Abstract
In recent years, there has been a growing demand for cybersecurity experts, and, according to predictions, this demand will continue to increase. Cyber Ranges can fill this gap by combining hands-on experience with educational courses, and conducting cybersecurity competitions. In this paper, we conduct a systematic survey of ten Cyber Ranges that were developed in the last decade, with a structured interview. The purpose of the interview is to find details about essential components, and especially the tools used to design, create, implement and operate a Cyber Range platform, and to present the findings.
1. Introduction
In recent years, cyber attacks, especially those targeting systems that keep or process sensitive information, are becoming more sophisticated. Critical National Infrastructures are the main targets of cyber attacks since essential information or services depend on their systems, and their protection becomes a significant issue that is concerning both organizations and nations [1,2,3,4]. Attacks to such critical systems include penetrations to their network and installation of malicious tools or programs that can reveal sensitive data or alter the behaviour of specific physical equipment.
Following this increase in cyber attacks, the need for professionals will also continue to increase in the upcoming years. According to predictions from Cybersecurity Ventures, an estimated 3.5 million cybersecurity jobs will be available and eventually unfilled by 2021. While global Cybercrime damages are predicted to reach $6 Trillion annually by 2021 [5], 61% of companies find most of the cybersecurity applicants unqualified [6]. The majority of chief information security officers around the world are worried about the cybersecurity skills gap, with 58% of CISOs believing the problem of not having an expert cyber staff will worsen [7].
Gartner Inc. [8] delivered its first-ever forecast report titled: “Forecast Analysis: Container Management (Software and Services) Worldwide”, for the software container management software and services market, stating that adoption of the technology will be widespread. Software containers have enjoyed massive growth in recent years. Popular with developers, they provide a way for applications to be built once and run in any kind of computing environment, helping make enterprises much more agile. Gartner reckons that software containers will become the “default choice for 75% of new customer enterprise applications” by 2024. As a result, 15% of all applications will be running in containers by then, up from just 5% today.
Training activities and environments that can support challenging situations, followed by concrete guidance, procedures, and tools are needed. These platforms can help individuals to react in different, unpredictable situations in a collective and collaborative way. This environment should blend simulations and emulations of real components and systems, embedding different attack and defense mechanisms [9] and must be able to adapt to a variety of different incidents, in order to be cost-effective and attractive for organizations and educational institutes. Experiential learning is an educational technique that proposes the active involvement of the participants in order to help them learn through experience—an efficient method for delivering experiencing learning exercises as part of serious games. Cyber ranges are exercising environments that contain both physical and virtual components and can be used to represent realistic scenarios for training [10].
In recent years, cyber ranges have been offering additional features/capabilities from a simple simulation environment. Chandra [11] proposed that efficiency may be achieved by harnessing operating system container technology. Carnegie Mellon University [12] has developed by SEI open-source software tools to create secure and realistic cyber simulations. These tools recreate the real world and make training exercises more realistic.
In this article, we present the current state of the art on testbeds and cyber ranges that are used for training and research purposes. A systematic review of the literature on cyber range systems was carried out and the study revealed that there is a variety of implementations with different approaches that have been developed in different environments, using real, virtual, or hybrid equipment. Moreover, in order to better understand what the important components of a modern cyber range (CR) are, we conducted structured interviews with technical directors that have developed and used recently cyber ranges and present the findings.
The contributions of the article are:
- It presents the current state of the art on testbeds and cyber ranges.
- It presents the findings of a set of structured interviews with organizations that have a testbed and cyber range.
- It discusses the findings and gives insights of modern cyber ranges.
The findings of the research will be a guide for the effort to design, develop and implementation of a Cyber Range platform for the University of West Attica (UNIWA) but can also be a guide for other cyber ranges that are under development. UNIWA was founded in March 2018, from the merging process of two Technological Institutes. It operates with high educational and research standards and strives to respond to the ever-increasing demands of modern society for the creation of executives that have attained a solid scientific and technological background. UNIWA is the third-largest in Greece in terms of student numbers, approximately 52,000 undergraduates, 1150 postgraduates, and 210 doctoral students. The aim of a modern cyber range should be to enhance courses with hands-on experience of participants. In addition, it will enhance the research goals of the university through using a more complex and realistic environment than it currently has. UNIWA has a cybersecurity team (INSSec) with active participation in national and international cybersecurity exercises over the last decade as well as CTF competitions such as UniCTF 2019 and UniCTF 2020. In addition, it organized the CTF competition [13], UniwaCTF 2019, a competition between Greek universities. A Cyber Range system will enhance the realism of CTF contests, allowing UNIWA to organize more complex cyber exercises, such as the blue vs. red team..
The remainder of the paper is organized as follows: Section 2 discusses related surveys and showcases the value of this article. Section 3 introduces the key concepts and the overall architecture of current testbeds and cyber ranges. Section 4 presents the findings of the questionnaire. Section 6 discusses the findings and concludes the paper.
2. Related Surveys
During this literature review conducted from March to June 2020, several cyber ranges and testbeds were identified in different domains, such as Educational, CTF, Industrial Control Systems, Cyber Physical, and SCADA.
Davis and Magrath (2013) [14] conduct a survey of Cyber Ranges and classified their findings into three categories: Modeling and Simulation, Ad-hoc or Overlay, and Emulations. Specifically, their survey had the purpose of assisting organizations to select and build their desired CR capability. Hence, they surveyed the available options for constructing and managing a CR, for monitoring and analysis, training scenarios, communities for collaboration, and commercial offerings. They categorized CR using a two-level model. Firstly, they distinguished the CRs by their type, as Simulation, Ad-hoc or Overlay and Emulation. They also named the fourth category as Analytics without actually using it. Following previously defined methodologies, they categorized a CR as simulation when utilizing software models of real cases, as overlay if they use the real production equipment, and as emulation in the case of running the real applications on separate equipment. The second-level criteria of their categorization have been the sector the CR supports and the categories have been academic, military or commercial. The survey makes interesting points about the above-mentioned categories. Simulation CRs are sterilized, emulation ones have more realistic behaviour, but they are expensive, while overlays are only a small minority. According to the survey, the emulation CRs are the best category, especially when using virtualization. Moreover, the survey states that the main use of CRs is training, leaving far behind cybersecurity testing and research and development. This survey is quite broad as it covers almost 30 CRs, and it fulfills its aim. It refers widely to military developed and operated cases. This is expected as, at the time, military implementations had quite a few operating CRs. However, this survey is already seven years old, meaning that a lot of things have changed since. Moreover, it overlooks the cases where several categories are combined in hybrid cross-category environments.
Holm (2015) [15] surveyed 30 ICS testbeds. This survey has been a part of a study about critical infrastructures and eventually refers specifically to Industrial Control Systems (ICS). The study was motivated by the increasing vulnerability of ICS to cyber-attacks. It was titled “Virtual Industrial Control System Testbed” and was performed for FOI, the Swedish Defense Research Agency. The main purpose of the study was to specify the way to create a high-fidelity Virtual Industrial Control System (VICS) and the first step had been surveying the existing relevant testbeds through five Research Questions. The expected outcome would be the creation of a new testbed (CRATE). The survey collected information from 30 ICS testbeds in 12 countries. The study covers several testbed characteristics like the three methods that can be used to implement ICS in testbeds (virtualization, simulation, and hardware), including relevant subcategories (Operating System virtualization, Programming Language virtualization, Library virtualization) and categorization of these testbeds’ objectives into 11 categories (Vulnerability analysis, Education, Tests of defense mechanisms, Power system control tests, Performance analysis, Creation of standards, Honeynet, Impact analysis, Test robustness, Tests in general, Threat analysis). Furthermore, the survey presents per category how the reviewed 30 testbeds implement their control center, communication architecture, field devices, and observed/controlled processes. The available categories are again Virtualization, Simulation, Emulation, and Hardware. However, this survey leaves room for hybrid methods. In addition, the survey states Fidelity, Repeatability, Measurement Accuracy, and Safe execution of tests as the basic requirements that testbeds should comply. It is clarified though that these requirements are not a product of the survey itself, but they pre-existed. The survey concludes that none of the questioned testbeds implements an overlay model (enables executing a real field device inside a virtual/emulated container). The complexity of ICS accounts for this conclusion. Finally, it distinguishes vulnerabilities as Policy and Procedure Vulnerabilities, Platform Vulnerabilities, and Network Vulnerabilities. Finally, the survey describes the architecture and functionality of a designed testbed (CRATE). This survey follows a stable methodology, approaching the testbeds from various different angles. Moreover, the analysis has taken into account a satisfactory amount of 30 testbeds. However, its main focus is the industrial (ICS) testbeds, and, eventually, the results are narrowed to this specific category of testbeds. In addition, since the time of the survey (2015), ICS systems have become more connected and have revealed more surface to the attackers. Unavoidably, the survey and its vulnerability analysis haven’t taken into account the evolved and interconnected situation nowadays.
Yamin [16] presents a survey of Cyber Ranges and security testbeds and provide a taxonomy and an architectural model of a generic Cyber Range. Their work begins with the definition of a cyber exercise where they define the stages of such an exercise as well as the teams involved (white, blue, red). They identify a gap in existing surveys as they characterize them as sectorial or outdated. The chosen methodology of this survey has been the systematic literature review which consists of eight stages (Statement of purpose, protocol establishment, a search of the sources, screening of the literature, assessment, data extraction, synthesis of the outcome, review). During this process, they produce an initial taxonomy where a CR consists of five basic pillars (scenario, monitoring, teaming, scoring, management). Indicative of the width of the survey is the variety of cyber exercise teams/roles they have identified (red, blue, white, orange, purple, yellow, green, autonomous). An outcome of the survey is a classification of the capabilities and functionalities of modern CRs as well as a new taxonomy based on the information gathered, with six pillars (scenario, monitoring, learning, management, teaming, environment) has been produced. The survey has researched and recorded a multitude of simulation, emulation, hardware, management, monitoring, traffic generation, and other relevant tools and solutions implemented in contemporary CRs. In addition, the functional architecture of a generic Cyber Range is described. Based on the surveyed CRs, the survey attempts to predict the future shape of the Cyber Range environment. This survey is, by all means, an impressive work that firstly analyses and then combines data from multiple papers mainly for the period 2015–2017. The survey performs a wide approach and analysis of the literature. However, the survey concludes in a rather conservative manner, and the predicted future cyber ranges don’t quite differ from the present ones.
Kucek (2020) [17] investigates the underlying infrastructures and CTF environments, specifically open-source CTF environments, and examined eight open-source CTF environments. The survey aims to be used as a valuable reference for whoever is involved in CTF challenges. Starting from 28 platforms, the survey shortlisted 12 environments that are open-source and finally managed to examine eight of them (CTFd, FaceboookCTF, HackTheArch, Mellivora, Pedagogic-CTF, PicoCTF, RootTheBox, WrathCTF), and to extract valuable conclusions and comparison data. The study was motivated by the popularity of CTF events combined with the lack of studies that examine the underlying infrastructure and configuration of real-time cyber exercises like CTFs. Once more, it starts with a questionnaire of four Research Questions (RQs). The survey distinguished the open-source CTF environments and attempted empirical research of them. They followed an organized methodology of five comprehensive steps (general review, shortlist of open-source CTFs, install, configure challenges, conclusions). In order to empirically examine each of the eight shortlisted environments, the survey conducted 16 different challenges categorized in five CTF types (quiz, jeopardy, Attack-defense, Mixtures, King of the Hill). Some interesting results include the architecture of the platforms. Some of them run on a certain O/S, while others run on any O/S. The next (higher) layer above the O/S is either the container layer or the virtualization one. The CTF challenges are configured on top of these layers. The survey concludes that the examined environments differ in some features they support and the respective configurations that are available. All the examined platforms have some generic features (participant registration, challenge provision, user manual, scoring methodology). The platforms differ in the specifics and the available options of the mentioned features. The survey has been both original and ambitious to deepen the performed analysis. However, its main objective is the CTF implementations and, consequently, it is narrowed to this specific category of testbeds. Moreover, the actual research is limited to eight CTF environments. Starting from around 30 candidate Cyber Ranges, they finally realized the empirical study on eight of them because of various reasons (proprietary environments, lack of adequate documentation, etc.).
Ukwandu [18] present a survey of Cyber Ranges and security testbeds. In this very recent survey, only publications from selected databases and only from the last five years (2015–2020) are examined. A taxonomy is developed to provide a broader comprehension of the future of Cyber Ranges and testbeds. The paper makes multiple references to the smart-everything technological transformation which must be taken into account when assessing or training in cybersecurity. Once more, the followed approach has been the chain: plan, select, extract, execute. The survey is presented as an overview of the Cyber Ranges and Test Beds which can be found in the literature and 44 CRs are identified. These instances are categorized in multiple ways, initially based on their application (Military/Defense/intelligence, Academic, Commercial, Law Enforcement, etc.) and their type (Private, Public, Federated). In addition, the teaming options are presented. The survey presents a classification of the found CRs according to their implementation method (Emulation, Simulation, Overlay, Live). The survey describes in fair detail the architecture and interconnection of CR building blocks. The survey provides a definition of a CR scenario and then different scenario options and differentiation factors (design, validation, deployment) are described. The stages that a training testbed should include are presented in an impressively simple but straightforward plan. The different approaches to training are described (gamification, Mock Attack Training, Role-Based Training, exercises). The survey argues in favor of the differentiation between Cyber Ranges and Test Beds. It presents Cyber Ranges as far more complicated than Testbeds. This argument concludes with the need for different taxonomies, respectively. Finally, according to the survey, the future shape of Cyber Ranges and Test Beds is going to combine real-time, intelligent implementations featuring mobility, automatic configuration, and integration of different technologies, applications, and appliances. Throughout this extensive analysis, the survey doesn’t avoid some minor contradictions. Moreover, our survey integrates a structured interview that has been performed on a selected group of representative cyber ranges.
As shown in Table 1, we classify the surveys according to the following criteria:

Table 1.
Related surveys on Cyber Ranges and TestBeds.
- Focus area: We categorize surveys in relation to their scope.
- Method: this category indicates the method of collection and analysis of the data that are related to the CRs.
Most of the surveys, including ours, have a broad scope, while only two of them were focused on a specific area of research, ICS and CTFs. The main difference of our survey as compared to the previous ones is the use of mixed data collection methods that included both literature review and structured interviews with Universities and agencies that have deployed and run such CRs. This method helped us cover the lack of published information in terms of architecture, topology and tools.
3. Background
Among many cyber incidents that have occurred in the last decade, two of them can be considered as major triggers for the development of Cyber Ranges—firstly the attack against the nuclear program of Iran. This attack that was revealed in 2010 used the computer worm Stuxnet and specifically targeted the programmable logic controllers (PLCs) used to automate machine processing systems. Since then, the malware has been mutated and discovered in other industrial and energy installations. Secondly, on 23 December 2015 via a series of cyber-attacks, cyber attackers remotely controlled the Ukrainian power grid, specifically the SCADA distribution management system, and eventually caused a significant power outage to the Ukrainian constituency. The above mentioned incidents have been more than persuasive of the vulnerability of industrial systems. This resulted in widely opening the way for the development of cyber ranges.
Initially, an up-to-date survey of the present situation of Cyber Range systems was conducted. This survey has revealed multiple useful outcomes. Some of them are the characteristics of modern cyber ranges and testing beds, the various development platforms used, the tools and methods which are implemented, how fast do the implementations occur, how are the exercises conducted and executed, how are the relevant scenarios created and implemented, etc.
Apart from the need to test and evaluate the cybersecurity aspect of applications, tools, and systems, cyber ranges are extremely useful for the capacity building of cyber experts. They must develop and possess several abilities like being deeply technically skilled, capable of recognizing and responding to complicated and urgent situations, able to assess risks and vulnerabilities, to handle uncertainty, to solve problems to provide explanations to think adversarial. In a nutshell, today’s security experts must possess a “security mindset” as described in [19].
Various definitions of cyber ranges have been given in the relevant literature and publications. The definition given in NIST one-pager [20] has been chosen as the first among equals. Thus, according to NIST, cyber ranges are interactive, simulated representations of an organization’s local network, system, tools, applications that are connected to a simulated Internet level environment. They provide a safe, legal environment to gain hands-on cyber skills and a secure environment for product development and security posture testing.
The research performed reveals that the environment of cyber ranges in terms of their development can be categorized into three main types: simulation, emulation, and hybrid. A Simulation involves using a model, a virtual instance in order to recreate a complex network environment based on the real network components’ behaviour. Emulation is when the cyber range runs on the dedicated physical network infrastructure of the CR. Hybrid emerges from a customized combination of any of the above types. An additional category refers to overlay cyber ranges which are the instances that run in parallel with the actual production systems on the real equipment and infrastructure.
Recently, attention to Cyber Ranges has been growing. Cyber range systems are predominantly used for three main objectives: Research, Training and Exercise.
- Research (testing implementations including methods, tools, building blocks and systems)
- Training/Education (academia, specialized security courses and cyber-security certifications)
- Exercises/Competitions on Cyber Security (security training by means of cyber security exercises like Capture the Flag or Cyber Defense Exercises).
Research demands for environments that are fully controlled and isolated but at the same time complex to develop and test a new tool, or to design new attack techniques or methods. The training serves cybersecurity practice and education. Trainees have the opportunity to practice various cyber range scenarios, according to their specific training needs. The third and maybe most popular category of cyber range use nowadays is for cyber exercises. Here, the users compete in cyber contests, capture the flag competitions, hack the box challenges, and attack/defense games.
We can also categorize cyber ranges based on their operator. The main players for the development of Cyber Ranges and similar testbeds have been universities, government agencies, military research centers, international organizations, and their affiliates. While the details of some Cyber Ranges are publicly available, there also exist cyber ranges that are funded by the military and governments throughout the world and their details are eventually classified. Throughout the recent development and widening of the cyber range constituency, the concept of a federation of cyber ranges has emerged. The concept of federation relies on the consideration that a single cyber range would have enormous costs and would be extremely complicated if it was to have all the necessary features and functionalities, the whole package. Therefore, it would be better organized, and also modular and in effect realistic, if multiple cyber ranges, each within a specific area of expertise, could collaborate in order to offer to their users a wide variety of use cases and different scenarios. For example, some cyber ranges simulate social media networks or publicly available internet resources while other cyber ranges may be specialized in simulating industrial control systems or critical infrastructures. The combination of the capabilities of different cyber ranges would result in the development of a much broader simulation environment available for their end-users, while at the same time the overall cost would remain unchanged. Following this concept, several cyber range federations are being developed. Such an example is the Cyber Ranges Federation project which aims at building an EU-wide cyber range. Participants of this federation include eleven EU member states, the European Space Agency (ESA) as well as the European Defence Agency (EDA). Another relevant initiative is the CyberSec4Europe project which refers to designing, testing and demonstrating potential governance structures for a future European Cybersecurity Competence Network. One more example is the ECHO project (European network of Cybersecurity centers and competence Hub for innovation and Operations) launched by the European Commission with the vision to establish and operate a Cybersecurity Competence Network.
The Deployment models of cloud computing are categorized into four commonly used categories. Private Cloud, Public Cloud, Community Cloud and Hybrid Cloud. Additionally, there are three Services models of Cloud Computing: Infrastructure, Software, and Platform as a Service (IaaS, SaaS, PaaS). In the SaaS model, a software provider sells a software application that can be used on-demand. In the IaaS, the provider offers as service computing resources like storage, server or peripherals. The users can have a virtual server in a very short time, and they pay only for the resources they use. The PaaS model represents an abstraction layer between the IaaS and SaaS and its target group includes deployers and developers. Infrastructure platforms and tools include OpenStack [21], Opennebula [22], Proxmox [23], VMware [24], Public cloud (AWS), Minimega [25] and KVM [26].
Infrastructure as code (IaC) is another step ahead towards infrastructure agility and flexibility. With IaC, the management of infrastructure (networks, virtual machines, load balancers, and connection topology) is realized in a descriptive model. Some Infrastructure as code (IaC) tools that we came across in our survey include Chef [27], Puppet [28], Ansible [29], SaltStack [28], Terraform [30], and Vagrant [27].
In the present paragraph, some terms that are necessary for the forthcoming analysis are defined. When we talk about deployment, we refer to the process of putting a new application, or a new version of an application, to run on a prepared application server. Orchestration is the arrangement or coordination of multiple systems that are designed to cooperate. Provisioning (used by DEVOps) refers to getting computers or virtual hosts to use and installing needed libraries or services to them. Configuration management (CM) is a system engineering process for the establishment and maintenance of a product’s performance, functional, and physical attributes with its requirements, design and operational information. Configuration management aims at bringing consistency in the infrastructure. The above-mentioned tools (Chef, Puppet, Ansible, SaltStack) are all “configuration management” tools, which means they are designed to install and manage software on existing servers, whereas Terraform is an “orchestration tool”, meaning that it is designed to provision the servers themselves, leaving the configuration of these servers to other tools. These two categories are not mutually exclusive, as most configuration management tools can do some degree of provisioning and most orchestration tools can do some degree of configuration management.
Using the cyber range background and environment as described in the previous paragraphs, we now move forward to explain the features of the cyber ranges we found in our survey. We analyze 25 CRs, and we write about features that they use (see Table 2) like objective, environment, supporting sector, etc. Research (R), Training (T), Exercise (E), Education (ED), Operations (O), Testing (TE), Academic (A), Military (M), Government (G), Private Enterprise (PE), Industry (I), Demonstrations (DM), Development (DV),Testing (TS), Emulation (EM), Simulation (S), Hybrid/Cyber Physical (HCP), VMWARE (VW), Openstack (O), Minimega (MN), TerraForm (TR), Public cloud AWS (AW), QEMU / KVM (Q), Virtualbox (VB), Custom (C), Yes (Y), No (N), Not Available (N/A), Docker (D), Instructors (IN), Provided on demand (OD), In house (IH), On-Premise (OP), Online (ON) and On-Site (OS). Then, based on these findings, we select the ten most representative cyber-ranges, and we moved forward with the structured interview (Table 3 and Table 4).

Table 2.
Summary of cyber ranges and testBeds.

Table 3.
Cyber Ranges’ features.

Table 4.
Cyber Ranges’ tools.
4. Analysis of Results
Due to the lack of several features that are not mentioned in the publications but also to have a better picture of the systems used, a structured questionnaire [61] (see Appendix A) was created and sent to selected universities and research centers that develop and maintain such systems (see Table 3 and Table 4).
Table 3 has the following analysis: Web (W), Cryptography (C), Forensics (F), Exploitation (E), Steganography (S), DDoS (DD), APT (AP), Ransomware (R), SQL Injections (SI), Malware Analysis (MA), Reverse Engineering (RE), Risk Management (RM), Information Security Economics (ISE), Cyber Crisis Management (CM), Cyber Policy Analysis (CP), Digital Forensics (DF), Software Security (SS, ICS Security (IC), Custom (CU), Request Base (RB), Digital Forensics (DF), Network security (NS), Web Security (WS), Software Security (SS), ICS Security (IC), OT Security (OS), Hardware Security (HS), Cloud Security (CS), Data-driven cybersecurity management (CM), On Premise (OP), Remote Access (RA), Local (L), SOC (SC), NOC (NC), CERT (CR), CSIRT (CS), CISO (CO), IT-Team (IT), Legal (LG), Managers (M), C-levels (CV), BLUE (B), RED (RD), GREEN (G), YELLOW (YL), WHITE (WT), PURPLE (P),Event (EV), Workshop (WS), Exercise (EX), and Educational Institutions (EI).
Table 4 has the following analysis: Manual Scripting (MS), Ansible (A), Docker containers (DC), Vagrant (V), Packer (P), Openstack Heat (OH), PROXMOX (PR), Virtualbox (VB), Openstack (O), Cloudformation (CL), VXLAN (VX), Labtainers designer tool (LDT), Custom (C), Artifacts Gathered (AG), Jeopardy Board (J), CloudCTF (CC), Internal Tools (IT), JSON (JS), YAML (YM), Multiple Formats (ML), XML (X), Automatic (A), Xentop (XT), API (AP), OSSIM (OS), Snort (SN), Suricata (SU), Netflow (N), Wireshark (W), MALCOM (M), Nagios (NG), Cloudwatch (CW), DNP3 (D), Bespoke (B), OpenFlow (OF), GHOSTS (G), AutoIT (AI), Bot(BT), Yes (Y), and Not Available (N/A).
The motivation for the questionnaire was, despite a large number of published works and surveys [14,15,16,17,18], the lack of data on the tools used for the development and management of Cyber Ranges, when used to organize cybersecurity exercises and provide a data-set for further research. At first, it was checked to see if there are cyber range systems in universities and research centers in Greece. The limited number of existing systems that are located in Greece led us to broaden the search in Europe, Asia and the rest of the world.
The questionnaire was addressed to technical directors or managers who were directly involved with the Cyber Range. The survey was conducted from 01/06/2020 until 04/08/2020. The results of the research were produced by 10 different systems located in nine different countries and two continents. The countries are the USA, the United Kingdom, Italy, Norway, Sweden, Finland, the Czech Republic, Belgium and Austria.
The first question was about the objective of the Cyber Range and, as expected, participants answered that their main objective is training.
The largest percentage of the participants use CR systems for research, training and security exercises [16,18]. No participant has developed their system exclusively to cover a single objective, and, more specifically, 80% of participants cover at least two, as shown in Figure 1.
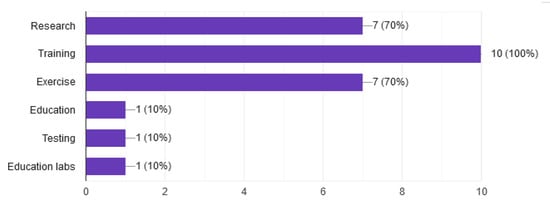
Figure 1.
Objectives of the Cyber Range.
Question 2. The questionnaire was sent to the CR system providers covering all four key areas [14] Academic, Government, Military, and Private Enterprise. We have covered this requirement due to the feedback from all areas, Figure 2.
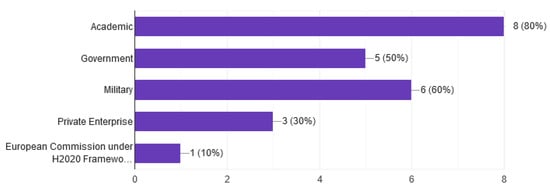
Figure 2.
Sectors of the Cyber Range.
Of course, the majority of the answers as shown in the figure supporting sector are mainly from the Academic sector. This is because military and Private Enterprise providers do not disclose details about their systems due to confidentiality, and the existing literature is limited. However, we have managed to cover all areas, even for the military and Private Enterprise sectors, and draw useful conclusions about technologies, implementations, and development tools as shown in the next questions.
In question 3, we have another categorization of a cyber range, which is the domain that the systems operate. Another area that is flourishing is the conduct of cybersecurity exercises [62,63,64]. As expected, the results of the domain cybersecurity competition are very high, Figure 3, about 80%, as well as in SCADA, reach 60%. An interesting conclusion from the analysis of the results is that 30% of the systems are focused only on conducting security exercises, and 20% only on SCADA.
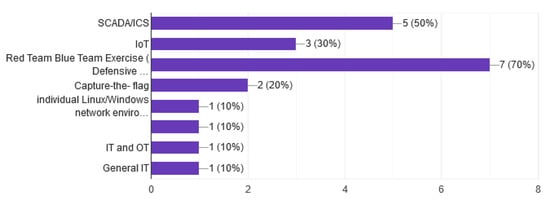
Figure 3.
Domains of the Cyber Range.
Mainly after the incident of Iran’s nuclear program, and the attack of the Ukraine power grid, a great development in cyber range systems aimed at improving the security of SCADA and ICS and OT generally was observed. By correlating questions 3, 4, and 5, we observe that cyber ranges do not focus only on only one domain as before but have evolved by adding new components and managed to cover many domains like business, banking, telecom, health, and transport.
Question 4 describes the security challenges that occur in Cyber Range platforms. The most popular challenge is web security that is provided by all responders. In addition, as shown in Figure 4, the Forensics come first with 80% and Exploitation and Malware analysis follows with 70%. Additionally, one of the responders stated that they can create any challenge based on specific demands.
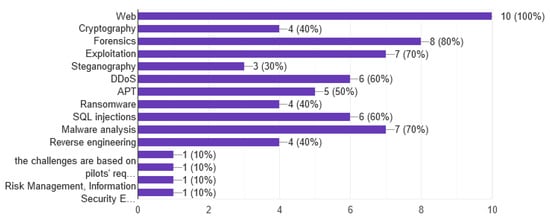
Figure 4.
Security challenges of the Cyber Range.
The content of security challenges [17] varies and depends on the type of cybersecurity competition or curriculum of the university/research center. Cyber security exercises allow students to gain hands-on experiences while immersed in environments that mimic real-world operational systems. Highly realistic training allows students to gain valuable experience that employers are looking for [65]. A very interesting approach is the inclusion of challenges like Risk Management, Information Security Economics, Cyber Crisis Management, and Cyber Policy Analysis. These are hot areas and we suggest other universities to add these kinds of challenges to their cyber range platforms.
A key motivation of our research is the development and implementation of a CR platform for the University of West Attica that covers three areas of research, education and conducting security exercises. Wanting to more deeply cover the educational side, we sought to find out if the CR platform is also used for educational purposes. All responders answered positively. According to Beveridge [65], injecting realism into cybersecurity training and education is beneficial to rapidly train qualified, skilled and experienced cybersecurity professionals. Additionally, we asked which courses they use for the CR platform. The most popular courses as shown in Figure 5 are network security by 80%, followed by web security and digital forensics by 70%, and software security by 60%.
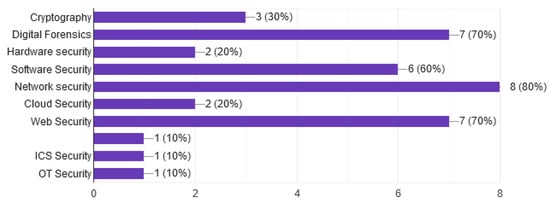
Figure 5.
Educational courses of the Cyber Range.
Universities are linked to the educational curriculum courses related to emerging technologies such as cloud security, OT security and Data-driven cybersecurity management. Cyber ranges can combine security courses and hands-on experience and give cybersecurity experts the mentality, the problem solving capability and the appropriate technical tools for capacity building.
Another categorization of Cyber Ranges is the type of environment. Davis [14] in 2013 categorize CR and security testbeds in three main categories emulation, simulation, and Ad-hoc or Overlay. In our questionnaire, we asked the participants to identify the environment also in three categories—the first is emulation: testbed built with real hardware or software, the second is a simulation: testbed built with software virtualization, and the last is Hybrid/Cyber-Physical: virtual testbeds connected with real hardware. Apart from one participant who had developed an emulated environment and two participants who have developed a simulation environment, all responders have chosen a mixed type of environment, as shown in Figure 6.
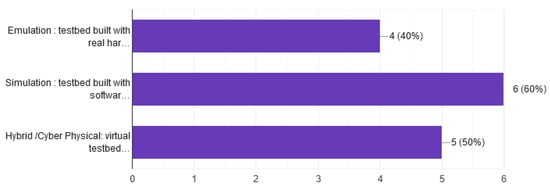
Figure 6.
Types of environment.
The rapid virtualization growth helps create complex environments, thus managing to achieve the highest possible accuracy, fidelity, scalability and flexibility while reducing implementation costs. Additionally, by using a simulation/hybrid environment, a university can develop a CR [35,66,67,68], while, before 2010, CR was developed for military purposes only (Emulab [69], NCR, StealthNet, and LARIAT [70]) mainly due to high development and maintenance costs.
In question 7, we discuss which type of virtualization technology is chosen for the development of CR, and, according to ECSO [71], there are two types, conventional and cloud virtualization. Conventional virtualization uses hypervisor-based technology and containers, mostly Docker. A list of both types of hypervisors containVirtualbox, Vmware, XenServer, Hyper-V, QEMU, etc. Cloud virtualization is divided into three types, public, private, and hybrid. The best advance of the cloud is the sharing of resources, great capabilities for automation and minimization of cost reduction [29]. OpenNebula, CloudStack, and OpenStack [27] are mostly used to deploy cloud virtualization [21,22,23]. The finding of questionnaires, as shown in Figure 7, says that up 50% uses the cloud, both Openstack and AWS, and 40% use traditional technology. In addition, we conclude that OpenStack is the main tool (44%) used to deploy cloud infrastructure.
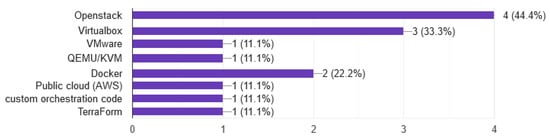
Figure 7.
Infrastructure platform.
The development of cloud computing has opened new horizons for the evolution of cyber ranges. Cloud environments constitute internet-based platforms to be used for computer technology. The technology used to develop the CR platforms is mainly open source and the use of commercial tools is partial. We found that the use of container technology has little impact on the systems we analyzed. We believe that there should be greater development through container technology since they improve realism and user behaviour [12].
Question 8 is about the type of access that CRs can provide to platform participants. As presented in Figure 8, these are on-premises 70%, remote access 80% and 10% local. Moreover, 60% of CRs can provide both types of access, on-premises and remote access. In addition, finally, one platform can provide only on-premises access. The advantage [65] of providing remote access to participants is important for conducting distance learning courses, or long-distance security competitions.
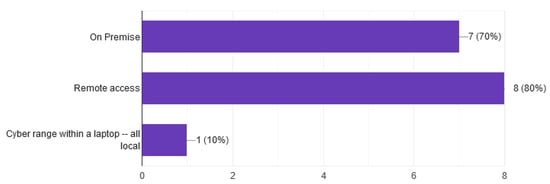
Figure 8.
Type of access.
Question 9 is one of the most important questions we asked in the questionnaire. When searching in the literature to find out how to implement a Cyber Range system, the result was disappointing and the findings were negligible, especially regarding military and commercial systems. With the main motivation of discovering the design technology and the implementation tools, we proceeded to compile this question. As shown in Figure 9, the technology of CRs is dominated by the use of Infrastructure as code (IaC) tools [27,28,29,30] and especially Ansible with 40%, Vagrant, and Packer. In addition, in a small percentage, where obviously there is no cloud infrastructure, the configuration of virtual machines is done with the use of manual scripting with an imprint in the speed of implementation and in the flexibility of configuration.
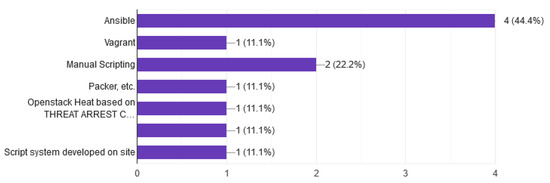
Figure 9.
Set up VMs.
Today, IaC is the process of managing and provisioning computer data centers through machine-readable definition files, rather than physical hardware configuration or interactive configuration tools. IaC tools are used to configure systems, deploy software and updates, and orchestrate. The biggest advantage is the speed and ease of their use as opposed to manual scripting.
The tools used for the network topology are shown in Figure 10. Network tools provided by the infrastructure platform are mainly used. This can guide researchers/developers to invest in network tools that can be adopted by other CR systems.
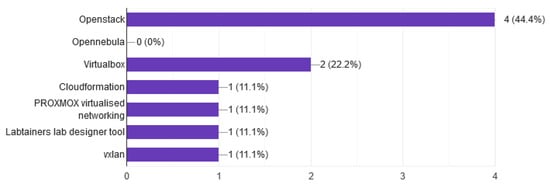
Figure 10.
Network topology.
In order to keep scoring during cybersecurity competitions like cyber security exercises or CTFs, several tools and mechanisms are provided. These tools are responsible for counting the flags in CTF [17] and awarding points, or artifacts from a CDX. As shown in Figure 11, the majority of scoring tools are custom made and depending on challenge, architecture of exercises, and infrastructure platforms.
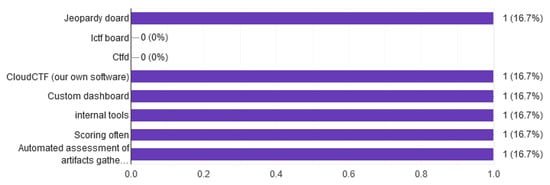
Figure 11.
Scoring tools for Cyber Ranges.
JSON and YAML are the main scripting language that is used as shown in Figure 12, for designing a CTF or CDX. In addition, with the use of scripting language, it became possible to create dynamic scenarios. Planning an exercise requires a script. The scenario was initially static and required the configuration of all parameters during the development of each exercise. This resulted in complex development and management of exercises, required high management costs, and demanded long development times recently, with the development of dynamic scripts [4,72] based on scripting languages such as JSON, YAML and XML or IaC [30] Tools.
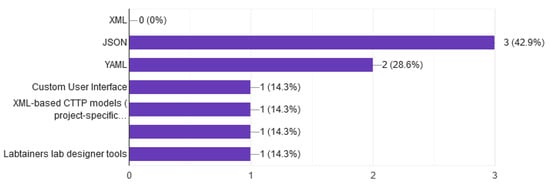
Figure 12.
Tools to create cyber security scenarios.
A CR platform should have the right tools for managing users and groups as shown in Figure 13. Moreover, the CR must have a graphical user interface (GUI), capable of managing resources [28] like memory, usage, performance, reports, error logs, alert, etc. The responders identified that most use tools that are provided by the platform (OpenStack, Proxmox, AWS) or developed their own tools.
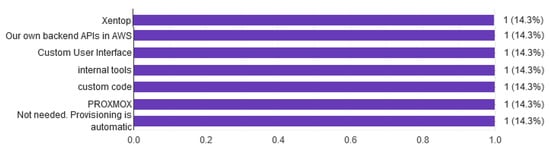
Figure 13.
Tools to manage.
Dynamic scenarios require minimal administrative effort and in less time (from seconds to a few minutes) that could include new environments with different network topologies.This may be an opportunity for researchers/developers to produce tools that can be used by other systems.
The CR platform must be able to monitor data. It must have all the necessary components for supervision, whether they are exercise training, research, or testing a system. The tools deploy depending on the type of exercise or field of the research. The responders answered that they are mostly used for monitoring purposes and open-source tools (see Figure 14), mainly SIEM tools such as OSSIM or Nagios. IDS tools such as Snort or Suricata are also used.
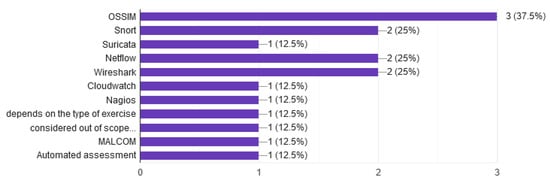
Figure 14.
Tools to monitor.
CR platforms use tools [73,74,75] for monitor data. OpenFlow and DNP3 have been used by the responders in several occasions, but mainly in-house tools or scripts are used, as shown in Figure 15. Testing of security tools [76] should take place under conditions that are as realistic as possible. Network traffic of the testing infrastructure should approach a real network of a company or a university [77]. Based on the answers, we don’t find a tool that has a high level of acceptance yet.
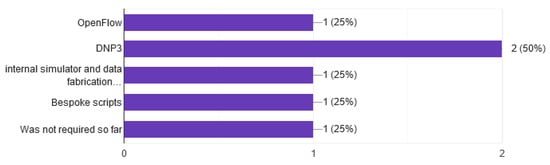
Figure 15.
Network traffic.
Another example of an automation user/team is the automation of the red team in conducting cybersecurity attacks. The use of such an automated team covers the need to find qualified cybersecurity experts with knowledge of attacking systems, which is very difficult. There are published papers describing how to create such red teams mostly in the military domain such as K0ala from Lincoln Laboratory [70] and SVED from FOI [48] that used for automating the behaviour of a red team. GHOSTS as shown in Figure 16, a tool developed by the SEI, creates non-player characters (NPCs) that behave realistically without human intervention in order to help build complex cyber simulations. GHOSTS create NPCs that behave like real people to generate context-driven traffic. As a result, creators of simulations can challenge participants in blue or red teams with engaging content that helps them develop elite skill sets [12,78] and red team automation. From the answers, we notice that systems have used the GHOSTS tool [12] that develops SEI and provided through GITHUB, while the other platforms have developed their own tools.
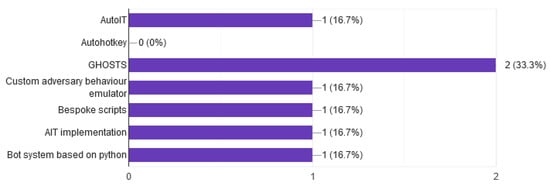
Figure 16.
User behaviour.
In general, scripting languages are capable of creating complex environments, including realistic user behaviour, thus improving realism. In such a use case scenario, an automated user can send or receive emails, browse the internet site, open office documents or print them, etc., resembling a typical office user that works in a company working environment. Realistic user behaviour is an important part of creating complex cybersecurity exercises.
In question 10, we identify how many groups can participate in an exercise. The answers were quite different and related not only to the implementation of the CR but also to the capacity of the infrastructure of the environment that supports it. The answers varied from systems that support only groups with one user to systems with a capacity of thousands of groups. However, on average, systems support up to 10 groups. Moreover, we examined the total number of participants that varies from one to thousands of simultaneous users. The average of users falls in the range between 50 and 100. Another point of measurement of the analysis and complexity of the exercises [79] is the number of different teams [16] that participate. As expected, the teams [80] that mainly participate are the blue 80% and the red 70%. In addition, apart from two participants who did not inform us about the teams, at least half of the participants stated that blue, red, yellow, purple, green, and white teams take part in the exercises as shown in Figure 17.
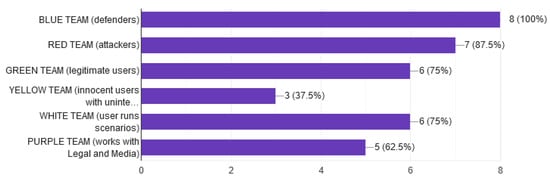
Figure 17.
Cyber Security Teams.
One main purpose of question 10 was also to identify the complexity of the exercises and the capacity of the cyber ranges. The roles of the participants are also very important, since they support, as shown in Figure 18, the development of security teams such as SOC, NOC, CERT, and CSIRT. It is also interesting that, in some cases, some other roles were used from CRs such as Managers, C-level executives, and legal representatives.
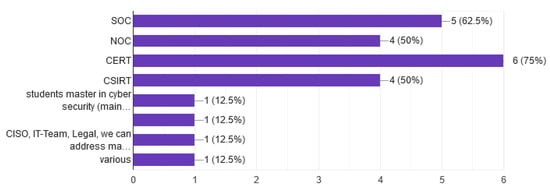
Figure 18.
Roles of participants.
In question 11, we asked the participants if the CR platform has already been used. As shown in Figure 19, 90% of the respondents answered positively. In many cases, a system is created for research purposes, such as a research program that has an expiration date. The CR systems analyzed in this questionnaire are already used for educational, research, or CDX and presented in a public event.
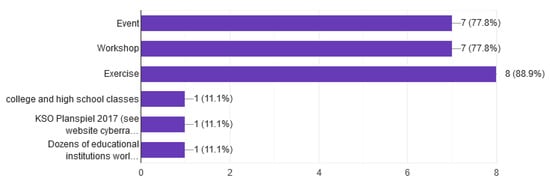
Figure 19.
What type of event.
The last question is about datasets. An important element of datasets is whether they contain measurable data. Researchers using datasets can evaluate the performance of IDSs, measuring their accuracy, false positives, and overall efficiency. In Figure 20, the results showed that a large percentage, around 60%, of the systems produce datasets or this action is included in the upcoming plans.
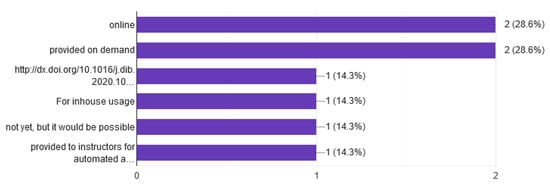
Figure 20.
Dataset.
The creation of a dataset that contains capture network traces, from cybersecurity exercises, can enhance or produce new sophisticated methods on detection techniques for cybersecurity attacks (see Figure 21).
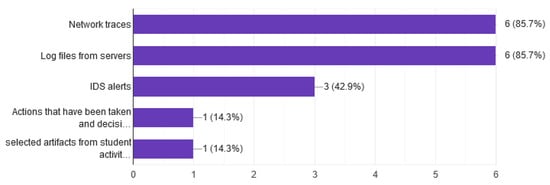
Figure 21.
Dataset.
5. Challenges and Future Directions
CR research teams should be focusing on improving various aspects of their testbeds. In addition, modern CRs should be enriched with novel features, such as various telecommunication capabilities, emulated Banking systems, hospitals [81], simulated smart grids, automated vehicles [82], Virtual Cyber Centres of Operation, wireless sensor networks, real time Intrusion Detection Systems [83], honeypots [84], novel authentication mechanisms [85], mobile security scenarios, and several privacy mechanisms. By adding these features, new attack scenarios can be easily deployed on a testbed, revealing vulnerabilities of the various systems and thus giving the researchers the opportunity of developing innovative defence mechanisms. Moreover, any novel CR should be built in a way that could be easily used for research purposes inside EU projects. This could be accomplished if the CRs are capable of being connected to various real-world devices to the network, making it that way ideal for launching attacks and testing the defence mechanisms of various systems. One other important aspect that should be taken into account is the capability of modern CRs to create measurable data in a semi automated way with limited human intervention.
Modern CRs should include a portable version for demonstration purposes and for easy deployment as a modern teaching instrument in various cyber security events that take place around Europe. Moreover, research teams should also be working towards the capability of their CRs to provide remote access to researchers. Via such a federated model, researchers all around the world will be given the opportunity to implement various protocols and study their behaviour in custom tailor-made environments. Finally, the need for moving from traditional cyber ranges to digital twins is a trend that is going to become dominant in the near future, especially for replicating critical infrastructures.
6. Conclusions
In this paper, we present a systematic survey of ten Cyber Ranges with a structured interview. The purpose of the questionnaire is to examine key components that consist of a Cyber Range platform, and particularly the tools used to design, create, implement, and operate a cyber range platform. As analysed in Section 4, most of the current cyber ranges are moving towards more realistic and competitive scenarios that can help the users receive focused experiential learning. The combination of emulated and simulated into hybrid environments can help a cyber range to be more adaptive, expandable, and thus efficient. One important aspect of a modern cyber range is the datasets that are produced and how these can be shared with other scholars in order to help them test new security mechanisms.
The findings of the research will be a guide for the effort to design, develop and implementation a Cyber Range platform for the University of West Attica (UNIWA) but can also be a guide for other cyber ranges that are under development.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, N.C., G.K. and L.M.; Methodology, N.C., I.K. and L.M.; Software, M.A.F., G.P. and G.K.; Validation, G.P., I.K. and L.M.; formal analysis, I.K., M.A.F. and G.K.; investigation, N.C., G.K., I.K. and L.M.; resources, M.A.F., G.K. and N.C.; data curation, N.C., G.P., I.K. and L.M.; writing—original draft preparation, N.C., G.K. and M.A.F.; writing—review and editing, I.K., G.P. and L.M.; visualization, M.A.F., N.C., G.K. and L.M.; supervision, I.K., G.P. and L.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
All authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A. Questionnaire
Cyber Range Questionnaire [61]
- What is the objective of the Cyber Range? (select all that apply)
- What is the supporting sector of the Cyber Range? (select all that apply)
- What is the domain that is emulated or replicated in the operational environment? (select all that apply)
- What type of security challenges are provided? (select all that apply)
- Is the Cyber Range used for educational purposes?
- What is the type of Cyber Range environment?
- Which infrastructure platform(s) is (are) used to develop the Cyber Range?
- What type of access does it provide to participants? (select all that apply)
- What tools are used to
- i.
- Set up Vms?
- ii.
- Set up network topology?
- iii.
- Keep scoring? (flag dashboards, log analyzers, etc.)
- iv.
- Create cyber security scenarios?
- v.
- Manage the Cyber Range? (resources)
- vi.
- Monitoring the exercises ? (SIEM, IDS, etc.)
- vii.
- Generate network traffic?
- viii.
- Generate user behaviour?
- ix.
- Other functions?
- Teams, Roles and Participants
- i.
- How many teams can participate at the same time?
- ii.
- Total number of active participants?
- iii.
- PARTICIPANTS: What are the roles/functions? (select all that apply) iv. Roles
- Has the Cyber Range been used already?
- Has the Cyber Range provided any dataset?
- i.
- if yes the dataset is?
- ii.
- What type of information does the dataset contain?
References
- Maglaras, L.A.; Kim, K.H.; Janicke, H.; Ferrag, M.A.; Rallis, S.; Fragkou, P.; Maglaras, A.; Cruz, T.J. Cyber security of critical infrastructures. ICT Express 2018, 4, 42–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrag, M.A. EPEC: An efficient privacy-preserving energy consumption scheme for smart grid communications. Telecommun. Syst. 2017, 66, 671–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrag, M.A.; Nafa, M.; Ghanemi, S. EPSA: An efficient and privacy-preserving scheme against wormhole attack on reactive routing for mobile ad hoc social networks. Int. J. Secur. Netw. 2016, 11, 107–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braghin, C.; Cimato, S.; Damiani, E.; Frati, F.; Mauri, L.; Riccobene, E. A Model Driven Approach for Cyber Security Scenarios Deployment. In Computer Security; Fournaris, A.P., Athanatos, M., Lampropoulos, K., Ioannidis, S., Hatzivasilis, G., Damiani, E., Abie, H., Ranise, S., Verderame, L., Siena, A., et al., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 107–122. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, M. Signs your cyber security is doomed to fail. Comput. Fraud. Secur. 2020, 2020, 10–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crumpler, W.; Lewis, J.A. Cybersecurity Workforce Gap; Center for Strategic and International Studies (CSIS): Washington, DC, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Angafor, G.N.; Yevseyeva, I.; He, Y. Bridging the Cyber Security Skills Gap: Using Tabletop Exercises to Solve the CSSG Crisis. In Proceedings of the IFIP Joint International Conference on Serious Games, Stoke-on-Trent, UK, 19–20 November 2020; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 117–131. [Google Scholar]
- Gartner, I. Forecast Analysis: Container Management (Software and Services); Gartner, Inc.: Stamford, CT, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Stewart, B.; Rosa, L.; Maglaras, L.A.; Cruz, T.J.; Ferrag, M.A.; Simoes, P.; Janicke, H. A novel intrusion detection mechanism for scada systems which automatically adapts to network topology changes. EAI Endorsed Trans. Ind. Networks Intell. Syst. 2017, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallaq, B.; Nicholson, A.; Smith, R.; Maglaras, L.; Janicke, H.; Jones, K. CYRAN: A hybrid cyber range for testing security on ICS/SCADA systems. In Cyber Security and Threats: Concepts, Methodologies, Tools, and Applications; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2018; pp. 622–637. [Google Scholar]
- Chandra, Y.; Mishra, P.K. Design of Cyber Warfare Testbed. In Software Engineering; Hoda, M.N., Chauhan, N., Quadri, S.M.K., Srivastava, P.R., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 249–256. [Google Scholar]
- Updyke, D.; Dobson, G.; Podnar, T.; Osterritter, L.; Earl, B.; Cerini, A. GHOSTS in the Machine: A Framework for Cyber-Warfare Exercise NPC Simulation; Technical Report CMU/SEI-2018-TR-005; Software Engineering Institute, Carnegie Mellon University: Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- UNIWA. UNIWA CTF. Available online: http://www.pdsn.uniwa.gr/profile/inssec/ (accessed on 17 January 2021).
- Davis, J.; Magrath, S. A Survey of Cyber Ranges and Testbeds Executive; Cyber Electronic Warfare Division DSTO (Defence Science and Technology Organisation): Edinburgh, Australia, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Holm, H.; Karresand, M.; Vidström, A.; Westring, E. A Survey of Industrial Control System Testbeds. In Secure IT Systems; Buchegger, S., Dam, M., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 11–26. [Google Scholar]
- Yamin, M.M.; Katt, B.; Gkioulos, V. Cyber ranges and security testbeds: Scenarios, functions, tools and architecture. Comput. Secur. 2020, 88, 101636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucek, S.; Leitner, M. An Empirical Survey of Functions and Configurations of Open-Source Capture the Flag (CTF) Environments. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2020, 151, 102470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ukwandu, E.; Farah, M.A.B.; Hindy, H.; Brosset, D.; Kavallieros, D.; Atkinson, R.; Tachtatzis, C.; Bures, M.; Andonovic, I.; Bellekens, X. A review of cyber-ranges and test-beds: Current and future trends. Sensors 2020, 20, 7148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dark, M. Thinking about Cybersecurity. IEEE Secur. Priv. 2015, 13, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NIST. Cyber Ranges; NIST: Gaithersburg, MD, USA.
- Braghin, C.; Cimato, S.; Damiani, E.; Frati, F.; Riccobene, E.; Astaneh, S. Towards the Monitoring and Evaluation of Trainees’ Activities in Cyber Ranges. In International Workshop on Model-Driven Simulation and Training Environments for Cybersecurity; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 79–91. [Google Scholar]
- Eichler, Z. Cloud-Based Security Research Testbed: A DDoS Use Case. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Network Operations and Management Symposium (NOMS), Krakow, Poland, 5–9 May 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Goldman, R. Learning Proxmox VE; Packt Publishing Ltd.: Birmingham, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Østby, G.; Berg, L.; Kianpour, M.; Katt, B.; Kowalski, S.J. A Socio-Technical Framework to Improve cyber security training: A Work in Progress. In Proceedings of the fifth Workshop on Socio-Technical Perspective in IS development, Stockholm, Sweden, 10 June 2019; pp. 81–96. [Google Scholar]
- Raybourn, E.M.; Kunz, M.; Fritz, D.; Urias, V. A Zero-Entry Cyber Range Environment for Future Learning Ecosystems. In Cyber-Physical Systems Security; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 93–109. [Google Scholar]
- Pham, C.; Tang, D.; Chinen, K.I.; Beuran, R. Cyris: A cyber range instantiation system for facilitating security training. In Proceedings of the Seventh Symposium on Information and Communication Technology, Ho Chi Minh, Vietnam, 8–9 December 2016; pp. 251–258. [Google Scholar]
- Luchian, E.; Filip, C.; Rus, A.B.; Ivanciu, I.; Dobrota, V. Automation of the infrastructure and services for an openstack deployment using chef tool. In Proceedings of the 2016 15th RoEduNet Conference: Networking in Education and Research, Bucharest, Romania, 7–9 September 2016; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Kostromin, R. Survey of Software Configuration Management Tools of Nodes in Heterogeneous Distributed Computing Environment. Available online: http://ceur-ws.org/Vol-2638/paper15.pdf (accessed on 17 January 2021).
- Tkachuk, R.V.; Ilie, D.; Tutschku, K. Orchestrating Future Service Chains in the Next, Generation of Clouds. In Proceedings of the 15th SNCNW 2019, Lulea, Sweden, 4–5 June 2019; pp. 18–22. [Google Scholar]
- Brikman, Y. Why We Use Terraform and not Chef, Puppet, Ansible, Saltstack, or Cloudformation. 2016. Available online: https://lsi.vc.ehu.eus/pablogn/docencia/AS/Act7%20Admin.%20centralizada%20infrastructure-as-code,%20Configuration%20Management/Terraform%20Chef%20Puppet%20Ansible%20Salt.pdf (accessed on 17 January 2021).
- Pernik, P. Improving Cyber Security: NATO and the EU; International Center for Defence Studies: Tallinn, Estonia, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Vykopal, J.; Ošlejšek, R.; Čeleda, P.; Vizvary, M.; Tovarňák, D. Kypo Cyber Range: Design and Use Cases. 2017. Available online: https://is.muni.cz/publication/1386573/en/KYPO-Cyber-Range-Design-and-Use-Cases/Vykopal-Oslejsek-Celeda-Vizvary (accessed on 17 January 2021).
- Vykopal, J.; Vizvary, M.; Oslejsek, R.; Celeda, P.; Tovarnak, D. Lessons learned from complex hands-on defence exercises in a cyber range. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Frontiers in Education Conference (FIE), Indianapolis, IN, USA, 18–21 October 2017; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Range, F.C. Florida Cyber Range. Available online: https://floridacyberrange.org/ (accessed on 24 November 2020).
- Range, V.C. About the Virginia Cyber Range. Available online: https://www.virginiacyberrange.org/ (accessed on 25 November 2020).
- Darwish, O.; Stone, C.M.; Karajeh, O.; Alsinglawi, B. Survey of Educational Cyber Ranges. In Proceedings of the Workshops of the International Conference on Advanced Information Networking and Applications, Caserta, Italy, 15–17 April 2020; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 1037–1045. [Google Scholar]
- Debatty, T.; Mees, W. Building a Cyber Range for training CyberDefense Situation Awareness. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Military Communications and Information Systems (ICMCIS), Budva, Montenegro, 14–15 May 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llopis, S.; Hingant, J.; Pérez, I.; Esteve, M.; Carvajal, F.; Mees, W.; Debatty, T. A comparative analysis of visualisation techniques to achieve cyber situational awareness in the military. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Military Communications and Information Systems (ICMCIS), Warsaw, Poland, 22–23 May 2018; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitner, M.; Frank, M.; Hotwagner, W.; Langner, G.; Maurhart, O.; Pahi, T.; Reuter, L.; Skopik, F.; Smith, P.; Warum, M. AIT Cyber Range: Flexible Cyber Security Environment for Exercises, Training and Research. In Proceedings of the European Interdisciplinary Cybersecurity Conference (EICC), Rennes, France, 18 November 2020; pp. 18–19. [Google Scholar]
- Frank, M.; Leitner, M.; Pahi, T. Design Considerations for Cyber Security Testbeds: A Case Study on a Cyber Security Testbed for Education. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 15th Intl Conf on Dependable, Autonomic and Secure Computing, 15th Intl Conf on Pervasive Intelligence and Computing, 3rd Intl Conf on Big Data Intelligence and Computing and Cyber Science and Technology Congress(DASC/PiCom/DataCom/CyberSciTech), Orlando, FL, USA, 6–10 November 2017; pp. 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucek, S.; Leitner, M. Training the Human-in-the-Loop in Industrial Cyber Ranges. In Digital Transformation in Semiconductor Manufacturing; Keil, S., Lasch, R., Lindner, F., Lohmer, J., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 107–118. [Google Scholar]
- Irvine, C.E.; Thompson, M.F.; McCarrin, M.; Khosalim, J. Live Lesson: Labtainers: A Docker-based Framework for Cybersecurity Labs. In Proceedings of the 2017 USENIX Workshop on Advances in Security Education (ASE 17), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 5 August 2017; USENIX Association: Vancouver, BC, Canada, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, M.F.; Irvine, C.E. Individualizing Cybersecurity Lab Exercises with Labtainers. IEEE Secur. Priv. 2018, 16, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kianpour, M.; Kowalski, S.; Zoto, E.; Frantz, C.; Øverby, H. Designing Serious Games for Cyber Ranges: A Socio-technical Approach. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE European Symposium on Security and Privacy Workshops (EuroS PW), Stockholm, Sweden, 17–19 June 2019; pp. 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokkonen, T.; Hämäläinen, T.; Silokunnas, M.; Siltanen, J.; Zolotukhin, M.; Neijonen, M. Analysis of Approaches to Internet Traffic Generation for Cyber Security Research and Exercise. In Internet of Things, Smart Spaces, and Next, Generation Networks and Systems; Balandin, S., Andreev, S., Koucheryavy, Y., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 254–267. [Google Scholar]
- Karjalainen, M.; Kokkonen, T.; Puuska, S. Pedagogical Aspects of Cyber Security Exercises. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE European Symposium on Security and Privacy Workshops (EuroS PW), Stockholm, Sweden, 17–19 June 2019; pp. 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustafsson, T.; Almroth, J. Cyber Range Automation Overview with a Case Study of CRATE. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Tommy_Gustafsson2/publication/346559585_Cyber_range_automation_overview_with_a_case_study_of_CRATE/links/5fc73339299bf188d4e8f40b/Cyber-range-automation-overview-with-a-case-study-of-CRATE.pdf (accessed on 17 January 2021).
- Holm, H.; Sommestad, T. SVED: Scanning, Vulnerabilities, Exploits and Detection. In Proceedings of the MILCOM 2016—2016 IEEE Military Communications Conference, Baltimore, MD, USA, 1–3 November 2016; pp. 976–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rege, A.; Adams, J.; Parker, E.; Singer, B.; Masceri, N.; Pandit, R. Using cybersecurity exercises to study adversarial intrusion chains, decision-making, and group dynamics. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Cyber Warfare and Security, Dublin, Ireland, 29–30 June 2017; Academic Conferences International Limited: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 351–360. [Google Scholar]
- Silensec. Silensec. Available online: https://www.silensec.com/about-us/cyberranges (accessed on 24 November 2020).
- Hara, K. Cyber Range CYBERIUM for Training Security Meisters to Deal with Cyber Attacks. Fujitsu Sci. Tech. J. 2019, 55, 59–63. [Google Scholar]
- Nuari. Nuari. Available online: https://nuari.net/ (accessed on 24 November 2020).
- Center, G.C. Georgia Cyber Center. Available online: https://www.gacybercenter.org/ (accessed on 24 November 2020).
- IBM. IBM Xforce. Available online: https://exchange.xforce.ibmcloud.com/ (accessed on 25 November 2020).
- Cybexer. Cybexer. Available online: https://cybexer.com/ (accessed on 25 November 2020).
- Airbus. Airbus Cyber Range. Available online: https://airbus-cyber-security.com/products-and-services/prevent/cyberrange/ (accessed on 25 November 2020).
- Raytheon. Raytheon Cyber Range. Available online: https://www.raytheon.com/cyber/capabilities/range (accessed on 25 November 2020).
- DIATEAM. Hns-Platform Cyber Range. Available online: https://www.hns-platform.com/ (accessed on 25 November 2020).
- Cyberbit. Cyberbit Cyber Range. Available online: https://www.cyberbit.com/platform/cyber-range/ (accessed on 25 November 2020).
- Range, C.W. Cyber Warfare Range. Available online: https://www.azcwr.org/ (accessed on 25 November 2020).
- Chouliaras, N. Cyber Range Questionnaire. Available online: https://docs.google.com/forms/d/e/1FAIpQLSek34D2Ks4laS4AmajwHZAGqWGOrQxCOGIM3Lcmyaof2xyd2w/viewform?usp=sf_link (accessed on 15 September 2020).
- Seker, E.; Ozbenli, H.H. The Concept of Cyber Defence Exercises (CDX): Planning, Execution, Evaluation. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Cyber Security and Protection of Digital Services (Cyber Security), Oxford, UK, 3–4 June 2018; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Forero, C.A.M. Tabletop Exercise For Cybersecurity Educational Training; Theoretical Grounding in addition, Development. Master’s Thesis, University of Tartu Institute of Computer Science, Tartu, Estonia, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Kick, J. Cyber Exercise Playbook; Technical Report; MITRE CORP: Bedford, MA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Beveridge, R. Effectiveness of Increasing Realism Into Cybersecurity Training. Int. J. Cyber Res. Educ. (IJCRE) 2020, 2, 40–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Technology, J.J.S. RGCE Organizational Environments. Available online: https://jyvsectec.fi/2018/01/rgce-organizational-environments/ (accessed on 25 November 2020).
- Teknisk-Naturvitenskapelige Universitet, N. Om Norwegian Cyber Range. Available online: https://www.ntnu.no/ncr (accessed on 25 November 2020).
- University, M. KYPO Cyber Range Platform. Available online: https://crp.kypo.muni.cz/ (accessed on 25 November 2020).
- Nussbaum, L. Testbeds Support for Reproducible Research. In Proceedings of the Reproducibility Workshop; 2017; pp. 24–26. [Google Scholar]
- Braje, T.M. Advanced Tools for Cyber Ranges; Technical Report; MIT Lincoln Laboratory: Lexington, KY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- (ECSO), E.C.S.O. Understanding Cyber Ranges: From Hype to Reality. Available online: https://ecs-org.eu/documents/publications/5fdb291cdf5e7.pdf (accessed on 25 November 2020).
- Russo, E.; Costa, G.; Armando, A. Building Next, Generation Cyber Ranges with CRACK. Comput. Secur. 2020, 95, 101837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behal, S.; Kumar, K. Characterization and Comparison of DDoS Attack Tools and Traffic Generators: A Review. IJ Netw. Secur. 2017, 19, 383–393. [Google Scholar]
- Patil, B.R.; Moharir, M.; Mohanty, P.K.; Shobha, G.; Sajeev, S. Ostinato—A Powerful Traffic Generator. In Proceedings of the 2017 2nd International Conference on Computational Systems and Information Technology for Sustainable Solution (CSITSS), Bangalore, India, 21–23 December 2017; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Botta, A.; Dainotti, A.; Pescapè, A. A tool for the generation of realistic network workload for emerging networking scenarios. Comput. Netw. 2012, 56, 3531–3547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erlacher, F.; Dressler, F. How to Test an IDS? GENESIDS: An Automated System for Generating Attack Traffic. In Proceedings of the 2018 Workshop on Traffic Measurements for Cybersecurity, Budapest, Hungary, 20–24 August 2018; pp. 46–51. [Google Scholar]
- Berk, V.H.; de Souza, I.G.; Murphy, J.P. Generating realistic environments for cyber operations development, testing, and training. In Sensors, and Command, Control, Communications, and Intelligence (C3I) Technologies for Homeland Security and Homeland Defense XI; Carapezza, E.M., Ed.; International Society for Optics and Photonics, SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2012; Volume 8359, pp. 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Applebaum, A.; Miller, D.; Strom, B.; Korban, C.; Wolf, R. Intelligent, automated red team emulation. In Proceedings of the 32nd Annual Conference on Computer Security Applications, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 5–9 December 2016; pp. 363–373. [Google Scholar]
- Kokkonen, T.; Puuska, S. Blue team communication and reporting for enhancing situational awareness from white team perspective in cyber security exercises. In Internet of Things, Smart Spaces, and Next, Generation Networks and Systems; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 277–288. [Google Scholar]
- NCCDC. National CCDC. Collegiate Cyber Defense Competition. Available online: https://www.nationalccdc.org/ (accessed on 25 September 2020).
- Evans, M.; He, Y.; Maglaras, L.; Janicke, H. HEART-IS: A novel technique for evaluating human error-related information security incidents. Comput. Secur. 2019, 80, 74–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosmanos, D.; Prodromou, N.; Argyriou, A.; Maglaras, L.A.; Janicke, H. MIMO techniques for jamming threat suppression in vehicular networks. Mob. Inf. Syst. 2016, 2016, 8141204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrag, M.A.; Maglaras, L.; Ahmim, A.; Derdour, M.; Janicke, H. Rdtids: Rules and decision tree-based intrusion detection system for internet-of-things networks. Future Internet 2020, 12, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doubleday, H.; Maglaras, L.; Janicke, H. SSH Honeypot: Building, Deploying and Analysis. 2016. Available online: https://dora.dmu.ac.uk/handle/2086/12079 (accessed on 17 January 2021).
- Papaspirou, V.; Maglaras, L.; Ferrag, M.A.; Kantzavelou, I.; Janicke, H.; Douligeris, C. A novel Two-Factor HoneyToken Authentication Mechanism. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2012.08782. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).