COVID-19 Detection Empowered with Machine Learning and Deep Learning Techniques: A Systematic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
- ➢
- Determining the significance of available datasets from literature used for the prediction of COVID-19.
- ➢
- To analyze the ML and DL techniques that were applied to detect the COVID-19.
- ➢
- Identification of challenges and future research directions related to the implications of ML/DL techniques for COVID detection.
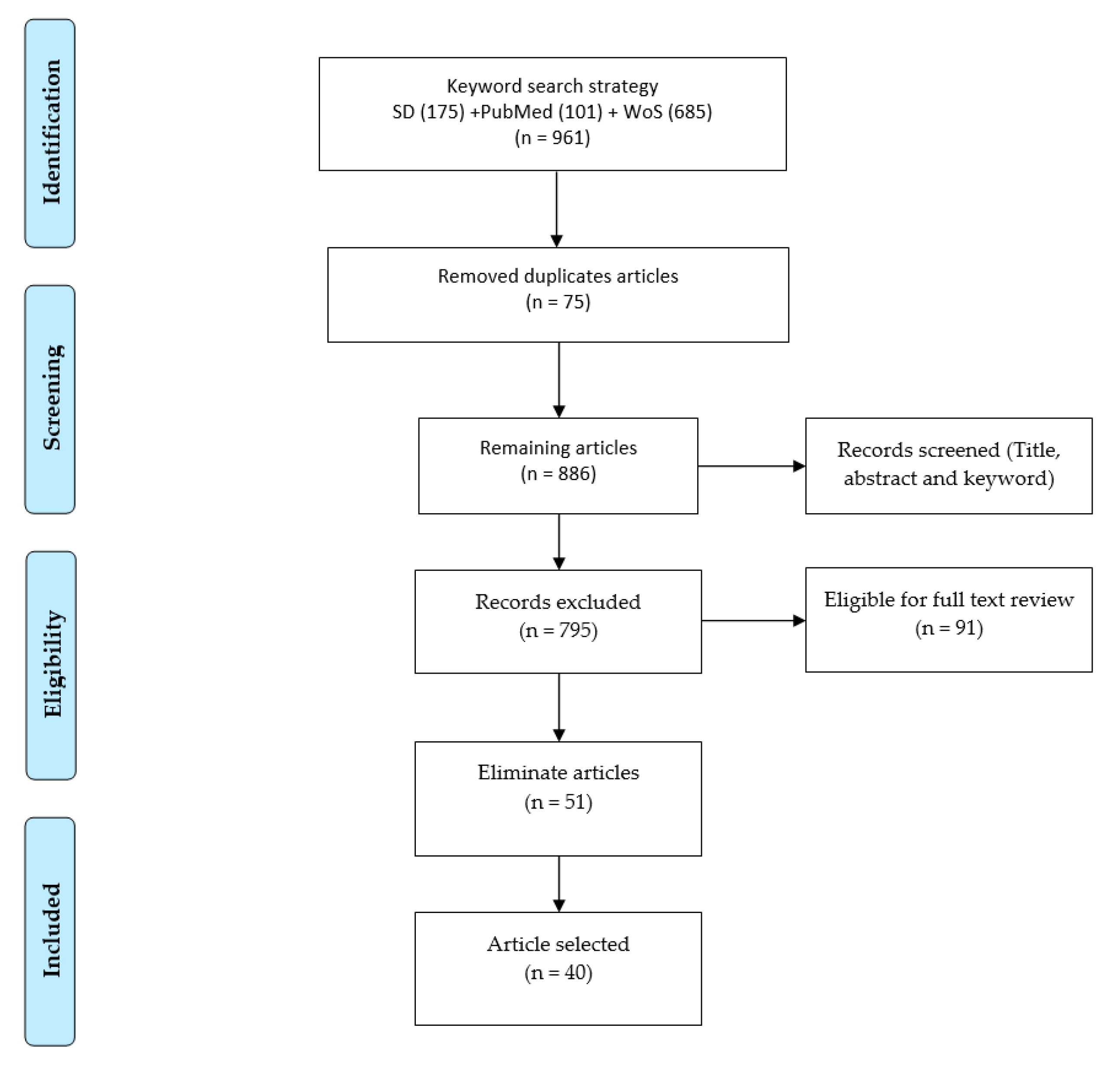
2. Review Methodology
2.1. Selection of Digital Archives
2.2. Search Code Strategy
Machine and Deep Learning Techniques
2.3. Eligibility Criteria and Article Screening
2.4. Data Segregation and Categorization
3. Results and Discussion
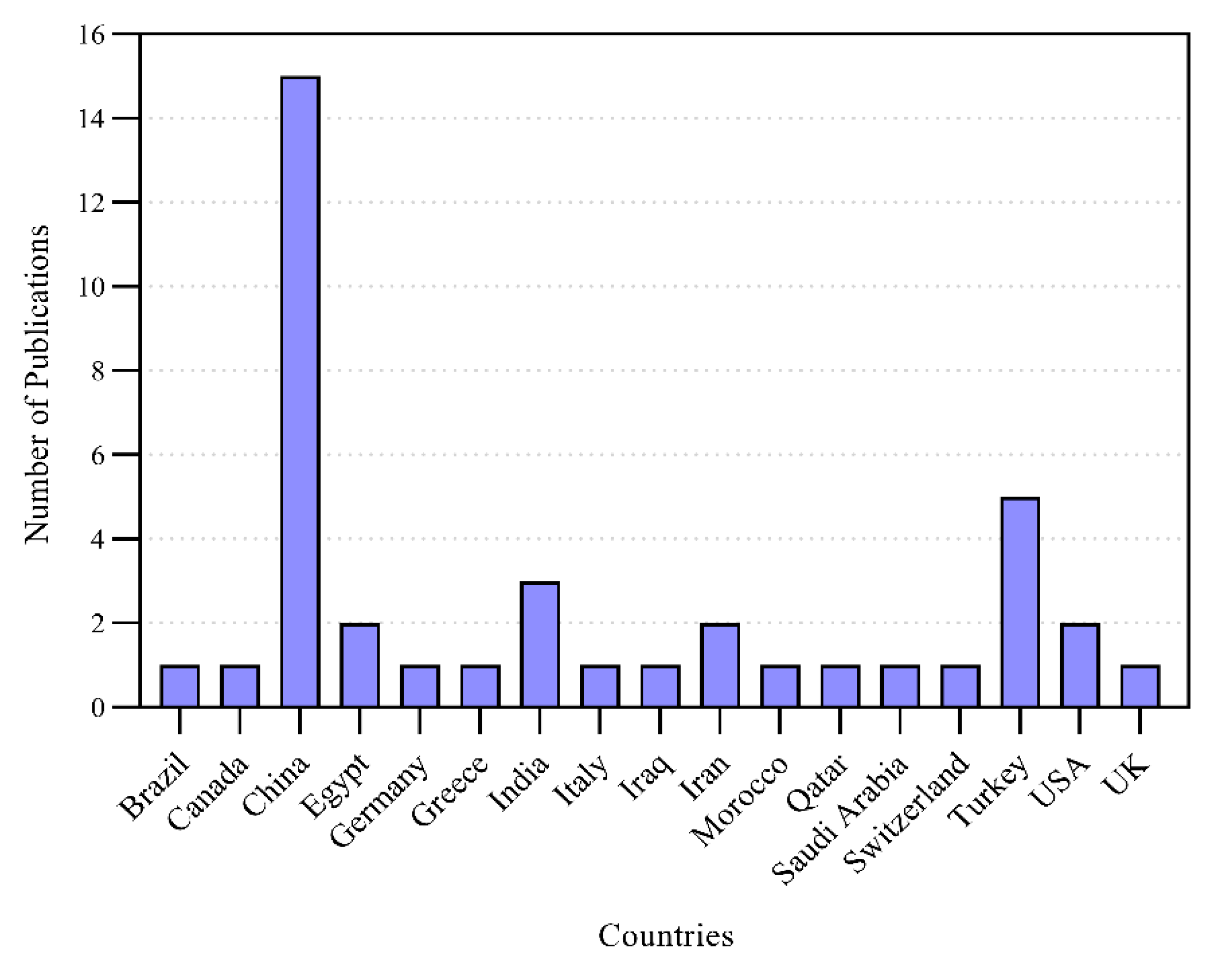
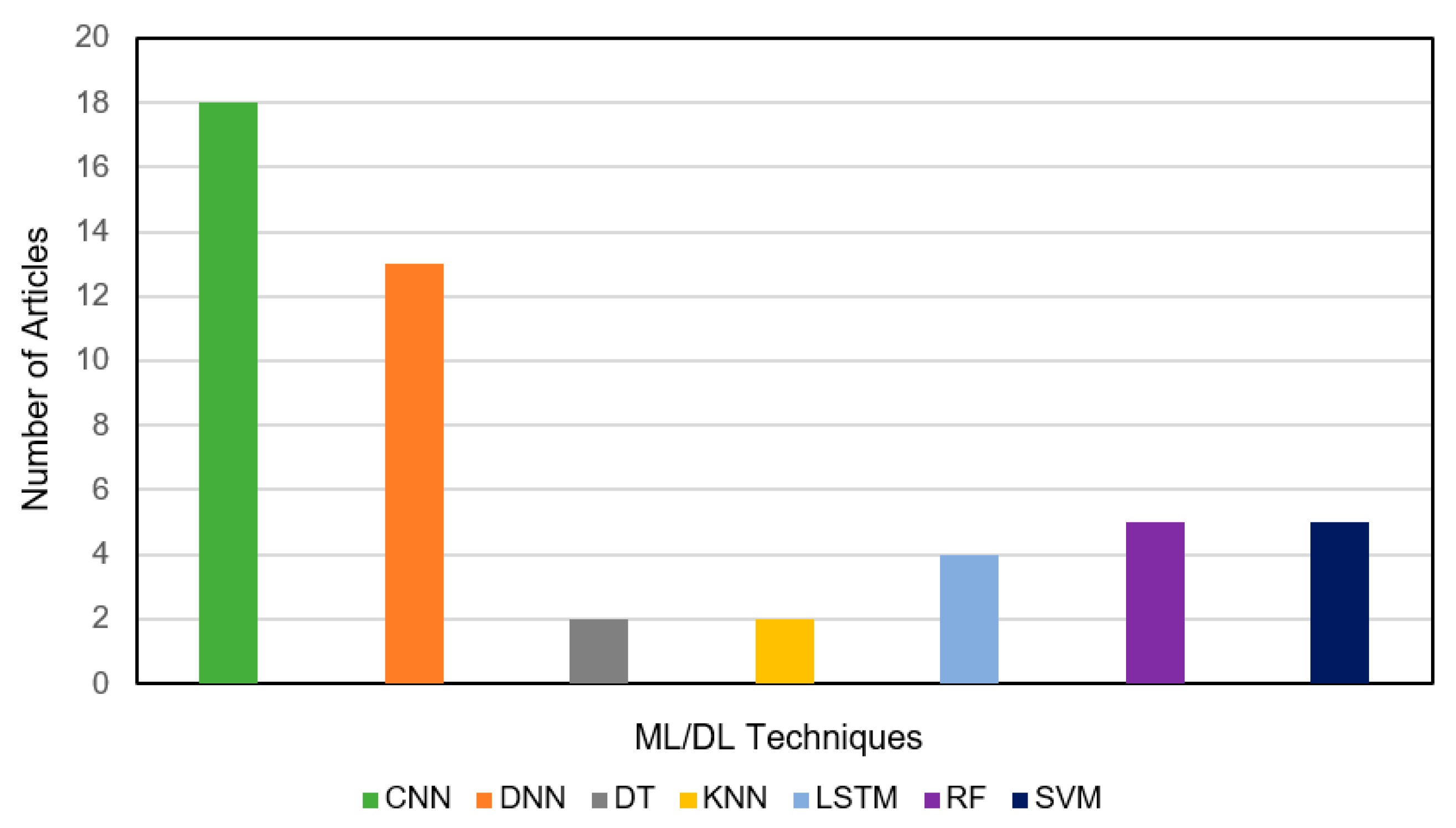
3.1. Analysis of Extracted Data
3.2. Investigation on Classification Performance
4. State-of-the-Art COVID-19 Detection Using Anal Swab-Based Diagnosis
- Stop traveling from in and out of China to control the transmission.
- Developed quarantine centers for suspected cases to get the best treatment.
- China developed mobile apps for tracking suspected, confirmed cases, and interaction with individuals having COVID-19 symptoms.
- Develop public awareness regarding self-protection, epidemiologic investigation, cleaning, and disinfecting the environment.
- The government installed many intelligent based systems to monitor the public temperature, such as airports, metro stations, hospitals, communities.
5. Challenges and Future Research Directions
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ML | Machine Learning |
| MLT | Machine Learning Techniques |
| CT | Computer Tomography |
| CAD | Computer-Aided Diagnosis |
| CNN | Convolutional Neural Network |
| D.N.N | Deep Neural Network |
| DL | Deep Learning |
| DT | Decision Tree |
| RF | Random Forest |
| SVM | Support Vector Machine |
| SARS | Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome |
| K-NN | K-Nearest Neighbors |
| L.S.T.M. | Long Short-Term Memory |
| SD | Science Direct |
| W.O.S | Web of Science |
| X-ray | X-radiation |
| M.R.I | Magnetic Resource Imaging |
| MERS | Middle East Respiratory syndrome |
| RT-PCR | Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction |
| A.U.C. | Area under the Receiver Operating Characteristic Curve |
References
- Salman, F.M.; Abu-Naser, S.S.; Alajrami, E.; Abu-Nasser, B.S.; Alashqar, B.A. Covid-19 detection using artificial intelligence. IJAER 2020, 4, 18–25. [Google Scholar]
- Coronavirus. (COVID-19) Cases Statistics and Research Our World in Data. Available online: https://ourworldindata.org/covid-cases (accessed on 3 April 2021).
- Apostolopoulos, I.D.; Mpesiana, T.A. Covid-19: Automatic detection from X-ray images utilizing transfer learning with convolutional neural networks. Phys. Eng. Sci. Med. 2020, 43, 635–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, T.; Yang, Z.; Hou, H.; Zhan, C.; Chen, C.; Lv, W.; Tao, Q.; Sun, Z.; Xia, L.J.R. Correlation of chest C.T. and RT-PCR testing for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in China: A report of 1014 cases. Radiology 2020, 296, E32–E40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Xie, J.; Lin, M.; Ying, L.; Pang, P.; Ji, W.J.R. Sensitivity of chest C.T. for COVID-19: Comparison to RT-PCR. Radiology 2020, 296, E115–E117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, D.A. An analysis of 38 pregnant women with COVID-19, their newborn infants, and maternal-fetal transmission of SARS-CoV-2: Maternal coronavirus infections and pregnancy outcomes. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2020, 144, 799–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, L. China Daily Website-Connecting China Connecting the World. Available online: http://www.chinadaily.com.cn/ (accessed on 15 March 2021).
- Bai, H.X.; Hsieh, B.; Xiong, Z.; Halsey, K.; Choi, J.W.; Tran, T.M.L.; Pan, I.; Shi, L.-B.; Wang, D.-C.; Mei, J.J.R. Performance of radiologists in differentiating COVID-19 from non-COVID-19 viral pneumonia at chest CT. Radiology 2020, 296, E46–E54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, F.; Wang, J.; Shi, J.; Wu, Z.; Wang, Q.; Tang, Z.; He, K.; Shi, Y.; Shen, D.J. Review of artificial intelligence techniques in imaging data acquisition, segmentation and diagnosis for covid-19. IEEE Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 14, 4–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Lei, P.; Zeng, B.; Li, Z.; Yu, P.; Fan, B.; Wang, C.; Li, Z.; Zhou, J.; Hu, S.; et al. Coronavirus disease (COVID-19): Spectrum of C.T. findings and temporal progression of the disease. Acad. Radiol. 2020, 27, 603–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozturk, T.; Talo, M.; Yildirim, E.A.; Baloglu, U.B.; Yildirim, O.; Acharya, U.R. Automated detection of COVID-19 cases using deep neural networks with X-ray images. Comput. Biol. Med. 2020, 121, 103792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karar, M.E.; Hemdan, E.E.-D.; Shouman, M.A. Cascaded deep learning classifiers for computer-aided diagnosis of COVID-19 and pneumonia diseases in X-ray scans. Complex Intell. Syst. 2021, 7, 235–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hizukuri, A.; Nakayama, R.; Nara, M.; Suzuki, M.; Namba, K. Computer-Aided Diagnosis Scheme for Distinguishing Between Benign and Malignant Masses on Breast DCE-MRI Images Using Deep Convolutional Neural Network with Bayesian Optimization. J. Digit. Imaging 2021, 34, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latif, S.; Qadir, J.; Farooq, S.; Imran, M.A. How 5g wireless (and concomitant technologies) will revolutionize healthcare? Future Internet 2017, 9, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Islam, N.; Jan, Z.; Din, I.U.; Rodrigues, J.J.C. A novel deep learning based framework for the detection and classification of breast cancer using transfer learning. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2019, 125, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakhani, P.; Sundaram, B. Deep learning at chest radiography: Automated classification of pulmonary tuberculosis by using convolutional neural networks. Radiology 2017, 284, 574–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toğaçar, M.; Ergen, B.; Cömert, Z.; Özyurt, F. A deep feature learning model for pneumonia detection applying a combination of mRMR feature selection and machine learning models. IRBM 2020, 41, 212–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burlina, P.; Billings, S.; Joshi, N.; Albayda, J. Automated diagnosis of myositis from muscle ultrasound: Exploring the use of machine learning and deep learning methods. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0184059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canayaz, M. MH-COVIDNet: Diagnosis of COVID-19 using deep neural networks and meta-heuristic-based feature selection on X-ray images. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2021, 64, 102257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedik, A.; Iliyasu, A.M.; El-Rahiem, A.; Abdel Samea, M.E.; Abdel-Raheem, A.; Hammad, M.; Peng, J.; El-Samie, A.; Fathi, E.; El-Latif, A.A.A. Deploying machine and deep learning models for efficient data-augmented detection of COVID-19 infections. Viruses 2020, 12, 769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.-W.; Lin, X. Big data deep learning: Challenges and perspectives. IEEE Access 2014, 2, 514–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsalem, M.; Zaidan, A.; Zaidan, B.; Albahri, O.; Alamoodi, A.; Albahri, A.; Mohsin, A.; Mohammed, K.I. Multiclass benchmarking framework for automated acute Leukaemia detection and classification based on B.W.M. and group-VIKOR. J. Med. Syst. 2019, 43, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Abbas, S.; Khan, K.M.; Al Ghamdi, M.A.; Rehman, A. Intelligent forecasting model of COVID-19 novel coronavirus outbreak empowered with deep extreme learning machine. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2020, 64, 1329–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaidan, A.; Zaidan, B.; Alsalem, M.; Albahri, O.; Albahri, A.; Qahtan, M.Y. Applications. Multi-agent learning neural network and Bayesian model for real-time IoT skin detectors: A new evaluation and benchmarking methodology. Neural Comput. Appl. 2020, 32, 8315–8366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yas, Q.M.; Zaidan, A.; Zaidan, B.; Rahmatullah, B.; Karim, H.A. Comprehensive insights into evaluation and benchmarking of real-time skin detectors: Review, open issues & challenges, and recommended solutions. Measurement 2018, 114, 243–260. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Qin, L.; Xu, Z.; Yin, Y.; Wang, X.; Kong, B.; Bai, J.; Lu, Y.; Fang, Z.; Song, Q. Artificial intelligence distinguishes COVID-19 from community acquired pneumonia on chest CT. Radiology 2020, 296, E65–E71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.B.; Ehrenfeld, J.M. The role of augmented intelligence (A.I.) in detecting and preventing the spread of novel coronavirus. J. Med Syst. 2020, 44, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otoom, M.; Otoum, N.; Alzubaidi, M.A.; Etoom, Y.; Banihani, R. An IoT-based framework for early identification and monitoring of COVID-19 cases. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2020, 62, 102149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. Int. J. Surg. 2010, 8, 336–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albahri, A.; Hamid, R.A.; Alwan, J.K.; Al-Qays, Z.; Zaidan, A.; Zaidan, B.; Albahri, A.; AlAmoodi, A.; Khlaf, J.M.; Almahdi, E.M. Role of biological data mining and machine learning techniques in detecting and diagnosing the novel coronavirus (COVID-19): A systematic review. J. Med. Syst. 2020, 44, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thenault, R.; Kaulanjan, K.; Darde, T.; Rioux-Leclercq, N.; Bensalah, K.; Mermier, M.; Khene, Z.-E.; Peyronnet, B.; Shariat, S.; Pradere, B.; et al. The Application of Artificial Intelligence in Prostate Cancer Management—What Improvements Can Be Expected? A Systematic Review. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 6428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kooi, T.; Litjens, G.; Van Ginneken, B.; Gubern-Mérida, A.; Sánchez, C.I.; Mann, R.; den Heeten, A.; Karssemeijer, N. Large scale deep learning for computer aided detection of mammographic lesions. Med. Image Anal. 2017, 35, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yassin, N.I.; Omran, S.; El Houby, E.M.; Allam, H. Machine learning techniques for breast cancer computer aided diagnosis using different image modalities: A systematic review. Comput. Methods Progr. Biomed. 2018, 156, 25–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pehrson, L.M.; Nielsen, M.B.; Ammitzbøl, L.C. Automatic pulmonary nodule detection applying deep learning or machine learning algorithms to the LIDC-IDRI database: A systematic review. Diagnostics 2019, 9, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narin, A.; Kaya, C.; Pamuk, Z. Automatic detection of coronavirus disease (covid-19) using X-ray images and deep convolutional neural networks. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.10849. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, A.I.; Shah, J.L.; Bhat, M.M. CoroNet: A deep neural network for detection and diagnosis of COVID-19 from chest X-ray images. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2020, 196, 105581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunese, L.; Mercaldo, F.; Reginelli, A.; Santone, A. Explainable deep learning for pulmonary disease and coronavirus COVID-19 detection from X-rays. Comput. Methods Progr. Biomed. 2020, 196, 105608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, T.D. Classification of COVID-19 chest X-rays with deep learning: New models or fine tuning? Health Inf. Sci. Syst. 2021, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardakani, A.A.; Kanafi, A.R.; Acharya, U.R.; Khadem, N.; Mohammadi, A. Application of deep learning technique to manage COVID-19 in routine clinical practice using C.T. images: Results of 10 convolutional neural networks. Comput. Biol. Med. 2020, 121, 103795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Jiang, X.; Ma, C.; Du, P.; Li, X.; Lv, S.; Yu, L.; Ni, Q.; Chen, Y.; Su, J.; et al. A deep learning system to screen novel coronavirus disease 2019 pneumonia. Engineering 2020, 6, 1122–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.; Deng, X.; Fu, Q.; Zhou, Q.; Feng, J.; Ma, H.; Liu, W.; Wang, X. Deep learning-based detection for COVID-19 from chest C.T. using weak label. MedRxiv 2020, 39, 2615–2625. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Kang, B.; Ma, J.; Zeng, X.; Xiao, M.; Guo, J.; Cai, M.; Yang, J.; Li, Y.; Meng, X.; et al. A deep learning algorithm using C.T. images to screen for Corona Virus Disease (COVID-19). Eur. Radiol. 2021, 31, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Y.; Zheng, S.; Li, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Huang, Z.; Chen, J.; Zhao, H.; Jie, Y.; Wang, R.; et al. Deep learning enables accurate diagnosis of novel coronavirus (COVID-19) with C.T. images. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinform. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ardakani, A.A.; Acharya, U.R.; Habibollahi, S.; Mohammadi, A. COVIDiag: A clinical CAD system to diagnose COVID-19 pneumonia based on C.T. findings. Eur. Radiol. 2021, 31, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Lin, Z.Q.; Wong, A. Covid-net: A tailored deep convolutional neural network design for detection of covid-19 cases from chest X-ray images. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethy, P.K.; Behera, S.K.; Ratha, P.K.; Biswas, P. Detection of coronavirus disease (COVID-19) based on deep features and support vector machine. Electr. Electron. Eng. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemdan, E.E.-D.; Shouman, M.A.; Karar, M.E. Covidx-net: A framework of deep learning classifiers to diagnose covid-19 in X-ray images. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.11055. [Google Scholar]
- Narayanan, B.N.; Hardie, R.C.; Krishnaraja, V.; Karam, C.; Davuluru, V.S.P. Transfer-to-Transfer Learning Approach for Computer Aided Detection of COVID-19 in Chest Radiographs. AI 2020, 1, 539–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gozes, O.; Frid-Adar, M.; Greenspan, H.; Browning, P.D.; Zhang, H.; Ji, W.; Bernheim, A.; Siegel, E. Rapid ai development cycle for the coronavirus (covid-19) pandemic: Initial results for automated detection & patient monitoring using deep learning ct image analysis. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.05037. [Google Scholar]
- Barstugan, M.; Ozkaya, U.; Ozturk, S. Coronavirus (covid-19) classification using ct images by machine learning methods. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.09424. [Google Scholar]
- Ghoshal, B.; Tucker, A. Estimating uncertainty and interpretability in deep learning for coronavirus (COVID-19) detection. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.10769. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, X.; Fang, C.; Zhou, Y.; Bai, S.; Liu, Z.; Xia, L.; Chen, Q.; Xu, Y.; Xia, T.; Gong, S.; et al. Predicting COVID-19 malignant progression with A.I. techniques. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, C.; Chen, W.; Cao, Y.; Xu, Z.; Tan, Z.; Zhang, X.; Deng, L.; Zheng, C.; Zhou, J.; Shi, H.; et al. Development and evaluation of an artificial intelligence system for COVID-19 diagnosis. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, S.; Wang, B.; Xu, H.; Luo, C.; Wei, L.; Zhao, W.; Hou, X.; Ma, W.; Xu, Z.; Zheng, Z.; et al. AI-assisted CT imaging analysis for COVID-19 screening: Building and deploying a medical A.I. system in four weeks. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, M.E.; Rahman, T.; Khandakar, A.; Mazhar, R.; Kadir, M.A.; Mahbub, Z.B.; Islam, K.R.; Khan, M.S.; Iqbal, A.; Al Emadi, N.; et al. Can AI help in screening viral and COVID-19 pneumonia? IEEE Access 2020, 8, 132665–132676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maghdid, H.S.; Asaad, A.T.; Ghafoor, K.Z.; Sadiq, A.S.; Khan, M.K. Diagnosing COVID-19 pneumonia from X-ray and C.T. images using deep learning and transfer learning algorithms. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.00038. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Xie, Y.; Li, Y.; Shen, C.; Xia, Y. Covid-19 screening on chest X-ray images using deep learning based anomaly detection. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.12338. [Google Scholar]
- de Moraes, B.A.F.; Miraglia, J.L.; Donato, T.H.R.; Filho, A.D.P.C. COVID-19 diagnosis prediction in emergency care patients: A machine learning approach. MedRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Coffee, M.; Bari, A.; Wang, J.; Jiang, X.; Huang, J.; Shi, J.; Dai, J.; Cai, J.; Zhang, T.; et al. Towards an artificial intelligence framework for data-driven prediction of coronavirus clinical severity. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2020, 63, 537–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zha, Y.; Li, W.; Wu, Q.; Li, X.; Niu, M.; Wang, M.; Qiu, X.; Li, H.; Yu, H.; et al. A fully automatic deep learning system for COVID-19 diagnostic and prognostic analysis. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhang, Y.; He, X.; Xie, P. Covid-ct-dataset: A ct scan dataset about covid-19. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.13865. [Google Scholar]
- Asnaoui, K.E.; Chawki, Y.; Idri, A. Automated methods for detection and classification pneumonia based on X-ray images using deep learning. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.14363. [Google Scholar]
- Bhandary, A.; Prabhu, G.A.; Rajinikanth, V.; Thanaraj, K.P.; Satapathy, S.C.; Robbins, D.E.; Shasky, C.; Zhang, Y.-D.; Tavares, J.M.R.; Raja, N.S.M. Deep-learning framework to detect lung abnormality–A study with chest X-ray and lung C.T. scan images. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2020, 129, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, M.; Hafeez, A. Covid-resnet: A deep learning framework for screening of covid19 from radiographs. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.14395. [Google Scholar]
- Abbas, A.; Abdelsamea, M.M.; Gaber, M.M. Classification of COVID-19 in chest X-ray images using DeTraC deep convolutional neural network. Appl. Intell. 2021, 51, 854–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, M.; Döhmen, T.; Rebholz-Schuhmann, D.; Decker, S.; Cochez, M.; Beyan, O. Deepcovidexplainer: Explainable covid-19 predictions based on chest X-ray images. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.04582. [Google Scholar]
- Sitaula, C.; Hossain, M.B. Attention-based VGG-16 model for COVID-19 chest X-ray image classification. Appl. Intell. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keles, A.; Keles, M.B.; Keles, A. COV19-CNNet and COV19-ResNet: Diagnostic inference Engines for early detection of COVID-19. Cogn. Comput. 2021, 13, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Chandra, T.B.; Verma, K.; Singh, B.K.; Jain, D.; Netam, S.S. Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) detection in Chest X-Ray images using majority voting based classifier ensemble. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 165, 113909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, L.; Meng, W.; Li, J.; Tong, C.; Li, Y.; Cai, J.; Yang, Z.; Zhu, J. Rapid and accurate identification of COVID-19 infection through machine learning based on clinical available blood test results. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukar, M.; Gunčar, G.; Vovko, T.; Podnar, S.; Černelč, P.; Brvar, M.; Zalaznik, M.; Notar, M.; Moškon, S.; Notar, M. COVID-19 diagnosis by routine blood tests using machine learning. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2006.03476. [Google Scholar]
- Arpaci, I.; Huang, S.; Al-Emran, M.; Al-Kabi, M.N.; Peng, M. Predicting the COVID-19 infection with fourteen clinical features using machine learning classification algorithms. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2021, 80, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Das, N.N.; Kumar, N.; Kaur, M.; Kumar, V.; Singh, D. Automated deep transfer learning-based approach for detection of COVID-19 infection in chest X-rays. IRBM 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.-H.; Chen, K.-Y.; Shih, S.-R.; Ho, M.-C.; Tai, H.-C.; Chang, K.-J.; Chen, A.; Chen, C.-N. Multi-reader multi-case study for performance evaluation of high-risk thyroid ultrasound with computer-aided detection. Cancers 2020, 12, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riou, J.; Althaus, C.L. Pattern of early human-to-human transmission of Wuhan 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV), December 2019 to January 2020. Eurosurveillance 2020, 25, 2000058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ki, M. Epidemiologic characteristics of early cases with 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) disease in Korea. Epidemiol. Health 2020, 42, e2020007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.-L.; Ao, M.-Y.; Zhou, X.; Zhu, W.-F.; Nie, H.-Y.; Fang, J.-H.; Sun, X.; Zheng, B.; Chen, X.-F. China’s practice to prevent and control COVID-19 in the context of large population movement. Infect. Dis. Poverty 2020, 9, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, Y.; Park, S.; Ye, J.C. Deep learning covid-19 features on cxr using limited training data sets. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2020, 39, 2688–2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swapnarekha, H.; Behera, H.S.; Nayak, J.; Naik, B. Role of intelligent computing in COVID-19 prognosis: A state-of-the-art review. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2020, 138, 109947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammed, K.; Zaidan, A.; Zaidan, B.; Albahri, O.; Alsalem, M.; Albahri, A.; Hadi, A.; Hashim, M. Real-time remote-health monitoring systems: A review on patients prioritisation for multiple-chronic diseases, taxonomy analysis, concerns and solution procedure. J. Med. Syst. 2019, 43, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heo, L.; Feig, M. Modeling of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) proteins by machine learning and physics-based refinement. BioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhavoronkov, A.; Zagribelnyy, B.; Zhebrak, A.; Aladinskiy, V.; Terentiev, V.; Vanhaelen, Q.; Bezrukov, D.S.; Polykovskiy, D.; Shayakhmetov, R.; Filimonov, A. Potential non-covalent SARS-CoV-2 3C-like protease inhibitors designed using generative deep learning approaches and reviewed by human medicinal chemist in virtual reality. ChemRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poyiadji, N.; Shahin, G.; Noujaim, D.; Stone, M.; Patel, S.; Griffith, B. COVID-19–associated acute hemorrhagic necrotizing encephalopathy: Imaging features. Radiology 2020, 296, E119–E120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbas, A.; Abdelsamea, M.M.; Gaber, M. 4S-DT: Self Supervised Super Sample Decomposition for Transfer learning with application to COVID-19 detection. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2007.11450. [Google Scholar]
- Stochiţoiu, R.D.; Rebedea, T.; Popescu, I.; Leordeanu, M. A self-supervised neural-analytic method to predict the evolution of covid-19 in Romania. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2006.12926. [Google Scholar]
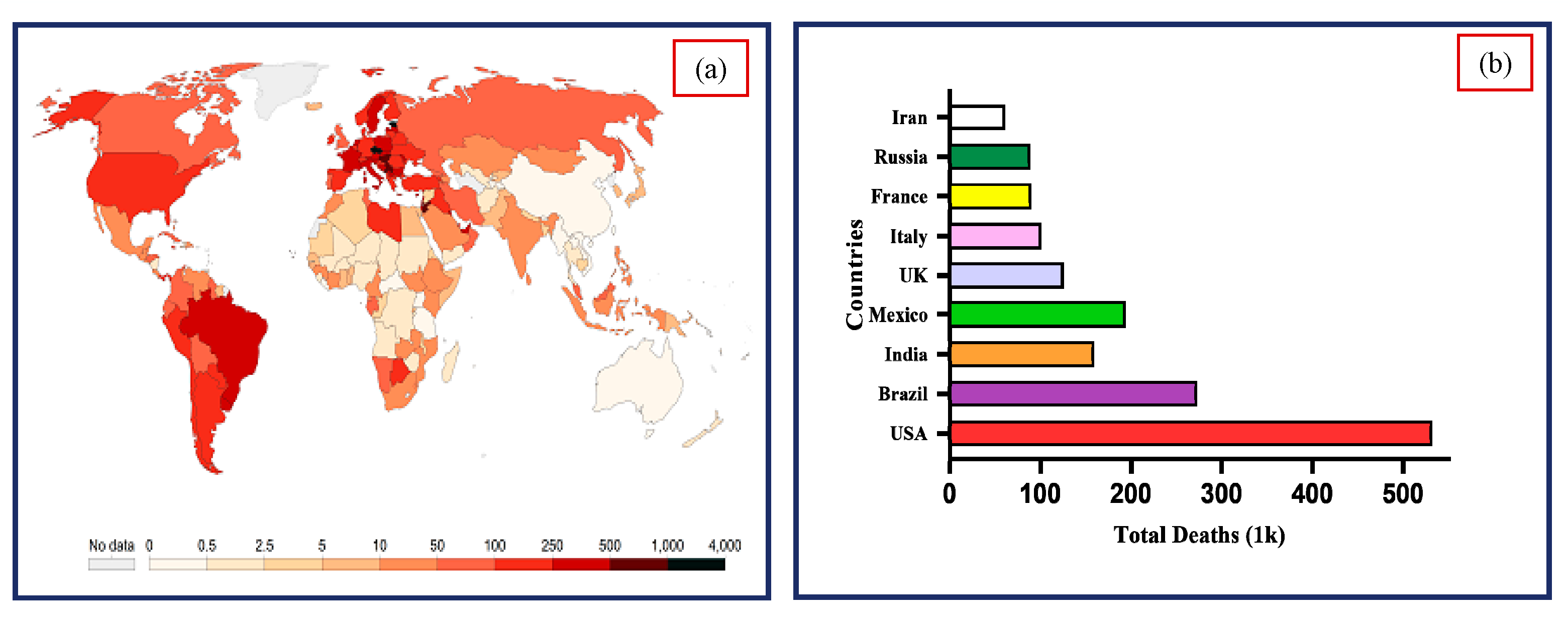
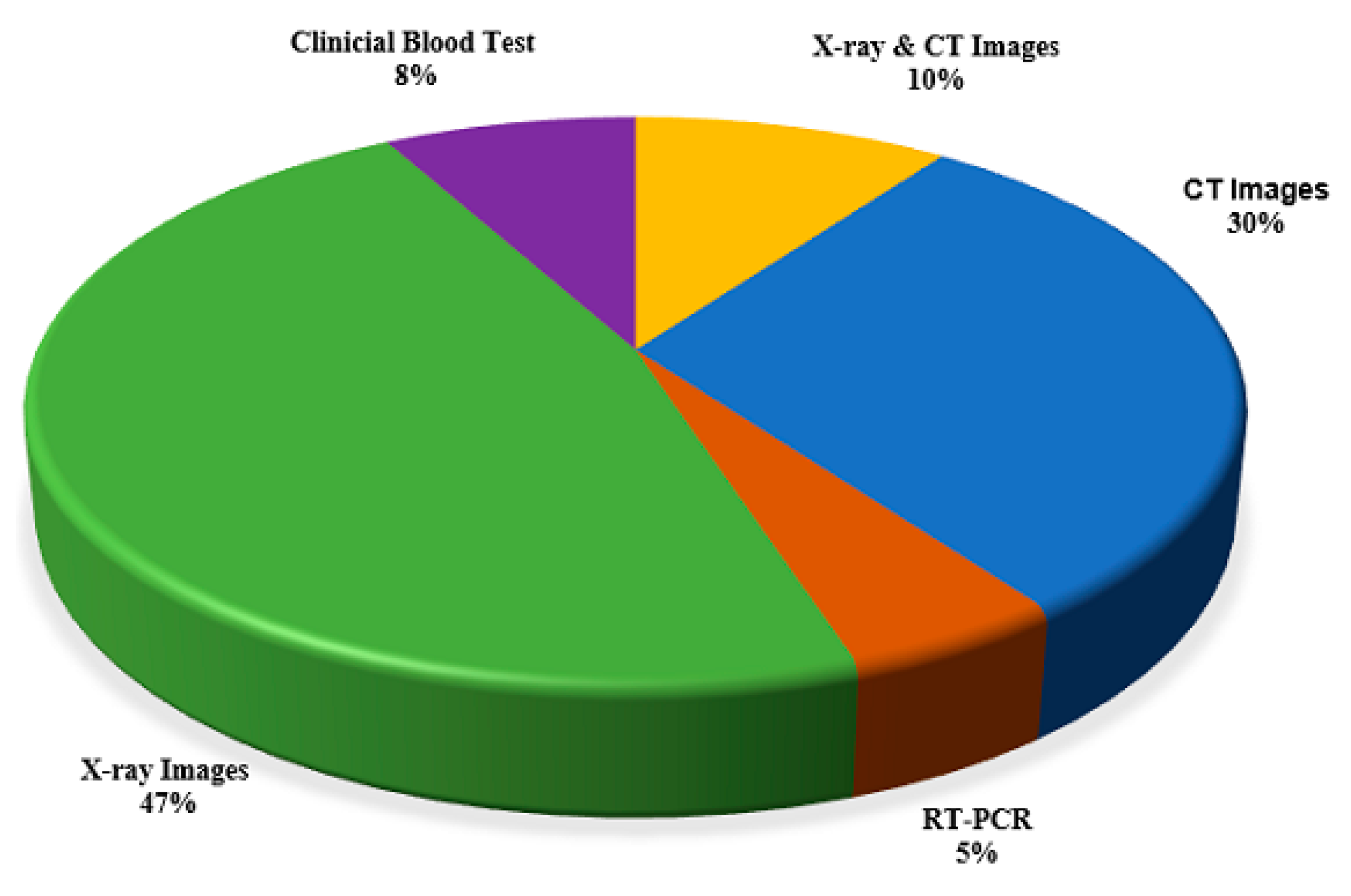
| Reference | Test Data | COVID-19 Positive | Pneumonia/Other Infection | Healthy | Total | Sources/Links |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [35] | Chest X-ray CT Images | 50 | * NA | 50 | 100 | https://github.com/ieee8023/covid-chestxray-dataset https://www.kaggle.com/paultimothymooney/chest-xray |
| [36] | Chest X-ray | 284 | 657 | 310 | 1251 | https://github.com/ieee8023/covid-chestxray-dataset https://www.kaggle.com/paultimothymooney/chest-xray |
| [37] | Chest X-ray | 250 | 2753 | 3520 | 6523 | https://github.com/ieee8023/covid-chestxray-dataset https://github.com/muhammedtalo/COVID-19 https://www.kaggle.com/nih-chest-xrays/sample |
| [38] | Chest X-ray | 274 | 2051 | 1341 | 3666 | https://www.kaggle.com/tawsifurrahman/covid19-radiography-database https://github.com/agchung/Figure1-COVID-chestxray-dataset https://github.com/ieee8023/covid-chestxray-dataset |
| [26] | CT Images | 1296 | 1735 | 1325 | 4356 | https://github.com/bkong999/COVNet |
| [39] | CT Images | 510 | 510 | * NA | 1020 | Alexion, Toshiba Medical System, Japan |
| [11] | Chest X-ray | 250 | 500 | 1000 | 1750 | https://github.com/ieee8023/COVID-chestxray-dataset |
| [40] | CT Images | 219 | 224 | 175 | 618 | Hospital of Zhejiang University Hospital of Wenzhou Hospital of Wenling |
| [41] | CT Images | 313 | * NA | 229 | 542 | Union Hospital Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, China. |
| [42] | CT Images | 325 | 740 | * NA | 1065 | Xi’an Jiaotong University First Affiliated Hospital Nanchang University First Hospital Xi’an No.8 Hospital of Xi’an Medical College, China |
| [43] | CT Images | 777 | ** NS | 708 | 1485 | The Third Affiliated Hospital and Sun Yat-Sen Memorial Hospital, Sun Yat-sen University Guangzhou Renmin Hospital of Wuhan University, China |
| [44] | CT Images | 306 | * NA | 306 | 612 | University of Medical Science (I.U.M.S.), Iran |
| [3] | Chest X-ray | 224 | 700 | 504 | 1428 | https://github.com/ieee8023/covid-chestxray-dataset https://www.kaggle.com/andrewmvd/convid19-X-rays |
| [45] | Chest X-ray | 53 | 5526 | 8066 | 13,645 | https://github.com/agchung/Figure1-COVID-chestxray-dataset https://github.com/agchung/Actualmed-COVID-chestxray-dataset https://www.kaggle.com/tawsifurrahman/covid19-radiography-database https://www.kaggle.com/c/rsna-pneumonia-detection-challenge/data |
| [46] | Chest X-ray | 127 | 127 | 127 | 381 | https://openi.nlm.nih.gov/ www.kaggle.com www.github.com |
| [47] | Chest X-ray | 25 | * NA | 25 | 50 | https://github.com/ieee8023/covid-chestxray-dataset https://www.pyimagesearch.com/category/medical/ |
| [48] | Chest X-ray | 239 + 2265 (BIMCV) | 4273 + 951 | 1583 | 9311 | Japanese Radiological Scientific Technology (J.R.S.T.) Shenzhen Dataset, Montgomery Dataset University of Montreal, Valencian Region Medical Image Bank (B.I.M.C.V.) https://github.com/ieee8023/covid-chestxray-dataset |
| [49] | CT Images | 56 | 52 | 49 | 157 | http://www.chainz.cn/Hospital in Wenzhou, ChinaEI-Camino Hospital, USA |
| [50] | CT Images (abdominal) | 53 | ** NS | * NA | 150 | https://www.sirm.org/en/ |
| [51] | Chest X-ray | 68 | 2786 | 1583+ 1504 | 5941 | https://github.com/ieee8023/covid-chestxray-dataset |
| [52] | CT Images | 133 | ** N.S. | * NA | 199 | Wuhan Pulmonary Hospital, china |
| [53] | Chest X-ray andCT Images | 2228 | 3308 | 2381 | 7917 | https://github.com/ChenWWWeixiang/diagnosis_covid19 https://tianchi.aliyun.com/competition/entrance/231601/information Wuhan Union Hospital and Jianghan Mobile cabin Hospital, China |
| [54] | CT Images | 877 | * NA | 541 | 1418 | Beijing Tsinghua Changgung Hospital, China, Wuhan No.7 Hospital, Wuhan Leishenshan Hospital, Zhongnan Hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan, Tianyou Hospital Affiliated to Wuhan University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China |
| [55] | Chest X-ray | 423 | 1485 | 1579 | 3487 | https://www.kaggle.com/tawsifurrahman/covid19-radiography-database https://www.sirm.org/category/senza-categoria/covid-19/ https://github.com/ieee8023/covid-chestxray-dataset https://www.kaggle.com/paultimothymooney/chest-xray-pneumonia |
| [56] | Chest X-ray and CT Images | 288 | ** NS | 238 | 526 | https://www.bsti.org.uk/training-and-education/covid-19-bsti-imaging-database/ https://radiopaedia.org/articles/normal-chest-imaging-examples?lang=gb https://www.kaggle.com/paultimothymooney/chest-xray-pneumonia/metadata |
| [57] | Chest X-ray | 100 | ** NS | 1431 | 1531 | https://github.com/ieee8023/covid-chestxray-dataset |
| [58] | RT-PCR | 102 | ** NS | * NA | 235 | Hospital Israelita Albert Einstein, Brazil |
| [59] | RT-PCR | ** NS | ** NS | * NA | 53 | Wenzhou Central Hospital and Cangnan People’s Hospital Wenzhou, China |
| [60] | Chest CT Images | 924 | 4448 | * NA | 5372 | Renmin Hospital of Wuhan University, Henan Provincial People’s hospital, First Hospital of China Medical University First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University Beijing Youan Hospital of Capital Medical University, Huangshi Central Hospital, |
| [61] | Chest CT Images | 349 | * NA | 463 | 812 | https://www.sirm.org/ https://radiopaedia.org/ https://www.kaggle.com/tawsifurrahman/covid19-radiography-database/ https://coronacases.org/ https://www.eurorad.org/ |
| [62] | Chest X-ray CT Images | ** NS | 4273 | 1583 | 5856 | [63] |
| [64] | Chest X-ray | 45 | 931 | 660 | 1636 | https://github.com/lindawangg/COVID-Net https://www.kaggle.com/c/rsna-pneumonia-detection-challenge/data |
| [65] | Chest X-ray | 105 | * NA | 80 | 185 | https://github.com/ieee8023/covid-chestxray-dataset |
| [66] | Chest X-ray | 680 | 1845 + 3457 | 9977 | 15,959 | https://www.kaggle.com/c/rsna-pneumonia-detection-challenge https://www.kaggle.com/tawsifurrahman/covid19-radiography-database https://github.com/ieee8023/covid-chestxray-dataset https://github.com/muhammedtalo/COVID-19 |
| [67] | Chest X-ray | 534 | 1157 | 1310 | 3001 | https://github.com/ieee8023/covid-chestxray-dataset https://www.kaggle.com/paultimothymooney/chest-Xray |
| [68] | Chest X-ray | 210 | 350 | 350 | 910 | https://www.kaggle.com/tawsifurrahman/covid19-radiography-database |
| [69] | Chest X-ray | 696 | 696 | 696 | 2088 | https://github.com/ieee8023/covid-chestxray-dataset |
| [70] | Clinical Blood Test | Suspected Covid-19 105 | 148 | * NA | 253 | Gansu Provincial Hospital, Lanzhou Pulmonary Hospital, The First Hospital of Lanzhou University, The First People’s Hospital of Lanzhou City, Lanzhou University Second Hospital, China |
| [71] | Clinical Blood Test | 160 | 5333 | * NA | 5493 | University Medical Centre Ljubljana (U.M.C.L.), Slovenia |
| [72] | Clinical Blood Test | 82 | * NA | 32 | 114 | Taizhou Hospital Zhejiang, China |
| Reference | Test Type | ML/DL Techniques | Prediction Results | Country | Cited by No of Papers |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [26] | CT Images | CNN, COVNet | AUC 0.96 | China | 553 |
| [39] | CT Images | CNNs, ResNet-101 & Xception | AUC of 0.99 Sensitivity 98.02% Specificity 99.51% | Iran | 120 |
| [41] | CT Images | 3-D DNN, DeCoVNet | Accuracy 0.90 | China | 205 |
| [42] | C.T. Images | Inception Transfer learning model establish the algorithm | Accuracy of 89.5% with Specificity of 0.88 and Sensitivity of 0.87 | China | 376 |
| [43] | C.T. Images | D.N.N., DRE-Net | A.U.C. of 0.99 Sensitivity of 0.93 | China | 198 |
| [49] | CT Images | 2D and 3D deep learning (Resnet-50-2D) and AI Models | AUC of 0.99 Sensitive 92.2% Specificity 92.2% | China | 306 |
| [50] | C.T. Images | Classification Stage 1 SVM, Stage 2 GLCM, GLSZ MDWT | Accuracy of 99.68% | Turkey | 103 |
| [52] | C.T. Images | Multilayer perceptron and LSTM | AUC of 0.954 | China | 48 |
| [54] | CT Images | Combined model 3D UNet++ and RestNet-50 | AUC of 0.991 Sensitivity of 0.974 and specificity of 0.922 | China | 99 |
| [60] | C.T. Images | 3D-DNN, COVID-19Net | AUC 0.86 Sensitivity of 79.35% and specificity of 71.43% | China | 95 |
| [61] | C.T. Images | CNN, Multi-task learning, self-supervised learning, DenseNet-169 | Accuracy of 0.89 and AUC 0.90 | China | 175 |
| [44] | C.T. Images | Five classifiers, Decision tree, k-nearest neighbor, naïve Bayes, support vector machine, Proposed COVIDiag model | Accuracy of 91.4% sensitivity of 93.24%, and specificity of 90.32% | Iran | 7 |
| [36] | X-ray Images | CNN, CoroNet | Overall Accuracy 89.6% | India | 159 |
| [37] | X-ray Images | CNN VGG16 | Average accuracy 0.97% | Italy | 69 |
| [11] | X-ray Images | CNN DarkCovidNet | Accuracy of 98.08% | Turkey | 417 |
| [40] | CT Images | 3-D CNN ResNet-18 | Overall Accuracy 86.7% | China | 443 |
| [3] | X-ray Images | CNN, MobileNet v2 | Accuracy of 96.78% Sensitive 98.66% Specificity 96.46% | Greece | 480 |
| [45] | X-ray Images | D.N.N., VGG-19 ResNet-50, COVID-Net | Accuracy of 93.3% | Canada | 558 |
| [46] | X-ray Images | CNN, RestNet50 + SVM | Accuracy of 95.33% | India | 250 |
| [47] | X-ray Images | D-CNN, VGG19, DenseNet201 | Classification with F1-scores of 0.89 and 0.91 | Egypt | 251 |
| [68] | X-ray Images | CNN, COV19-ResNet, COV19-CNNet | Accuracy of 97.61% | Turkey | 1 |
| [48] | X-ray Images | ResNet50, DenseNet201, Inception-v3, and Xception | AUC 0.996, Overall sensitivity of 0.94 | USA | 2 |
| [51] | X-ray Images | CNN, Bayesian ResNet50V2 | Accuracy of 89.92% | UK | 104 |
| [55] | X-ray Images | DCNN, CheXNet + DenseNet-201 | Accuracy of 99.7% precision, sensitivity of 99.7% and specificity is 99.55% | Qatar | 161 |
| [57] | X-ray Images | CNN, Classification Grad-CAM | AUC 95.13%, the sensitivity of 90%, and specificity of 87.84% | China | 161 |
| [64] | X-ray Images | CNN, COVID-ResNet | Accuracy of 96.23% | USA | 125 |
| [65] | X-ray Images | D-CNN, DeTraC | Accuracy of 95.12% Sensitivity of 97.91% and Specificity of 91.87% | Egypt | 161 |
| [66] | X-ray Images | D.N.N., Deep COVID Explainer | Positive Predictive Value 96.12% and recall of 94.3% | Germany | 34 |
| [67] | X-ray Images | VGG-16 VGG-19 | Accuracy of 87.49% | Australia | 5 |
| [38] | X-ray Images | CNN, AlexNet, GoogleNet, SqueezeNet | Overall accuracy 99% | Saudi Arabia | 4 |
| [69] | X-ray Images | Classification Models K.N.N., ANN, D.T., SVM, | Overall accuracy of 93.41% | India | 8 |
| [35] | Chest X-ray CT Images | CNN, RestNet50, Inception V3, Inception-RestNetV2 | Accuracy of 98% | Turkey | 408 |
| [53] | Chest X-ray CT Images | D-CNN, A.I. system | A.U.C. of 97.91% The sensitivity of 90.19% and specificity of 95.76% | China | 97 |
| [56] | Chest X-ray CT Images | Simple 2-D CNN Model and pre-trained AlexNet with transfer learning | Accuracy of 98% on X-ray images and 94.1% on C.T. images | Iraq | 80 |
| [62] | Chest X-ray CT Images | D-CNN, Resnet50, MobileNet_V2, Inception_Resnet_V2 | Accuracy of 96.61% | Morocco | 39 |
| [58] | RT-PCR | Support Vector Machine, Random Forests, Neural Networks, Logistic Regression | AUC 0.847, Sensitivity 0.67, Specificity 0.85 | Brazil | 31 |
| [59] | RT-PCR | Support Vector Machine, K.N.N., Decision Tree, Random Forest | Accuracy of 80% | China | 147 |
| [70] | Clinical Blood Test | Random Forests (R.F.) | Accuracy of 0.9512, Sensitivity 0.9697, and Specificity 0.9595 | China | 27 |
| [71] | Clinical Blood Test | CRISP-DM, Random Forest, Deep Neural Network, Extreme gradient Boosting Machine (XGBoost) | A.U.C. of 0.97, Sensitivity 81.9%, and specificity of 97.9% | Switzerland | 5 |
| [72] | Clinical Blood Test | Six Classification Model BayesNet, logistic-regression, lazy-classifier, meta-classifier, classification via regression, decision-tree (J48) | Accuracy of 84.24% | Turkey | 0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rehman, A.; Iqbal, M.A.; Xing, H.; Ahmed, I. COVID-19 Detection Empowered with Machine Learning and Deep Learning Techniques: A Systematic Review. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 3414. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11083414
Rehman A, Iqbal MA, Xing H, Ahmed I. COVID-19 Detection Empowered with Machine Learning and Deep Learning Techniques: A Systematic Review. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(8):3414. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11083414
Chicago/Turabian StyleRehman, Amir, Muhammad Azhar Iqbal, Huanlai Xing, and Irfan Ahmed. 2021. "COVID-19 Detection Empowered with Machine Learning and Deep Learning Techniques: A Systematic Review" Applied Sciences 11, no. 8: 3414. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11083414
APA StyleRehman, A., Iqbal, M. A., Xing, H., & Ahmed, I. (2021). COVID-19 Detection Empowered with Machine Learning and Deep Learning Techniques: A Systematic Review. Applied Sciences, 11(8), 3414. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11083414






