Chaotic Communication System with Symmetry-Based Modulation
Abstract
1. Introduction
- A novel modulation technique exploiting the geometric properties of the discrete chaotic models obtained by symmetric integration is presented.
- The proposed approach allows avoiding changes in phase space and spectral characteristics of the carrier because chaotic oscillators do not bifurcate during SCM.
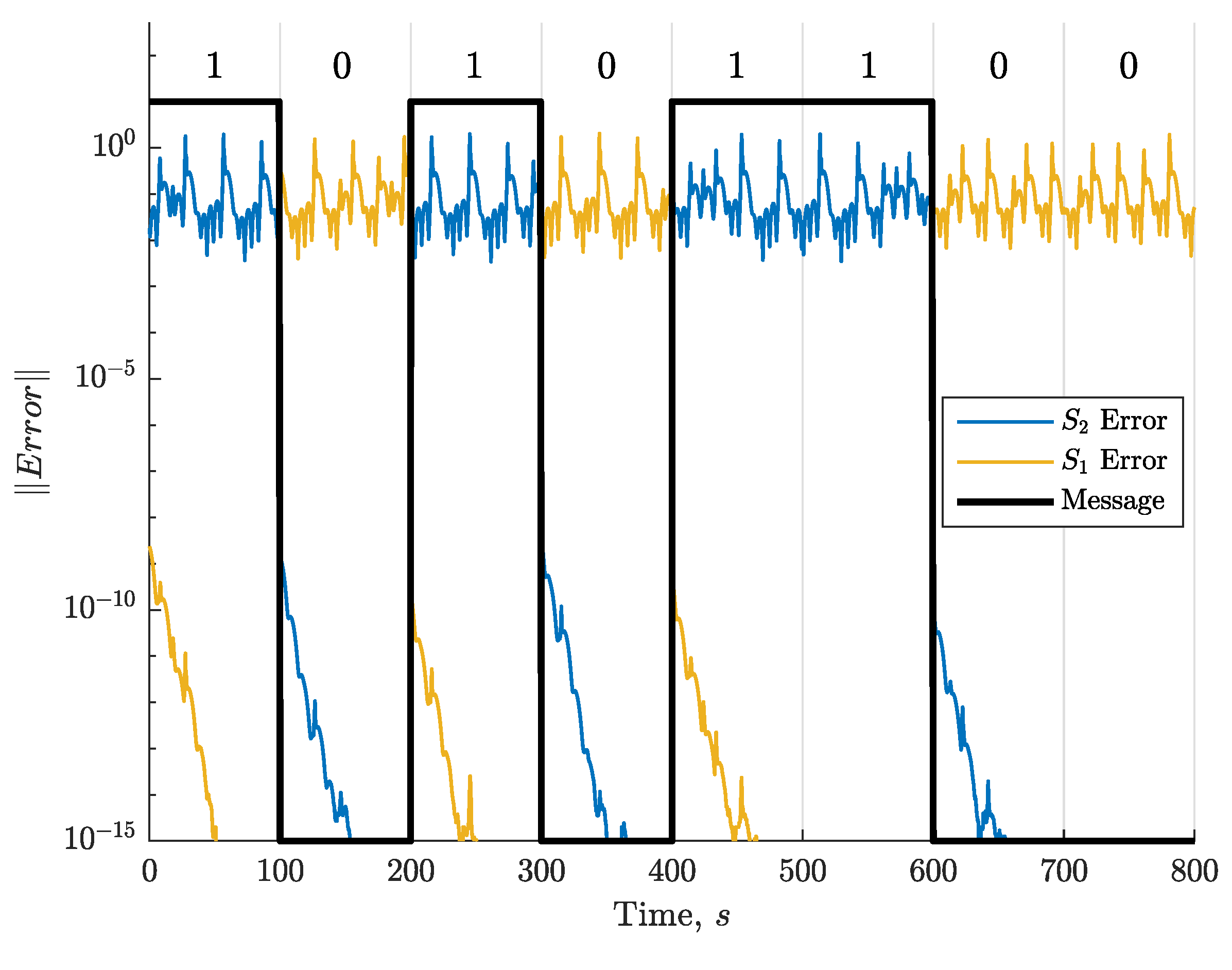
- The possibility of data transfer by symmetry-based modulation is experimentally shown. The throughput of the communication channel in the absence of disturbances is estimated.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synchronization of Chaotic Systems
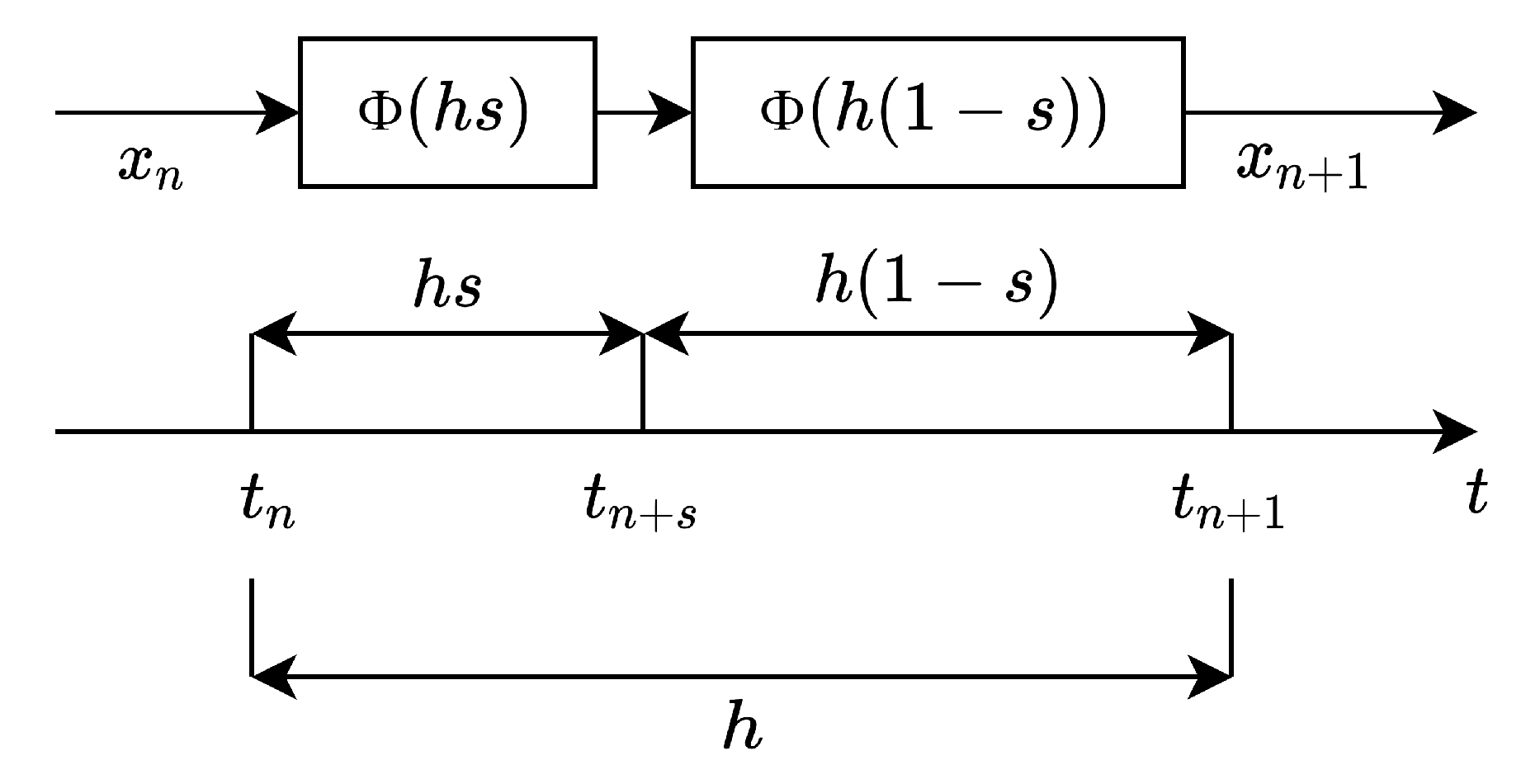
2.2. Semi-Implicit Symmetric Integration Method and Variable Symmetry Approach
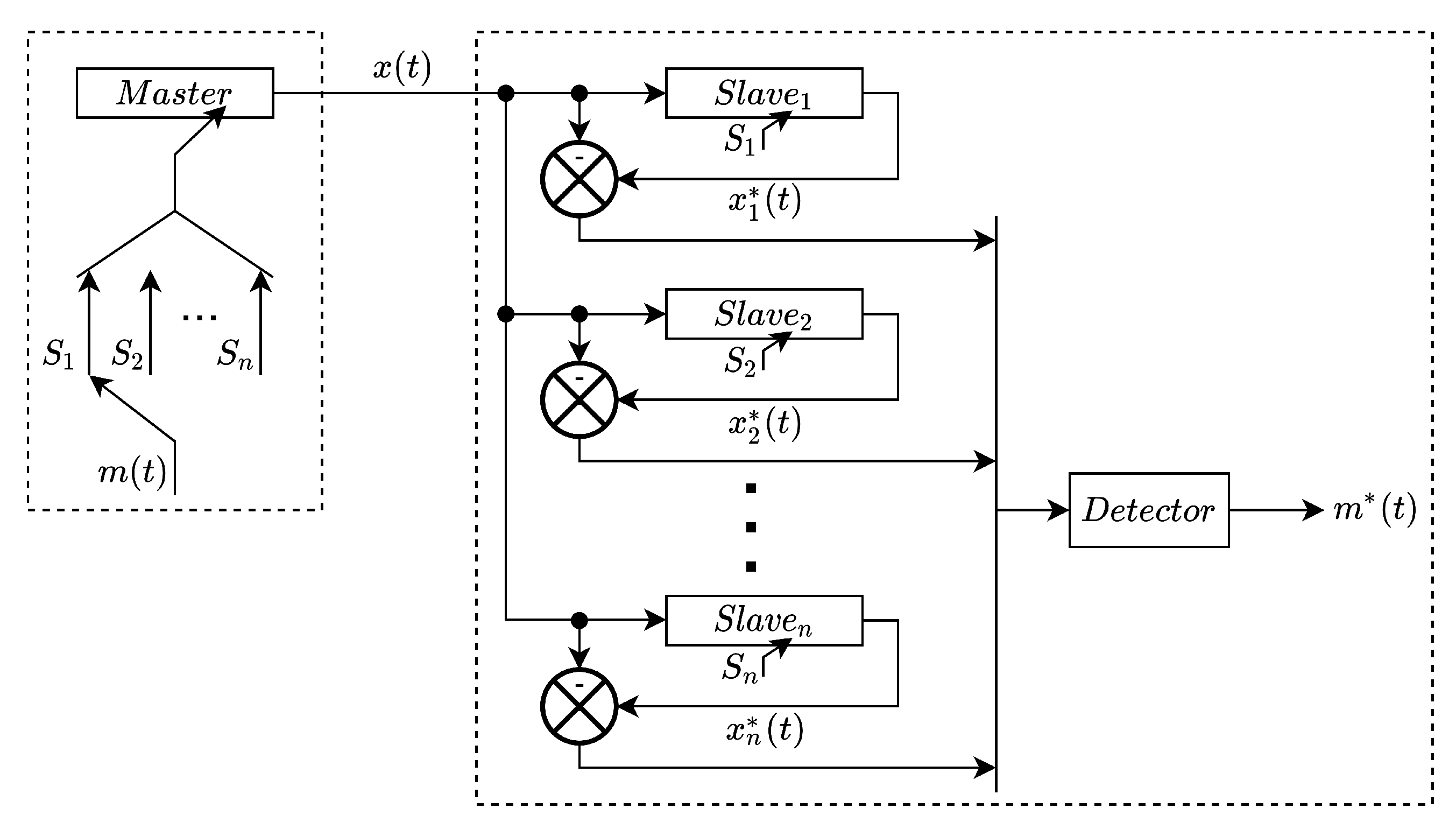
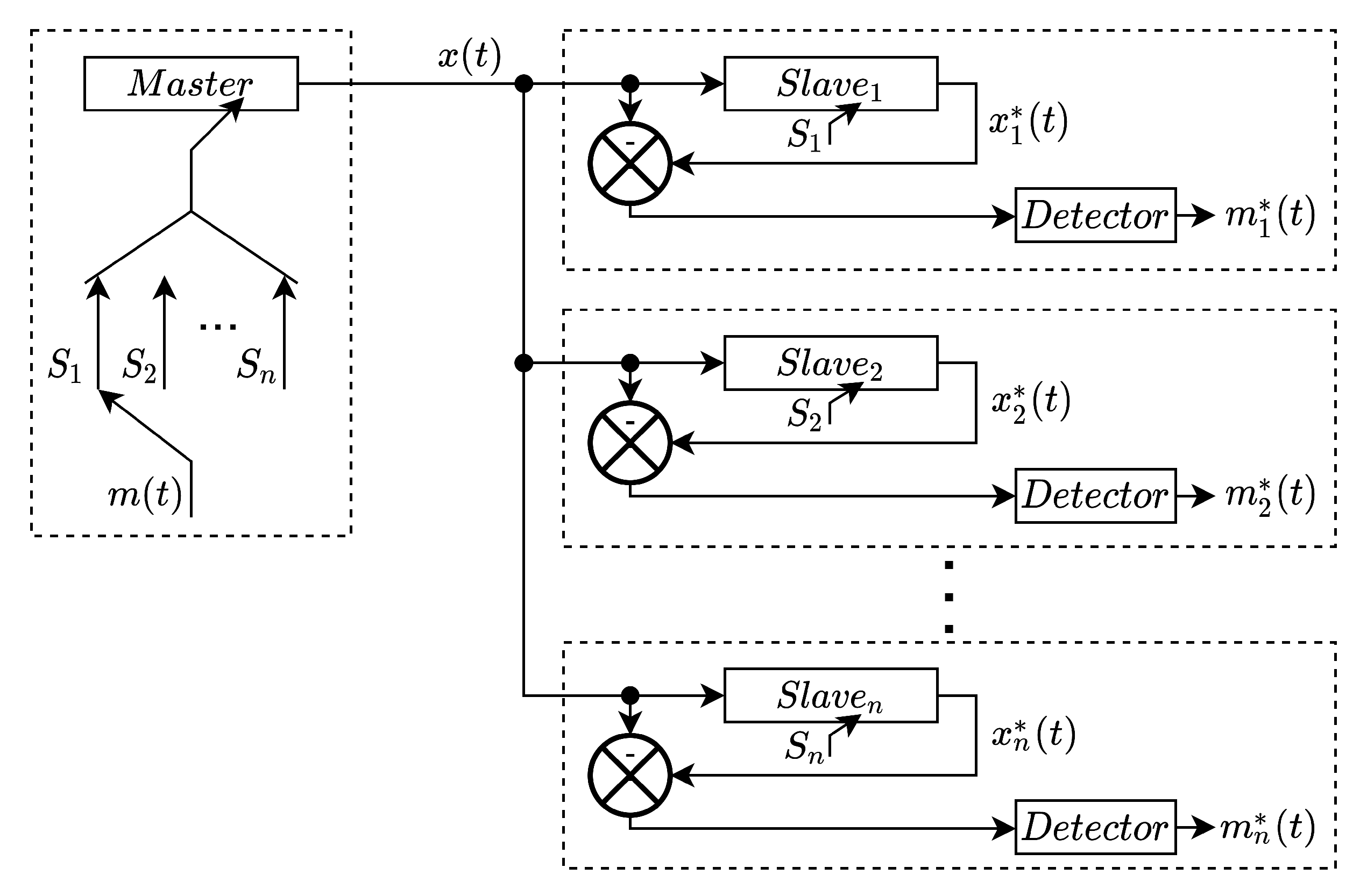
2.3. Communication System Architecture
3. Experimental Results
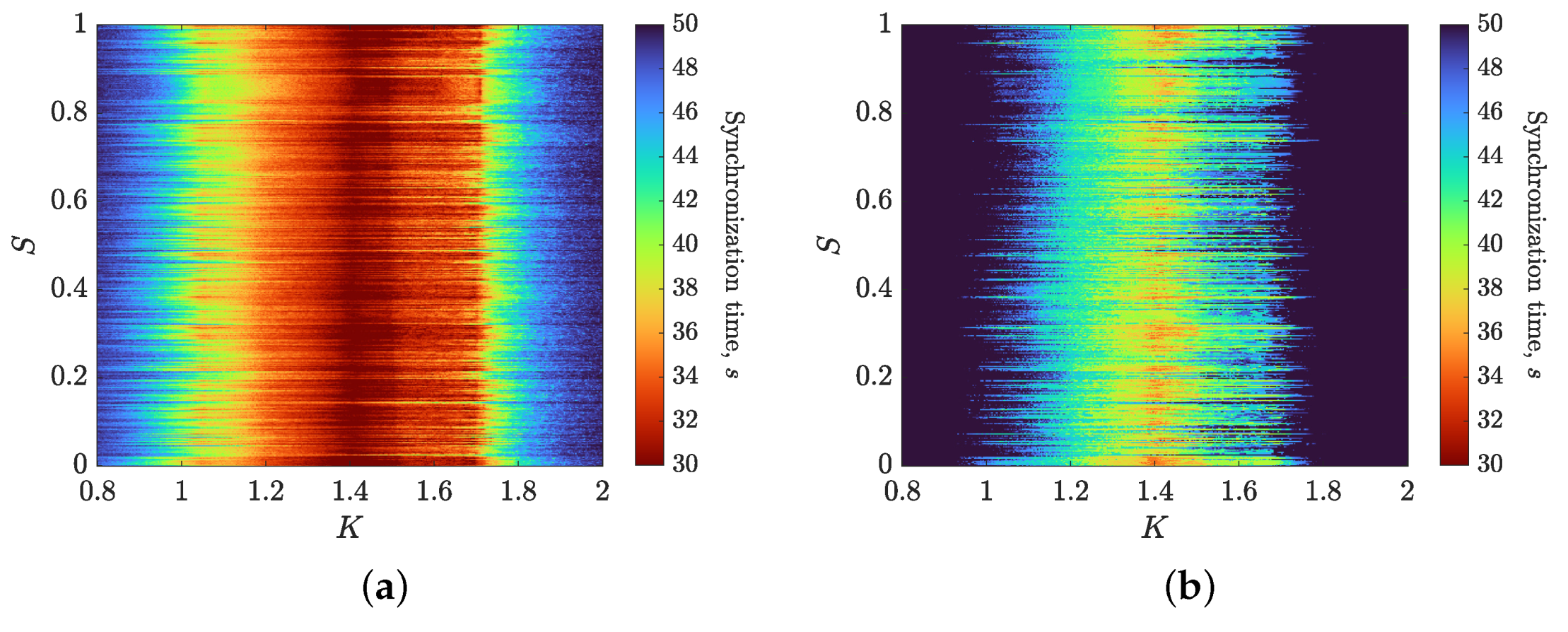
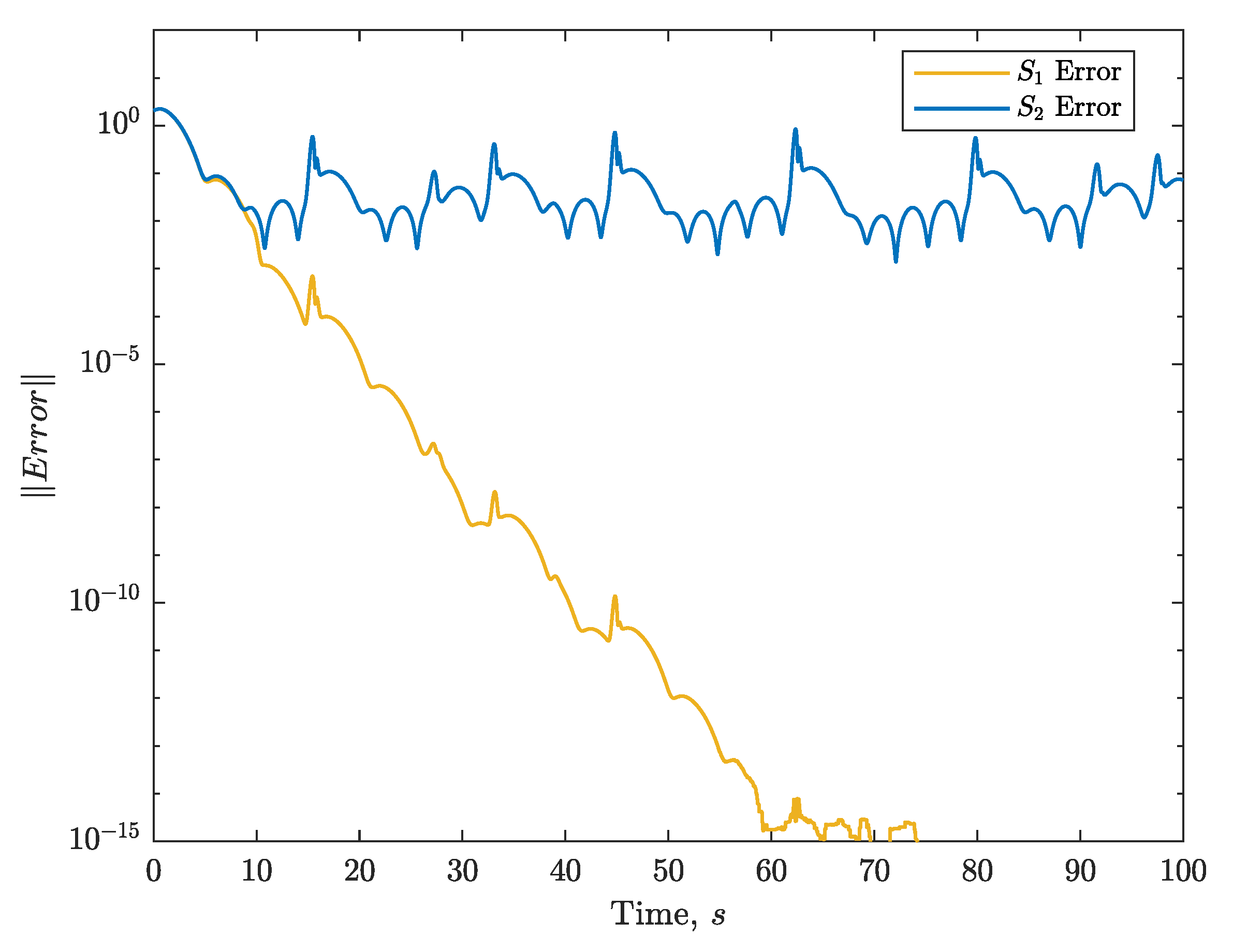
3.1. SCM Transfer Analysis
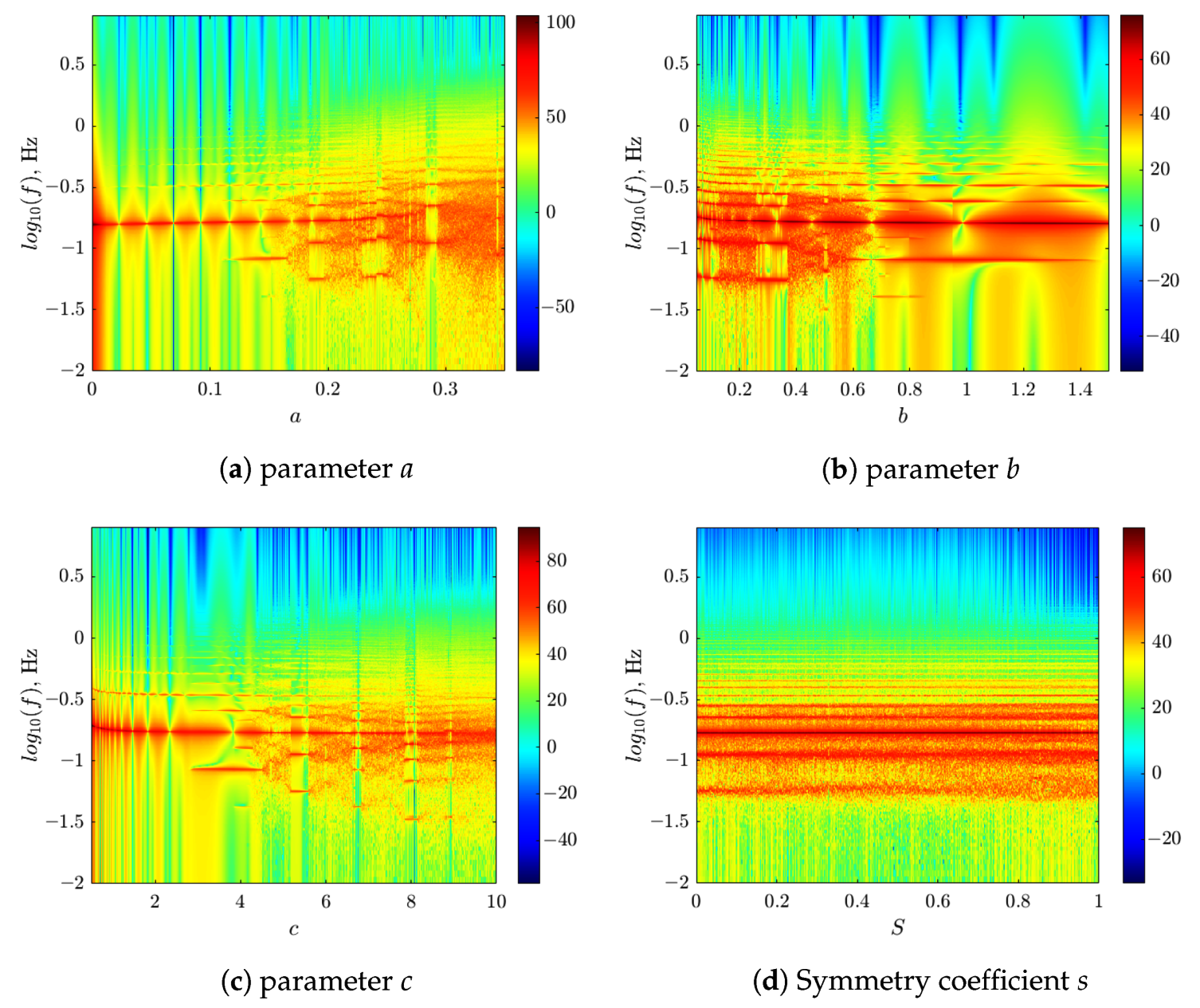
3.2. Comparing the SCM Approach with Parameter-Based Modulation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- The proposed novel digital communication method based on the synchronization of chaotic systems (symmetry coefficient modulation, SCM) allows the transmission of binary-coded messages. The underlying theoretical concept of using semi-implicit models with variable symmetry coefficient for chaotic signals generation is experimentally verified.
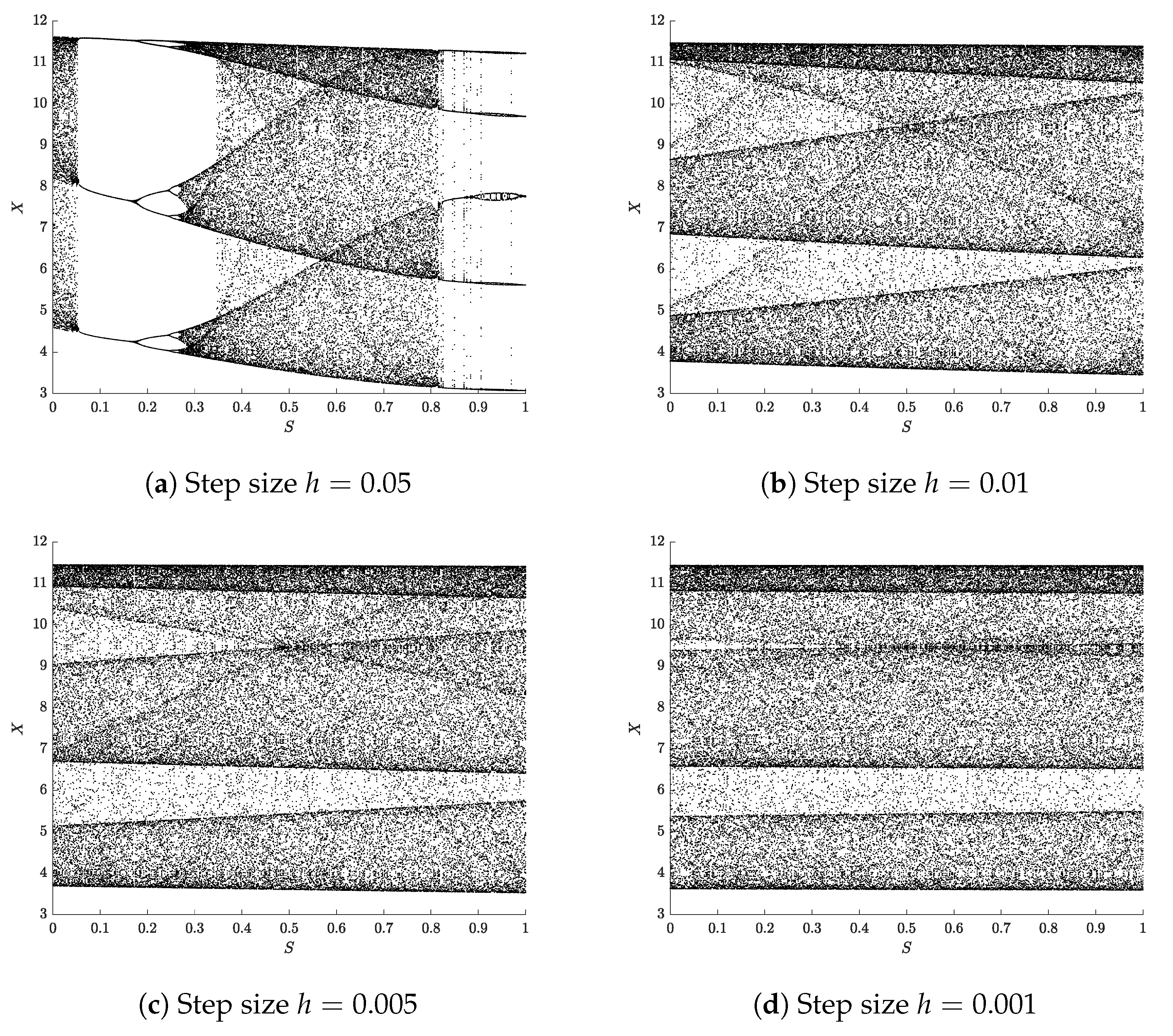
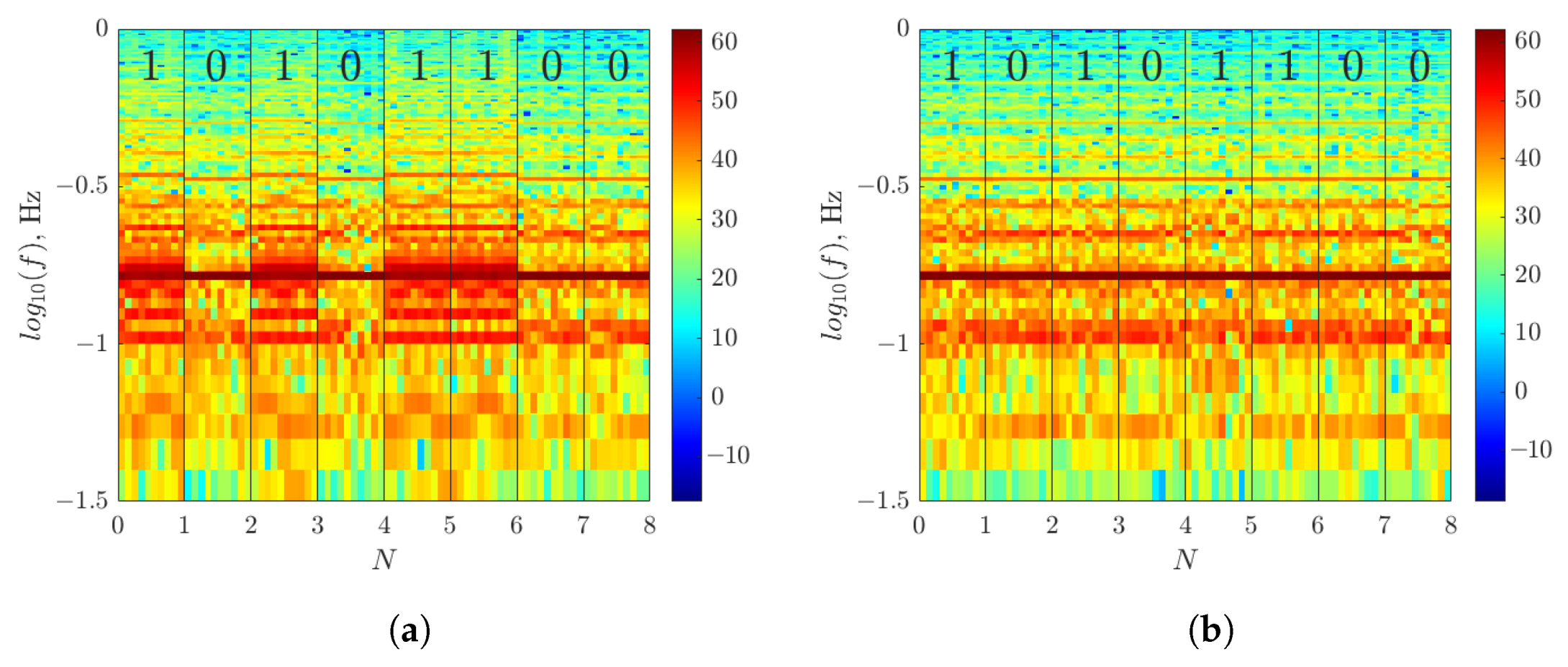
- It is shown that, unlike the bifurcation parameters, the switching of symmetry coefficient does not affect the behavior of the transmitting chaotic system, making the symmetry-based modulation more suitable for covert messaging. A presented comparison with parameter-based modulation confirmed these theoretical assumptions.
- We explicitly show that the transfer of the parameter by the modulation method leads to noticeable changes in the spectrum of systems even with a slight (10%) change in the bifurcation parameter, while a significant (more than 50%) change in the symmetry coefficient does not result in the significant difference in the spectrogram.
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Datta, D.; Mitra, P.; Dutta, H.S. FPGA implementation of high-performance digital down converter for software defined radio. Microsyst. Technol. 2019, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuomo, K.; Oppenheim, V.; Strogatz, S. Synchronization of Lorenz-based chaotic circuits with applications to communications. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Analog Digit. Signal Process. 1993, 40, 626–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dedieu, H.; Kennedy, M.P.; Hasler, M. Chaos shift keying: Modulation and demodulation of a chaotic carrier using self-synchronizing Chua’s circuits. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Analog Digit. Signal Process. 1993, 40, 634–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dmitriev, A.S.; Panas, A.I.; Starkov, S.O. Experiments on speech and music signals transmission using chaos. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 1995, 5, 1249–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koronovskii, A.A.; Moskalenvo, O.I.; Khramov, A.E. On the use of chaotic synchronization for secure communication. Physics-Uspekhi 2009, 52, 1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.P.; Bai, C.; Liu, J.; Baptista, M.S.; Grebogi, C. Experimental validation of wireless communication with chaos. Chaos 2016, 26, 083117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riaz, A.; Ali, M. Chaotic communications, their applications and advantages over traditional methods of communication. In Proceedings of the 2008 6th International Symposium on Communication Systems, Networks and Digital Signal Processing, Graz, Austria, 25 July 2008; pp. 21–24. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, C.; Ren, H.P.; Grebogi, C.; Baptista, M.S. Chaos-based underwater communication with arbitrary transducers and bandwidth. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.P.; Baptista, M.S.; Grebogi, C. Wireless communication with chaos. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2013, 110, 184101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, T.L.; Lin, H.R.; Wan, P.Y.; Yan, J.J. Improved Attribute-Based Encryption Using Chaos Synchronization and Its Application to MQTT Security. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaddoum, G. Wireless Chaos-Based Communication Systems: A Comprehensive Survey. IEEE Access 2016, 4, 2621–2648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pecora, L.; Carroll, T. Synchronization in chaotic systems. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1990, 64, 821–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sira-Ramirez, H.; Cruz-Hernandez, C. Synchronization of chaotic systems: A generalized Hamiltonian systems approach. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 2001, 11, 1382–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, E.A.; Grosu, I. An open-plus-closed-loop (OPCL) control of complex dynamic systems. Physica D Nonlinear Phenom. 1995, 85, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haken, H. An approach to self-organization. In Self-Organizing Systems: The Emergence of Order; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1987; pp. 417–437. [Google Scholar]
- Karimov, A.I.; Tutueva, A.V.; Karimov, T.I.; Druzhina, O.S.; Butusov, D.N. Adaptive Generalized Synchronization between Circuit and Computer Implementations of the Rössler System. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butusov, D.N.; Karimov, T.I.; Lizunova, I.A.; Soldatkina, A.A.; Popova, E.N. Synchronization of Analog and Discrete Rössler Chaotic Systems. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Russia Section Young Researchers in Electrical and Electronic Engineering Conference (2017 ElConRus), St. Petersburg and Moscow, Russia, 1–3 February 2017; pp. 265–270. [Google Scholar]
- Butusov, D.N.; Karimov, A.I.; Tutueva, A.V. Symmetric extrapolation solvers for ordinary differential equations. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE NW Russia Young Researchers in Electrical and Electronic Engineering Conference (EIConRusNW), St. Petersburg, Russia, 2–3 February 2016; pp. 162–167. [Google Scholar]
- Voroshilova, A.; Wafubwa, J. Discrete competitive Lotka–Volterra model with controllable phase volume. Systems 2020, 8, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butusov, D.N.; Ostrovskii, V.Y.; Karimov, A.I.; Andreev, V.S. Semi-explicit composition methods in memcapacitor circuit simulation. Int. J. Embed. Real-Time Commun. Syst. 2019, 10, 37–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tutueva, A.V.; Karimov, T.I.; Andreev, V.S.; Zubarev, A.V.; Rodionova, E.A.; Butusov, D.N. Synchronization of Chaotic Systems via Adaptive Control of Symmetry Coefficient in Semi-Implicit Models. In Proceedings of the 2020 Ural Smart Energy Conference (USEC), Ekaterinburg, Russia, 13–15 November 2020; pp. 143–146. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, T.; Chua, L.O. Secure communication via chaotic parameter modulation. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Fundam. Theory Appl. 1996, 43, 817–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butusov, D.N.; Pesterev, D.O.; Tutueva, A.V.; Kaplun, D.I.; Nepomuceno, E.G. New technique to quantify chaotic dynamics based on differences between semi-implicit integration schemes. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2021, 92, 105467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaddoum, G.; Coulon, M.; Roviras, D.; Chargé, P. Theoretical performance for asynchronous multi-user chaos-based communication systems on fading channels. Signal Process. 2010, 11, 2923–2933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rulkov, N.F.; Sushchik, M.M.; Tsimring, L.S.; Volkovskii, A.R. Digital communication using chaotic-pulse-position modulation. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Fundam. Theory Appl. 2001, 48, 1436–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
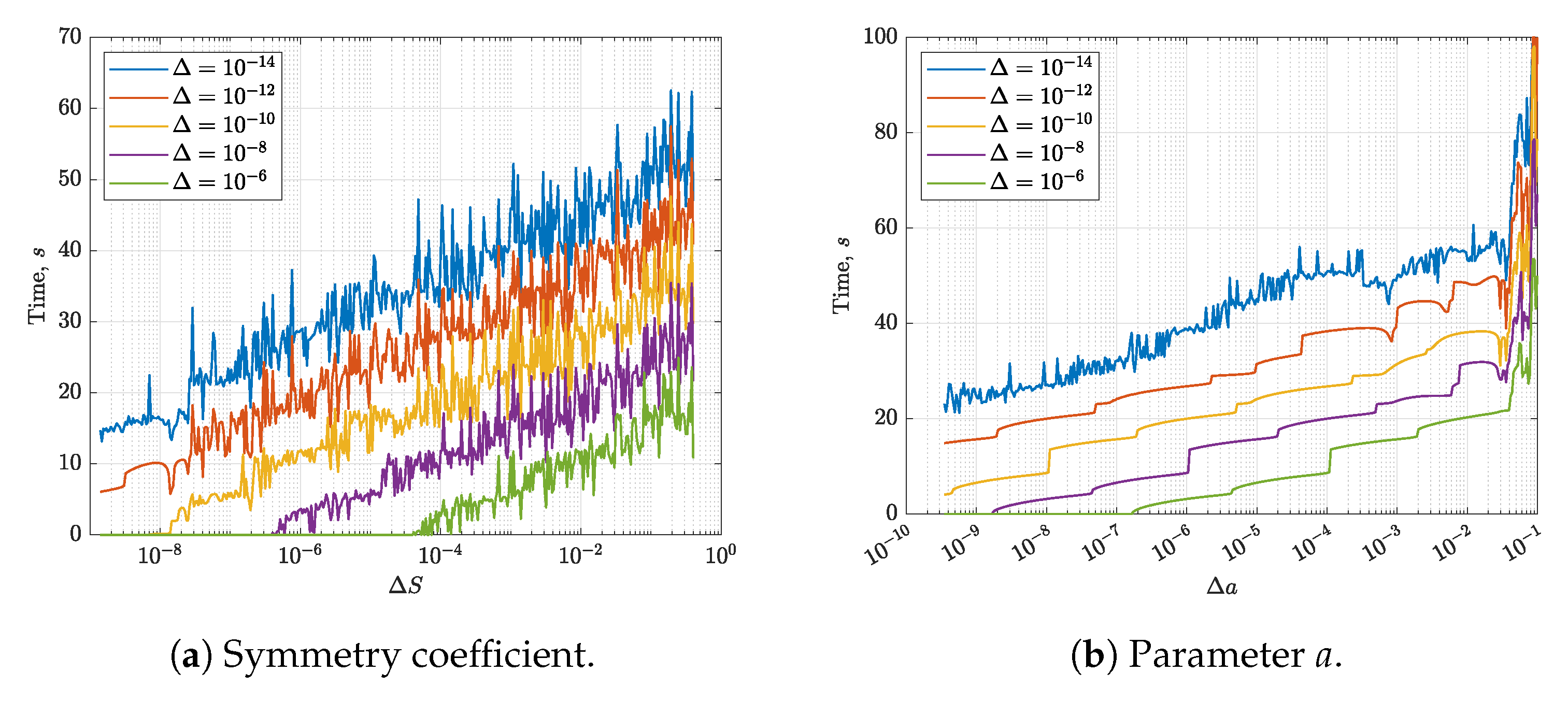

| Symmetry Coefficient | Parameter a | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Transfer Rate, Mbit/s | Transfer Rate, Mbit/s | ||
| 0.1 | 0.4 | 0.1 | 0.18 |
| 0.01 | 0.5 | 0.01 | 0.47 |
| 0.001 | 0.666 | 0.001 | 0.6 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Karimov, T.; Rybin, V.; Kolev, G.; Rodionova, E.; Butusov, D. Chaotic Communication System with Symmetry-Based Modulation. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 3698. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11083698
Karimov T, Rybin V, Kolev G, Rodionova E, Butusov D. Chaotic Communication System with Symmetry-Based Modulation. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(8):3698. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11083698
Chicago/Turabian StyleKarimov, Timur, Vyacheslav Rybin, Georgii Kolev, Ekaterina Rodionova, and Denis Butusov. 2021. "Chaotic Communication System with Symmetry-Based Modulation" Applied Sciences 11, no. 8: 3698. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11083698
APA StyleKarimov, T., Rybin, V., Kolev, G., Rodionova, E., & Butusov, D. (2021). Chaotic Communication System with Symmetry-Based Modulation. Applied Sciences, 11(8), 3698. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11083698







