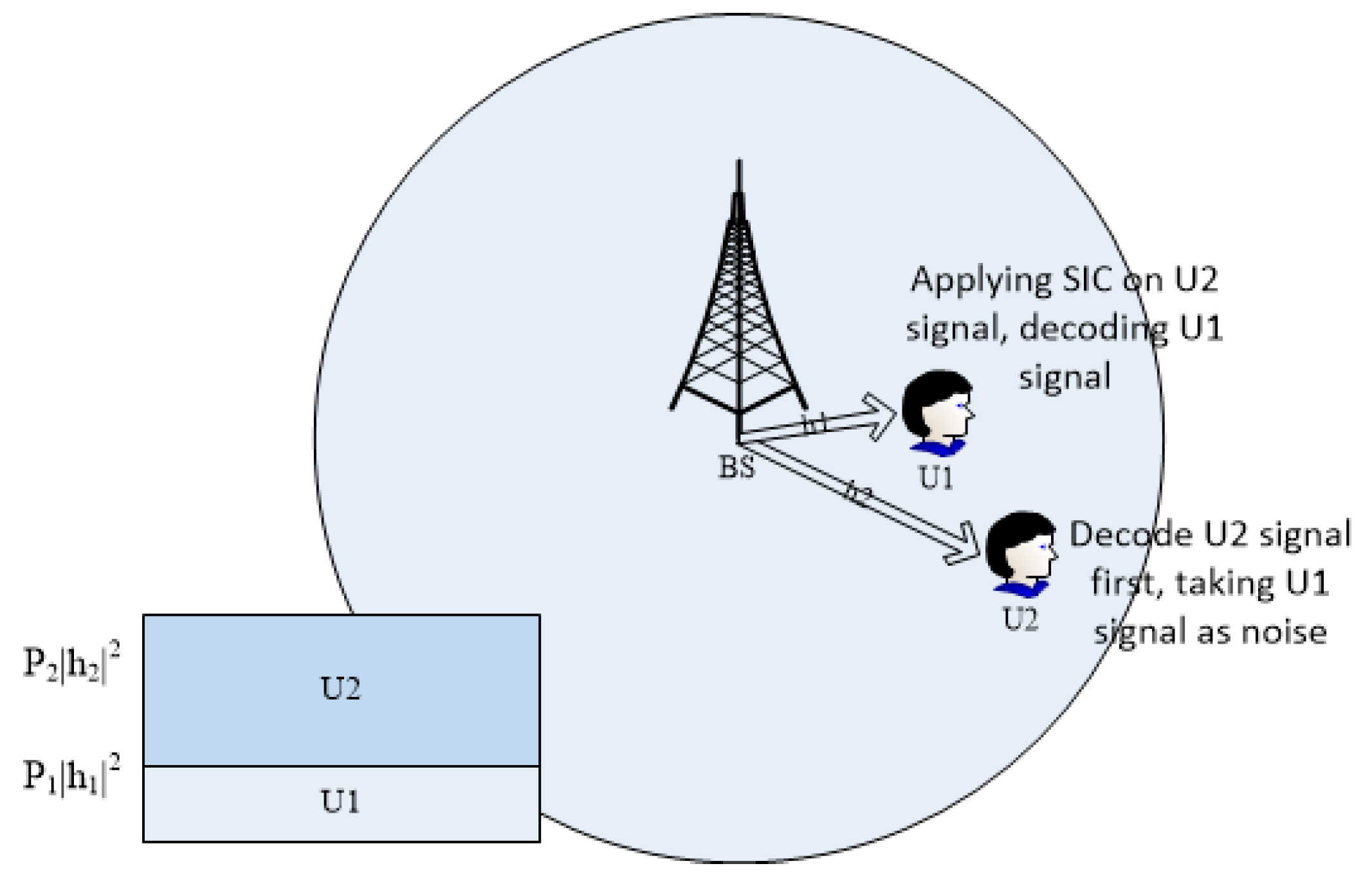
2. Power Domain-NOMA
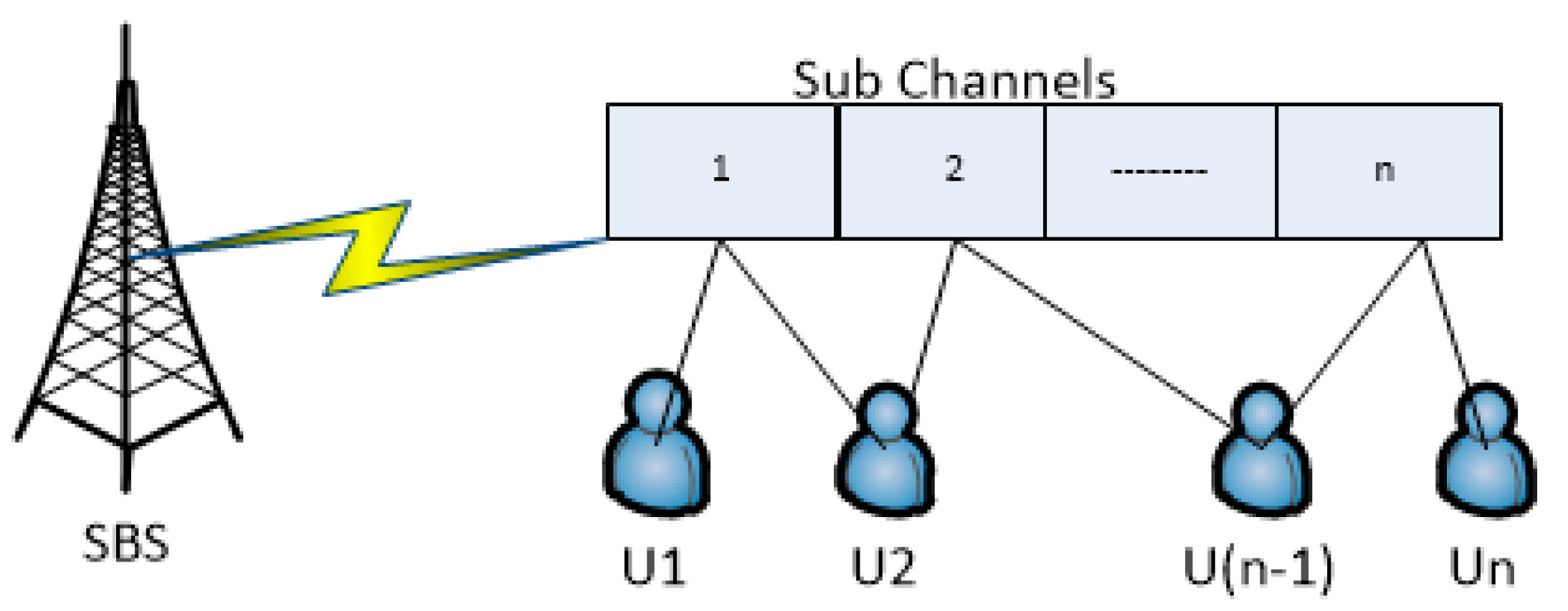
3. System Model
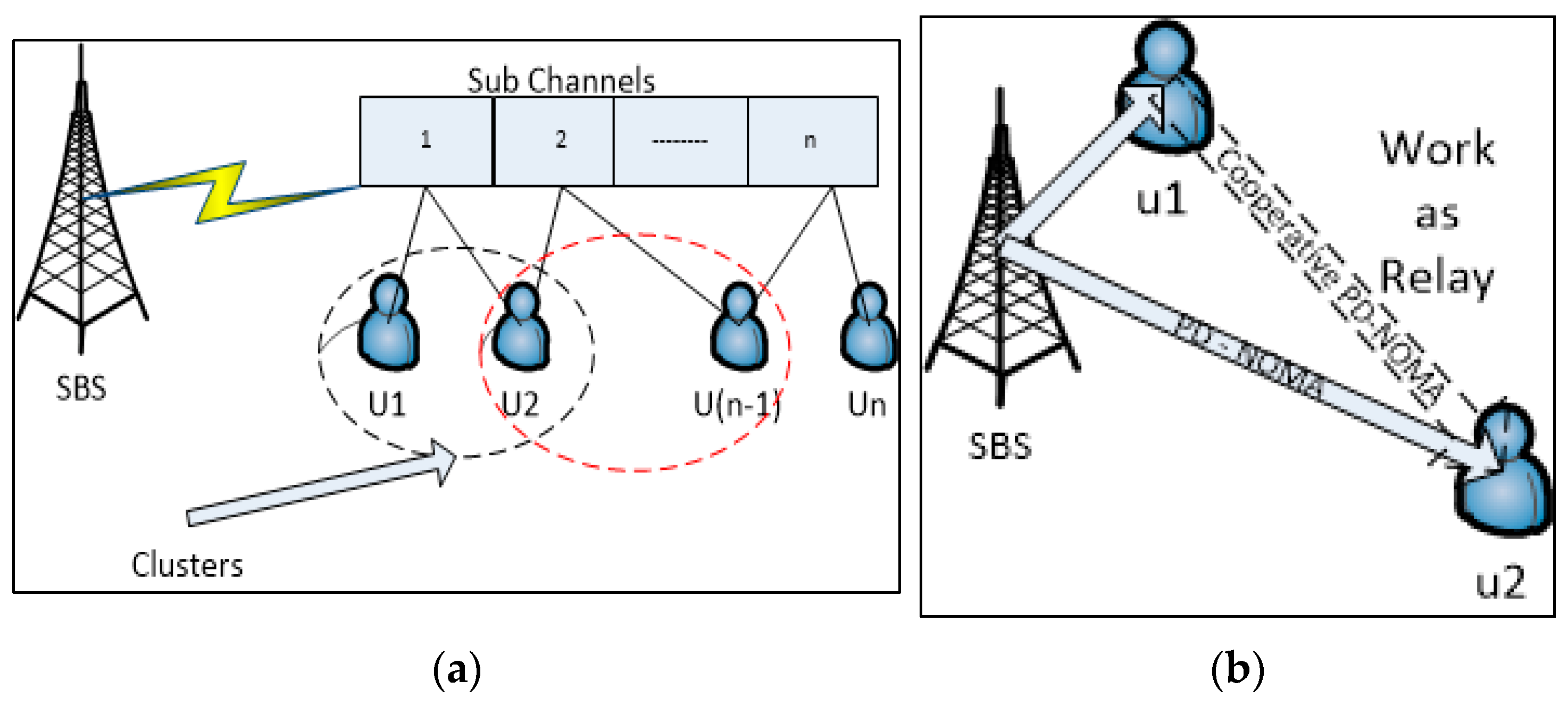
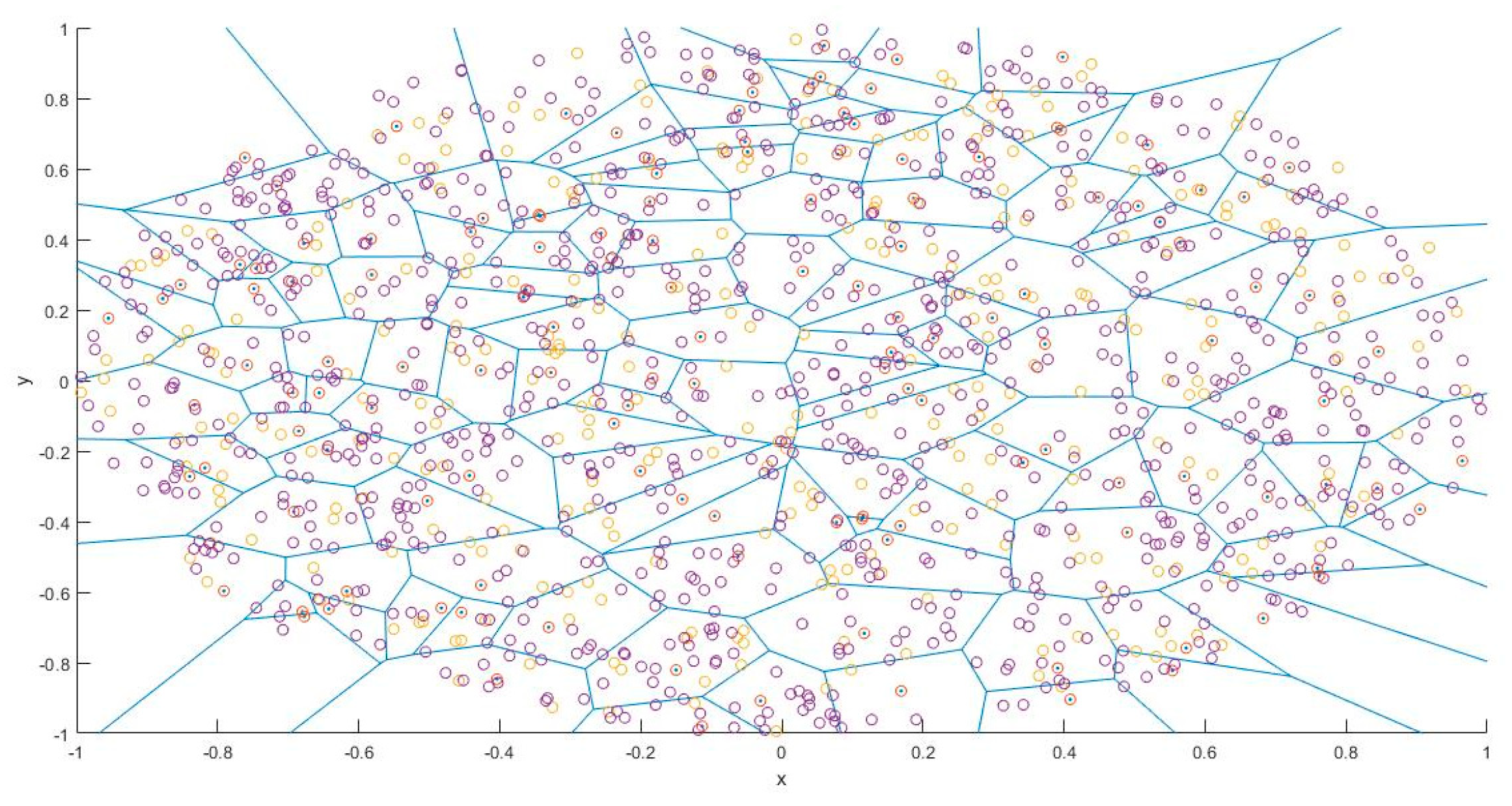
3.1. Clustered PD-NOMA
- Step 1.
- The user will send their respective channel state information (CSI) to the corresponding SBS, and the SBS forms the CSI set ‘I’, within the threshold value ‘T’, where T ≥ 1.
- Step 2.
- The SBS finds the channel gain difference based on the correlation between the users linked with the same SBS.
- Step 3.
- The SBS calculates the distance dj,n as the channel gain difference between the jth and kth user.Ij,k = {dj,k → ||hj| − |hk||; corresponding (j,n) → (|hj·hk|/|hj||hk|) ˃ ρ},Where ‘ρ’ represents a pre-defined real value (0 ≤ ρ ≤ 1).
- Step 4.
- The SBS forms the cluster with users having the maximum channel gain difference.(j,k)* = argmax {dj,k}, T = T − (dj,k) until the difference with the nth user is computed.
- Step 5.
- Among the residual users, users with the most significant channel gain difference will be selected by the SBS, eventually improving system capacity. Ɐ(j,k)n the users will be evaluated based on the respective channel gain difference.
3.2. Power Allocation
3.3. Cooperated Clustered PD-NOMA
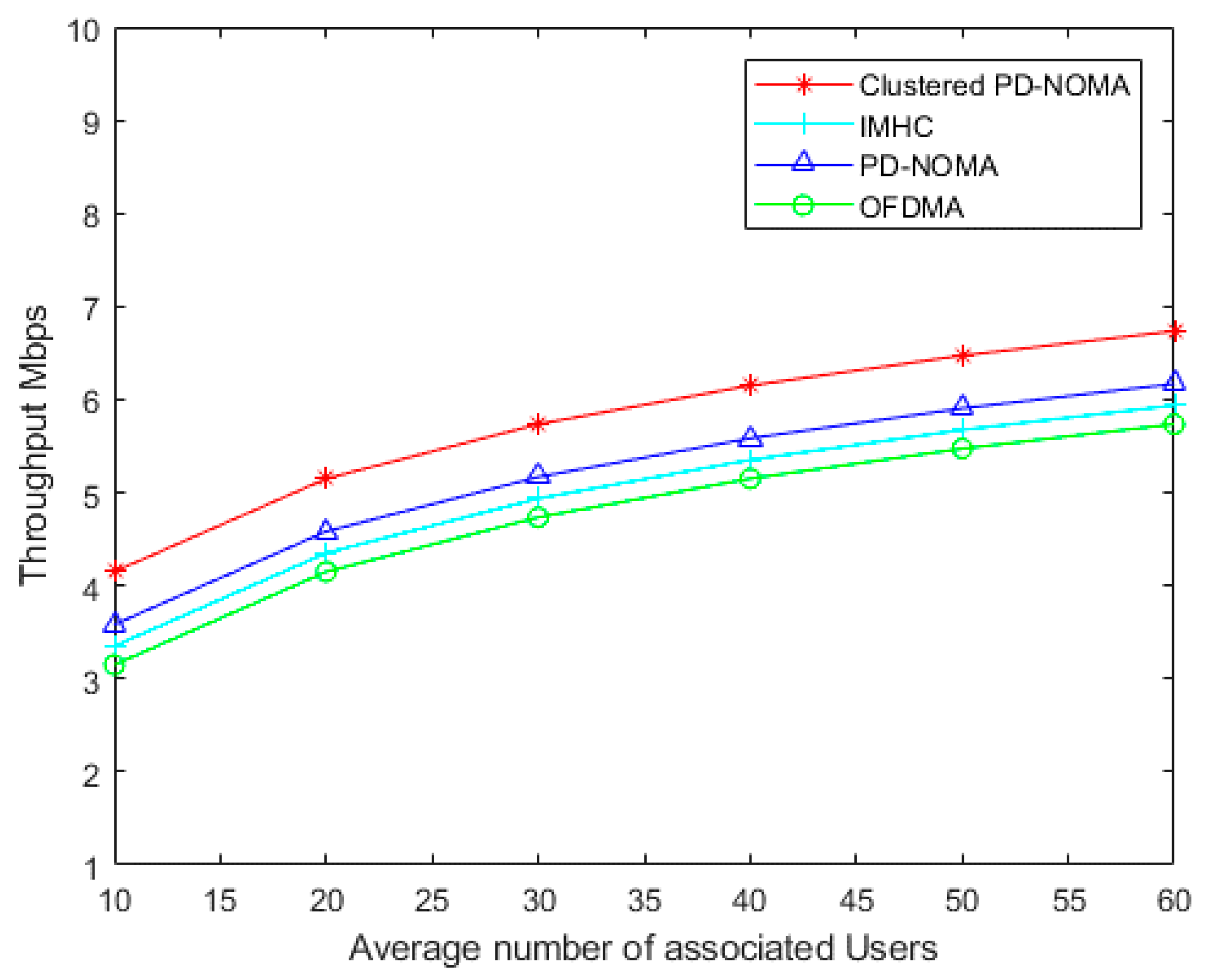
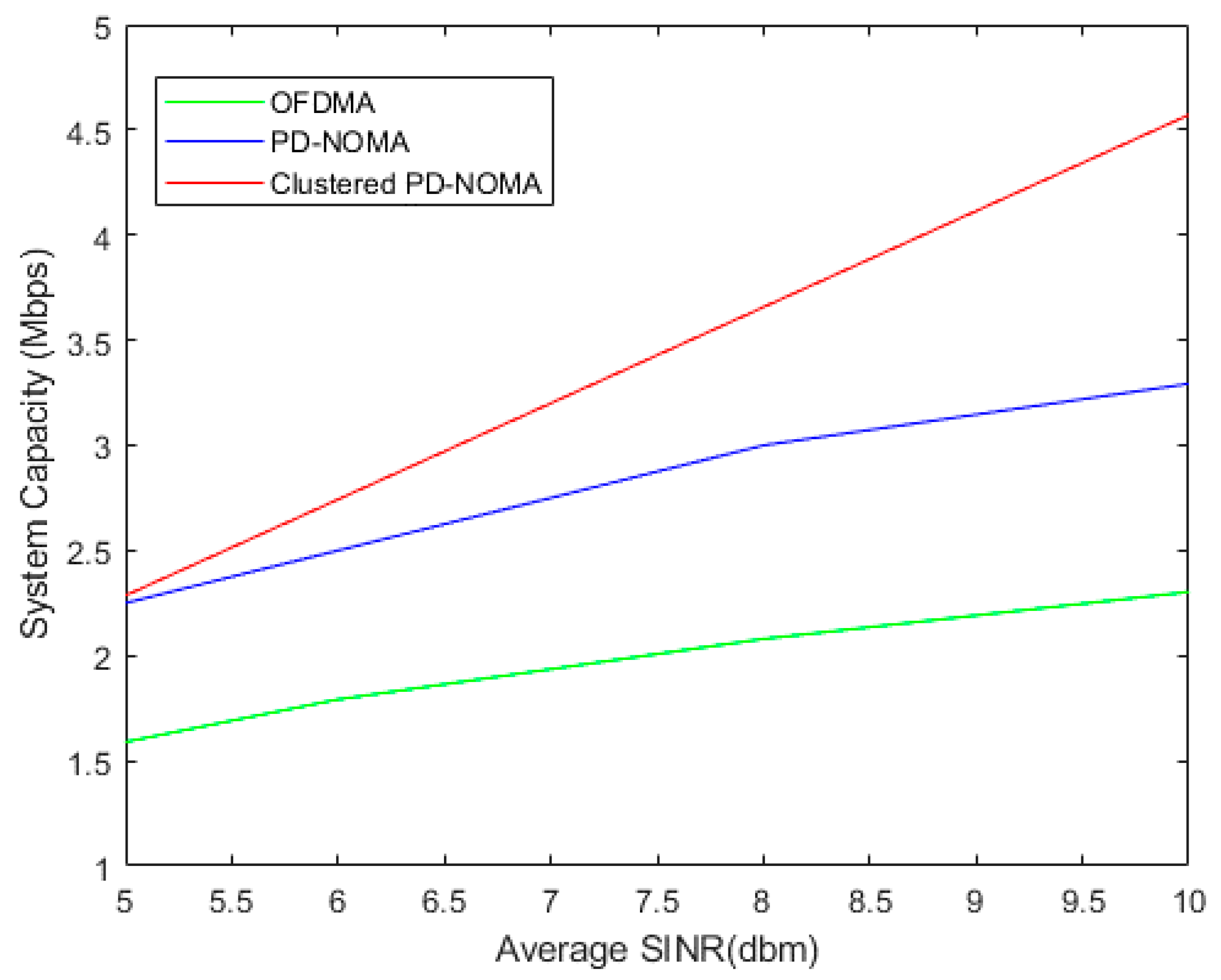
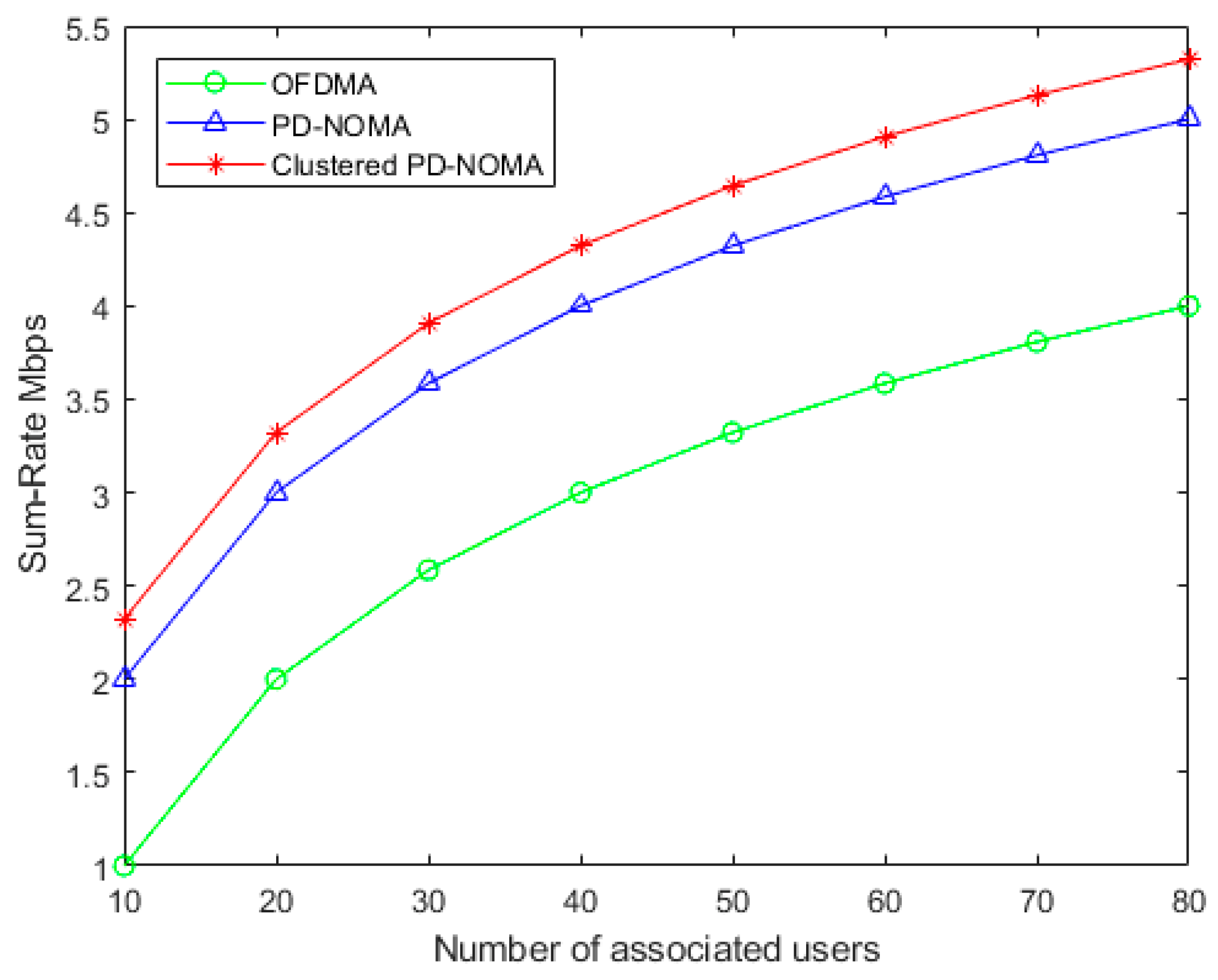
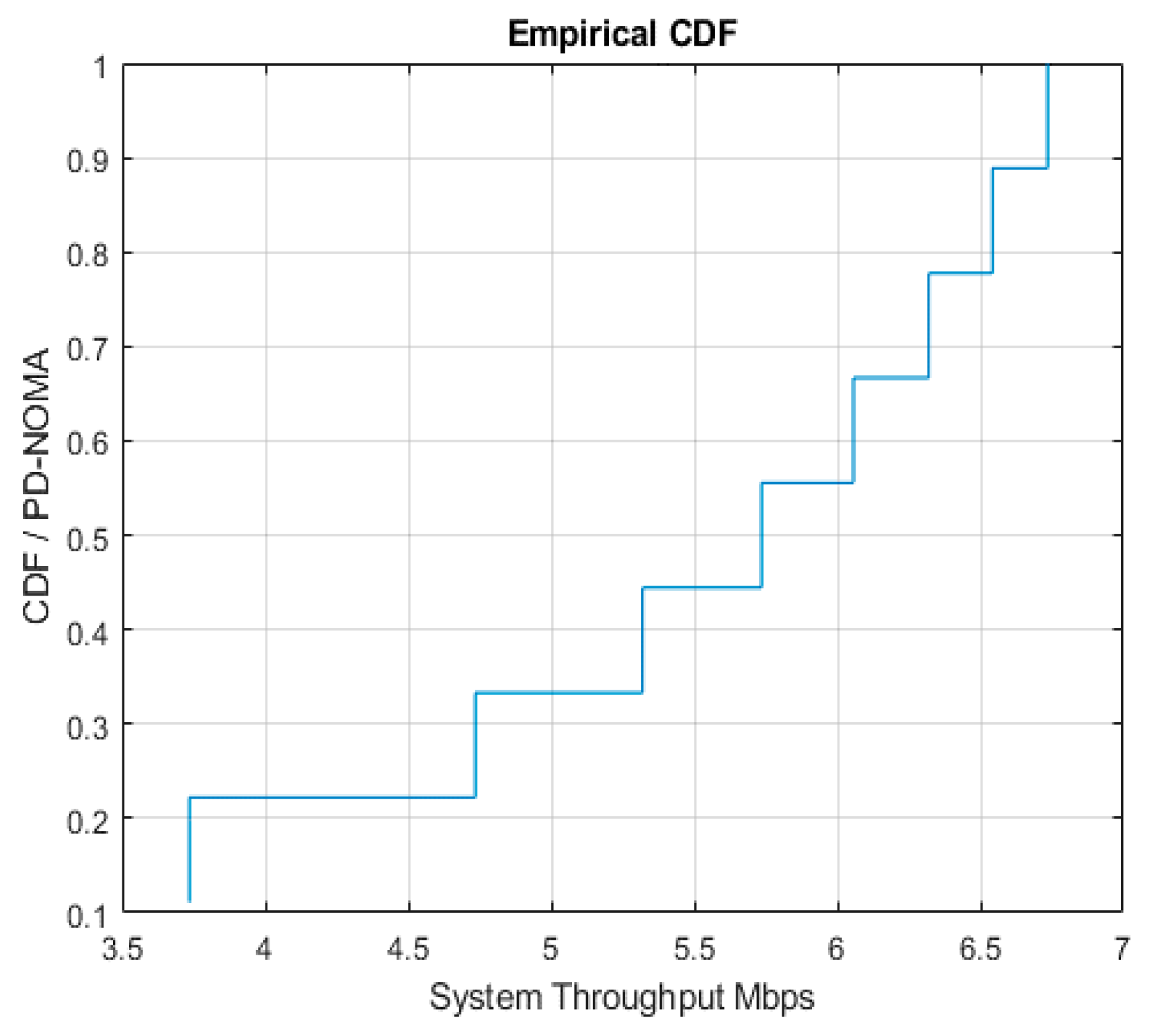
4. Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Farhan, N.; Rizvi, S. An Interference-Managed Hybrid Clustering Algorithm to Improve System Throughput. Sensors 2022, 22, 1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L.; Yang, L.; Zhang, Q.; Zhou, T.; Hua, J. Cluster-based energy-efficient joint user association and resource allocation for B5G ultra-dense network. Phys. Commun. 2021, 46, 101311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhan, N.; Rizvi, S.; Shabbir, A.; Memon, I. Clustering Approaches for Efficient Radio Resource Management in Heterogeneous Networks. Vfast Trans. Softw. Eng. 2021, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldababsa, M.; Toka, M.; Gökçeli, S.; Kurt, G.K.; Kucur, O. A tutorial on nonorthogonal multiple access for 5G and beyond. Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput. 2018, 2018, 9713450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chaieb, C.; Abdelkefi, F.; Ajib, W. Joint user association and sub-channel assignment in wireless networks with heterogeneous multiple access and heterogeneous base stations. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 31st Annual International Symposium on Personal, Indoor and Mobile Radio Communications, London, UK, 31 August–3 September 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Saito, Y.; Kishiyama, Y.; Benjebbour, A.; Nakamura, T.; Li, A.; Higuchi, K. Non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA) for cellular future radio access. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE 77th Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC Spring), Dresden, Germany, 2–5 June 2013; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Sadat, H.; Abaza, M.; Mansour, A.; Alfalou, A. A Survey of NOMA for VLC Systems: Research Challenges and Future Trends. Sensors 2022, 22, 1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, F.; Ye, G.; Zhang, H.; Cheng, J.; Leung, V.C. Energy-efficient joint user association and power allocation in a heterogeneous network. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2020, 19, 7008–7020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celik, A.; Tsai, M.-C.; Radaydeh, R.M.; Al-Qahtani, F.S.; Alouini, M.-S. Distributed user clustering and resource allocation for imperfect NOMA in heterogeneous networks. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2019, 67, 7211–7227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forouzan, N.; Rabiei, A.M.; Vehkaperä, M.; Wichman, R. A distributed resource allocation scheme for self-backhauled full-duplex small cell networks. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2021, 70, 1461–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.; Yue, X.; Liu, Y.; Ding, Z.; Nallanathan, A. User association and resource allocation in unified NOMA enabled heterogeneous ultra dense networks. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2018, 56, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, G.; Zhao, X.; Li, Y.; Huang, C.; Sun, E.; Huang, W. Resource allocation for energy efficient user association in user-centric ultra-dense networks integrating NOMA and beamforming. AEU-Int. J. Electron. Commun. 2020, 124, 153270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, W. Joint resource allocation and user association for heterogeneous services in multi-access edge computing networks. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 12272–12282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjebbour, A.; Saito, Y.; Kishiyama, Y.; Li, A.; Harada, A.; Nakamura, T. Concept and practical considerations of non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA) for future radio access. In Proceedings of the 2013 International Symposium on Intelligent Signal Processing and Communication Systems, Naha, Japan, 12–15 November 2013; pp. 770–774. [Google Scholar]
- Islam, S.R.; Avazov, N.; Dobre, O.A.; Kwak, K.-S. Power-domain non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA) in 5G systems: Potentials and challenges. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2016, 19, 721–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, Z.; Yang, L.; Ng, D.W.K.; Yuan, J.; Hanzo, L. On the performance gain of NOMA over OMA in uplink communication systems. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2019, 68, 536–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marcano, A.S.; Christiansen, H.L. Impact of NOMA on network capacity dimensioning for 5G HetNets. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 13587–13603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, T.-H.; Nguyen, T.-V.; Kim, S. Cooperative NOMA-enabled SWIPT IoT networks with imperfect SIC: Performance analysis and deep learning evaluation. IEEE Internet Things J. 2021, 9, 2253–2266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liaqat, M.; Noordin, K.A.; Abdul Latef, T.; Dimyati, K. Power-domain non orthogonal multiple access (PD-NOMA) in cooperative networks: An overview. Wirel. Netw. 2020, 26, 181–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Yue, X.; Peng, Z. Full-duplex user relaying for NOMA system with self-energy recycling. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 67057–67069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, C.-B.; Do, D.-T.; Zaharis, Z.D.; Mavromoustakis, C.X.; Mastorakis, G.; Markakis, E.K. System performance analysis in cognitive radio-aided NOMA network: An application to vehicle-to-everything communications. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2021, 120, 1975–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, D.; Shin, W.; Lee, J.; Poor, H.V. Sum-throughput maximization in NOMA-based WPCN: A cluster-specific beamforming approach. IEEE Internet Things J. 2021, 8, 10543–10556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higuchi, K.; Benjebbour, A. Non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA) with successive interference cancellation for future radio access. IEICE Trans. Commun. 2015, 98, 403–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, K.; Liu, Y.; Ding, Z.; Nallanathan, A.; Peng, M. User association and power allocation for multi-cell non-orthogonal multiple access networks. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2019, 18, 5284–5298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; Zhu, X.; Jiang, Y.; Wei, Z.; Sun, S.; Xiong, X. Toward UL-DL Rate Balancing: Joint Resource Allocation and Hybrid-Mode Multiple Access for UAV-BS Assisted Communication Systems. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2022, 70, 2757–2771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Wang, Z.; Huang, Q. Cyclical NOMA based UAV-enabled wireless network. IEEE Access 2018, 7, 4248–4259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, L.; Yuan, D.; Ho, C.K.; Sun, S. Power and channel allocation for non-orthogonal multiple access in 5G systems: Tractability and computation. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2016, 15, 8580–8594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akhtar, T.; Tselios, C.; Politis, I. Radio resource management: Approaches and implementations from 4G to 5G and beyond. Wirel. Netw. 2021, 27, 693–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maraqa, O.; Rajasekaran, A.S.; Al-Ahmadi, S.; Yanikomeroglu, H.; Sait, S.M. A survey of rate-optimal power domain NOMA with enabling technologies of future wireless networks. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2020, 22, 2192–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimy, B.; Lim, S.; Kim, H.; Suh, S.; Kwun, J.; Choi, S.; Lee, C.; Lee, S.; Hong, D. Non-orthogonal multiple access in a downlink multiuser beamforming system. In Proceedings of the MILCOM 2013–2013 IEEE Military Communications Conference, San Diego, CA, USA, 18–20 November 2013; pp. 1278–1283. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, W.U.; Li, X.; Ihsan, A.; Ali, Z.; Elhalawany, B.M.; Sidhu, G.A.S. Energy efficiency maximization for beyond 5G NOMA-enabled heterogeneous networks. Peer-to-Peer Netw. Appl. 2021, 14, 3250–3264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M.; Rasheed, H. Performance of orthogonal beamforming with NOMA for smart grid communication in the presence of impulsive noise. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2020, 45, 6331–6345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laneman, J.N.; Tse, D.N.; Wornell, G.W. Cooperative diversity in wireless networks: Efficient protocols and outage behavior. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2004, 50, 3062–3080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xia, M.; Aïssa, S. Coordinated multi-point transmission: A poisson-delaunay triangulation based approach. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2020, 19, 2946–2959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khan, W.U.; Liu, J.; Jameel, F.; Sharma, V.; Jäntti, R.; Han, Z. Spectral efficiency optimization for next generation NOMA-enabled IoT networks. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2020, 69, 15284–15297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Research Work | Contribution | Sum Rate | Capacity | Clustering | Ultra-Dense HetNet | User Association |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [11] | Proposed a unified NOMA framework for user association and resource allocation to achieve massive connectivity. | ✓ | ✓ | |||
| [12] | Energy efficiency maximization is achieved by proposing a joint optimization framework of PD-NOMA and beam forming. | ✓ | ||||
| [17] | System level performance analysis with hybrid PD-NOMA and OFDMA schemes. | ✓ | ✓ | |||
| [24] | PD-NOMA, game theory algorithms are proposed based on QoS threshold to improve user association and power allocation. | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| [22] | Proposed a cluster specific beam-forming algorithm to maximize sum-throughput. | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| Sub Carrier Bandwidth | 5 MHz |
| System Bandwidth (W) | 10 MHz |
| Transmission Power of Pico BSs (HSBS) | 25 dBm |
| Transmission Power of Femto BSs (LSBS) | 10 dBm |
| Channel Gain (MBS) | 14 dBi |
| Channel Gain (SBS) | 7 dBi |
| Indoor/Outdoor Path Loss Coefficient | 2 |
| Radius of MBS (Macro BS) | 500 m |
| Radius of HSBS (Pico BS) | 25 m |
| Radius of LSBS (Femto BS) | 10 m |
| No. of HSBS | 10 |
| No. of LSBS | 30 |
| No. of Users | 2–60 |
| No. of Sub-Carriers NOMA | 5 |
| AWGN | 169 dBm/Hz |
| Fading | Rayleigh |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hasan, N.; Rizvi, S.; Shabbir, A. A Clustered PD-NOMA in an Ultra-Dense Heterogeneous Network with Improved System Capacity and Throughput. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 5206. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12105206
Hasan N, Rizvi S, Shabbir A. A Clustered PD-NOMA in an Ultra-Dense Heterogeneous Network with Improved System Capacity and Throughput. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(10):5206. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12105206
Chicago/Turabian StyleHasan, Naureen, Safdar Rizvi, and Amna Shabbir. 2022. "A Clustered PD-NOMA in an Ultra-Dense Heterogeneous Network with Improved System Capacity and Throughput" Applied Sciences 12, no. 10: 5206. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12105206
APA StyleHasan, N., Rizvi, S., & Shabbir, A. (2022). A Clustered PD-NOMA in an Ultra-Dense Heterogeneous Network with Improved System Capacity and Throughput. Applied Sciences, 12(10), 5206. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12105206







