Analytical Model Formulation of Steel Plate Reinforced Concrete Walls against Hard Projectile Impact
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Impact Resistance Theories
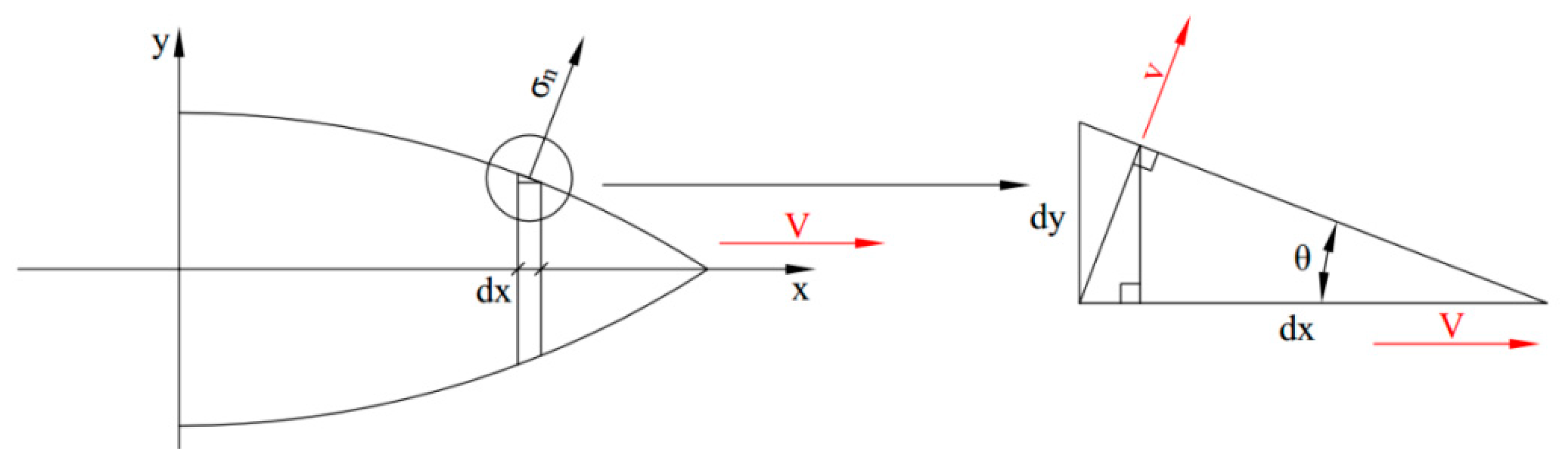
2.1. Cavity Expansion Analysis for Concrete
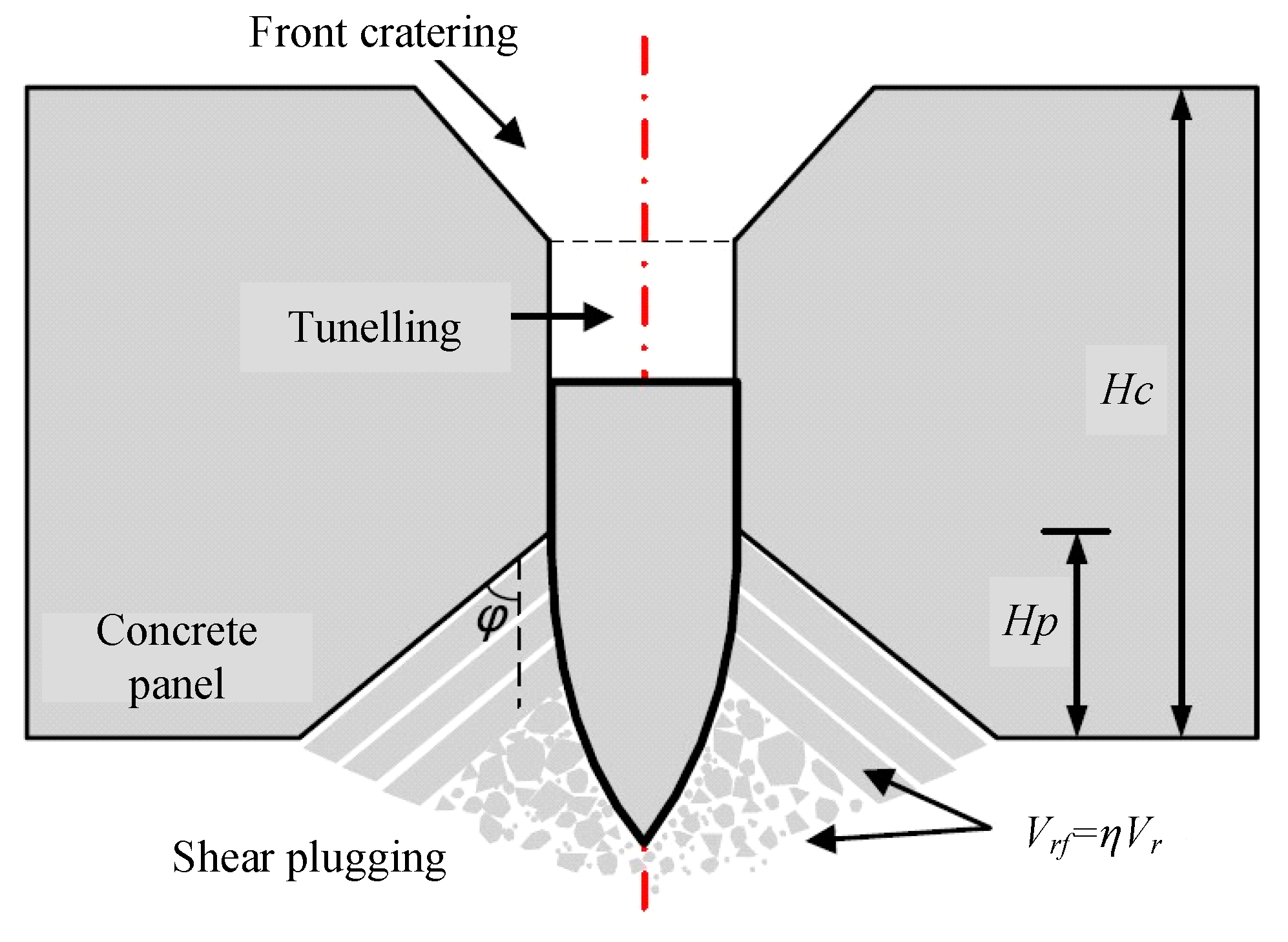
2.2. Perforation with Shear Plugging
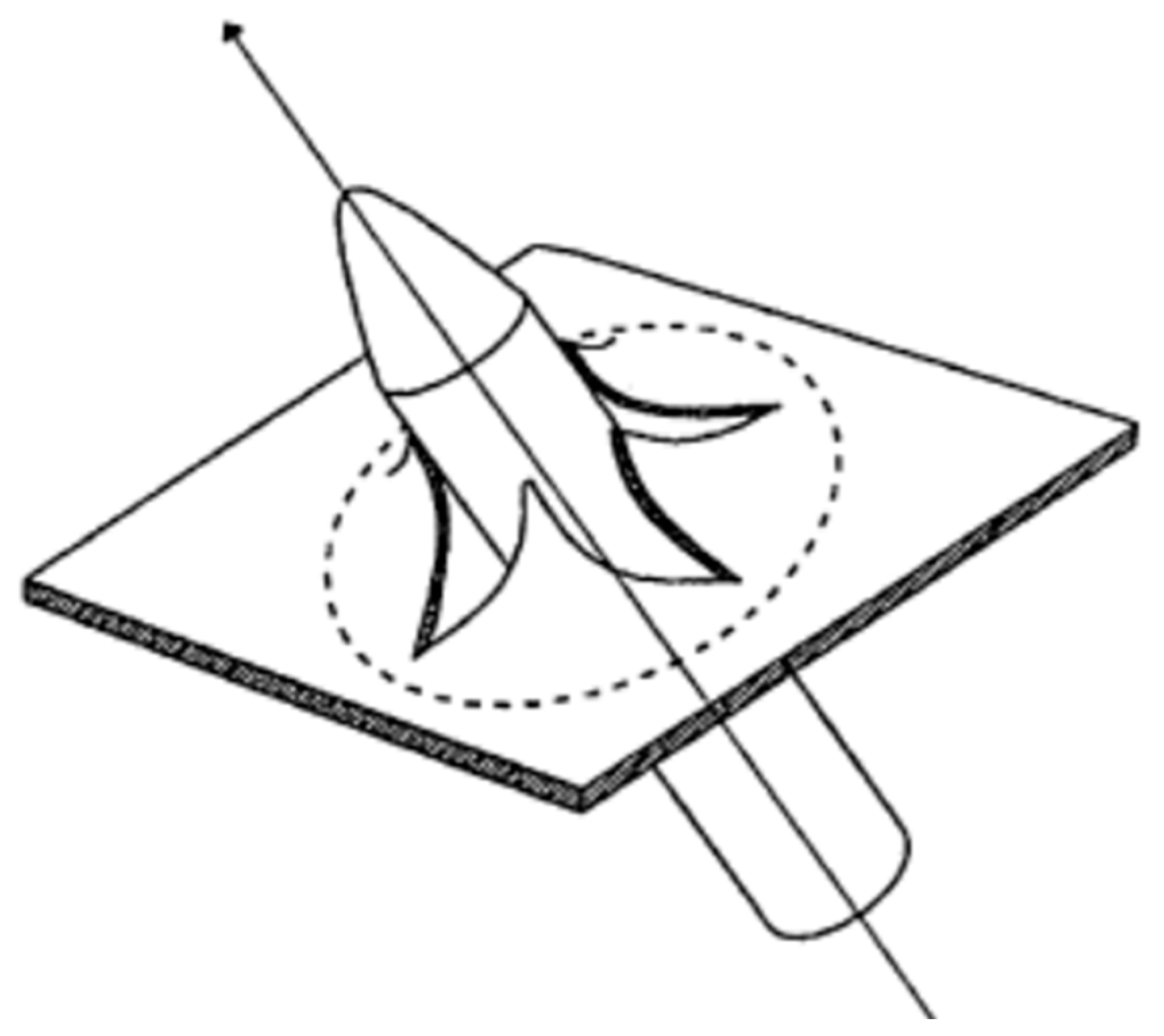
2.3. Thin Plate Petaling
3. Perforation Model Validation
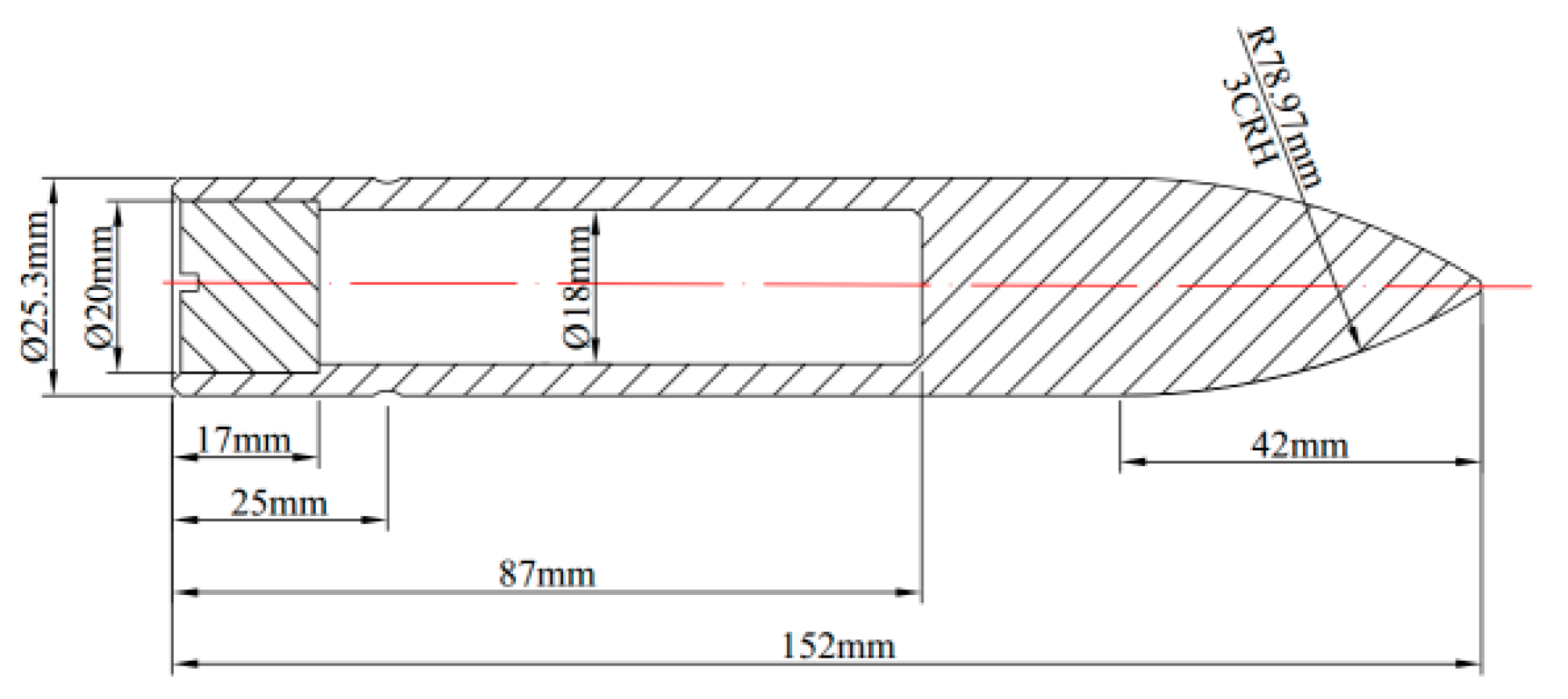
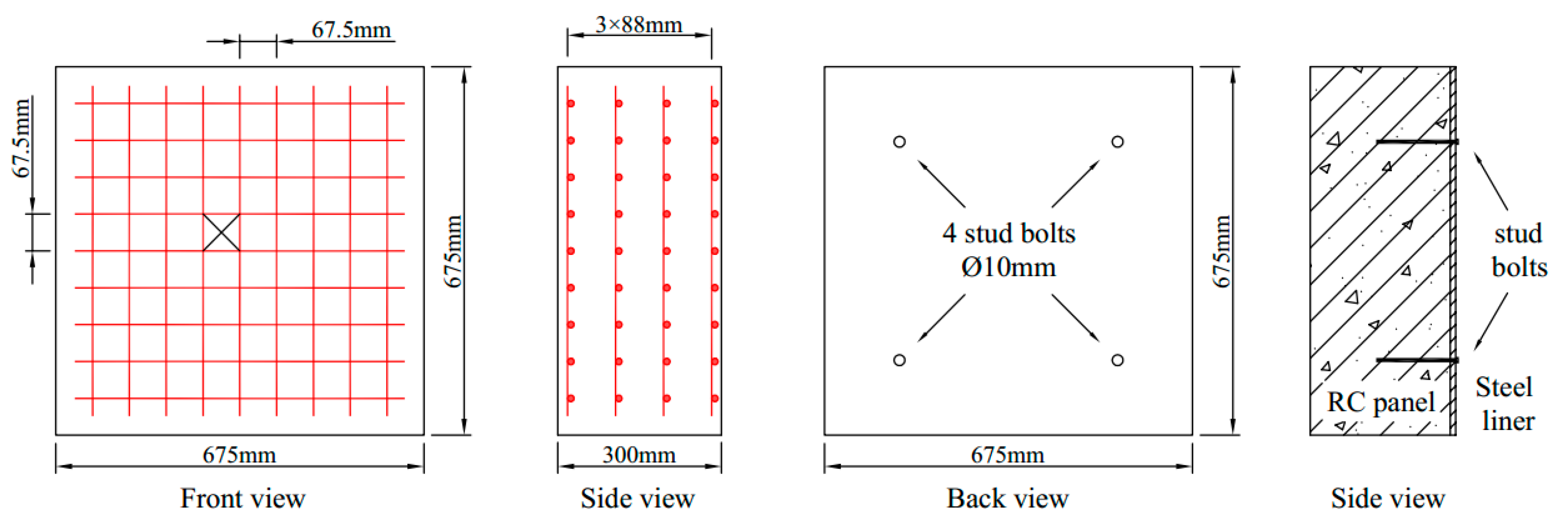
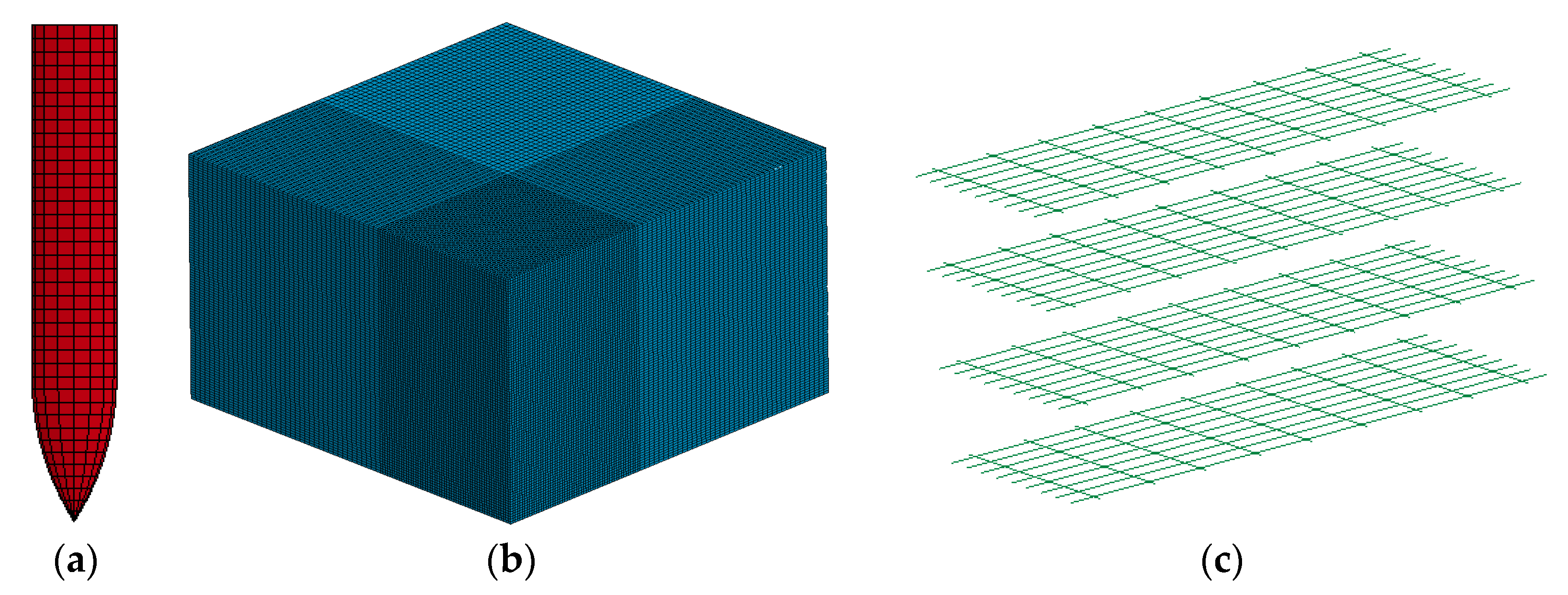
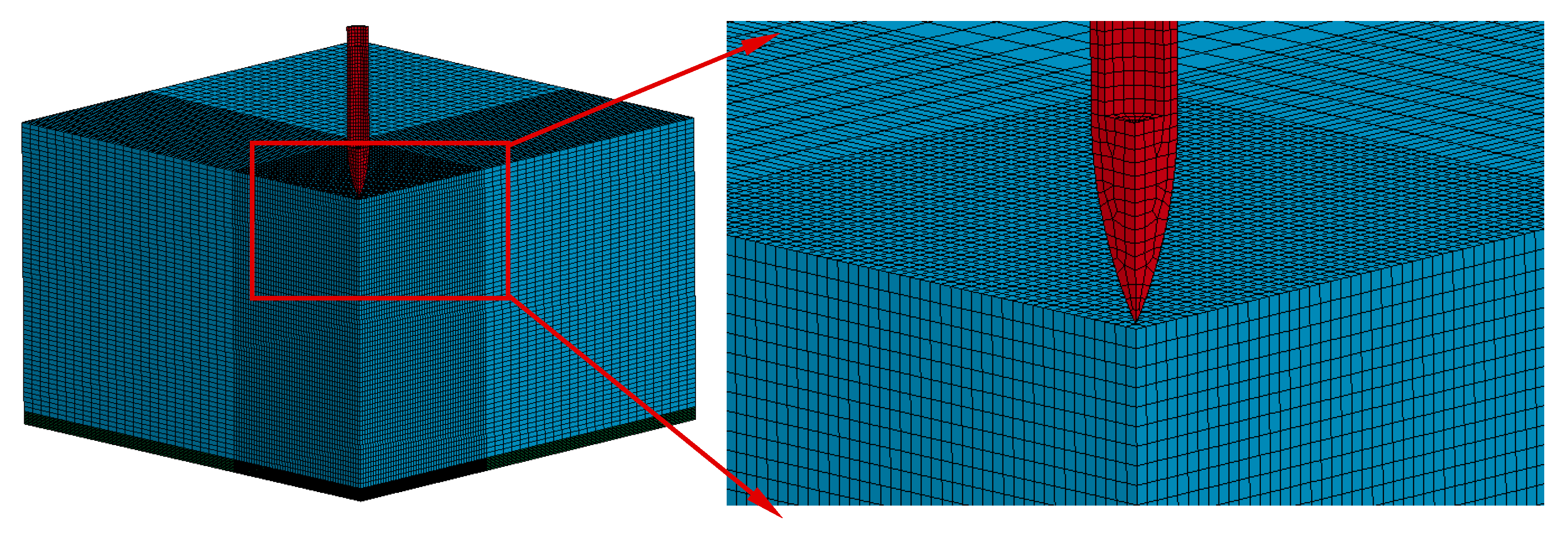
3.1. Perforation Test and FE Model
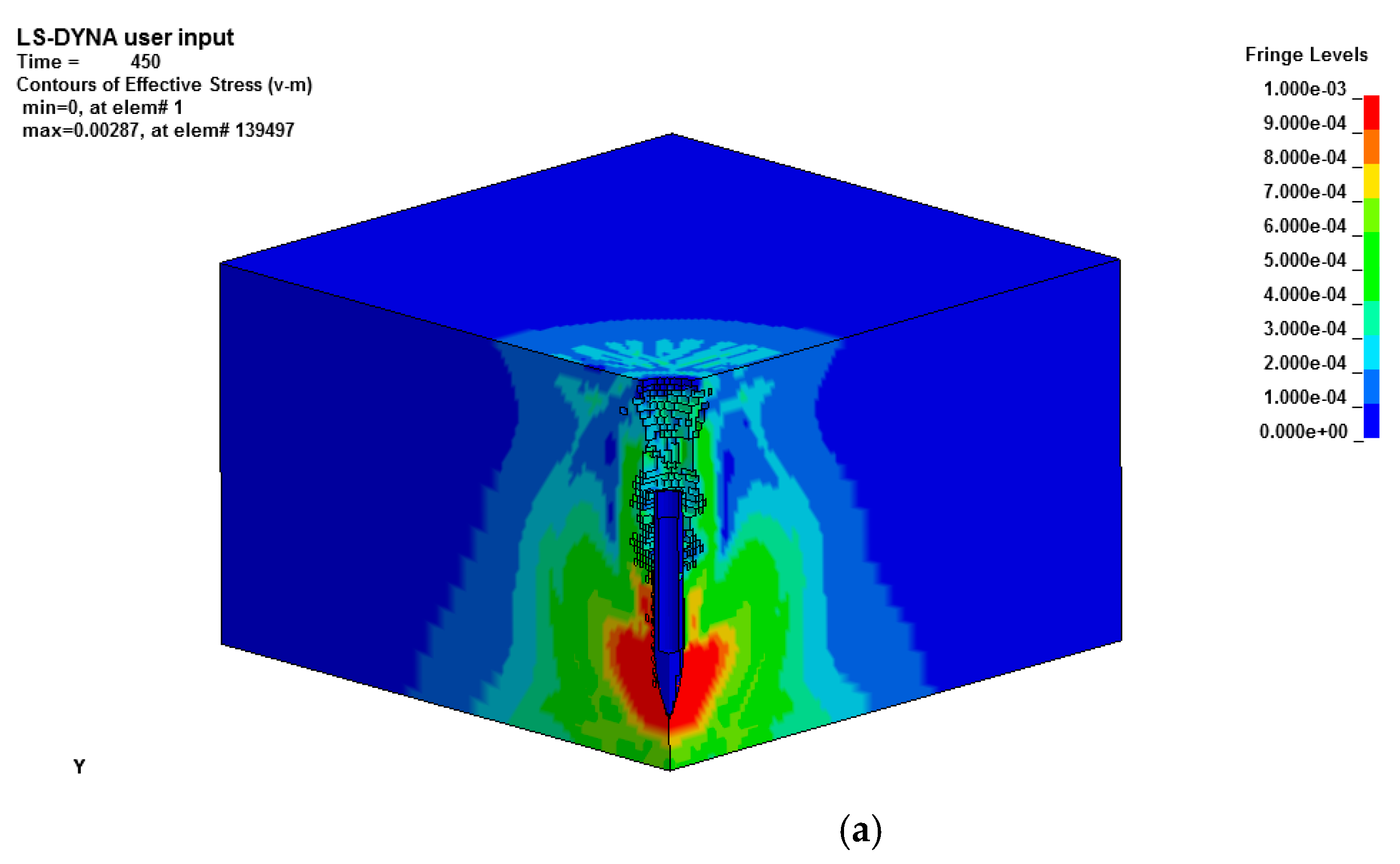
3.2. Numerical Results, Validation and Discussion
4. Numerical Study of SC Walls Perforation
4.1. Model Setting
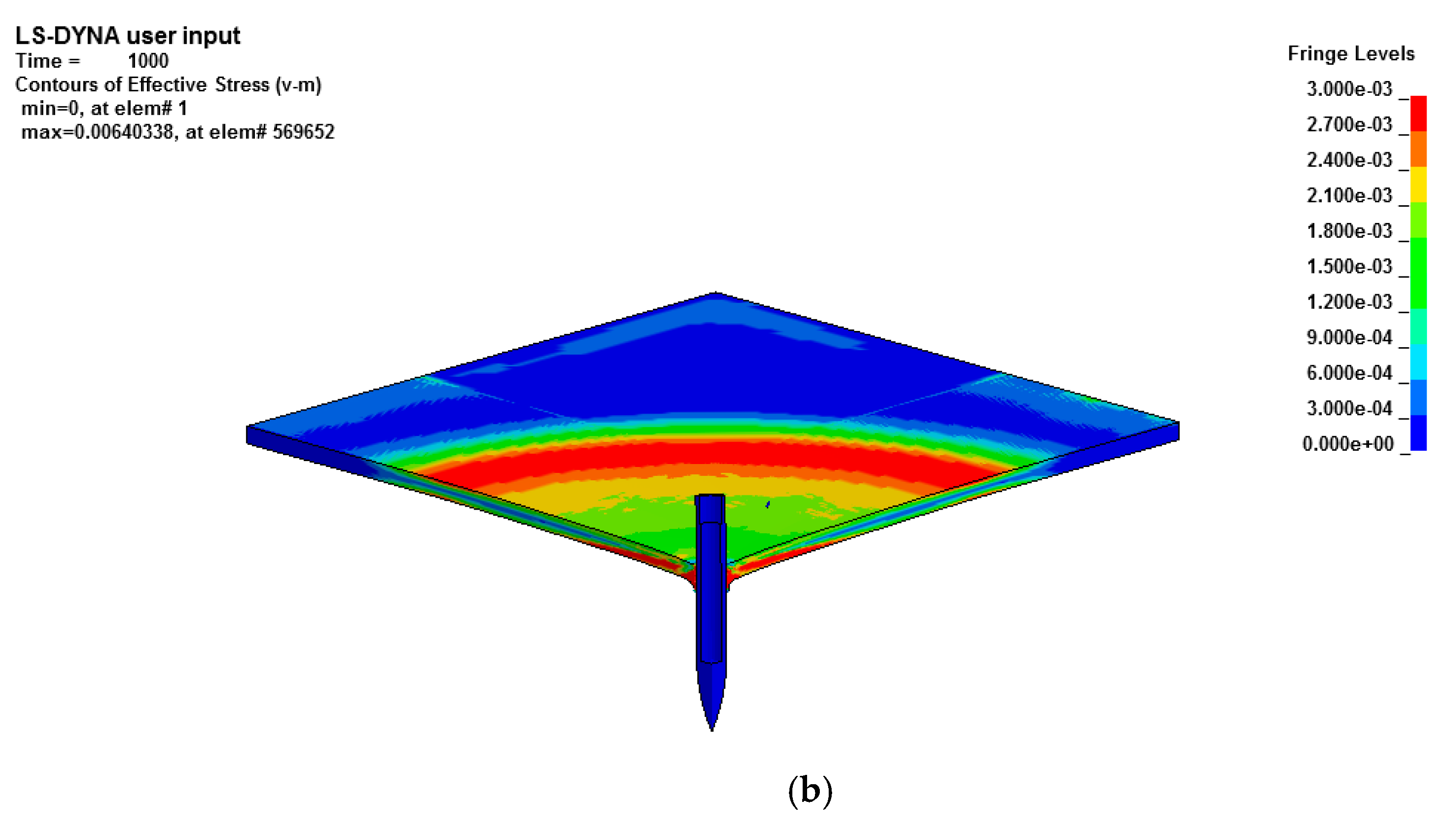
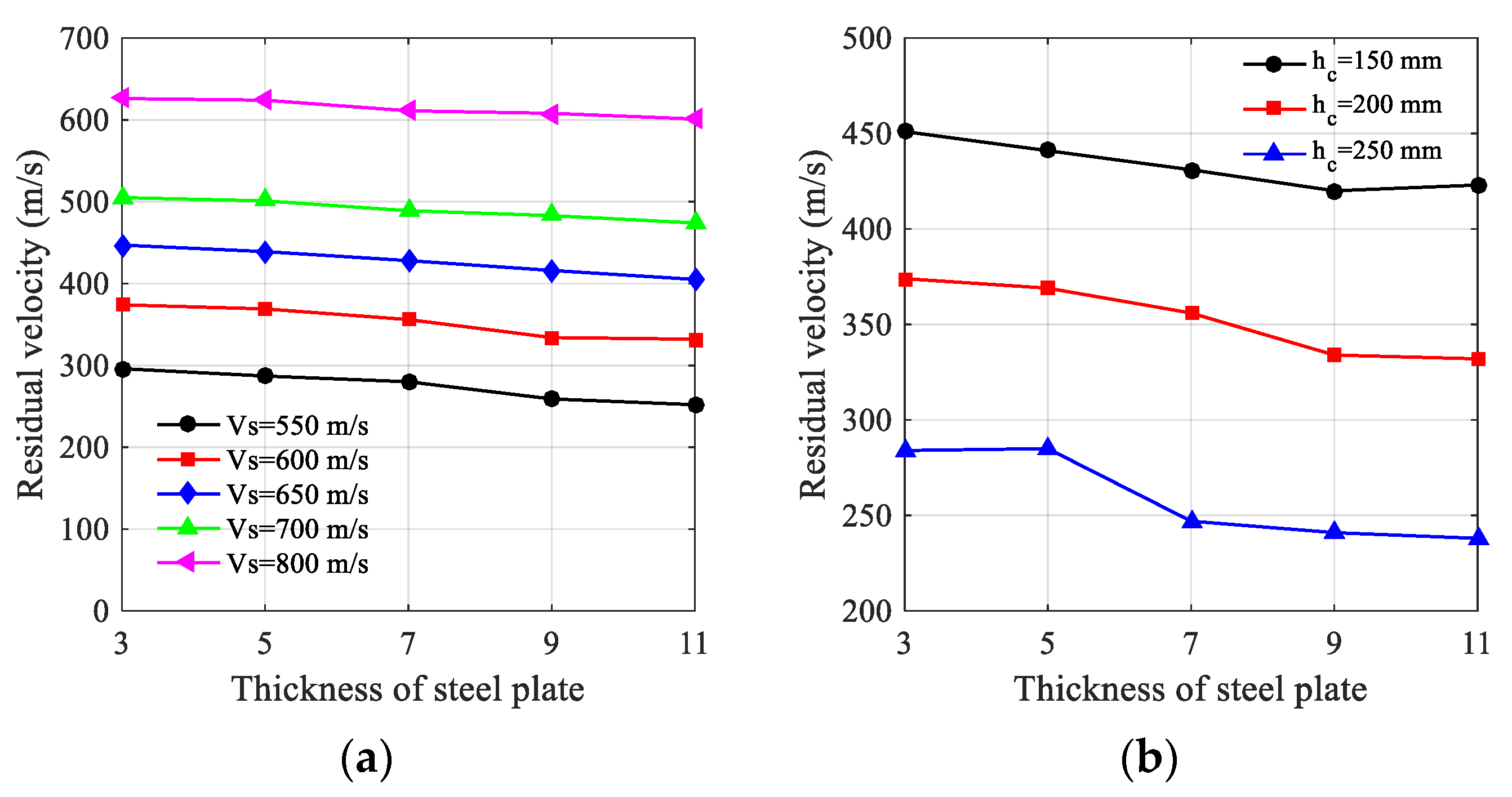
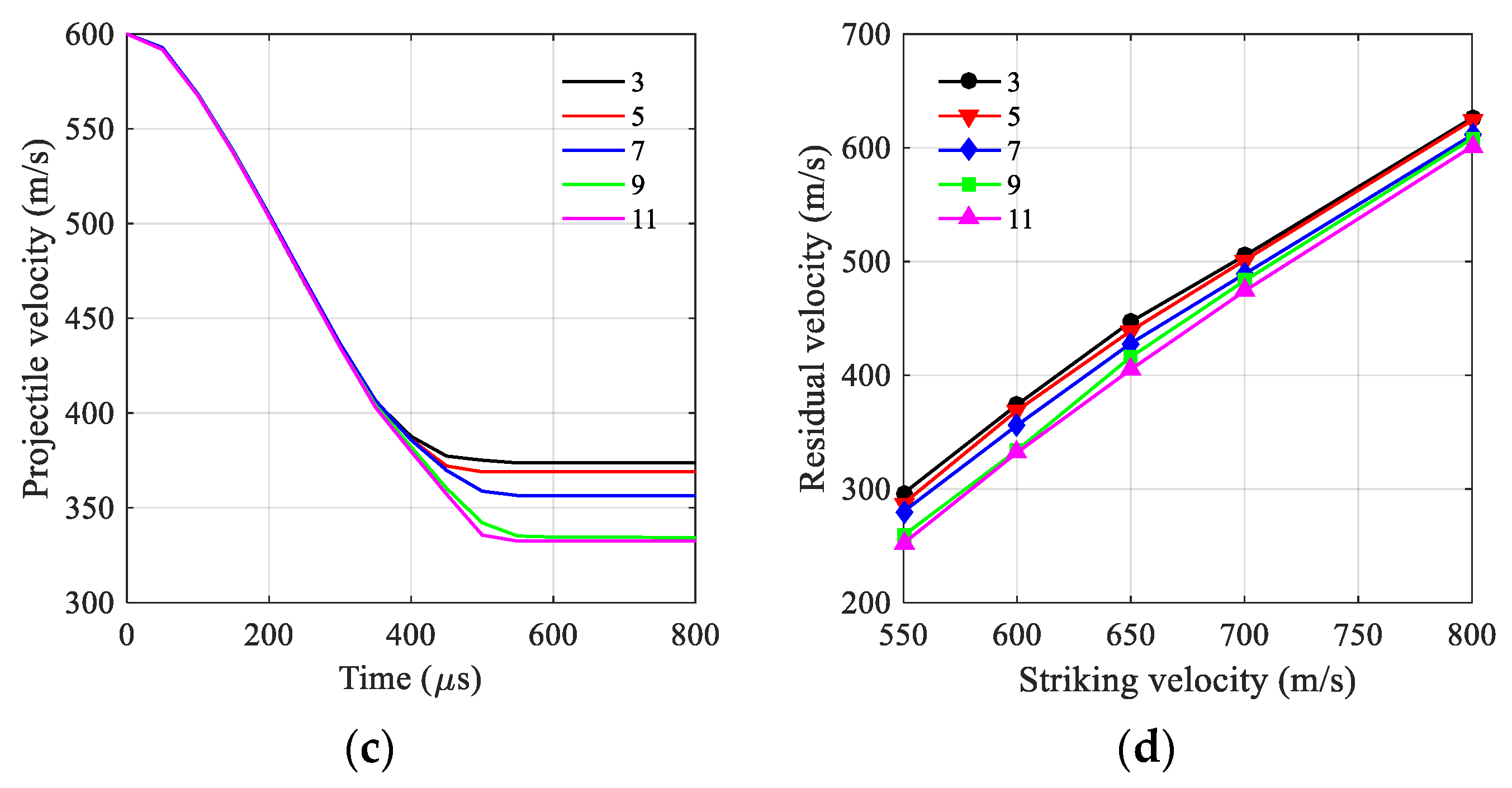
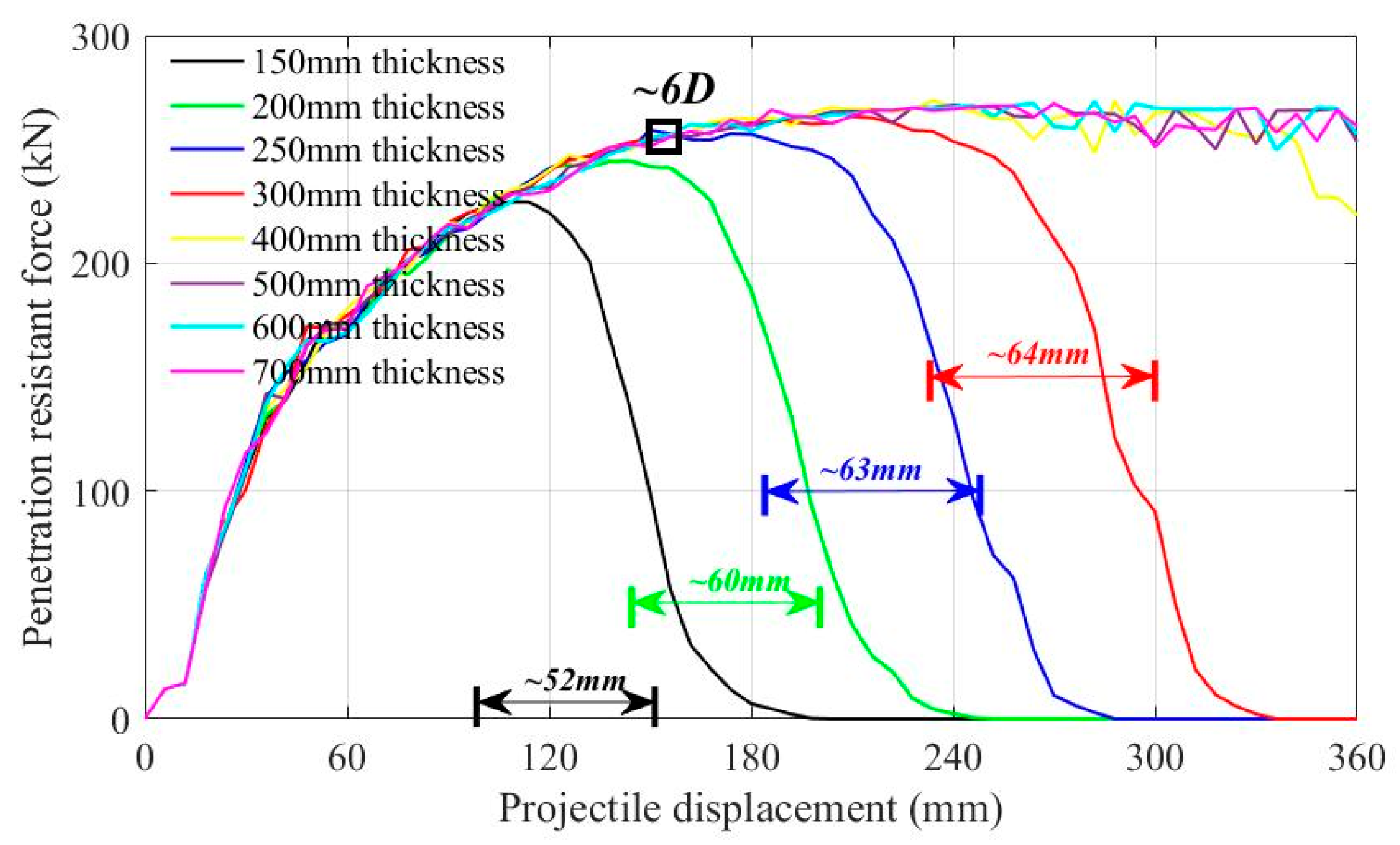
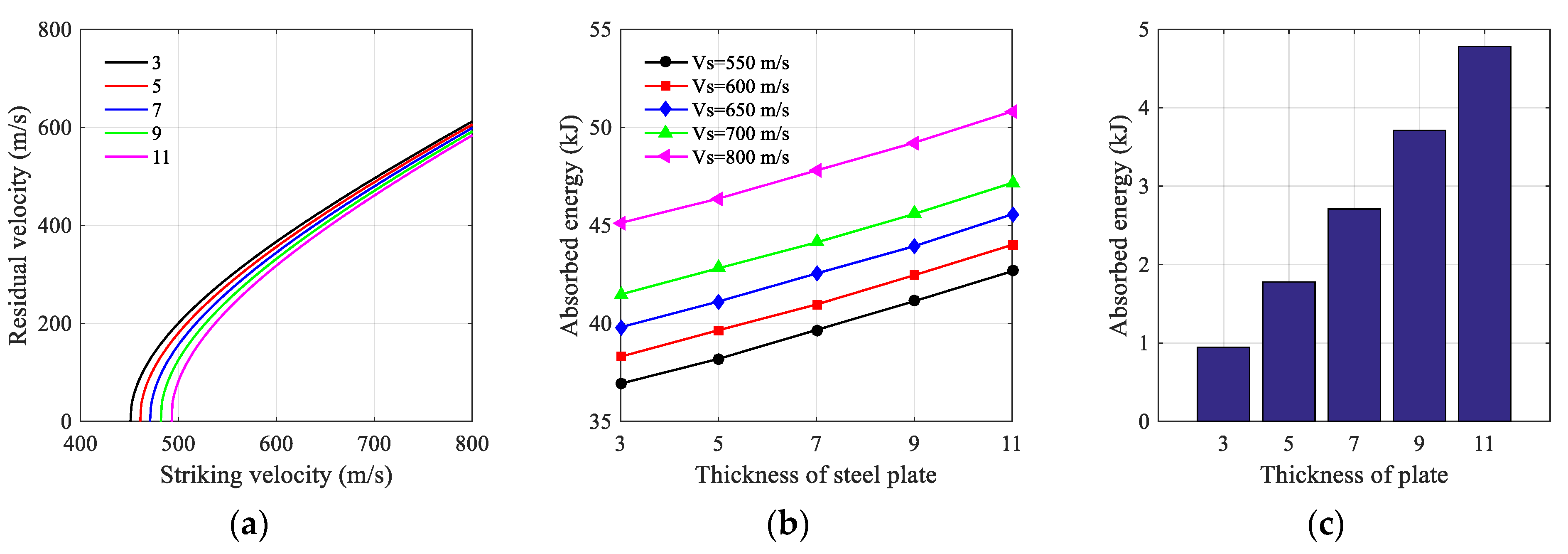
4.2. Results Discussion of SC Walls Perforation
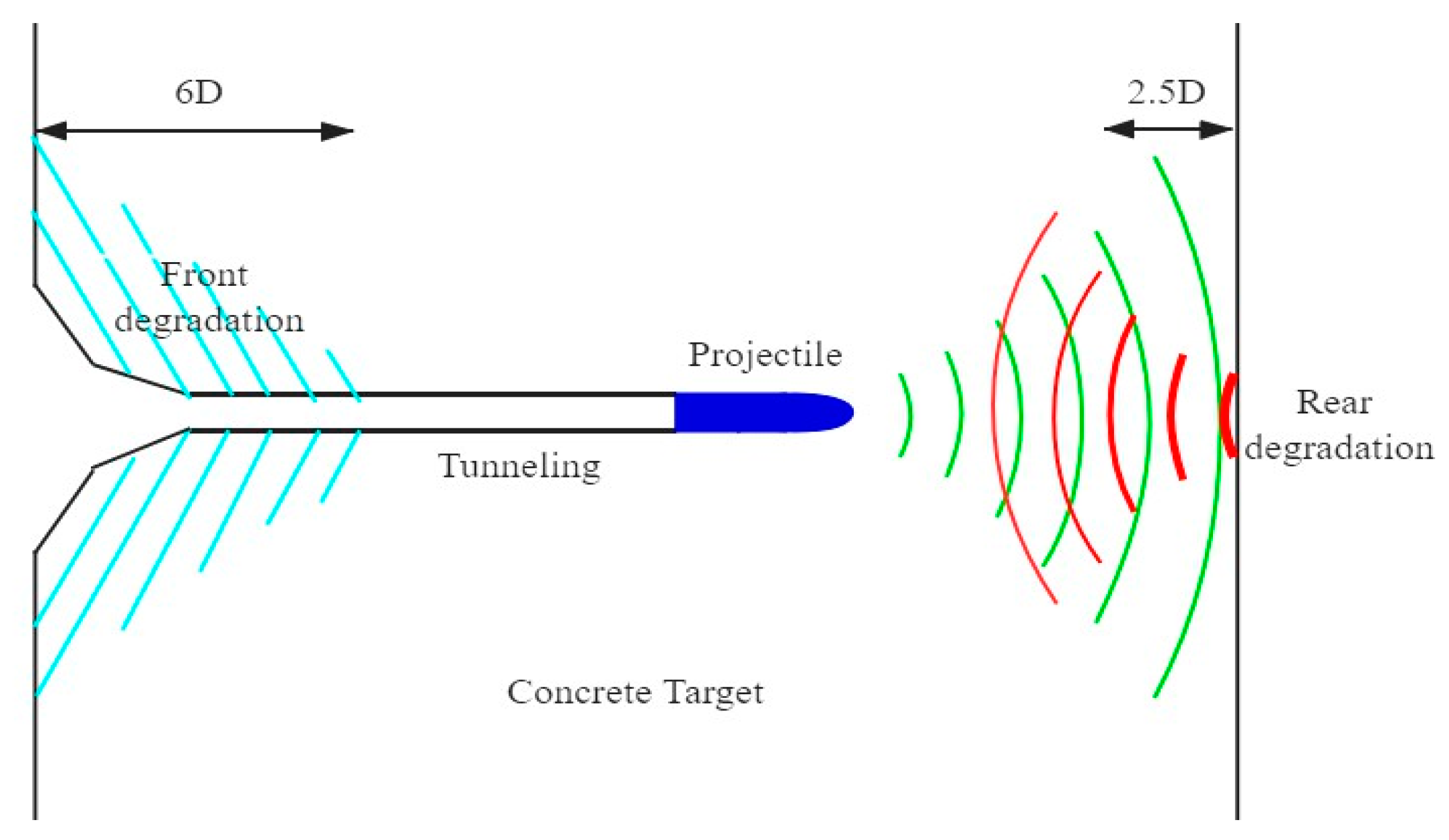
4.3. Free Surface Boundary Effect
5. Theoretical Analyses of Hard Projectile Perforation on SC Walls
5.1. Penetration Resistance Force
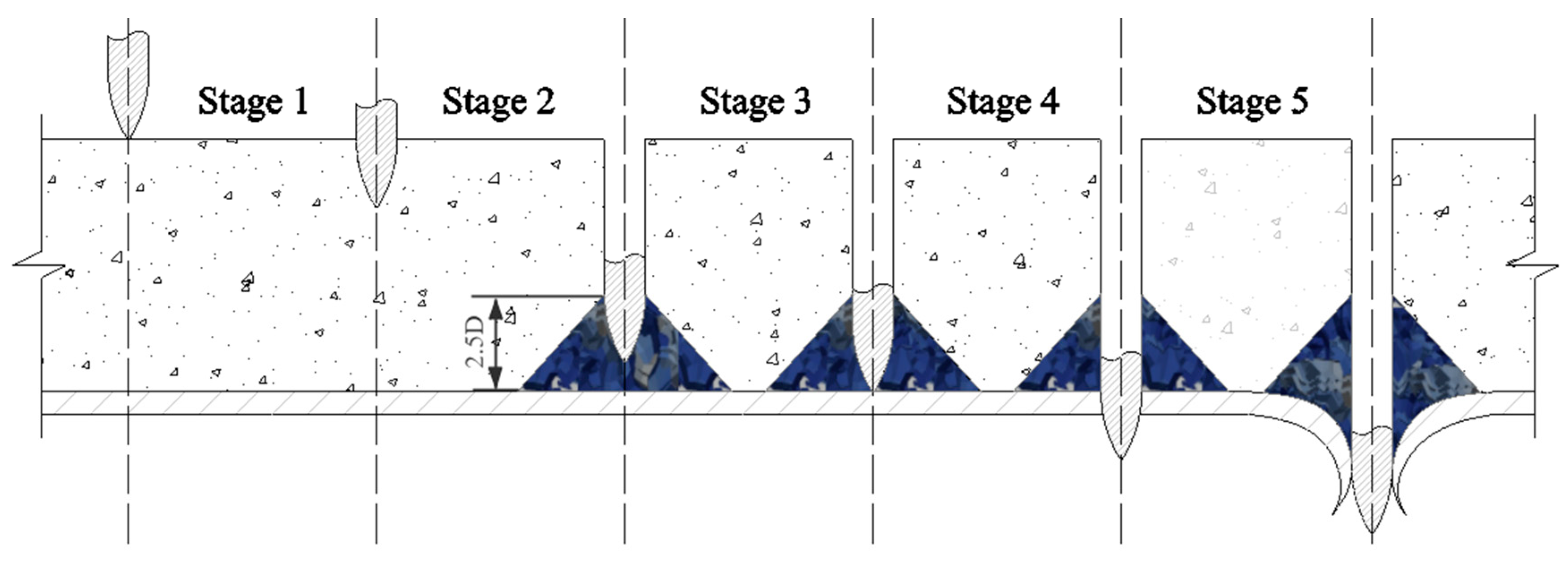
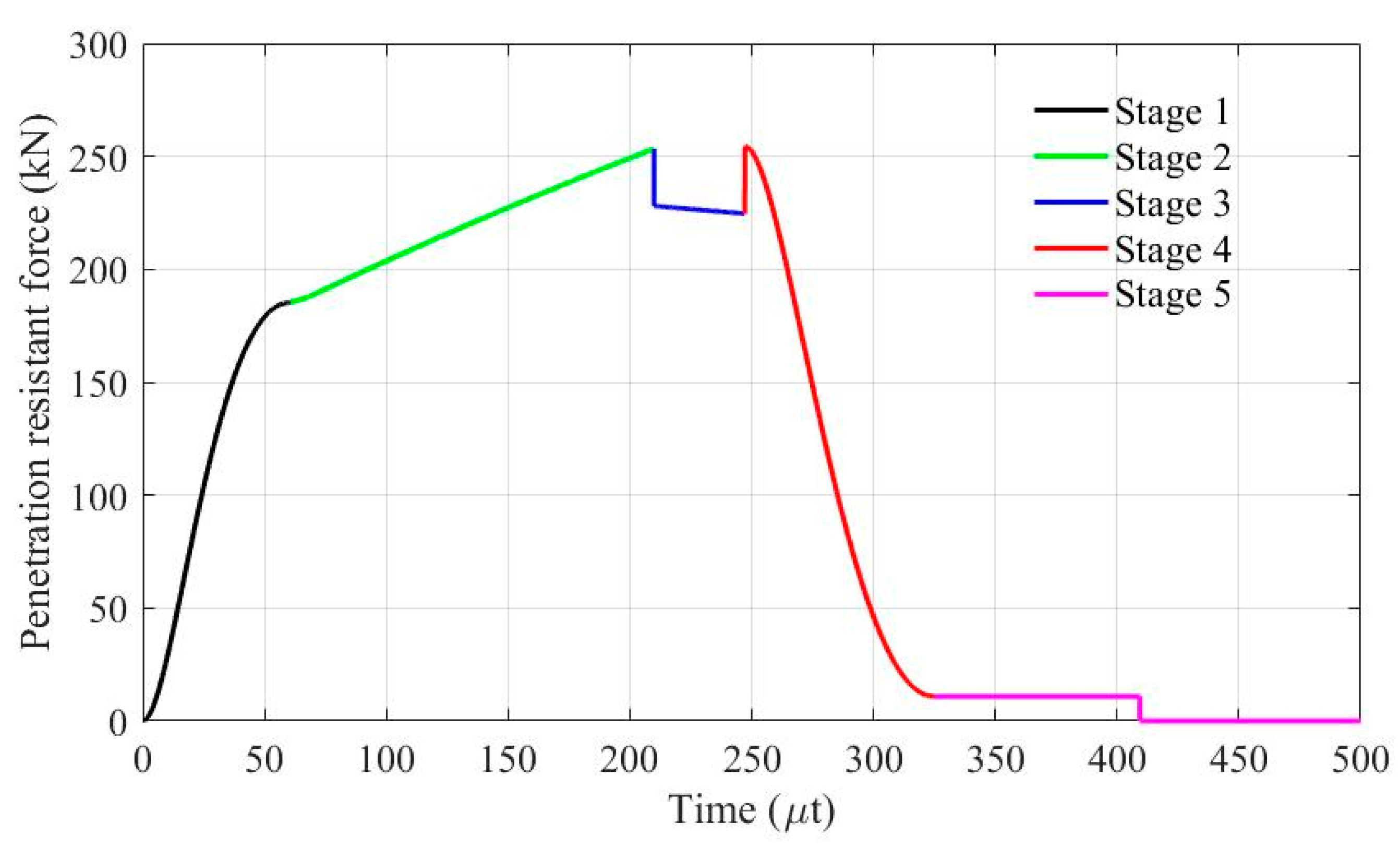
5.2. Stages of SC Walls Perforation
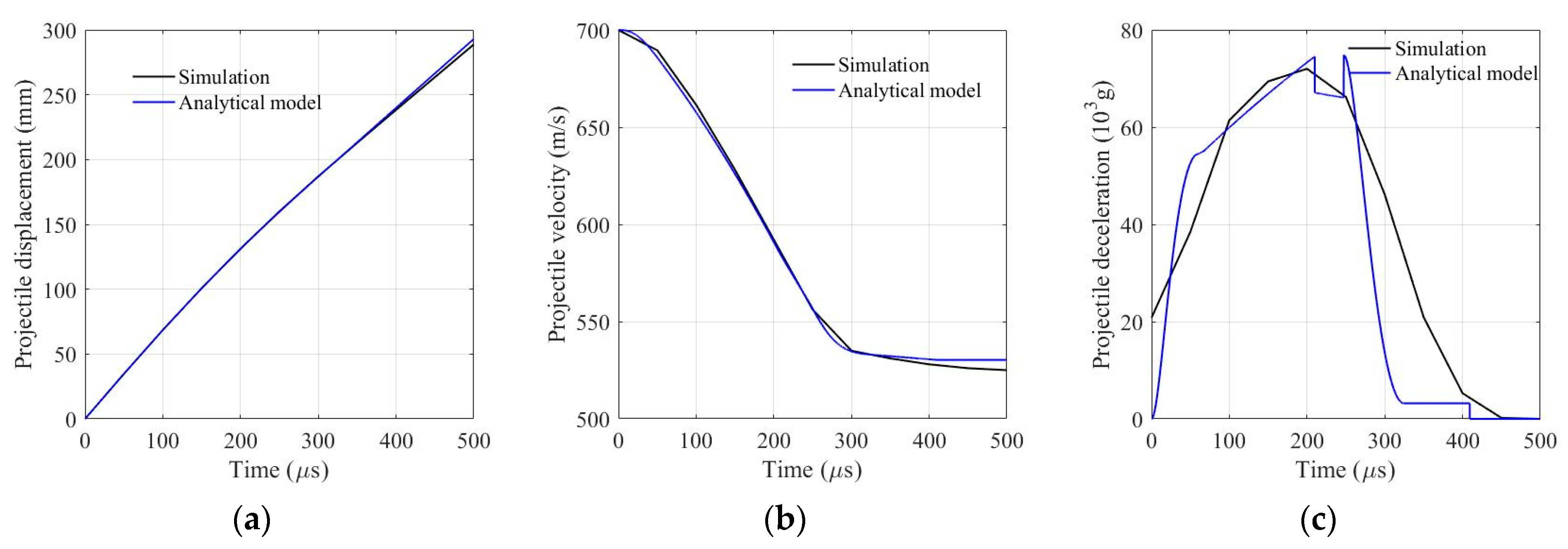
5.3. Analytical Model Validation against FE Simulation
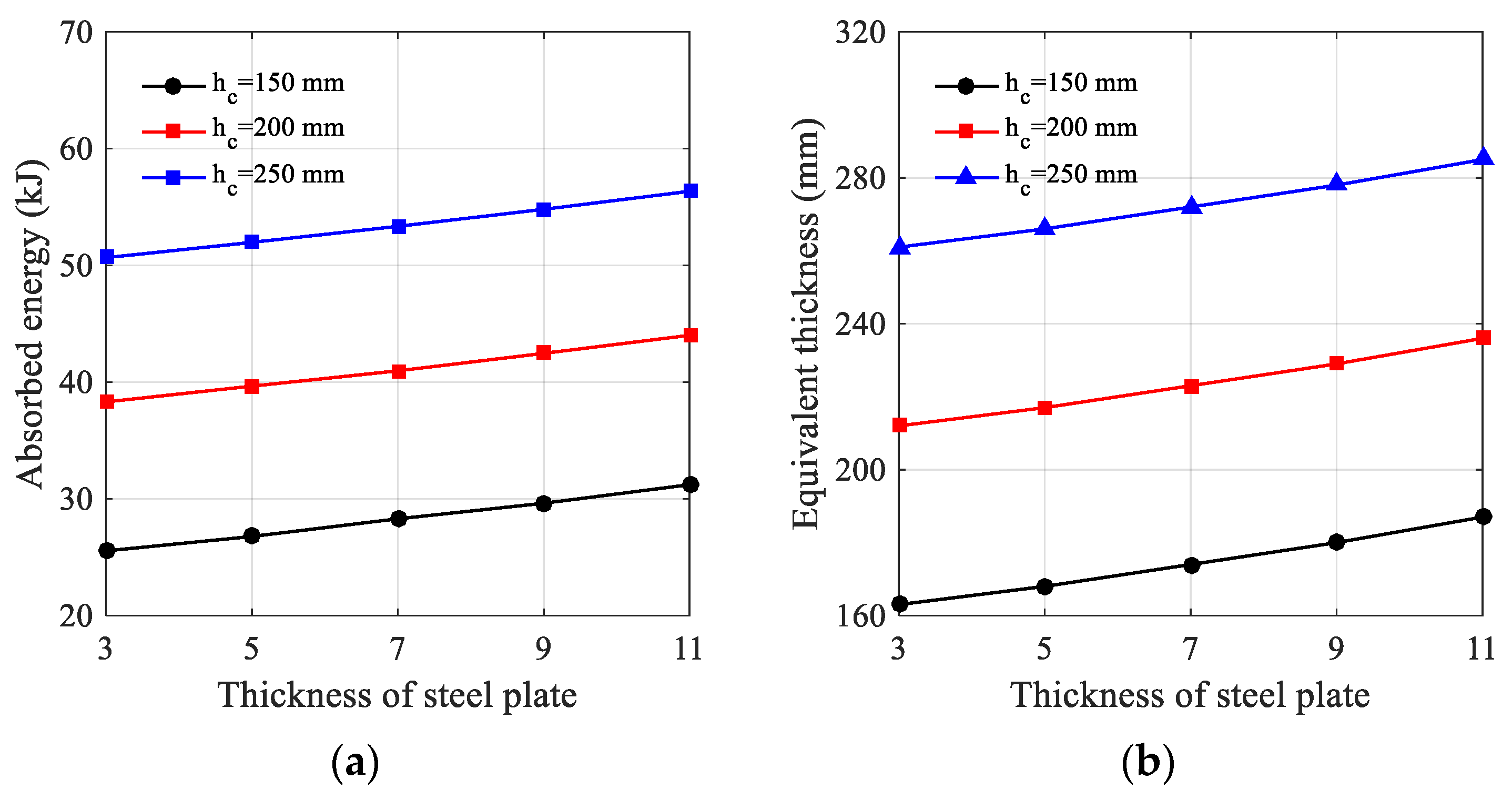
5.4. Rear Steel Plate Effect
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thai, D.K.; Kim, S.E.; Bui, T.Q. Modified empirical formulas for predicting the thickness of RC panels under impact loading. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 169, 261–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.; Shin, J.; Kim, K.; Varma, A. Local responses of steel-plate composite walls subjected to impact loads: Intermediate scale tests. Eng. Struct. 2020, 206, 110131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, D.L.; Sun, J.G.; Wu, H.; Hao, Y.F.; Wang, Z.; Cui, L.F. Experimental and numerical studies on the impact resistance of large-scale liquefied natural gas (LNG) storage outer tank against the accidental missile. Thin-Walled Struct. 2021, 158, 107189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remennikov, A.; Ying, K.S.; Uy, B. Static and Dynamic Behaviour of Non-Composite Steel-Concrete-Steel Protective Panels under Large Deformation; Research Publishing Services: Singapore, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Remennikov, A.M.; Kong, S.Y. Numerical simulation and validation of impact response of axially restrained steel-concrete-steel sandwich panels. Compos. Struct. 2012, 94, 3546–3555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Sun, W.; Liu, Z.; Chong, C.; Wang, X. An armour-piercing projectile penetration in a double layered target of ultra-high-performance fiber reinforced concrete and armour steel: Experimental and numerical analyses. Mater. Des. 2016, 102, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, I. An experimental study on local behavior of reinforced concrete slabs to missile impact. Nucl. Eng. Des. 1991, 130, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsubota, H.; Yasai, Y.; Noshika, N.; Morikawa, H.; Uchida, T.; Ohno, T.; Kogure, K. Quantitative studies on impact resistance of reinforced concrete panels with steel plates under impact loading part I: Scaled model impact tests. In Transactions of the 12th SMiRT; International Association for Structural Mechanics in Reactor Technology, IASMiRT: Stuttgart, Germany, 1993; pp. 169–174. [Google Scholar]
- Abdel-Kader, M.; Fouda, A. Effect of reinforcement on the response of concrete panels to impact of hard projectiles. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2014, 63, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, J.; Takiguchi, K.; Nishimura, K.; Matsuzawa, K.; Tsutsui, M.; Ohashi, Y.; Kojima, I.; Torita, H. Experimental study on behavior of RC panels covered with steel plates subjected to missile impact. In Transactions of the 18th SMiRT; International Association for Structural Mechanics in Reactor Technology, IASMiRT: Beijing, China, 2005; pp. 2604–2615. [Google Scholar]
- Mizuno, J.; Sawamoto, Y.; Yamashita, T.; Koshika, N.; Niwa, N.; Suzuki, A. Investigation on impact resistance of steel plate reinforced concrete barriers against aircraft impact part 1: Test program and results. In Transactions of the 18th SMiRT; International Association for Structural Mechanics in Reactor Technology, IASMiRT: Beijing, China, 2005; pp. 2566–2579. [Google Scholar]
- Bruhl, J.C.; Varma, A.H.; Johnson, W.H. Design of composite SC walls to prevent perforation from missile impact. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2015, 75, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grisaro, H.; Dancygier, A.N. Assessment of the perforation limit of a composite RC barrier with a rear steel plate to impact of a non-deforming projectile. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2014, 64, 122–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Fang, Q.; Peng, Y.; Gong, Z.M.; Kong, X.Z. Hard projectile perforation on the monolithic and segmented RC panels with a rear steel plate. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2015, 76, 232–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.K.; Kim, S.E. Comparative assessment of impact resistance of SC and RC panels using finite element analysis. Prog. Nucl. Energy 2016, 90, 105–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Sun, W.; Wang, L.; Chen, L.; Xue, S.; Li, W. Terminal ballistic and static impactive loading on thick concrete target. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 251, 118899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wierzbicki, T. Petalling of plates under explosive and impact loading. Int. J. Impact Eng. 1999, 22, 935–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, R.F.; Hill, R.; Mott, N.F. The theory of indentation and hardness tests. Proc. Phys. Soc. 2002, 57, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forrestal, M.J.; Luk, V.K. Dynamic spherical cavity-expansion in a compressible elastic-plastic solid. J. Appl. Mech. 1988, 55, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Li, W.; Wang, X.; Song, M.; Ren, H.; Li, W. Dynamic spherical cavity expansion analysis of rate-dependent concrete material with scale effect. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2015, 84, 24–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forrestal, M.J.; Altman, B.S.; Cargile, J.D.; Hanchak, S.J. An empirical equation for penetration depth of ogive-nose projectiles into concrete targets. Int. J. Impact Eng. 1994, 15, 395–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forrestal, M.J.; Frew, D.J.; Hanchak, S.J.; Brar, N.S. Penetration of grout and concrete targets with ogive-nose steel projectiles. Int. J. Impact Eng. 1996, 18, 465–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Forrestal, M.J.; Tzou, D.Y. A spherical cavity-expansion penetration model for concrete targets. Int. J. Solids Struct. 1997, 34, 4127–4146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, Z.; Dekel, E. The penetration of rigid long rods-revisited. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2009, 36, 551–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.Z.; Wu, H.; Fang, Q.; Zhang, W.; Xiao, Y.K. Projectile penetration into mortar targets with a broad range of striking velocities: Test and analyses. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2017, 106, 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Song, M.; Sun, W.; Wang, L.; Li, W.; Li, W. Thick plain concrete targets subjected to high speed penetration of 30CrMnSiNi2A steel projectiles: Tests and analyses. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2018, 122, 305–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, Z.; Vayig, Y.; Malka-Markovitz, A. The scaling issue in the penetration of concrete targets by rigid projectiles-Revisited. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2020, 140, 103561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Wu, H.; Fang, Q.; Gong, Z.M.; Kong, X.Z. A note on the deep penetration and perforation of hard projectiles into thick targets. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2015, 85, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landkof, B.; Goldsmith, W. Petalling of thin, metallic plates during penetration by cylindro-conical projectiles. Int. J. Solids Struct. 1985, 21, 245–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, G.; Beissel, S.; Holmquist, T.; Frew, D. Computed radial stresses in a concrete target penetrated by a steel projectile. In Proceedings of the Structures under Shock and Impact V, Thessaloniki, Greece, 24–26 June 1998; pp. 793–806. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, W.; Shi, Z.; Chen, B.; Feng, J. Numerical Study on RC Multilayer Perforation with Application to GA-BP Neural Network Investigation. Civ. Eng. J. 2020, 6, 806–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmquist, T.J.; Johnson, G.R.; Cook, W.H. A computational constitutive model for concrete subjected to large strains, high strain rates and high pressures. In Proceedings of the 14th International Symposium on Ballistics, Quebec City, QC, Canada, 26–29 September 1993; pp. 591–600. [Google Scholar]
- Polanco-Loria, M.; Hopperstad, O.S.; Børvik, T.; Berstad, T. Numerical predictions of ballistic limits for concrete slabs using a modified version of the HJC concrete model. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2008, 35, 290–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, G.R.; Cook, W.H. A constitutive model and data for materials subjected to large strains, high strain rates, and high temperatures. In Proceedings of the 7th International Symposium on Ballistics, The Hague, The Netherlands, 19–21 April 1983; pp. 541–547. [Google Scholar]
- Kurtaran, H.; Buyuk, M.; Eskandarian, A. Ballistic impact simulation of GT model vehicle door using finite element method. Theor. Appl. Fract. Mech. 2003, 40, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burley, M.; Campbell, J.E.; Dean, J.; Clyne, T.W. Johnson-Cook parameter evaluation from ballistic impact data via iterative FEM modelling. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2018, 112, 180–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.C.; Chen, Y.J.; Wang, Y.; Lu, J.S. Damage mechanism and response of reinforced concrete containment structure under internal blast loading. Theor. Appl. Fract. Mech. 2012, 61, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Zha, X.; Ye, J. The influence of joints and composite floor slabs on effective tying of steel structures in preventing progressive collapse. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2010, 66, 442–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X. Adiabatic shear localization for steels based on Johnson-Cook model and second-and fourth-order gradient plasticity models. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2007, 14, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oucif, C.; Mauludin, L.M. Numerical modeling of high velocity impact applied to reinforced concrete panel. Undergr. Space 2019, 4, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frew, J.D.; Hanchak, J.S.; Greent, L.M.; Forrestal, J.M. Penetration of concrete targets with ogive-nose steel rods. Int. J. Impact Eng. 1998, 21, 489–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Lu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Huang, F. Perforation experiments of concrete targets with residual velocity measurements. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2013, 57, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Hanchak, J.S.; Forrestal, J.M.; Young, R.E.; Ehrgott, Q.J. Perforation of concrete slabs with 48 MPa (7 ksi) and 140 MPa (20 ksi) unconfined compressive strengths. Int. J. Impact Eng. 1992, 12, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forrestal, M.J. Penetration into dry porous rock. Int. J. Solids Struct. 1986, 22, 1485–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Wang, M.; Jie, L.; Li, M. A model of depth calculation for projectile penetration into dry sand and comparison with experiments. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2014, 73, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| RO | G | A | B | C | N | FC | T | EPSO | EFMIN |
| 2.24 | 0.1486 | 0.79 | 1.6 | 0.007 | 0.61 | 4.1 × 10−4 | 4.1× 10−5 | 1× 10−6 | 0.01 |
| SFMAX | PC | UC | PL | UL | D1 | D2 | K1 | K2 | K3 |
| 7.0 | 1.6× 10−4 | 0.001 | 0.008 | 0.1 | 0.04 | 1.0 | 0.85 | −1.71 | 2.08 |
| RO | G | A | B | N | C | M | TM | TR | EPSO |
| 7.896 | 0.818 | 3.5× 10−3 | 2.75× 10−3 | 0.36 | 0.022 | 1 | 1793 | 293 | 1× 10−6 |
| CP | PC | SPALL | IT | D1 | D2 | D3 | D4 | D5 | C2/P |
| 0.452× 10−5 | 0 | 2 | 0 | −0.8 | 2.1 | −0.5 | 0.0002 | 0.61 | 1 |
| Part | Projectile | Concrete Slab | Steel Mesh | Steel Plate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of elements | 800 | 1,822,500 | 8712 | 18,496 |
| Vs (m/s) | Vr,e (m/s) | Vr,n (m/s) |
|---|---|---|
| 436 | 137 | 187 |
| 482 | 207 | 238 |
| 544 | 304 | 334 |
| 651 | 451 | 474 |
| Part | Projectile | Concrete | Rear Steel Plate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of elements | 696 | 376,875 | 50,000 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pu, B.; Wang, X.; Li, W.; Feng, J. Analytical Model Formulation of Steel Plate Reinforced Concrete Walls against Hard Projectile Impact. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 518. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12010518
Pu B, Wang X, Li W, Feng J. Analytical Model Formulation of Steel Plate Reinforced Concrete Walls against Hard Projectile Impact. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(1):518. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12010518
Chicago/Turabian StylePu, Bo, Xiaoming Wang, Weibing Li, and Jun Feng. 2022. "Analytical Model Formulation of Steel Plate Reinforced Concrete Walls against Hard Projectile Impact" Applied Sciences 12, no. 1: 518. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12010518
APA StylePu, B., Wang, X., Li, W., & Feng, J. (2022). Analytical Model Formulation of Steel Plate Reinforced Concrete Walls against Hard Projectile Impact. Applied Sciences, 12(1), 518. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12010518






