Aggression Detection in Social Media from Textual Data Using Deep Learning Models
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- 1.
- The proposed model extracts eight novel emotional features from the textual tweets to evaluate their roles in identifying aggressive statements.
- 2.
- The DNN model is optimized with fine-tuned parameters, consuming fewer (possible number of) layers compared to its competitors to identify aggression.
- 3.
- The proposed DNN model is compared with the existing state-of-the-art models using various evaluation measures.
- 4.
- A hybridized model for combining manual feature extraction, feature selection, and feeding these features to a neural network for behavior analysis of tweets is presented for better performance.
2. Related Work
3. Methodology
3.1. Evaluation Metrics
3.2. Dataset
3.3. Preprocessing
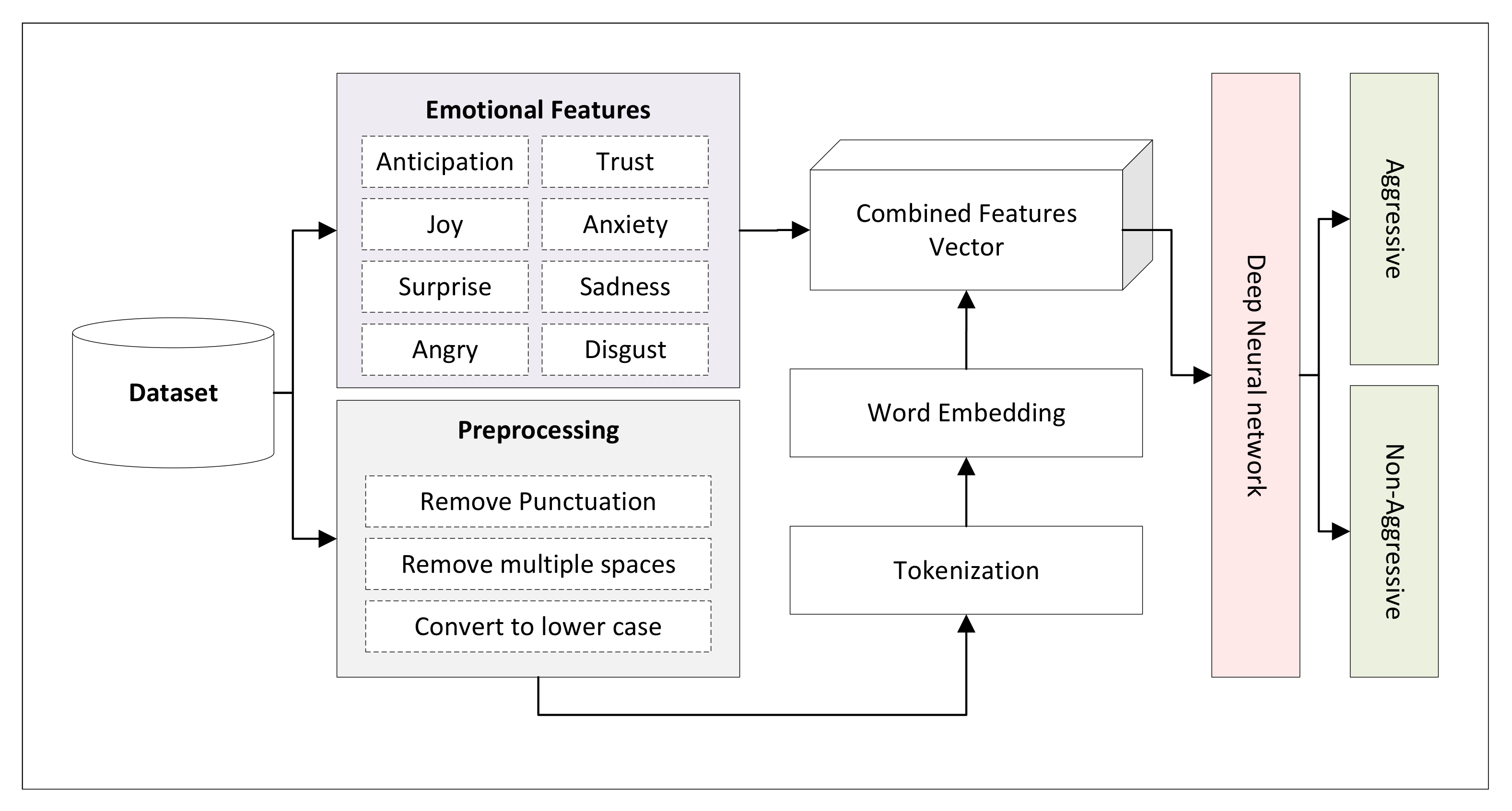
3.4. Feature Extraction
3.4.1. Discrete Emotions
3.4.2. Word2Vec
3.5. Feature Selection
3.6. Machine Learning Models
3.7. Deep Learning Models
Proposed Model
| Algorithm 1: Proposed algorithm for feature engineering step |
 |
4. Results
4.1. Experiments with Word2vec
4.2. Experiments with Combined Word2vec and Emotional Features
4.3. Hypothesis Testing and Significance of the Emotional Features
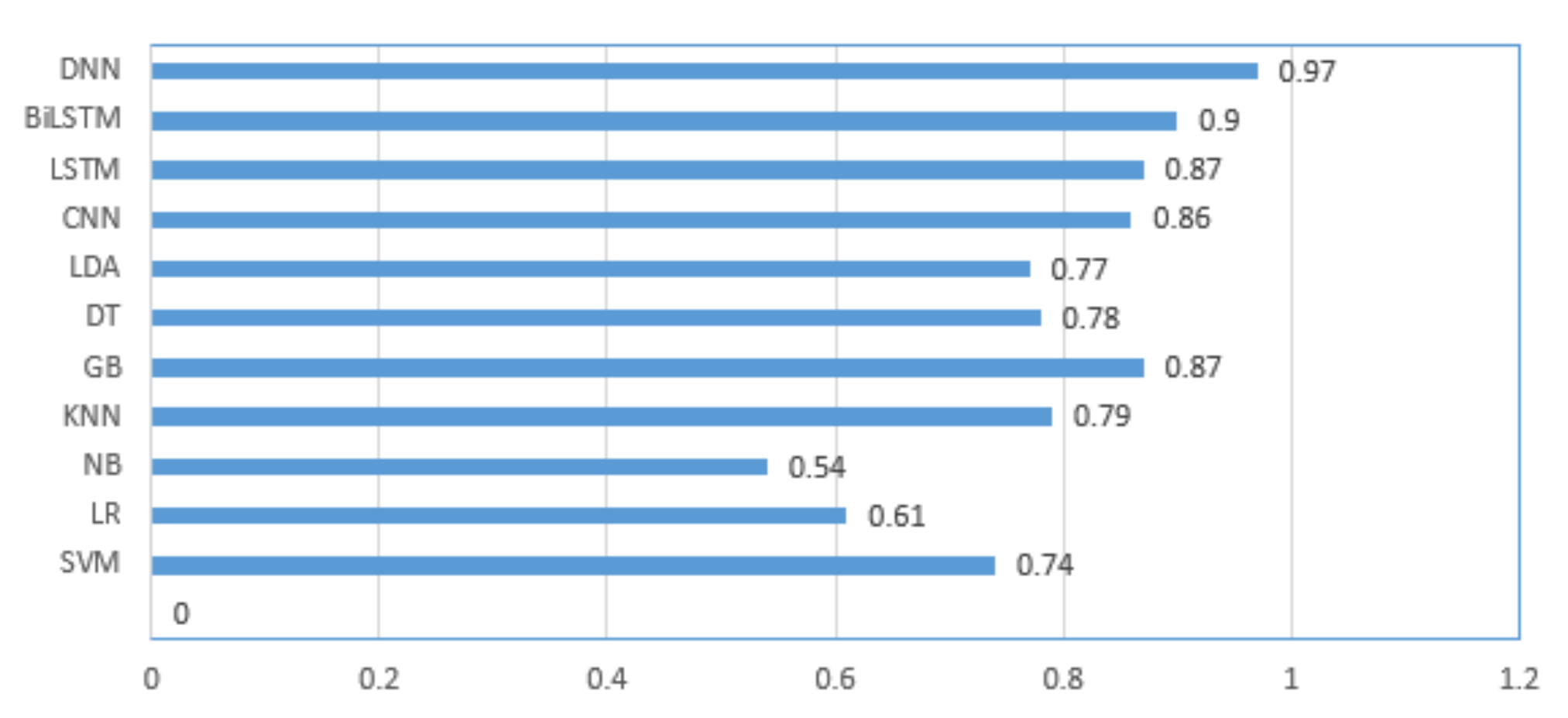
4.4. Comparison of the Proposed Model with the State-of-the-Art
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nurrahmi, H.; Nurjanah, D. Indonesian twitter cyberbullying detection using text classification and user credibility. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Information and Communications Technology (ICOIACT), Yogyakarta, Indonesia, 6–7 March 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Machackova, H. Bystander reactions to cyberbullying and cyberaggression: Individual, contextual, and social factors. Curr. Opin. Psychol. 2020, 36, 130–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oriola, O.; Kotzé, E. Evaluating machine learning techniques for detecting offensive and hate speech in South African tweets. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 21496–21509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visualizing Eight Years of Twitter’s Evolution: 2012–2019. 14 November 2019. Available online: https://blog.gdeltproject.org/visualizing-eight-years-of-twitters-evolution2012-2019/ (accessed on 12 February 2022).
- Hosseinmardi, H.; Rafiq, R.I.; Han, R.; Lv, Q.; Mishra, S. Prediction of cyberbullying incidents in a media-based social network. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE/ACM International Conference on Advances in Social Networks Analysis and Mining (ASONAM), San Francisco, CA, USA, 18–21 August 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Hemmatian, F.; Sohrabi, M.K. A survey on classification techniques for opinion mining and sentiment analysis. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2019, 52, 1495–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X. Efficient english text classification using selected machine learning techniques. Alex. Eng. J. 2021, 60, 3401–3409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haidar, B.; Chamoun, M.; Serhrouchni, A. A multilingual system for cyberbullying detection: Arabic content detection using machine learning. Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 2017, 2, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khairy, M.; Mahmoud, T.M.; Abd-El-Hafeez, T. Automatic Detection of Cyberbullying and Abusive Language in Arabic Content on Social Networks: A Survey. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2021, 189, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torfi, A.; Shirvani, R.A.; Keneshloo, Y.; Tavaf, N.; Fox, E.A. Natural language processing advancements by deep learning: A survey. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.01200. [Google Scholar]
- Lauriola, I.; Lavelli, A.; Aiolli, F. An Introduction to Deep Learning in Natural Language Processing: Models, Techniques, and Tools. Neurocomputing 2022, 470, 443–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hee, C.; Lefever, E.; Verhoeven, B.; Mennes, J.; Desmet, B.; De Pauw, G.; Daelemans, W.; Hoste, V. Detection and fine-grained classification of cyberbullying events. In Proceedings of the International Conference Recent Advances in Natural Language Processing (RANLP), Hissar, Bulgaria, 5–11 September 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y. Detecting Offensive Language in Social Medias for Protection of Adolescent Online Safety. Master’s Thesis, Penn State University, State College, PA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Balakrishnan, V.; Khan, S.; Arabnia, H.R. Improving cyberbullying detection using Twitter users’ psychological features and machine learning. Comput. Secur. 2020, 90, 101710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhter, M.P.; Jiangbin, Z.; Naqvi, I.R.; Abdelmajeed, M.; Sadiq, M.T. Automatic detection of offensive language for urdu and roman urdu. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 91213–91226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Lahiri, B.; Ojha, A.K. Aggressive and offensive language identification in hindi, bangla, and english: A comparative study. SN Comput. Sci. 2021, 2, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaza-del-Arco, F.M.; Molina-González, M.D.; Urena-López, L.A.; Martín-Valdivia, M.T. Comparing pre-trained language models for Spanish hate speech detection. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 166, 114120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herwanto, G.B.; Ningtyas, A.M.; Nugraha, K.E.; Trisna, I.N. Hate speech and abusive language classification using fastText. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Seminar on Research of Information Technology and Intelligent Systems (ISRITI), Yogyakarta, Indonesia, 5–6 December 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Fortuna, P.; Soler-Company, J.; Wanner, L. How well do hate speech, toxicity, abusive and offensive language classification models generalize across datasets? Inf. Process. Manag. 2021, 58, 102524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alotaibi, A.; Hasanat, M.H.A. Racism Detection in Twitter Using Deep Learning and Text Mining Techniques for the Arabic Language. In Proceedings of the 2020 First International Conference of Smart Systems and Emerging Technologies (SMARTTECH), Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, 3–5 November 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Malmasi, S.; Zampieri, M. Challenges in discriminating profanity from hate speech. J. Exp. Theor. Artif. Intell. 2018, 30, 187–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garaigordobil, M.; Mollo-Torrico, J.P.; Machimbarrena, J.M.; Páez, D. Cyberaggression in adolescents of Bolivia: Connection with psychopathological symptoms, adaptive and predictor variables. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chatzakou, D.; Kourtellis, N.; Blackburn, J.; De Cristofaro, E.; Stringhini, G.; Vakali, A. Mean birds: Detecting aggression and bullying on twitter. In Proceedings of the 2017 ACM on Web Science Conference, Troy, NY, USA, 25–28 June 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Gitari, N.D.; Zuping, Z.; Damien, H.; Long, J. A lexicon-based approach for hate speech detection. Int. J. Multimed. Ubiquitous Eng. 2015, 10, 215–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zois, D.S.; Kapodistria, A.; Yao, M.; Chelmis, C. Optimal online cyberbullying detection. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Calgary, AB, Canada, 15–20 April 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Pawar, R.; Raje, R.R. Multilingual cyberbullying detection system. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Electro Information Technology (EIT), Brookings, SD, USA, 20–22 May 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Sadiq, S.; Mehmood, A.; Ullah, S.; Ahmad, M.; Choi, G.S.; On, B.W. Aggression detection through deep neural model on twitter. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2021, 114, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigurbergsson, G.I.; Derczynski, L. Offensive language and hate speech detection for Danish. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1908.04531. [Google Scholar]
- Schneider, J.M.; Roller, R.; Bourgonje, P.; Hegele, S.; Rehm, G. Towards the automatic classification of offensive language and related phenomena in German tweets. In Proceedings of the 14th Conference on Natural Language Processing KONVENS, Vienna, Austria, 19–21 September 2018; p. 95. [Google Scholar]
- Pelle, R.; Alcântara, C.; Moreira, V.P. A classifier ensemble for offensive text detection. In Proceedings of the 24th Brazilian Symposium on Multimedia and the Web, Salvador, Brazil, 16–19 October 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Haidar, B.; Chamoun, M.; Serhrouchni, A. Multilingual cyberbullying detection system: Detecting cyberbullying in Arabic content. In Proceedings of the 2017 1st Cyber Security in Networking Conference (CSNet), Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 18–20 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ibrohim, M.O.; Budi, I. A dataset and preliminaries study for abusive language detection in Indonesian social media. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2018, 135, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrohim, M.O.; Budi, I. Multi-label hate speech and abusive language detection in Indonesian twitter. In Proceedings of the Third Workshop on Abusive Language Online, Florence, Italy, 1 August 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Desrul, D.R.K.; Romadhony, A. Abusive language detection on Indonesian online news comments. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Seminar on Research of Information Technology and Intelligent Systems (ISRITI), Yogyakarta, Indonesia, 5–6 December 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Di Capua, M.; Di Nardo, E. Unsupervised cyber bullying detection in social networks. In Proceedings of the 2016 23rd International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), Cancun, Mexico, 4–8 December 2016. [Google Scholar]
- González-Ibánez, R. Identifying sarcasm in twitter: A closer look. In Proceedings of the 49th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, Stroudsburg, PA, USA, 19–24 June 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Chia, Z.L.; Ptaszynski, M.; Masui, F.; Leliwa, G.; Wroczynski, M. Machine Learning and feature engineering-based study into sarcasm and irony classification with application to cyberbullying detection. Inf. Process. Manag. 2021, 58, 102600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, P.J.; Hu, Y.H.; Chen, K.; Tarn, J.M.; Cheng, L.E. Cyberbullying Detection on Social Network Services. In Proceedings of the 22nd Pacific Asia Conference on Information Systems, PACIS 2018, Yokohama, Japan, 26–30 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Ajlan, M.A.; Ykhlef, M. Optimized Twitter Cyberbullying Detection based on Deep Learning. In Proceedings of the 2018 21st Saudi Computer Society National Computer Conference (NCC), Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, 25–26 April 2018; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, M.T.; Rahman, M.; Nur, S.; Islam, A.; Das, D. Deployment of Machine Learning and Deep Learning Algorithms in Detecting Cyberbullying in Bangla and Romanized Bangla text: A Comparative Study. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Advances in Electrical, Computing, Communication and Sustainable Technologies (ICAECT), Bhilai, India, 19–20 February 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Dadvar, M.; Eckert, K. Cyberbullying detection in social networks using deep learning based models. In International Conference on Big Data Analytics and Knowledge Discovery; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Malik, M.; Hussain, A. Helpfulness of product reviews as a function of discrete positive and negative emotions. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2017, 73, 290–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Plutchik, R. The Psychology and Biology of Emotion; HarperCollins College Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammad, S.M.; Turney, P.D. Nrc emotion lexicon. Natl. Res. Counc. Can. 2013, 2. Available online: http://www.saifmohammad.com/WebDocs/NRCemotionlexicon.pdf (accessed on 12 February 2022).
- Mikolov, T.; Sutskever, I.; Chen, K.; Corrado, G.S.; Dean, J. Distributed representations of words and phrases and their compositionality. In Proceedings of the 27th Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Lake Tahoe, NV, USA, 5–10 December 2013; pp. 3111–3119. [Google Scholar]
- Kulkarni, N. A comparative study of Word Embedding Techniques to extract features from Text. Turk. J. Comput. Math. Educ. 2021, 12, 3550–3557. [Google Scholar]
- Kumari, K.; Singh, J.P.; Dwivedi, Y.K.; Rana, N.P. Towards Cyberbullying-free social media in smart cities: A unified multi-modal approach. Soft Comput. 2020, 24, 11059–11070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsubait, T.; Alfageh, D. Comparison of Machine Learning Techniques for Cyberbullying Detection on YouTube Arabic Comments. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Netw. Secur. 2021, 21, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Hakak, S.; Alazab, M.; Khan, S.; Gadekallu, T.R.; Maddikunta, P.K.; Khan, W.Z. An ensemble machine learning approach through effective feature extraction to classify fake news. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2021, 117, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salton, G.; Buckley, C. Term-weighting approaches in automatic text retrieval. Inf. Process. Manag. 1988, 24, 513–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bejani; Mahdi, M.; Ghatee, M. A systematic review on overfitting control in shallow and deep neural networks. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2021, 54, 6391–6438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergara, J.R. A review of feature selection methods based on mutual information. Neural Comput. Appl. 2014, 24, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H. Feature selection based on mutual information with correlation coefficient. Appl. Intell. 2022, 52, 5457–5474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri, F.; Yousefi, M.R.; Lucas, C.; Shakery, A.; Yazdani, N. Mutual information-based feature selection for intrusion detection systems. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2011, 34, 1184–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, J.; Yang, Y.; Li, L.; Bai, X.; Zhang, S.; Deng, C. Maximum relevance minimum common redundancy feature selection for nonlinear data. Inf. Sci. 2017, 409, 68–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, R.; Ranganathan, P. Common pitfalls in statistical analysis: Linear regression analysis. Perspect. Clin. Res. 2017, 8, 100. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Yan, S.; Wong, K. Verbal aggression detection on Twitter comments: Convolutional neural network for short-text sentiment analysis. Neural Comput. Appl. 2020, 32, 10809–10818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
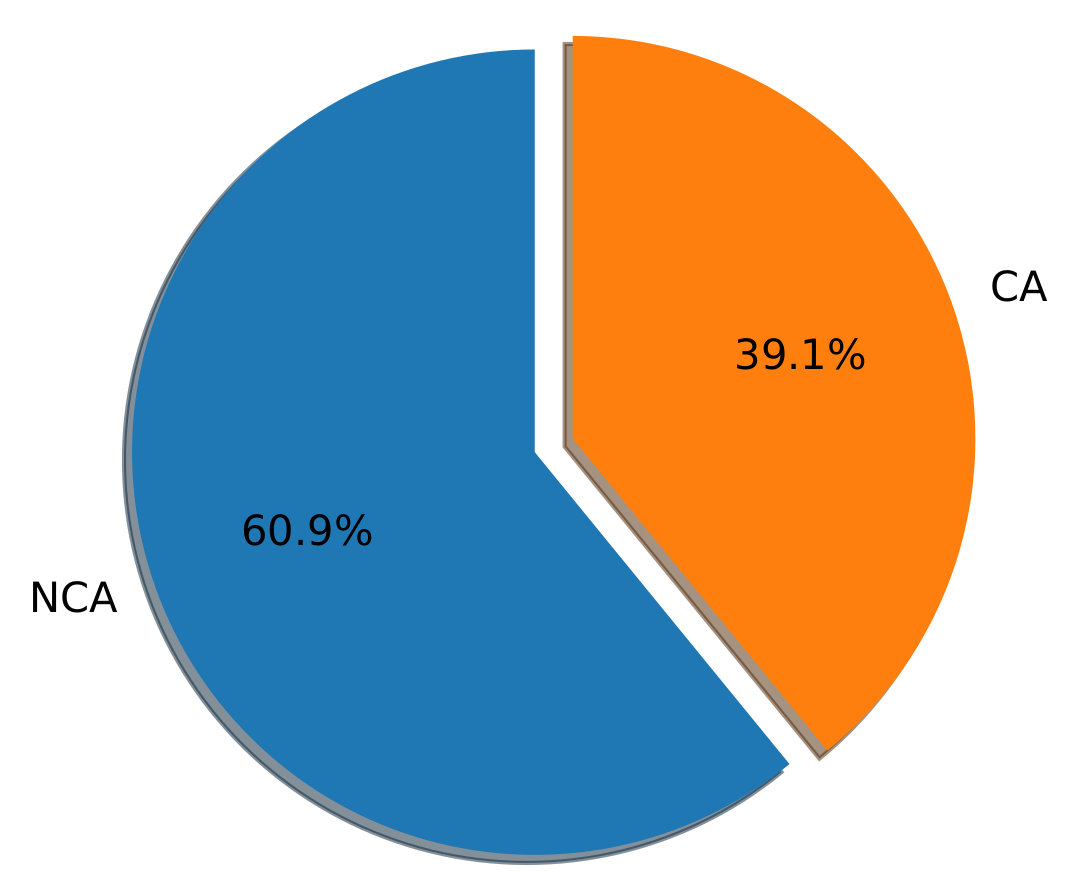

| Dataset Name | Total Tweets | Aggressive | Non Aggressive |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cyber_ Troll | 20,001 | 7822 | 12,179 |
| Hyper Parameters | DNN | CNN | LSTM | BiLSTM |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LSTM units | - | - | 2 | 2 |
| Hidden neurons | - | - | 512,256 | 512,256 |
| Dense layers | 3(256,128,1) | 1 (3) | 2 (256,2) | 2 (256,2) |
| Max- pooling | - | 4 | - | - |
| Act func on hidden Layer | ReLU | ReLU | ReLU | ReLU |
| Act func on output Layer | Softmax | Softmax | Softmax | Softmax |
| Epochs | 100 | 200 | 200 | 200 |
| Batch_size | 128 | 128 | 128 | 128 |
| Optimizer | Adam | Adam | Adam | Adam |
| Models | Precision | Recall | F1-Score | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SVM | 67.21 ± 0.23 | 67.74 ± 0.85 | 64.24 ± 0.74 | 62.17 ± 0.36 |
| LR | 62.36 ± 0.18 | 49.24 ± 0.73 | 44.96 ± 0.19 | 58.14 ± 0.90 |
| NB | 62.75 ± 0.22 | 49.74 ± 0.69 | 44.09 ± 0.74 | 48.27 ± 0.18 |
| KNN | 67.36 ± 0.77 | 67.88 ± 0.37 | 67.08 ± 0.74 | 66.23 ± 0.88 |
| GB | 77.82 ± 0.58 | 76.66 ± 0.69 | 77.10 ± 0.27 | 76.71 ± 0.05 |
| DT | 75.08 ± 0.41 | 74.47 ± 0.81 | 74.33 ± 0.38 | 73.13 ± 0.61 |
| LDA | 69.94 ± 0.04 | 69.94 ± 0.82 | 68.31 ± 0.36 | 68.55 ± 0.54 |
| Models | Precision | Recall | F1-Score | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LSTM | 80.25 ± 0.24 | 82.15 ± 0.47 | 80.65 ± 0.85 | 82.15 ± 0.15 |
| BiLSTM | 83.17 ± 0.74 | 85.84 ± 0.21 | 84.76 ± 0.86 | 85.17 ± 0.48 |
| CNN | 81.14 ± 0.47 | 80.38 ± 0.16 | 79.96 ± 0.84 | 82.14 ± 0.37 |
| DNN | 86.28 ± 0.08 | 87.74 ± 0.19 | 87.11 ± 0.83 | 88.34 ± 0.17 |
| Models | Precision | Recall | F1-Score | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SVM | 80.15 ± 0.85 | 80.69 ± 0.21 | 74.37 ± 0.96 | 78.48 ± 0.65 |
| LR | 78.17 ± 0.73 | 59.67 ± 0.09 | 61.36 ± 0.19 | 68.48 ± 0.54 |
| NB | 82.18 ± 0.38 | 59.64 ± 0.63 | 54.19 ± 0.37 | 56.90 ± 0.71 |
| KNN | 79.15 ± 0.81 | 79.37 ± 0.94 | 79.16 ± 0.09 | 76.38 ± 0.73 |
| GB | 83.28 ± 0.54 | 84.08 ± 0.66 | 84.18 ± 0.75 | 86.06 ± 0.77 |
| DT | 77.17 ± 0.19 | 78.85 ± 0.84 | 78.25 ± 0.07 | 75.37 ± 0.96 |
| LDA | 78.27 ± 0.21 | 78.18 ± 0.29 | 77.39 ± 0.74 | 75.69 ± 0.24 |
| Models | Precision | Recall | F1-Score | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LSTM | 88.41 ± 0.67 | 86.96 ± 0.75 | 87.47 ± 0.67 | 88.14 ± 0.27 |
| BiLSTM | 91.21 ± 0.74 | 90.86 ± 0.41 | 90.96 ± 0.96 | 91.43 ± 0.17 |
| CNN | 88.75 ± 0.56 | 87.34 ± 0.63 | 86.41 ± 0.38 | 84.74 ± 0.68 |
| DNN | 97.17 ± 0.48 | 96.73 ± 0.91 | 97.18 ± 0.19 | 96.07 ± 0.28 |
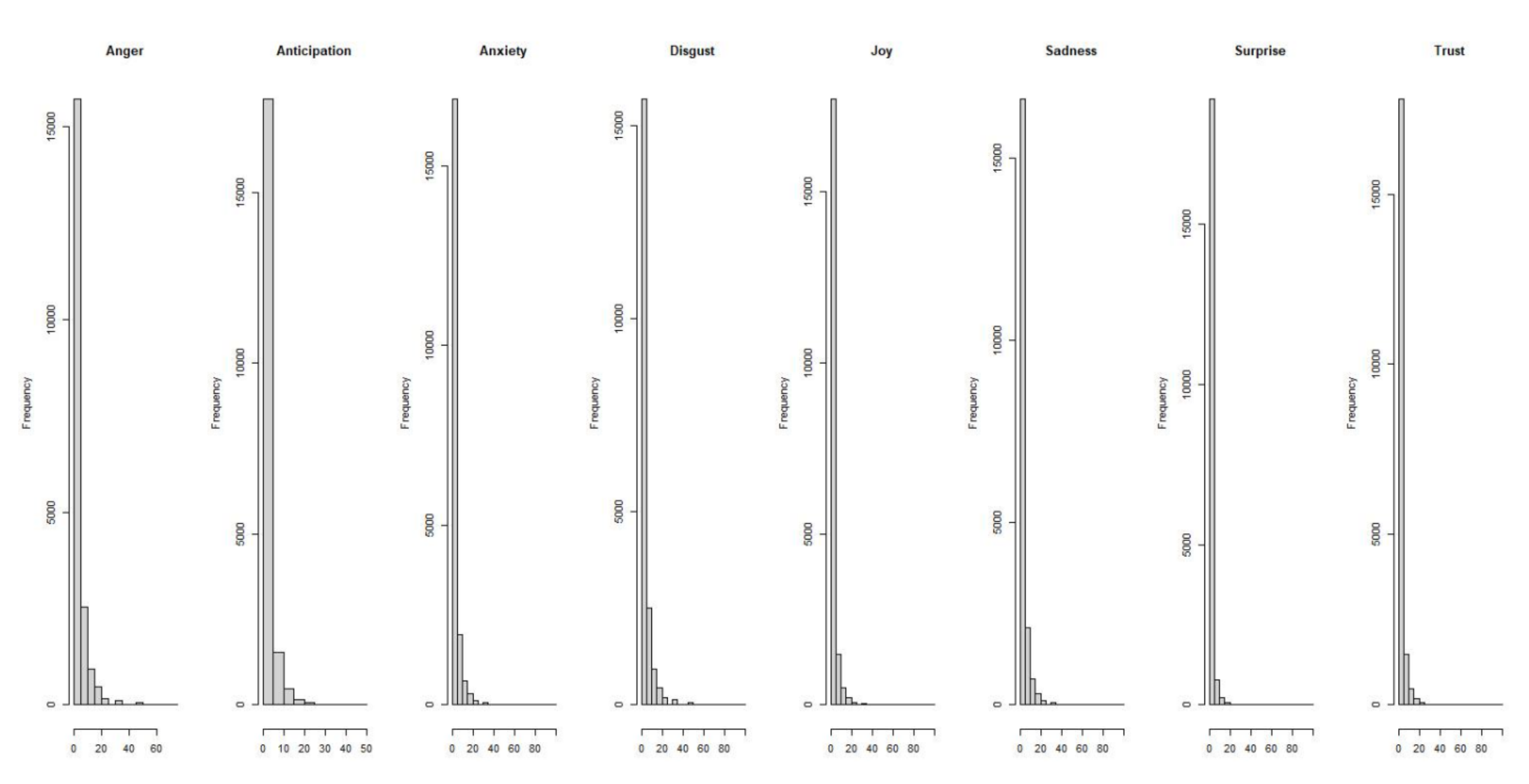
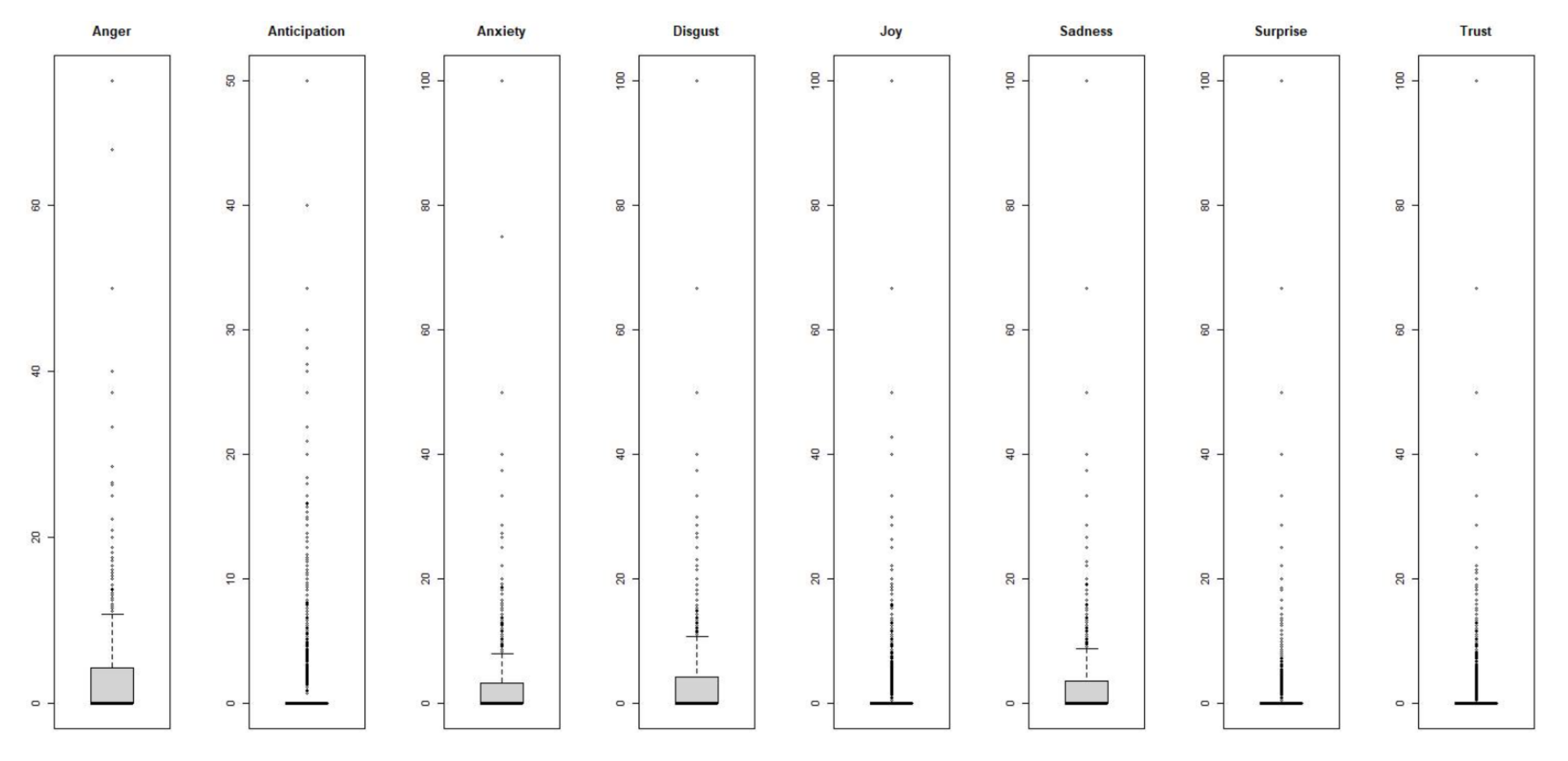
| Emotional Feature | N | Mean | SD | Min | Q1 | Q3 | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anger | 20,001 | 3.014 | 5.964 | 0 | 0 | 4.348 | 75 |
| Anticipation | 20,001 | 1.472 | 3.708 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 50 |
| Anxiety | 20,001 | 2.162 | 4.874 | 0 | 0 | 3.333 | 100 |
| Disgust | 20,001 | 3.109 | 6.235 | 0 | 0 | 4.348 | 100 |
| Joy | 20,001 | 1.532 | 4.097 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 |
| Sadness | 20,001 | 2.292 | 5.038 | 0 | 0 | 3.571 | 100 |
| Surprise | 20,001 | 0.748 | 2.753 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 |
| Trust | 20,001 | 1.485 | 3.864 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 |
| Estimate | Standard Error | z Value | Pr(>|z|) | Significance | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | −0.5531 | 0.0205 | −26.9310 | <2 × 10 | *** |
| Anger | 0.0003 | 0.0057 | 0.0520 | 0.9588 | |
| Anticipation | 0.0023 | 0.0059 | 0.3970 | 0.6914 | |
| Anxiety | −0.0088 | 0.0066 | −1.3270 | 0.1846 | |
| Disgust | 0.0474 | 0.0054 | 8.7020 | <2 × 10 | *** |
| Joy | −0.0380 | 0.0067 | −5.7090 | 1.13 × 10 | *** |
| Sadness | 0.0228 | 0.0064 | 3.5660 | 0.0004 | *** |
| Surprise | −0.0061 | 0.0079 | −0.7690 | 0.4420 | |
| Trust | −0.0140 | 0.0063 | −2.2390 | 0.0252 | * |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khan, U.; Khan, S.; Rizwan, A.; Atteia, G.; Jamjoom, M.M.; Samee, N.A. Aggression Detection in Social Media from Textual Data Using Deep Learning Models. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 5083. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12105083
Khan U, Khan S, Rizwan A, Atteia G, Jamjoom MM, Samee NA. Aggression Detection in Social Media from Textual Data Using Deep Learning Models. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(10):5083. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12105083
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhan, Umair, Salabat Khan, Atif Rizwan, Ghada Atteia, Mona M. Jamjoom, and Nagwan Abdel Samee. 2022. "Aggression Detection in Social Media from Textual Data Using Deep Learning Models" Applied Sciences 12, no. 10: 5083. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12105083
APA StyleKhan, U., Khan, S., Rizwan, A., Atteia, G., Jamjoom, M. M., & Samee, N. A. (2022). Aggression Detection in Social Media from Textual Data Using Deep Learning Models. Applied Sciences, 12(10), 5083. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12105083








