Abstract
Wearable electronics have been receiving increasing attention for the past few decades. Particularly, fiber-based electronics are considered to be ideal for many applications for their flexibility, lightweight, breathability, and comfortability. Furthermore, fibers and fiber-based textiles can be 3D-molded with ease and potentially integrated with everyday clothes or accessories. These properties are especially desired in the fields of bio-related sensors and energy-storage systems. Wearable sensors utilize a tight interface with human skin and clothes for continuous environmental scanning and non-invasive health monitoring. At the same time, their flexible and lightweight properties allow more convenient and user-friendly experiences to the wearers. Similarly, for the wearable devices to be more accessible, it is crucial to incorporate energy harvesting and storage systems into the device themselves, removing the need to attach an external power source. This review summarizes the recent applications of fibers and fiber-based textiles in mechanical, photonic, and biomedical sensors. Pressure and strain sensors and their implementation as electronic skins will be explored, along with other various fiber sensors capable of imaging objects or monitoring safety and health markers. In addition, we attempt to elucidate recent studies in energy-storing fibers and their implication in self-powered and fully wireless wearable devices.
1. Introduction
The demand for personal devices capable of biological and environmental sensing is greater, now more than ever. In particular, wearable devices have been receiving much attention, due to their ability to sense the physiological and environmental states while being worn [1,2,3,4]. These wearable devices can aid individuals who are exposed to physical injuries or hazardous environments by detecting physical impact, biofluid-based biomarkers, or environmental cues [5,6,7,8]. For these devices to perform their function while being worn, they need to be flexible, stretchable, and durable [9,10,11,12,13]. These mechanical requirements have shifted the recent attention to fibers. A paper review and analysis from the author’s side shows that the number of publications whose title includes “electronic fibers” has risen by more than ten folds in the last decade compared to the previous decade indicating the increased academic interest in fiber-based electronics. The development of the electronic fibers became possible, due to the convergence of rapidly advancing fields of nanotechnology, electronics, and material engineering that has granted functionalities to conventionally passive fibers. For example, incorporating active materials, such as metals, conductive polymers, and carbon-based nanomaterials into fiber created conductive fibers that can be a building block of wearable electronic devices [14,15,16,17,18]. These fiber-based wearable devices, compared to conventional planar wearable devices, have several benefits. In addition to the flexibility and stretchability of many current wearable devices, fiber-based wearable devices also offer breathability, the ability to conform to complex body structures, and resistance to wear and even washing [1,5,12]. Moreover, fiber materials can be carefully selected according to their physical and chemical properties, and various combinations of active materials offer different functionalities, such as high elasticity, conductivity, and resistivity to different stimuli. Further, fiber-based textile manufacturing has been used as a popular and well-established technique for decades, exploiting the hierarchical frame, which comprises fiber, yarn, and fabric, suggesting the ease of scalability and integration into conventional garments. Therefore, recent attention has been focused on fiber-based electronics capable of physiological and environmental sensing. The fiber-based electronics are not limited to wearable sensors. Recently, fiber-based energy-storage systems have been receiving increasing attention, due to their self-powering potential for complete wearability [19,20,21]. In this review, various types of fiber-based sensors with motion and accident detection [2,22], biomarker detection [11,23], and environment detection [24,25] capabilities are explored, along with popular fabrication methods, such as coating, spinning, and thermal drawing process (TDP). In addition, fiber-based batteries and supercapacitors are investigated. Lastly, current trends and challenges of fiber-based wearable devices are discussed.
2. Fabrication Techniques for Fiber-Based Electronics
Fibers for sensors and energy-storage systems are synthesized through various manufacturing processes. Materials and fabrication methods should be carefully selected, considering not only the performance of the fibers, but also the economic aspect. Numerous manufacturing methods have been utilized, such as dip-coating, spinning, deposition, and thermal drawing. The advantages and disadvantages of the most commonly used fiber manufacturing processes are compared in Table 1. Dip-coating is a method of coating fibers by dipping them into a solution containing active materials. The coating can be done relatively quickly without special equipment, making it suitable for mass production. However, it consumes excessive solution and active materials, and the resulting fibers are associated with poor performance. Wet-spinning is a method of extruding a solution of polymers and active materials. Although the manufacturing process is complicated and time-consuming, it boasts tunability of the fiber diameter and excellent dispersion of the filler materials [26]. A similar method, dry-spinning, does not require purification, so it is more productive than wet-spinning [27]. Melt-spinning extrudes materials by applying heat and making them viscous. It can be simple and cost-effective. However, it is compatible with only a limited concentration of active filler materials. Electrospinning is a method of manufacturing nanofibers by pulling a polymer solution using electric force. A deposition is the process of growing a thin film on a substrate. Chemical vapor deposition is a method of chemically depositing a gas reactant using plasma or thermal energy. Compared to other methods, it has the advantage of having high bonding properties with active materials. Electrodeposition is a method of depositing colloidal particles in a solution onto a conductive material using an electric field [28]. It is possible to manufacture fibers with high conductivity at a low cost, but its process takes a long time. Lastly, thermal drawing is a scale-down method to fabricate fibers by applying temperature to a preform that can incorporate various materials. The resulting fiber’s structure follows that of the preform, and this makes complicated fiber designs possible. Furthermore, the fiber’s thickness can be easily adjusted by varying the temperature and external force of the capstan. It is also characterized to be very simple and expandable [29].

Table 1.
Comparison of common fabrication methods for fiber-based electronics.
3. Fiber-Based Sensors
In this chapter, we introduce fiber-based tactile sensors, chemical sensors, photosensors, and temperature sensors. These sensors can detect changes in physiological and external environmental factors in real-time. The fabrication methods, materials, and sensing and mechanical properties of these fiber sensors are summarized in Table 2.

Table 2.
Summary of fiber-based sensors.
3.1. Tactile Sensing Fibers
Pressure and strain sensors have been a popular field of research for decades. They electrically mimic the function of mechanoreceptors inside human skin (hence the name e-skin) and show promising applicability in soft robotics and sensory prostheses [5]. Conventionally these e-skins were fabricated in a film using an elastic polymer substrate and conductive polymers or nanomaterials [6,59]. These film e-skins usually adhere to the surface of robots and human skins for monitoring environmental and physiological stimuli, such as external pressure, heartbeat, or joint angle [60,61]. Although these film e-skins showed great sensing capabilities, flexibility and stretchability, the longevity and breathability remain questionable, limiting their long-term usage, especially as wearable sensors [1,12]. Therefore, many studies attempted to fabricate wearable e-skins using functional fiber-based textiles [19,43,62,63]. These textile tactile sensors can be classified by the sensing mechanisms: (1) Resistive sensors [10,40,64,65,66,67], (2) piezoelectric sensors [43], and (3) capacitive sensors [62,68,69]. To measure the sensitivity of resistive and capacitive tactile sensors, Gauge Factor (GF) is often used. GF can be calculated by ΔR/R0/ε or ΔC/C0/ε for resistive and capacitive sensors, respectively (ΔR: change in resistance under the stain, R0: baseline resistance, ε: strain). A number of factors can influence GF, such as the filler materials, percolation network, piezoresistive mechanism, and structure of the sensor. [69,70]. Therefore, GF can be calibrated by tuning these factors. For example, woven or knitted structures of conductive fibers provide several electrical contacts and tend to increase GF [19]. However, it has been suggested that the higher GF is associated with lower stretchability [13,71]. In the case of capacitive sensors, the parallel plate capacitor design leads to the changes in surface area and dielectric layer thickness at the same time in response to mechanical stimuli. This causes a linear sensitivity and a maximum GF of 1 [13,72].
The resistive tactile sensors are the most popularly studied for their simplicity. These conductive sensors change their resistance in response to the mechanical stress, and this change in the resistance can be used to determine the amplitude of the stress. Pre-existing natural fibers can simply be made into resistive textile tactile sensors via the outside coating method. In one study, Zhang et al. reported that depositing nickel (Ni) onto cotton fabric via the electroless deposition (ELD) technique resulted in highly conductive fabrics (21.82 S/cm) that are capable of detecting strains via resistive changes [73]. This cotton fabric strain sensor suffered from limited stretchability of 14% and durability (50% decrease in sensitivity after ~300 stretch cycles), due to the mechanical characteristics of deposited Ni. Nonetheless, this fabric sensor showed promising applicability as a wearable strain sensor as it was able to be fixed onto the fingers and arm joints to detect bending. Dip-coating of various carbon-based materials and polymers is also a popular method of fabricating conductive natural fabrics because it is highly effective and cost-effective. One study fabricated conductive cotton and wool fabric by dip-coating them in a solution containing graphene nanoplate (GNP) and carbon black (CB) [12]. Both the conductive cotton and wool fabrics showed good stretchability and strain sensing ability up to 150%, with a maximum GF of 6 for cotton fabric and 0.5 for wool fabric. Furthermore, the sensitivity of the conductive fabrics decreased insignificantly after 1000 cycles of 75% stretching. These sensors were then taped onto a volunteer’s finger and detected fast finger movements, further suggesting the usefulness of natural fabric-based sensors as wearable devices. Among many carbon-based materials used to make conductive textiles, carbon nanotubes (CNTs) are most popularly selected for their high surface area, high electrical conductivity, and high stability [65,74,75,76,77,78]. A strain sensor based on a conductive cotton fabric was made by dip-coating a pristine cotton fabric into a solution of single-walled CNT (SWCNT) (Figure 1a) [30]. This sensor was able to sense the strain up to 100%, and due to its high flexibility and stretchability, this fabric sensor could be twisted and knotted. Furthermore, it was possible to wash the sensor using a washing machine and detergent eight times with an acceptable change in resistance, implying potential applicability of this sensor as a wearable device. Polymer fibers have also been utilized to fabricate textile tactile sensors. Chen et al. fabricated a strain sensor by dip-coating polyurethane (PU) fiber-knitted fabric into silver nanowire (AgNW) solution [31]. This PU fabric sensor showed a good stretchability of up to 140% and a maximum GF of 10. What’s more, the flexibility and stretchability of this fabric sensor allowed it to be weaved into an e-textile for 2D force mapping. Other fibers and active materials have also been used, such as cellulose acetate fiber (CAF) and reduced graphene oxide (RGO) [79].
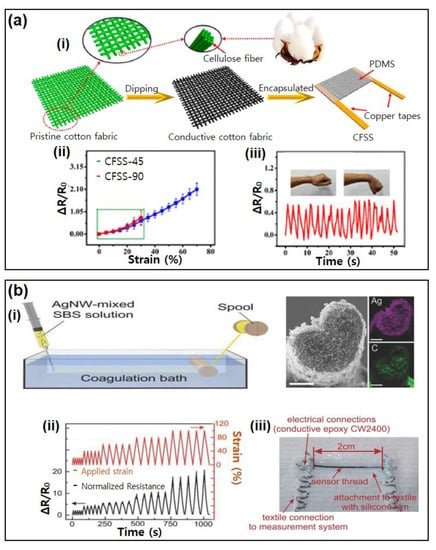
Figure 1.
Fiber-based resistive tactile sensors. (a) (i) Natural fabrics can be made into tactile sensors through dip-coating. Pristine cotton fabric was dipped into a solution of multilayer graphene. (ii) The behavior of this sensor’s resistance in response to strain. (iii) The cotton fabric-based tactile sensor was attached to a human wrist to monitor wrist bending. Reproduced with permission from [30], Copyright (2020), American Chemical Society. (b) (i) Conductive composite fibers can be fabricated through spinning methods. SBS-AgNW mixture was wet-spun into a conductive composite fiber (left). Cross-sectional image of SBS-AgNW fiber (right). (ii) The behavior of SBS-AgNW fiber’s resistance in response to strain. Reproduced with permission from [63], Copyright (2015), Wiley. (iii) A fibrous sensor was attached to a textile using a silicone film. Reproduced with permission from [41], Copyright (2008), MDPI.
Conductive composite fibers have also been fabricated as resistive tactile sensors. These fibers with endogenous conductivity are usually fabricated with an elastic polymer incorporated with conductive fillers, via spinning methods. Melt-spinning is popularly used for its economical fabrication of conductive fibers. Bautista-Quijano et al. fabricated melt-spun polycarbonate (PC) and multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNT) into a fiber with a diameter of around 300 μm [40]. This fiber strain sensor showed limited stretchability (less than 20% stretching before breakage) and conductivity of 2 × 10−5 S/c, but the maximum GF was relatively high at 16. In another study, thermoplastic elastomer (TPE) was mixed with CB and melt-spun into a fiber with a diameter of 315 μm [41]. This fiber was capable of sensing strain up to 80% with a higher maximum GF of 20 and conductivity 1 × 10−3 S/cm. This sensor withstood eight times of washing with detergent without any significant conductivity loss. Moreover, the researchers were able to attach 21 fiber sensors onto a t-shirt of a subject using silicone films to classify the wearer’s body position. Inherently, melt-spinning limits the concentration of the fillers, resulting in low conductivity [40,69] Wet-spinning is another conductive composite fiber fabrication method that allows outstanding dispersion of filler into the fiber with good mechanical properties [69,70]. In a study by Lee et al. a mixture of styrene-butadiene-styrene (SBS) and AgNW was wet-spun a conductive fiber (Figure 1b) [34]. In addition to the high electrical conductivity of 2450 S/cm, this fiber was also very stretchable up to 900% and able to sense strain up to 220% with a maximum GF of 15. Although a cyclic loading test with 1000 cycles revealed limited durability, the high stretchability and wide range of sensing allowed the researchers to attach these SBS-AgNW fiber sensors onto latex gloves to monitor finger joint movements and decipher sign language. In a more recent study by Tang et al., Ecoflex silicone, and MWCNT based core-sheath fiber was fabricated through the coaxial wet-spinning method, and its applicability as a wearable strain sensor was tested [35]. The conductive core was spun from an MWCNT-dispersed silicone solution, and the insulation sheath was spun from a pure silicone solution. Although its conductivity of 1 × 10−2 S/cm was lower than that of SBS-AgNW fiber, it showed a high stretchability of 300% and a maximum GF of 1378. Furthermore, its resistance was stable during 10,000 cycles of 100% strain, indicating excellent durability. The researchers then weaved silicone-MWCNT fiber sensors into a fabric glove to detect finger motions. Conductive polymers have also been utilized as conductive fillers. One study utilized PU and poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) polystyrene sulfonate (PEDOT:PSS) to fabricate a conductive fiber via wet-spinning [36]. This fiber showed a relatively good electrical conductivity at 9 S/cm coupled with a high maximum GF of 10,000 and a wide strain sensing range (0–200%). Electrospun nanofibers can also be made into strain sensors. Liu et al. electrospun a mixture of Polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) and PEDOT:PSS and encapsulated the electrospun nanofibers between Kapton and Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) [44]. The resultant conductive nanofiber-based strain sensor had a limited sensing range between −1.2% and 1.2%, but it showed a relatively high GF of 396 and a fast response time. Additionally, the researchers attached the PEDOT-PVA fiber sensor onto a finger to detect the finger bending while powering it with solar cells.
Recently, increasing attention has been given to piezoelectric textile tactile sensors. These sensors are able to transform mechanical stimuli into electrical energy, providing simultaneous sensing and self-powering capabilities. In one study by Gou et al., electrospun polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) and Barium titanate (BaTiO3) mixture was used to fabricate piezoelectric nanofibers [45]. The PVDF-BaTiO3 nanofibers comprised a pressure-sensor capable of detecting up to 40 kPa. This sensor’s sensibility was measured to be 17 mV/kPa, and its piezoelectricity remained stable over 1750 cycles of pressure loading, boasting its good durability. Similarly, Zhu et al. coaxially electrospun a pressure-sensing nanofiber with PVDF-BaTiO3 as a core and PVDF and graphene oxide (PVDF-GO) as a conductive sheath [46]. This nanofiber-based sensor showed a wider sensing range (80–230 kPa) and higher sensitivity (10.89 mV/kPa). Furthermore, an array of these textile sensors was able to create a 2D map of the pressed objects and monitor various joint movements when attached to a human arm. The above-mentioned examples utilized piezoelectric nanofibers to fabricate planer textile sensors. Furthermore, those sensors employed piezoelectric ceramics. While piezoelectric ceramics provide high piezoelectric outputs, they are mechanically hard, lowering their flexibility and stretchability [26]. On the other hand, there are efforts to create single piezoelectric fiber-based sensors using piezopolymers with an inherent flexibility that can further capitalize on the mechanical merits of the fibers and their potential to be integrated into conventional garments. Lund et al. reported a simple melt-spinning method for fabricating a piezoelectric fiber with a core-sheath structure with a diameter of 60 µm [42]. The conductive core was composed of CB and polyethylene, and PVDF sheath that acted as a piezoelectric layer. The researchers weaved these fibers into a textile, which in turn was sewn into a bag strap to harvest energy as the wearer walked on stairs. Importantly, it should be noted that the tactile sensing capability of this fiber was not tested, and the limited stretchability of 20% was suggested. For wearable sensors, stretchability is an important factor that influences the comfort and durability of the device. In a study by Sim et al., a piezoelectric fiber capable of pressure and strain sensing was made by wrapping electrospun polyvinylidene fluoride trifluoroethylene (PVDF–TrFE) mat between an inner electrode (silver-coated nylon yarn) and an outer electrode (CNT sheet) (Figure 2a) [43]. Although this fiber was thicker with a diameter of 320 µm, it boasted enhanced stretchability of 50% and pressure-sensing capability up to 160kPa. This fiber’s flexibility and stretchability allowed it to be knotted, coiled, and weaved into the fabric. The coiled PVDF-TrEF fibers preserved their sensitivity during a cyclic loading test with 400,000 cycles of 50% strain.
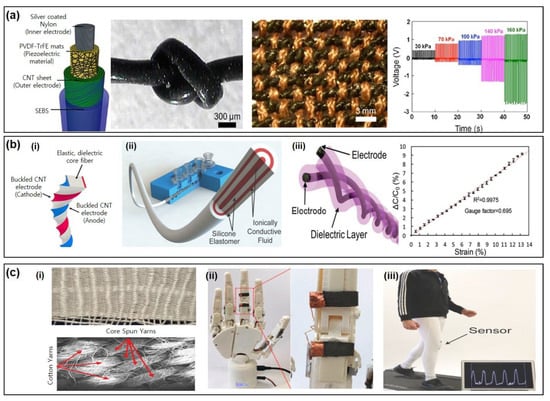
Figure 2.
Fiber-based piezoelectric and capacitive tactile sensors. (a) Piezoelectric tactile fiber sensor was fabricated with an electrospun PVDF-TrFE fiber wrapped with silver-coated nylon yarn. This fiber sensor was flexible enough to be yarn and made into a textile. Reproduced with permission from [43], Copyright (2015), Wiley. (b) Core-spinning with silver fiber and cotton fiber. This fiber was integrated into cotton fabric. Reproduced with permission from [80], Copyright (2019), Wiley. (c) (i) Multicore-shell printing with dielectric elastomer and ionically conductive fluid. (ii) This fiber sensor was sewn onto pants to detect walking. Reproduced with permission from [81], Copyright (2015), Wiley. (iii) Cotton fabric based capacitive tactile sensors were attached to a robotic hand. Reproduced with permission from [80], Copyright (2020), American Chemical Society.
Lastly, capacitive sensors composed of two opposite electrodes and one dielectric layer between the electrodes have been developed. Direct current can generate capacitance between the two electrodes whose amplitude depends on the geometric parameters, such as the distance and the area between the two electrodes. Therefore, a tactile stimulus shifts the sensor’s geometry and capacitance. This change in capacitance is measured and utilized to determine the amplitude of the applied stimuli. The capacitive sensors tend to show a linear sensitivity and better durability, especially compared to resistive sensors [13,22,82]. Wu et al. made an electric layer with silk fabric and AgNWs coated on the outside and separated by a polyester fabric dielectric layer [83]. This fabric-based sensor was capable of detecting pressure up to 5 kPa with 0.3 GF and stretching up to 25%. Furthermore, this sensor was used to create a 2D map of the applied pressure and attached to a volunteer’s arm to recognize the movement of an arm. Other studies reported fiber-based capacitive tactile sensors [40,54,81,82,84]. Cooper et al. fabricated elastomeric fibers through a melt extrusion method with a hollow core, in which eutectic gallium indium (EGaIn) was filled and acted as an electrode [84]. Two of these fibers were twisted together to form two EGaIn electrodes separated by the dielectric elastomeric outer layer. This capacitive sensor showed a GF of 0.82 and stretchability up to 100%. This fiber sensor was thicker in diameter (diameter of 850 μm), compared to other fiber-based tactile sensors. Nonetheless, this sensor was capable of detecting not only strain and pressure, but also torsion. Twisting two electrode-fibers together has also been utilized in other studies. In a study by Zhang et al. silver-nylon fiber as an electrode was core-spun with cotton fiber that acted as a dielectric layer (Figure 2b) [54]. Similarly, the researchers twisted core-spun fibers, and the resultant tactile-sensor fiber showed a diameter less than 600 μm. The GF was reported to be 0.7, and the strain detection range was limited to less than 18%. However, this fiber showed very stable electrical characteristics after 10,000 cycles of 15% strain and the ability to be weaved into the fabric. The researchers were able to use this fabric to detect pressure below 200 kPa. These fiber-based capacitive sensors require binding two fibers to fabricate one sensor. On the other hand, all-in-one fiber capacitive sensors were reported [68,81]. A strip was cut from a silicone rubber film to create a fiber with a square cross-section with 2 mm thickness and 2 mm width [81]. On two opposing sides of the fiber, MWCNT sheets were attached and acted as two electrodes that were separated by the fiber core (silicone rubber). Although this fiber sensor was thick, it was capable of sensing strain up to 200% with 0.6 GF. In another study, Frutiger et al. utilized multi-shell printing to fabricate a fiber whose inside was composed of two ionic conductive layers separated and encapsulated by the silicone elastomer dielectric layer (Figure 2c) [68]. The multi-shell printed fiber strain sensor with a diameter of 1.5 mm showed a strain detection range up to 700% with a GF of 0.35.
In summary, resistive, piezoelectric, and capacitive types of fiber-based tactile sensors were explored. Active materials, such as metals, carbon-based materials, and conductive polymers have been utilized along with natural fabrics or polymer fibers to fabricate flexible, stretchable, and durable fiber-based tactile sensors. Applications of these sensors in physiological monitoring have been introduced, such as pulse and joint motion detection. The physiological monitoring capability has been suggested to be useful in sports and rehabilitation settings [3,4,80]. However, none of the fiber-based wearable tactile sensors has yet been commercialized to our knowledge, probably due to the limited durability and the resistance to various environmental factors of these fibers, which should be addressed in the future.
3.2. Chemical Sensing Fibers
Chemicals present in our body or surroundings provide countless information. Accordingly, chemical sensors with continuous real-time monitoring of chemical markers can be developed into wearable devices. These chemical sensors are categorized to be environmental scanning or health monitoring. Chemical sensors for environmental scanning can mimic the olfactory system by detecting and quantifying local exposure to hazardous vapors, such as nitrogen dioxide (NO2) [85,86,87], ammonia (NH3) [88], and hydrogen chloride (HCl) [89]. Chemical sensors for healthcare typically detect the markers in sweat [90,91,92,93], tears [94,95,96], saliva [97,98], and respiration [99,100,101]. In particular, fiber-based chemical sensors are able to be used in sports apparel to detect pH, cortisol, glucose, and sodium ions in sweat. Sweat can provide a simple and convenient medical examination in a non-invasive manner [102]. The fiber-based sweat sensors have the advantages of being comfortable, breathable, and reduced risk of skin contamination compared to the patch-type, which is directly attached to the skin. In the aspect of sensing mechanism, chemical sensing fibers have been fabricated based on the (1) chemiluminescence, (2) chemiresistive, and (3) electrochemical mechanism.
Various sensing materials have been studied for vapor sensing fibers based on chemiluminescence and chemiresistive mechanisms. Chemiluminescent sensing has advantages in terms of measurement simplicity, portability, and low cost [103]. In a pre-existing chemiluminescent-based approach, luminescence signals are collected through a thermal-drawn optical fiber and transmits it to a photodetector at the end of the fiber [104]. In order to increase sensitivity and optical transmission, Gumennik et al. fabricated an optical fiber with photoconductive detectors embedded along the fiber axis to detect the emitting light in the hollow core, as shown in Figure 3a [55]. The peroxide vapor reacts with the sensing agent coated on the hollow core to emit light, and the electrical signal is recorded by an electrode in contact with an amorphous Se97S3-based photodetector. As shown in Figure 3b, the fiber can detect a low concentration of NO2 at 10 parts-per-billion (ppb).
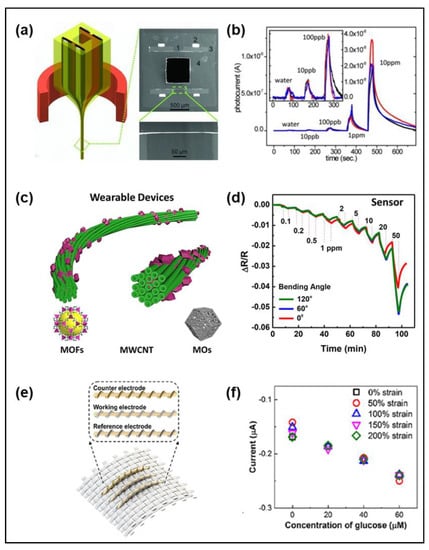
Figure 3.
Chemical sensing fiber. (a) Cross-sectional SEM image of the chemiluminescent fiber. (b) Sensitivity to peroxide vapor down to 10 ppb. Reproduced with permission from [55], Copyright (2012), Wiley. (c) Schematics of MOFs/MWCNT fiber. (d) Sensitivity to NO2 down to 0.1 ppm under bending. Reproduced with permission from [47], Copyright (2017), American Chemical Society. (e) Schematic of the fibers integrated into a textile. (f) The calibration plot of the chronoamperometric responses of the fiber up to 200% strain. Reproduced with permission from [39], Copyright (2019), American Chemical Society.
Early flexible chemisresistive gas sensors were synthesized using metal oxides and conductive polymers [105,106,107]. However, due to the decrease in sensitivity of these sensors at a high temperature [108], carbon-based materials or metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) have been used for chemiresistive fiber via chemical vapor deposition (CVD) or dip-coating. MOFs are attracting attention as sensor materials, due to their high porosity, structural flexibility, and large surface area [109]. Rui et al. developed the hybrid fiber in which ZIF-67-Co MOFs combined with highly conductive MWCNTs [47]. The MOFs/MWCNT sheet synthesized by CVD is twisted into the fiber, which has a negative resistance response to NO2 (Figure 3c,d). Although the sensitivity of fibers synthesized by CVD is quite high, the long manufacturing time can limit mass production. Yun et al. demonstrated the RGO-based fiber fabricated by dip-coating with biomolecular glue, which showed a response to NO2 gas with a low detection limit and excellent electrical conductivity retention at a bending radius of 1 mm [110]. As it is woven with other fibers with a built-in electric circuit, LED light is turned on by NO2 exposure. In order to further increasing the sensitivity, efforts are being made to increase the surface area of the active materials. Recently, metal oxides, which can increase the active site area and charge transfer coefficient by absorbing oxygen atoms, such as zinc oxide (ZnO), have been used as coating materials by making mesoporous structures through the calcination process [32].
Recently, many studies have utilized three-electrode electrochemical platforms, which have the advantage of miniaturization, high sensitivity, and free-labeling, for detecting pH, cortisol, glucose, and sodium ions in sweat. Liu et al. fabricated the polyester threads coated with carbon ink and glucose oxidation for the working electrode and detected glucose with a highly linear response in the buffer and blood samples [111]. Another sweat sensor for glucose detection was produced by dry spinning gold nanowire (AuNW) and an elastic polymer, as shown in Figure 3e [39]. For the working electrode, the dry spun AuNWs-fiber was functionalized with glucose oxidase via electrochemical deposition. The fiber achieved a linear response up to 200% strain with a sensitivity of 11.7 μA mM−1 cm−2 (Figure 3f). The current from the fiber attached to the forearm increased for 1 h after a meal and decreased after 2 h. By the same synthesis method, a gold fiber coated with polyaniline (PANI) detected the hydrogen ion via the deprotonation and reprotonation process [112]. Sekar et al. developed the commercial carbon yarn integrated with ellipsoidal iron(III) oxide (Fe2O3) by the simple hydrothermal method to detect cortisol for recognizing the stress response [56]. The same group improved biocompatibility by incorporating ZnO nanorods into carbon yarns [113]. For monitoring the salinity level of sweat, the PEDOT:PSS-based fiber can be used for detecting the sodium chloride concentration [37]. The PEDOT:PSS fiber was simply fabricated through the wet-spinning process, and its conductivity varied with the concentration of sodium chloride with the high output signal. Since these sweat sensors can detect biomarkers non-invasively, they are easy to access in clinical trials, but it is still difficult to commercialize, due to the low sweat volumes, irregular sweating without stimulation, and the possibility of evaporation.
3.3. Photo-Sensing Fibers
Photosensors are used for imaging or scanning, ultraviolet (UV) radiation monitoring, and optical communication in medical, military, and security systems. However, photosensors with lenses or beam splitters have a large size, heavy weight, and limited sustainability and field of view [114]. The fiber-based photosensors do not require a lens and can be woven into a lightweight and low optical density textiles to detect the direction and wavelength of an electromagnetic field over a large area. On the other hand, excessive exposure to UV rays can lead to erythema, cataracts, and skin cancer, so UV monitoring is very necessary for people who stay outdoors for long periods of time [115]. The fiber-based UV sensors can be lightly worn on the wrist and can provide the degree of UV light exposure in real-time. These fibers typically are fabricated as a photoconductive semiconductor p–n diode junction contacted by adjacent electrodes.
The first photo-sensing fiber for imaging was fabricated by the TDP in 2004 [50]. The fiber was composed of amorphous chalcogenide glass (As40Se50Te10Sn5) core in contact with Tin microwires and enclosed with a transparent insulating polymer (Figure 4a). Chalcogenide glasses have photo-sensing capability that generates an electron-hole pair upon exposure light in visible and Infrared (IR) ranges and the current flows through the microwires. The fibers were flexible enough to be woven into the spectrometric textile (Figure 4b). More complex functions can be performed by combining multiple optoelectronic within a single fiber. The eight detectors arranged in the optical fiber could extract information about the direction and wavelength of incident radiation over a visible spectrum (Figure 4c,d) [57]. A 32 by 32 array measuring 0.1 square meters reconstructed diffraction images of polychromatic illumination for all rotation angles of the object. However, the amorphous semiconductor core has difficulties in achieving high light absorption and effective contact with the electrode. Another approach relied on the mechanism of sonochemical nanowire growth in amorphous selenium (Se) domains [116]. This method could determine the phase and direction of crystalline nanowires that make direct contact with the electrodes and maintain the sensitivity, light absorption, and response speed for effective photo-sensing. Because of their complex structure, fiber sensors for imaging or scanning are mostly synthesized through thermal drawing. Photo-sensing fibers can also be used for optical communications. Rein et al. integrated light-emitting, and photo-sensing p-i-n diodes into optical fibers via thermal drawing [51]. The commercialized semiconducting diodes were inserted in pockets, and thermal drawing was performed while feeding two wires to the fiber. A three-megahertz two-way optical communication was demonstrated between the fabrics containing light-emitting and photo-sensing fibers.
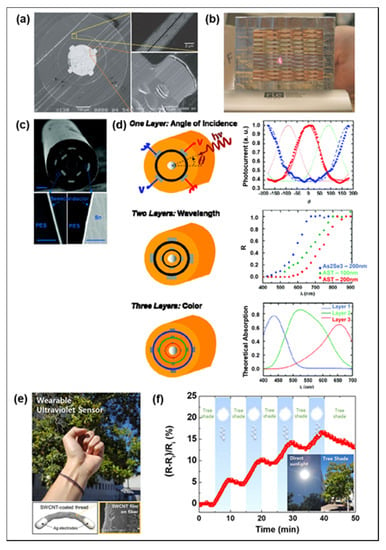
Figure 4.
Photosensing fiber. (a) Cross-sectional SEM image of the photosensing fiber. (b) A woven spectrometric textile. Reproduced with permission from [50], Copyright (2004), Nature Publishing Group. (c) Cross-sectional SEM image of the double-layer fiber (d) Schematics of 3 types of fibers for detecting the direction, wavelength, and spectrum of incident radiation. Reproduced with permission from [57], Copyright (2009), American Chemical Society. (e) Top: UV monitoring fiber is worn on the wrist. Bottom: Schematic and SEM image of the fiber. (f) Normalized resistance of the fiber under natural sunlight and tree shade. Reproduced with permission from [33], Copyright (2018), American Chemical Society.
UV monitoring sensors utilize the change in conductivity by adsorption/desorption between oxygen molecules and the holes of semiconductor ZnO [117,118,119], gallium nitride (GaN) [120,121], titanium dioxide (TiO2) [122], and CNT [123]. Zhang et al. fabricated the Kevlar fiber coated with ZnO nanowires by plasma etching, which directly responded to UV exposure from 0.2 to 1 mW cm−2 [124]. Xu et al. fabricated a self-powered p-CuZnS/n-TiO2 fiber for the UV monitoring with high outstanding responsibility and ultrahigh photocurrent [58]. TiO2 nanotube arrays had a large bandgap around the UV region, but their quantum efficiency is low due to the high recombination rate of electron-hole pairs. To overcome this limitation, CuZnS is used as a p-type transparent conductor, which is advantageous to improve photocurrent. The p-CuZnS/n-TiO2 fibers could be worn as a bracelet and provide the measurement of UV exposure through a smartphone. Although these solid-state sensors have shown high performance in UV detection, they are limited by the complex processing and high manufacturing cost, and more importantly, poor mechanical properties. In contrast, as shown in Figure 4e, cotton yarns coated with SWCNT ink had high bendability and stretchability with immediate resistance response selectively at UV wavelengths of 254 and 365 nm, excluding visible and infrared wavelengths [33]. The resistance of the fiber increased under natural light and recovered under the shade of trees (Figure 4f). However, baseline drift was observed, due to adsorption of other gas molecules in the air, which reduce the accuracy of the sensor.
3.4. Temperature Sensing Fibers
Temperature sensors provide important information about the dynamics of physical, chemical, and biological phenomena [25]. These sensors are continually being developed for healthcare monitoring, industrial processing, and military support. In the healthcare field, temperature is essential information on diagnosis for infections, inflammatory diseases, and diabetic complications [125]. In particular, diabetic patients are insensitive to temperature changes, due to poor blood circulation and temperature monitoring, wearable devices can detect their inflammation more quickly [126]. Existing IR imaging systems for temperature measurement have a long equilibration time, due to large thermal mass, making real-time monitoring difficult. As another example, patch-type temperature sensors are not very flexible and bendable, which are difficult to incorporate into clothes. The fiber-based temperature sensors are flexible enough to be woven into a fabric for measuring the temperature of the whole body. They typically consist of a heat-sensitive material in contact with the electrode based on the (1) thermoresistive and (2) thermoelectrics mechanism.
Temperature sensing fibers can be simply synthesized by dip-coating commercial threads with thermoresistors that have a positive or negative temperature coefficient, such as a polypyrrole [127,128], CNT [129], PEDOT: PSS [130,131], and RGO [132]. The polypyrrole-coated threads were reported to have good linearity, and electrical response retains 18.75% for nine cycles between 65 °C and room temperature [133]. The PEDOT:PSS-coated cotton threads showed high linearity in a wide range of −50 °C to 80 °C with high sensitivity [134]. RGO is easily dispersed in a solution and has better thermal conductivity than other carbon materials, so it is widely used as a temperature sensor material. The RGO-coated threads woven in a textile structure showed excellent sensitivity and near-constant resistance under bending and compression cycles [135]. This flexible textile could transmit temperature data wirelessly via self-powered Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) or low-powered Bluetooth. Trung et al. fabricated freestanding single RGO-based fiber via wet-spinning, which showed a fast response time of 7 s and a great recovery time of 20 s (Figure 5a,b) [38]. The fiber integrated into the forearm band or undershirt measured the temperature response, while directly in contact with the skin, and it did not show changes in resistance, due to body movements.
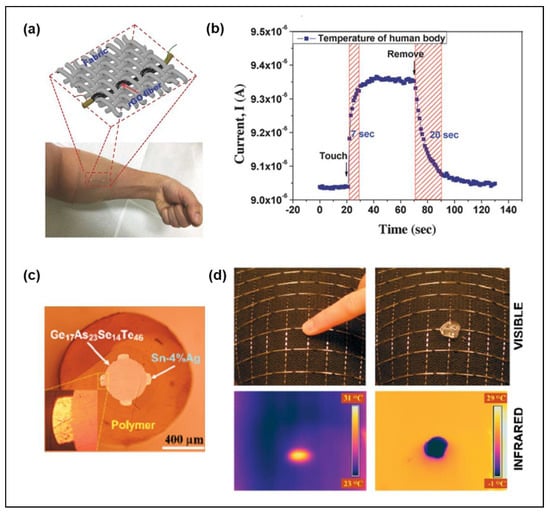
Figure 5.
Temperature sensing fiber. (a) Schematic of an RGO-based fiber knitted into the fabric and worn on the arm. (b) The fiber showed fast response time (7 s) and a great recovery time of (20 s). Reproduced with permission from [38], Copyright (2018), Wiley. (c) Cross-sectional micrograph image of the chalcogenide-based fiber. (d) The 8 × 8 fiber array detected heating locally with the touch of a finger and cooling with a piece of ice. Reproduced with permission from [25], Copyright (2006), Wiley.
Although dip-coated and wet-spun fibers have the advantages of being quick and simple, their temperature resolution is not so high. As shown in Figure 5c, the temperature sensing fiber composed of a chalcogenide semiconductor Ge17As23Se14Te46 (GAST) with two metallic electrodes (Sn96Ag4) was fabricated through the TDP [25]. The electronic mobility gap of the amorphous GAST semiconductor was small, so it exhibited a high electrical response with a small temperature change. The 8 × 8 fiber array with separation distance placed on curved objects reconstructed differential thermal maps in two situations: Heated locally with the touch of a finger and cooled with a piece of ice (Figure 5d). With the TDP, Zhang et al. fabricated fiber based on thermoelectric (TE) materials, p-type Bi0.5Sb1.5Te3, and n-type Bi2Se3 [52]. The thermoelectric effect refers to a phenomenon in which an electromotive force is generated due to a temperature difference, or a temperature difference is generated by applying an electric current. In the former, the temperature can be monitored inversely through the electromotive force. Two types of TE fibers covered on different regions of a plastic cup reached high output voltage and power density under the temperature difference of 60 °C. Additionally, the TE fiber-based textile achieved a cooling of up to 5 °C by inputting current of 2 mA.
4. Fiber-Based Energy-Storage Systems
In order to achieve more accessible smart textiles, energy-storage systems need to be integrated into the wearable device without compromising energy-storage capabilities, aesthetic appearance, and comfort. Due to their lack of flexibility, commercialized lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) have limited applicability in wearable devices. Recently, many researchers developed ways to provide a flexible and safe energy-storage system with sufficient energy density in wearable devices. The single fiber energy-storage systems can be woven into the fabric-shaped devices and combined with other fiber sensors. In this section, fiber-based electrochemical energy-storage systems, such as fiber-based batteries and supercapacitors, are reviewed. Their main features are summarized in Table 3.

Table 3.
Main features of fiber-based batteries and supercapacitors.
4.1. Fiber-Based Battery
Lithium-ion batteries have made remarkable advances in human life over the past 20 years. Many portable devices, for instance, mobile phones, laptop computers, smartwatches, wireless earphones, and even vehicles, contain rechargeable batteries based on lithium ion. Recently, many studies have fabricated flexible LIBs, especially fiber-based lithium-ion batteries (FBLIBs) [136,137,138]. For ideal FBLIBs, safety and electrochemical and mechanical properties should be considered. In order to maintain stable electrochemical performances even with repeated external forces, all components, including cathode, anode, separator, and electrolyte of FBLIBs, should have sufficient flexibility and fatigue resistance.
In many cases, MWCNT is used as an active material (anode) or conductive framework combined with other active material particles (cathode), due to its remarkable mechanical and electrical properties. For example, the FBLIB was fabricated by twisting an aligned MWCNT/MnO2 fiber and a lithium wire as cathode and anode, respectively (Figure 6a) [139]. However, FBLIBs with MWCNT had unsatisfactory scalability and specific/volumetric capacities. The intrinsically low capacities originate from the dead volume as MWCNT does not store energy when it is used in the cathode. To store more energy, Lin et al. proposed a silicon (Si)-based FBLIB with a theoretical capacity of Si is ~4200 mAh/g (MWCNT: ~300 mAh/g) (Figure 6b) [48]. In the study, they coated a thin layer of Si on the aligned MWCNT by CVD to form a core-sheath structured fiber. However, this fiber battery was a half cell, and most of all, the capacity retention needed to be significantly improved for wide applications.
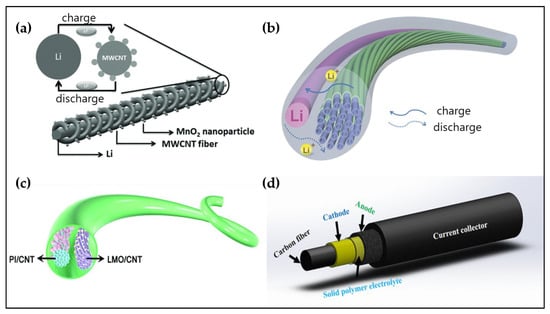
Figure 6.
Schematic illustration of representative fiber-based lithium-ion batteries. (a) MWCNT-based battery fiber. Reproduced with permission from [139], Copyright (2013), Wiley. (b) Si-based battery fiber. Reproduced with permission from [48], Copyright (2014), Wiley. (c) Aqueous lithium-ion battery fiber. Reproduced with permission from [140], Copyright (2016), Royal Society of Chemistry. (d) All-solid-state battery fiber. Reproduced with permission from [141], Copyright (2019), American Chemical Society.
Zhang et al. focused on aqueous fiber-based lithium-ion batteries (AFBLIBs) to mitigate safety and environmental issues (Figure 6c) [140]. They inserted paired two electrodes with a separator into a heat-shrinkable tube and injected an aqueous lithium sulfate (Li2SO4) solution (0.5 M). Conventional LIBs generally use flammable organic electrolytes, and therefore, have safety problems. However, AFBLIBs are non-flammable and have no risk of explosion. Furthermore, AFBLIBs are not toxic and environmentally friendly. Due to these advantages, AFBLIBs are being actively developed by many research groups. Besides AFBLIBs, another strategy to secure safety can be fiber-based all-solid-state batteries(FBASSBs). The electrodes and electrolytes of FBASSBs are all-solid-state instead of liquid-state or polymer gel-state as in the conventional FBLIBs. Yadav et al. reported an FBASSB with the coaxial structure using lithium iron phosphate(LiFePO4), lithium titanate(Li4Ti5O12), and polyethylene oxide with a lithium trifluoromethanesulfonate as a cathode, anode, and electrolyte, respectively, as shown in Figure 6d [141].
Although LIBs are one of the most active research areas, some challenges, such as the high cost of LIBs, the combustibility of organic electrolytes, and the lack of sustainability of lithium resources, remain to be solved. To address these issues fundamentally, non-lithium-ion batteries based on alternative materials, including metal-air battery (MAB), lithium–sulfur battery (Li-S battery), and sodium (Na)-based battery, have been investigated. One of the promising types of non-lithium-ion batteries is a MAB [147]. By repeating oxygen oxidation and reduction reactions, it can store about 10 times more energy compared to conventional LIBs. Moreover, since MABs use oxygen (O2) or carbon dioxide (CO2) in the air as the cathode, it can be lighter than LIBs that use conventional electrodes. Over the past 10 years, a wide variety of fiber-based metal-air batteries (FBMABs) have been reported, including Zn [142,148], Al [143], Li [149,150,151,152,153,154], etc. Zinc has the advantages of high power/energy density, excellent safety, and eco-friendly characteristics. Park et al. proposed a fiber-based Zn-air battery by coating gelatin-based gel polymer electrolyte on the Zn electrode using the cellophane template to pour the gel solution (Figure 7a) [142]. On the other hand, aluminum (Al) is one of the most abundant and sustainable metals in nature and has a high volumetric capacity, due to its low mass density and three-electron-redox properties [155]. Xu et al. proposed a fiber-based Al-air battery by coating a gel electrolyte and wrapping cross-stacked CNT/silver-nanoparticle hybrid sheets (Figure 7b) [143]. However, current Al-air batteries have the problem of the passivation of Al, as well as the lower energy density.
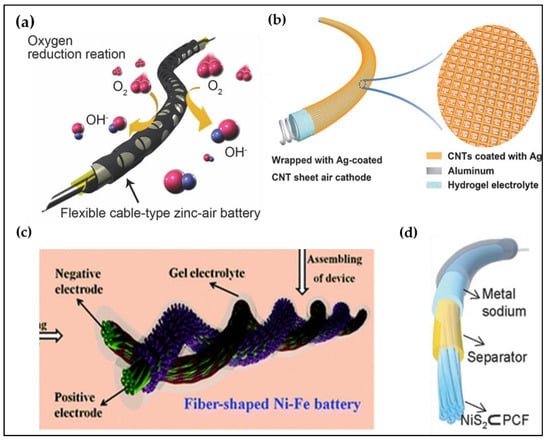
Figure 7.
Schematic illustration of representative fiber-based non-lithium-ion batteries. (a) Zn-based metal-air battery fiber. Reproduced with permission from [142], Copyright (2015), Wiley. (b) Al-based metal-air battery fiber. Reproduced with permission from [143], Copyright (2016), Wiley. (c) Ni-Fe based Ni-metal battery fiber. Reproduced with permission from [144], Copyright (2019), Royal Society of Chemistry. (d) Sodium-based metal-air battery fiber. Reproduced with permission from [145], Copyright (2018), Wiley.
Other than LIBs and MABs, many other types of batteries have been reported to fabricate ideal batteries for wearable textiles. One of them is a Ni-metal battery. Ni-metal batteries, including Ni–Zn batteries [156], have received great attention, due to their energy density similar to LIBs, ionic conductivity, environmentally friendly characteristics, and low cost. Fiber-based Ni-Fe battery was reported recently (Figure 7c) [144]. The researchers in this study fabricated a Ni-based positive electrode and a Fe-based negative electrode by using a facile hydrothermal method, while twisting these two electrodes together with a post-annealing treatment. Unlike Ni–Zn batteries, Ni–Fe based batteries used Fe2O3 and Fe3O4 as the anode materials. These oxides are abundant, inexpensive, non-toxic, and highly resistant to corrosion. Sodium is chemically similar to lithium as it belongs to the same group in the periodic table, hence Na-based battery was also simultaneously developed with LIB in the late 1980s. Many research groups reported flexible fiber-based sodium batteries as sodium has the advantages of abundance, low cost, and environmental sustainability. Chen et al. proposed a fiber-based sodium battery by inserting the yolk–shell NiS2 nanoparticles embedded in porous carbon fibers (NiS2⊂PCF), sodium foil, and the separator into a heat-shrinkable polyethylene tube with the sealing process using a heat gun and a hot melt adhesive (Figure 7d) [145].
4.2. Fiber-Based Supercapacitor
The energy-storage mechanism of supercapacitors is different from that of batteries. There are three types of supercapacitors; electrochemical double-layer capacitor (EDLC), pseudocapacitor, and hybrid capacitor. Since all of them store energy on the surface of electrodes, it is important to secure large surface areas of electrodes. Generally, supercapacitors can provide a higher power density, longer cycle life, and faster charging than batteries. Therefore, many researchers have proposed fiber-based supercapacitors with highly flexible, great mechanical, and electrical properties [157]. They generally used carbon-based materials, conductive polymers, metal oxide nanoparticles, and their composites as electrodes for supercapacitors (Table 4). Generally, carbon-based materials have excellent conductivity, chemical stability, long cycle life, relatively low mass density, and high stretchability. Furthermore, they are widely used to secure large surface areas of electrodes. However, the carbon-based materials are associated with limited capacitance and energy density, compared with pseudocapacitive materials, such as metal oxides. By contrast, metal oxides have high mass density and lower degrees of flexibility and stretchability. Conductive polymers have the advantages of high faradaic capacitance, conductivity, flexibility, and stretchability. Currently, efforts are being made to enhance the power density and energy density of conductive polymers.

Table 4.
Characteristics of electrode materials for supercapacitors.
Fiber-based supercapacitors are composed of three main components (electrodes, electrolytes, and encapsulation layers) and are designed in three main types of configuration (parallel, twisted, coaxial). In the case of electrolytes, they are often gel or solid, rather than liquid, which has a risk of leakage and corrosion. Moreover, gel or solid electrolyte can act as a separator, as well as an ion-conducting medium and the manufacturing process can be relatively simple. Regardless of the type of configuration, it is very important to uniformly coat electrolytes without defects to avoid problems, such as an increase in resistance at the electrolyte-electrolyte or electrolyte-electrode interfaces. The most common gel electrolyte is made of PVA with non-volatile acids (e.g., H2SO4) as an ionic conductor. Meng et al. proposed a unique all-graphene core–sheath fiber composed of graphene fiber core with a sheath of 3D graphene network by intertwining two graphene-based electrodes with sulfuric acid (H2SO4)-PVA gel polyelectrolyte (Figure 8a) [146]. These graphene fibers had high mechanical strength and flexibility, electrical and thermal conductivities, and lightweight. Due to these characteristics, they achieved an efficient fiber-based supercapacitor. However, carbon-based materials generally have limited energy density because no redox reaction is involved. To enhance energy density, a pseudocapacitive mechanism using reversible Faradaic reactions through redox reactions or intercalations has been introduced by replacing carbon-based materials with metal oxides or conductive polymers, as shown in Figure 8b [49]. To fabricate this supercapacitor fiber, researchers deposited manganese (IV) oxide (MnO2) using the electrodeposition method.
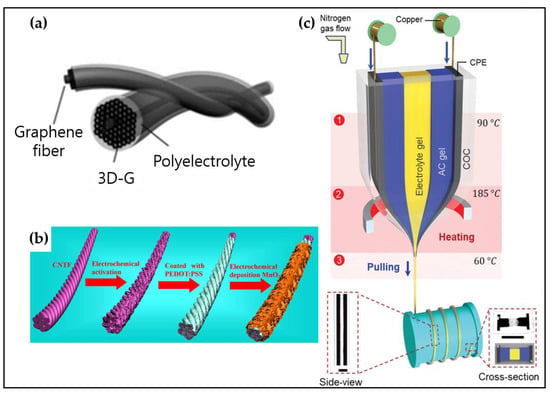
Figure 8.
Schematic illustration of representative fiber-based supercapacitors. (a) Carbon-based supercapacitor fiber. Reproduced with permission from [146], Copyright (2013), Wiley. (b) Metal oxide-based supercapacitor fiber. Reproduced with permission from [49], Copyright (2017), Elsevier Ltd. (c) The longest supercapacitor fiber fabricated by the TDP. Reproduced with permission from [53], Copyright (2020), Wiley.
Commonly, clothing fabrication requires a huge amount of fiber. Therefore, to open the era of smart textile, mass productivity and production convenience must be achieved. Khudiyev et al. showed the longest functional supercapacitor fiber fabricated by the TDP (Figure 8c) [53]. They also demonstrated great diverse multifunctional structures in 2D and 3D with good electrochemical and mechanical stabilities.
5. Conclusions and Perspectives
Fiber-based wearable devices have attracted the attention of many researchers, due to the intrinsic flexible, stretchable, durable, and breathable properties of fibers. Particularly, fiber-based sensors capable of measuring physiological and environmental states, while being comfortably worn hold great potential to be ideal wearable devices. Various types of sensors have been fabricated with fibers, including tactile sensors, chemical sensors, photosensors, and temperature sensors. These flexible and stretchable fiber-based sensors can be resistant to wear and wash and integrated into conventional garments, suggesting the ease of scalability. Furthermore, recent advancements in fiber-based energy-storage systems present possibilities to remove external power sources and fabricate self-powering wearable devices. Although fiber-based devices hold great potentials to be ideal wearable devices, they are not without limitations. Currently, there exist four major limitations of fiber-based wearable devices, which includes (1) performance, (2) wearability, (3) fabrication, and (4) integration (Figure 9).
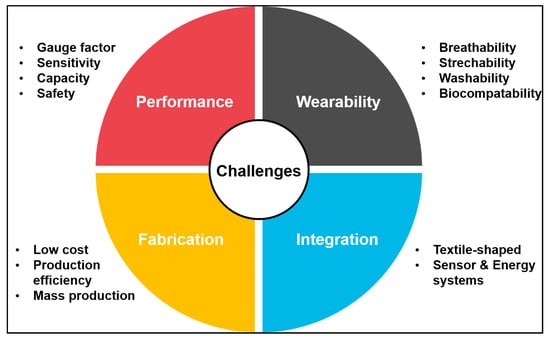
Figure 9.
Challenges of fiber-based electronics toward wearable applications.
- (1)
- Performance: The performance of fiber-based electronics may deteriorate, due to temperature, humidity, and gas in the air that is also the limitation of current wearable electronics. This type of performance degradation can be prevented through suitable packaging technologies by protecting the internal materials of the device from H2O or O2 in the air or preventing chemical reactions with active materials. However, in the case of fiber electronics, the packaging materials also need excellent flexibility and stretchability in order to maintain the performance without failure after bending or stretching deformation. While high-density polyethylene and polypropylene are being used as packaging materials because of their high flexibility and good processability, high moisture permeability makes them unsuitable as a package material. Therefore, maintaining the performance of fiber-based electronics through packaging with sufficient stability against external environments, excellent durability, and mechanical properties is an important challenge.
- (2)
- Wearability: Ideal wearable devices need to be worn with comfort and minimal interference with body movements. To achieve this, the devices need to be flexible, stretchable, and breathable. Fibers’ inherent flexibility and breathability have made them attractive building blocks of wearable devices. However, while stretchability is a critical factor for wearability, apart from strain sensors, many fiber-based wearable sensors, and energy-storage systems showed only limited stretchability or did not report it. The durability of the device is also of great importance for wearability and can be evaluated using cycling loading-unloading and washing tests. Currently, the washability remains to be a limitation as only a handful of fiber-based sensors and energy-storage systems reported acceptable performance change after a few washing cycles.
- (3)
- Fabrication: In this review, we introduced popular fabrication methods for fibers, but all have unique disadvantages. For example, dip coatings have poor mechanical properties, due to weak interfacial bonding and it is not suitable for industrial manufacturing, due to the increase in manufacturing time and cost. Considering it, thermal drawing can be an ideal method for its production effectiveness. Thermal drawing can produce kilometers of fiber from centimeters of preforms at once. Moreover, the one-step process of thermal drawing provides ease of incorporating complex designs into fibers, such as a cladding layer that improves washability and biocompatibility without further processing. However, the problem remains that the number of possible materials for thermal drawing is limited, as summarized in Table 1.
- (4)
- Integration: Despite its relatively recent beginning, extensive research has been done in fiber-based wearable sensors and energy-storage systems. While the integration of the two is needed for complete wearability of the device, it remains to be investigated. The answer to how previously mentioned various sensors and energy-storages can be integrated is not yet clear. The ways to provide energy to the fiber-based energy-storage systems are being actively explored in the fields of fiber-based energy harvesters, solar cells, and rational charging systems. Recently, interesting studies have incorporated wearable energy harvesters and energy-storage systems using a fiber-based triboelectric nanogenerator and flexible supercapacitors [158] and fabric-based solar cells [159].
The above-mentioned challenges of the fiber-based devices have been the hurdle for the commercialization of the technologies. However, recent research achievement in fibers by the development of new manufacturing skills or use of more suitable materials is addressing many current limitations, which will facilitate the deployment of fibers in the field of wearable electronics in the future.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, writing—original draft preparation, J.L., S.J., H.S.; writing—review and editing, J.T.L., S.P.; funding acquisition, J.T.L. and S.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by Basic Science Research Program through National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF-2020R1C1C1007589, NRF-2020R1C1C1003656), Technology Innovation Program (20012464) funded By the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy (MOTIE, Korea), Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute (ETRI) grant (20ZB1100, Development of Creative Technology for ICT) funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT, Smart Project Program through KAIST-Khalifa Joint Research Center (KK-JRC), End Run Project with SMC funded by STARTUP KAIST and College of Engineering Global Initiative Convergence Research Program.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Heo, J.S.; Eom, J.; Kim, Y.-H.; Park, S.K. Recent Progress of Textile-Based Wearable Electronics: A Comprehensive Review of Materials, Devices, and Applications. Small 2018, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukhopadhyay, S.C. Wearable Sensors for Human Activity Monitoring: A Review. IEEE Sens. J. 2015, 15, 1321–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seshadri, D.R.; Li, R.T.; Voos, J.E.; Rowbottom, J.R.; Alfes, C.M.; Zorman, C.A.; Drummond, C.K. Wearable sensors for monitoring the physiological and biochemical profile of the athlete. NPJ Digit. Med. 2019, 2, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, S.; Park, H.-S.; Bonato, P.; Chan, L.; Rodgers, M. A review of wearable sensors and systems with application in rehabilitation. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2012, 9, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.C.; Mun, J.; Kwon, S.Y.; Park, S.; Bao, Z.; Park, S. Electronic Skin: Recent Progress and Future Prospects for Skin-Attachable Devices for Health Monitoring, Robotics, and Prosthetics. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, e1904765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Tian, H.; Li, M.; Jian, J.; Wei, Y.; Tian, Y.; Wang, D.-Y.; Pang, Y.; Geng, X.; et al. Multilayer Graphene Epidermal Electronic Skin. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 8839–8846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Tan, J.; Zhu, J.; Lin, S.; Zhao, Y.; Yu, W.; Hojaiji, H.; Wang, B.; Yang, S.; Cheng, X.; et al. A programmable epidermal micro-fluidic valving system for wearable biofluid management and contextual biomarker analysis. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.Q.; Yao, J.D.; Wang, B.; Yang, G.W. Light-controlling, flexible and transparent ethanol gas sensor based on ZnO nano-particles for wearable devices. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Zhang, T.; Chen, H.; Wang, F.; Pu, Y.; Gao, C.; Li, S. Mini Review on Flexible and Wearable Electronics for Monitoring Human Health Information. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2019, 14, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Li, Y.; Dai, K.; Liu, M.; Zhou, K.; Zheng, G.; Liu, C.; Shen, C. Conductive thermoplastic polyurethane composites with tunable piezoresistivity by modulating the filler dimensionality for flexible strain sensors. Compos. Part. A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2017, 101, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Windmiller, J.R.; Wang, J. Wearable electrochemical sensors and biosensors: A review. Electroanalysis 2013, 25, 29–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souri, H.; Bhattacharyya, D. Highly Stretchable Multifunctional Wearable Devices Based on Conductive Cotton and Wool Fabrics. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 20845–20853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amjadi, M.; Kyung, K.U.; Park, I.; Sitti, M. Stretchable, skin-mountable, and wearable strain sensors and their potential applications: A review. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 1678–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, B.; Lee, J.; Han, H.; Woo, J.; Park, K.; Seo, J.; Lee, T. Highly Conductive Fiber with Waterproof and Self-Cleaning Properties for Textile Electronics. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 36094–36101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loke, G.; Alain, J.; Yan, W.; Khudiyev, T.; Noel, G.; Yuan, R.; Missakian, A.; Fink, Y. Computing Fabrics. Phys. B Condens. Matter. 2020, 2, 786–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Guo, Y.; Jia, X.; Choe, H.K.; Grena, B.; Kang, J.; Park, J.; Lu, C.; Canales, A.; Chen, R.; et al. One-step optogenetics with mul-tifunctional flexible polymer fibers. Nat. Neurosci. 2017, 20, 612–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ding, J.; Qi, B.; Tao, W.; Wang, J.; Zhao, C.; Peng, H.; Shi, J. Multifunctional Fibers to Shape Future Biomedical Devices. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, G.; Zhou, J.; Xin, Y.; Tao, R.; Jin, G.; Lubineau, G. Copolymer-enabled stretchable conductive polymer fibers. Polymer 2019, 177, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Fu, Y.; Cai, X.; Kafafy, H.; Wu, H.; Peng, M.; Hou, S.; Lv, Z.; Ye, S.; Zou, D. Flexible fiber-type zinc–carbon battery based on carbon fiber electrodes. Nano Energy 2013, 2, 1242–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, V.T.; Kim, H.; Ghosh, A.; Kim, J.; Chang, J.; Vu, Q.A.; Pham, D.T.; Lee, J.-H.; Kim, S.-W.; Lee, Y.H. Coaxial Fiber Supercapacitor Using All-Carbon Material Electrodes. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 5940–5947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.I.; Lee, M.; Liu, Y.; Moon, S.; Hwang, G.T.; Zhu, G.; Kim, J.E.; Kim, S.O.; Kim, D.K.; Wang, Z.L.; et al. Flexible nanocomposite gen-erator made of BaTiO3 nanoparticles and graphitic carbons. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 2999–3004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Lu, C.; Zhang, K. Textile-Based Strain Sensor for Human Motion Detection. Energy Environ. Mater. 2020, 3, 80–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandodkar, A.J.; Wang, J. Non-invasive wearable electrochemical sensors: A review. Trends Biotechnol. 2014, 32, 363–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayindir, M.; Sorin, F.; Abouraddy, A.F.; Viens, J.; Hart, S.D.; Joannopoulos, J.D.; Fink, Y. Metal–insulator–semiconductor optoelectronic fibres. Nature 2004, 431, 826–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayindir, M.; Abouraddy, A.F.; Arnold, J.; Joannopoulos, J.D.; Fink, Y. Thermal-Sensing Fiber Devices by Multimaterial Codrawing. Adv. Mater. 2006, 18, 845–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, K.; Peng, X.; Wang, Z.L. Fiber/Fabric-Based Piezoelectric and Triboelectric Nanogenerators for Flexible/Stretchable and Wearable Electronics and Artificial Intelligence. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, e1902549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, B.; Chang, D.; Xu, Z.; Gao, C. A Review on Graphene Fibers: Expectations, Advances, and Prospects. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, e1902664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basile, F.; Benito, P.; Fornasari, G.; Monti, M.; Scavetta, E.; Tonelli, D.; Vaccari, A. A novel electrochemical route for the catalytic coating of metallic supports. Prep. Catal. V Sci. Bases Prep. Heterog. Catal. Proc. Fifth Int. Symp. 2010, 175, 51–58. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, W.; Dong, C.; Xiang, Y.; Jiang, S.; Leber, A.; Loke, G.; Xu, W.; Hou, C.; Zhou, S.; Chen, M.; et al. Thermally drawn advanced functional fibers: New frontier of flexible electronics. Mater. Today 2020, 35, 168–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Pan, J.; Xu, A.; Luo, L.; Cheng, D.; Cai, G.; Wang, J.; Tang, B.; Wang, X. Conductive Cotton Fabrics for Motion Sensing and Heating Applications. Polymers 2018, 10, 568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Liu, S.; Wang, P.; Liu, H.; Liu, L. Highly stretchable fiber-shaped e-textiles for strain/pressure sensing, full-range human motions detection, health monitoring, and 2D force mapping. J. Mater. Sci. 2018, 53, 2995–3005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Chen, R.; Qi, W.; Cai, L.; Sun, Y.; Sun, M.; Li, C.; Yang, X.; Xiang, L.; Xie, D.; et al. Reduced Graphene Oxide/Mesoporous ZnO NSs Hybrid Fibers for Flexible, Stretchable, Twisted, and Wearable NO2 E-Textile Gas Sensor. ACS Sens. 2019, 4, 2809–2818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.J.; Moon, D.-I.; Seol, M.-L.; Kim, B.; Han, J.-W.; Meyyappan, M. Wearable UV Sensor Based on Carbon Nanotube-Coated Cotton Thread. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 40198–40202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Shin, S.; Lee, S.; Seo, J.; Lee, J.; Son, S.; Cho, H.J.; Algadi, H.; Al-Sayari, S.; Kim, D.E.; et al. Ag nanowire reinforced highly stretchable conductive fibers for wearable electronics. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 3114–3121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Jia, S.; Wang, F.; Bian, C.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, B. Highly Stretchable Core–Sheath Fibers via Wet-Spinning for Wearable Strain Sensors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 6624–6635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seyedin, M.Z.; Razal, J.; Innis, P.C.; Wallace, G.G. Strain-Responsive Polyurethane/PEDOT:PSS Elastomeric Composite Fibers with High Electrical Conductivity. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 2957–2966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, T.; Kim, Y.; Jeong, S.-M.; Kim, C.-H.; Kim, S.-M.; Park, S.Y.; Yoon, M.-H.; Ju, S. Human sweat monitoring using polymer-based fiber. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trung, T.Q.; Le, H.S.; Dang, T.M.L.; Ju, S.; Park, S.Y.; Lee, N.-E. Freestanding, Fiber-Based, Wearable Temperature Sensor with Tunable Thermal Index for Healthcare Monitoring. Adv. Health Mater. 2018, 7, e1800074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhai, Q.; Dong, D.; An, T.; Gong, S.; Shi, Q.; Cheng, W. Highly Stretchable and Strain-Insensitive Fiber-Based Wearable Electro-chemical Biosensor to Monitor Glucose in the Sweat. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 6569–6576. [Google Scholar]
- Bautista-Quijano, J.R.; Pötschke, P.; Brünig, H.; Heinrich, G. Strain sensing, electrical and mechanical properties of polycar-bonate/multiwall carbon nanotube monofilament fibers fabricated by melt spinning. Polymer 2016, 82, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattmann, C.; Clemens, F.; Tröster, G. Sensor for Measuring Strain in Textile. Sensors 2008, 8, 3719–3732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lund, A.; Rundqvist, K.; Nilsson, E.; Yu, L.; Hagström, B.; Müller, C. Energy harvesting textiles for a rainy day: Woven piezoelectrics based on melt-spun PVDF microfibres with a conducting core. npj Flex. Electron. 2018, 2, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, H.J.; Choi, C.; Lee, C.J.; Kim, Y.T.; Spinks, G.; Lima, M.D.; Baughman, R.H.; Kim, S.J. Flexible, stretchable and weavable piezoelectric fiber. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2015, 17, 1270–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Fang, G.; Wan, J.; Zhou, H.; Long, H.; Zhao, X. Electrospun PEDOT:PSS–PVA nanofiber based ultrahigh-strain sensors with controllable electrical conductivity. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 18962–18966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Tan, C.; Shi, K.; Li, J.; Wang, X.X.; Sun, B.; Huang, X.; Long, Y.Z.; Jiang, P. Wireless piezoelectric devices based on electrospun PVDF/BaTiO3 NW nanocomposite fibers for human motion monitoring. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 17751–17760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Lou, M.; Abdalla, I.; Yu, J.; Li, Z.; Ding, B. Highly shape adaptive fiber based electronic skin for sensitive joint motion monitoring and tactile sensing. Nano Energy 2020, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rui, K.; Wang, X.; Du, M.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Ma, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Li, D.; Huang, X.; Sun, G.; et al. Dual-Function Metal–Organic Framework-Based Wearable Fibers for Gas Probing and Energy Storage. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 2837–2842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Weng, W.; Ren, J.; Qiu, L.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, P.; Chen, X.; Deng, J.; Wang, Y.; Peng, H. Twisted Aligned Carbon Nanotube/Silicon Composite Fiber Anode for Flexible Wire-Shaped Lithium-Ion Battery. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 1217–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Sun, J.; Pan, Z.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, C.; Yao, Y.; Lu, W.; Li, Q.; et al. Stretchable fiber-shaped asymmetric supercapacitors with ultrahigh energy density. Nano Energy 2017, 39, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mechanics, Q.; Matos, D.; Complete, P. Metal—insulator—semiconductor optoelectronic fibres. Nature 2004, 431, 826–829. [Google Scholar]
- Rein, M.; Favrod, V.D.; Hou, C.; Khudiyev, T.; Stolyarov, A.; Cox, J.; Chung, C.-C.; Chhav, C.; Ellis, M.; Joannopoulos, J.; et al. Diode fibres for fabric-based optical communications. Nat. Cell Biol. 2018, 560, 214–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Wang, Z.; Srinivasan, B.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Li, K.; Boussard-Pledel, C.; Troles, J.; Bureau, B.; Wei, L. Ultraflexible Glassy Semiconductor Fibers for Thermal Sensing and Positioning. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 2441–2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khudiyev, T.; Lee, J.T.; Cox, J.R.; Argentieri, E.; Loke, G.; Yuan, R. 100 m Long Thermally Drawn Supercapacitor Fibers with Applications to 3D Printing and Textiles. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 2004971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, Y.L.; Xia, Y.; Zhang, P.F.; Kirk, T.V.; Chen, X.D. Textile-Only Capacitive Sensors for Facile Fabric Integration without Compromise of Wearability. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2019, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gumennik, A.; Stolyarov, A.M.; Schell, B.R.; Hou, C.; Lestoquoy, G.; Sorin, F.; McDaniel, W.; Rose, A.; Joannopoulos, J.D.; Fink, Y. All-in-Fiber Chemical Sensing. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 6005–6009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekar, M.; Pandiaraj, M.; Bhansali, S.; Ponpandian, N.; Viswanathan, C. Carbon fiber based electrochemical sensor for sweat cortisol measurement. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorin, F.; Shapira, O.; Abouraddy, A.F.; Spencer, M.; Orf, N.D.; Joannopoulos, J.D.; Fink, Y. Exploiting Collective Effects of Multiple Optoelectronic Devices Integrated in a Single Fiber. Nano Lett. 2009, 9, 2630–2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Chen, J.; Cai, S.; Long, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Su, L.; Peng, H.; Fang, X. A Real-Time Wearable UV-Radiation Monitor based on a High-Performance p-CuZnS/n-TiO2 Photodetector. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipomi, D.J.; Vosgueritchian, M.; Tee, B.C.-K.; Hellstrom, S.L.; Lee, J.A.; Fox, C.H.; Bao, Z. Skin-like pressure and strain sensors based on transparent elastic films of carbon nanotubes. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2011, 6, 788–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.; Yang, J.C.; Kim, J.-O.; Park, H.; Kwon, S.Y.; Lee, S.; Sim, J.Y.; Oh, H.W.; Kim, J.; Park, S. Pressure Insensitive Strain Sensor with Facile Solution-Based Process for Tactile Sensing Applications. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 7546–7553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nela, L.; Tang, J.; Cao, Q.; Tulevski, G.S.; Han, S.-J. Large-Area High-Performance Flexible Pressure Sensor with Carbon Nanotube Active Matrix for Electronic Skin. Nano Lett. 2018, 18, 2054–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Huang, Y.; Cai, X.; Liu, C.; Liu, P. Capacitive wearable tactile sensor based on smart textile substrate with carbon black/silicone rubber composite dielectric. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2016, 27, 045105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Lou, Z.; Chen, D.; Jiang, K.; Shen, G. Polymer-Enhanced Highly Stretchable Conductive Fiber Strain Sensor Used for Electronic Data Gloves. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2016, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Long, H.; Miao, M. High sensitivity knitted fabric strain sensors. Smart Mater. Struct. 2016, 25, 105008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Dai, K.; Zheng, G.; Zhang, B.; Liu, C.; Shen, C. High-Performance Wearable Strain Sensor Based on Gra-phene/Cotton Fabric with High Durability and Low Detection Limit. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 12, 1474–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Chen, S.; Lin, Y.; Yuan, X.; Liu, L. Silver nanowires coated on cotton for flexible pressure sensors. J. Mater. Chem. C 2016, 4, 935–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-Q.; Huang, P.; Zhu, W.-B.; Fu, S.; Hu, N.; Liao, K. Flexible wire-shaped strain sensor from cotton thread for human health and motion detection. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, srep45013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frutiger, A.; Muth, J.T.; Vogt, D.M.; Mengüç, Y.; Campo, A.; Valentine, A.D.; Walsh, C.J.; Lewis, J.A. Capacitive Soft Strain Sensors via Multicore-Shell Fiber Printing. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 2440–2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyedin, S.; Zhang, P.; Naebe, M.; Qin, S.; Chen, J.; Wang, X.; Razal, J. Textile strain sensors: A review of the fabrication technologies, performance evaluation and applications. Mater. Horizons 2019, 6, 219–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, W.; Shu, L.; Li, Q.; Chen, S.; Wang, F.; Tao, X. Fiber-Based Wearable Electronics: A Review of Materials, Fabrication, Devices, and Applications. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 5310–5336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, Y.R.; Park, H.; Jin, S.W.; Hong, S.Y.; Lee, S.-S.; Ha, J.S. Highly Stretchable and Sensitive Strain Sensors Using Fragmentized Graphene Foam. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 4228–4236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nur, R.; Matsuhisa, N.; Jiang, Z.; Nayeem, O.G.; Yokota, T.; Someya, T. A Highly Sensitive Capacitive-type Strain Sensor Using Wrinkled Ultrathin Gold Films. Nano Lett. 2018, 18, 5610–5617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Zhou, G.; Rao, W.; Fan, L.; Xu, W.; Xu, J. A simple method of fabricating nickel-coated cotton fabrics for wearable strain sensor. Cellulose 2018, 25, 4859–4870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyedin, S.; Razal, J.; Innis, P.C.; Wallace, G.G. A facile approach to spinning multifunctional conductive elastomer fibres with nanocarbon fillers. Smart Mater. Struct. 2016, 25, 35015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souri, H.; Bhattacharyya, D. Highly sensitive, stretchable and wearable strain sensors using fragmented conductive cotton fabric. J. Mater. Chem. C 2018, 6, 10524–10531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, S.; Lee, P.; Chou, J.B.; Xu, R.; Zhao, R.; Hart, A.J.; Kim, S.-G. Extremely Elastic Wearable Carbon Nanotube Fiber Strain Sensor for Monitoring of Human Motion. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 5929–5936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadi, S.; Pan, J.; Xu, A.; Cheng, D.; Cai, G.; Wang, X. Direct dip-coating of carbon nanotubes onto polydopamine-templated cotton fabrics for wearable applications. Cellulose 2019, 26, 7569–7579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilotti, E.; Zhang, R.; Deng, H.; Baxendale, M.; Peijs, T. Fabrication and property prediction of conductive and strain sensing TPU/CNT nanocomposite fibres. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 9449–9455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, F.; Li, X.; Peng, H.; Li, F.; Yang, K.; Yuan, W. A highly sensitive, multifunctional, and wearable mechanical sensor based on RGO/synergetic fiber bundles for monitoring human actions and physiological signals. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 285, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Lu, M.; Yang, H.; Avila, J.R.; Shi, B.; Ren, L.; Wei, G.; Liu, X.; Yin, W. Textile Based Capacitive Sensor for Physical Rehabilitation via Surface Topological Modification. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 8191–8201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, C.; Lee, J.M.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, S.J.; Di, J.; Baughman, R.H. Twistable and Stretchable Sandwich Structured Fiber for Wearable Sensors and Supercapacitors. Nano Lett. 2016, 16, 7677–7684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Kwon, H.; Seo, J.; Shin, S.; Koo, J.H.; Pang, C.; Son, S.; Kim, J.H.; Jang, Y.H.; Kim, D.E.; et al. Conductive Fiber-Based Ultrasensitive Textile Pressure Sensor for Wearable Electronics. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 2433–2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, R.; Ma, L.; Patil, A.; Hou, C.; Zhu, S.; Fan, X.; Lin, H.; Yu, W.; Guo, W.; Liu, X.Y. All-Textile Electronic Skin Enabled by Highly Elastic Spacer Fabric and Conductive Fibers. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 33336–33346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, C.B.; Arutselvan, K.; Liu, Y.; Armstrong, D.; Lin, Y.; Khan, M.R.; Genzer, J.; Dickey, M.D. Stretchable capacitive sensors of torsion, strain, and touch using double helix liquid metal fibers. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 1605630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, E.; Meyyappan, M.; Nalwa, H.S. Flexible Graphene-Based Wearable Gas and Chemical Sensors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 34544–34586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.G.; Jun, J.; Lee, J.S.; Jang, J. A highly sensitive wireless nitrogen dioxide gas sensor based on an organic conductive nano-composite paste. J. Mater. Chem. A. 2019, 7, 8451–8459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Teng, C.; Sun, Y.; Cai, L.; Xu, J.L.; Sun, M.; Li, X.; Yang, X.; Xiang, L.; Xie, D.; et al. Sprayed, Scalable, Wearable, and Portable NO2 Sensor Array Using Fully Flexible AgNPs-All-Carbon Nanostructures. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 34485–34493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maity, D.; Kumar, R.T.R. Polyaniline Anchored MWCNTs on Fabric for High Performance Wearable Ammonia Sensor. ACS Sens. 2018, 3, 1822–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kincal, D.; Kumar, A.; Child, A.D.; Reynolds, J.R. Conductivity switching in polypyrrole-coated textile fabrics as gas sensors. Synth. Met. 1998, 92, 53–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, D.P.; Ratterman, M.E.; Griffin, D.K.; Hou, L.; Kelley-Loughnane, N.; Naik, R.R.; Hagen, J.A.; Papautsky, I.; Heikenfeld, J.C. Adhesive RFID Sensor Patch for Monitoring of Sweat Electrolytes. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2015, 62, 1457–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, L.-C.; Gao, W.; Chao, M.; Bariya, M.; Ngo, Q.P.; Shahpar, Z.; Nyein, H.Y.Y.; Park, H.; Sun, J.; Jung, Y.; et al. Methylxanthine Drug Monitoring with Wearable Sweat Sensors. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, e1707442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parlak, O.; Keene, S.T.; Marais, A.; Curto, V.F.; Salleo, A. Molecularly selective nanoporous membrane-based wearable organic electrochemical device for noninvasive cortisol sensing. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaar2904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parrilla, M.; Guinovart, T.; Ferré, J.; Blondeau, P.; Andrade, F.J. A Wearable Paper-Based Sweat Sensor for Human Perspiration Monitoring. Adv. Heal. Mater. 2019, 8, e1900342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iguchi, S.; Kudo, H.; Saito, T.; Ogawa, M.; Saito, H.; Otsuka, K.; Funakubo, A.; Mitsubayashi, K. A flexible and wearable biosensor for tear glucose measurement. Biomed. Microdevices 2007, 9, 603–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kim, M.; Lee, M.-S.; Kim, K.; Ji, S.; Kim, Y.-T.; Park, J.; Na, K.; Bae, K.-H.; Kim, H.K.; et al. Wearable smart sensor systems integrated on soft contact lenses for wireless ocular diagnostics. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsherif, M.; Hassan, M.U.; Yetisen, A.K.; Butt, H. Wearable Contact Lens Biosensors for Continuous Glucose Monitoring Using Smartphones. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 5452–5462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malon, R.S.P.; Chua, K.Y.; Wicaksono, D.H.B.; Córcoles, E.P. Cotton fabric-based electrochemical device for lactate measurement in saliva. Analyst 2014, 139, 3009–3016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Imani, S.; De Araujo, W.R.; Warchall, J.; Valdés-Ramírez, G.; Paixão, T.R.; Mercier, P.P.; Wang, J. Wearable salivary uric acid mouthguard biosensor with integrated wireless electronics. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 74, 1061–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Y.; Jian, J.; Tu, T.; Yang, Z.; Ling, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Qiao, Y.; Tian, H.; Yang, Y.; et al. Wearable humidity sensor based on porous graphene network for respiration monitoring. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 116, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Jiang, Y.; Tai, H.; Liu, B.; Duan, Z.; Yuan, Z.; Pan, H.; Xie, G.; Du, X.; Su, Y. An integrated flexible self-powered wearable respiration sensor. Nano Energy 2019, 63, 103829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, P.; Li, S.; Jiang, X.; Wang, Q.; Fan, F.; Yan, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, P.; Yu, Y. Noninvasive and Wearable Respiration Sensor Based on Organic Semi-conductor Film with Strong Electron Affinity. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 10320–10327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bariya, M.; Nyein, H.Y.Y.; Javey, A. Wearable sweat sensors. Nat. Electron. 2018, 1, 160–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loke, G.; Yan, W.; Khudiyev, T.; Noel, G.; Fink, Y. Recent Progress and Perspectives of Thermally Drawn Multimaterial Fiber Electronics. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, e1904911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stolyarov, A.M.; Gumennik, A.; McDaniel, W.; Shapira, O.; Schell, B.; Sorin, F.; Kuriki, K.; Benoit, G.; Rose, A.; Joannopoulos, J.D.; et al. Enhanced chemiluminescent detection scheme for trace vapor sensing in pneumatically-tuned hollow core photonic bandgap fibers. Opt. Express 2012, 20, 12407–12415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, G.; Buckley, L. Conductive polymer-coated fabrics for chemical sensing. Synth. Met. 1996, 78, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.-S.; Kim, W.-S.; Kim, D.-H.; Kim, H.-C.; Hohng, S.; Yu, W.-R. Fabrication of SnO2nanotube microyarn and its gas sensing behavior. Smart Mater. Struct. 2011, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Qin, Z.; Liu, X.; Liang, B.; Liu, N.; Zhou, Z.; Zhu, M. Flexible sensing fibers based on polyaniline-coated polyurethane for chloroform vapor detection. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 10327–10333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alrammouz, R.; Podlecki, J.; Abboud, P.; Sorli, B.; Habchi, R. A review on flexible gas sensors: From materials to devices. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2018, 284, 209–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumann, A.E.; Burns, D.A.; Liu, B.; Thoi, V.S. Metal-organic framework functionalization and design strategies for advanced electrochemical energy storage devices. Commun. Chem. 2019, 2, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, Y.J.; Hong, W.G.; Choi, N.-J.; Kim, B.H.; Jun, Y.; Lee, H.-K. Ultrasensitive and Highly Selective Graphene-Based Single Yarn for Use in Wearable Gas Sensor. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, srep10904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Lillehoj, P.B. Embroidered electrochemical sensors for biomolecular detection. Lab. Chip. 2016, 16, 2093–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Zhai, Q.; Zhao, Y.; An, T.; Gong, S.; Guo, Z.; Shi, Q.; Yong, Z.; Cheng, W. Stretchable gold fiber-based wearable electrochemical sensor toward pH monitoring. J. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 8, 3655–3660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madhu, S.; Anthuuvan, A.J.; Ramasamy, S.; Manickam, P.; Bhansali, S.; Nagamony, P.; Viswanathan, C. ZnO Nanorod Integrated Flexible Carbon Fibers for Sweat Cortisol Detection. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 2020, 2, 499–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abouraddy, A.F.; Shapira, O.; Bayindir, M.; Arnold, J.; Sorin, F.; Hinczewski, D.S.; Joannopoulos, J.D.; Fink, Y. Large-scale optical-field measurements with geometric fibre constructs. Nat. Mater. 2006, 5, 532–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, W.; Sastry, M.; Gooding, J.J.; Ramanathan, R.; Bansal, V. Recent Advances and a Roadmap to Wearable UV Sensor Technologies. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2020, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.; Qu, Y.; Das Gupta, T.; Darga, A.; Nguyên, D.T.; Page, A.G.; Rossi, M.; Ceriotti, M.; Sorin, F. Semiconducting Nanowire-Based Optoelectronic Fibers. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soci, C.; Zhang, A.; Xiang, B.; Dayeh, S.A.; Aplin, D.P.R.; Park, J.; Bao, X.Y.; Lo, Y.H.; Wang, D. ZnO Nanowire UV Photodetectors with High Internal Gain. Nano Lett. 2007, 7, 1003–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Fang, G.; Zeng, W.; Zhou, H.; Cheng, F.; Zheng, Q.; Yuan, L.; Zou, X.; Zhao, X. Direct Growth of Lateral ZnO Nanorod UV Photodetectors with Schottky Contact by a Single-Step Hydrothermal Reaction. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2010, 2, 1973–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, V.Q.; Trung, T.Q.; Duy, L.T.; Kim, B.-Y.; Siddiqui, S.; Lee, W.; Lee, N.-E. High-Performance Flexible Ultraviolet (UV) Phototransistor Using Hybrid Channel of Vertical ZnO Nanorods and Graphene. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 11032–11040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, K.S.; Kinniburgh, M.; Beresford, R. Photoconductive ultraviolet sensor using Mg-doped GaN on Si(111). Appl. Phys. Lett. 1995, 66, 3518–3520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-J.; Kwon, Y.-J.; Won, C.-H.; Lee, J.-H.; Hahm, S.-H. Dual-wavelength sensitive AlGaN/GaN metal-insulator-semiconductor-insulator-metal ultraviolet sensor with balanced ultraviolet/visible rejection ratios. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 103, 111110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossein-Babaei, F.; Lajvardi, M.M.; Boroumand, F.A. Large area Ag-TiO2 UV radiation sensor fabricated on a thermally oxidized titanium chip. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2012, 173, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khiabani, P.S.; Kashi, M.B.; Zhang, X.; Pardehkhorram, R.; Markhali, B.P.; Soeriyadi, A.H.; Micolich, A.P.; Gooding, J.J. A graphene-based sensor for real time monitoring of sun exposure. Carbon 2018, 138, 215–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Bai, S.; Su, C.; Zheng, Y.; Qin, Y.; Xu, C.; Wang, Z.L. A High-Reliability Kevlar Fiber-ZnO Nanowires Hybrid Nanogenerator and its Application on Self-Powered UV Detection. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 5794–5798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, M.; Lim, S.; Ko, H. Wearable and flexible sensors for user-interactive health-monitoring devices. J. Mater. Chem. B 2018, 6, 4043–4064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martín-Vaquero, J.; Encinas, A.H.; Queiruga-Dios, A.; Pérez, J.B.; Martínez-Nova, A.; González, J.T.; Bullón-Carbajo, C. Review on Wearables to Monitor Foot Temperature in Diabetic Patients. Sensors 2019, 19, 776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Gui, Q.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Liao, S.; Wang, Y. A Polypyrrole Elastomer Based on Confined Polymerization in a Host Polymer Network for Highly Stretchable Temperature and Strain Sensors. Small 2018, 14, e1800394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, D.; Xu, B.; Cai, Z. Polypyrrole coated knitted fabric for robust wearable sensor and heater. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2018, 29, 9218–9226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.J.; Maharjan, S.; Liao, K.-S.; McElhenny, B.P.; Wright, K.D.; Dillon, E.P.; Neupane, R.; Zhu, Z.; Chen, S.; Barron, A.R.; et al. Poly(octadecyl acrylate)-Grafted Multiwalled Carbon Nanotube Composites for Wearable Temperature Sensors. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2020, 3, 2288–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Cui, Y. Development of Flexible and Wearable Temperature Sensors Based on PEDOT:PSS. IEEE Trans. Electron. Devices 2019, 66, 3129–3133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-F.; Sekine, T.; Takeda, Y.; Yokosawa, K.; Matsui, H.; Kumaki, D.; Shiba, T.; Nishikawa, T.; Tokito, S. Fully Printed PEDOT:PSS-based Temperature Sensor with High Humidity Stability for Wireless Healthcare Monitoring. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Tan, Q.; Kou, H.; Zhang, L.; Wang, J.; Lv, W.; Dong, H.; Xiong, J. A Flexible Temperature Sensor Based on Reduced Graphene Oxide for Robot Skin Used in Internet of Things. Sensors 2018, 18, 1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Gui, Q.; Liao, S.; Jia, H.; Wang, Y. Coiled Fiber-Shaped Stretchable Thermal Sensors for Wearable Electronics. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2016, 1, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-W.; Han, D.-C.; Shin, H.-J.; Yeom, S.-H.; Ju, B.-K.; Lee, W. PEDOT:PSS-Based Temperature-Detection Thread for Wearable Devices. Sensors 2018, 18, 2996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afroj, S.; Karim, N.; Wang, Z.; Tan, S.; He, P.; Holwill, M.; Ghazaryan, D.; Fernando, A.; Novoselov, K.S. Engineering Graphene Flakes for Wearable Textile Sensors via Highly Scalable and Ultrafast Yarn Dyeing Technique. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 3847–3857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Bai, W.; Ren, J.; Weng, W.; Lin, H.; Zhang, Z.; Peng, H. Super-stretchy lithium-ion battery based on carbon nanotube fiber. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 11054–11059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Zhang, Y.; Bai, W.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Z.; Fang, X.; Weng, W.; Wang, Y.; Penget, H. Elastic and wearable wire-shaped lithium-ion battery with high electrochemical performance. Angew. Chem. 2014, 53, 7864–7869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, W.; Sun, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, H.; Ren, J.; Lu, X.; Wang, M.; Peng, H. Winding Aligned Carbon Nanotube Composite Yarns into Coaxial Fiber Full Batteries with High Performances. Nano Lett. 2014, 14, 3432–3438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Li, L.; Chen, C.; Chen, X.; Cai, Z.; Qiu, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, X.; Peng, H. Twisting carbon nanotube fibers for both wire-shaped micro-supercapacitor and micro-battery. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 1155–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Lo, C.-M.; Zhao, Y.; Jiao, Y.; Zheng, G.; Peng, H. A fiber-shaped aqueous lithium ion battery with high power density. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 9002–9008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, A.K.; De, B.; Singh, S.K.; Sinha, P.; Kar, K.K. Facile Development Strategy of a Single Carbon-Fiber-Based All-Solid-State Flexible Lithium-Ion Battery for Wearable Electronics. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 7974–7980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.; Park, M.; Nam, G.; Lee, J.S.; Cho, J. All-solid-state cable-type flexible zinc-air battery. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 1396–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Ren, J.; Zhang, Y.; Peng, H. An All-Solid-State Fiber-Shaped Aluminum-Air Battery with Flexibility, Stretchability, and High Electrochemical Performance. Angew. Chem. 2016, 128, 8111–8114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, C.; Sun, J.; Guo, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, Z.; He, B.; Pan, Z.; Yao, Y. Flexible all-solid-state fiber-shaped Ni–Fe batteries with high electrochemical performance. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 520–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Sun, S.; Zhai, T.; Yang, M.; Zhao, X.; Xia, H. Yolk-Shell NiS2 Nanoparticle-Embedded Carbon Fibers for Flexible Fiber-Shaped Sodium Battery. Adv. Energy Mater. 2018, 8, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Hu, C.; Cheng, H.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Shi, G.; Qu, L. All-Graphene Core-Sheath Microfibers for All-Solid-State, Stretchable Fibriform Supercapacitors and Wearable Electronic Textiles. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 2326–2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Chang, Z.; Li, Z.; Zhang, X. Flexible Metal-Air Batteries: Progress, Challenges, and Perspectives. Small Methods 2018, 2, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, Z.; Ren, J.; Wang, Y.; Peng, H. Flexible, Stretchable, and Rechargeable Fiber-Shaped Zinc-Air Battery Based on Cross-Stacked Carbon Nanotube Sheets. Angew. Chem. 2015, 127, 15610–15614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Guo, Z.; Xu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Peng, H. High-Performance Lithium-Air Battery with a Coaxial-Fiber Architecture. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 4487–4491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, J.; Li, M.; Bi, X.; Liu, T.; He, T.; Cheng, J.; Zhang, F.; Li, Y.; et al. Bamboo-Like Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Nanotube Forests as Durable Metal-Free Catalysts for Self-Powered Flexible Li–CO2 Batteries. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Pan, J.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, X.; Liu, L.; Peng, H. A Li–Air Battery with Ultralong Cycle Life in Ambient Air. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, J.; Li, H.; Sun, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Liao, M.; Sun, X.; Peng, H. A Lithium-Air Battery Stably Working at High Temperature with High Rate Performance. Small 2018, 14, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Li, X.; Yang, C.; Li, Y.; Guo, K.; Cheng, J.; Yuan, D.; Song, C.; Lu, J.; Wang, B. A Quasi-Solid-State Flexible Fiber-Shaped Li–CO2 Battery with Low Overpotential and High Energy Efficiency. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, T.; Wang, T.; Li, X.; Jia, Y.; Cheng, J.; Guan, Q.; Liu, E.; Peng, H.; et al. Highly Surface-Wrinkled and N-Doped CNTs Anchored on Metal Wire: A Novel Fiber-Shaped Cathode toward High-Performance Flexible Li–CO2 Batteries. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Elia, G.A.; Marquardt, K.; Hoeppner, K.; Fantini, S.; Lin, R.; Knipping, E.; Peters, W.; Drillet, J.-F.; Passerini, S.; Hahn, R. An Overview and Future Perspectives of Aluminum Batteries. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 7564–7579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Meng, Y.; Lai, Z.; Zhang, X.; Yu, M.; Fang, P.; Wu, M.; Tong, Y.; Lu, X. An Ultrastable and High-Performance Flexible Fiber-Shaped Ni-Zn Battery based on a Ni-NiO Heterostructured Nanosheet Cathode. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, S.; Karahan, H.E.; Wang, C.; Pei, Z.; Wei, L.; Chen, Y. 1D Supercapacitors for Emerging Electronics: Current Status and Future Directions. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, e1902387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, X.; Zi, Y.; Wang, S.; Li, Z.; Zheng, L.; Yi, F.; Li, S.; Wang, Z.L. A Flexible Fiber-Based Supercapacitor-Triboelectric-Nanogenerator Power System for Wearable Electronics. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 4830–4836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, Z.; Zhang, N.; Sun, P.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, C.; Fan, H.J.; Fan, X.; Mai, W. Tailorable and Wearable Textile Devices for Solar Energy Harvesting and Simultaneous Storage. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 9201–9207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).