Review on Complete Mueller Matrix Optical Scanning Microscopy Imaging
Abstract
1. Introduction
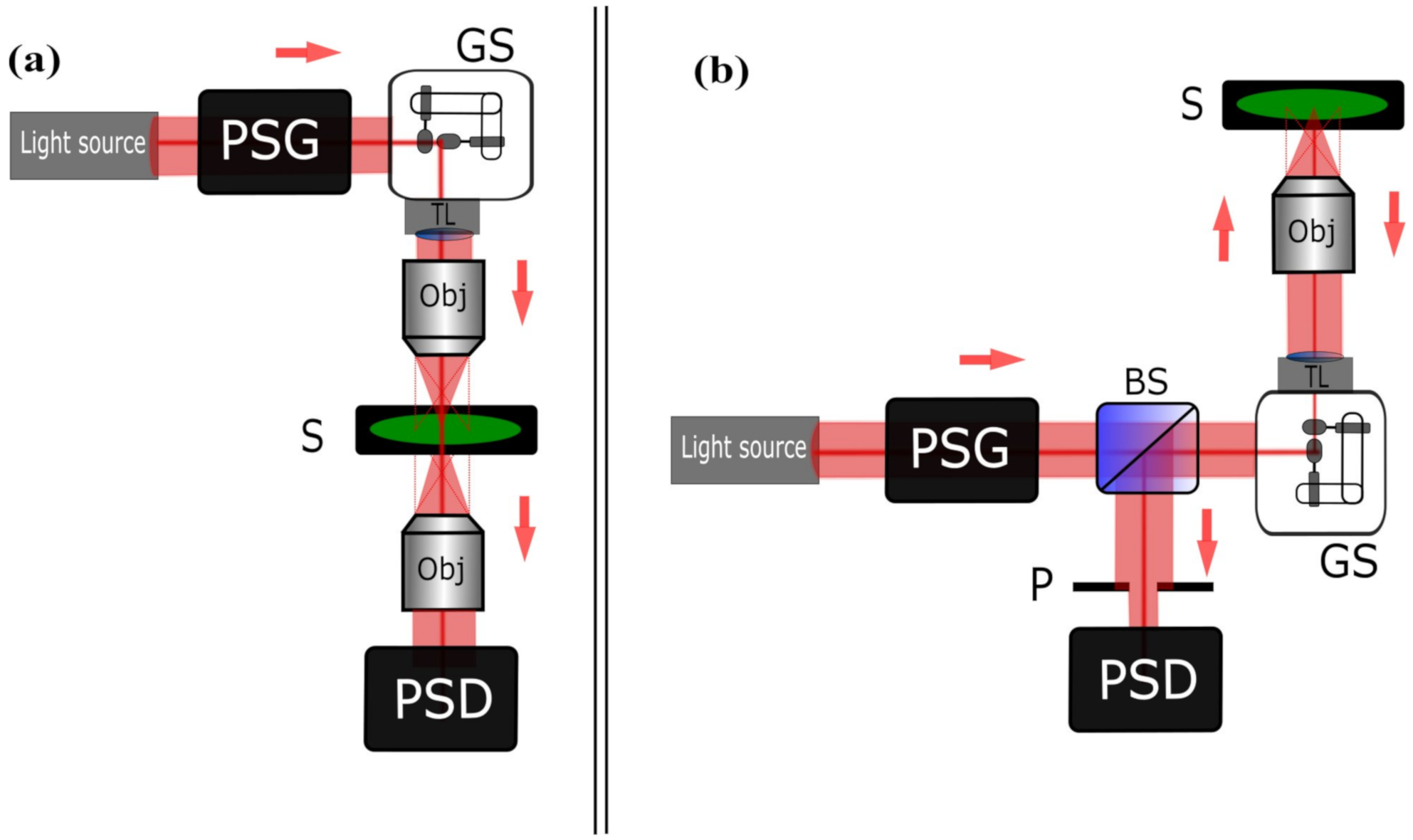
2. Mueller Matrix Optical Scanning Architecture
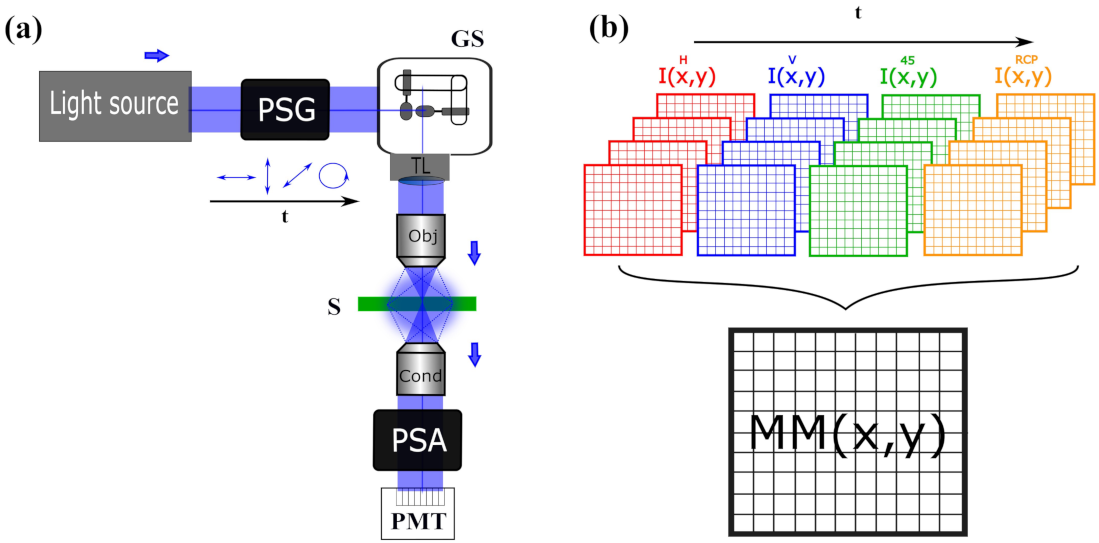
2.1. Temporal Domain Encoding/Decoding
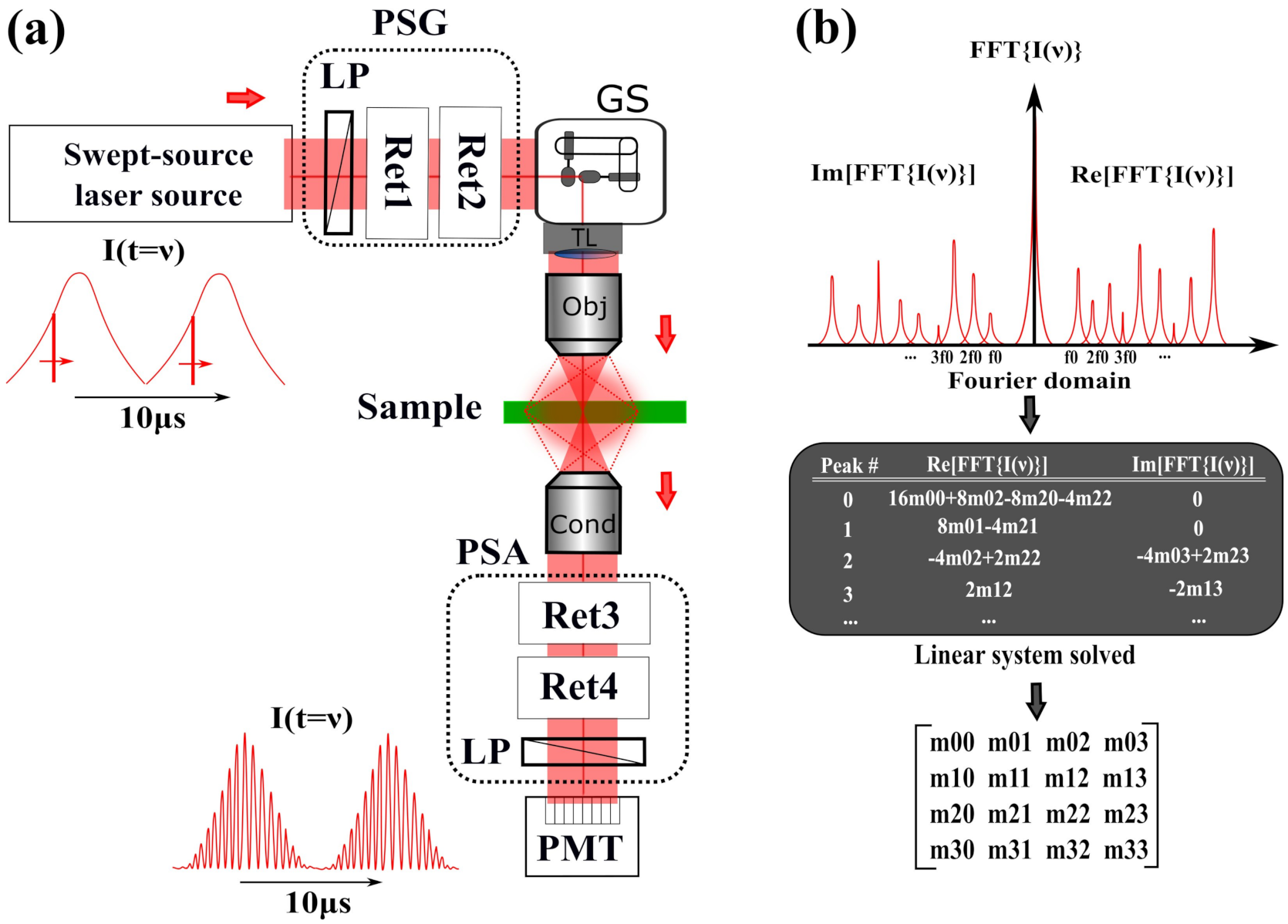
2.2. Spectral Domain Encoding/Decoding
3. Mueller Matrix Applications
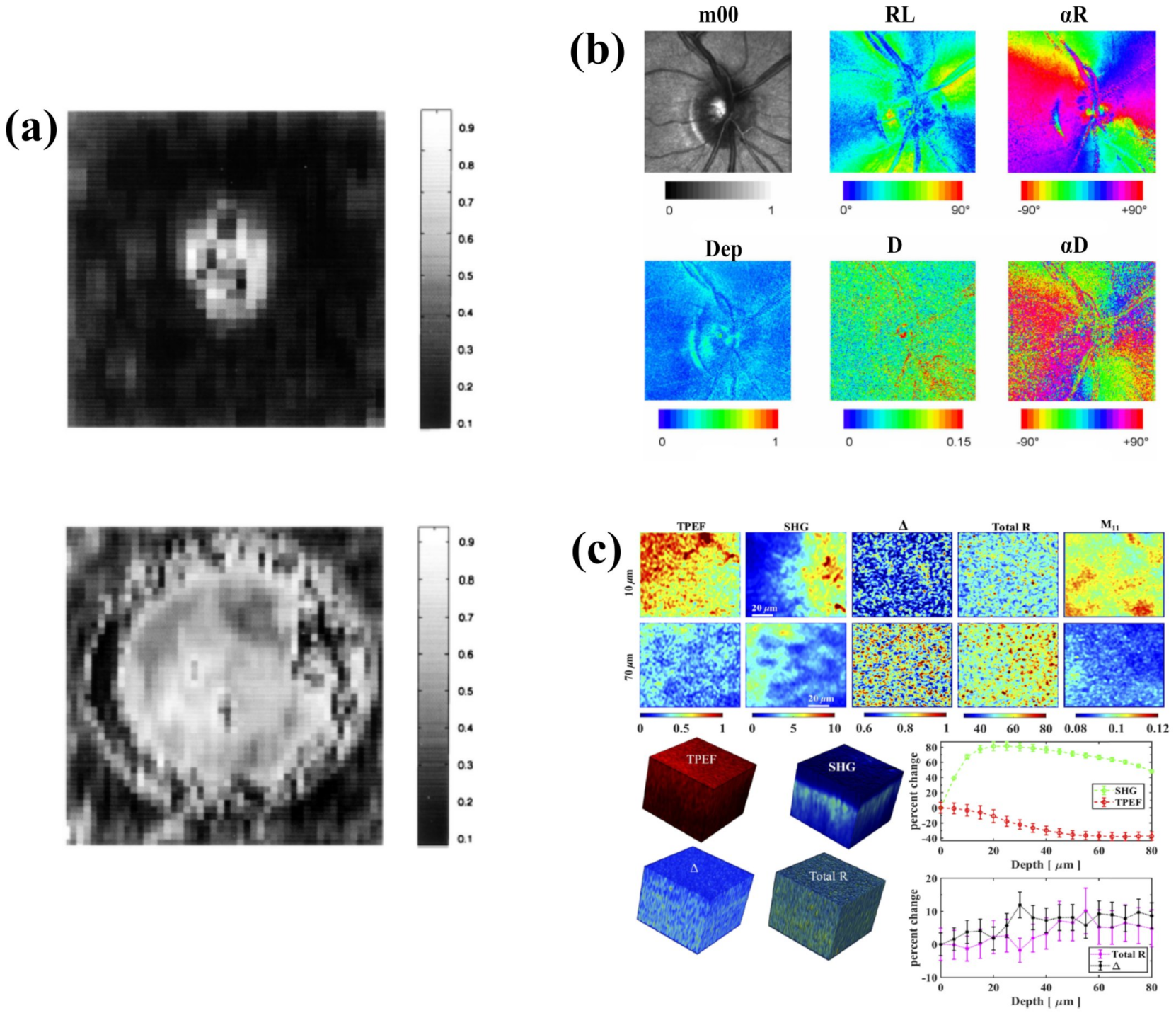
3.1. Ophthalmology
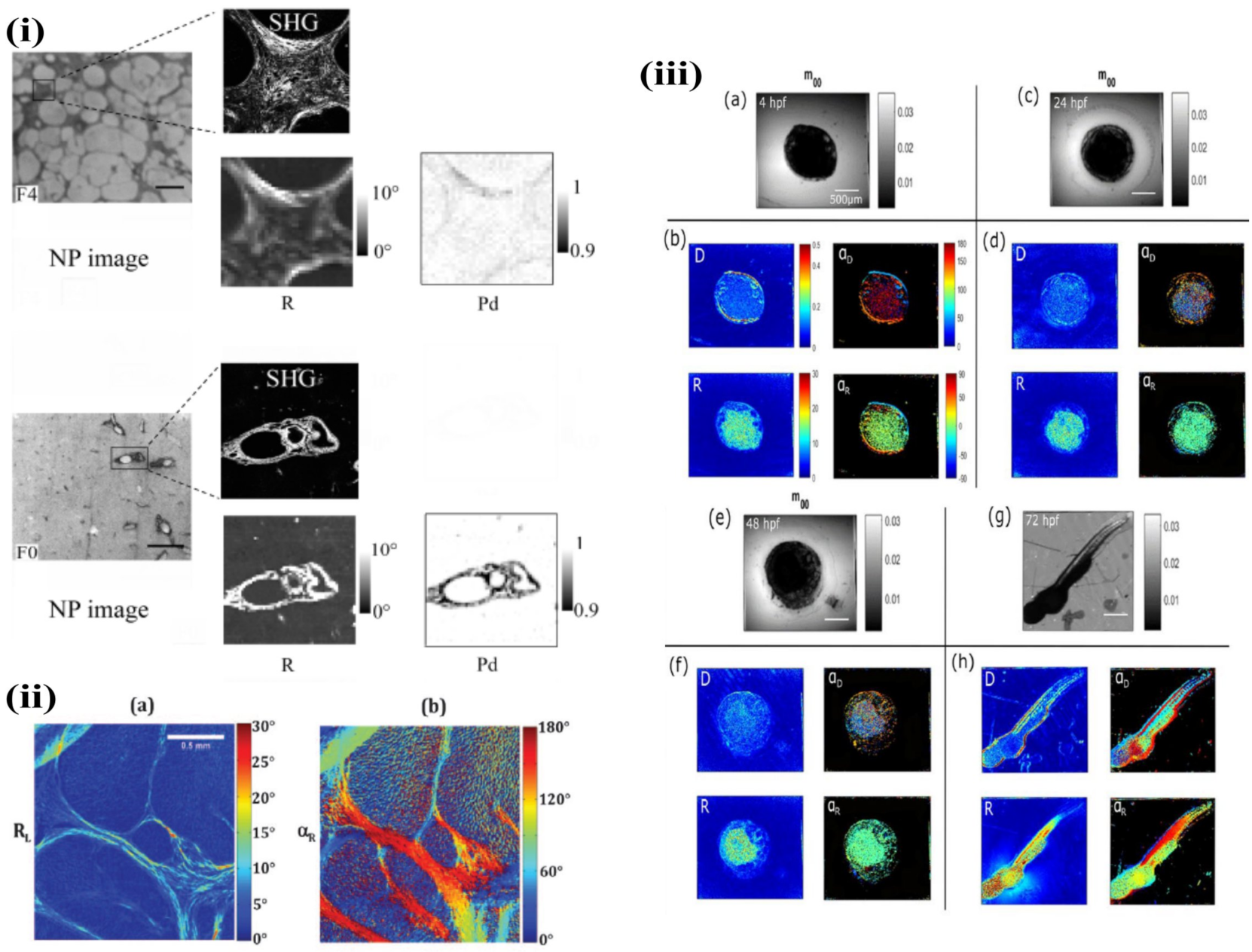
3.2. Biomedical Diagnosis and Tissue Organization
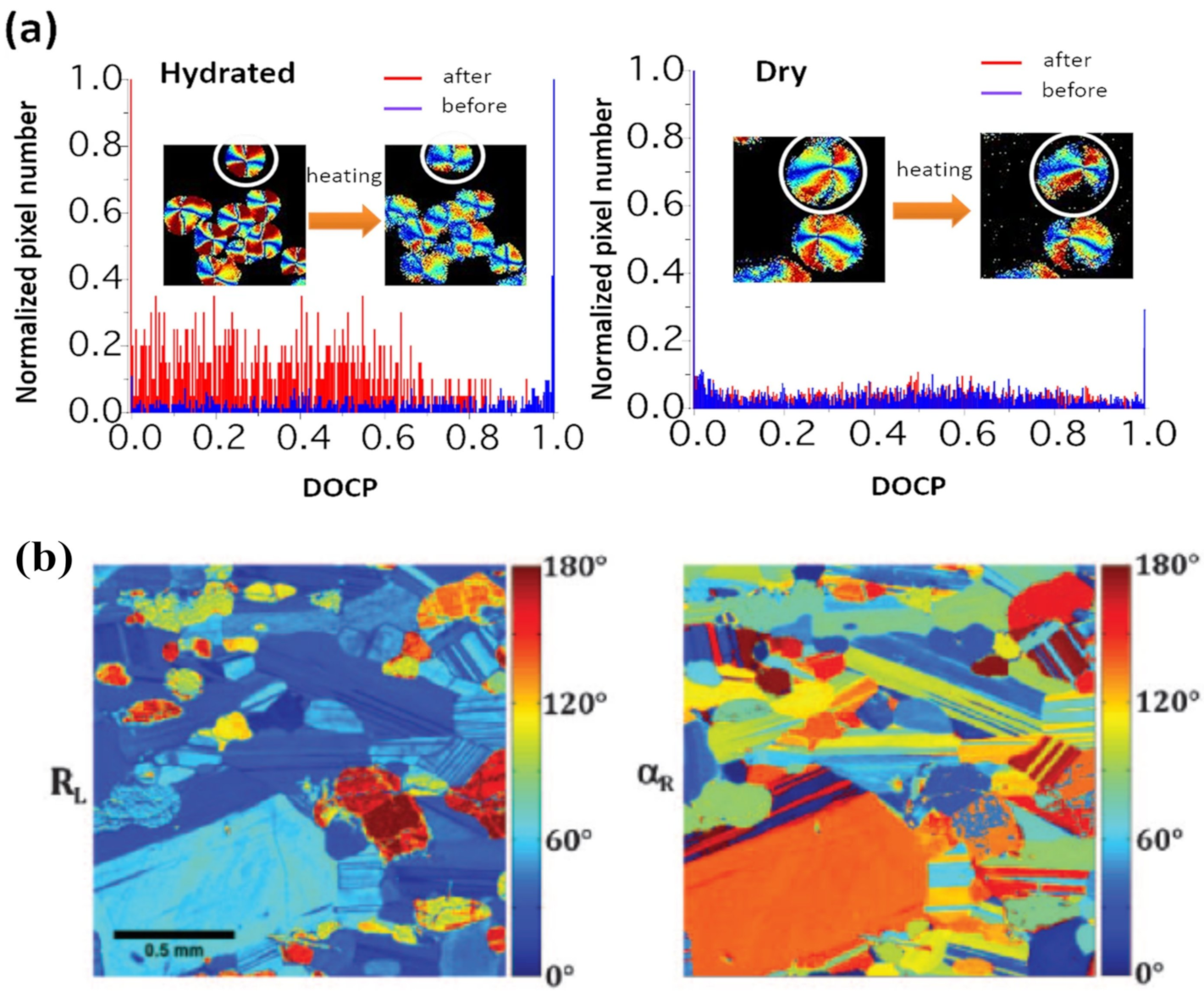
3.3. Material Science
4. Conclusions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MM | Mueller Matrix |
| CCD | Charge-Coupled Device |
| CMOS | Complementary Metal–Oxide–Semiconductor |
| SLM | Scanning Laser Microscopy |
| PSG | Polarization States Generator |
| DOLP | Degree of Linear Polarization |
| DOCP | Degree of Circular Polarization |
| PSA | Polarization States Analyzer |
| PSD | Polarization States Detector |
| ECM | Eigenvalue Calibration Method |
| CN | Condition Number |
| EWV | Equally Weighted Variance |
| PSF | Point Spread Function |
| GS | Galvanometric Scanner |
| OCT | Optical Coherent Tomography |
| SNR | Signal-to-Noise Ratio |
| RCP | Right Circular Polarization |
| PC | Pockels Cell |
| PMT | Photomultiplier tube |
| DoA | Division of Amplitude |
| LCVR | Liquid Crystal Variable Retarder |
| TPEF | Two-Photon Excitation Fluorescence |
| SHG | Second Harmonic Generation |
| PEM | Photoelastic Modulator |
| SS | Swept-Source |
| DAQ | Data Acquisition |
| FPGA | Field-Programmable Gate Array |
| PMT | Photomultiplier Tube |
| hpf | hours post fertilization |
References
- McMaster, W.H. Polarization and the Stokes Parameters. Am. J. Phys. 1954, 22, 351–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huard, S. Polarization of Light. In Polarization of Light, 1st ed.; John Wiley & Sons Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Anche, R.; Sen, A.K.; Anupama, G.; Sankarasubramanian, K.; Skidmored, W. Analysis of polarization introduced due to the telescope optics of the Thirty Meter Telescope. J. Astron. Telesc. Instrum. Syst. 2018, 4, 01800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patty, C.; ten Kate, I.; Jan Buma, W.; van Spanning, R.; Steinbach, G.; Ariese, F.; Snik, F. Circular spectropolarimetric sensing of vegetation in the field: possibilities for the remote detection of extraterrestrial life. Astrobiology 2019, 19, 1221–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyo, J.; Goldstein, D.; Chenault, D.; Shaw, J. Review of passive imaging polarimetry for remote sensing applications. Appl. Opt. 2006, 45, 5453–5469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, P.; Hu, X.; Trepte, C.; Lucker, P. A vector radiative transfer model for coupled atmosphere and ocean systems based on successive order of scattering method. Opt. Express 2009, 17, 2057–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fade, J.; Panigrahi, S.; Carre, A.; Frein, L.; Hamel, C.; Bretenaker, F.; Ramachandran, H.; Alouini, M. Long-range polarimetric imaging through fog. Appl. Opt. 2014, 53, 3854–3865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goudail, F.; Boffety, M.; Roussel, S.; Lucker, P. Optimal configuration of static Mueller imagers for target detection. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 2017, 34, 1054–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hielscher, H.; Eick, A.; Mourant, J.; Shen, D.; Freyer, J.; Bigio, I. Diffuse backscattering Mueller matrices of highly scattering media. Opt. Express 1997, 1, 441–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sankaran, V.; Walsh, J.; Maitland, D. Comparative study of polarized light propagation in biologic tissues. J. Biomed. Opt. 2002, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuchin, V.; Wang, L.; Zinnyakov, D. Polarized light interaction with strongly scattering media. Opt. Polariz. Biomed. Appl. 2006, 4, 45–67. [Google Scholar]
- Anna, G.; Goudail, F.; Daniel, D. Polarimetric target detection in the presence of spatially fluctuating Mueller matrices. Opt. Lett. 2011, 36, 4590–4592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doronin, A.; Macdonald, C.; Meglinski, I. Propagation of coherent polarized light in turbid highly scattering medium. J. Biomed. Opt. 2014, 19, 025005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Hu, H.; Xiaobo, L.; Guan, Z.; Zhu, W.; Jiang, J.; Liu, K.; Liu, T. An Angle of Polarization (AoP) Visualization Method for DoFP Polarization Image Sensors Based on Three Dimensional HSI Color Space. Sensors 2019, 19, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, H. The foundations of optics. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 1948, 38, 661–662. [Google Scholar]
- Snik, F.; Craven-Jones, J.; Escuti, M.; Fineschi, S.; Harrington, D.; De Martino, A.; Mawet, M.; Riedi, J.; Tyo, J. Measurement of the optical activity of anisotropic samples by transmission Mueller matrix ellipsometry. Polariz. Meas. Anal. Remote Sens. XI 2014, 9099, 9099B. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, J.; He, C.; Elson, D. Real time complete Stokes polarimetric imager based on a linear polarizer array camera for tissue polarimetric imaging. Biomed. Opt. Express 2017, 8, 4933–4946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lapray, P.; Gendre, L.; Foulonneau, A.; Bigué, L. An FPGA-based pipeline for micropolarizer array imaging. Int. J. Circuit Theory Appl. 2018, 46, 1675–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rankin, D.; Matthies, L.; Hertas, A. Daytime Water Detection by Fusing Multiple Cues for Autonomous Off-Road Navigation. In Proceedings of the 24th Army Science Conference, Orlando, FL, USA, 29 November–2 December 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Hasegawa, R.; Matsusaka, S.; Hidai, H.; Chiba, A.; Morita, N.; Takashi, O. In-process estimation of fracture surface morphology during wheel scribing of a glass sheet by high-speed photoelastic observation. Precis. Eng. 2017, 48, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebhan, D.; Rosenberg, M.; Notni, G. Principle investigations on polarization image sensors. Photonics Educ. Meas. Sci. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, S.; Gruev, V. Calibration methods for division-of-focal-plane polarimeters. Opt. Express 2013, 21, 21039–21055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Chen, X.; Shi, Y.; Gu, H.; Jiang, H.; Liu, S. Metrology of Nanostructures by Tomographic Mueller-Matrix Scatterometry. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stokes, G. On the composition and resolution of streams of polarized light from different sources. Trans. Camb. Philos. Soc. 1992, 9, 339–416. [Google Scholar]
- Compain, E.; Poirier, S.; Drevillon, B. General and self-consistent method for the calibration of polarization modulators, polarimeters, and Mueller-matrix ellipsometers. Appl. Opt. 1999, 38, 3490–3502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laude-Boulesteix, B.; De Martino, A.; Drevillon, B.; Schwartz, L. Mueller polarimetric imaging system with liquid crystals. Appl. Opt. 2004, 43, 2824–2832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lara, D.; Dainty, C. Axially resolved complete Mueller matrix confocal microscopy. Appl. Opt. 2006, 45, 1917–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kemp, J. Piezo-optical birefringence modulators: new use for a long-know effect. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 1969, 59, 950–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabatke, D.; Descour, M.; Dereniak, E.; Sweatt, W.; Kemme, S.; Phipps, G. Optimization of retardance for a complete Stokes polarimeter. Opt. Lett. 2000, 25, 802–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macias-Romero, C.; Torok, P. Eigenvalue calibration methods for polarimetry. J. Eur. Opt. Soc. Rapid Publ. 2012, 7, 12004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Gratiet, A.; Dubreuil, M.; Rivet, S.; Le Grand, Y. Scanning Mueller polarimetric microscopy. Opt. Lett. 2016, 41, 4336–4339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, A.; Schneider, M.J.; Rosenheck. Optical Activity of Biological Membranes: Scattering Effects and Protein Conformation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1970, 66, 793–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorman, B.; Maestre, M. Experimental differential light-scattering correction to the circular dichroism of bacteriophage T2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1973, 70, 255–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinoco, I.J.; Maestre, M.F.; Bustamante, C.; Keller, D. Use of circularly polarized light to study biological macromolecules. Pure Appl. Chem. 1984, 56, 1423–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wells, K.; Beach, D.; Keller, D.; Bustamante, C. An analysis of circular intensity differential scattering measurements: Studies on the sperm cell of Eledone cirrhosa. Biopolymers 1986, 25, 2043–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaspro, A.; Bertolotto, M.; Vergani, L.; Nicolini, C. Polarized light scattering of nucleosomes and polynucleosomes-in situ and in vitro studies. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1991, 38, 670–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Gratiet, A.; Marongiu, R.; Diaspro, R. Circular Intensity Differential Scattering for Label-Free Chromatin Characterization: A Review for Optical Microscopy. Polymers 2020, 12, 2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mickols, W.; Maestre, M.; Tinoco, I.; Embury, S. Visualization of oriented hemoglobin S in individual erythrocytesby differential extinction of polarized light. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1985, 82, 6527–6531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keller, D.; Bustamante, C.; Maestre, M.; Tinoco, I. Imaging of optically active biological structures by use of circularly polarized light. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1985, 82, 401–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beach, D.; Wells, K.; Husher, F.; Bustamante, C. Differential polarization microscope using an image dissector camera and phase-lock detection. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 1987, 58, 1987–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Keller, C.; Bustamante, C. Differential Polarization Imaging I: Theory and Applications. Polariz. Spectrosc. Ordered Syst. 1987, 242, 313–356. [Google Scholar]
- Finzi, L.; Ulibarri, L.; Bustamante, C. Differential polarization imaging. V. Numerical aperture effects and the contribution of preferential scattering and absorption to the circular dichroism images. Biophys. J. 1987, 59, 1183–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.; Kornfield, J. Polarization modulation laser scanning microscopy: A powerful tool to image molecular orientation and order. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 1994, 65, 2823–2828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bueno, J.M.; Artal, P. Double-pass imaging polarimetry in the human eye. Opt. Lett. 1999, 24, 64–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Gratiet, A.; D’Amora, M.; Duocastella, M.; Marongiu, R.; Bendandi, A.; Giordani, S.; Bianchini, P.; Diaspro, A. Zebrafish structural development in Mueller-matrix scanning microscopy. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Sheppard, C.; Shotton, D. Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy. In Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy, 1st ed.; Garland Science: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Azzam, R.M.A. Arrangement of four photodetectors for measuring the state of polarization of light. Opt. Lett. 2008, 10, 309–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Intaravanne, Y.; Chen, X. Recent advances in optical metasurfaces for polarization detection and engineered polarization profiles. Nanophotonics 2020, 9, 1003–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twietmeyer, K.; Chipman, R.; Elsner, A.; Zhao, Y.; VanNasdale, D. Mueller matrix retinal imager with optimized polarization conditions. Opt. Express 2008, 16, 21339–21354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazumder, N.; Xiang, L.; Qiu, J.; Kao, F. Investigating starch gelatinization through Stokes vector resolved second harmonic generation microscopy. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Saytashev, I.; Saha, S.; Chue-Sang, J.; Lopez, P.; Laughrey, M.; Ramella-Roman, J. Self validating Mueller matrix Micro - Mesoscope (SAMMM) for the characterization of biological media. Opt. Lett. 2020, 45, 2168–2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, V.; Saytashev, I.; Saha, S.; Lopez, P.; Laughrey, M.; Ramella-Roman, J. Depth-resolved Mueller matrix polarimetry microscopy of the rat cornea. Biomed. Opt. Express 2020, 11, 5982–5994. [Google Scholar]
- Alali, S.; Gribble, A.; Vitkin, I.A. Rapid wide-field Mueller matrix polarimetry imaging based on four photoelastic modulators with no moving parts. Opt. Lett. 2016, 41, 1038–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alenin, A.; Tyo, J. Generalized channeled polarimetry. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 2014, 31, 1013–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, A.; Huffman, D. A new polarization-modulated light scattering instrument. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 1973, 44, 1753–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronk, B.; Druger, S.; Czégé, J.; Van de Merwe, W. Measuring diameters of Rod-Shaped bacteria in vivo with polarized light scattering. Biophys. J. 1995, 69, 1170–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jellison, G.; Modine, F.; Chen, C. Calibration procedures for ellipsometer a two-modulator generalized. Polariz. Meas. Anal. Remote Sens. II 1999, 956, 3754. [Google Scholar]
- Arteaga, O.; Freudenthal, J.; Wang, B.; Nichols, S.; Kahr, B. Circular dichroism with multiple photoelastic modulators. Chim. Oggi 2012, 30, 6–9. [Google Scholar]
- Narushima, T.; Okamoto, H. Circular Dichroism Microscopy Free from Commingling Linear Dichroism via Discretely Modulated Circular Polarization. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arteaga, O.; El-Hachemi, Z.; Ossikovski, R. Snapshot circular dichroism measurements. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 6746–6756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oka, K.; Kinoshita, T.; Ise, A. Compact complete imaging polarimeter using birefringent wedge prisms. Opt. Express 2003, 11, 1510–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oka, K.; Kinoshita, T.; Ise, A. Channeled spectropolarimeter using a wavelength scanning laser and a channeled spectroscopic polarization state generator. In Polarization Science and Remote Sensing V; International Society for Optical Engineering: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2011; Volume 8160. [Google Scholar]
- Dubreuil, M.; Rivet, S.; Le Jeune, B.; Cariou, J. Snapshot Mueller matrix polarimeter by wavelength polarization coding. Opt. Express 2007, 15, 13660–13668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubreuil, M.; Tissier, F.; Le Roy, L.; Pennec, J.P.; Rivet, S.; Giroux-Metges, M.A.; Le Grand, Y. Polarization-resolved second harmonic microscopy of skeletal muscle in sepsis. Biomed. Opt. Express 2018, 9, 6350–6358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Gratiet, A.; Rivet, S.; Dubreuil, M.; Le Grand, Y. 100 kHz Mueller polarimeter in reflection configuration. Opt. Lett. 2015, 40, 645–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivet, S.; Bradu, A.; Podoleanu, A. 70 kHz full 4 × 4 Mueller polarimeter and simultaneous fiber calibration for endoscopic applications. Opt. Express 2015, 23, 23768–23786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chue-Sang, J.; Bay, Y.; Stoff, S.; Gonzalez, M.; Holness, N.; Gomes, J.; Jung, R.; Gandjbakhche, A.; Chernomordik, V.; Ramella-Roman, J. Use of Mueller matrix polarimetry and optical coherence tomography in the characterization of cervical collagen anisotropy. J. Biomed. Opt. 2017, 22, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Gratiet, A.; Pesce, L.; Oneto, M.; Marongiu, R.; Zanini, G.; Bianchini, P.; Diaspro, A. Circular intensity differential scattering (CIDS) scanning microscopy to image chromatin-DNA nuclear organization. OSA Contin. 2018, 1, 1068–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marongiu, R.; Le Gratiet, A.; Pesce, L.; Bianchini, P.; Diaspro, A. ExCIDS: a combined approach coupling Expansion Microscopy (ExM) and Circular Intensity Differential Scattering (CIDS) for chromatin-DNA imaging. OSA Contin. 2020, 3, 1770–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bueno, J.M.; Campbell, M.C.W. Confocal scanning laser ophthalmoscopy improvement by use of Mueller-matrix polarimetry. Opt. Lett. 2007, 27, 830–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alali, S.; Vitkin, A. Polarized light imaging in biomedicine: emerging Mueller matrix methodologies for bulk tissue assessment. J. Biomed. Opt. 2015, 20, 61104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Elson, D. Mueller polarimetric imaging for surgical and diagnostic applications: a review. J. Biophotonics 2017, 10, 950–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Liao, R.; Zeng, N.; Pengcheng, L.; Chen, Z.; Liu, X.; Hui, M. Mueller Matrix Polarimetry—An Emerging New Tool for Characterizing the Microstructural Feature of Complex Biological Specimen. J. Light. Technol. 2019, 37, 2534–2548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubreuil, M.; Babilotte, P.; Martin, L.; Sevrain, D.; Rivet, S.; Le Grand, Y.; Le Brun, G.; Turlin, B.; Le Jeune, B. Mueller matrix polarimetry for improved liver fibrosis diagnosis. Opt. Lett. 2012, 37, 1061–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben Hatit, S.; Foldyna, M.; De Martino, A.; Drévillon, B. Angle-resolved Mueller polarimeter using a microscope objective. Phys. Status Solidi (A) Appl. Mater. 2008, 205, 743–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arteaga, O.; Canillas, A. Measurement of the optical activity of anisotropic samples by transmission Mueller matrix ellipsometry. EPJ Web Conf. 2010, 5, 03001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aas, L.; Foldyna, M.; De Martino, A.; Drévillon, B. Near infra-red mueller matrix imaging system and application to retardance imaging of strain. Journal of biomedical optics. Thin Solid Films 2011, 519, 2737–2741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ossikovski, R.; De Martino, A. Differential Mueller matrix of a depolarizing homogeneous medium and its relation to the Mueller matrix logarithm. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 2015, 32, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheppard, C.A.B.; Le Gratiet, A.; Diaspro, R. Coherency and differential Mueller matrices for polarizing media. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 2018, 35, 2058–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
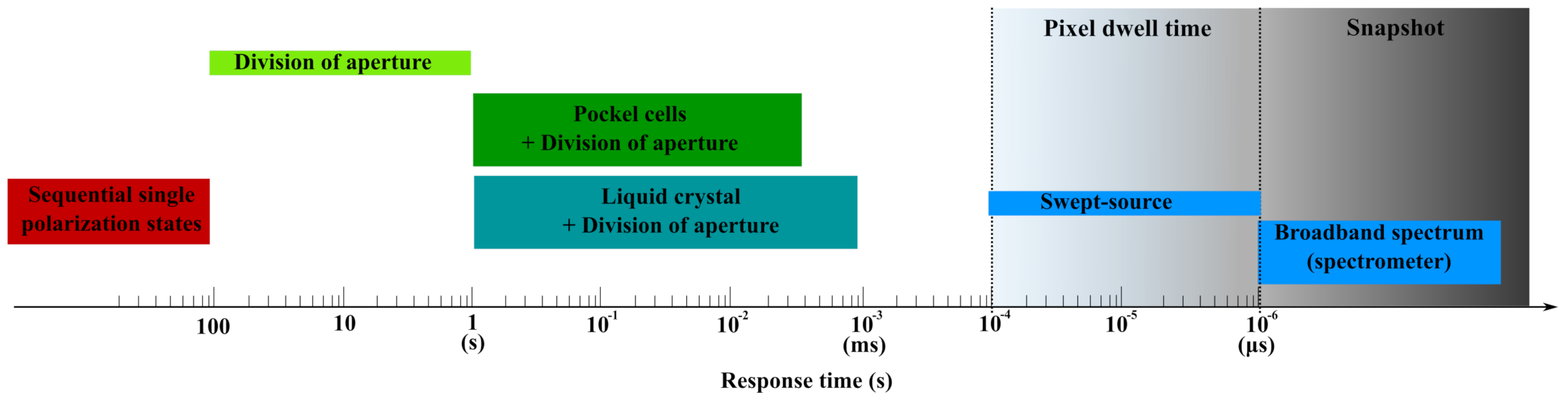
| Num. of Scan | Speed | Advantages | Disadvantages | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Single detection | 16 | few mins | Simple calibration Cheap | Precise alignment Active elements Succesive scans Post processing |
| Multiple detection | 4 to 8 | 50 ms to 10 s | Snapshot detection Cheap | Precise alignment Succesive scans Heavy calibration Spacy |
| Spectral detection | 1 | 10 s | Snapshot Compact Passive elements | Precise alignment Heavy calibration Complex modeling |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Le Gratiet, A.; Mohebi, A.; Callegari, F.; Bianchini, P.; Diaspro, A. Review on Complete Mueller Matrix Optical Scanning Microscopy Imaging. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1632. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11041632
Le Gratiet A, Mohebi A, Callegari F, Bianchini P, Diaspro A. Review on Complete Mueller Matrix Optical Scanning Microscopy Imaging. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(4):1632. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11041632
Chicago/Turabian StyleLe Gratiet, Aymeric, Ali Mohebi, Fabio Callegari, Paolo Bianchini, and Alberto Diaspro. 2021. "Review on Complete Mueller Matrix Optical Scanning Microscopy Imaging" Applied Sciences 11, no. 4: 1632. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11041632
APA StyleLe Gratiet, A., Mohebi, A., Callegari, F., Bianchini, P., & Diaspro, A. (2021). Review on Complete Mueller Matrix Optical Scanning Microscopy Imaging. Applied Sciences, 11(4), 1632. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11041632







