Behavioral Parameter Field for Human Abnormal Behavior Recognition in Low-Resolution Thermal Imaging Video
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Related Work
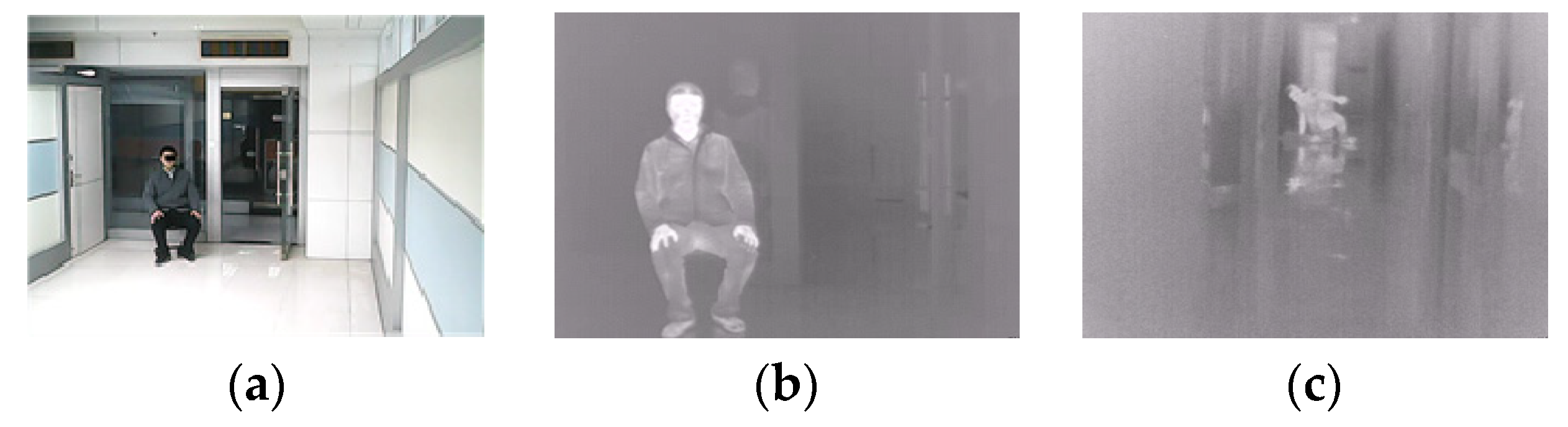
2.1. Thermal Imaging Behavior Recognition and Challenges
2.2. Behavior Recognition Method Based on Skeletal Keypoints
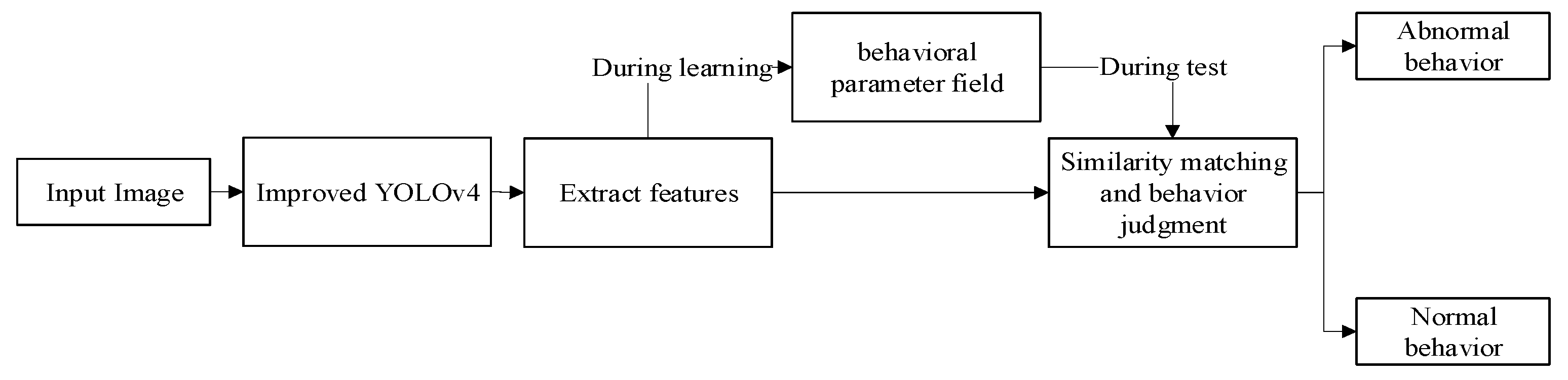
3. Method
3.1. Target Detection
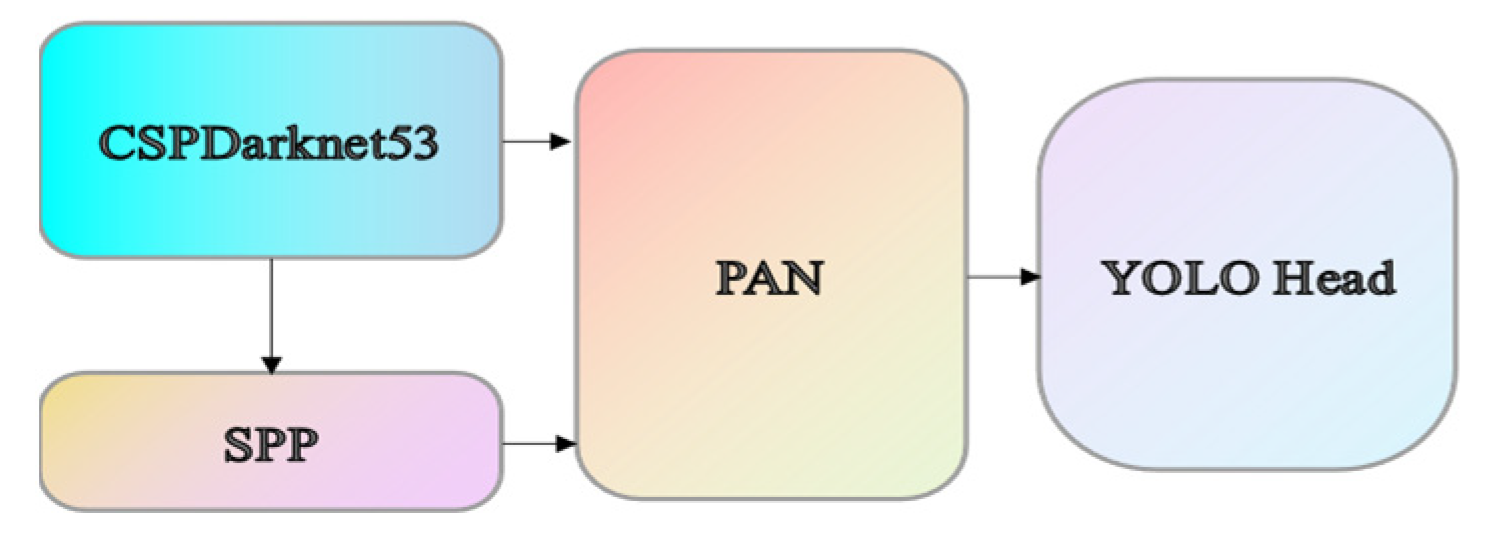
3.1.1. YOLOv4 Introduction
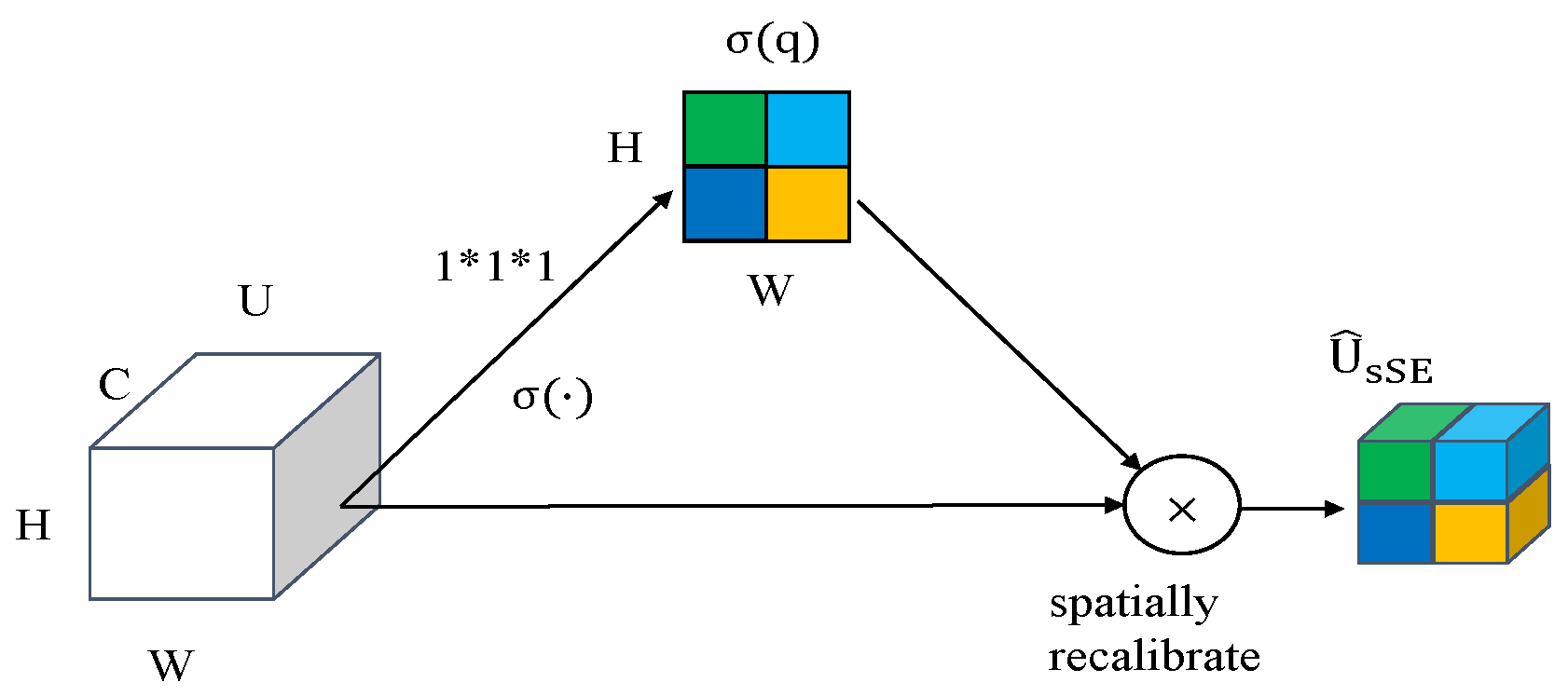
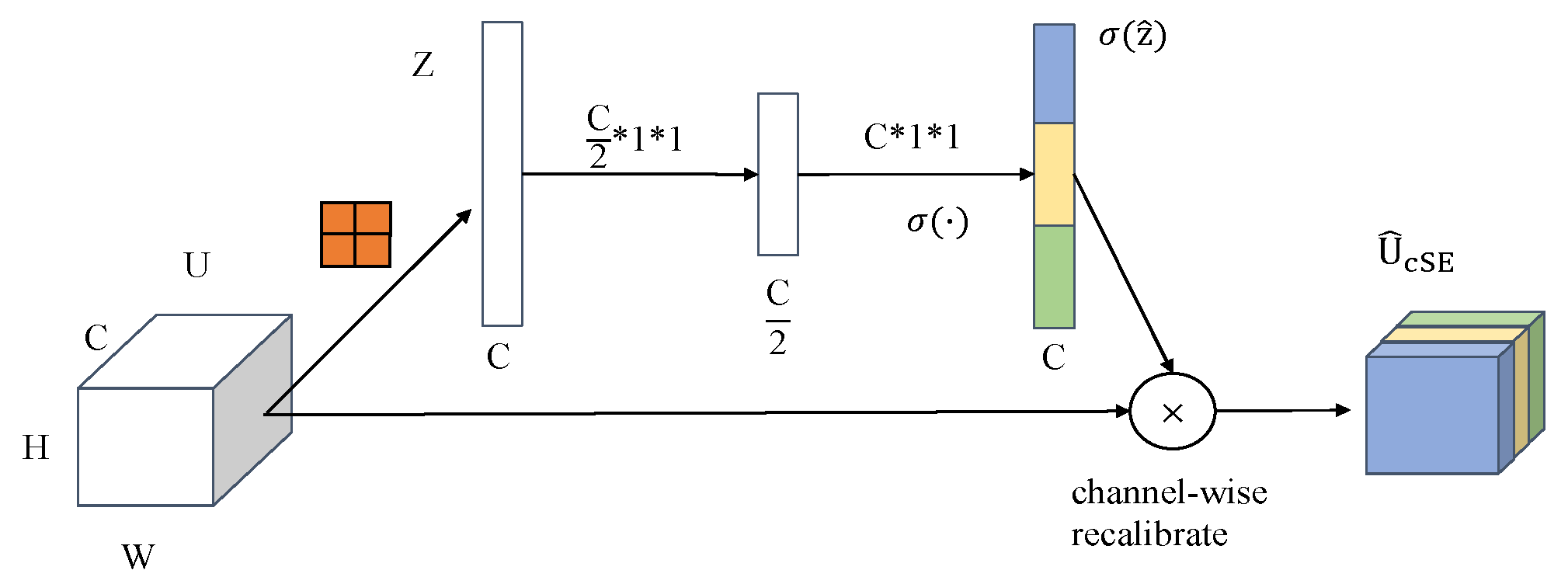
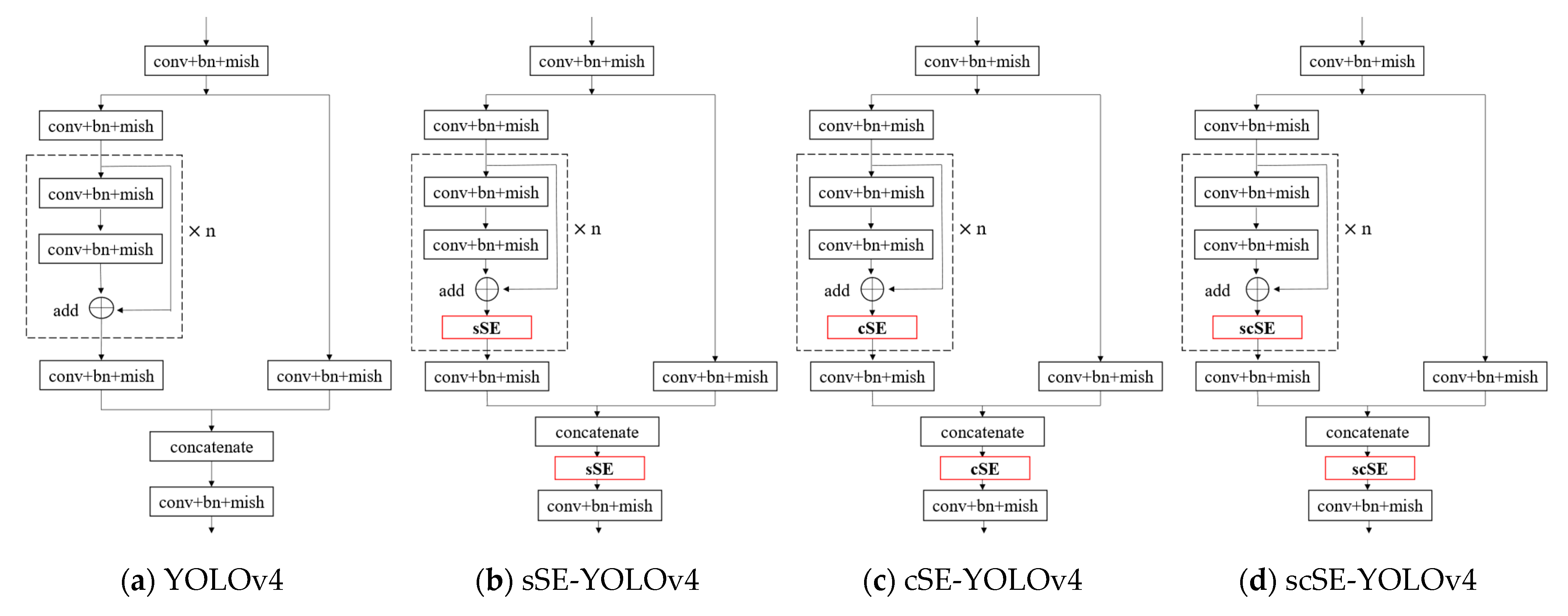
3.1.2. Improved YOLOv4 Algorithm
- sSE model;
- 2.
- cSE model;
- 3.
- scSE model;
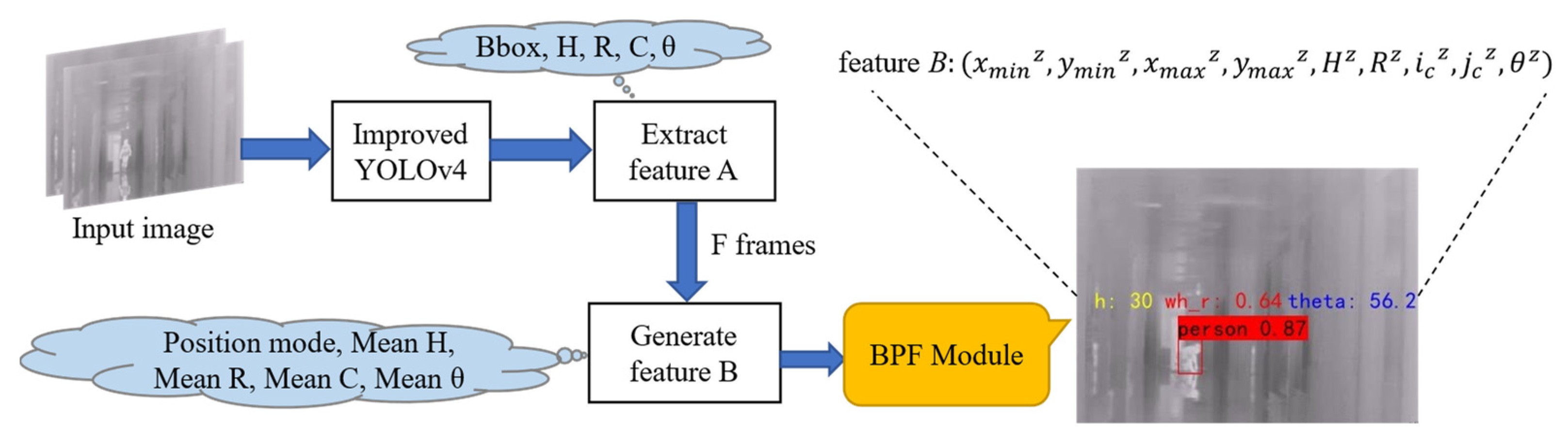
3.2. Behavioral Parameter Field
3.2.1. Feature Selection
- Bounding box and aspect ratio;
- 2.
- Center of mass;
- 3.
- Orientation angle;
3.2.2. Behavioral Parameter Field Composition
3.2.3. Self-Update Learning Strategy
- Direct update strategy;
- 2.
- Voting update strategy;
- 3.
- Similarity update strategy;
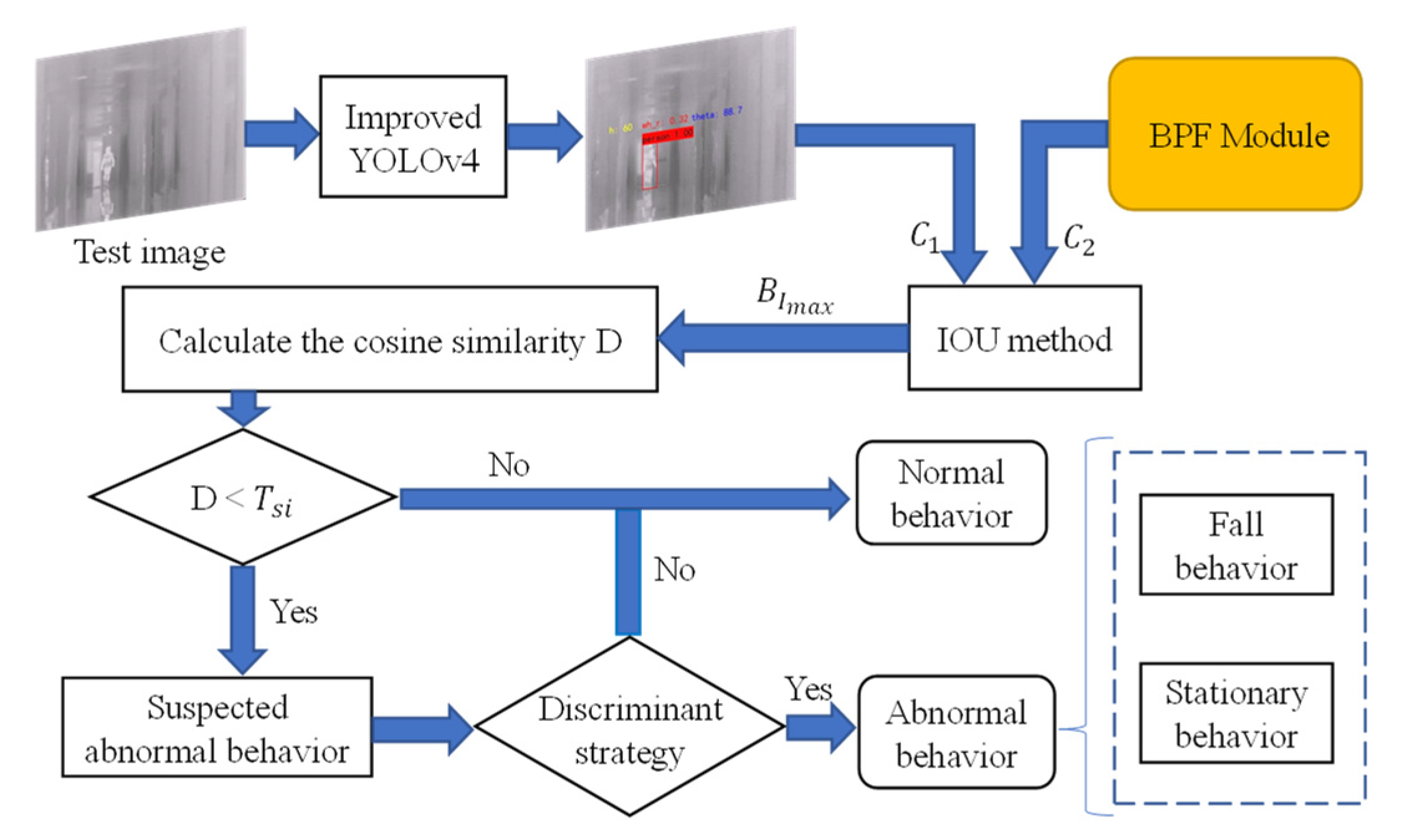
3.3. Abnormal Behavior Recognition
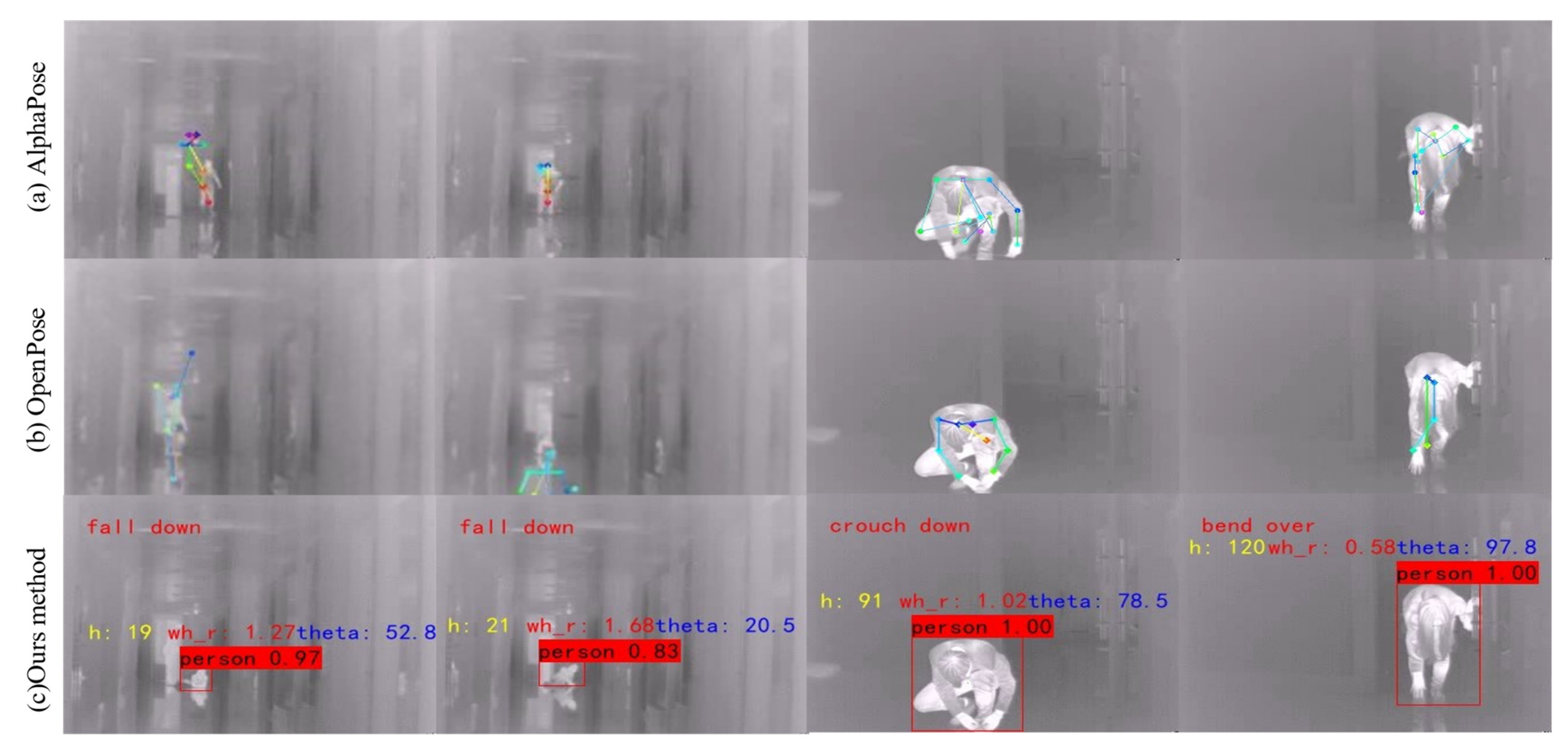
3.3.1. Judgment of Fall Events
3.3.2. Judgment of Long-Time Immobility Events
4. Experiments
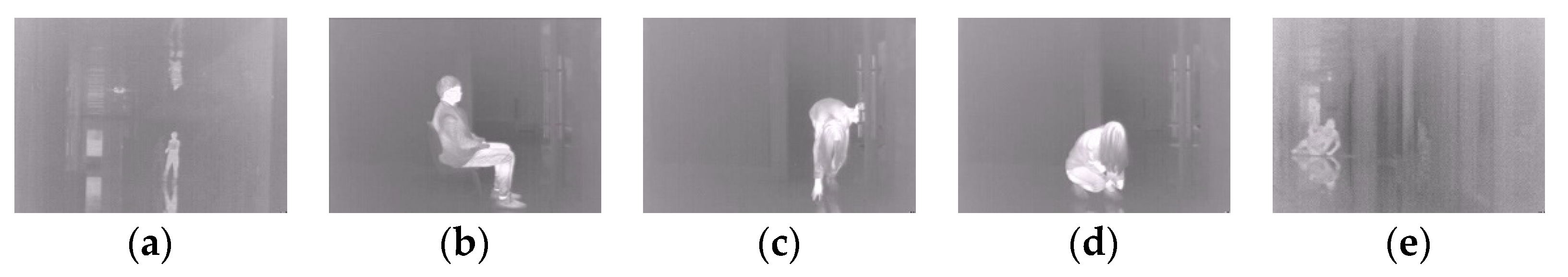
4.1. Experimental Data
4.2. Experimental Settings
Experimental Platform and Evaluation Metrics
4.3. Experimental Results and Analysis
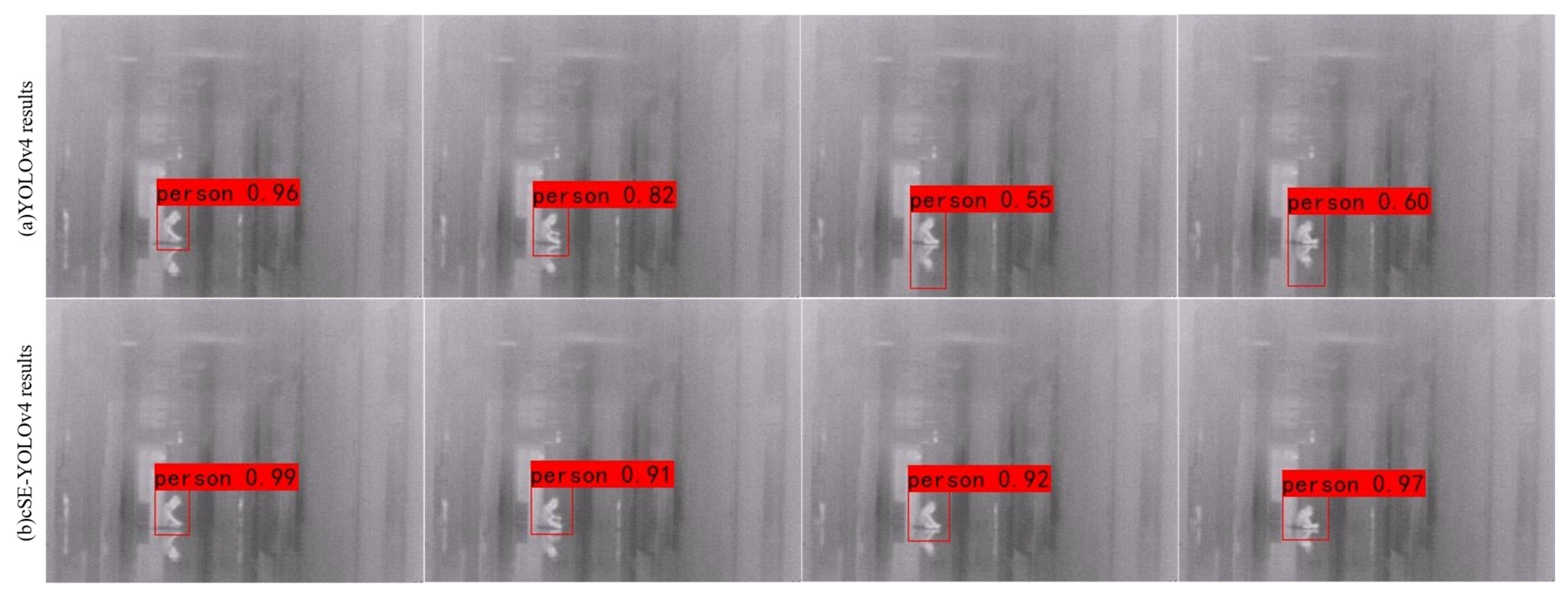
4.3.1. Target Detection Network Training and Testing
- Evaluation and analysis of the effectiveness of the improved YOLOv4 network model;
- 2.
- Performance comparison of different algorithms;
4.3.2. Experimental Testing of Abnormal Behavior Detection
- Comparison of experimental results of typical methods;
- 2.
- Update strategy ablation experiment;
- 3.
- BPF model performance test;
- 4.
- Sensitivity analysis of Hyperparameters;
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gade, R.; Moeslund, T.B. Thermal cameras and applications: A survey. Mach. Vis. Appl. 2014, 25, 245–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bobick, A.; Davis, J. An appearance-based representation of action. In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Pattern Recognition, Vienna, Austria, 25–29 August 1996; Volume 1, pp. 307–312. [Google Scholar]
- Weinland, D.; Ronfard, R.; Boyer, E. Free viewpoint action recognition using motion history volumes. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2006, 104, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shao, L.; Zhen, X.; Tao, D.; Li, X. Spatio-Temporal Laplacian Pyramid Coding for Action Recognition. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2013, 44, 817–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Ullah, M.M.; Klaser, A.; Laptev, I.; Schmid, C. Evaluation of local spatio-temporal features for action recognition. In Proceedings of the British Machine Vision Conference 2009, London, UK, 7–10 September 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Kläser, A.; Schmid, C.; Liu, C.-L. Dense Trajectories and Motion Boundary Descriptors for Action Recognition. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2013, 103, 60–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.; Schmid, C. Action Recognition with Improved Trajectories. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Sydney, Australia, 1–8 December 2013; pp. 3551–3558. [Google Scholar]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Two-Stream Convolutional Networks for Action Recognition in Videos. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1406.2199. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Xiong, Y.; Wang, Z.; Qiao, Y.; Lin, D.; Tang, X.; Van Gool, L. Temporal Segment Networks: Towards Good Practices for Deep Action Recognition; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 20–36. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, B.; Andonian, A.; Oliva, A.; Torralba, A. Temporal Relational Reasoning in Videos. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision—ECCV 2018, Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 831–846. [Google Scholar]
- Tran, D.; Bourdev, L.; Fergus, R.; Torresani, L.; Paluri, M. Learning Spatiotemporal Features with 3D Convolutional Networks. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Diba, A.; Fayyaz, M.; Sharma, V.; Karami, A.H.; Arzani, M.M.; Yousefzadeh, R.; Van Gool, L. Temporal 3d convnets: New architecture and transfer learning for video classification. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1711.08200. [Google Scholar]
- Carreira, J.; Zisserman, A. Quo Vadis, Action Recognition? A New Model and the Kinetics Dataset. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 4724–4733. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, S.; Xiong, Y.; Lin, D. Spatial temporal graph convolutional networks for skeleton-based action recognition. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New Orleans, LA, USA, 2–7 February 2018; Volume 32. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, L.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, J.; Lu, H. Skeleton-Based Action Recognition With Directed Graph Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 7904–7913. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Z.; Ouyang, W. Disentangling and Unifying Graph Convolutions for Skeleton-Based Action Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 140–149. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, H.-S.; Xie, S.; Tai, Y.-W.; Lu, C. RMPE: Regional Multi-person Pose Estimation. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2353–2362. [Google Scholar]
- Bochkovskiy, A.; Wang, C.Y.; Liao, H.Y.M. YOLOv4 Optimal Speed and Accuracy of Object Detection. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.10934. [Google Scholar]
- Roy, A.G.; Navab, N.; Wachinger, C. Concurrent spatial and channel ‘squeeze & excitation’ in fully convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Granada, Spain, 16–20 September 2018; pp. 421–429. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, C.; Du, Y.; Liu, J.; Lv, J.; Yang, L.; Meng, D.; Hauptmann, A.G. InfAR dataset: Infrared action recognition at different times. Neurocomputing 2016, 212, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Sun, S.; Li, J.; Li, D. Infrared behavior recognition based on spatio-temporal two-stream convolutional neural networks. J. Appl. Opt. 2018, 39, 743–750. [Google Scholar]
- Akula, A.; Shah, A.K.; Ghosh, R. Deep learning approach for human action recognition in infrared images. Cogn. Syst. Res. 2018, 50, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Hidalgo, G.; Simon, T.; Wei, S.E.; Sheikh, Y. OpenPose: Realtime Multi-Person 2D Pose Estimation Using Part Affinity Fields. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2021, 43, 172–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Redmon, J.; Farhadi, A. Yolov3: An incremental improvement. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.02767. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, R.; Peng, Y.; Xie, W.; Xie, G. Improved YOLOv4 Small Target Detection Algorithm with Embedded scSE Module. J. Graph. 2021, 42, 546–555. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Szegedy, C.; Reed, S.; Fu, C.Y.; Berg, A.C. SSD: Single shot multibox detector. In European Conference on Computer Vision; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 21–37. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Q.; Sheng, T.; Wang, Y.; Tang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Cai, L.; Ling, H. M2Det: A Single-Shot Object Detector Based on Multi-Level Feature Pyramid Network. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Honolulu, HI, USA, 27 January–1 February 2019; Volume 33, pp. 9259–9266. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Huang, D.; Wang, Y. Receptive Field Block Net for Accurate and Fast Object Detection. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 385–400. [Google Scholar]




| Model | AP@0.6/% | AP@0.7/% |
|---|---|---|
| YOLOv4(Baseline) | 97.97 | 95.09 |
| scSE-YOLOv4 | 95.67 | 92.63 |
| sSE-YOLOv4 | 89.32 | 81.78 |
| cSE-YOLOv4 | 98.31 | 98.31 |
| Model | FPS | AP@0.6/% |
|---|---|---|
| SSD [26] | 28 | 96.93 |
| YOLOv3 [25] | 23 | 97.28 |
| YOLOv4 [18] | 22 | 97.97 |
| M2Det [27] | 24 | 97.44 |
| RFBNet [28] | 27 | 93.98 |
| cSE-YOLOv4 | 22 | 98.31 |
| Strategy | Acc (Normal Behavior)/% | Acc (Abnormal Behavior)/% |
|---|---|---|
| Direct update strategy | 89.79 | 91.46 |
| Voting update strategy | 91.27 | 94.02 |
| Similarity update strategy | 91.42 | 94.28 |
| Test Set | Number | Acc/% | FNR/% | FPR/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| all | 56 | 94.64 | 5.56 | 5 |
| crouch down | 5 | 80.00 | 0.00 | 20.00 |
| sit down | 7 | 85.71 | 0.00 | 14.29 |
| bend over | 3 | 100.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| walk | 6 | 100.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| fall down | 18 | 94.44 | 5.56 | 0.00 |
| stay still | 17 | 94.11 | 5.88 | 0.00 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, B.; Jiang, X.; Dong, Z.; Li, J. Behavioral Parameter Field for Human Abnormal Behavior Recognition in Low-Resolution Thermal Imaging Video. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 402. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12010402
Wang B, Jiang X, Dong Z, Li J. Behavioral Parameter Field for Human Abnormal Behavior Recognition in Low-Resolution Thermal Imaging Video. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(1):402. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12010402
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Baodong, Xiaofeng Jiang, Zihao Dong, and Jinping Li. 2022. "Behavioral Parameter Field for Human Abnormal Behavior Recognition in Low-Resolution Thermal Imaging Video" Applied Sciences 12, no. 1: 402. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12010402
APA StyleWang, B., Jiang, X., Dong, Z., & Li, J. (2022). Behavioral Parameter Field for Human Abnormal Behavior Recognition in Low-Resolution Thermal Imaging Video. Applied Sciences, 12(1), 402. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12010402






