UAVC: A New Method for Correcting Lidar Overlap Factors Based on Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Vertical Detection
Abstract
1. Introduction
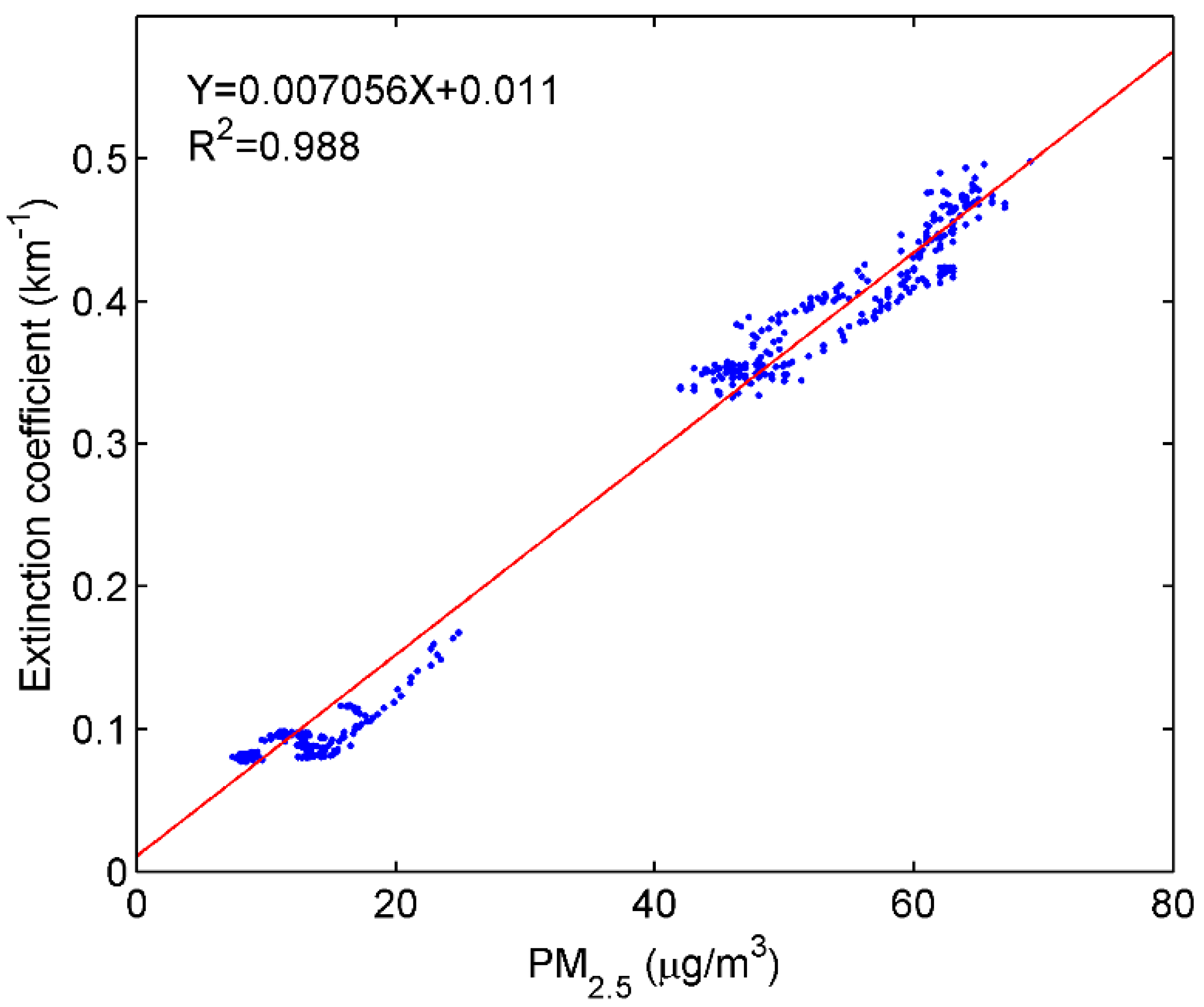
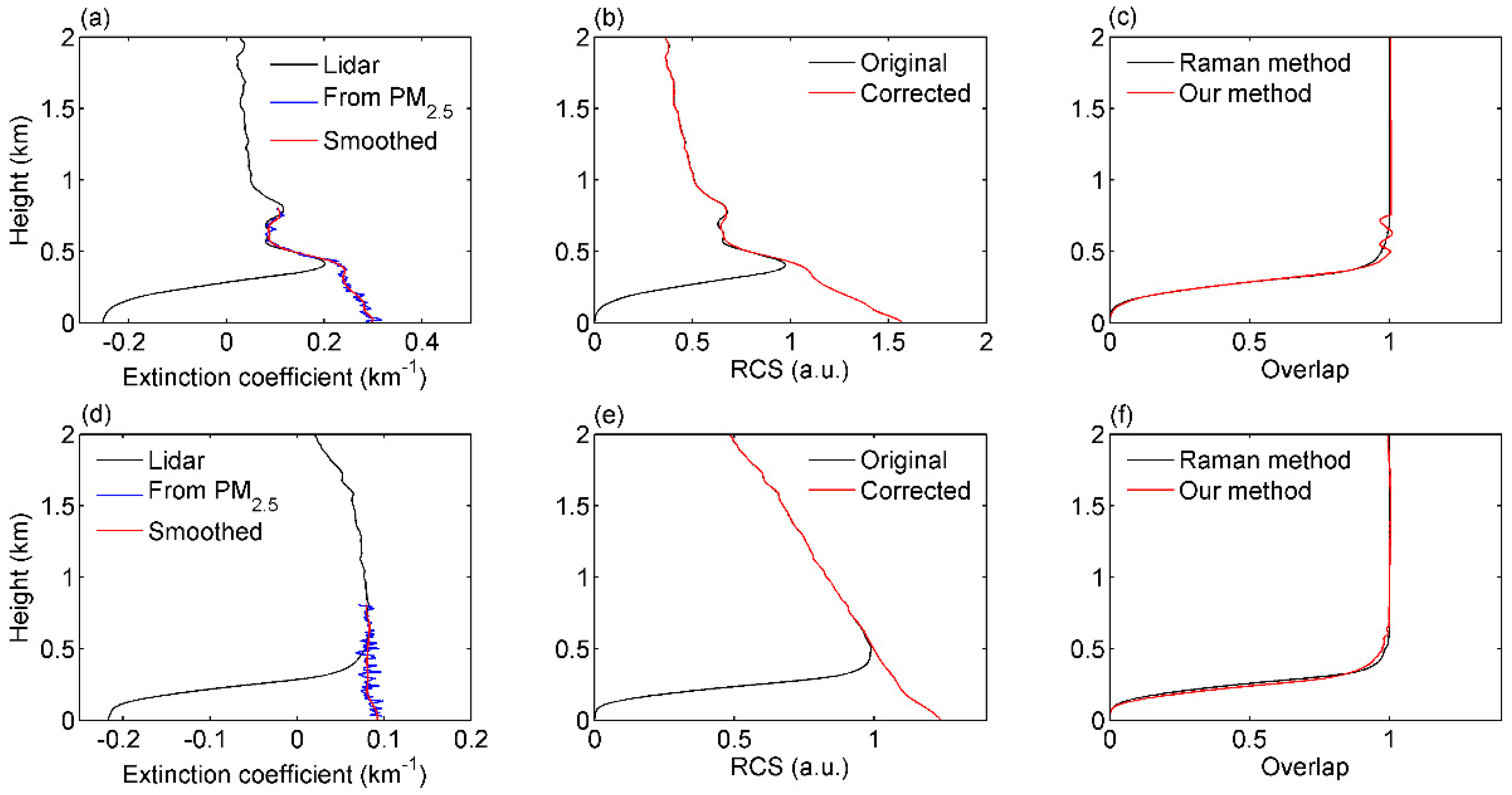
2. Experiment and Method
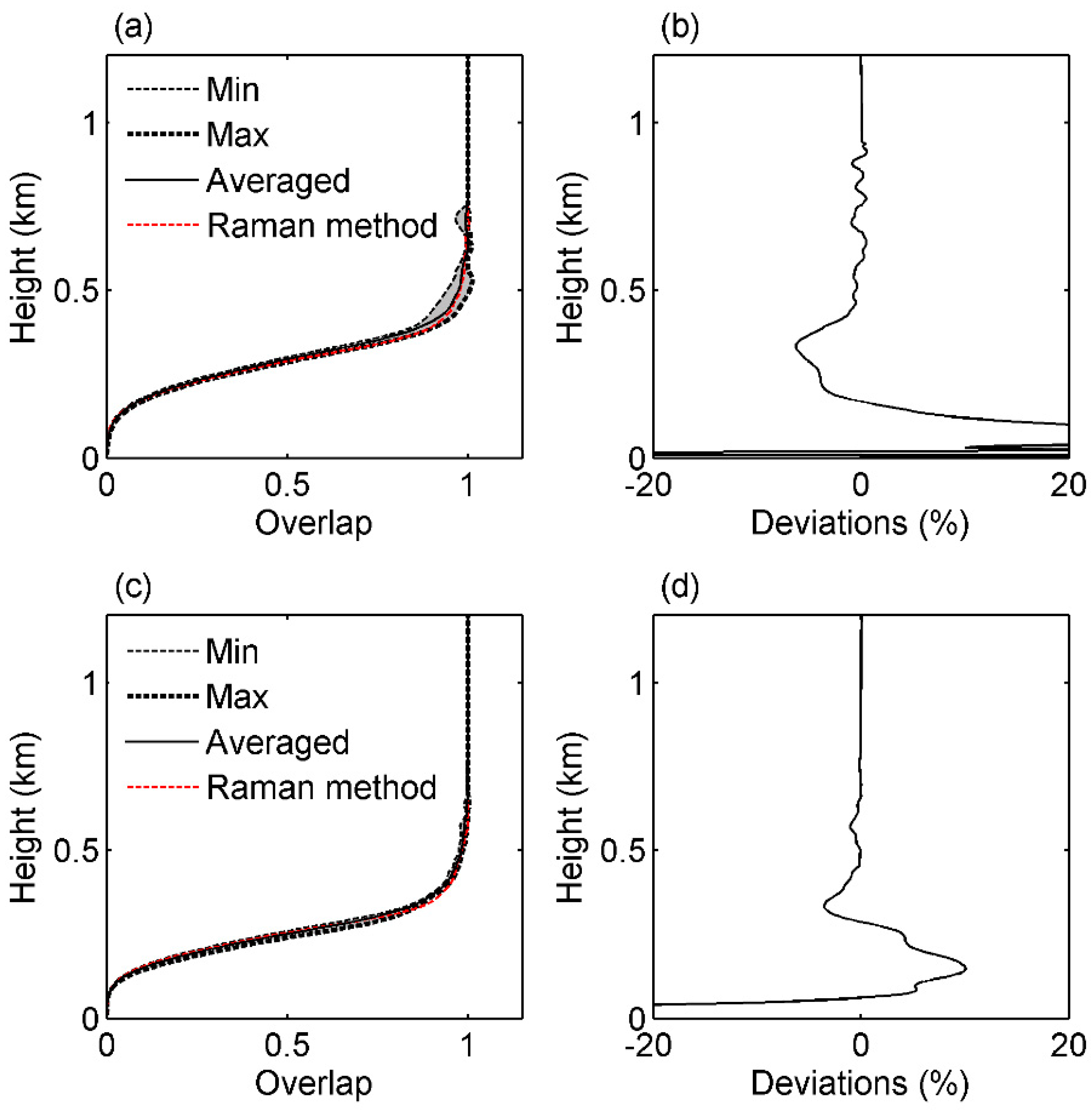
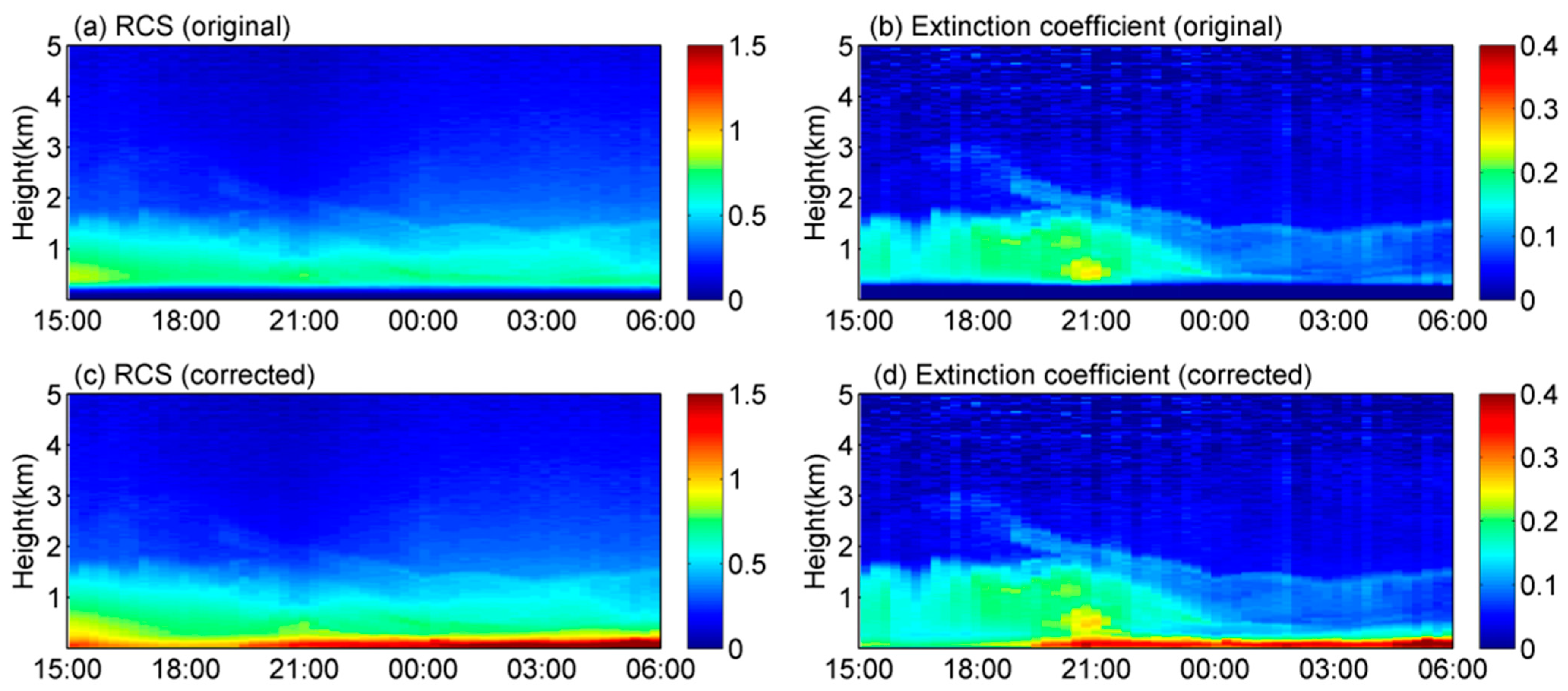
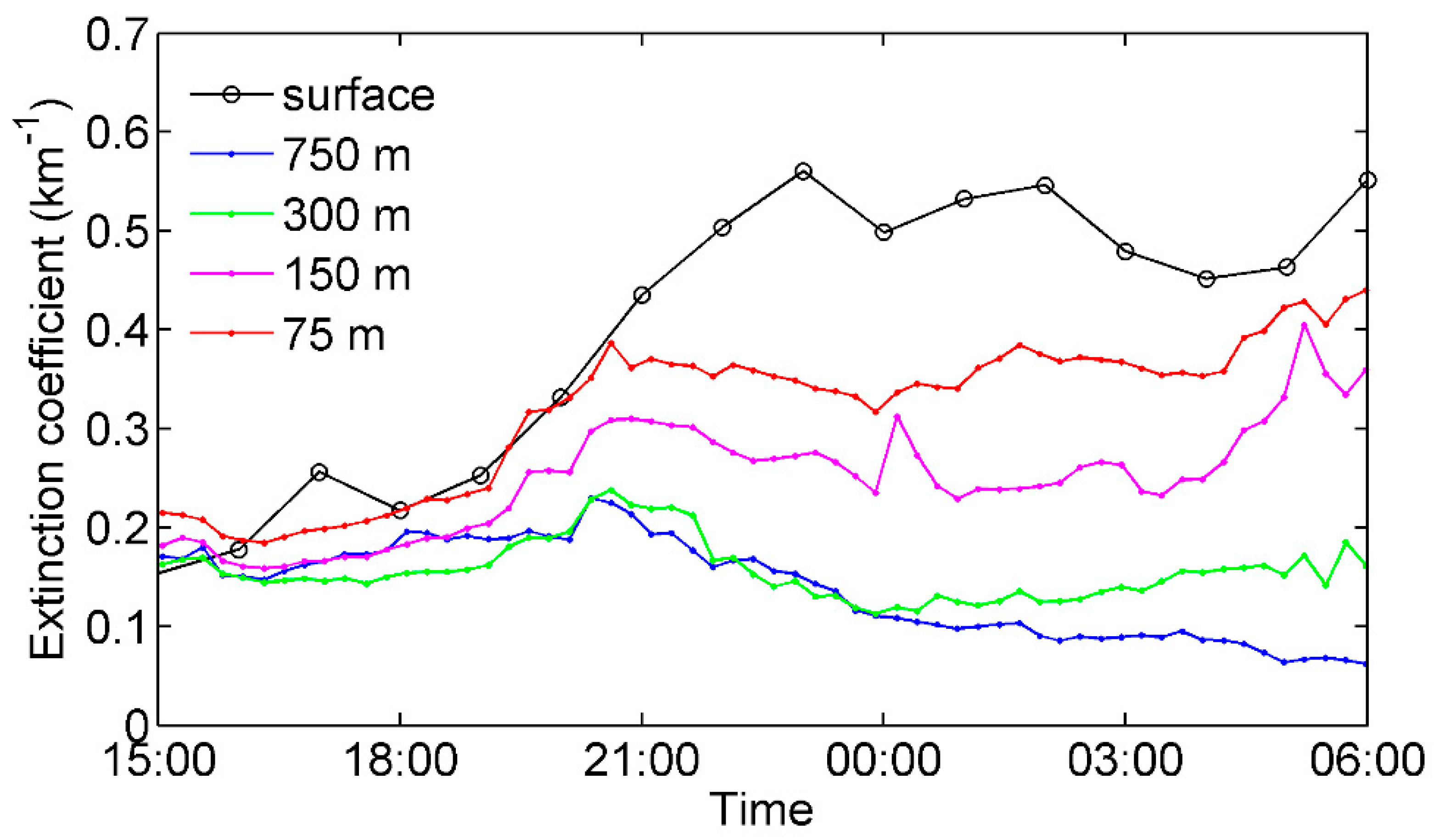
3. Results and Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rosenfeld, D.; Sherwood, S.; Wood, R.; Donner, L. Climate Effects of Aerosol-Cloud Interactions. Science 2014, 343, 379–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wang, T.; Solmon, F.; Zhuang, B.; Wu, H.; Xie, M.; Han, Y.; Wang, X. Impact of aerosols on regional climate in southern and northern China during strong/weak East Asian summer monsoon years. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 4069–4081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barlow, J.F.; Dunbar, T.M.; Nemitz, E.G.; Wood, C.R.; Gallagher, M.W.; Davies, F.; O’Connor, E.; Harrison, R.M. Boundary layer dynamics over London, UK, as observed using Doppler lidar during REPARTEE-II. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2011, 11, 2111–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkhardt, U.; Kärcher, B.; Schumann, U. Global Modeling of the Contrail and Contrail Cirrus Climate Impact. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2010, 91, 479–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsueh, H.T.; Ko, T.H.; Chou, W.C.; Hung, W.C.; Chu, H. Health risk of aerosols and toxic metals from incense and joss paper burning. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2011, 10, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.-W.; Vivian, E.; Mohammed, K.A.; Jakhar, S.; Vaughn, M.; Huang, J.; Zelicoff, A.; Xaverius, P.; Bai, Z.; Lin, S.; et al. Long-term ambient air pollution and lung function impairment in Chinese children from a high air pollution range area: The Seven Northeastern Cities (SNEC) study. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 138, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Sun, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Che, H.; Ma, Q.; Yu, X.; Yue, Y.; Zhang, Y. Characterization of submicron aerosols and effect on visibility during a severe haze-fog episode in Yangtze River Delta, China. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 120, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, L.; Chen, L.; Wang, X.; Yu, C.; Si, Y.; Zhang, Z. Interference of Heavy Aerosol Loading on the VIIRS Aerosol Optical Depth (AOD) Retrieval Algorithm. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J.B.; Prinn, R.G.; Wang, C. The impact of detailed urban-scale processing on the composition, distribution, and radiative forcing of anthropogenic aerosols. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Yim, S.Y.; Roth, M.; Ren, G.; Gao, Z.; Wang, T.; Li, Q.; Shi, C.; Ning, G.; et al. PM 2.5 Pollution Modulates Wintertime Urban Heat Island Intensity in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Megalopolis, China. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2020, 47, e2019GL084288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Y.; Cheng, Z.; Wang, S.; Jiang, J.; Chen, D.; Cai, S.; Fu, X.; Fu, Q.; Chen, C.; Xu, B.; et al. Characteristics and source apportionment of PM2.5 during a fall heavy haze episode in the Yangtze River Delta of China. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 123, 380–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Xie, C.-B.; Zhong, Z.-Q.; Wang, B.-X.; Wang, Z.-Z.; Dai, P.-D.; Shang, Z.; Tan, M.; Liu, N.; Wang, Y.-J. Development of High Spectral Resolution Lidar System for Measuring Aerosol and Cloud. J. Opt. Soc. Korea 2015, 19, 695–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.; Huang, J.; Chen, B.; Yi, Y.; Liu, J.; Bi, J.; Zhou, T.; Huang, Z.; Chen, S. Three-Year Continuous Observation of Pure and Polluted Dust Aerosols Over Northwest China Using the Ground-Based Lidar and Sun Photometer Data. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2019, 124, 1118–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Xu, C.; Ji, Y.; Hu, H. Aerosol microphysical parameters’ vertical profiles measured by a dual Raman-Mie lidar during 2007–2013 at Hefei, China. Appl. Opt. 2019, 58, 1537–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Fang, Z.; Xie, C.; Cohen, J.; Yang, Y.; Wang, B.; Xing, K.; Cao, Y. Two trans-boundary aerosol transport episodes in the western Yangtze River Delta, China: A perspective from ground-based lidar observation. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2021, 12, 370–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halldórsson, T.; Langerholc, J. Geometrical form factors for the lidar function. Appl. Opt. 1978, 17, 240–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.; Jiang, Y.; Wen, L.; Wen, D. Calculation of the overlap factor for scanning LiDAR based on the tridimensional ray-tracing method. Appl. Opt. 2017, 56, 4636–4645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stelmaszczyk, K.; Dell’Aglio, M.; Chudzyński, S.; Stacewicz, T.; Wöste, L. Analytical function for lidar geometrical compression form-factor calculations. Appl. Opt. 2005, 44, 1323–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasano, Y.; Shimizu, H.; Takeuchi, N.; Okuda, M. Geometrical form factor in the laser radar equation: An experimental determination. Appl. Opt. 1979, 18, 3908–3910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wandinger, U.; Ansmann, A. Experimental determination of the lidar overlap profile with Raman lidar. Appl. Opt. 2002, 41, 511–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Chen, S.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, H.; Guo, P.; Chen, B. Experimental determination of Raman lidar geometric form factor combining Raman and elastic return. Opt. Commun. 2014, 332, 296–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, C.; Zhao, Y.; Li, J.; Chu, Y. Geometrical constraint experimental determination of Raman lidar overlap profile. Appl. Opt. 2016, 55, 4924–4928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Gong, W.; Mao, F.; Pan, Z. Physical constraint method to determine optimal overlap factor of Raman lidar. J. Opt. 2017, 47, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero-Rascado, J.L.; Costa, M.J.; Bortoli, D.; Silva, A.M.; Lyamani, H.; Alados-Arboledas, L. Infrared lidar overlap function: An experimental determination. Opt. Express 2010, 18, 20350–20369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Tao, Z.; Liu, N.; Wu, D.; Xie, C.; Wang, Y. New experimental method for lidar overlap factor using a CCD side-scatter technique. Opt. Lett. 2015, 40, 1749–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernald, F.G. Analysis of atmospheric lidar observations: Some comments. Appl. Opt. 1984, 23, 652–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Wu, Y.; McCormick, M.P.; Lei, L.; Lee, R.B. Improved method to retrieve aerosol optical properties from combined elastic backscatter and Raman lidar data. Appl. Phys. A 2013, 116, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, D.; Ansmann, A.; Mattis, I.; Tesche, M.; Wandinger, U.; Althausen, D.; Pisani, G. Aerosol-type-dependent lidar ratios observed with Raman lidar. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2007, 112, D16202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Hua, D.; Wang, Y.; Yan, Q.; Li, S.; Li, Y.; Wang, H. Improvement of the signal to noise ratio of Lidar echo signal based on wavelet de-noising technique. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2013, 51, 961–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| Transmitter | |
| Transmitted wavelength | 355 nm |
| Pulse energy | 50 mJ |
| Pulse repetition rate | 10 Hz |
| Pulse duration | 8 ns |
| Laser beam divergence | 0.2 mrad |
| Receiver | |
| Telescope diameter | 400 mm |
| FOV | 0.5–2 mrad |
| Detect channels | 355, 387, 408 |
| Filter bandwidth | 1 nm |
| Data acquisition | |
| Sample rate | 40 MHz |
| Resolution | 12 bit |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, M.; Fang, Z.; Yang, H.; Cheng, L.; Chen, J.; Xie, C. UAVC: A New Method for Correcting Lidar Overlap Factors Based on Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Vertical Detection. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 184. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12010184
Zhao M, Fang Z, Yang H, Cheng L, Chen J, Xie C. UAVC: A New Method for Correcting Lidar Overlap Factors Based on Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Vertical Detection. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(1):184. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12010184
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Ming, Zhiyuan Fang, Hao Yang, Liangliang Cheng, Jianfeng Chen, and Chenbo Xie. 2022. "UAVC: A New Method for Correcting Lidar Overlap Factors Based on Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Vertical Detection" Applied Sciences 12, no. 1: 184. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12010184
APA StyleZhao, M., Fang, Z., Yang, H., Cheng, L., Chen, J., & Xie, C. (2022). UAVC: A New Method for Correcting Lidar Overlap Factors Based on Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Vertical Detection. Applied Sciences, 12(1), 184. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12010184








