Temperature Sensing with Nd3+ Doped YAS Laser Microresonators
Abstract
Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Background
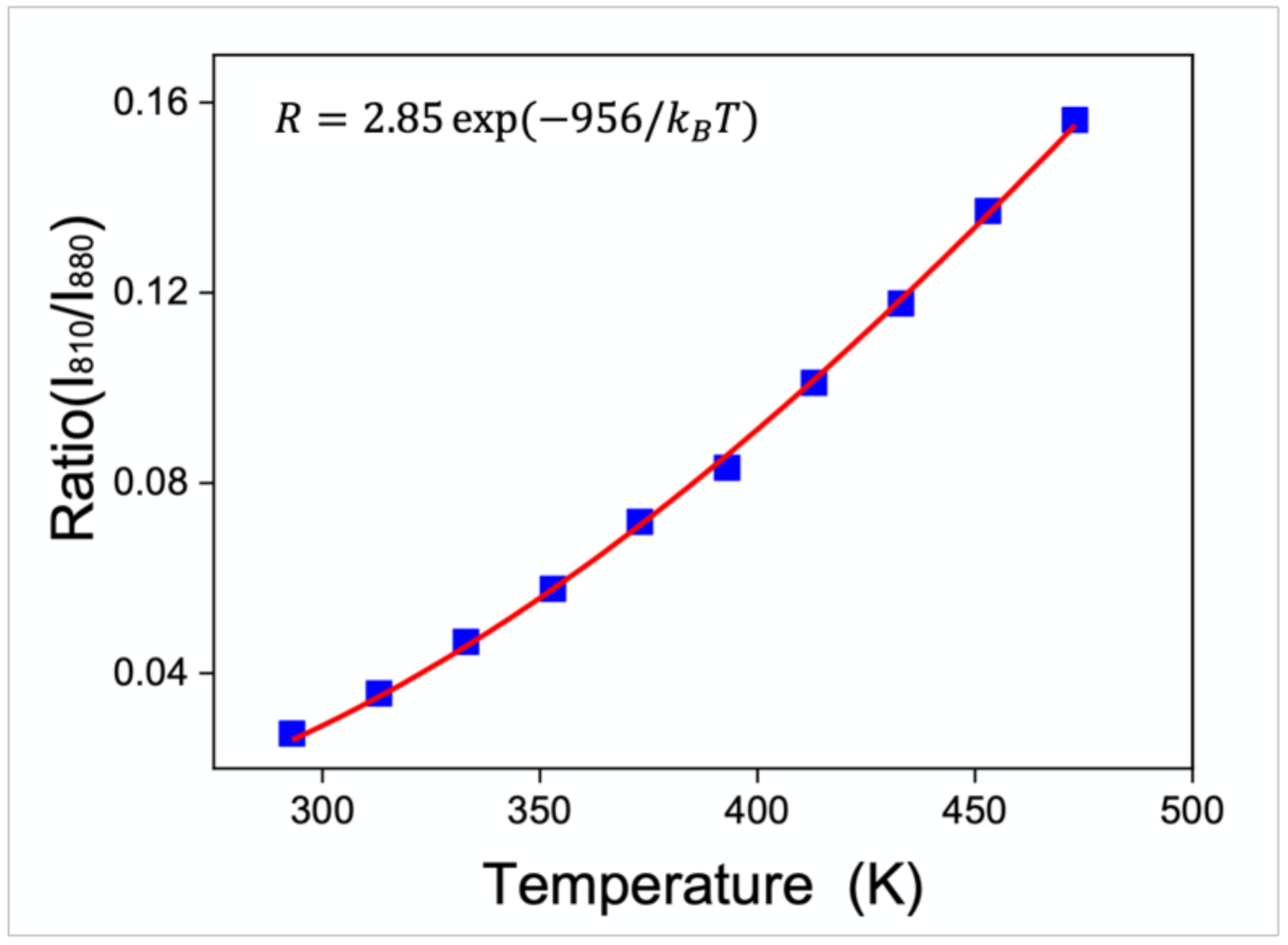
2.1. Fluorescence Intensity Ratio (FIR)
2.2. Whispering Gallery Modes (WGM)
2.3. Thermal Sensors
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Microsphere Production
3.2. Temperature Calibration
3.3. Optical Measurements
4. Results and Discussion
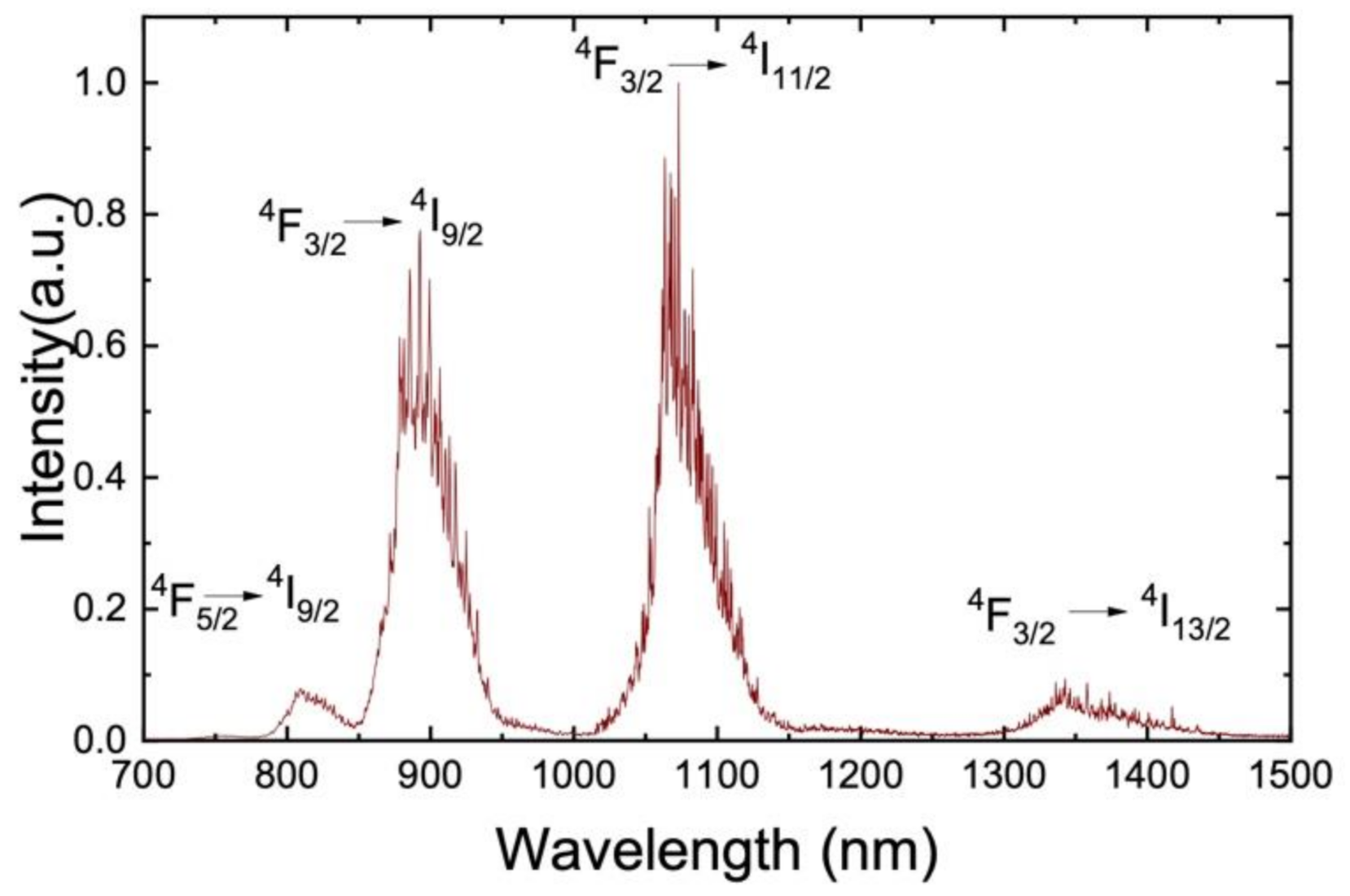
4.1. Emission Spectrum of Nd3+
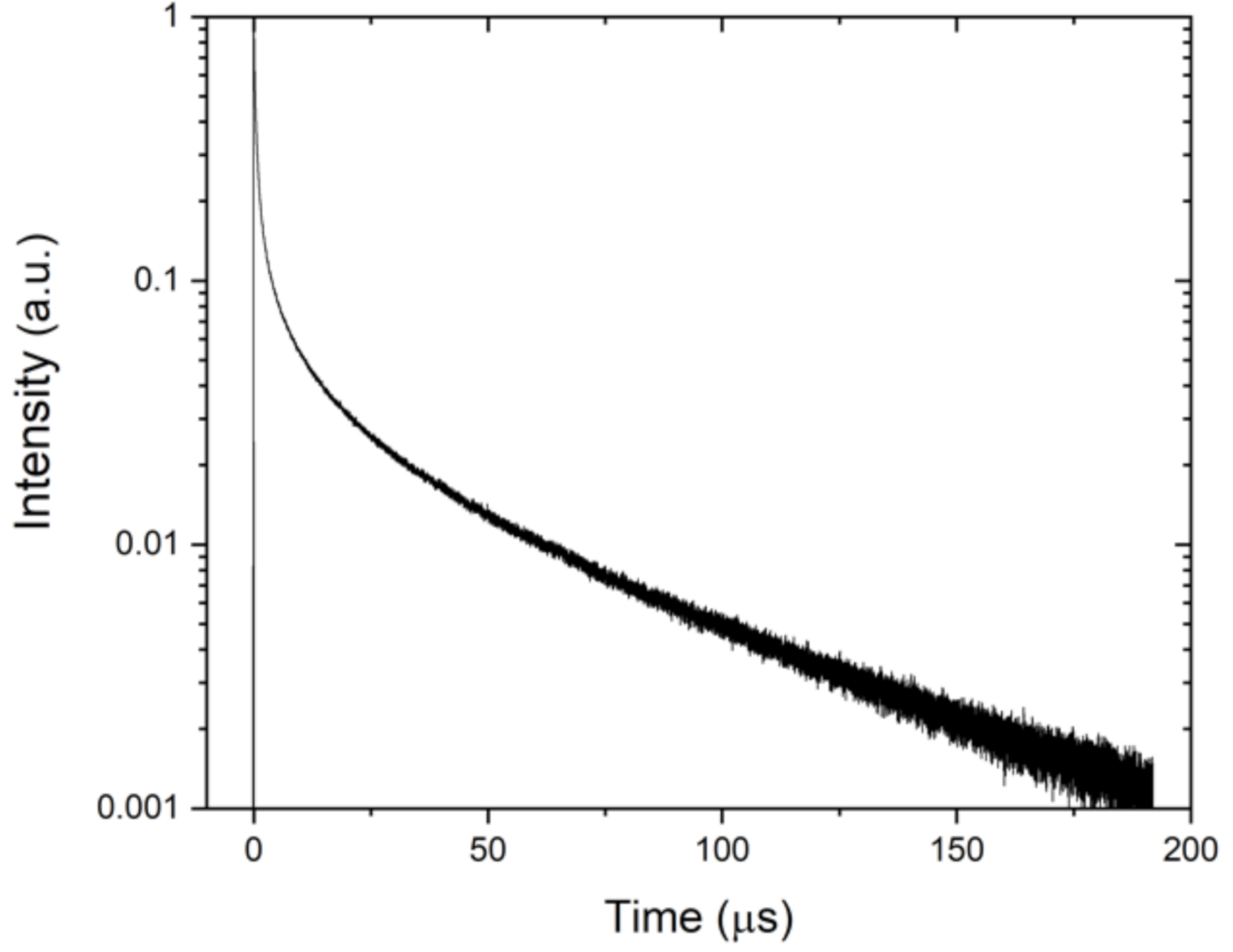
4.2. Temperature Calibration
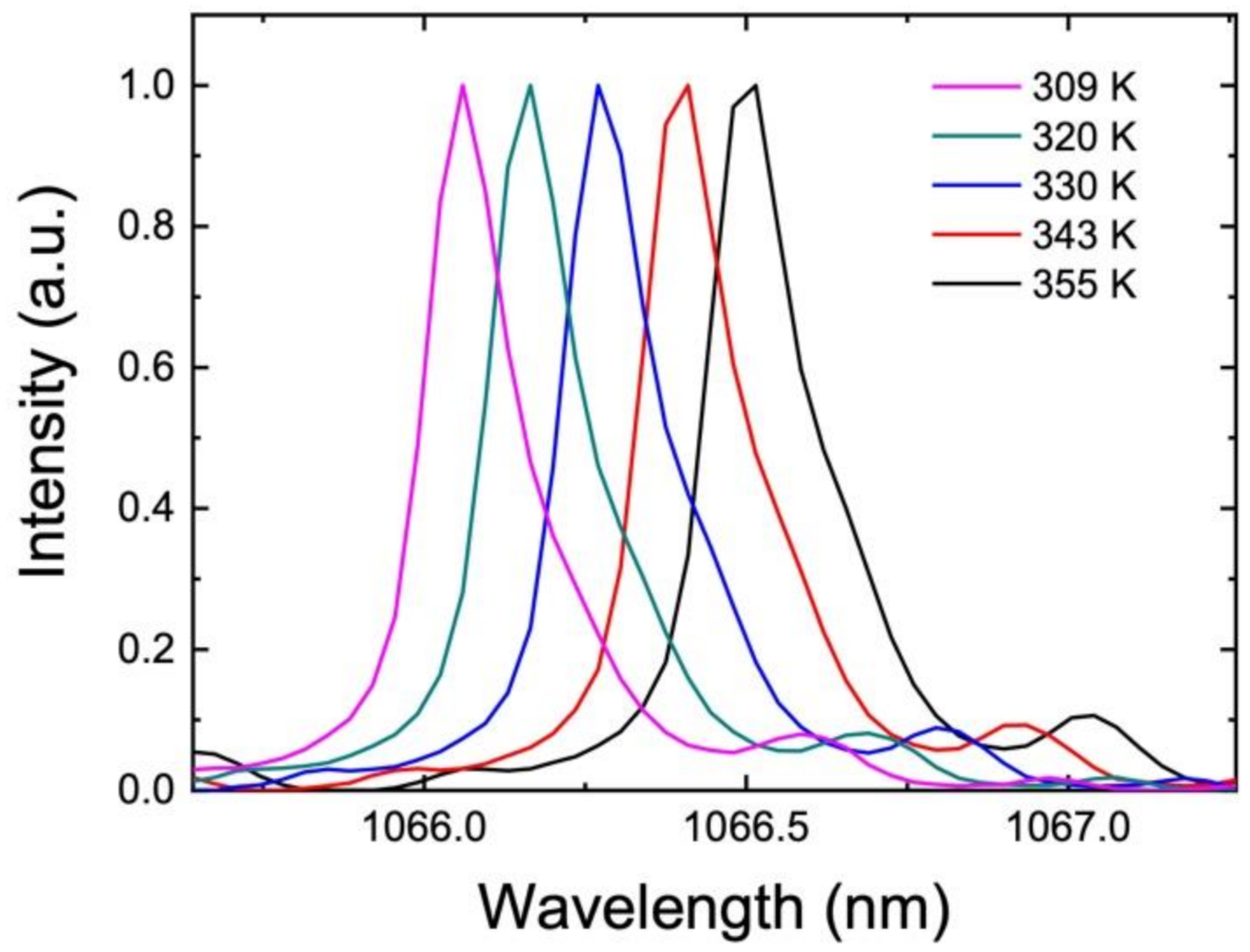
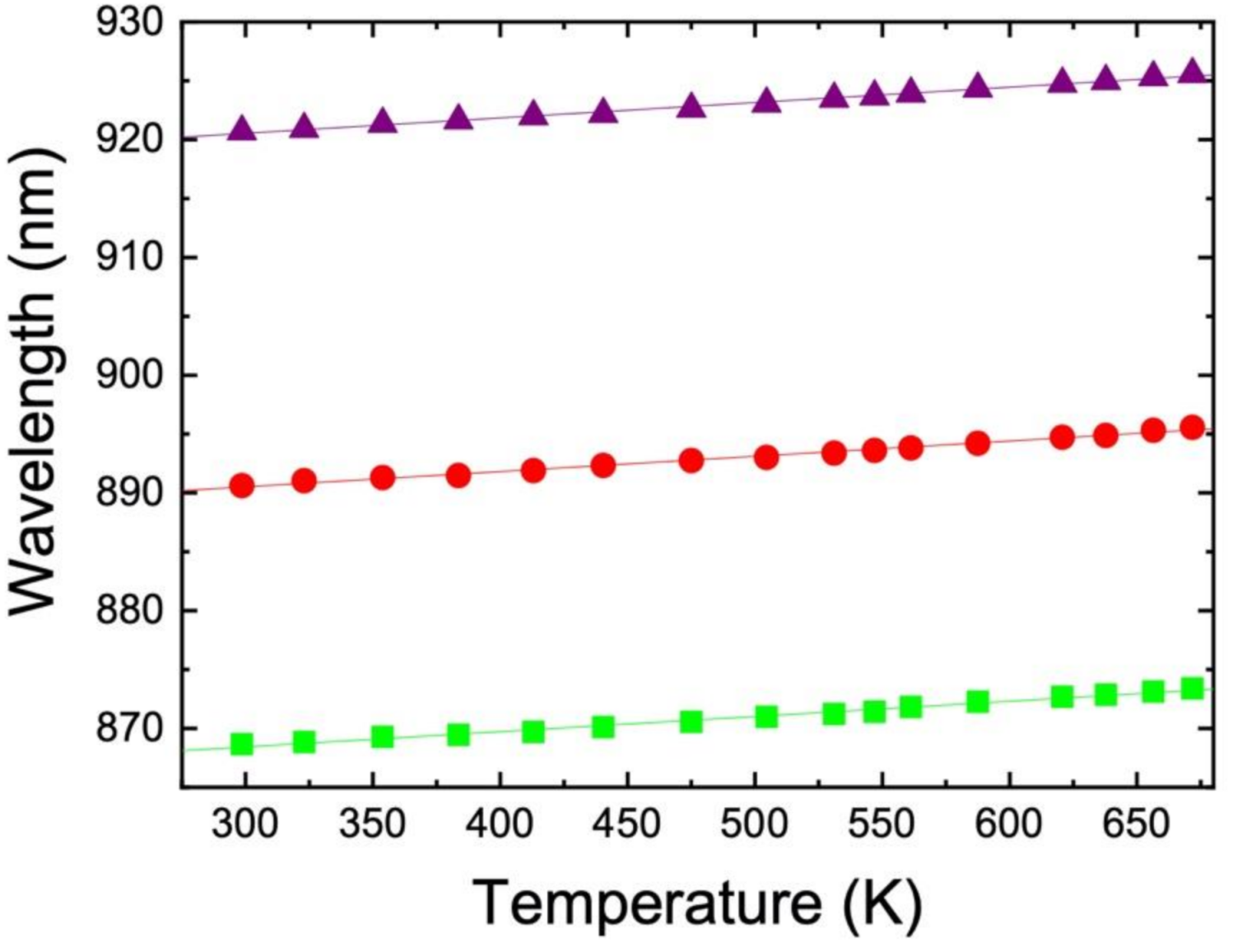
4.3. Displacement of the WGM
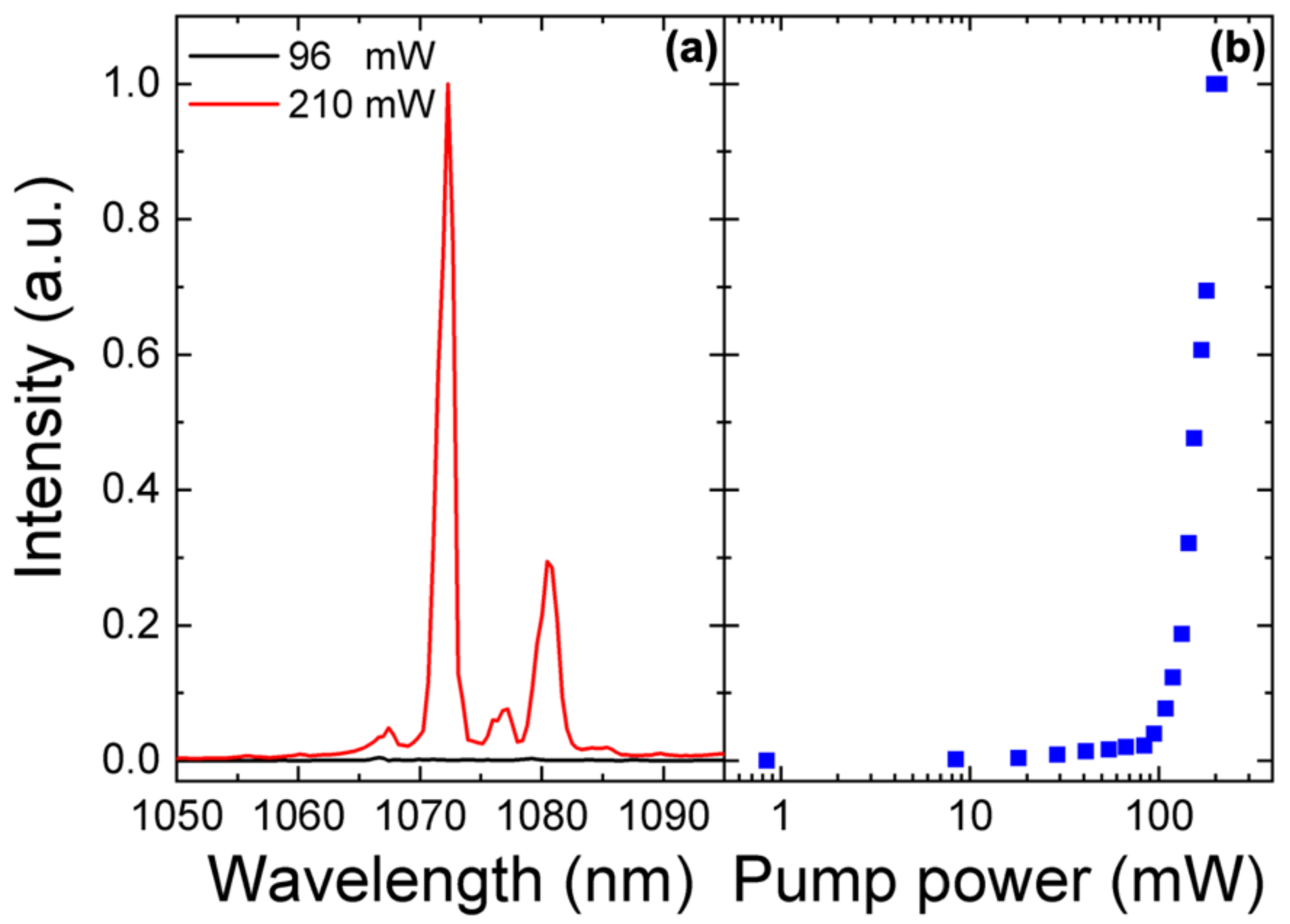
4.4. Laser Emission
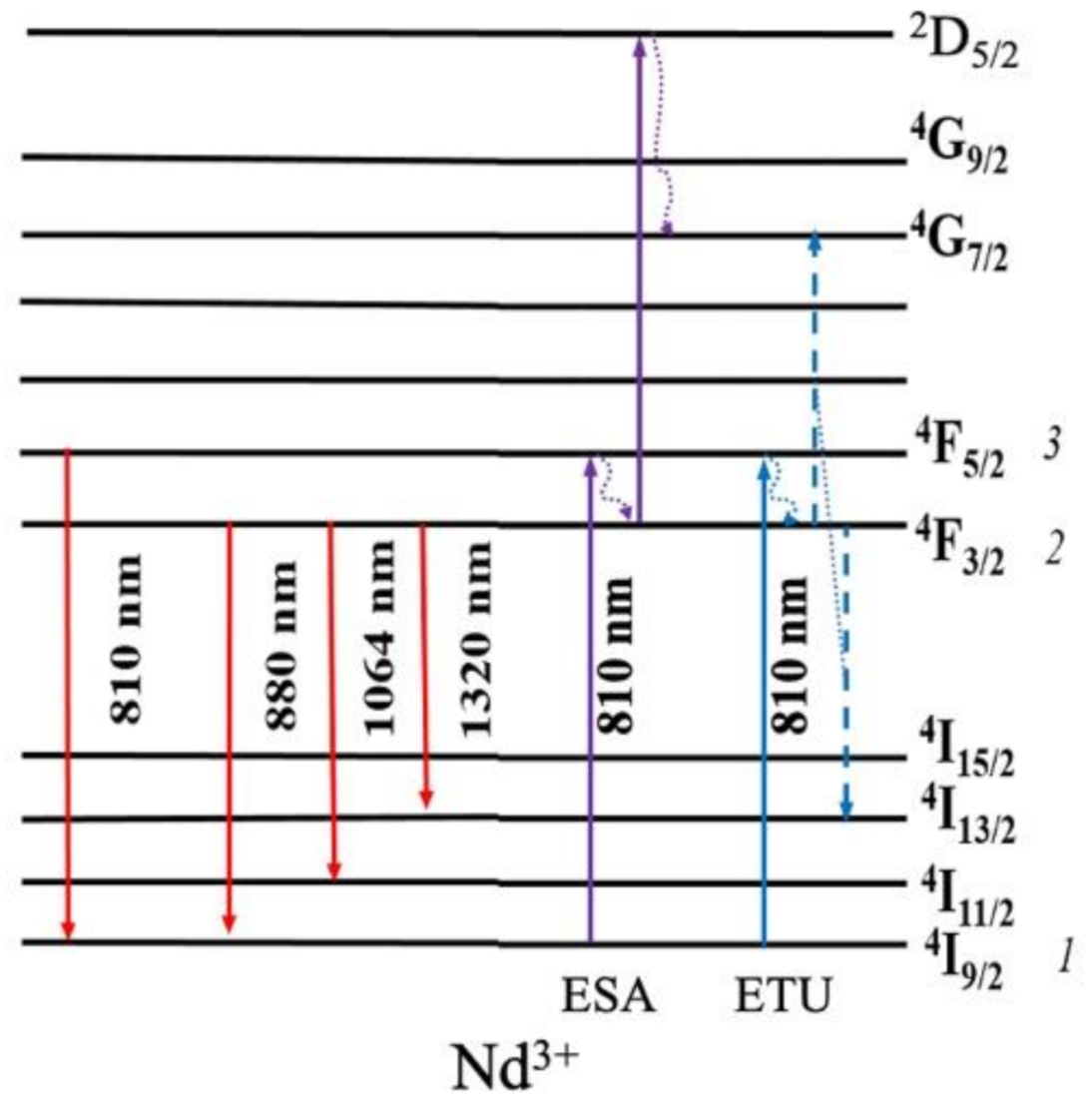
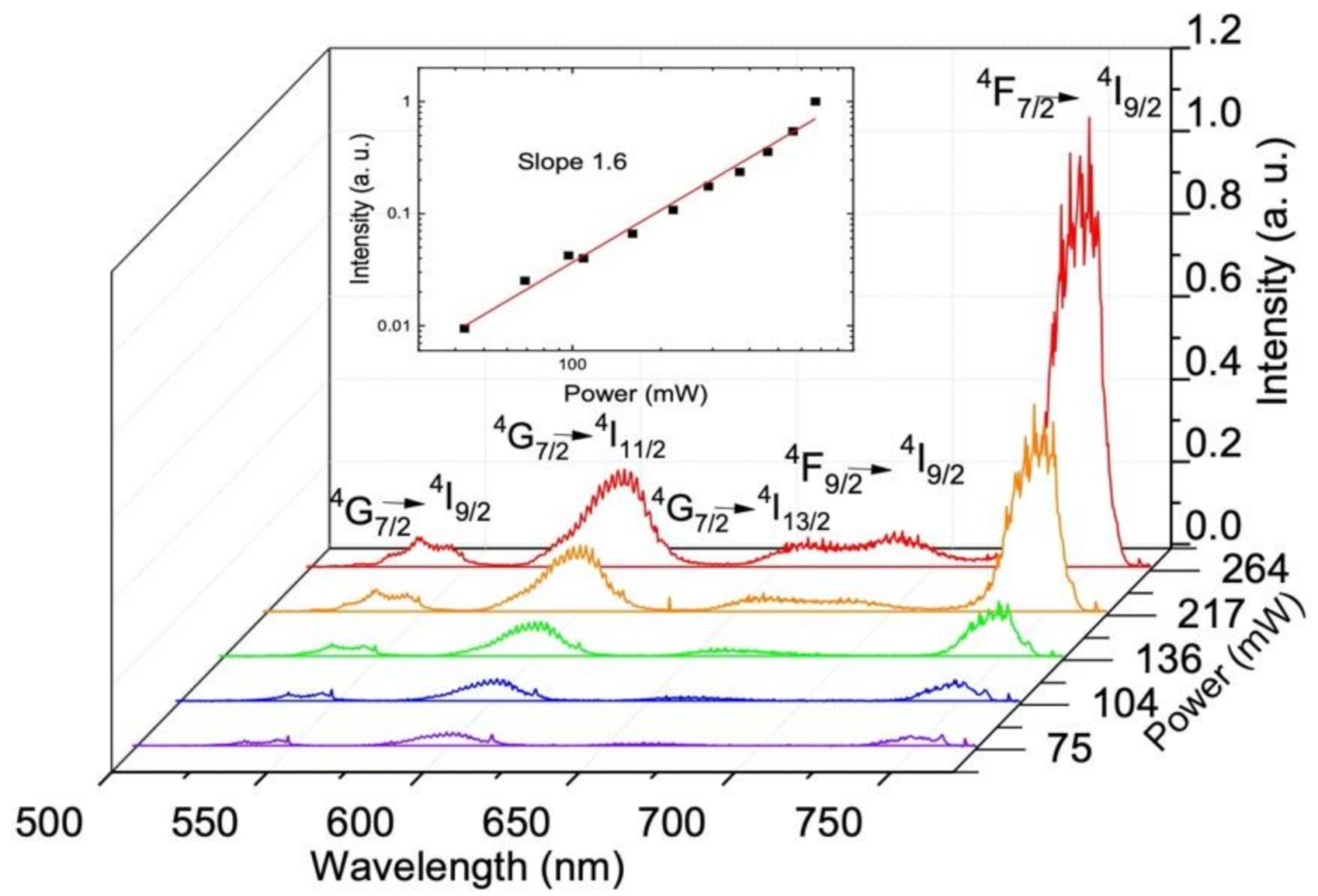
4.5. Upconversion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jensen, E.C. Use of fluorescent probes: Their effect on cell biology and limitations. Anat. Rec. Adv. Integr. Anat. Evol. Biol. 2012, 295, 2031–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medintz, I.L.; Uyeda, H.T.; Goldman, E.R.; Mattoussi, H. Quantum dot bioconjugates for imaging, labelling and sensing. Nat. Mater. 2005, 4, 435–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bünzli, J.-C.G. Lanthanide luminescence for biomedical analyses and imaging. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 2729–2755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horrocks, W.D.; Sudnick, D.R. Lanthanide ion luminescence probes of the structure of biological macromolecules. Acc. Chem. Res. 1981, 14, 384–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyatt, M.J.; Day, D.E. Glass properties in the yttria-alumina-silica system. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1987, 70, C-283–C-287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jander, P.; Brocklesby, W.S. Spectroscopy of yttria-alumina-silica glass doped with thulium and erbium. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 2004, 40, 509–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Qian, G.; Xiao, X.; Tian, X.; Ding, X.; Ma, Z.; Yang, L.; Guo, H.; Xu, S.; Yang, Z.; et al. The preparation of yttrium aluminosilicate (YAS) glass fiber with heavy doping of Tm3+ from polycrystalline YAG ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2018, 101, 4627–4633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaque, D.; Vetrone, F. Luminescence nanothermometry. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 4301–4326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Rodríguez, C.; Martín, L.L.; León-Luis, S.F.; Martín, I.R.; Kumar, K.K.; Jayasankar, C.K. Relevance of radiative transfer processes on Nd3+ doped phosphate glasses for temperature sensing by means of the fluorescence intensity ratio technique. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 195, 324–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín, L.L.; Haro-González, P.; Martín, I.R.; Navarro-Urrios, D.; Alonso, D.; Pérez-Rodríguez, C.; Jaque, D.; Capuj, N.E. Whispering-gallery modes in glass microspheres: Optimization of pumping in a modified confocal microscope. Opt. Lett. 2011, 36, 615–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wade, S.A. Temperature measurement using rare earth doped fibre fluorescence. Victoria 1999. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/45786919_Temperature_measurement_using_rare_earth_doped_fibre_fluorescence (accessed on 29 December 2020).
- Wade, S.A.; Collins, S.F.; Baxter, G.W. Fluorescence intensity ratio technique for optical fiber point temperature sensing. J. Appl. Phys. 2003, 94, 4743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, S.F.; Baxter, G.W.; Wade, S.A.; Sun, T.; Grattan, K.T.V.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Palmer, A.W. Comparison of fluorescence-based temperature sensor schemes: Theoretical analysis and experimental validation. J. Appl. Phys. 1998, 84, 4649–4654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yutian, W.; Likun, G. Rare earth doped optical fibers for temperature sensing utilizing ratio-based technology. J. Rare Earths 2006, 24, 171–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahala, K.J. Optical microcavities. In Proceedings of the 2005 European Quantum Electronics Conference, EQEC ’05, Munich, Germany, 12–17 June 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Matsko, A.B.; Savchenkov, A.A.; Strekalov, D.; Ilchenko, V.S.; Maleki, L. Review of applications of whispering-gallery mode resonators in photonics and nonlinear optics. IPN Prog. Rep. 2005, 42. Available online: http://engineering.nyu.edu/mechatronics/Control_Lab/Padmini/WGMLitSurvey/WGMReview.pdf (accessed on 29 December 2020).
- Zhu, J.; Özdemir, Ş.K.; Yilmaz, H.; Peng, B.; Dong, M.; Tomes, M.; Carmon, T.; Yang, L. Interfacing whispering-gallery microresonators and free space light with cavity enhanced Rayleigh scattering. Sci. Rep. 2015, 4, 6396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanditov, D.S.; Sydykov, B.S. Modulus of elasticity and thermal expansion coefficient of glassy solids. Phys. Solid State 2014, 56, 1006–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Rossmann, T.; Guo, Z. Temperature sensitivity of silica micro-resonators. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2008, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atroshchenko, G.N.; Sigaev, V.N. Glassy microspheres and their applications in nuclear medicine (review). Glas. Ceram. 2016, 72, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vollmer, F.; Arnold, S. Whispering-gallery-mode biosensing: Label-free detection down to single molecules. Nat. Methods 2008, 5, 591–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, S.; Ramjit, R.; Keng, D.; Kolchenko, V.; Teraoka, I. MicroParticle photophysics illuminates viral bio-sensing. Faraday Discuss. 2008, 137, 65–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Méndez-Ramos, J.; Abril, M.; Martín, I.R.; Rodríguez-Mendoza, U.R.; Lavín, V.; Rodríguez, V.D.; Núñez, P.; Lozano-Gorrín, A.D. Ultraviolet and visible upconversion luminescence in Nd3+-doped oxyfluoride glasses and glass ceramics obtained by different preparation methods. J. Appl. Phys. 2006, 99, 113510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Som, T.; Karmakar, B. Green and red fluorescence upconversion in neodymium-doped low phonon antimony glasses. J. Alloy. Compd. 2009, 476, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamelin, D.R.; Gudel, H.U. Upconversion Processes in Transition Metal and Rare Earth Metal Systems, In Transition Metal and Rare Earth Compounds; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2001; pp. 1–56. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Walo-Martín, D.; Paz-Buclatin, F.; Ríos, S.; Martín, I.R.; Martin, L.L.; Ródenas, A.; Sigaev, V.N.; Savinkov, V.I.; Shakhgildyan, G.Y. Temperature Sensing with Nd3+ Doped YAS Laser Microresonators. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1117. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11031117
Walo-Martín D, Paz-Buclatin F, Ríos S, Martín IR, Martin LL, Ródenas A, Sigaev VN, Savinkov VI, Shakhgildyan GY. Temperature Sensing with Nd3+ Doped YAS Laser Microresonators. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(3):1117. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11031117
Chicago/Turabian StyleWalo-Martín, Daniel, Franzette Paz-Buclatin, Susana Ríos, Inocencio R. Martín, Leopoldo L. Martin, Airán Ródenas, Vladimir N. Sigaev, Vitaliy I. Savinkov, and Georgiy Y. Shakhgildyan. 2021. "Temperature Sensing with Nd3+ Doped YAS Laser Microresonators" Applied Sciences 11, no. 3: 1117. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11031117
APA StyleWalo-Martín, D., Paz-Buclatin, F., Ríos, S., Martín, I. R., Martin, L. L., Ródenas, A., Sigaev, V. N., Savinkov, V. I., & Shakhgildyan, G. Y. (2021). Temperature Sensing with Nd3+ Doped YAS Laser Microresonators. Applied Sciences, 11(3), 1117. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11031117







