Filter Feeding and Carbon and Nitrogen Assimilation of a Freshwater Bivalve (Unio douglasiae) on a Toxic Cyanobacterium (Microcystis aeruginosa)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal Collection and Maintenance
2.2. Preparation of Experimental Water
2.3. Labeling and Grazing Experiments
2.4. Stable Isotope Analysis
2.5. Water Quality Analysis
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results
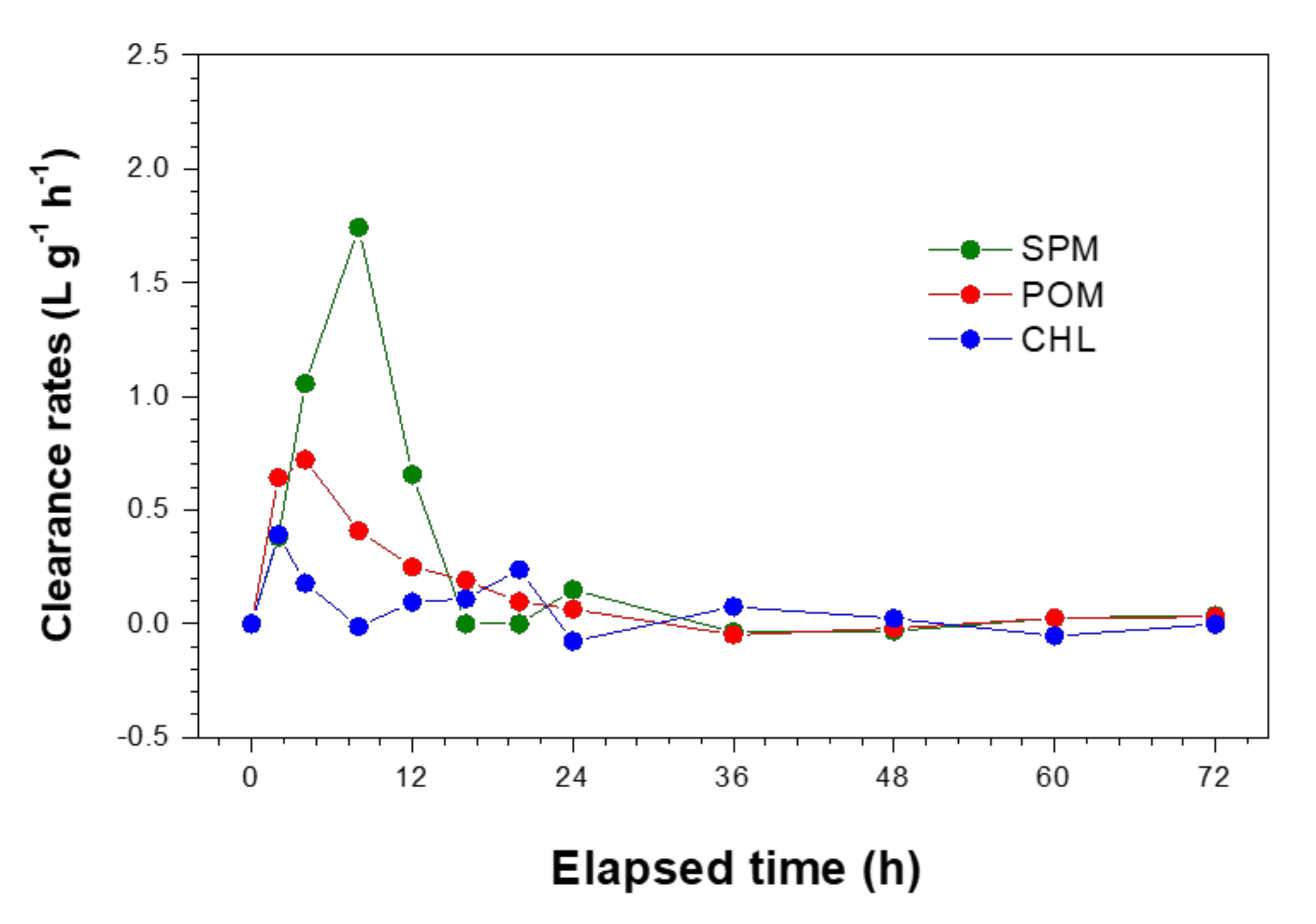
3.1. Mussel Grazing
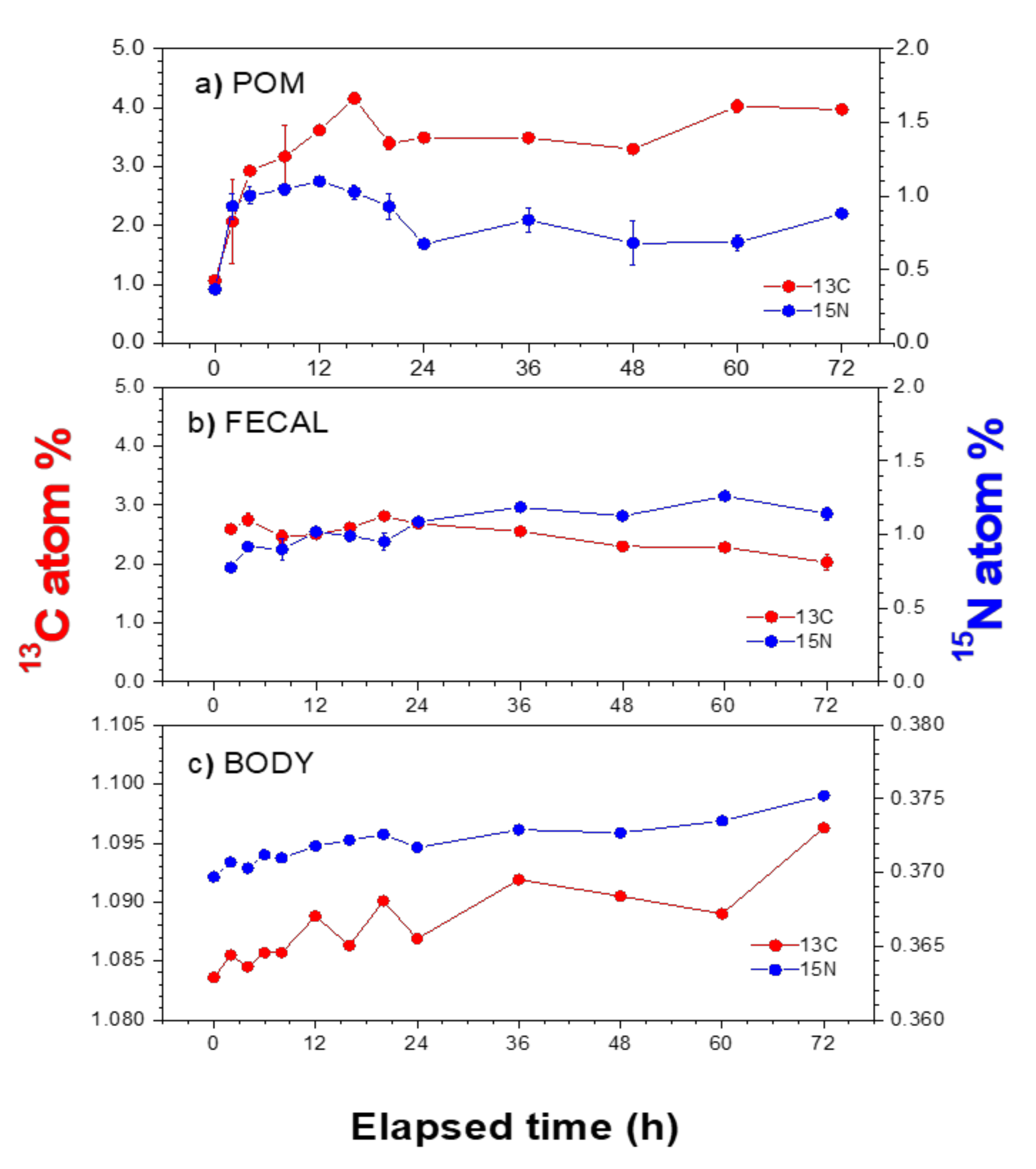
3.2. Atom% of 13C and 15N in POM and Mussel Samples
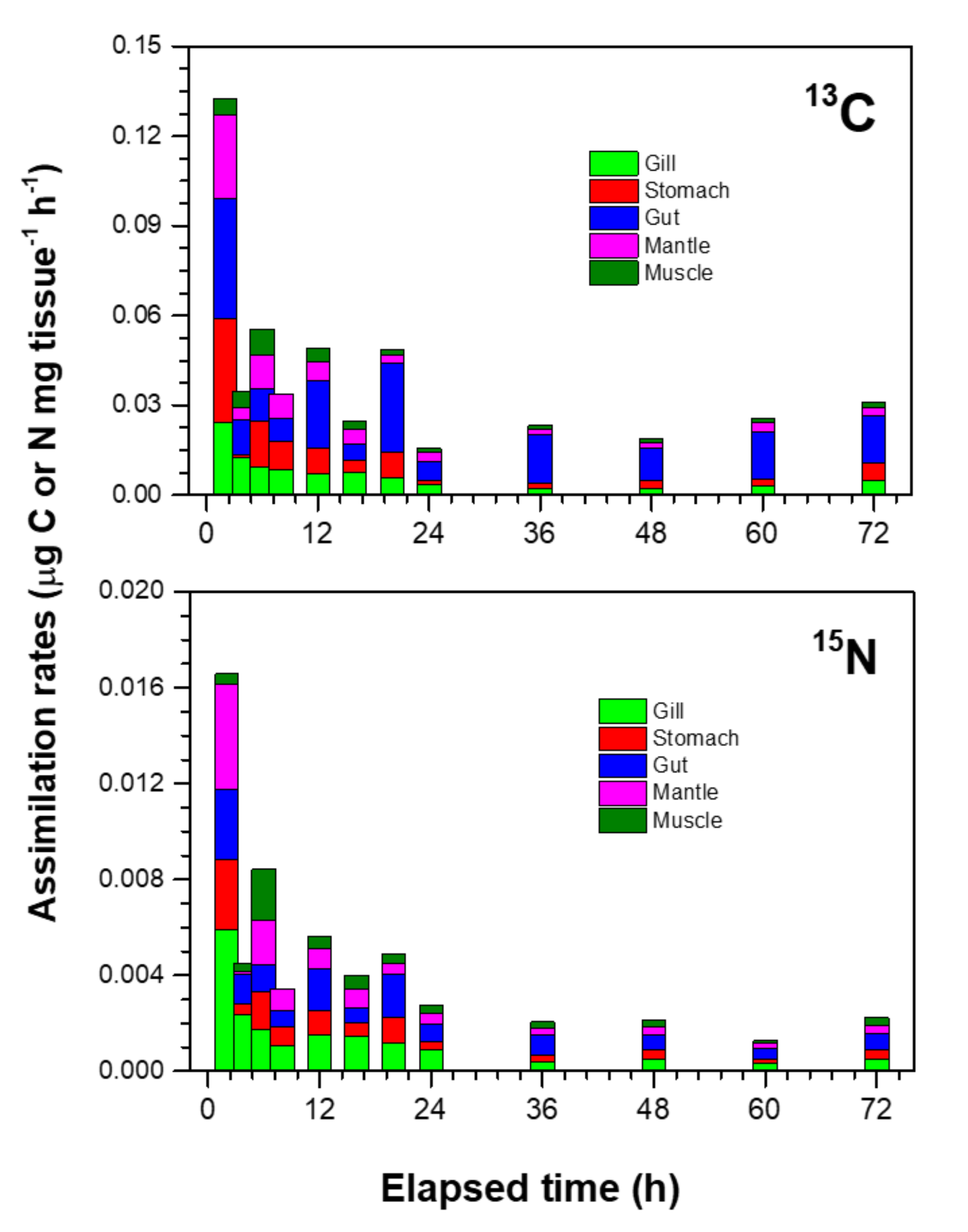
3.3. Assimilation Rates in Mussel Tissues
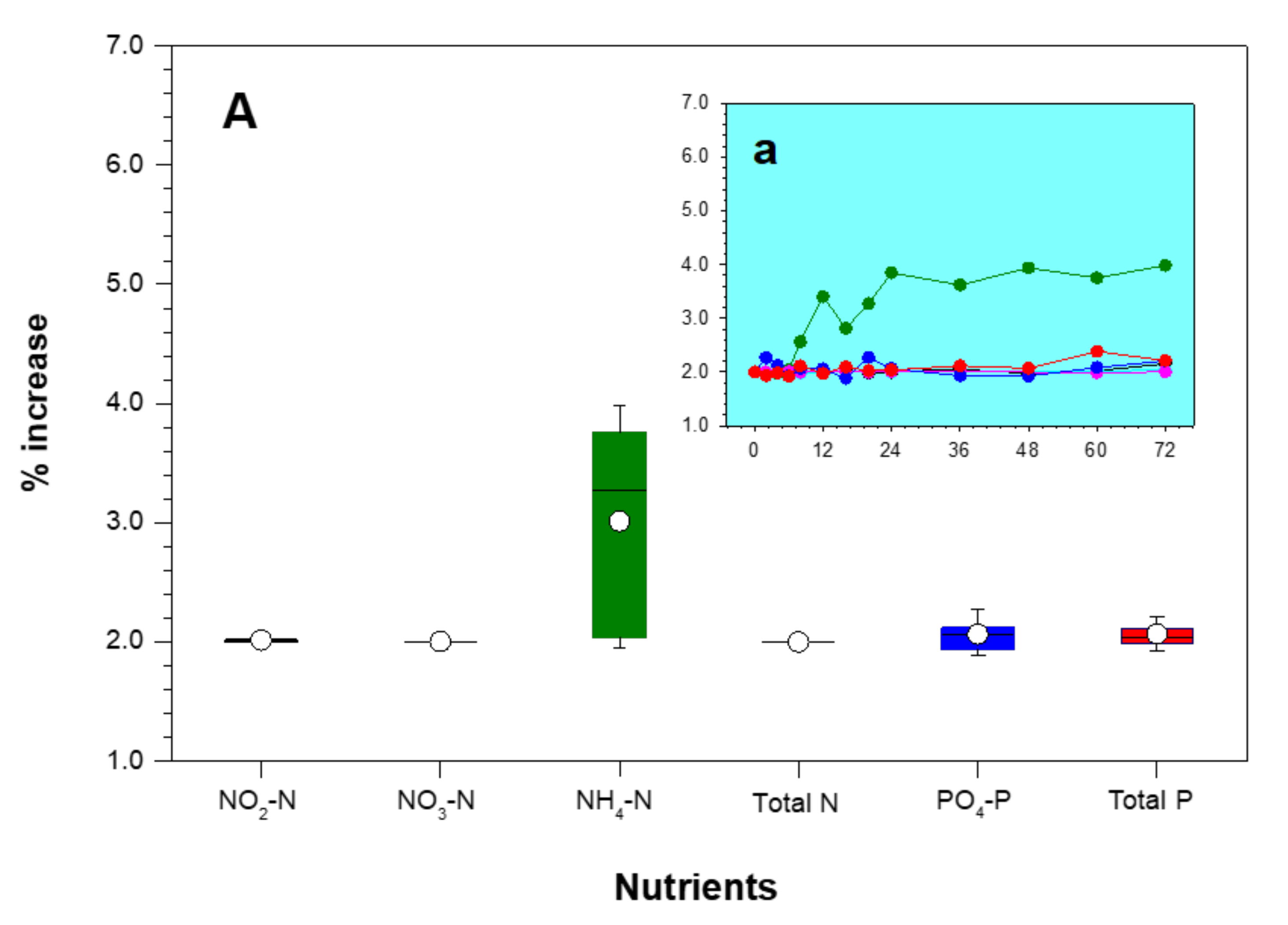
3.4. Changes in Water Quality
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Watters, G.T. A synthesis and review of the expanding range of the Asian freshwater Anodonta woodiana (LEA, 1834) (Bivalvia: Unionidae). Veliger 1997, 40, 152–156. [Google Scholar]
- Holland, R.E. Changes in plankton diatoms and water transparency in Hatchery Bay, Bass Island area, western Lake Erie since the establishment of the zebra mussel. J. Great Lakes Res. 1993, 19, 617–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotner, J.B.; Gardner, W.S.; Johnson, J.R.; Sada, R.H.; Cavaletto, J.F.; Heath, R.T. Effects of zebra mussels (Dreissena polymorpha) on bacterioplankton: Evidence for both size-selective consumption and growth stimulation. J. Great Lakes Res. 1995, 21, 517–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.J. Effects of zebra mussel (Dreissena polymorpha Pallas) on phytoplankton and bacterioplankton: Evidence for size-selective grazing. Korean J. Limnol 1996, 29, 363–378. [Google Scholar]
- Kwon, O.G.; Lee, J.S. Colored shells of Korea; Academy Publisher: Seoul, Korea, 1993; p. 446. [Google Scholar]
- Min, D.K. Mollusks in Korea; Min Molluscan Research Institute: Seoul, Korea, 2004; p. 566. [Google Scholar]
- International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN). The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Version 2021-1. 2021. Available online: https://www.iucnredlist.org (accessed on 4 July 2021).
- Kim, B.H.; Lee, J.H.; Hwang, S.J. Inter- and intra- specific differences in filtering activities between two unionids, Anodonta woodiana and Unio douglasiae, in ambient eutrophic lake waters. Ecol. Eng. 2011, 37, 1957–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beklioglu, M. A review on the control of eutrophication in deep and shallow lakes. Turk. J. Zool. 1999, 23, 327–336. [Google Scholar]
- Figueiredo, D.R.; Azeiteiro, U.M.; Esteves, S.M.; Goncalves, F.J.M.; Pereira, M.J. Microcystin-producing blooms-a serious global public health issue. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2004, 59, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bontes, B.M.; Verschoo, A.M.; Dionisio Pires, L.M.; Van Donk, E.; Ibelings, B.W. Functional response of Anodonta anatine feeding on a green algal and four strains of cyanobacteria, differing in shape, size and toxicity. Hydrobiologia 2007, 584, 191–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dionisio Pires, L.M.; Bontes, B.M.; Samchyshyna, L.; Jong, J.; Van Donk, E.; Ibelings, B.W. Grazing on microcystin-producing and microcystin-free phytoplankters by different filter-feeders: Implications for lake restoration. Aquat. Sci. 2007, 69, 534–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xie, P.; Wu, X.P. Grazing on toxic and nontoxic Microcystis aeruginosa PCC7820 by Unio douglasiae and Corbicula fluminea. Limnology 2009, 10, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, B.J.; Fry, B. Stable isotopes in ecosystem studies. Ann. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1987, 18, 293–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, B.J.; Howarth, R.W.; Garrett, R.H. Multiple stable isotopes used to trace the flow of organic matter in estuarine food webs. Science 1985, 227, 1361–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, P.L.; Anderson, R.K.; Lawrence, A. A δ13C and δ15N Tracer Study of Nutrition in Aquaculture: Penaeus vannamei in Pond Grow Out System. Stable Isotopes in Ecological Research; Rundel, P.W., Ehleringer, J.R., Nagy, K.A., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1989; Volume 68, pp. 288–303. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, B.H.; Hwang, S.O. The structure of the plankton community and the cyanobacteria bloom during the rainy season in mesoeutrophic lake (Lake Juam), Korea. J. Environ. Sanit. Eng. 2004, 19, 51–59. [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe, M.M.; Kawachi, M.; Hiroki, M.; Kasai, F. Microbial Culture Collections, NIES-Collection List of Strains: Microalgae and Protozoa, 6th ed.; National Institute for Environmental Studies: Tsukuba, Japan, 2000; p. 159. [Google Scholar]
- Coughlan, J. The estimation of filtration rates from the clearance of suspensions. Mar. Biol. 1969, 29, 170–180. [Google Scholar]
- Utermohl, H. Zur Ver vollkommung der quantitativen phytoplankton-methodik. Mitt. Int. Ver. Theor. Angew. Limnol. 1958, 9, 39–151. [Google Scholar]
- American Public Health Association (APHA). Standards Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 19th ed.; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 1995; p. 541. [Google Scholar]
- Bunn, S.E.; Loneragan, N.R.; Kempster, M.A. Effects of acid washing on stable isotope ratios of C and N in penaid shrimp and seagrass: Implications for food web studies using multiple stable isotopes. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1995, 40, 622–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, M.S.; Lee, W.S.; Kumar, K.S.; Shin, K.H.; Robarge, W.; Kim, M.S.; Lee, S.R. Effects of HCl pretreatment, drying, and storage on the stable isotope ratios of soil and sediment samples. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2016, 30, 1567–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hama, T.; Miyazaki, T.; Ogawa, Y.; Iwakuma, T.; Takahashi, M.; Otsuki, A.; Ichimura, S. Measurement of photosynthetic production of a marine phytoplankton population using a stable 13C isotope. Marine Biol. 1983, 73, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hama, T.; Handa, N.; Hama, J. Determination of amino acid production rate of a marine phytoplankton population with 13C and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1987, 32, 1144–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SPSS. SigmaPlot for Windows Version 3.2; SPSS Inc.: Chicago, IL, USA, 2004; Available online: http://www.sigmaplot.co.uk/ (accessed on 16 March 2021).
- Dame, R.F.; R. Zingmark, R.; Nelson, D. Filter Feeding Coupling between the Estuarine Water Column and Benthic Subsystems. Estuarine Perspectives; Kennedy, V.S., Ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1985; pp. 521–526. [Google Scholar]
- Dame, R.F.; Dankers, N.; Prins, T.; Jongsma, H.; Smaal, A. The influence of mussel beds on nutrients in the Western Wadden Sea and Eastern Scheldt estuaries. Estuaries 1991, 14, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalepa, T.F.; Schloesser, D.W. Zebra mussels: Biology, Impacts, and Control; Lewis Publishers: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1993; p. 832. [Google Scholar]
- Nalepa, T.F. Zebra mussels in the Saginaw Bay, Lake Huron ecosystem. J. Great Lakes Res. 1995, 21, 411–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- MacIsaac, H.J. Potential abiotic and biotic impacts of zebra mussels on the inland waters of North America. Am. Zool. 1996, 36, 287–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prins, T.C.; Small, A.C.; Dame, R.F. A review of the feedbacks between bivalve grazing and ecosystem processes. Aquat. Ecol. 1998, 31, 349–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaughn, C.C.; Gido, K.B.; Spooner, D.E. Ecosystem processes performed by unionid mussels in stream mesocosm: Species role and effects of abundance. Hydrobiologia 2004, 527, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.J.; Kim, H.S.; Park, J.H.; Kim, H.H. Effects of cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa on the filtration rate and mortality of the freshwater bivalve Corbicula leana. J. Environ. Biol. 2010, 31, 483–488. [Google Scholar]
- Reeders, H.H.; Bij de Vaate, A. Zebra mussel (Dreissena polymorpha): A new perspective for water quality management. Hydrobiologia 1990, 200, 437–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto, D.; Mena, G. Filter feeding by the freshwater mussel, Diplodon chilensis, as a biocontrol of salmon farming eutrophication. Aquaculture 1999, 171, 65–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakenkamp, C.C.; Ribblett, S.G.; Palmer, M.A.; Swan, C.M.; Reid, J.W.; Goodison, M.R. The impact of an introduced bivalve (Corbicula fluminea) on the benthos of a sandy stream. Freshwater Biol. 2001, 46, 491–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, Y.; Fatos Kerciku, F. Effects of filter-feeding bivalves on the distribution of water quality and nutrient cycling in a eutrophic coastal lagoon. J. Mar. Syst. 2000, 26, 209–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukushima, M.; Takamura, N.; Sun, L.; Nakagawa, M.; Matsushige, K.; Xie, P. Changes in plankton community following introduction of filter-feeding planktivorous fish. Freshwater Biol. 1999, 42, 719–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.H.; Choi, M.K.; Takamura, N. Dietary contributions of phytoplankton and zooplankton to young silver carps. Korean J. Limnol. 2001, 34, 98–105. [Google Scholar]
- Tieszen, L.L.; Boutton, T.W.; Tesdahl, K.G.; Slade, N.A. Fractionation and turnover of stable carbon isotopes in animal tissues: Implications for 13C analysis of diet. Oecologia 1983, 57, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raikow, D.F.; Hamilton, S.K. Bivalve diets in a midwestern US stream: A stable isotope enrichment study. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2001, 46, 514–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorrain, A.; Paulet, Y.M.; Chauvaud, L.; Savoye, N.; Donval, A.; Saout, C. Differential δ13C and δ15N signatures among scallop tissues: Implications for ecology and physiology. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2002, 275, 47–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Watanabe, Y.; Seikai, T.; Tominaga, O. Estimation of growth and food consumption in juvenile Japanese flounder Paralichthys olivaceus using carbon stable isotope ratio δ13C under laboratory conditions. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2005, 326, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIvor, A.L. Freshwater Mussels as Biofilters. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Cambridge, Cambridge, UK, 2004. Available online: https://ethos.bl.uk/OrderDetails.do?uin=uk.bl.ethos.616028 (accessed on 14 April 2021).
- Vaughn, C.C.; Hakenkamp, C.C. The functional role of burrowing bivalves in freshwater ecosystems. Freshwater Biol. 2001, 46, 1431–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nelson, K.A.; Leonard, L.A.; Posey, M.H.; Alphin, T.D.; Mallin, M.A. Using transplanted oyster beds to improve water quality in small tidal creeks: A pilot study. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2004, 298, 347–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.N.; Song, H.L.; Li, W.; Lu, X.W.; Nishimura, O. An integrated ecological floating-bed employing plant, freshwater clam and biofilm carrier for purification of eutrophic water. Ecol. Eng. 2010, 36, 382–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belanger, S.E. The effect of dissolved oxygen, sediment, and sewage treatment plant discharges upon growth, survival and density of Asiatic clams. Hydrobiologia 1991, 281, 113–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loayza-Muro, R.; Elías-Letts, R. Responses of the mussel Anodontites trapesialis (Unionidae) to environmental stressors: Effect of pH, temperature and metals on filtration rate. Environ. Pollut. 2007, 149, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoyama, A.; Park, H.D. Mechanism and prediction for contamination of freshwater bivalves (Unionidae) with the cyanobacterial toxin microcystin in hypereutrophic lake Suwa, Japan. Environ. Toxicol. 2002, 17, 424–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newton, T.J.; Allran, J.W.; O’Donnell, J.A.; Bartsch, M.R.; Richardson, W.B. Effects of ammonia on juvenile unionid mussels (Lampsilis cardium) in laboratory sediment toxicity tests. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2003, 22, 2554–2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newton, T.J.; Bartsch, M.R. Lethal and sublethal effects of ammonia to juvenile Lampsilis mussels (Unionidae) in sediment and water-only exposures. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2007, 26, 2057–2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
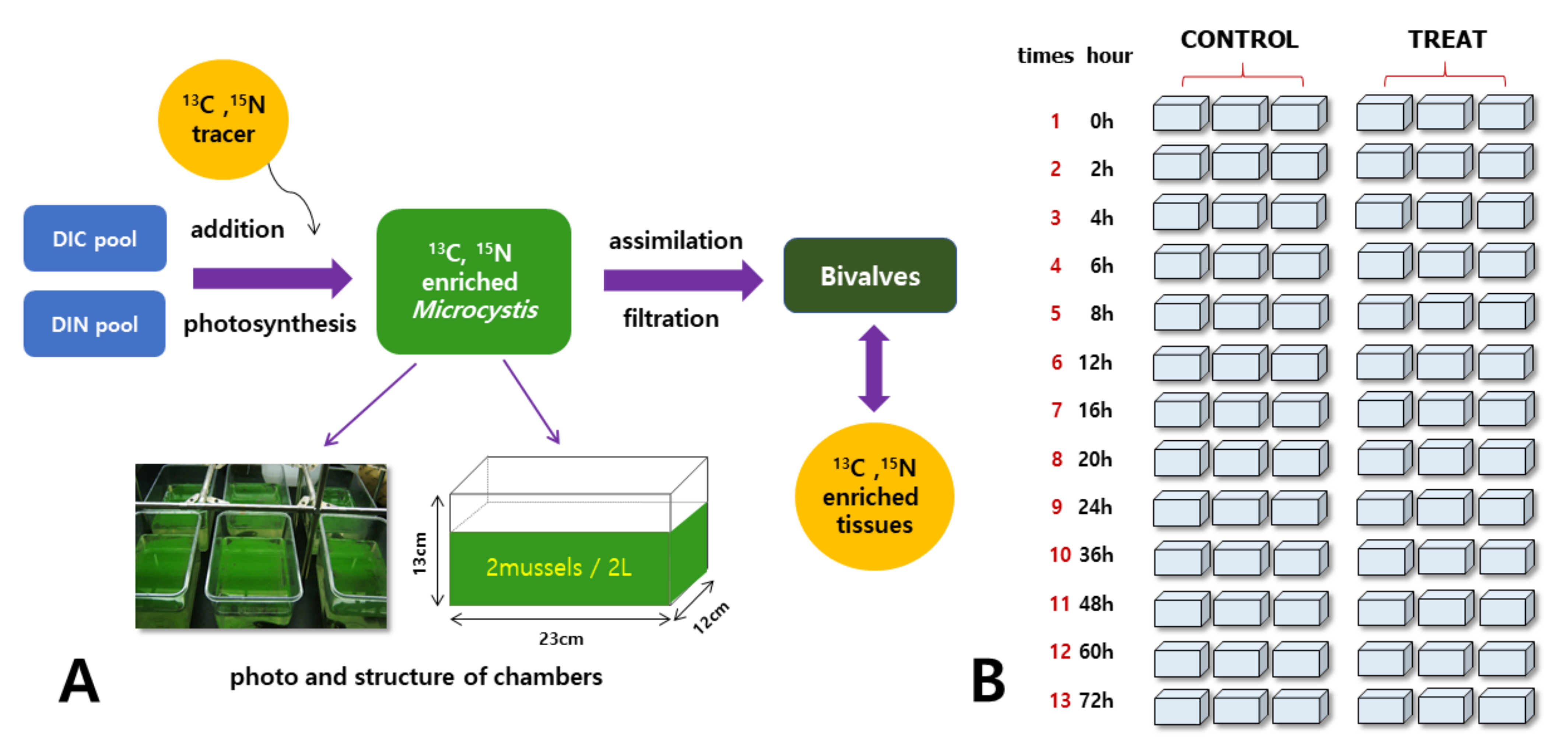

| Parameter | Conditions |
|---|---|
| Total volume of chamber (L) | 3.6 |
| Experimental volume (L) | 2 (M-water) |
| Animal density per chamber (indiv. L−1) | 1.0 |
| Experimental replications | 3 |
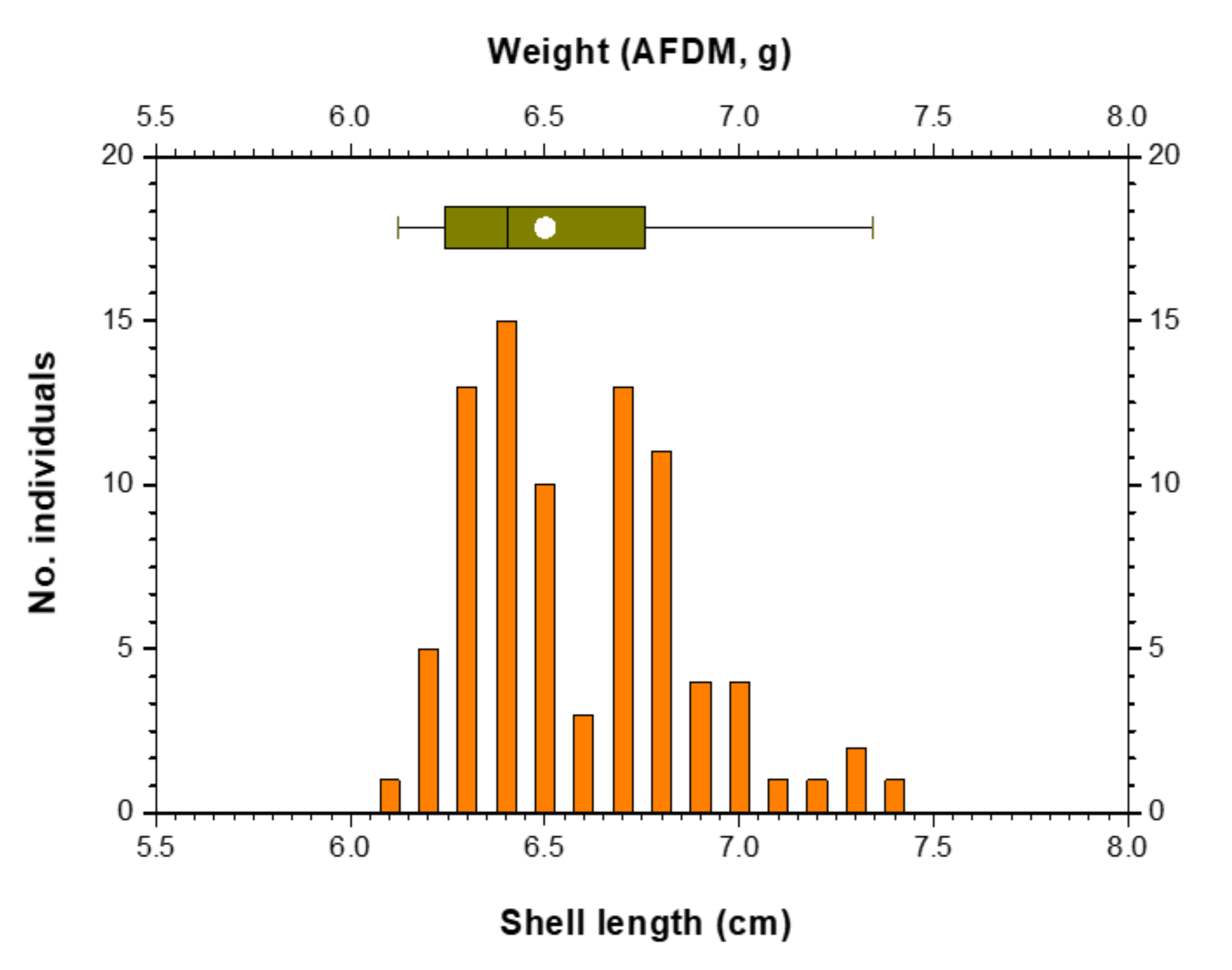
| Shell length of mussels (cm) | 6.59 ± 0.28 (6.10–7.40) |
| Ash-free dry matter of mussels (g) * | 0.34 ± 0.07 (0.23–0.58) |
| Water temperature of tank (°C) | 22 ± 2 |
| Light intensity (μmol·m−2 s−1) | 40–43 |
| Light:dark cycle (h) | 14:10 |
| Total experimental period (h) | 72 |
| Sampling time points (h) | 0, 2, 4, 6, 8, 12, 16, 20, 24, 36, 48, 60 and 72 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hwang, S.-J.; Lee, Y.-J.; Kim, M.-S.; Kim, B.-H. Filter Feeding and Carbon and Nitrogen Assimilation of a Freshwater Bivalve (Unio douglasiae) on a Toxic Cyanobacterium (Microcystis aeruginosa). Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 9294. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11199294
Hwang S-J, Lee Y-J, Kim M-S, Kim B-H. Filter Feeding and Carbon and Nitrogen Assimilation of a Freshwater Bivalve (Unio douglasiae) on a Toxic Cyanobacterium (Microcystis aeruginosa). Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(19):9294. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11199294
Chicago/Turabian StyleHwang, Soon-Jin, Yun-Ju Lee, Min-Seob Kim, and Baik-Ho Kim. 2021. "Filter Feeding and Carbon and Nitrogen Assimilation of a Freshwater Bivalve (Unio douglasiae) on a Toxic Cyanobacterium (Microcystis aeruginosa)" Applied Sciences 11, no. 19: 9294. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11199294
APA StyleHwang, S.-J., Lee, Y.-J., Kim, M.-S., & Kim, B.-H. (2021). Filter Feeding and Carbon and Nitrogen Assimilation of a Freshwater Bivalve (Unio douglasiae) on a Toxic Cyanobacterium (Microcystis aeruginosa). Applied Sciences, 11(19), 9294. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11199294









