Emmer-Based Beverage Fortified with Fruit Juices
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Food Materials
2.2. Microorganism and Culture Media
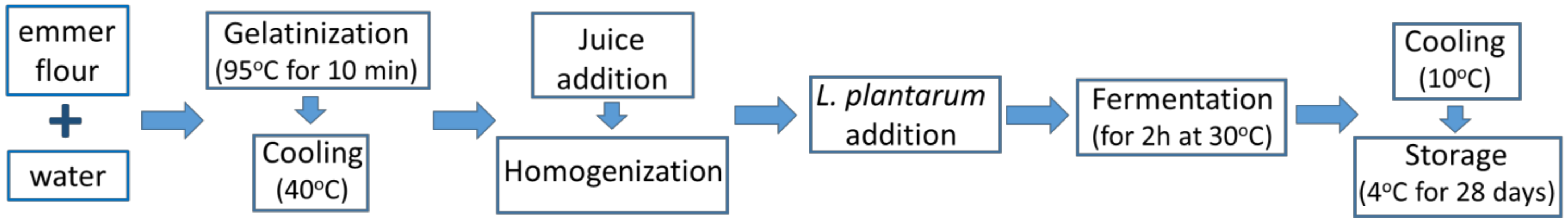
2.3. Emmer Beverages Production
2.4. Analyses
2.4.1. Total Acidity and pH
2.4.2. Viscosity and Water Holding Capacity
2.4.3. Color
2.4.4. Preparation of Beverages Extracts
2.4.5. Free Radical-Scavenging Activity (FRSA) and Total Phenolic Content (TPC)
2.4.6. Reducing Sugars
2.4.7. Microbiological Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Acidification Trend
3.2. Physicochemical Characteristics and Antioxidant Activity
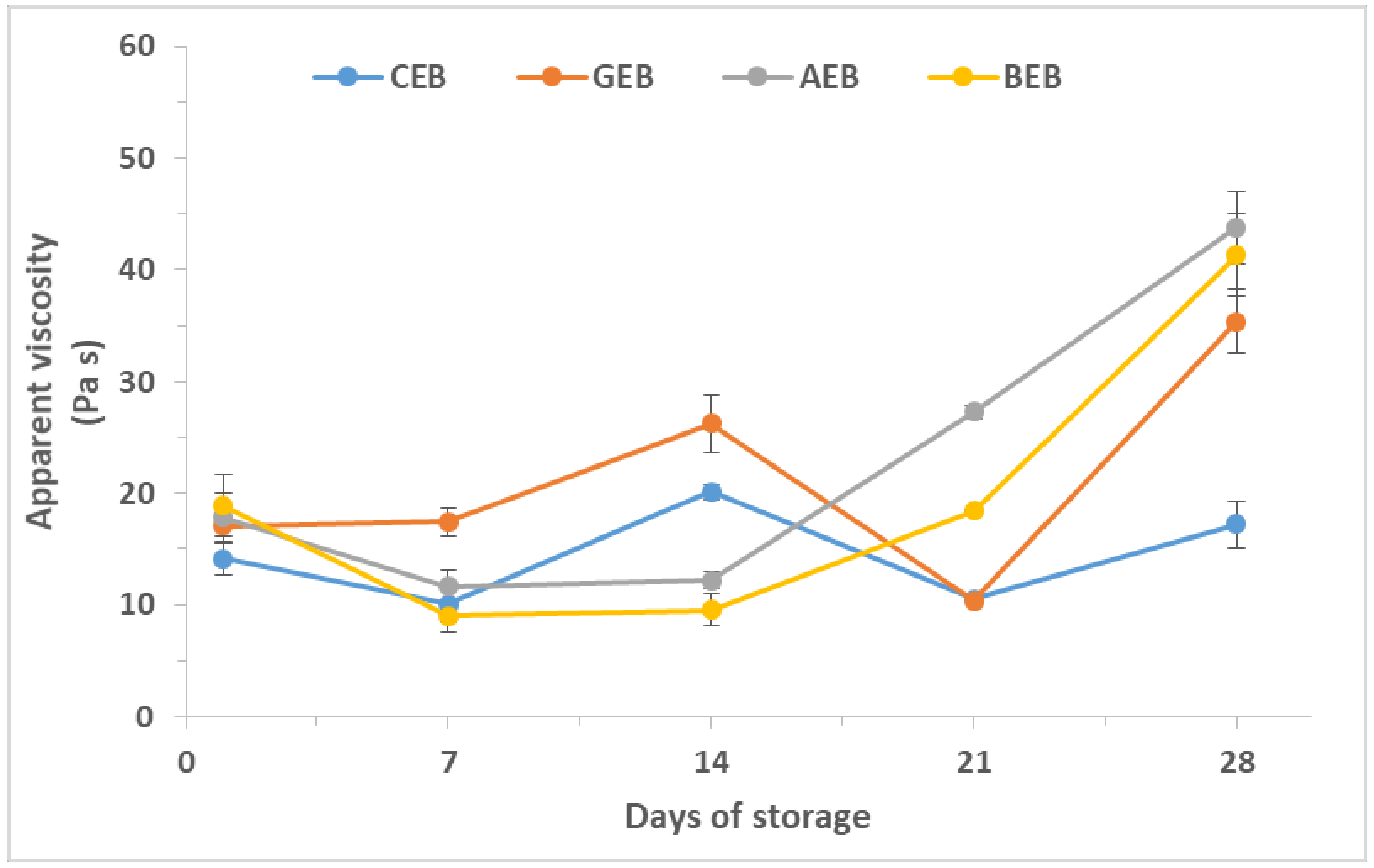
3.3. Viscosity
3.4. Color Characteristics
3.5. Starter Culture Viability
4. Conclusions
- Total phenolic content and antioxidant activity were significantly increased by the addition of juices.
- The probiotic cells maintained a high viability throughout 28-day storage.
- Lower pH values (3.35–3.56 compared to 5.44 in control), higher viscosity and increased red color of the emmer-based beverages fortified with fruit juices were observed.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bimbo, F.; Bonanno, A.; Nocella, G.; Viscecchia, R.; Nardone, G.; De Devitiis, B.; Carlucci, D. Consumers’ acceptance and preferences for nutrition-modified and functional dairy products: A systematic review. Appetite 2017, 113, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijaya Kumar, B.; Vijayendra, S.V.N.; Reddy, O.V.S. Trends in dairy and non-dairy probiotic products—A review. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 52, 6112–6124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandylis, P.; Pissaridi, K.; Bekatorou, A.; Kanellaki, M.; Koutinas, A.A. Dairy and non-dairy probiotic beverages. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2016, 7, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazio, A.; La Torre, C.; Caroleo, M.C.; Caputo, P.; Cannataro, R.; Plastina, P.; Cione, E. Effect of addition of pectins from jujubes (Ziziphus jujuba Mill.) on vitamin C production during heterolactic fermentation. Molecules 2020, 25, 2706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łopusiewicz, Ł.; Drozłowska, E.; Siedlecka, P.; Mężyńska, M.; Bartkowiak, A.; Sienkiewicz, M.; Zielińska-Bliźniewska, H.; Kwiatkowski, P. Development, characterization, and bioactivity of non-dairy Kefir-like fermented beverage based on flaxseed oil cake. Foods 2019, 8, 544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aspri, M.; Papademas, P.; Tsaltas, D. Review on non-dairy probiotics and their use in non-dairy based products. Fermentation 2020, 6, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geisslitz, S.; Longin, C.F.H.; Scherf, K.A.; Koehler, P. Comparative study on gluten protein composition of ancient (einkorn, emmer and spelt) and modern wheat species (durum and common wheat). Foods 2019, 8, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christopher, A.; Sarkar, D.; Shetty, K. Human health-relevant bioactive functionalities of ancient emmer wheat. In Functional Foods and Biotechnology: Sources of Functional Foods and Ingredients, 1st ed.; Shetty, K., Sarkar, D., Eds.; CRC Press/Taylor & Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Ranucci, D.; Miraglia, D.; Branciari, R.; Morganti, G.; Roila, R.; Zhou, K.; Jiang, H.; Braconi, P. Frankfurters made with pork meat, emmer wheat (Triticum dicoccum Schübler) and almonds nut (Prunus dulcis Mill.): Evaluation during storage of a novel food from an ancient recipe. Meat Sci. 2018, 145, 440–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witczak, T.; Gałkowska, D. Sorption and thermal characteristics of ancient grain pasta of various compositions. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 137, 110433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozzon, M.; Boselli, E.; Obiedziński, M.W.; Frega, N.G. Occurrence of biogenic amines in beers produced with malted organic Emmer wheat (Triticum dicoccum). Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2015, 32, 756–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coda, R.; Lanera, A.; Trani, A.; Gobbetti, M.; Di Cagno, R. Yogurt-like beverages made of a mixture of cereals, soy and grape must: Microbiology, texture, nutritional and sensory properties. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2012, 155, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coda, R.; Rizzello, C.G.; Trani, A.; Gobbetti, M. Manufacture and characterization of functional emmer beverages fermented by selected lactic acid bacteria. Food Microbiol. 2011, 28, 526–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seddik, H.A.; Bendali, F.; Gancel, F.; Fliss, I.; Spano, G.; Drider, D. Lactobacillus plantarum and its probiotic and food potentialities. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2017, 9, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behera, S.S.; Ray, R.C.; Zdolec, N. Lactobacillus plantarum with functional properties: An approach to increase safety and shelf-life of fermented foods. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 9361614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiş, M.S.; Păucean, A.; Man, S.M.; Vodnar, D.C.; Teleky, B.-E.; Pop, C.R.; Stan, L.; Borsai, O.; Kadar, C.B.; Urcan, A.C.; et al. Quinoa Sourdough Fermented with Lactobacillus plantarum ATCC 8014 Designed for Gluten-Free Muffins—A Powerful Tool to Enhance Bioactive Compounds. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 7140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łaszkiewicz, B.; Szymański, P.; Zielińska, D.; Kołożyn-Krajewska, D. Application of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum SCH1 for the Bioconservation of Cooked Sausage Made from Mechanically Separated Poultry Meat. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidira, M.; Santarmaki, V.; Kiourtzidis, M.; Argyri, A.A.; Papadopoulou, O.S.; Chorianopoulos, N.; Tassou, C.; Kaloutsas, S.; Galanis, A.; Kourkoutas, Y. Evaluation of immobilized Lactobacillus plantarum 2035 on whey protein as adjunct probiotic culture in yoghurt production. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 75, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulou, O.S.; Argyri, A.A.; Varzakis, E.; Sidira, M.; Kourkoutas, Y.; Galanis, A.; Tassou, C.; Chorianopoulos, N.G. Use of lactobacilli strains with probiotic potential in traditional fermented milk and their impact on quality and safety related to Listeria monocytogenes. Int. Dairy J. 2019, 98, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotzamanidis, C.; Kourelis, A.; Litopoulou-Tzanetaki, E.; Tzanetakis, N.; Yiangou, M. Evaluation of adhesion capacity, cell surface traits and immunomodulatory activity of presumptive probiotic Lactobacillus strains. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2010, 140, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santarmaki, V.; Kourkoutas, Y.; Zoumpopoulou, G.; Mavrogonatou, E.; Kiourtzidis, M.; Chorianopoulos, N.; Tassou, C.; Tsakalidou, E.; Simopoulos, C.; Ypsilantis, P. Survival, intestinal mucosa adhesion, and immunomodulatory potential of Lactobacillus plantarum strains. Curr. Microbiol. 2017, 74, 1061–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidor, A.; Drożdżyńska, A.; Gramza-Michałowska, A. Black chokeberry (Aronia melanocarpa) and its products as potential health-promoting factors-An overview. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 89, 45–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandylis, P.; Kokkinomagoulos, E. Food applications and potential health benefits of pomegranate and its derivatives. Foods 2020, 9, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bochnak-Niedźwiecka, J.; Świeca, M. Quality of new functional powdered beverages enriched with lyophilized fruits—potentially bioaccessible antioxidant properties, nutritional value, and consumer analysis. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayta, M.; Alpaslan, M.; Köse, E. The effect of fermentation on viscosity and protein solubility of Boza, a traditional cereal-based fermented Turkish beverage. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2001, 213, 335–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.W.; Rhee, C. Processing suitability of a rice and pine nut (Pinus koraiensis) beverage. Food Hydrocoll. 2003, 17, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrellou, D.; Solomakou, N.; Kokkinomagoulos, E.; Kandylis, P. Yogurts supplemented with juices from grapes and berries. Foods 2020, 9, 1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giri, S.S.; Sen, S.S.; Saha, S.; Sukumaran, V.; Park, S.C. Use of a potential probiotic, Lactobacillus plantarum L7, for the preparation of a rice-based fermented beverage. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paz, P.C.; Janny, R.J.; Håkansson, Å. Safeguarding of quinoa beverage production by fermentation with Lactobacillus plantarum DSM 9843. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2020, 324, 108630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charalampopoulos, D.; Wang, R.; Pandiella, S.S.; Webb, C. Application of cereals and cereal components in functional foods: A review. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2002, 79, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augusto, P.E.; Falguera, V.; Cristianini, M.; Ibarz, A. Rheological behavior of tomato juice: Steady-state shear and time-dependent modeling. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2012, 5, 1715–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattes, R.D.; Rothacker, D. Beverage viscosity is inversely related to postprandial hunger in humans. Physiol. Behav. 2001, 74, 551–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juvonen, K.R.; Purhonen, A.K.; Salmenkallio-Marttila, M.; Lähteenmäki, L.; Laaksonen, D.E.; Herzig, K.H.; Uusitupa, M.I.J.; Poutanen, K.S.; Karhunen, L.J. Viscosity of oat bran-enriched beverages influences gastrointestinal hormonal responses in healthy humans. J. Nutr. 2009, 139, 461–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes, M.; Duarte, C.M.; Nunes, C.; Raymundo, A.; Sousa, I. Flow behaviour of vegetable beverages to replace milk. In Proceedings of the Iberian Meeting on Rheology (IBEREO 2019); Galindo-Rosales, F., Campo-Deaño, L., Afonso, A., Alves, M., Pinho, F., Eds.; Springer Proceedings in Materials; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Liu, J.; Bi, J.; Cao, F.; Ding, Y.; Peng, J. Effects of high pressure homogenization on physical stability and carotenoid degradation kinetics of carrot beverage during storage. J. Food Eng. 2019, 263, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magala, M.; Kohajdova, Z.; Karovičová, J.; Greifova, M.; Hojerova, J. Application of lactic acid bacteria for production of fermented beverages based on rice flour. Czech J. Food Sci. 2015, 33, 458–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Liang, S.; Wang, H.; Guo, M. Physiochemical properties and probiotic survivability of symbiotic oat-based beverage. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2018, 27, 735–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, W.; Xu, B. Development of an orange juice beverage formulated with oat beta-glucan and whey protein isolate. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2018, 98, 4685–4691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Bi, X.; Huang, W.; Wu, J.; Hu, X.; Liao, X. Changes of quality of high hydrostatic pressure processed cloudy and clear strawberry juices during storage. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2012, 16, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebruers, K.; Dornez, E.; Boros, D.; Dynkowska, W.; Bedo, Z.; Rakszegi, M.; Delcour, J.A.; Courtin, C.M. Variation in the content of dietary fiber and components thereof in wheats in the HEALTHGRAIN diversity screen. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 9740–9749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasquez-Orejarena, E.; Simons, C.T.; Litchfield, J.H.; Alvarez, V.B. Functional properties of a high protein beverage stabilized with oat-β-glucan. J. Food Sci. 2018, 83, 1360–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faccin, G.L.; Miotto, L.A.; do Nascimento Vieira, L.; Barreto, P.L.M.; Amante, E.R. Chemical, sensorial and rheological properties of a new organic rice bran beverage. Rice Sci. 2009, 16, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, A.A.; Aly, M.M.; El-Hadidie, S.T. Production of cereal-based probiotic beverages. World Appl. Sci. J. 2012, 19, 1367–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, P.; de Chiara, M.L.V.; Capozzi, V.; Arena, M.P.; Amodio, M.L.; Rascón, A.; Dueñas, M.T.; López, P.; Spano, G. Lactobacillus plantarum strains for multifunctional oat-based foods. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 68, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rein, M.J.; Heinonen, M. Stability and enhancement of berry juice color. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 3106–3114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoo, H.E.; Azlan, A.; Tang, S.T.; Lim, S.M. Anthocyanidins and anthocyanins: Colored pigments as food, pharmaceutical ingredients, and the potential health benefits. Food Nutr. Res. 2017, 61, 1361779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez-Molina, E.; Moreno, D.A.; Garcia-Viguera, C. Aronia-enriched lemon juice: A new highly antioxidant beverage. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 11327–11333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Vicente, A.; Serrano, P.; Abellán, P.; García-Viguera, C. Influence of packaging material on pomegranate juice colour and bioactive compounds, during storage. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2004, 84, 639–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.; Hwang, E.S. Quality characteristics and antioxidant activity of yogurt supplemented with aronia (Aronia melanocarpa) juice. Prev. Nutr. Food Sci. 2016, 21, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barba, F.J.; Jäger, H.; Meneses, N.; Esteve, M.J.; Frígola, A.; Knorr, D. Evaluation of quality changes of blueberry juice during refrigerated storage after high-pressure and pulsed electric fields processing. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2012, 14, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, A.L.F.; Maciel, T.C.; Rodrigues, S. Probiotic beverage from cashew apple juice fermented with Lactobacillus casei. Food Res. Int. 2011, 44, 1276–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, H.; Koguchi, M.; Ishiguro, Y.; Mikykawa, T. Changes in carrot juice components due to fermentation by selected lactic acid bacteria. Food Sci. Technol. Int. Tokyo 1996, 2, 246–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reque, P.M.; Steffens, R.S.; Jablonski, A.; Flôres, S.H.; Rios, A.D.O.; de Jong, E.V. Cold storage of blueberry (Vaccinium spp.) fruits and juice: Anthocyanin stability and antioxidant activity. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2014, 33, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, J.; Fan, L. Evaluation of the composition of Chinese bayberry wine and its effects on the color changes during storage. Food Chem. 2019, 276, 451–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bomdespacho, L.D.Q.; Silva, B.T.R.D.; Lapa-Guimaraes, J.; Ditchfield, C.; Petrus, R.R. Cultivar affects the color change kinetics of sugarcane juice. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 38, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sah, B.N.P.; Vasiljevic, T.; McKechnie, S.; Donkor, O.N. Physicochemical, textural and rheological properties of probiotic yogurt fortified with fibre-rich pineapple peel powder during refrigerated storage. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 65, 978–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmerón, I.; Thomas, K.; Pandiella, S.S. Effect of potentially probiotic lactic acid bacteria on the physicochemical composition and acceptance of fermented cereal beverages. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 15, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kechagia, M.; Basoulis, D.; Konstantopoulou, S.; Dimitriadi, D.; Gyftopoulou, K.; Skarmoutsou, N.; Fakiri, E.M. Health benefits of probiotics: A review. ISRN Nutr. 2013, 2013, 481651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, C.; Guarner, F.; Reid, G.; Gibson, G.R.; Merenstein, D.J.; Pot, B.; Morelli, L.; Canani, R.B.; Flint, H.J.; Salminen, S.; et al. The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics consensus statement on the scope and appropriate use of the term probiotic. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 11, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Analyses | Days | CEB | GEB | AEB | BEB |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | Initial After 2 h fermentation 1 7 14 21 28 | 6.64 ± 0.01 c,D 5.79 ± 0.06 b,D 5.71 ± 0.01 b,C 5.69 ± 0.06 b,C 5.66 ± 0.04 b,C 5.35 ± 0.05 a,C 5.44 ± 0.06 a,C | 5.61 ± 0.08 e,C 4.15 ± 0.07 d,B 3.98 ± 0.08 d,B 3.66 ± 0.06 c,AB 3.56 ± 0.01 bc,B 3.32 ± 0.02 a,A 3.37 ± 0.03 ab,A | 4.69 ± 0.06 e,B 4.42 ± 0.03 d,C 4.09 ± 0.02 c,B 3.82 ± 0.02 b,B 3.57 ± 0.04 a,B 3.51 ± 0.04 a,B 3.56 ± 0.01 a,B | 3.99 ± 0.08 d,A 3.80 ± 0.03 cd,A 3.72 ± 0.05 c,A 3.52 ± 0.06 b,A 3.36 ± 0.03 ab,A 3.29 ± 0.01 a,A 3.35 ± 0.04 ab,A |
| Acidity (% w/w lactic acid) | Initial 1 7 14 21 28 | 0.03 ± 0.00 a,A 0.04 ± 0.00 a,A 0.04 ± 0.00 a,A 0.04 ± 0.00 a,A 0.07 ± 0.00 b,A 0.07 ± 0.00 b,A | 0.08 ± 0.02 a,AB 0.28 ± 0.00 b,B 0.39 ± 0.01 c,B 0.50 ± 0.01 d,B 0.56 ± 0.02 e,B 0.56 ± 0.00 e,B | 0.16 ± 0.01 a,B 0.32 ± 0.02 b,B 0.38 ± 0.07 bc,B 0.49 ± 0.01 cd,B 0.54 ± 0.00 d,B 0.58 ± 0.02 d,B | 0.30 ± 0.03 a,C 0.53 ± 0.03 b,C 0.58 ± 0.08 bc,B 0.74 ± 0.01 cd,C 0.82 ± 0.00 d,C 0.83 ± 0.04 d,C |
| Reducing sugars (% w/w glucose) | Initial 1 7 14 21 28 | 0.21 ± 0.04 c,A 0.09 ± 0.01 b,A 0.02 ± 0.00 a,A 0.03 ± 0.01 a,A 0.02 ± 0.00 a,A 0.02 ± 0.01 a,A | 4.62 ± 0.18 c,C 3.99 ± 0.09 b,C 3.90 ± 0.07 b,C 3.84 ± 0.03 b,D 3.58 ± 0.22 b,C 2.76 ± 0.03 a,C | 2.27 ± 0.04 d,B 1.54 ± 0.08 c,B 1.38 ± 0.04 bc,B 1.30 ± 0.01 ab,B 1.27 ± 0.00 ab,B 1.15 ± 0.07 a,B | 2.12 ± 0.16 c,B 1.53 ± 0.04 b,B 1.43 ± 0.06 ab,B 1.38 ± 0.01 ab,C 1.26 ± 0.06 ab,B 1.21 ± 0.03 a,B |
| Beverage | DPPH● | Total Phenolic Content mg GAE 100 g−1 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| % Inhibition | μmol TE 100 g−1 | ||
| CEB | 3 ± 2 a | 12 ± 3 a | 3.8 ± 0.3 a |
| GEB | 52 ± 3 b | 94 ± 4 b | 22.3 ± 2.2 b |
| AEB | 77 ± 2 d | 136 ± 4 d | 31.9 ± 0.7 c |
| BEB | 65 ± 4 c | 116 ± 6 c | 30.0 ± 1.7 c |
| Analyses | Days | CEB | GEB | AEB | BEB | Significance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Consistency index K (Pa s) | 1 7 14 21 28 significance | 10.07 ± 1.41 ab,A 7.39 ± 1.24 a,AB 14.32 ± 0.06 bc,AB 11.85 ± 1.39 bc,B 15.56 ± 1.41 c,A ** | 12.31 ± 1.41 a,AB 11.93 ± 1.00 a,B 18.25 ± 2.23 b,B 7.14 ± 0.88 a,A 21.10 ± 1.41 b,A *** | 14.86 ± 1.41 bc,B 8.31 ± 1.41 a,AB 8.90 ± 1.41 ab,A 18.80 ± 0.04 c,C 35.20 ± 2.83 d,B *** | 13.17 ± 1.41 b,B 6.35 ± 1.41 a,A 11.06 ± 1.34 ab,A 14.02 ± 0.84 b,B 32.88 ± 2.83 c,B *** | ** * * ** ** |
| Flow behavior index n | 1 7 14 21 28 significance | 0.34 ± 0.03 ab,AB 0.39 ± 0.01 b,C 0.37 ± 0.00 b,B 0.25 ± 0.03 a,A 0.36 ± 0.03 b,A ** | 0.37 ± 0.03 a,B 0.31 ± 0.02 a,B 0.37 ± 0.01 a,B 0.26 ± 0.05 a,A 0.26 ± 0.03 a,A * | 0.26 ± 0.03 a,A 0.21 ± 0.01 a,A 0.24 ± 0.01 a,A 0.32 ± 0.05 a,A 0.32 ± 0.13 a,A ns | 0.31 ± 0.01 ab,AB 0.29 ± 0.03 a,B 0.32 ± 0.03 ab,B 0.39 ± 0.02 b,A 0.29 ± 0.01 a,A * | * * ** ns ns |
| Correlation coefficient R2 | 1 7 14 21 28 significance | 0.982 ± 0.002 a,B 0.972 ± 0.002 a,A 0.998 ± 0.001 b,B 0.993 ± 0.004 b,AB 0.993 ± 0.002 b,A *** | 0.996 ± 0.002 b,C 0.977 ± 0.002 ab,A 0.991 ± 0.010 ab,B 0.966 ± 0.013 a,A 0.996 ± 0.001 b,A * | 0.953 ± 0.004 a,A 0.995 ± 0.003 b,B 0.953 ± 0.004 a,A 0.995 ± 0.003 b,A 0.996 ± 0.003 b,A *** | 0.995 ± 0.001 ab,C 0.991 ± 0.001 a,B 0.997 ± 0.001 b,B 0.997 ± 0.001 b,B 0.995 ± 0.001 ab,A * | *** ** ** * ns |
| Analyses | Days | CEB | GEB | AEB | BEB |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L* | 0 1 7 14 21 28 | 54.61 ± 0.07 a 65.40 ± 0.23 cd 64.64 ± 1.18 bc 66.63 ± 1.75 d 64.02 ± 0.98 bc 63.61 ± 0.87 b | 39.36 ± 0.08 a 53.91 ± 0.19 d 50.09 ± 0.87 c 54.57 ± 1.25 d 47.50 ± 2.85 b 46.13 ± 0.07 b | 43.20 ± 0.01 a 48.28 ± 0.03 b 49.57 ± 3.69 bc 54.27 ± 0.65 d 56.12 ± 3.04 d 52.91 ± 0.07 cd | 29.15 ± 0.07 a 31.74 ± 0.04 abc 35.28 ± 3.45 d 32.68 ± 1.50 bcd 34.49 ± 0.74 cd 31.09 ± 0.19 ab |
| a* | 0 1 7 14 21 28 | 0.64 ± 0.01 b 0.51 ± 0.02 ab 0.09 ± 0.39 a 0.07 ± 0.23 a 0.13 ± 0.12 a 0.30 ± 0.40 ab | 3.74 ± 0.02 a 12.28 ± 0.05 c 9.81 ± 0.24 b 12.01 ± 0.2 c 9.98 ± 0.11 b 10.31 ± 1.02 b | 5.68 ± 0.02 a 6.56 ± 0.01 b 7.71 ± 0.28 c 8.06 ± 0.43 c 9.16 ± 0.54 d 9.38 ± 0.41 d | 10.55 ± 0.09 a 14.70 ± 0.04 b 17.00 ± 2.21 b 23.34 ± 1.52 d 21.45 ± 0.60 c 19.37 ± 0.39 c |
| b* | 0 1 7 14 21 28 | 7.40 ± 0.01 b 9.76 ± 0.10 d 7.15 ± 0.35 ab 7.94 ± 0.09 c 6.77 ± 0.39 a 9.57 ± 0.03 a | 1.04 ± 0.01 a 6.23 ± 0.05 e 2.81 ± 0.05 b 4.53 ± 0.39 d 2.41 ± 0.14 b 3.87 ± 0.65 c | 5.60 ± 0.02 a 5.84 ± 0.01 a 7.60 ± 1.02 b 7.75 ± 0.59 b 9.13 ± 1.43 c 10.0 ± 0.39 c | 2.11 ± 0.05 a 3.03 ± 0.03 b 3.50 ± 0.40 b 5.75 ± 0.59 d 4.90 ± 0.04 c 4.96 ± 0.06 c |
| C* | 0 1 7 14 21 28 | 7.42 ± 0.01 b 9.77 ± 0.10 d 7.16 ± 0.35 b 7.94 ± 0.09 c 6.77 ± 0.39 a 9.58 ± 0.04 d | 3.88 ± 0.02 a 13.77 ± 0.07 d 10.21 ± 0.24 b 12.84 ± 0.26 c 10.27 ± 0.14 b 11.01 ± 1.18 b | 7.98 ± 0.01 a 8.79 ± 0.01 a 10.84 ± 0.91 b 11.18 ± 0.72 b 12.94 ± 1.40 c 13.70 ± 0.57 c | 10.76 ± 0.07 a 15.01 ± 0.03 b 17.36 ± 2.24 c 24.04 ± 1.62 e 22.00 ± 0.58 de 19.99 ± 0.39 d |
| °hue | 0 1 7 14 21 28 | 85.05 ± 0.07 a 87.03 ± 0.13 ab 89.42 ± 3.09 b 89.51 ± 1.64 b 88.96 ± 0.98 b 88.22 ± 2.39 b | 15.49 ± 0.14 b 26.89 ± 0.11 d 15.97 ± 0.19 b 20.65 ± 1.58 c 13.58 ± 0.64 a 20.36 ± 1.42 c | 44.59 ± 0.16 abc 41.69 ± 0.05 a 44.40 ± 2.82 abc 43.85 ± 0.65 ab 44.66 ± 2.82 bc 46.84 ± 0.12 c | 11.31 ± 0.34 a 11.66 ± 0.13 a 11.65 ± 0.20 a 13.81 ± 0.49 c 12.88 ± 0.43 b 14.35 ± 0.16 c |
| Days | CEB | GEB | AEB | BEB | Significance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial 1 7 14 21 28 significance | 8.08 ± 0.03 b,A 8.46 ± 0.10 c,A 8.26 ± 0.08 bc,A 8.06 ± 0.11 b,A 7.32 ± 0.16 a,A 7.18 ± 0.14 a,A *** | 8.08 ± 0.03 b,A 8.54 ± 0.10 c,A 8.45 ± 0.06 c,AB 8.25 ± 0.14 bc,AB 8.00 ± 0.11 b,B 7.61 ± 0.18 a,B *** | 8.08 ± 0.03 a,A 8.91 ± 0.15 d,B 8.60 ± 0.10 c,B 8.46 ± 0.09 bc,B 8.24 ± 0.05 ab,B 8.04 ± 0.14 a,C *** | 8.08 ± 0.03 ab,A 8.55 ± 0.06 d,C 8.40 ± 0.08 cd,AB 8.31 ± 0.11 bcd,AB 8.17 ± 0.06 abc,B 7.95 ± 0.15 a,BC *** | ns ** ** * *** *** |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dimitrellou, D.; Kandylis, P.; Kokkinomagoulos, E.; Hatzikamari, M.; Bekatorou, A. Emmer-Based Beverage Fortified with Fruit Juices. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 3116. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11073116
Dimitrellou D, Kandylis P, Kokkinomagoulos E, Hatzikamari M, Bekatorou A. Emmer-Based Beverage Fortified with Fruit Juices. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(7):3116. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11073116
Chicago/Turabian StyleDimitrellou, Dimitra, Panagiotis Kandylis, Evangelos Kokkinomagoulos, Magdalini Hatzikamari, and Argyro Bekatorou. 2021. "Emmer-Based Beverage Fortified with Fruit Juices" Applied Sciences 11, no. 7: 3116. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11073116
APA StyleDimitrellou, D., Kandylis, P., Kokkinomagoulos, E., Hatzikamari, M., & Bekatorou, A. (2021). Emmer-Based Beverage Fortified with Fruit Juices. Applied Sciences, 11(7), 3116. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11073116








