Abstract
The failed dental implant associated with maxillary sinusitis is a multifactorial phenomenon and should be investigated thoroughly. The inflammatory process induced by accumulated biofilm and wear debris may increase mucous secretion and mucous thickening, which finally may lead to severe complications such as maxillary sinusitis. The inflammatory cytokines might compromise the long-term osseointegration of the related implant. In this study, implants retrieved from three patients who experienced implant failure relating to maxillary sinusitis were investigated using scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy. SEM analysis of the implant apical region revealed a less-compact bone structure, indicating the high bone turnover due to an inflammatory process. The ratio of calcium (Ca) and phosphorus (P) was negligible in all specimens. Detection of fluorine (F), sodium (Na), silicon (Si), gold (Au), aluminum (Al), and magnesium (Mg) confirmed the contamination. The selected cases presented different biological aspects that might play the central role in the failed dental implants associated with maxillary sinusitis: the contamination of potentially toxic elements, microorganism infection, and long perforation of implant apex into the sinus. Each of the above phenomena needs to be confirmed with further clinical study with a larger number of failed implants and accompanying tissue samples.
1. Introduction
Dental implant installation in the maxillary posterior region requires meticulous consideration and thorough evaluation because of the distinguished bone quality as well as the position of the maxillary sinusitis. In many cases, due to early loss of the maxillary molars, pneumatization of the sinus, low bone quality, and atrophied alveolar ridge are challenges facing the surgeon in achieving an initial degree of stability and satisfying bone osseointegration of the dental implant. In some cases, a short dental implant is a reliable choice for dental rehabilitation in the maxillary posterior region [1]. Other authors also reported cases of regular length implants with the blunt apex inserted into the sinus [2]. This type of sinus floor perforation without tearing the Shneiderian membrane is a modification of closed sinus lifting without augmentation, which creates a void peripheral to the fixture. However, the osseointegration of the implant apex that perforates the sinus is unpredictable.
Maxillary sinus lifting and bone grafting procedures are recommended in the maxillary molar area with vertical bone height as much as 5 mm or less to improve the bone quantity and implant osseointegration. Sinus augmentation is highly predictable with many studies reporting over 95% success [3]. The survival rate of implants placed in sinuses augmented with the lateral window technique varied between 61.7% and 100%, with an average survival rate of 91.8% [4]. However, during the implantation process in the maxillary posterior region, with or without the sinus lifting procedure, several complications may develop. Perforation of the Schneiderian sinus membrane during the implant installation tends to heal spontaneously [5,6]; however, cases of odontogenic maxillary sinusitis (OMS) due to implant penetration into the maxillary sinus have been reported [7]. The incidence of OMS after maxillary sinus lifting is 0% to 20% [7,8,9].
The etiology of implant failure related to OMS has been rarely reported in the literature. In a previous study, Pettersson et al. [10] reported that titanium (Ti) particles can activate the macrophages to interleukin 1 beta (IL-1β). In orthopedic research, aseptic loosening of an orthopedic Ti implant is a well-established complication. A complex process of inflammation and osteolysis is supposed to be the pathogenesis of the implant-associated osteolytic phenomenon, which is dependent on innate and adaptive immune reactions [11]. Wear debris and particle phagocytosis by macrophages, fibroblasts, and osteoblasts represent a key role in the innate immune response, which provokes the elevation in the level of proinflammatory cytokines [for example, IL-1β, interleukin-6 (IL-6), tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α), and prostaglandin E2 (PGE2)] [11]. In addition to the phagocytosis of wear debris, the interaction between the particle and cell surface is believed to be a component of this biological response [12]. These inflammatory cytokines stimulate osteolysis by their regulation on osteoclasts and their monocytic precursors. The receptor activator of NF-κB (RANK)/the receptor activator of nuclear factor (NF)-κB-ligand (RANKL) is the central signaling pathway for the activation of osteoclasts that regulates the osteolytic process [13].
Unlike an orthopedic implant, a dental implant is exposed to a complex oral cavity environment with species-rich heterogeneous microorganisms and chemical compositions. The extraosseous surface of the implants and abutments will develop a biofilm within the oral cavity environment, which will trigger infection and cause inflammatory destruction of peri-implant tissue [14]. In addition, salivary chemical compositions and microorganism products can potentially dissolve the titanium oxide (TiO2) layer. If the losing of TiO2 layer occurs continuously, the titanium particles and ion releasing into the surrounding environment and tissue will take place. Ti particles and ions can also be released during the implantation procedure from metallic instruments, from the implant surfaces during insertion, and from the implant-abutment interface during connection and functional loading [15].
Even though the oral galvanism phenomenon that causes the Ti ions releasing in the peri-implant tissue are under concern recently [15], there is no reported evidence confirming the Ti ions released due to galvanic current activities will cause OMS; instead, metal debris released during installation is likely the main trigger of irritation. The infiltration of microorganisms should also be considered. Brook [16] reported the finding of aerobic and anaerobic organisms in the normal maxillary sinus, which is evidence of the potential of some complications causing by the perforated implant apical region into the sinus cavity, in the same pattern with apical infection. The inflammatory process induced by accumulated biofilm in combination with released wear debris may increase mucous secretion and mucosal thickening; this in turn can cause formation of retention pseudocyst, which finally may lead to severe complications such as maxillary sinusitis [4]. Those multifactor processes might compromise the long-term osseointegration of the related implant and should be investigated thoroughly. The distribution and concentrations of Ti ions and particles in the tissues surrounding a dental implant linked to sinusitis remain unclear.
In this study, the micro-surfaces of failed implants linked to OMS in three patients were investigated under scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and the elemental composition of the fixture surfaces and attached bone was assessed by energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS).
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Cases
Implants retrieved from three patients who experienced implant failure relating to maxillary sinusitis were investigated. Ethics approval was approved by the Seoul Nation University Institutional Review Board (S-D20170005). Patient data, including the indication for implant removal, were collected through the electronic medical record system.
2.1.1. Case 1: Fractured and Damaged Implant-Related Sinusitis Case
A 56-year-old male patient was referred from a local clinic to the Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery (OMFS) Department of Seoul National University Dental Hospital (SNUDH) to have his #16i implant removed due to fracture. The patient had a smoking habit and an allergy to nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (ibuprofen).
The panoramic radiograph (Figure 1A) and Water’s view revealed generalized alveolar bone loss and calculi deposition, with furcation involvement of the #36, #37, #46, and #47 teeth; a retention pseudocyst in the right maxillary sinus; and mucosal thickening of both sinuses (Figure 1A,B, arrows). Using CT, the #16i implant fixture with missing abutment in the #16i implant area and the mucosal thickening and retention pseudocyst were also observed in the right maxillary sinus (Figure 1B). The surgical treatment for the right maxillary sinusitis and fractured #16i implant included a modified endoscopic-assisted sinus surgery (MESS) [9], a novel and an efficient way for approaching the maxillary sinus, irrigation of the sinus to ensure complete removal of the inflammatory tissues and foreign body, and #16i implant removal under conscious sedation (Figure 1C,D). The patient was recommended to quit smoking before operation and stay smoke-free at least 4 weeks after it. Otherwise, the patient did not have any general pathology and underwent uneventful healing postoperation. After complete healing following the surgery, bone grafting was planned in the implant extraction site with the possibility for removal of the #17i implant due to displacement into the maxillary sinus. Six months after the first surgery, the second surgery involving bone graft and #17i implant removal was carried out. The patient displayed uneventful healing upon clinical examination and radiographic examination and, six months after the second surgery, the microplate was removed and an implant installation operation was carried out at the previous implant extraction site using a 4.0 × 8.5 mm Luna® implant (Shinhung Co., Seoul, Korea). During the immediate postoperative examination, improved aeration was observed in the area of the right maxillary sinus.
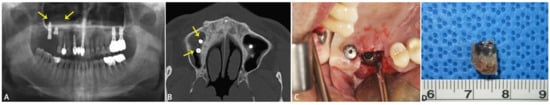
Figure 1.
Preoperative radiographic examination of case 1. The panoramic radiograph shows generalized alveolar bone loss and calculi deposition; furcation involvement of the #36, #37, #46, and #47 teeth; and a round retention pseudocyst surrounding the #16i and #17i implants (marked with arrows) (A). Upon CT examination, the #16i implant fixture had a missing abutment and, together with the #17i implant in the right maxillary sinus (marked with arrows), mucosal thickening and retention pseudocyst were observed in the right maxillary sinus in the axial view (B). Intraoperative view of #16i implant removal (C). The #16i implant was removed using forceps and trephine burr (D).
2.1.2. Case 2: Fungal Sinusitis with Involved BRONJ Case
A 79-year-old female patient was referred from a local dental clinic to our institution for treatment of bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the jaw (BRONJ) in 2019. The patient had a chief complaint of pain and swelling on both sides of the maxilla and the left mandible area. The patient had a medical history of osteoporosis, rheumatism, and heart valve defect and reported that she receives daily injections of osteoporosis drugs and consumes medication for high blood pressure.
Upon clinical examination, buccal bone exposure was observed in the #16 and #26i areas. The panoramic radiograph and Water’s view showed generalized alveolar bone loss and calculi deposition, apical involvement of the #36 tooth; furcation involvement of the #37 tooth; peri-implant bone loss around the #15, #24, #25, and #26 teeth; and left maxillary sinus opacification (Figure 2A). CT imaging showed bone fracture and sequestrum formation in the right and left sides of the maxilla and left mandible. Cortex destruction, sequestrum, calculated marrow attachment, and adjacent bone sclerosis were observed in the areas of #11 through #17, #24 through #27, and #36 and #37 teeth, and the upper and lower cortices were overserved, thus being lost in the area of maxillary bone destruction (Figure 2B). The laboratory complete blood count showed a reduced red blood cell (RBC) count of 3.14 × 106/μL (reference range: 4–5.40 × 106/μL), hemoglobin (Hgb) concentration of 9.7 g/dL (reference range: 12–16 g/dL), and hematocrit of 30.4% (reference range: 36%–48%) and an increased absolute neutrophil count of 7354/μL (reference range: 1800–7000/μL).
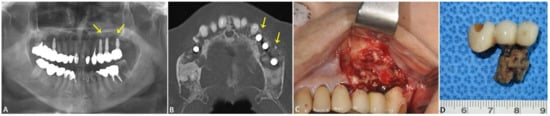
Figure 2.
Preoperative radiographic examination of case 2. The panoramic radiograph shows generalized alveolar bone loss and calculi deposition, apical involvement of the #36 tooth; furcation involvement of the #37 tooth; peri-implant bone loss around the #15, #24, #25, and #26 teeth; and left maxillary sinus opacification (marked with arrows) (A). CT imaging showed bone fracture and sequestrum formation in the right and left sides of the maxilla and left mandible. Cortex destruction, sequestrum, calculated marrow attachment, and adjacent bone sclerosis were observed in the areas of #11 to #17, #24 to #27 (marked with arrows), and #36 and #37 teeth, and the upper and lower cortices were overserved, thus lost in the area of maxillary bone destruction in the axial view (B). Intraoperative view of the partial maxillectomy (#25i, #26i, and #27i alveolotomy) surgical procedure. Necrotic bony exposure was observed on the buccal side of the left maxilla (C). The extracted #25i, #26i, and #27i implants with necrotic bone attachment (D).
Based on the clinical, radiological and laboratory findings, MESS on combination with mass excision of the left maxillary sinus (#25i, #26i, and #27i alveolotomy) were planned under conscious sedation (Figure 2C,D) [9]. After administration of the local anesthesia in the surgical site using 2% lidocaine with 1:1,000,000 epinephrine, an incision line was made using blade no. 15 from the first premolar to the second molar. A full mucoperiosteal flap was elevated exposing the inflamed necrotic bone tissue. The osteolytic bone destruction was already expanded into the maxillary anterior sinus wall. The inflammatory exudate from the sinus was immediately aspirated using a 5 cc syringe. Since the bone destruction was already expanded, after the necrotic bony removal, the left maxillary sinus was exposed. With the utilization of 0°, 15°, 30°, and 75° endoscopes, the sinus was carefully inspected and the remaining inflammatory tissue was removed and irrigated. After maxillary sinus packing with osteomeatal unit enlargement, the window on the anterior maxillary wall was fixed using two pieces of six-hole miniplate and predrilled holes. The surgical wound was sutured in two layers using 5-0 and 4-0 Vicryl® (Polyglactin 910®, Johnson & Johnson Co., New Brunswick, NJ, USA). The patient was instructed according to the standard sinus surgery instructions, such as keeping one’s head elevated in orthostatic position during sleep. After surgical treatment, the patient was closely followed.
2.1.3. Case 3: Apicoectomy of Fixture Case
A 39-year-old female patient presented to the OMFS Department of SNUDH in June 2020 with persistent pain in the right maxillary area. The patient reported that her dental pain had started one year ago, when she received a crown of porcelain fused to metal on the #15 tooth and a #16i implant installation with sinus lifting. Six months later, she had visited an ear, nose, and throat service and underwent cyst removal. However, since then, the dental pain had persisted and recurrence of the right maxillary sinus cyst was suspected. The patient did not have any significant medical history except an allergy to amoxicillin.
The patient exhibited pain upon palpation and swelling and redness in the buccal area of the #15 and #16 teeth of the right maxilla. Via panoramic radiography and Water’s view, an impacted #18 tooth and submerged #36 and #46 teeth were observed (Figure 3A). Using computed tomography (CT), a retention pseudocyst in the right maxillary sinus and slight mucosal thickening of both maxillary sinuses were observed (Figure 3B).
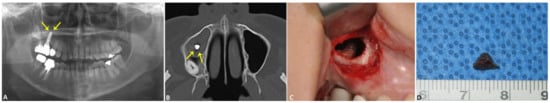
Figure 3.
Preoperative radiographic examination of case 3. The panoramic radiograph shows an impacted #18 tooth, submerged #36 and #46 teeth, and a displaced #16i implant protruding into the right maxillary sinus (marked with arrows) (A). The CT imaging shows a retention pseudocyst in the right maxillary sinus and slight mucosal thickening of both maxillary sinuses. The apical portion of the protruded #16i implant is visible from the axial view (marked with arrows) (B). Intraoperative view of the #16i implant cutting. After careful removal of the inflamed cystic lesions for the sinus, the apical portion of the #16i implant was cut using a high-speed fissure burr (C). The 5-mm apical portion of the #16 implant (D).
After careful consultation with the patient, immediate MESS with a #16i-apex, 5-mm cutting and smoothing surgery were scheduled. Under conscious sedation with 5 mg/mL of intravenous (IV) midazolam, a 13 × 9 mm bony sinus window was created on the anterolateral wall of the right maxillary sinus via the MESS approach, using a small round burr. The bony window was then secured using a four-hole Ti microplate with two microscrews® (KLS Martin Co., Tuttlingen, Germany). After making two more additional holes for microscrew fixation for the final fixation, the bone window was removed. Upon reaching the maxillary sinus, the inflammatory exudate was aspirated with a 5-cc syringe, and the inflamed tissues and the retention pseudocyst were completely removed using a slide curved periosteal elevator and sinus forceps under endoscopic examination. Following complete removal of the pseudocyst, the 5-mm apical tip of the protruded #16i-implant was cut and smoothened using a high-speed fissure burr (Figure 3C,D). After careful irrigation of the sinus to remove any leftover inflamed tissue and Ti particles, the bony window was repositioned and the soft tissue was sutured in two layers using 5-0 and 4-0 Vicryl® (Polyglactin 910®; Johnson & Johnson Co., New Brunswick, NJ, USA). The patient was hospitalized for one day and received standard postoperative care for maxillary sinusitis. The young patient did not have any history of general pathology and underwent good postoperative healing.
The immediate postoperative radiogram showed 5 mm of the apical portion of the #16i implant removed, with the microplate and microscrews fixated in place, and a drain inserted. The biopsy results confirmed an antral pseudocyst. A reduction of haziness in the right maxillary sinus was also observed. The patient’s symptoms improved during the follow-up period and no complications associated with the sinus surgery were reported. Six months after the surgery, the #16i implant remained in good function and the patient was without symptoms.
2.2. SEM and EDS Investigations of the Implant Surface
The implant fixtures and surrounding tissue collected during the resection surgery were immediately placed in a mixture of 2.5% glutaraldehyde (GA) in 0.1 M of phosphate buffer (PB) after slight irrigation. The implant fixtures underwent coating before SEM examination (JSM-7800F Prime®; Jeol Ltd., Tokyo, Japan). The examined regions were the implant surface and attached bone tissue at the upper, middle, and apical parts of the fixture. The surface was scanned thoroughly under 500× magnification and areas with representative features were chosen for micrography and element analysis (Figure 4). The EDS points were designed as “patient number-EDS number-position of the analyzed point on the fixture” (T: thread, U: upper one-third of the fixture, M: middle one-third of the fixture, A: apical one-third of the fixture). The SEM was operated at 10 kV and 65×, 500×, 1000×, 2500×, 5000×, 10,000×, and 20,000× micrographs were acquired.
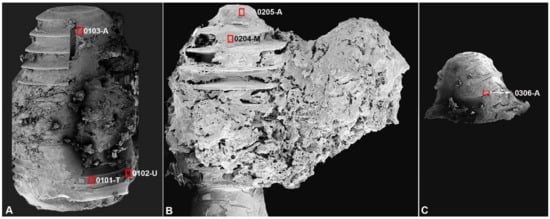
Figure 4.
SEM photograph showing the whole implant specimens with the marking of SEM-EDS examined points. In the implant fixture from case 1, the high magnification micrograph and EDS analysis were performed at three points: one in the thread surface to show the fixture morphology (0101-T), one on the attached bone in the upper region (0102-U), and one on the attached bone in the apical region (0103-A), to compare the bone structure and chemical composition at these two regions (A). In implant fixture and attached bone mass from case 2, two points in the apical area of the implant, one on the integrated bone in the middle of the fixture (0204-M), and one on the fixture surface in the apical region (0205-A) were chosen to examine the BRONJ—affected and fungal-infected bone and implant morphology (B). In the implant apex from case 3, the exposed surface of the fixture thread was chosen to be analyzed by EDS (C).
The element composition of the specimens was accessed by using an EDS instrument (XFlash® 6, Bruker, Berlin, Germany) connected to a microscope detector and the ESPRIT® analysis software (Bruker, Berlin, Germany). The EDS method involved qualitative and semi-quantitative microanalysis, including element distribution mapping. In the distribution maps, provided relative concentrations were indicated by color density. The representative point of each region was chosen and analyzed under a magnification of 10,000×. The mass concentration (C) ranges in element concentration determined from EDS were classified as: major: C > 0.1 mass fraction (greater than 10% mass), minor: 0.01 ≤ C ≤ 0.1 (1% mass to 10% mass), and trace: C < 0.01 (below 1% mass).
3. Results
Morphologic SEM analysis of failed implants linked to sinusitis revealed a less-compact bone structure in the implant apical region. This aspect is indicative of high rates of bone turnover due to the inflammatory process. SEM photography of the implant surface also revealed the typical microstructure of the sandblasted and acid-etched surfaces. However, at some point, irregular and defective surfaces were also observed (Table 1).

Table 1.
EDS data and surface morphology of SEM results.
In case 1, the implant fixture was directly related to the mucous retention cyst of the maxillary sinus in the apical region. The high magnification micrograph and EDS analysis were performed at three points: one in the thread surface to show the fixture morphology, one on the attached bone in the upper region, and one on the attached bone in the apical region to compare the bone structure and chemical composition at these two regions (Figure 4A). SEM micrograph of the exposed implant surface revealed the pattern of sandblasting and acid etching surface (Figure 5, 0101-T, white asterisk). EDS analysis of this region showed a homogenous Ti surface covered by a Ti oxide layer (% mass Ti: 82.98%, oxygen (O): 10.93%). In addition, minor signs of carbon (C) and fluorine (F), together with traces of gold (Au), sodium (Na), calcium (Ca), phosphorus (P), and silicon (Si), were recorded. Bone tissue attached at the implant upper part (Figure 5, 0102-U, white asterisk) was found to have a more compact structure than bone in the apical region, per both SEM micrograph analysis and EDS composition results (Figure 5, 0103-A) (% mass of Ca in 0101-T was 35.61% vs. 29.26% in 0103-A). The Ca/P ratio of bone in the upper region was higher than that in the apical region (4.1 vs. 2.6). Noticeably, a significant level of zirconium (Zr) (9.19%) was detected in this upper bone region, together with trace signals of Ti, Na, and Si. The bone at the apical region (Figure 5, 0103-A) exhibited a nonhomogeneous structure, with not only organic particles (Figure 5, 0103-A, blue arrowheads) but also significant signs of Na, Si, Ti, and traces of Au, aluminum (Al), and magnesium (Mg). A Ti particle was also detected and is displayed on the distribution map (Figure 5, 0103-A, distribution map, arrow).
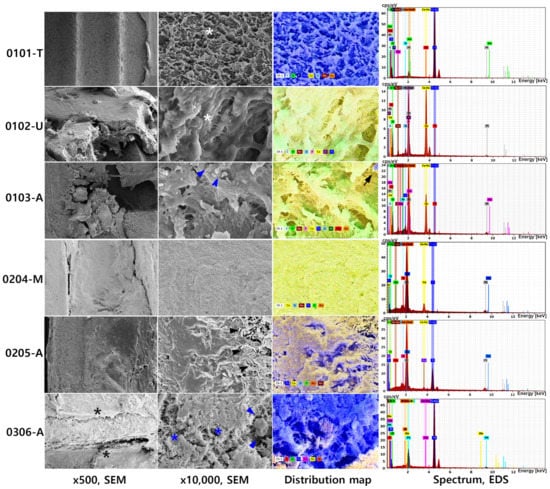
Figure 5.
SEM micrograph at 500× and 10,000× magnification, EDS elemental distribution map and a spectrum of representative points pertaining to the three failed implants. In case 1, the SEM micrograph of the exposed implant surface revealed the pattern of sandblasting and acid etching surface (0101-T, white asterisk). Bone tissue attached at the implant upper part (0102-U, white asterisk) was found to have a more compact structure than bone in the apical region, per both SEM micrograph analysis and EDS composition results (0103-A, blue arrowhead). A Ti particle was also detected and is displayed on the distribution map (0103-A, distribution map, arrow). The Ca/P ratio of bone in 0102-U is higher than that in 0103-A (4.1 vs. 2.6). Noticeably, a significant level of zirconium (Zr) (9.19%) was detected in 0102-U, together with trace signals of Ti, Na, and Si. In case 2, The integrated bone on the implant surface showed a pattern of sclerosing bone with rare signs of bone lacunae (0204-M). In the apical region of the implant, massive infiltration of fungal hyphae was seen (0205-A, arrows). EDS analysis was performed at the implant surface and also revealed a significantly high percentage of Au (15.68%), along with two other major components, which were Ti and O. Si. In case 3, the implant surface was covered in organic membrane tissue, which can be observed on the low magnification (0306-A, black asterisks), blood cells (0306-A, blue arrowheads), and fibrin (0306-A, blue asterisks). Ti, O, and C were major compositions of this region, with a high percentage of Ti (71.06%).
In case 2, the implant was removed along the infected bone by mass excision, and the final biopsy result confirmed that the patient had fungal maxillary sinusitis. Two points in the apical area of the implant, one on the integrated bone in the middle of the fixture, and one on the fixture surface in the apical region were chosen to examine the BRONJ-affected and fungal-infected bone and implant morphology (Figure 4b). The integrated bone on the implant surface showed a pattern of sclerosing bone with rare signs of bone lacunae (Figure 5, 0204-M). High levels of Ca (40.75%) and O (31.06%) were detected. Au was also recorded to have a significantly high mass percentage (14.17%). Other detected elements were Si and Na, and a low signal of Ti was observed (1.01%). In the apical region of the implant, a massive infiltration of fungal hyphae was seen (Figure 5, 0205-A, black arrowheads). EDS analysis was performed at the implant surface and also revealed a significantly high percentage of Au (15.68%), along with two other major components, which were Ti and O; Si, Ca, Na were detected at low percentages in this region.
In case 3, the implant apex was analyzed after retrieval during the implant apex-cutting surgery (Figure 4c). The implant surface was covered in organic membrane tissue, which can be observed on the low magnification (Figure 5, 0306-A, black asterisks). In ×10,000 magnifications, the blood cells (Figure 5, 0306-A, blue arrowheads) and fibrin were observed (Figure 5, 0306-A, blue asterisks). After broadly scanning, the exposed surface of the fixture thread was chosen to be analyzed by EDS (Figure 4c). Ti, O, and C were major compositions of this region, with a high percentage of Ti (71.06%). Si and Ca were detected at trace amounts on this surface.
4. Discussion
Maxillary sinusitis develops primarily in association with reduced drainage of the maxillary sinus and relates to nasal septum deformity, nasal polyposis, and allergies. For an accurate diagnosis and treatment strategy, a meticulous history and clinical examination are essential. Perforation combined with dysfunction of the mucociliary action of the maxillary sinus membrane caused by odontogenic sources was reported. Along with the increasing of implant rehabilitation treatment, the extension of dental implants inside the maxillary sinus cavity and its impacts have been reported by many authors [7]. The depth of the implant extension inside the sinus cavity is supposed to correlate with the Schneiderian membrane’s reaction. When the penetrating length of the implant is less than 2 mm, spontaneous covering of the implants with the sinus mucosa seems to occur. Also, new bone formation occurred in the maxillary floor, above the dental implant, when penetration occurred without tearing of the Schneiderian membrane [6]. On the other hand, when the penetrating length of the implant is greater than 2 mm, the Schneiderian membrane does not spontaneously heal and debris accumulates on the exposed implant surfaces, which could lead to an inflammatory reaction and then sinusitis. However, the mechanism of the inflammation process caused by the extension of implants inside the maxillary sinus and perforating the Schneiderian membrane have not been systematically evaluated before [6].
In this study, the radiological examination of OMS was conducted, focusing on the thickening of the maxillary sinus membrane and mucosa. Among three patients, two had OMS with retention cyst and one had fungal sinusitis. With SEM and EDS, it was found that the integrated bone at the implant apex had an irregular structure with an abnormal Ca/P ratio and contamination by other elements. In the patient with fungal sinusitis, fungal hyphae were detected at the implant apex. It is suggested that the fungal hyphae had infiltrated from the sinus to the alveolar bone through the implant position, which caused infection of the alveolar bone and led to mass excision of the maxillary posterior.
In addition to Ti as a major component of dental implants, O and C are commonly found in the chemical composition of dental implants; all of these are not considered harmful elements [17,18]. However, several studies have reported findings of other elements in the implant surface such as nitrogen (N), F, P, chloride (Cl), and Na together with some inorganic impurities such as Al, zinc (Zn), Si, and Mg, among others [17,19]. These inorganic chemical compositions are suggested to be the products of a corrosion process [20]. The detachment of ions and metal particles into the peri-implant tissue may result in a biological response that can be devastating and enhance the high risk of severe complications. Some metals associated with alloys used in dental implants, such as copper (Cu), Al, Ag, vanadium (V) and Mn (Manganese), are associated with high cytotoxicity and reduced cell viability. Park et al. [21] studied the cytocompatibility of pure metals and experimental binary Ti alloys for implant materials and suggested that the ranking of pure metal cytotoxicity from most potent to least potent was as follows: Cu > Al > Ag (Silver) > V > Mn > Cr (Chromium) > Zr > Nb (Niobium) > Mo (Molybdenum) > commercial pure Ti (CP-Ti). Li et al. [22] demonstrated a possible effect of Al nanoparticles (AlNPs) in the immune system, in that AlNP exposure caused cytokine-level changes in the spleen, thymus, and serum, besides causing damage to immune organs and dysfunction of immune cells. To date, the systemic toxicity of AlNPs derived from dental implants has not been reported. Locally, AlNPs, with their triggering of immune cell dysfunction, could be the suggested trigger of abnormal immune-related cytokine behavior, which led to an inflammatory reaction of the Schneiderian membrane in the present context.
The EDS analysis is a semi-quantitative technique dominantly used to analyze implant surface characteristics in different scenarios [23]. Although it has been proven to be a reliable and a practical method, there is no consensus on the chemical compositions of dental implants. Ti concentration in CP-Ti implants is reported to range approximately from 22.5% [18] to 100% [17], while also finding the existence of some impure contents such as Al, Fe, Si and Na [24]. In this study, EDS compositional maps of the failed implants provide evidence of C and O enrichment in the surrounding bone. In addition, the Ca level was high while the P level was low or undetectable in all three cases. The Ca/P ratio may vary depending on the bone type, location, and loading function; and the determination of this ratio can reveal the bone density change. Theoretically, the fraction of Ca in hydroxyapatite is 40.3% and that in P is 18.4%. Green et al. [25] reported that the Ca/P ratio in monkey mandible was 1.56 to 1.68. In the infected bone region of the current cases, the Ca/P ratio was almost negligible. This finding confirmed the heterogeneous morpho-chemistry of the affected bone. The Ti components of the implant are within the normal range; however, minor components including F, Na, and Si and traces of other elements such as Au, Al, and Mg revealed the contamination of the implant, which may be the reason for the sinus membrane irritation and inflammation. The presence of Si, Na, Al, and Mg come from the manufacturer and surface finishing process in the Ti implant preparation [26]. The Si contamination can also originate from the ion dissolution from the glass storage vials [27]. Na and F can come from the body fluids or the environment during handling installation. The Au can be the dissolved product from the intraoral gold prosthesis during function or galvanic current activity.
Previous studies suggested that some micro- and submicro-sized metal particles trapped by the mucus tissue of the upper respiratory tract can travel through the mechanical barrier of the mucosal tissue and penetrate the tissue, which may initiate various pathological states. A study by Čabanová et al. [28] found metal particles such as Ti, Zn, Fe, and Ba from the cytological mucus and hypertrophic tissue samples from a patient diagnosed with chronic hypertrophic rhinosinusitis characterized by scanning electron microscopy and Raman microspectroscopy. Another study by Jiang et al. [29] found Ca and Zn elements in the fungal ball specimens by the x-ray fluorescence technique. These findings suggest that some metal particles trapped in the maxillary sinus mucus membrane might cause maxillary sinusitis.
Although dental titanium implants penetrated into a healthy maxillary sinus does have significant complications, reaching up to 3.4% of clinical complication and 14.8% radiographic complication [7], however, recent review studies show that titanium implants in the human body may give rise to metal toxicity, defined as yellow nail syndrome. The most common symptom of titanium toxicity was sinusitis, where most patients complained of postnasal drip and a “strange cough” as the main feature [30,31].
Perforation of maxillary sinus should be avoided by meticulously evaluating the anatomical structure and its position by the surgeon. In case of intentional sinus perforation without augmentation, the design of the fixture apical region should be blunt without a self-tapper effect to avoid the tearing of Schneiderian membrane. The presence and extension of septa or a full partition of the sinus by a septum should be evaluated in both panoramic and CT views to prevent the sinus membrane from tearing during the sinus lifting. The surgeon should avoid the vigorous instrument manipulation during the procedure. It should be noted that even with sufficient prophylactic measurements such as antibiotic medication and excellent surgery, early complications such as infection and late complications including maxillary sinusitis and failed implants can occur [32]. Furthermore, as presented in three selected cases, many factors can contribute to the initiation and progression of the inflammatory process that leads to maxillary sinusitis and implant failure, and the influence of each factor needs further study. Therefore, implants should be monitored under a strict periodic follow-up. The success rate of dental implants in the maxillary molar region can be improved by a comprehensive understanding of its anatomy and its function as well as any potential complications that may arise during and after its surgery, and their appropriate management protocols.
5. Conclusions
The selected three cases in this study presented different biological aspects that might play the central role in the failed dental implants associated with OMS. In case 1, the detection of elements potentially toxic to cells in the apical region may explain the irritation reaction of the sinus membrane, which led to maxillary sinusitis and inflammation of the peri-implant bone with bone turnover and loss of normal structure, then implant failure. In case 2, the fungal infection was the main cause of the failed implant and OMS. However, it is unclear whether the primary fungal infection was from the sinus cavity or an intraoral infection. In case 3, the irregular bone structure and absence of contaminated elements suggested the failure of implant osseointegration may be due to the long perforation of the implant apical region into the sinus cavity. Each of the above phenomena can be the potential etiology of the failed implant associated with OMS and needs to be confirmed with further clinical study and analysis of a larger number of failed implants and accompanying human tissue samples.
Author Contributions
T.T.H.N. collected the data and wrote the manuscript, M.Y.E. revised and corrected the manuscript, B.S.-I. collected the data and wrote the manuscript, H.M. revised and corrected the manuscript, and S.M.K. designed and wrote the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This retrospective data analysis was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Seoul National University (S-D20170005).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by grant no 01-2017-0010 from the SNUDH Research Fund.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Esfahrood, Z.R.; Ahmadi, L.; Karami, E.; Asghari, S. Short dental implants in the posterior maxilla: A review of the literature. J. Korean Assoc. Oral. Maxillofac Surg. 2017, 43, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santosh, V.; Bhukya, P.; Medisetty, B.; Rampalli, V.C.; Kumaar, P.A. Outcomes of intentional perforation of the maxillary sinus floor during implant placement: A single-center, prospective study in 57 subjects. J. Dent. Implant. 2019, 9, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Fabbro, M.; Rosano, G.; Taschieri, S. Implant survival rates after maxillary sinus augmentation. Eur. J. Oral Sci. 2008, 116, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallace, S.S.; Froum, S.J. Effect of maxillary sinus augmentation on the survival of endosseous dental implants. A systematic review. Ann. Periodontol. 2003, 8, 328–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Branemark, P.I.; Adell, R.; Albrektsson, T.; Lekholm, U.; Lindstrom, J.; Rockler, B. An experimental and clinical study of osseointegrated implants penetrating the nasal cavity and maxillary sinus. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Surg. 1984, 4, 497–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabrizi, R.; Amid, R.; Taha Ozkan, B.; Khorshidi, H.; Langner, N.J. Effects of exposing dental implant to the maxillary sinus cavity. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2012, 23, 767–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ragucci, G.M.; Elnayef, B.; Suarez-Lopez Del Amo, F.; Wang, H.L.; Hernandez-Alfaro, F.; Gargallo-Albiol, J. Influence of exposing dental implants into the sinus cavity on survival and complications rate: A systematic review. Int. J. Implant. Dent. 2019, 5, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayabasoglu, G.; Nacar, A.; Altundag, A.; Cayonu, M.; Muhtarogullari, M.; Cingi, C. A retrospective analysis of the relationship between rhinosinusitis and sinus lift dental implantation. Head Face Med. 2014, 10, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.M. The removal of an implant beneath the optic canal by modified endoscopic-assisted sinus surgery. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2017, 274, 1167–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettersson, M.; Kelk, P.; Belibasakis, G.N.; Bylund, D.; Molin Thoren, M.; Johansson, A. Titanium ions form particles that activate and execute interleukin-1beta release from lipopolysaccharide-primed macrophages. J. Periodontal Res. 2017, 52, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- St Pierre, C.A.; Chan, M.; Iwakura, Y.; Ayers, D.C.; Kurt-Jones, E.A.; Finberg, R.W. Periprosthetic osteolysis: Characterizing the innate immune response to titanium wear-particles. J. Orthop. Res. 2010, 28, 1418–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallo, J.; Kamínek, P.; Tichá, V.; Riháková, P.; Ditmar, R. Particle disease. A comprehensive theory of periprosthetic osteolysis: A review. Biomed. Pap. Med. Fac. Univ. Palacky Olomouc Czech. Repub. 2002, 146, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landgraeber, S.; Jäger, M.; Jacobs, J.J.; Hallab, N.J. The pathology of orthopedic implant failure is mediated by innate immune system cytokines. Mediat. Inflamm. 2014, 2014, 185150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belibasakis, G.N.; Charalampakis, G.; Bostanci, N.; Stadlinger, B. Peri-implant infections of oral biofilm etiology. Adv. Exp Med. Biol. 2015, 830, 69–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado-Ruiz, R.; Romanos, G. Potential causes of titanium particle and ion release in implant dentistry: A systematic review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brook, I. Aerobic and anaerobic bacterial flora of normal maxillary sinuses. Laryngoscope 1981, 91, 372–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guler, B.; Uraz, A.; Cetiner, D. The chemical surface evaluation of black and white porous titanium granules and different commercial dental implants with energy-dispersive x-ray spectroscopy analysis. Clin. Implant. Dent. Relat. Res. 2019, 2, 352–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dohan Ehrenfest, D.M.; Vazquez, L.; Park, Y.J.; Sammartino, G.; Bernard, J.P. Identification card and codification of the chemical and morphological characteristics of 14 dental implant surfaces. J. Oral. Implantol. 2011, 37, 525–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schupbach, P.; Glauser, R.; Bauer, S. Al2O3 Particles on Titanium dental implant systems following sandblasting and acid-etching process. Int. J. Biomater. 2019, 2019, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, D.C.; Valderrama, P.; Wilson, T.G.; Palmer, K.; Thomas, A.; Sridhar, S.; Adapalli, A.; Burbano, M.; Wadhwani, C. Titanium corrosion mechanisms in the oral environment: A Retrieval Study. Materials 2013, 6, 5258–5274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.J.; Song, Y.H.; An, J.H.; Song, H.J.; Anusavice, K.J. Cytocompatibility of pure metals and experimental binary titanium alloys for implant materials. J. Dent. 2013, 41, 1251–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Huang, T.; Wang, Y.; Pan, B.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Q.; Niu, Q. Toxicity of alumina nanoparticles in the immune system of mice. Nanomedicine 2020, 15, 927–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, J.I.; Newbury, D.E.; Echlin, P.; Joy, D.C.; Lyman, C.E.; Lifshin, E.; Sawyer, L.; Michael, J.R. Scanning Electron Mi-croscopy and X-ray Microanalysis, 3rd ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2003; pp. 391–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duddeck, D.U.; Albrektsson, T.; Wennerberg, A.; Larsson, C.; Beuer, F. On the cleanliness of different oral implant systems: A pilot study. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, L.J.; Eick, J.D.; Miller, W.A.; Leitner, J.W. Electron microprobe analysis of Ca, P, and Mg in mandibular bone. J. Dent. Res. 1970, 49, 608–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibli, J.A.; Marcantonio, E.; d’Avila, S.; Guastaldi, A.C.; Marcantonio, E., Jr. Analysis of failed commercially pure titanium dental implants: A scanning electron microscopy and energy-dispersive spectrometer x-ray study. J. Periodontol. 2005, 76, 1092–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esposito, M.; Lausmaa, J.; Hirsch, J.M.; Thomsen, P. Surface analysis of failed oral titanium implants. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1999, 48, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čabanová, K.; Motyka, O.; Čábalová, L.; Hrabovská, K.; Bielniková, H.; Kuzníková, Ľ.; Dvořáčková, J.; Zeleník, K.; Komínek, P.; Kukutschová, J. Metal particles in mucus and hypertrophic tissue of the inferior nasal turbinates from the human upper respiratory tract. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2020, 27, 28146–28154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Z.; Zhang, K.; Huang, W.; Yuan, Q. A preliminary study on sinus fungus ball with Micro-CT and X-Ray Fluorescence technique. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0148515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berglund, F.; Carlmark, B. Titanium, sinusitis, and the yellow nail syndrome. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2011, 143, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.T.; Eo, M.Y.; Nguyen, T.T.H.; Kim, S.M. General review of titanium toxicity. Int. J. Implant. Dent. 2019, 5, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Jang, H. A review of complications of maxillary sinus augmentation and available treatment methods. J. Korean Assoc. Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2019, 45, 220–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).