Saururus chinensis Prevents Estrogen Deficiency-Induced Osteoporosis in Rats: A Metabolomic Study Using UPLC/Q-TOF MS
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Reagents
2.2. Metabolic Profiling
2.3. Data Processing and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effect of SCE on Body Weight and Serum Biochemistry
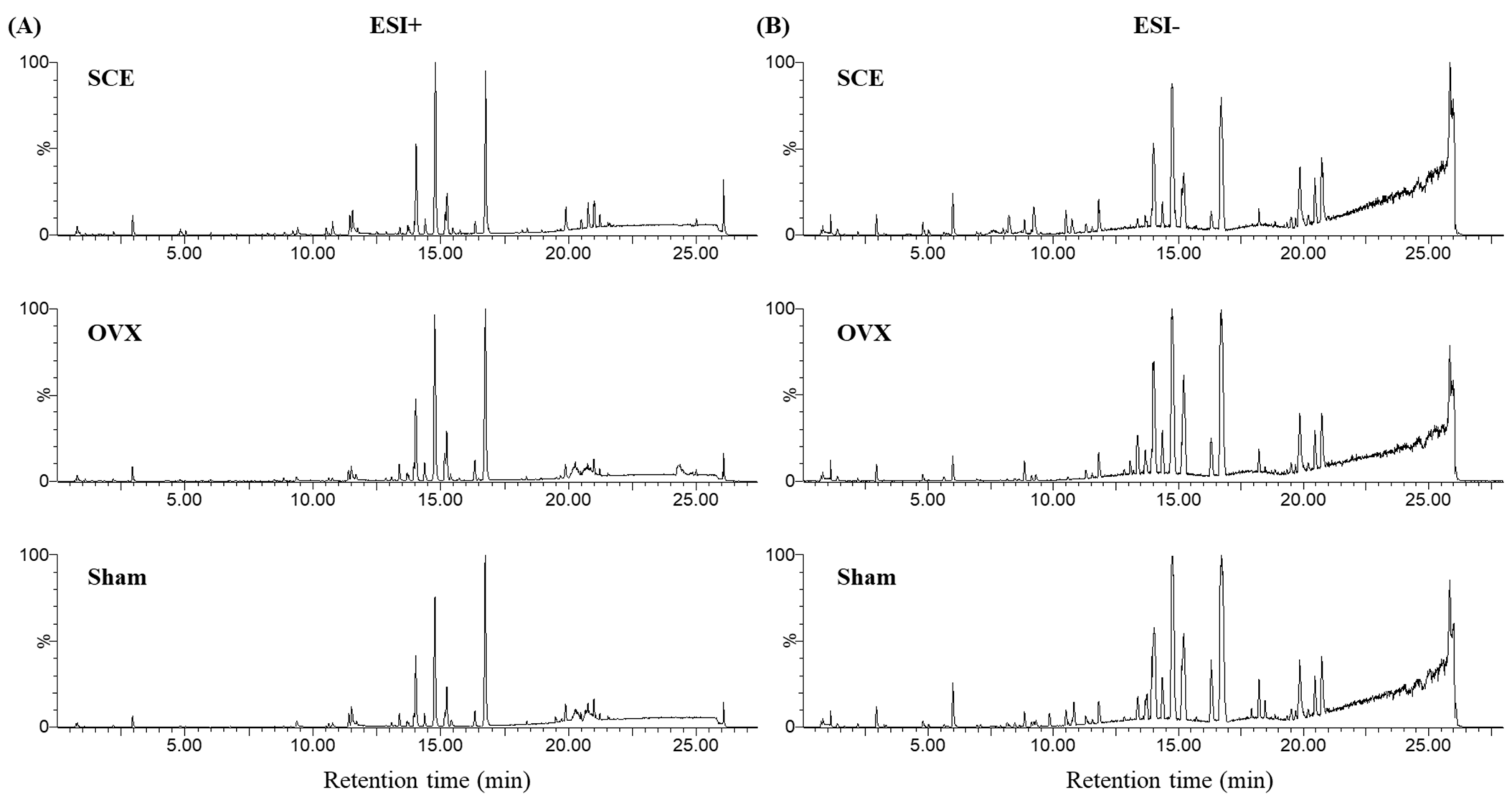
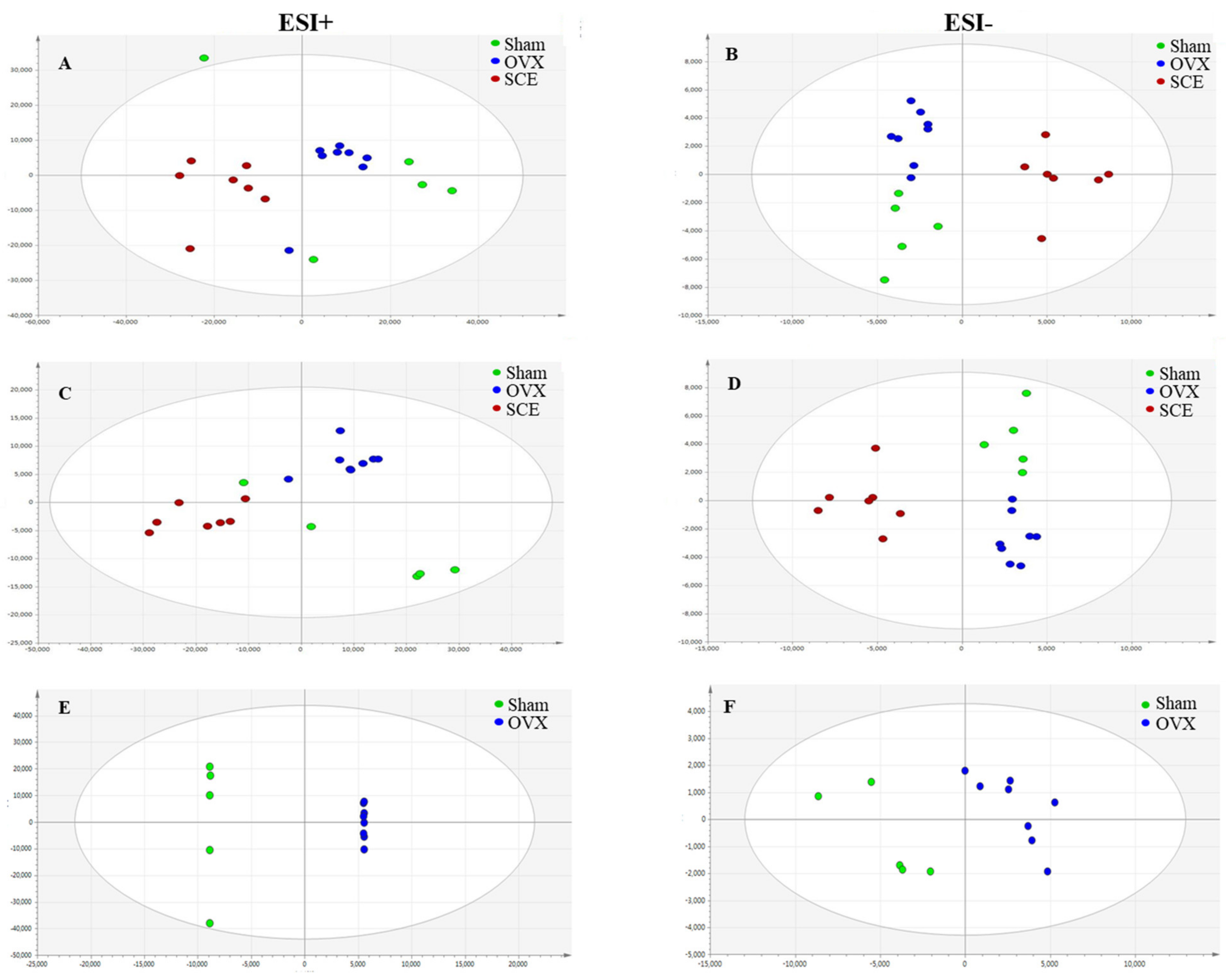
3.2. Metabolic Profiling Analysis
3.3. Identification of Potential Biomarkers
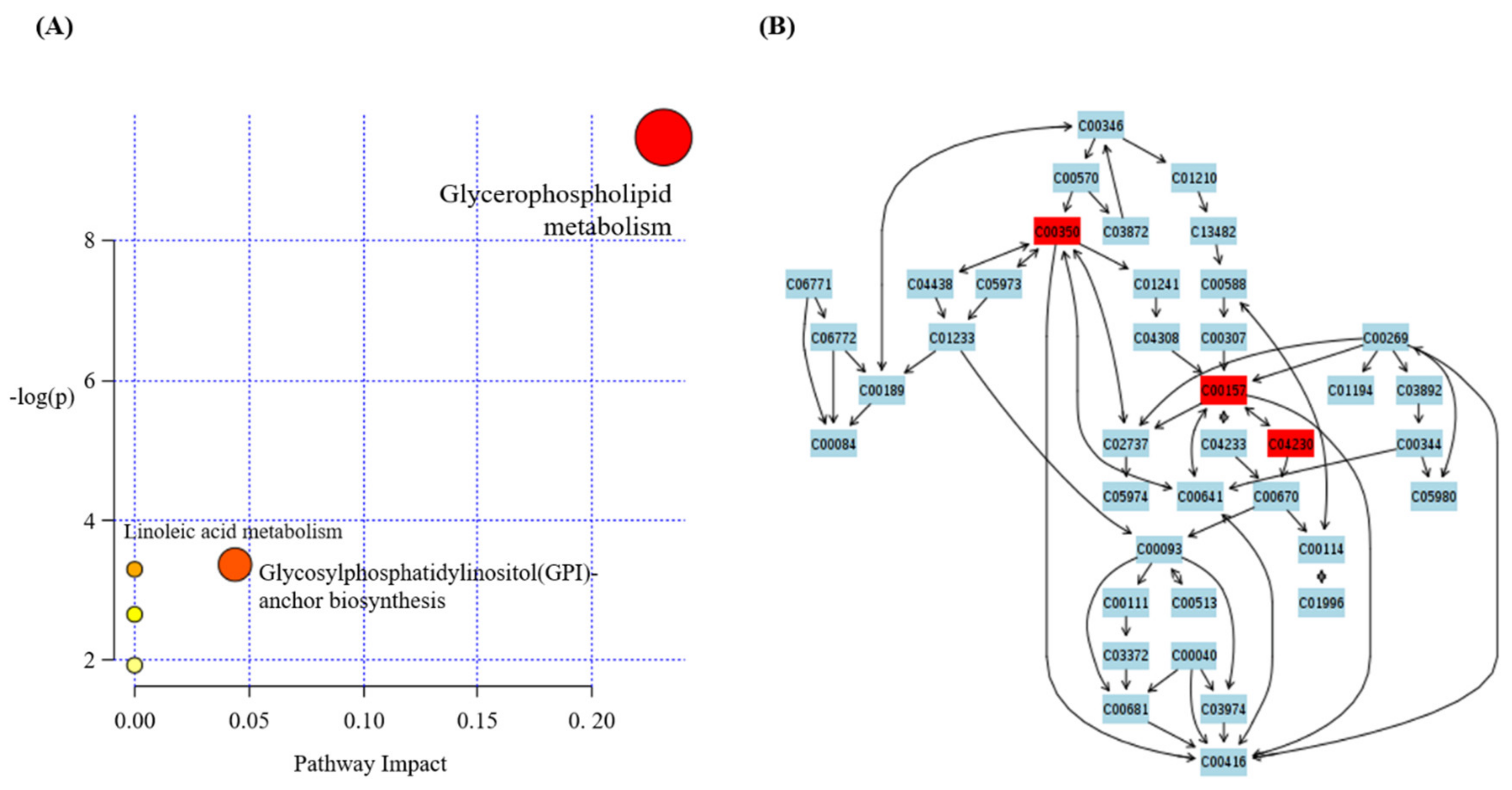
3.4. Effect of SCE on Metabolic Pathway
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gambassiani, M.; Cagnacci, A.; Lello, S. Hormone replacement therapy and prevention of chronic conditions. Climacteric 2019, 22, 303–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marjoribanks, J.; Farquhar, C.; Roberts, H.; Lethaby, A.; Lee, J. Long-term hormone therapy for perimenopausal and postmenopausal woman. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2017, 1, CD004143. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pandey, M.K.; Gupta, S.C.; Karelia, D.; Gilhooley, P.J.; Shakibaei, M.; Aggarwal, B.B. Dietary nutraceuticals as backbone for bone health. Biotechnol. Adv. 2018, 36, 1633–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taku, K.; Melby, M.K.; Takebayashi, J.; Mizuno, S.; Ishimi, Y.; Omori, T.; Watanabe, S. Effect of soy isoflavone extract supplements on bone mineral density in menopausal women: Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 19, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ryu, S.Y.; Oh, K.S.; Kim, Y.S.; Lee, B.H. Antihypertensive, vasorelaxant and inotripic effects of an ethanolic extract of the roots of Saururus Chinensis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2008, 18, 284–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.H.; Kim, D.H.; Oh, I.Y.; Kim, S.Y.; Lim, Y.Y.; Kim, H.M.; Kim, Y.H.; Chio, Y.M.; Kim, S.E.; Kim, B.J.; et al. Inhibitory effects of saururi chinensis extracts on melanin biosynthesis in B16F10 melanoma cells. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2013, 36, 772–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, H.Y.; Cho, C.W.; Song, Y.S. Antioxidative and anti-inflammatory effects of Saururus chinensis methanol extract in RAW 264.7 macrophages. J. Med. Food 2005, 8, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, M.J.; Davaatseren, M.; Hur, H.J.; Kim, H.J.; Ryu, S.Y.; Choi, Y.H.; Cha, M.R.; Kwon, D.Y. Antiosteoporotic activity of Saururus chinensis extract in ovariectomized rats. Phytother. Res. 2012, 26, 1182–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, K.Y.; Yang, D.; Chang, E.J.; Lee, Y.; Huang, H.; Sung, S.H.; Lee, Z.H.; Kim, Y.C.; Kim, H.H. Inhibition of osteoclast differentiation and bone resorption by sauchinone. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2007, 74, 911–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.N.; Kim, M.H.; Kim, Y.S.; Ryu, S.Y.; Min, Y.K.; Kim, S.H. Inhibitory effect of (-)-saucerneol on osteoclast differentiation and bone pit formation. Phytother. Res. 2009, 23, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.J.; Jiang, Z.M.; Chen, Y.; Xiao, P.T.; Wang, Z.Y.; Huang, T.Q.; Liu, E. Network pharmacology approach to elucidate possible action mechanisms of Sinomenii Caulis for treating osteoporosis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 257, 112871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, C.L.; Park, K.H.; Kang, S.S.; Cho, K.M.; Lee, D.H. Isoflavone-enriched soybean leaves attenuate overiectomy-induced osteoporosis in rats by anti-inflammatory activity. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2020, jsfa10763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, E.; Kim, J.; Kim, M.C.; Yeo, S.; Kim, J.; Park, S.; Jo, M.; Choi, C.W.; Kim, H.S.; Lee, S.W.; et al. Anti-osteoporotic effects of kikoamine B isolated from Lycii Radicis Cortex extract on osteoblast and osteoclast cells and ovariecromized osteoporosis model mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Lan, W.; Zheng, G.; Gao, X. Metabolomics: A high-throughput platform for metabolite profile exploration. Methods Mol. Biol. 2018, 1754, 265–292. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Capati, A.; Ijare, O.B.; Bezabeh, T. Diagnostic applications of nuclear magnetic resonance-based urinary metabolomics. Magn. Reson. Insights 2017, 10, 1178623X17694346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Sun, H.; Zhang, A.; Liu, Z.; Zou, D.; Song, Y.; Wang, X. High-throughput LC-MS method for the rapid characterization of multiple chemical constituents and metabolites of Da-Bu-Yin-Wan. J. Sep. Sci. 2017, 40, 4102–4112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindon, J.C.; Holmes, E.; Bollard, M.E.; Stanley, E.G.; Bicholson, J.K. Metabonomics technologies and their applications in physiological monitoring, drug safety assessment and disease diagnosis. Biomarkers 2004, 9, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhao, L.; Xiong, Z. Kidney tissue targeted metabolic profiling of glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis and the proposed therapeutic effects of Rhizoma Drynariae studied using UHPLC/MS/MS. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2014, 28, 878–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Feng, G.; Zhao, B.; Zhao, J.; Pi, Z.; Liu, S.; Song, F.; Liu, Z. A non-target urinary and serum metabolomics strategy reveals therapeutical mechanism of Radix Astragali on adjuvant-induced arthritis rats. J. Chromatogr. B 2017, 1048, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jambocus, N.G.S.; Saari, N.; Ismail, A.; Khatib, A.; Mahomoodally, M.F.; Hamid, A.A. An investigation into the antiobesity effects of Marinda citrifolia L. leaf extract in high fat diet induced obese rats using a (1)H NMR metabolomics approach. J. Diabetes Res. 2016, 2016, 2391592. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, Y.S.; Chen, W.C.; Kuo, T.C.; Ho, C.T.; Kuo, C.H.; Tseng, Y.J.; Lu, K.H.; Lin, S.H.; Panyod, S.; Sheen, L.Y. Mass-spectrometry-based serum metabolomics of a C57BL/6J mouse model of high-fat-diet-induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease development. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 7873–7884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Zhang, A.; Sun, H.; Zhou, X.; Guan, Y.; Liu, Q.; Kong, L.; Wang, X. Metabolomics-proteomics profiles delineate metabolic changes in kidney fibrosis disease. Proteomics 2015, 15, 3699–3710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Li, R.; Wei, S.; Gao, S.; Xu, Z.; Liu, H.; Wang, R.; Li, H.; Cai, H.; Wang, J.; et al. Metabolomics combined with network pharmacology exploration reveals the modulatory properties of Astragali Radix extract in the treatment of liver fibrosis. Chin. Med. 2019, 14, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shon, J.C.; Kim, W.C.; Ryu, R.; Wy, Z.; Seo, J.S.; Choi, M.S.; Liu, K.H. Plasma lipidomics reveals insights into anti-obesity effect of Chrysanthemum morifolium Ramat leaves and its constituent luteolin in high-fat diet-induced dyslipidemic mice. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolfender, J.L.; Marti, G.; Thomas, A.; Bertrand, S. Current approaches and challengers for the metabolites profiling of complex natural extracts. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1382, 136–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Zhao, A.; Hou, X.; Zheng, X.; Chen, P.; Bao, Y.; Jia, W.; Hu, C.; Zhang, Z.L.; Jia, W. Discovery of potential biomarkers for osteoporosis using LC-MS/MS metabolomic methods. Osteoporos. Int. 2019, 30, 1491–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, S.; Yu, M.; Lu, X.; Huo, T.; Ge, L.; Yang, J.; Wu, C.; Li, F. Urinary metabolomic study on biochemical changes in chronic unpredictable mild stress model of depression. Clin. Chim. Acta 2010, 411, 204–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huo, T.; Cai, S.; Lu, X.; Sha, Y.; Yu, M.; Li, F. Metabolomic study of biochemical changes in the serum of type 2 diabetes mellitus patients after the treatment of metformin hydrochloride. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2009, 49, 976–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, L.S.; Chio, J.H.; Sung, M.J.; Hur, J.Y.; Hur, H.J.; Park, J.D.; Kim, Y.C.; Gu, E.J.; Min, B.; Kim, H.J. Green tea changes serum and liver metabolomic profiles in mice with high-fat diet-induced obesity. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2015, 59, 784–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Nabarawi, N.; El-Wakd, M.; Salem, M. Atorvastatin, a double weapon in osteoporosis treatment: An experimental and clinical study. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2017, 11, 1383–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hertrampf, T.; Schleipen, B.; Offermanns, C.; Velders, M.; Laudenbach, U.; Diel, P. Comparison of the bone protective effects of an isoflavone-rich diet with dietary and subcutaneous administrations of genistein in ovariectomized rats. Toxicol. Lett. 2009, 184, 198–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, H.; Bao, J.; An, G.; Ouyang, G.; Zhang, P.; Wang, C.; Ying, H.; Ouyang, P.; Ma, B.; Zhang, Q. Association between the metabolome and bone mineral density in pre- and post-menopausal Chinese women using GC-MS. Mol. Biosyst. 2016, 12, 2265–2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, L.; Wang, Y.; Liu, L.; Zhao, L.; Han, T.; Zhang, Q.; Qin, L. A 1HNMR-based metabonomics study of postmenopausal osteoporosis and intervention effects of Er-Xian decoction in ovariectomized rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2011, 12, 7635–7651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Li, X.; Zhang, D.; Chen, H.; Chao, Y.; Wu, K.; Dong, X.; Su, J. Integrative Bone Metabolomics—Lipidomics Strategy for Pathological Mechanism of Postmenopausal Osteoporosis Mouse Model. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 16456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, Y.; Wang, F.; Wang, Z.; Lu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Wang, K.; Shen, H.; Yang, P.; Li, S.; et al. Quantitative profiling of glycerophospholipids during mouse and human macrophage differentiation using targeted mass spectrometry. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, S.; Lu, X.; Zheng, S.; Li, F.; Xiong, Z. Metabonomic study on the anti-osteoporosis effect of Rhizoma Drynariae and its action mechanism using ultra-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2012, 139, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibanez, L.; Ferrandiz, M.L.; Brines, R.; Guede, D.; Cuadrado, A.; Alcaraz, M.J. Effects of Nrf2 deficiency on bone microarchitecture in an experimental model of osteoporosis. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2014, 2014, 726590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Liu, Y.; Cheng, M.; Zhang, X.; Xiao, H. A metabolomics study of the inhibitory effect of 17-beta-estradiol on osteoclast proliferation and differentiation. Mol. Biosyst. 2015, 11, 635–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Refaey, M.; Watkins, C.P.; Kennedy, E.J.; Chang, A.; Zhong, Q.; Ding, K.H.; Shi, X.; Xu, J.; Bollag, W.B.; Hill, W.D.; et al. Oxidation of the aromatic amino acids tryptophan and tyrosine disrupts their anabolic effects on bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2015, 410, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, K.S.; Albro, M.; Dwyer, T.M.; Frerman, F.E. Kinetic mechanism of glutaryl-CoA dehydrogenase. Biochemistry 2006, 45, 15853–15861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuda, S.; Hayashi, T.; Egawa, T. The effects of caffeine on metabolomic responses to muscle contraction in rat skeletal muscle. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, A.; Maxwell, J.D.; Ang, L.; Davis, T.; Hodges, S.; Northfield, T.C.; Zaidi, M.; Pazianas, M. Ursodeoxycholic acid enhances fractional calcium absorption in primary biliary cirrhosis. Osteoporos. Int. 2002, 13, 677–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loomes, K.M.; Spino, C.; Goodrich, N.P.; Hangartner, T.N.; Marker, A.E.; Heubi, J.E.; Kamath, B.M.; Shneider, B.L.; Rosenthal, P.; Hertel, P.M.; et al. Bone Density in children with chronic liver disease correlates with growth and cholestasis. Hepatology 2019, 69, 245–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanly, R.; Ryan, N.; Snelling, H.; Walker-Bone, K.; Dizdarevic, S.; Peters, A.M. Association between bile acid turnover and osteoporosis in postmenopausal women. Nucl. Med. Commut. 2013, 34, 597–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, D.; Li, J.; Chen, K.; Rong, X.; Guo, J. Untargeted metabolomics reveals the protective effects of Fufang Zhenshu Tiaozhi (FTZ) on aging-induced osteoporosis in mice. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
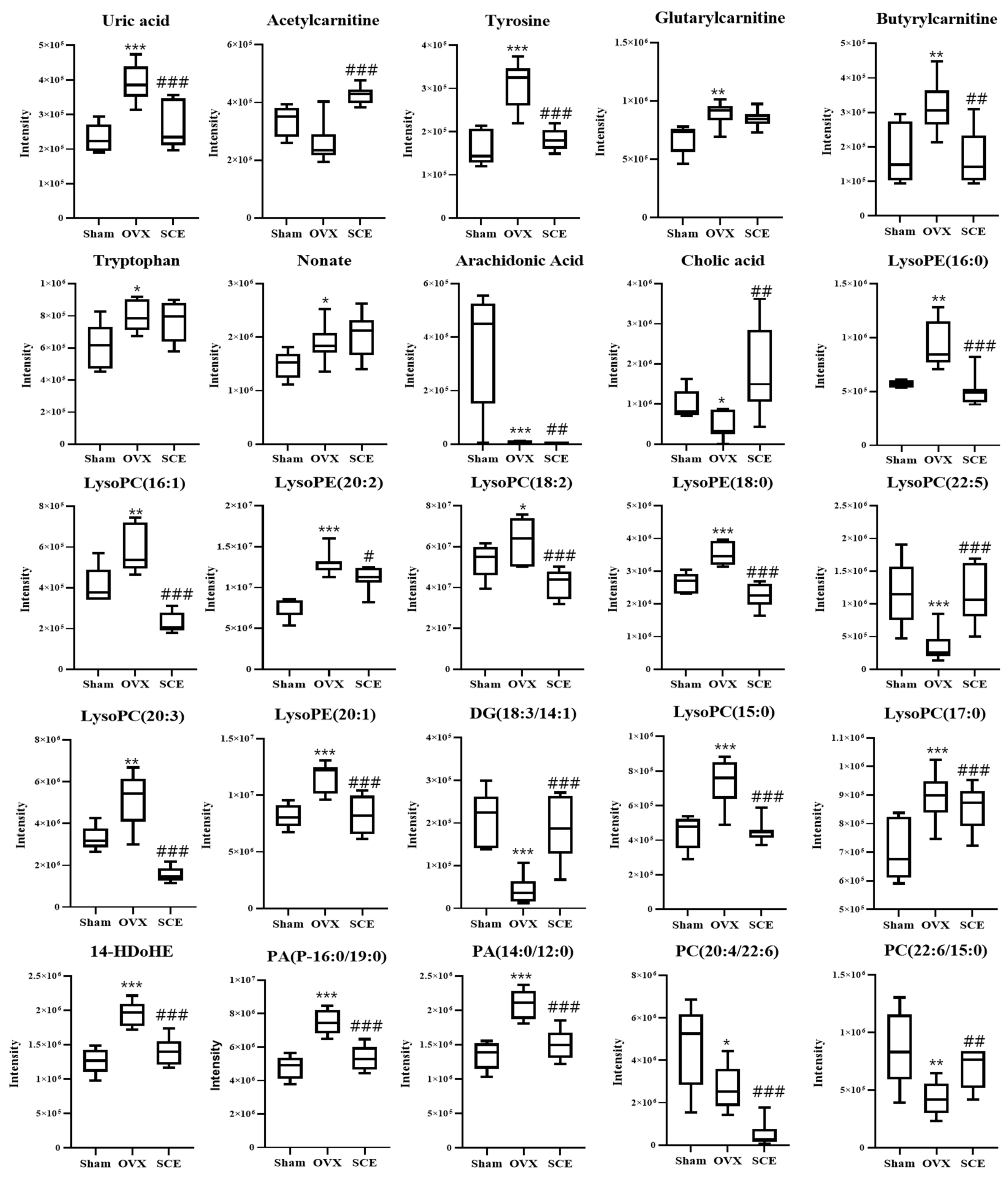
| Mass Fragment | Metabolites b | Adduct | Elemental Composition | Fold Change | Change Trend Compared with OVX Group a | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OVX/Sham | SCE/OVX | Sham | SCE | ||||
| 167.0206 | Uric acid | [M-H]- | C5H4N4O3 | 1.81 | 0.67 | ↓ *** | ↓ *** |
| 204.1219 | Acetylcarnitine | [M+H]+ | C9H18NO4 | 0.77 | 1.65 | ↑ | ↑ *** |
| 180.0662 | Tyrosine | [M-H]- | C9H11NO3 | 2.06 | 0.59 | ↓ *** | ↓ *** |
| 276.1477 | Glutarylcarnitine | [M+H]+ | C12H22NO6 | 1.32 | 0.95 | ↓ ** | ↓ |
| 232.1546 | Butyrylcarnitine | [M+H]+ | C11H21NO4 | 1.75 | 0.55 | ↓ ** | ↓ ** |
| 203.0828 | Tryptophan | [M-H]- | C11H12N2O2 | 1.34 | 0.95 | ↓ * | ↓ |
| 187.0996 | Nonate | [M-H]- | C9H16O4 | 1.30 | 1.08 | ↓ * | ↑ |
| 349.2361 | Arachidonic acid | [M+FA-H]- | C20H32O2 | 0.02 | 0.30 | ↑ *** | ↓ ** |
| 407.2763 | Cholic acid | [M-H]- | C24H40O5 | 0.45 | 4.18 | ↑ * | ↑ ** |
| 512.2966 | LysoPE(16:0) | [M+CH3COO]- | C21H44NO7P | 1.62 | 0.54 | ↓ ** | ↓ *** |
| 494.3177 | LysoPC(16:1) | [M+H]+ | C24H48NO7P | 1.44 | 0.39 | ↓ ** | ↓ *** |
| 564.3281 | LysoPE(20:2) | [M+CH3COO]- | C25H48NO7P | 1.73 | 0.86 | ↓ *** | ↓ * |
| 520.3392 | LysoPC(18:2) | [M+H]+ | C26H50NO7P | 1.23 | 0.64 | ↓ * | ↓ *** |
| 540.3308 | LysoPE(18:0) | [M+CH3COO]- | C23H48NO7P | 1.30 | 0.63 | ↓ *** | ↓ *** |
| 570.3566 | LysoPC(22:5) | [M+H]+ | C30H52NO7P | 0.31 | 3.19 | ↑ *** | ↑ *** |
| 546.3596 | LysoPC(20:3) | [M+H]+ | C28H52O7NP | 1.58 | 0.30 | ↓ ** | ↓ *** |
| 566.3455 | LysoPE(20:1) | [M+CH3COO]- | C25H50NO7P | 1.42 | 0.72 | ↓ *** | ↓ *** |
| 605.4123 | DG(18:3/14:1) | [M+2Na-H] | C35H60O5 | 0.21 | 4.41 | ↑ *** | ↑ *** |
| 480.3074 | LysoPC(15:0) | [M-H]- | C23H48NO7P | 1.51 | 0.62 | ↓ *** | ↓ *** |
| 568.3600 | LysoPC(17:0) | [M+CH3COO]- | C25H52NO7P | 1.29 | 0.73 | ↓ *** | ↓ *** |
| 711.4693 | 14-HDoHE | [2M-H]- | C23H32O3 | 1.53 | 0.72 | ↓ *** | ↓ *** |
| 711.4706 | PA(P-16:0/19:0) | [M+K-2H]- | C38H75O7P | 1.53 | 0.71 | ↓ *** | ↓ *** |
| 601.3294 | PA(14:0/12:0) | [M+K-2H]- | C29H57O8P | 1.53 | 0.71 | ↓ *** | ↓ *** |
| 854.5827 | PC(20:4/22:6) | [M+H]+ | C50H80NO8P | 0.57 | 0.16 | ↑ * | ↓ *** |
| 850.5619 | PC(22:6/15:0) | [M+CH3COO]- | C45H78NO8P | 0.43 | 1.62 | ↑ ** | ↑ ** |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, S.; Jang, G.J.; Yoo, M.; Hur, H.J.; Sung, M.J. Saururus chinensis Prevents Estrogen Deficiency-Induced Osteoporosis in Rats: A Metabolomic Study Using UPLC/Q-TOF MS. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1392. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11041392
Lee S, Jang GJ, Yoo M, Hur HJ, Sung MJ. Saururus chinensis Prevents Estrogen Deficiency-Induced Osteoporosis in Rats: A Metabolomic Study Using UPLC/Q-TOF MS. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(4):1392. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11041392
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Sanghee, Gwang Ju Jang, Miyoung Yoo, Haeng Jeon Hur, and Mi Jeong Sung. 2021. "Saururus chinensis Prevents Estrogen Deficiency-Induced Osteoporosis in Rats: A Metabolomic Study Using UPLC/Q-TOF MS" Applied Sciences 11, no. 4: 1392. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11041392
APA StyleLee, S., Jang, G. J., Yoo, M., Hur, H. J., & Sung, M. J. (2021). Saururus chinensis Prevents Estrogen Deficiency-Induced Osteoporosis in Rats: A Metabolomic Study Using UPLC/Q-TOF MS. Applied Sciences, 11(4), 1392. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11041392






