Abstract
The aim of this work was the synthesis of hybrid materials of iron (II)-based therapeutic systems via the sol-gel method. Increasing amounts of polyethylene glycol (PEG 6, 12, 24, 50 wt%) were added to SiO2/Fe20 wt% to modulate the release kinetics of the drug from the systems. Fourier-transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy was used to study the interactions between different components in the hybrid materials. The release kinetics in a simulated body fluid (SBF) were investigated, and the amount of Fe2+ released was detected via ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy (UV-Vis) after reaction with ortho-phenanthroline. Furthermore, biological characterization was carried out. The bioactivity of the synthesized hybrid materials was evaluated via the formation of a layer of hydroxyapatite on the surface of samples soaked in SBF using spectroscopy. Finally, the potential antibacterial properties of seven different materials against two different bacteria—E. coli and S. aureus—were investigated.
1. Introduction
The iron (II) citrate complex represents an effective solution for resolving iron-deficiency anaemia in people with chronic kidney conditions. This complex is usually used to treat low levels of iron in the blood. Iron is an important metal for human life because it is a cofactor of many types of enzymes and cytochromes of the mitochondrial electron transport chain, and it is part of the haemoglobin and myoglobin structures, which act as oxygen transporters. The use of ferrous organic complexes, such as iron (II) citrate, represents an excellent option to improve health care, since they increase bioavailability and solubility, solving the iron deficiency problem [1,2,3,4]. At the physiological pH of blood (7.4), high levels of Fe2+(aq) would theoretically result in the precipitation of iron (II) hydroxide. Complexation by citrate allows an almost 30-fold increase in the amount of Fe2+ that can be dissolved in the blood. Iron-based systems are also proven to be effective for antitumor treatment. Daily uptake of iron through food is not sufficient to provide an adequate level of this metal in the blood. Some nonspecific symptoms linked to iron deficiency are impaired concentration, loss of energy, and fatigue. However, the most serious effects of iron deficiency, such as anaemia, are associated with loss of hair, angular stomatitis, and premature birth and bone resorption in pregnant women [5].
Iron deficiency can occur in surgical patients due to blood loss or pre-existing anaemia. The encapsulation of the iron (II) citrate complex in porous silica biomaterials allows a slow release of iron, thus resolving problems linked to the lowering of the iron levels in patients’ blood [6].
Iron can also be toxic in excess; high concentrations of iron can promote pathogenic bacterial growth and modify their metabolic pattern [7]. Therefore, by modulating the iron concentration, it is possible to reduce bacterial growth.
Silica biomaterials have high biocompatibility, avoiding negative outcomes as a result of their implantation in bodily tissues; in addition, it is known from the literature [8,9,10] and from medical practice [11] that silica-based materials are able to form a hydroxyapatite layer on their surface that improves the interaction between medical devices and tissue. Drug trapping in its structure is enabled by its porosity [12].
One of the techniques that allow the synthesis of a hybrid biomaterial is the sol-gel method. It is well known that the characteristics of the synthesis methodology have a great influence on the structure, morphology, and chemical composition, as well as on the mechanical, thermal, and optical properties of the resultant product.
The formation of a sol followed by gelation, starting from inorganic materials as precursors, is the basis of the sol-gel technique. A three-dimensional network gel is formed via the condensation of hydrolysed species in solution. Parameters such as temperature, pH, water content, and precursor concentrations affect the structure of the initial gel and the properties of the material [13]. The main advantage of using the sol-gel method for biomaterial synthesis is the possibility of encapsulating different organic compounds and other bioactive molecules that can be used as carriers for drug delivery [14,15,16]. Indeed, it has been reported that gels can release drugs (such as anti-inflammatory agents, antibiotics, and antitumor agents) in a controlled manner [17,18,19,20]. Sol-gel preparation can be done with a wide variety of precursors, but silica-based carriers are preferred because they are a well-known system, inexpensive, and biodegradable [21]. Moreover, it has also been reported that silica/PEG hybrids allow us to obtain greater elasticity, to avoid particle agglomeration, and to create a network that entraps many kinds of drugs and compounds in only one step [22].
In this work, iron (II)-based biomaterials were synthesized via the sol-gel route. The aim was the synthesis of several hybrid materials in which increasing amounts of polyethylene glycol (PEG 6, 12, 24, 50 wt%) were added to SiO2/Fe20 wt%, while materials with different percentages of ferrous citrate complex (Fe(II)C 5, 10, 15, 20 wt%) were added to the silica matrix with 50 wt% of PEG.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Materials
First, 25.0 g of citric acid monohydrate (>99.5%, Fluka, Munich, Germany) was dissolved in 500 mL of Milli-Q water under continuous stirring and heating. After reaching 90 °C, 6.0 g of iron powder (>99%, Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) was added to the solution. After the complete iron reaction, the solution was cooled down to room temperature, obtaining a grey/pearly precipitate that was washed with water, filtered under vacuum, and freeze-dried at −20 °C [1]. The selectivity of Fe2+ was assessed by means of the colorimetric assay with 1,10-phenantroline and sodium thiocyanate, as reported elsewhere in [23].
2.2. Sol-Gel Synthesis
Silica matrices with different amounts of PEG (PEG, MW = 400, Sigma-Aldrich), (6, 12, 24, 50%) and Fe(II)C (5, 10, 15, 20%) were synthesized via the sol-gel technique. The inorganic silicate solutions were obtained by adding tetraethyl orthosilicate (TEOS, Sigma-Aldrich, Darmstadt, Germany) to ethanol (EtOH, Sigma-Aldrich) under continuous magnetic stirring.
Fe(II)C and PEG were added to silica solution (the molar ratios for the silica matrix were H2O/TEOS = 26.6 and EtOH/TEOS = 6). After the gelation process was complete, samples were dried at 50 °C for 24 h, obtaining glass materials that were finely grounded. Figure 1 shows a flow chart of the sol-gel procedure used to synthesize the hybrid materials, which are summarized in Table 1. During the synthesis, the ferrous ions are stable, as the authors have shown in a previous paper [23].
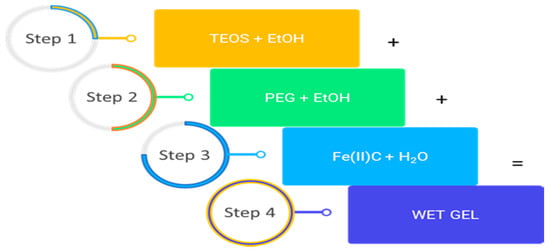
Figure 1.
Flow chart of sol-gel synthesis depicting the steps that lead to the formation of a gel from a liquid.

Table 1.
List of samples with the various percentage contents of PEG and Fe(II)C studied.
2.3. FTIR Analysis
Fourier-transform infrared (FTIR) analysis was carried out to investigate specific intermolecular interactions between organic and inorganic components. Transmittance spectra of samples were obtained using a Prestige 21 Shimadzu (Japan) instrument equipped with a DTGS KBr (deuterated triglycine sulphate with potassium bromide windows) detector, with a resolution of 2 cm−1 (45 scans). FTIR spectra were recorded in the 400–4000 cm−1 range, using a disk consisting of 2 mg of sample and 198 mg of KBr. The FTIR spectra were processed using Prestige software (IR solution).
2.4. In Vitro Release of Fe2+
The study of in vitro release was carried out to investigate the amounts of Fe2+ released from the hybrid glass materials. In particular, the release of Fe2+ from different materials was analysed at different release times using the normative reference A3500-Fe B, phenanthroline method. Powders of hybrid materials were soaked in 10 mL of SBF solution. Afterwards, 1.00 mL of this mixture containing the hybrid materials was added to a solution composed of 10% hydroxylamine hydrochloride, 10% acetate sodium, 0.1% 1,10-phenanthroline, and water. Release measurements, taken by means of a Shimadzu UV 700 Double-Beam Scanning UV-Vis spectrophotometer (Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan), were repeated three times on each hybrid. The absorbance of Fe2+ released was obtained at a wavelength of λ = 520.0 nm. Means ± standard deviation were calculated for each measure. The calibration curve of absorbance versus concentration was determined in the range 0–4.99 mg L−1. Over this interval, the data fitted the Beer–Lambert law:
where A is absorbance, ε is the molar absorptivity coefficient (M−1 cm−1), l is the path length in cm, and C is concentration (M).
A = ε l C = 1.265 C
2.5. Bioactivity Test
To investigate the formation of a hydroxyapatite layer on glass materials, 250 mg of powder and 250 mg of disk (obtained from the powders) were soaked in 50 mL of simulated body fluid (SBF) at 37 °C for 21 days. The SBF solution was replaced every two days to avoid the depletion of ionic species. Finally, exposed samples were dried and analysed using a Quanta 200 scanning electron microscope (SEM) equipped with electron dispersion spectroscopy (EDS) and X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis, along with a Philips 139 diffractometer equipped with a PW 1830 generator, tungsten lamp, and Cu anode, where the source of the X-rays was given by Cu-Kα radiation (λ = 0.15418 nm). The ratio between the total exposed surface and the volume of solution was chosen according to the literature [24].
2.6. Antibacterial Activity
The Kirby–Bauer test was performed on the glass hybrid materials to evaluate their possible use in preventing the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria. Escherichia coli (ATCC 25922) as Gram-negative bacteria (−) and Staphylococcus aureus (ATCC 25923) as Gram-positive bacteria (+) were grown in the absence and presence of specimens. A total of 100 mg of each of the glasses were finely ground to a powder and irradiated with UV light for 1 h for sterilization. Bacterial suspensions of 109 CFU/mL were obtained by diluting pellet strains in distilled saline water (0.9% NaCl). E. coli was plated on TBX medium (Tryptone Bile X-Gluc) (Liofilchem, Italy), while S. aureus was plated on Baird-Parker agar (Liofilchem, Italy). Both media were sterilized at 120 °C for 15 min. After autoclaving, Baird-Parker agar was cooled to 50 °C, and an emulsion of egg yolk containing potassium tellurite was added. After placing the materials on the centre of Petri plates, E. coli plates were grown at 44 °C for 24 h, while S. aureus plates were grown at 36 °C for 24 h. The diameter of inhibition halos (IDs) in relation to the Petri dish diameter (PPD) (6 cm) was calculated. Four measurements were carried out for each specimen to obtain the mean standard deviation. Data are expressed as bacterial viability (BV) (%).
where 100% BV represents the bacteria viability without samples. The mean standard deviation is expressed as a relative standard deviation (RSD).
BV = (PPD − IDs)/PPD × 100
A flow chart of antibacterial detection is represented in Figure S1.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. FTIR Analysis
FTIR analysis of hybrid materials allowed us to obtain information about interactions between the individual components. Figure 2 shows the FTIR spectra of SiO2 hybrid materials with increasing amounts of PEG. The silica spectrum in curve (a) shows asymmetric and symmetric stretching of Si–O–Si at 1080 cm−1, with a shoulder at 1200 cm−1. In addition, we can see the bending vibrations of Si–O–Si at 800 and 460 cm−1, whereas the band at 948 cm−1 is assigned to Si–OH bond vibrations. The intense band at 3450 cm−1 and the peak at 1640 cm−1 are due to stretching and bending vibrations of the OH of water. The broadness of the OH vibration suggests H-bonding between the OH of the solvent molecules and Si atoms. The addition of PEG to the silica matrix is confirmed by the increase in the intensity of the peaks at 2927 cm−1 and 1454 cm−1 that are associated with C–H asymmetric stretching and bending, respectively. In addition, we observe a shift of this peak in pure PEG to 2870 cm−1 [25,26,27]. The presence of Fe(II)C (Figure 3) is detectable in curves (b–d) by an increase in the intensity of the peak at 1722 cm−1, which is due to C=O stretching [28]. In addition, the increase in the intensity of the peak at 1560 cm−1, ascribed to the COO− group, is another sign of the encapsulation of Fe(II) citrate in the system [23].
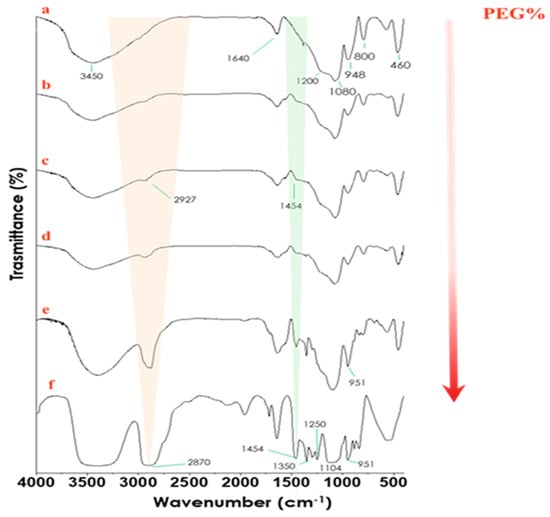
Figure 2.
FTIR spectra of SiO2 (a), SiO2/Fe(II)C20%/PEG6% (b), SiO2/Fe(II)C20%/PEG12% (c), SiO2/Fe(II)C20%/PEG24% (d), SiO2/Fe(II)C20%/PEG50% (e), and pure PEG (f).
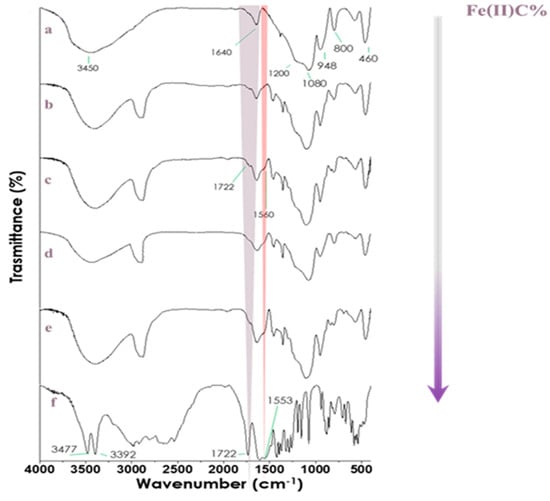
Figure 3.
FTIR spectra of SiO2 (a), SiO2/PEG50%/Fe(II)C 5% (b), SiO2/PEG50%/ Fe(II)C10 % (c), SiO2/PEG50%/ Fe(II)C15% (d), SiO2/PEG50%/ Fe(II)C20% (e), and pure Fe(II)C (f).
3.2. In Vitro Release
Controlled Fe2+ release is essential to evaluate the continuity and efficacy of treatments. The release was assayed by measuring the UV absorbance of Fe2+ at λ = 520.0 nm as a function of the concentration of the solution. A calibration curve was drawn using standard solutions with concentrations from 0 to 4.99 mg/L (Figure S2).
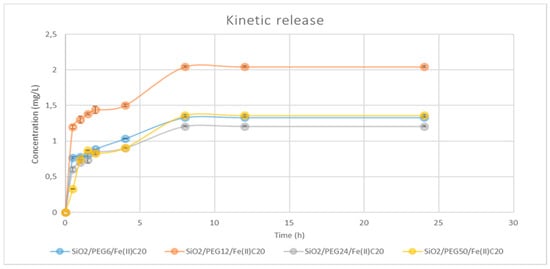
Figure 4.
Time-dependent drug release plot for SiO2/PEG 6, 12, 24, 50 wt%/Fe(II)C20%.
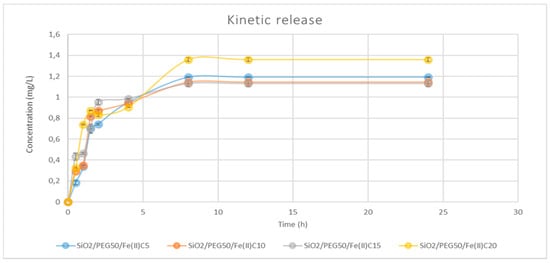
Figure 5.
Time-dependent drug release plot for SiO2/PEG50wt%/Fe(II)C 5, 10, 15, 20 wt%.
Regarding Fe(II)C 20 wt% with various amounts of PEG, the trend is quite similar for all of the systems.
In particular, the amount of Fe(II)C released was very fast in the first 5 h, and then it slowed down, ending after 8 h. Furthermore, the 12 wt% PEG system released a higher concentration of Fe(II)C, likely because this is incorporated into the porous matrix of the system and is more easily released than when the PEG concentration is greater, and forms stronger interactions within the system.
Instead, in the hybrid systems with a constant amount of PEG (50 wt%) and varying Fe(II)C content (5, 10, 15, or 20 wt%), the release of Fe(II)C was fast up to 4 h, and then it slowed down, ending after 8 h.
3.3. Bioactivity
Glasses exposed to SBF solution for 21 days were observed via SEM. In Figure 6 it is possible to see some globules on disks that are soaked in SBF. This shape is typical of hydroxyapatite formed on a glass surface. Those particles were visible over the entire surface of all materials. The EDS analysis (Figure 6) of the observed crystals shows their chemical composition. The atomic content ratio between Ca and P is 1.6 and is in agreement with the chemical formula of hydroxyapatite [29]. The mechanism of the hydroxyapatite formation is explained in Figure 7: the Si–OH groups present on the surface of the material combine with the positively charged Ca2 + ions present in the SBF fluid, forming calcium silicate. The accumulation of calcium ions allows the increase in the positive charge on the surface which, in turn, combines with the negative charge of the phosphate ions to form amorphous calcium phosphate, which spontaneously transforms into hydroxyapatite [Ca10(PO4)6(OH)2] [30].
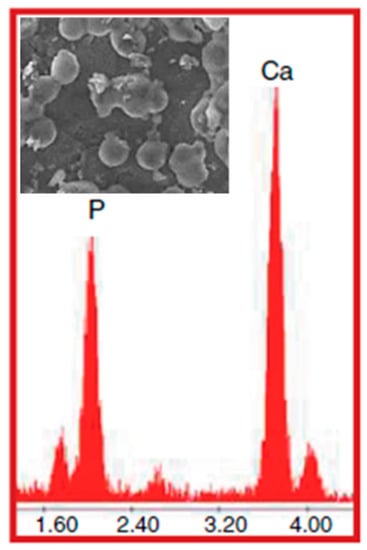
Figure 6.
SEM micrograph of globular hydroxyapatite crystals after the bioactivity test, and EDS elementary analyses of crystals.
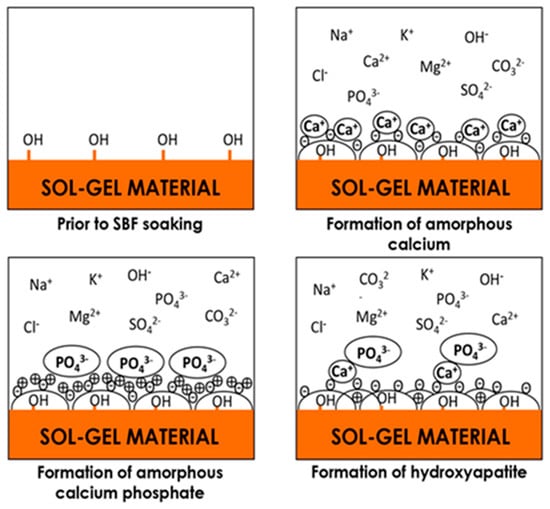
Figure 7.
Mechanism of hydroxyapatite formation.
Furthermore, XRD measurement was used to identify the presence of hydroxyapatite on the hybrid surface. The intense peaks of crystalline hydroxyapatite are visible in Figure 8 (◆), confirming that the material surface was covered by a hydroxyapatite layer after 21 days of soaking in SBF. In Figure S3, XRD measurements show the amorphous structure of the sample before being soaked in SBF. Moreover, this result suggests that the hydroxyapatite layer is too thick to allow the detection of XRD signals from the hybrids’ surface [24,31,32,33,34].
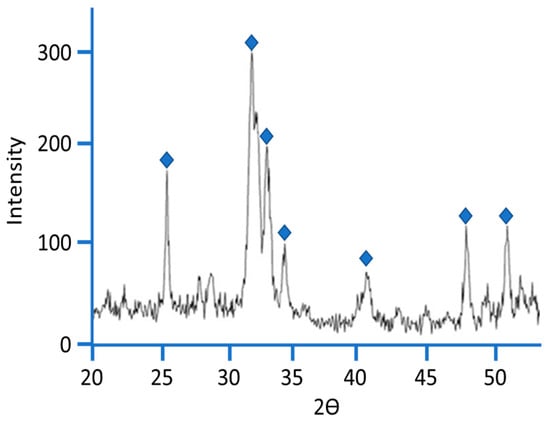
Figure 8.
A representative XRD of SiO2/PEG 50 wt%/Fe(II)C 20 wt% soaked in SBF solution for 21 days.
3.4. Antibacterial Activity
The antimicrobial properties of these materials were investigated via the Kirby–Bauer Test (Figure S4) to validate their safety by the ability to inhibit the growth of pathogenic bacterial strains.
Representative images (Figure 9A) of antibacterial tests of SiO2/PEG50% with increasing amounts of Fe(II)C in the hybrid matrix show that iron has an inhibitory effect on both bacterial strains tested. Indeed, the higher the iron concentration in the silica matrix, the higher the inhibitory effect on bacterial growth, as shown in (Figure 9B). In the literature, it is reported that despite iron being an essential nutrient for bacterial growth, thanks to its main role as an electron transporter, excessive concentrations can become toxic to most bacterial strains. Frawley et al. reported that alterations of the H2O2 and iron concentrations can produce high amounts of free radical species that damage the DNA, proteins, and lipids of bacterial cells [35].
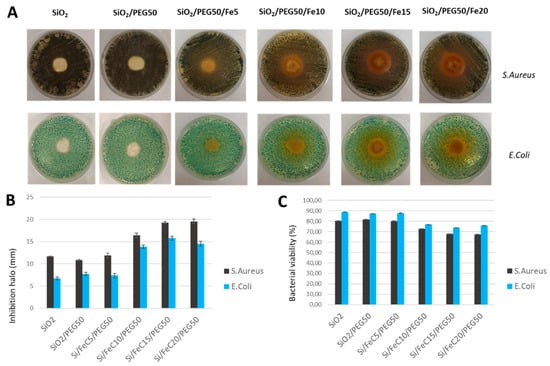
Figure 9.
(A) Representative inhibition halos (ID) of S. aureus and E. coli with SiO2/Fe(II)C 5, 10, 15, 20 wt%/PEG 50 wt%. (B) Diameter (mm) of inhibition halos of all materials incubated with S. aureus and E. coli. Values are the mean ± SD of measurements carried out on samples analysed three times. (C) Bacterial viability (%).
In accordance with Kalantari et al. [7], low concentrations of iron did not show a significant inhibition, while the bacterial growth of S. aureus and E. coli decreased when 20 wt% of Fe(II)C was encapsulated (Figure 9C).
The bacterial inhibitory effects of the increasing amounts of PEG in the SiO2 matrix when 20% of Fe(II)C was encapsulated were evaluated, as shown in Figure 10. The increasing amounts of PEG had an effect on E. coli and S. aureus growth, as can be seen from the Petri dish images in (Figure 10A). Thus, the highest concentration of PEG allows bacterial inhibition.
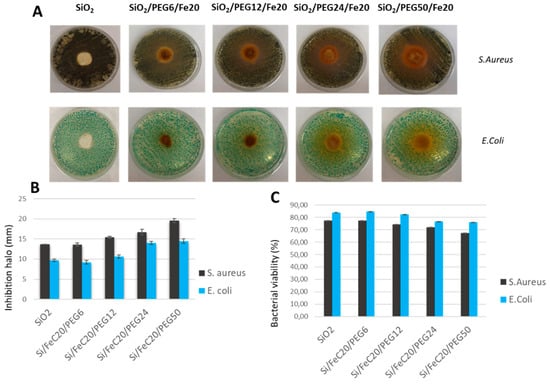
Figure 10.
(A) Representative inhibition halos (ID) of S. aureus and E. coli with SiO2/Fe(II)C 20%/PEG 6, 12, 24, 50 wt%. (B) Diameter (mm) of inhibition halos of all materials incubated with S. aureus and E. coli. The values are the mean ± SD of measurements carried out on samples analysed three times. (C) Bacterial viability (%).
4. Conclusions
The iron (II) citrate complex represents a solution for resolving iron-deficiency anaemia and improving health care, since it increases the bioavailability and solubility of iron. The sol-gel route allowed the synthesis of organic/inorganic hybrid materials consisting of a SiO2 inorganic matrix, in which different percentages of a polymer (PEG) and a compound (Fe(II)C) were entrapped.
The FTIR spectra of the hybrids showed the typical bands of the polymer and silica, along with the bands of citrate, indicating encapsulation of Fe(II)C in the system.
Fe(II)C release measurements were carried out to evaluate the hypothetical controlled release of the compound. Indeed, the results confirm that this system is able to release Fe(II)C in a controlled manner, because it was fast in the first few hours, and then it slowed down, ending after 8 h.
Furthermore, SEM and XRD analysis showed that the hybrids are bioactive, because they are able to form a hydroxyapatite layer on their surface.
Finally, the antibacterial activity of the materials was tested. E. coli and S. aureus were inoculated with the hybrid materials. According to the results obtained, a high concentration of iron is able to inhibit microbial growth, while increasing amounts of PEG do not show a significant inhibition of microbial growth.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/app11199311/s1, Figure S1: Flow-chart of antibacterial detection; Figure S2: Calibration curve based on the concentration of Fe2+ (r2 = 0.9973); Figure S3: Antimicrobial test performed by the Kirby-Bauer technique; Figure S4: XRD of sample before soaked in SBF.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.C.; methodology, M.C. and I.B.; software, Y.D. and A.D.; validation, M.C.; formal analysis, A.D. and Y.D.; investigation, A.D.; resources, M.C.; data curation, M.C. and I.B.; writing—original draft preparation, M.C.; writing—review and editing, M.C. and R.J.C.; visualization, M.C.; supervision, M.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Naviglio, D.; Salvatore, M.M.; Limatola, M.; Langella, C.; Faralli, S.; Ciaravolo, M.; Andolfi, A.; Salvatore, F.; Gallo, M. Iron (II) Citrate Complex as a Food Supplement: Synthesis, Characterization and Complex Stability. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guadagno, L.; Raimondo, M.; Longo, R.; Sarno, M.; Iuliano, M.; Mariconda, A.; Saturnino, C.; Ceramella, J.; Iacopetta, D.; Sinicropi, M.S. Development and characterization of antitumoral electrospun polycaprolactone/functionalized Fe3O4 hybrid membranes. Mater. Today Chem. 2020, 17, 100309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longo, R.; Gorrasi, G.; Guadagno, L. Electromagnetically Stimuli-Responsive Nanoparticles-Based Systems for Biomedical Applications: Recent Advances and Future Perspectives. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longo, R.; Guadagno, L.; Lamberti, P. Electromagnetic Characterization of Polycaprolactone electrospun nanofibers filled with Fe3O4 Nanoparticles. In Proceedings of the 4th International Symposium on Multidisciplinary Studies and Innovative Technologies (ISMSIT), Istanbul, Turkey, 22–24 October 2020; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco-Rojo, R.; Vaquero, M.P. Iron bioavailability from food fortification to precision nutrition. A review. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2019, 51, 126–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Ramírez, S.; Bisbe, E.; Shander, A.; Spahn, D.R.; Muñoz, M. Management of Perioperative Iron Deficiency Anemia. Acta Haematol. 2019, 142, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalantari, N.; Ghaffari, S. Evaluation of Toxicity of Heavy Metals for Escherichia coli Growth. Iran. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2008, 5, 173–178. [Google Scholar]
- Catauro, M.; Laudisio, G.; Costantini, A.; Fresa, A.; Branda, F. Low Temperature Synthesis, Structure and Bioactivity of 2CaO 3SiO2 Glass. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 1997, 10, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshikawa, C.; Qiu, J.; Huang, C.-F.; Shimizu, Y.; Suzuki, J.; Bosch, E.V.D. Non-biofouling property of well-defined concentrated polymer brushes. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2015, 127, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yoshikawa, C.; Hattori, S.; Honda, T.; Huang, C.-F.; Kobayashi, H. Non-biofouling property of well-defined concentrated poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate) brush. Mater. Lett. 2012, 83, 140–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiume, E.; Barberi, J.; Verné, E.; Baino, F. Bioactive Glasses: From Parent 45S5 Composition to Scaffold-Assisted Tissue-Healing Therapies. J. Funct. Biomater. 2018, 9, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ates, B.; Koytepe, S.; Balcioglu, S.; Ulu, A.; Gurses, C. Biomedical applications of hybrid polymer composite materials. In Hybrid Polymer Composite Materials; Woodhead Publishing: Malatya, Turkey, 2017; pp. 343–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, D.A.; Ko, E.I. Preparing Catalytic Materials by the Sol-Gel Method. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1995, 34, 421–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khamsehashari, N.; Hassanzadeh-Tabrizi, S.; Bigham, A. Effects of strontium adding on the drug delivery behavior of silica nanoparticles synthesized by P123-assisted sol-gel method. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2018, 205, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameeduzzafar; Imam, S.S.; Bukhari, S.N.A.; Ahmad, J.; Ali, A. Formulation and optimization of levofloxacin loaded chitosan nanoparticle for ocular delivery: In-vitro characterization, ocular tolerance and antibacterial activity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 108, 650–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, C.; Zhong, W. Sol-gel derived terbium-containing mesoporous bioactive glasses nanospheres: In vitro hydroxyapatite formation and drug delivery. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2017, 160, 406–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiménez-Flores, Y.; Suárez-Quezada, M.; Rojas-Trigos, J.B.; Lartundo-Rojas, L.; Suárez, V.; Mantilla, A. Sol-gel synthesis of calcium phosphate-based biomaterials—A review of environmentally benign, simple, and effective synthesis routes. J. Mater. Sci. 2017, 52, 9990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trofimov, A.D.; Ivanova, A.A.; Zyuzin, M.V.; Timin, A.S. Porous Inorganic Carriers Based on Silica, Calcium Carbonate and Calcium Phosphate for Controlled/Modulated Drug Delivery: Fresh Outlook and Future Perspectives. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tranquillo, E.; Barrino, F.; Poggetto, G.D.; Blanco, I. Sol-Gel Synthesis of Silica-Based Materials with Different Percentages of PEG or PCL and High Chlorogenic Acid Content. Materials 2019, 12, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Catauro, M.; Tranquillo, E.; Poggetto, G.D.; Pasquali, M.; Dell’Era, A.; Ciprioti, S.V. Influence of the Heat Treatment on the Particles Size and on the Crystalline Phase of TiO2 Synthesized by the Sol-Gel Method. Materials 2018, 11, 2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Croissant, J.; Fatieiev, Y.; Khashab, N. Degradability and Clearance of Silicon, Organosilica, Silsesquioxane, Silica Mixed Oxide, and Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapusuz, D. Sol-gel derived silica/polyethylene glycol hybrids as potential oligonucleotide vectors. J. Mater. Res. 2019, 34, 3787–3797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catauro, M.; Naviglio, D.; Risoluti, R.; Ciprioti, S.V. Sol-gel synthesis and thermal behavior of bioactive ferrous citrate–silica hybrid materials. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2018, 133, 1085–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kokubo, T.; Takadama, H. How useful is SBF in predicting in vivo bone bioactivity? Biomaterials 2006, 27, 2907–2915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catauro, M.; Bollino, F.; Papale, F.; Gallicchio, M.; Pacifico, S. Influence of the polymer amount on bioactivity and biocompatibility of SiO2/PEG hybrid materials synthesized by sol-gel technique. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2015, 48, 548–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catauro, M.; Piccolella, S.; Leonelli, C. FT-IR Characterization of Antimicrobial Hybrid Materials through Sol-Gel Synthesis. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Samal, S.; Tyc, O.; Heller, L.; Šittner, P.; Malik, M.; Poddar, P.; Catauro, M.; Blanco, I. Study of Interfacial Adhesion between Nickel-Titanium Shape Memory Alloy and a Polymer Matrix by Laser Surface Pattern. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Catauro, M.; Tranquillo, E.; Barrino, F.; Blanco, I.; Poggetto, F.D.; Naviglio, D. Drug Release of Hybrid Materials Containing Fe(II)Citrate Synthesized by Sol-Gel Technique. Materials 2018, 11, 2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Uchida, M.; Kim, H.-M.; Kokubo, T.; Miyaji, F.; Nakamura, T. Bonelike Apatite Formation Induced on Zirconia Gel in a Simulated Body Fluid and Its Modified Solutions. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2004, 84, 2041–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hench, L.L. Bioceramics: From Concept to Clinic. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1991, 74, 1487–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catauro, M.; Raucci, M.G.; De Gaetano, F.; Marotta, A. Sol-gel synthesis, characterization and bioactivity of polycaprolactone/SiO2 hybrid material. J. Mater. Sci. 2003, 38, 3097–3102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catauro, M.; Tranquillo, E.; Risoluti, R.; Ciprioti, S.V. Sol-Gel Synthesis, Spectroscopic and Thermal Behavior Study of SiO2/PEG Composites Containing Different Amount of Chlorogenic Acid. Polymers 2018, 10, 682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, J.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Cheng, H.; Seo, H.J. Surface reactivity and hydroxyapatite formation on Ca5MgSi3O12 ceramics in simulated body fluid. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 423, 900–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brundavanam, K.K.; Poinern, G.E.J.; Fawcett, D. Modelling the Crystal Structure of a 30 nm Sized Particle based Hydroxyapatite Powder Synthesised under the Influence of Ultrasound Irradiation from X-ray powder Diffraction Data. Am. J. Mater. Sci. 2013, 3, 84–90. [Google Scholar]
- Frawley, E.R.; Fang, F.C. The ins and outs of bacterial iron metabolism. Mol. Microbiol. 2014, 93, 609–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).