Plasma Treatment of Fish Cells: The Importance of Defining Cell Culture Conditions in Comparative Studies
Abstract
1. Introduction
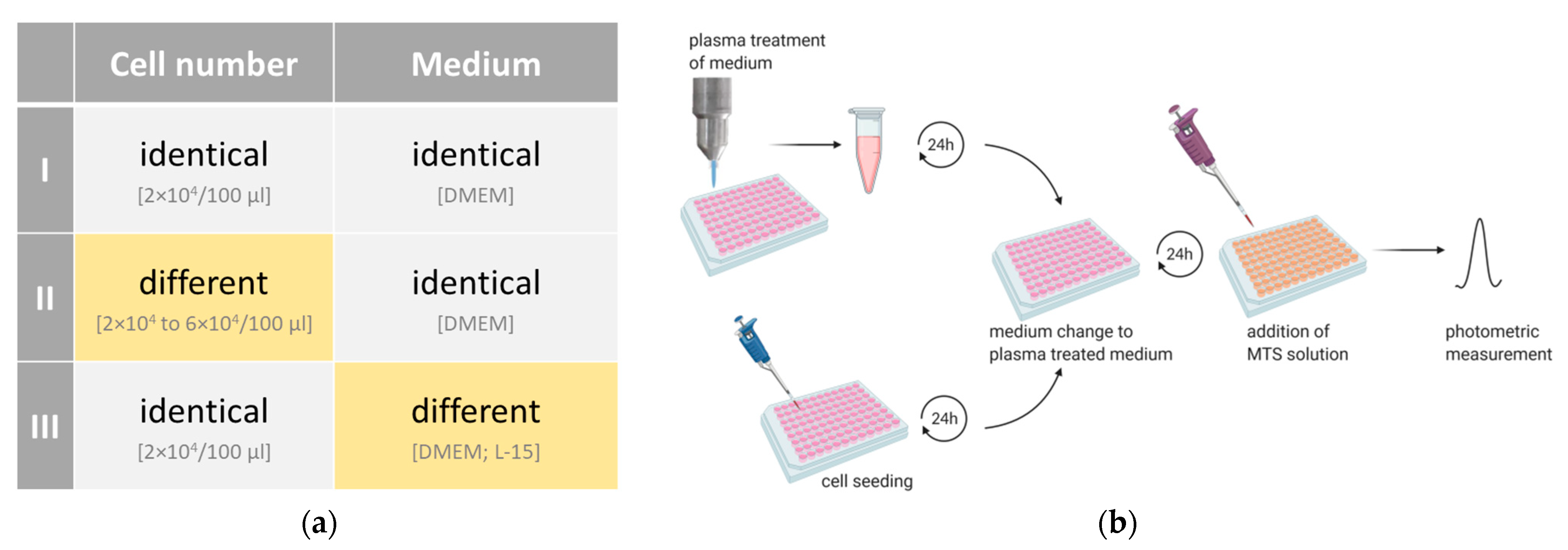
2. Materials and Methods
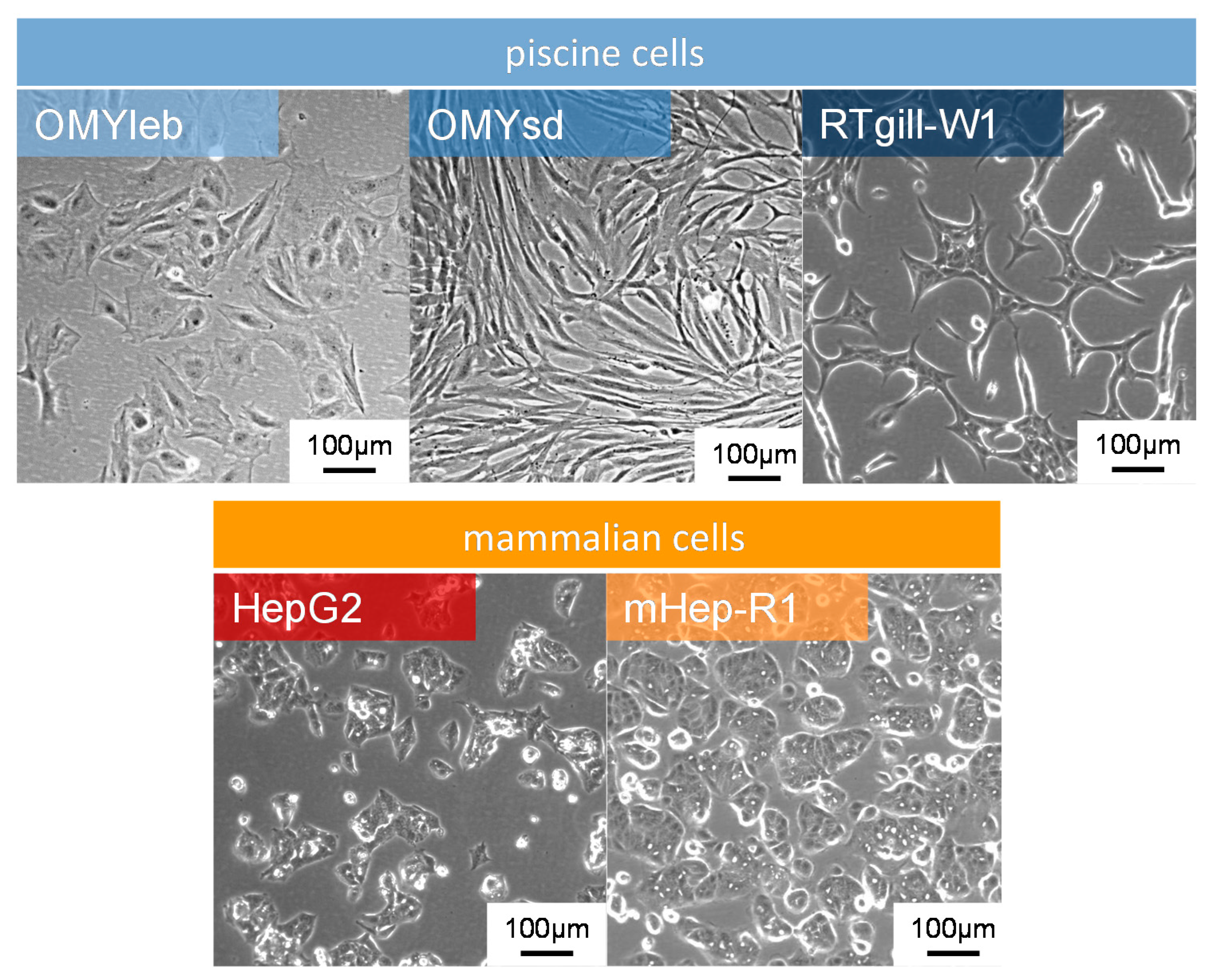
2.1. Cells
2.2. Plasma Treatment
2.3. Cell Viability
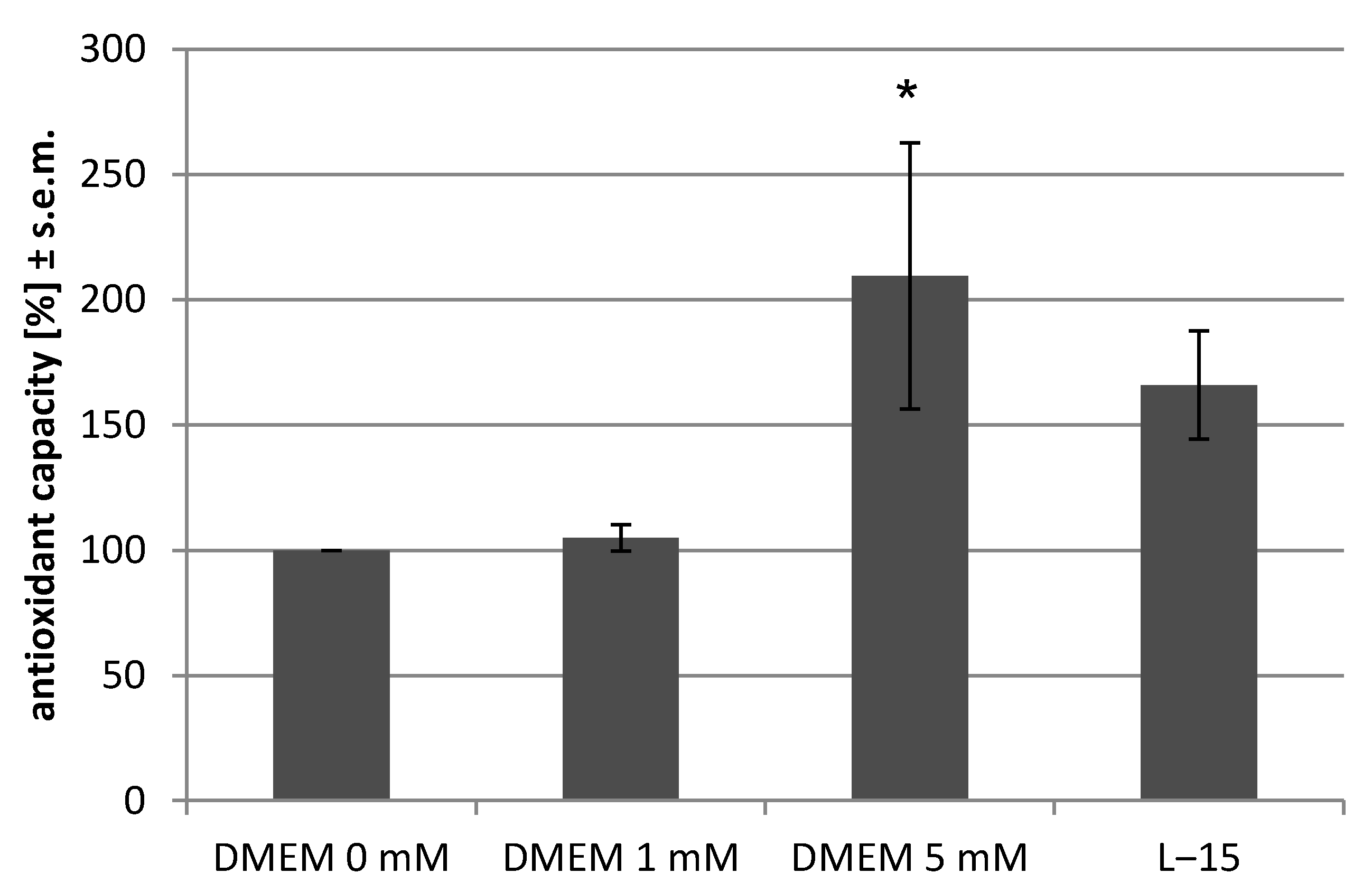
2.4. Antioxidant Assay
2.5. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Experimental Setup I: Identical Cell Number Seeded in Identical Medium
3.2. Experimental Setup II: Different Cell Number Seeded in Identical Medium
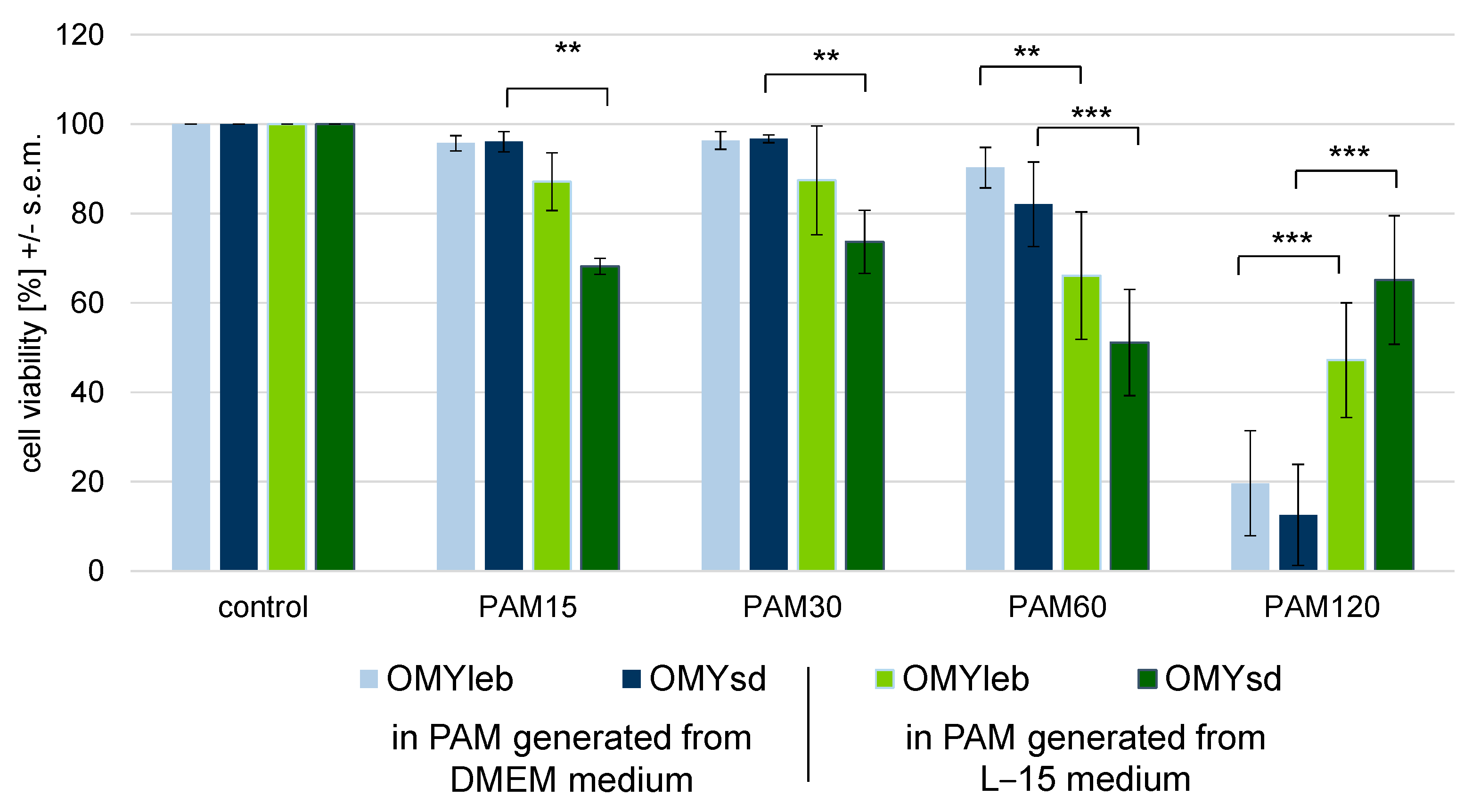
3.3. Experimental Setup III: Identical Cell Number Seeded in Different Media
4. Discussion
4.1. Fish Cells Respond Differently to Plasma Treatment than Mammalian Cells
4.2. The Choice of Culture Conditions Is Highly Relevant as Changes in the Antioxidant Capacity Make a Difference
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- He, R.; Li, Q.; Shen, W.; Wang, T.; Lu, H.; Lu, J.; Lu, F.; Luo, M.; Zhang, J.; Gao, H.; et al. The efficacy and safety of cold atmospheric plasma as a novel therapy for diabetic wound in vitro and in vivo. Int. Wound J. 2020, 17, 851–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaushik, N.K.; Ghimire, B.; Li, Y.; Adhikari, M.; Veerana, M.; Kaushik, N.; Jha, N.; Adhikari, B.; Lee, S.J.; Masur, K.; et al. Biological and medical applications of plasma-activated media, water and solutions. Biol. Chem. 2018, 400, 39–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semmler, M.L.; Bekeschus, S.; Schäfer, M.; Bernhardt, T.; Fischer, T.; Witzke, K.; Seebauer, C.; Rebl, H.; Grambow, E.; Vollmar, B.; et al. Molecular Mechanisms of the Efficacy of Cold Atmospheric Pressure Plasma (CAP) in Cancer Treatment. Cancers 2020, 12, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daeschlein, G.; Napp, M.; von Podewils, S. In vitro susceptibility of multidrug resistant skin and wound pathogens against low temperature atmospheric pressure plasma jet (APPJ) and dielectric barrier discharge plasma (DBD). Plasma Proc. Pol. 2014, 11, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, A.; Bekeschus, S.; Wende, K.; Vollmar, B.; von Woedtke, T. A cold plasma jet accelerates wound healing in a murine model of full-thickness skin wounds. Exp. Dermatol. 2017, 26, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernhardt, T.; Semmler, M.L.; Schäfer, M.; Bekeschus, S.; Emmert, S.; Boeckmann, L. Plasma Medicine: Applications of Cold Atmospheric Pressure Plasma in Dermatology. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 3873928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faílde, L.D.; Bermúdez, R.; Vigliano, F.; Coscelli, G.A.; Quiroga, M.I. Morphological, immunohistochemical and ultrastructural characterization of the skin of turbot (Psetta maxima L.). Tissue Cell 2014, 46, 334–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanitakis, J. Anatomy, histology and immunohistochemistry of normal human skin. Eur. J. Dermatol. 2002, 12, 390–399. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Abe, G.; Hayashi, T.; Yoshida, K.; Yoshida, T.; Kudoh, H.; Sakamoto, J.; Konishi, A.; Kamei, Y.; Takeuchi, T.; Tamura, K.; et al. Insights regarding skin regeneration in non-amniote vertebrates: Skin regeneration without scar formation and potential step-up to a higher level of regeneration. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 100, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Winkle, W. The epithelium in wound healing. Surg. Gynecol. Obstet. 1968, 127, 1089–1115. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kawasumi, A.; Sagawa, N.; Hayashi, S.; Yokoyama, H.; Tamura, K. Wound healing in mammals and amphibians: Toward limb regeneration in mammals. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2013, 367, 33–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebl, A.; Goldammer, T. Under control: The innate immunity of fish from the inhibitors’ perspective. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2018, 77, 328–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, M.; Kosaric, N.; Bonham, C.A.; Gurtner, G.C. Wound Healing: A Cellular Perspective. Physiol. Rev. 2019, 99, 665–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, L.A.; Whyte, S.K.; Braden, L.M.; Purcell, S.L.; Manning, A.J.; Muckle, A.; Fast, M.D. Impact of co-infection with Lepeophtheirus salmonis and Moritella viscosa on inflammatory and immune responses of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). J. Fish Dis. 2020, 43, 459–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pickering, A.D.; Willoughby, L.G. Epidermal lesions and fungal infection on the perch, Perca fluviatilis L., in Windermere. J. Fish Biol. 1977, 11, 349–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almazán-Rueda, P.; Schrama, J.W.; Verreth, J.A. Behavioural responses under different feeding methods and light regimes of the African catfish (Clarias gariepinus) juveniles. Aquaculture 2004, 231, 347–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dror, M.; Sinyakov, M.S.; Okun, E.; Dym, M.; Sredni, B.; Avtalion, R.R. Experimental handling stress as infection-facilitating factor for the goldfish ulcerative disease. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2006, 109, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tørud, B.; Håstein, T. Skin lesions in fish: Causes and solutions. Acta Vet. Scand. 2008, 50, S7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costello, M.J. The global economic cost of sea lice to the salmonid farming industry. J. Fish Dis. 2009, 32, 115–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalaiselvi Sivalingam, N.N.; Seepoo, A.M.; Gani, T.; Selvam, S.; Azeez Sait, S.H. Zebrafish fin-derived fibroblast cell line: A model for in vitro wound healing. J. Fish Dis. 2019, 42, 573–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, R.; Slanchev, K.; Kraus, C.; Knyphausen, P.; Eming, S.; Hammerschmidt, M. Adult Zebrafish as a Model System for Cutaneous Wound-Healing Research. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2013, 133, 1655–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sveen, L.; Karlsen, C.; Ytteborg, E. Mechanical induced wounds in fish—A review on models and healing mechanisms. Rev. Aquacult. 2020, 12, 2446–2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Woedtke, T.; Reuter, S.; Masur, K.; Weltmann, K.-D. Plasmas for medicine. Phys. Rep. 2013, 530, 291–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graves, D.B. Oxy-nitroso shielding burst model of cold atmospheric plasma therapeutics. Clin. Plasma Med. 2014, 2, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoentsch, M.; Bussiahn, R.; Rebl, H.; Bergemann, C.; Eggert, M.; Frank, M.; von Woedtke, T.; Nebe, B. Persistent effectivity of gas plasma-treated, long time-stored liquid on epithelial cell adhesion capacity and membrane morphology. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e104559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergemann, C.; Hoppe, C.; Karmazyna, M.; Höntsch, M.; Eggert, M.; Gerling, T.; Nebe, B. Physicochemical analysis of argon plasma-treated cell culture medium. In Plasma Science and Technology—Progress in Physical States and Chemical Reactions; Mieno, T., Ed.; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2016; pp. 155–172. ISBN 978-953-51-2280-7. [Google Scholar]
- Wende, K.; Straßenburg, S.; Haertel, B.; Harms, M.; Holtz, S.; Barton, A.; Masur, K.; von Woedtke, T.; Lindequist, U. Atmospheric pressure plasma jet treatment evokes transient oxidative stress in HaCaT keratinocytes and influences cell physiology. Cell Biol. Int. 2014, 38, 412–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalghatgi, S.; Kelly, C.M.; Cerchar, E.; Torabi, B.; Alekseev, O.; Fridman, A.; Friedman, G.; Azizkhan-Clifford, J. Effects of Non-Thermal Plasma on Mammalian Cells. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e16270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, H.; Nakamura, K.; Mizuno, M.; Ishikawa, K.; Takeda, K.; Kajiyama, H.; Utsumi, F.; Kikkawa, F.; Hori, M. Non-thermal atmospheric pressure plasma activates lactate in Ringer’s solution for anti-tumor effects. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turrini, E.; Laurita, R.; Simoncelli, E.; Stancampiano, A.; Catanzaro, E.; Calcabrini, C.; Carulli, G.; Rousseau, M.; Gherardi, M.; Maffei, F.; et al. Plasma-activated medium as an innovative anticancer strategy: Insight into its cellular and molecular impact on in vitro leukemia cells. Plasma Proc. Pol. 2020, 17, e2000007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sergeichev, K.F.; Lukina, N.A.; Sarimov, R.M.; Smirnov, I.G.; Simakin, A.V.; Dorokhov, A.S.; Gudkov, S.V. Physicochemical Properties of Pure Water Treated by Pure Argon Plasma Jet Generated by Microwave Discharge in Opened Atmosphere. Front. Phys. 2021, 8, 596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biscop, E.; Lin, A.; Van Boxem, W.; Van Loenhout, J.; De Backer, J.; Deben, C.; Dewilde, S.; Smits, E.; Bogaerts, A. The Influence of Cell Type and Culture Medium on Determining Cancer Selectivity of Cold Atmospheric Plasma Treatment. Cancers 2019, 11, 1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergemann, C.; Rebl, H.; Otto, A.; Matschke, S.; Nebe, B. Pyruvate as a cell-protective agent during cold atmospheric plasma treatment in vitro: Impact on basic research for selective killing of tumor cells. Plasma Process Polym. 2019, 16, 1900088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakers, S.; Klinger, M.; Kruse, C.; Gebert, M. Pros and cons of fish skin cells in culture: Long-term full skin and short-term scale cell culture from rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2011, 90, 1041–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rakers, S.; Imse, F.; Gebert, M. Real-time cell analysis: Sensitivity of different vertebrate cell cultures to copper sulfate measured by xCELLigence(®). Ecotoxicology 2014, 23, 1582–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, D.; Hohne, M.; Pinkert, C.; Piasecki, A.; Ummelmann, E.; Brinster, R.L. Immortalized differentiated hepatocyte lines derived from transgenic mice harboring SV40 T-antigen genes. Exp. Cell Res. 1988, 175, 354–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henning, W.; Bohn, W.; Nebe, B.; Knopp, A.; Rychly, J.; Strauss, M. Local increase of beta 1-integrin expression in cocultures of immortalized hepatocytes and sinusoidal endothelial cells. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 1994, 65, 189–199. [Google Scholar]
- Nebe, B.; Rychly, J.; Knopp, A.; Bohn, W. Mechanical induction of 1-integrin mediated calcium signaling in a hepatocyte cell line. Exp. Cell Res. 1995, 218, 479–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoentsch, M.; von Woedtke, T.; Weltmann, K.D.; Nebe, J.B. Time-dependent effects of low-temperature atmospheric pressure argon plasma on epithelial cell attachment, viability and tight junction formation in vitro. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2012, 45, 025206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weltmann, K.-.D.; Kindel, E.; Brandenburg, R.; Meyer, C.; Bussiahn, R.; Wilke, C.; von Woedtke, T. Atmospheric Pressure Plasma Jet for Medical Therapy: Plasma Parameters and Risk Estimation. Contrib. Plasma Phys. 2009, 49, 631–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etlinger, H.M.; Hodgins, H.O.; Chiller, J.M. Rainbow trout leukocyte culture: A simplified method. In Vitro 1976, 12, 599–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegl, E.; Albrecht, S.; Lüdtke, B. Long-term liquid culture of haematopoietic precursor cells from the head kidney and spleen of the rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Comp. Haematol. Int. 1993, 3, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Ostrikov, K. Dosing: The key to precision plasma oncology. Plasma Process Polym. 2020, 17, e1900178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puck, T.T.; Cieciura, S.J.; Robinson, A. Genetics of somatic mammalian cells III. Long-term cultivation of euploid cells from human and animal subjects. J. Exp. Med. 1958, 108, 945–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maranga, L.; Coroadinha, A.S.; Carrondo, M.J. Insect cell culture medium supplementation with fetal bovine serum and bovine serum albumin: Effects on baculovirus adsorption and infection kinetics. Biotechnol. Prog. 2002, 18, 855–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Zoelen, E.J.J.; Stortelers, C.; Lenferink, A.E.; Van de Poll, M.L. The EGF domain: Requirements for binding to receptors of the ErbB family. Vitam Horm. 2000, 59, 99–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Valk, J.; Bieback, K.; Buta, C.; Cochrane, B.; Dirks, W.G.; Fu, J.; Hickman, J.J.; Hohensee, C.; Kolar, R.; Liebsch, M.; et al. Fetal Bovine Serum (FBS): Past—Present—Future. ALTEX 2018, 35, 99–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gstraunthaler, G.; Lindl, T.; van der Valk, J. A plea to reduce or replace fetal bovine serum in cell culture media. Cytotechnology 2013, 65, 791–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hokanson, K.E.F.; Kleiner, C.F.; Thorslund, T.W. Effects of Constant Temperatures and Diel Temperature Fluctuations on Specific Growth and Mortality Rates and Yield of Juvenile Rainbow Trout, Salmo gairdneri. J. Fish. Res. Board Can. 1977, 34, 639–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swirplies, F.; Wuertz, S.; Baßmann, B.; Orban, A.; Schäfer, N.; Brunner, R.M.; Hadlich, F.; Goldammer, T.; Rebl, A. Identification of molecular stress indicators in pikeperch Sander lucioperca correlating with rising water temperatures. Aquaculture 2019, 501, 260–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van‘t Hoff, J.H. Études de Dynamique Chimique/Studies in Dynamic Chemistry; F. Muller & Co: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1884. [Google Scholar]
- Vickery, L.; Prentice, A.E.J.; Hobbs, J.K.; Mulholland, A.J.; Van der Kamp, M.W.; Pudney, C.R.; Parker, E.J.; Schipper, L.A. On the Temperature Dependence of Enzyme-Catalyzed Rates. Biochemistry 2016, 55, 1681–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Sáez, A.J.; Schwille, P. Stability of lipid domains. FEBS Lett. 2010, 584, 1653–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arora, M. Cell Culture Media: A Review. Mater. Methods 2013, 3, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adachi, T.; Tanaka, H.; Nonomura, S.; Hara, H.; Kondo, S.; Hori, M. Plasma-activated medium induces A549 cell injury via a spiral apoptotic cascade involving the mitochondrial-nuclear network. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2015, 79, 28–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tornin, J.; Mateu-Sanz, M.; Rodríguez, A.; Labay, C.; Rodríguez, R.; Canal, C. Pyruvate Plays a Main Role in the Antitumoral Selectivity of Cold Atmospheric Plasma in Osteosarcoma. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 10681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takai, E.; Kitamura, T.; Kuwabara, J.; Ikawa, S.; Yoshizawa, S.; Shiraki, K.; Kawasaki, H.; Arakawa, R.; Kitano, K. Chemical modification of amino acids by atmospheric-pressure cold plasma in aqueous solution. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2014, 47, 285403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stadtman, E.R.; Levine, R.L. Free radical-mediated oxidation of free amino acids and amino acid residues in proteins. Amino Acids 2003, 25, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Friedman, G.; Fridman, A.; Ji, H.F. Decomposition of sugars under non-thermal dielectric barrier discharge plasma. Clin. Plasma Med. 2014, 2, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, D.; Nourmohammadi, N.; Bian, K.; Murad, F.; Sherman, J.; Keidar, M. Stabilizing the cold plasma-stimulated medium by regulating medium’s composition. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halliwell, B. Cell culture, oxidative stress, and antioxidants: Avoiding pitfalls. Biomed. J. 2014, 37, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, R.; Adhikari, S.; Patro, B.S.; Chattopadhyay, S.; Mukherjee, T. Free radical scavenging behavior of folic acid: Evidence for possible antioxidant activity. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2001, 30, 1390–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
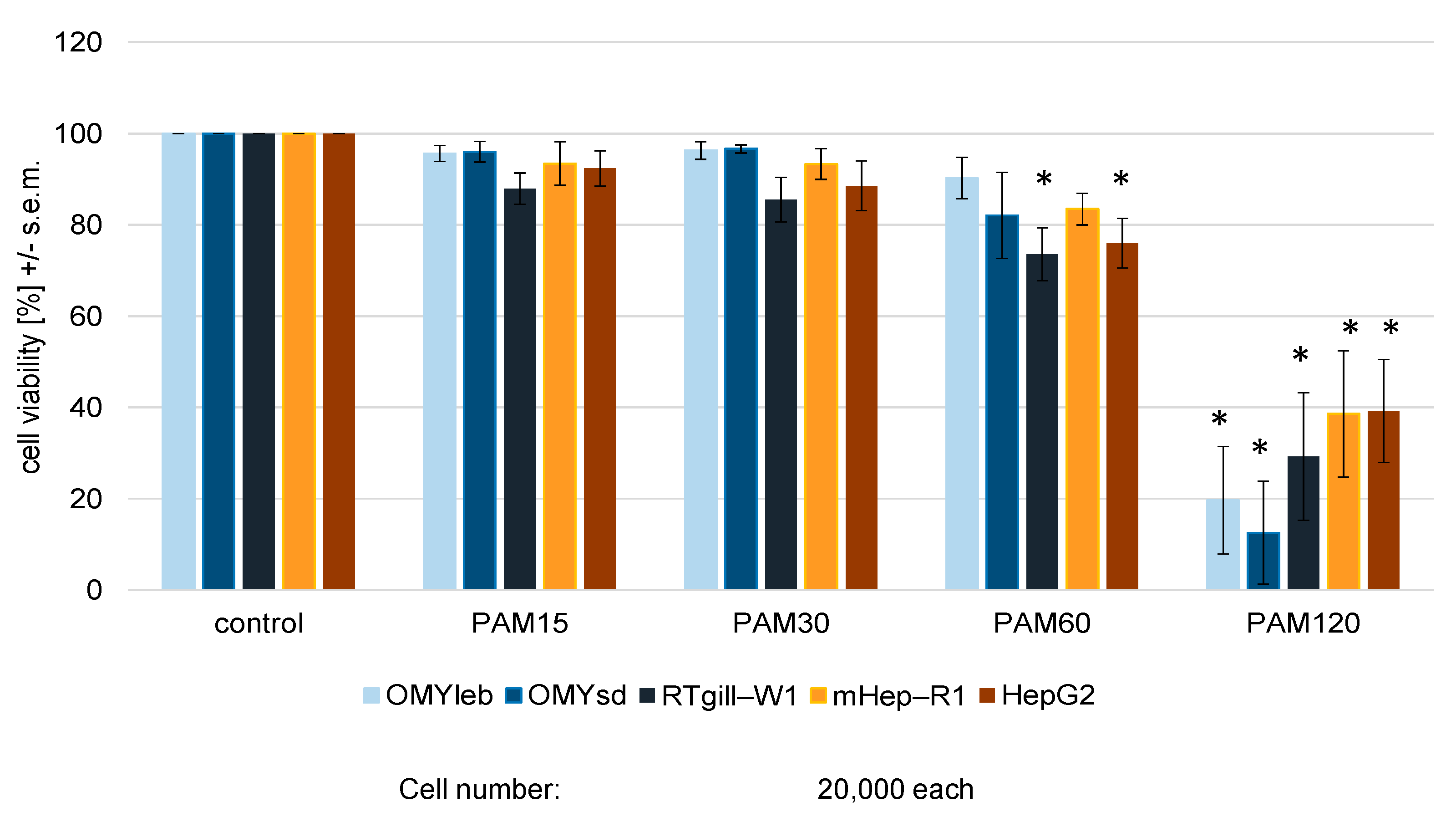


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rebl, H.; Bergemann, C.; Rakers, S.; Nebe, B.; Rebl, A. Plasma Treatment of Fish Cells: The Importance of Defining Cell Culture Conditions in Comparative Studies. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 2534. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11062534
Rebl H, Bergemann C, Rakers S, Nebe B, Rebl A. Plasma Treatment of Fish Cells: The Importance of Defining Cell Culture Conditions in Comparative Studies. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(6):2534. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11062534
Chicago/Turabian StyleRebl, Henrike, Claudia Bergemann, Sebastian Rakers, Barbara Nebe, and Alexander Rebl. 2021. "Plasma Treatment of Fish Cells: The Importance of Defining Cell Culture Conditions in Comparative Studies" Applied Sciences 11, no. 6: 2534. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11062534
APA StyleRebl, H., Bergemann, C., Rakers, S., Nebe, B., & Rebl, A. (2021). Plasma Treatment of Fish Cells: The Importance of Defining Cell Culture Conditions in Comparative Studies. Applied Sciences, 11(6), 2534. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11062534







