Application of Fe-Impregnated Biochar from Cattle Manure for Removing Pentavalent Antimony from Aqueous Solution
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation and Characterization of Fe-CMB
2.2. Batch Adsorption Experiments
2.3. Adsorption Modeling
3. Results and Discussion
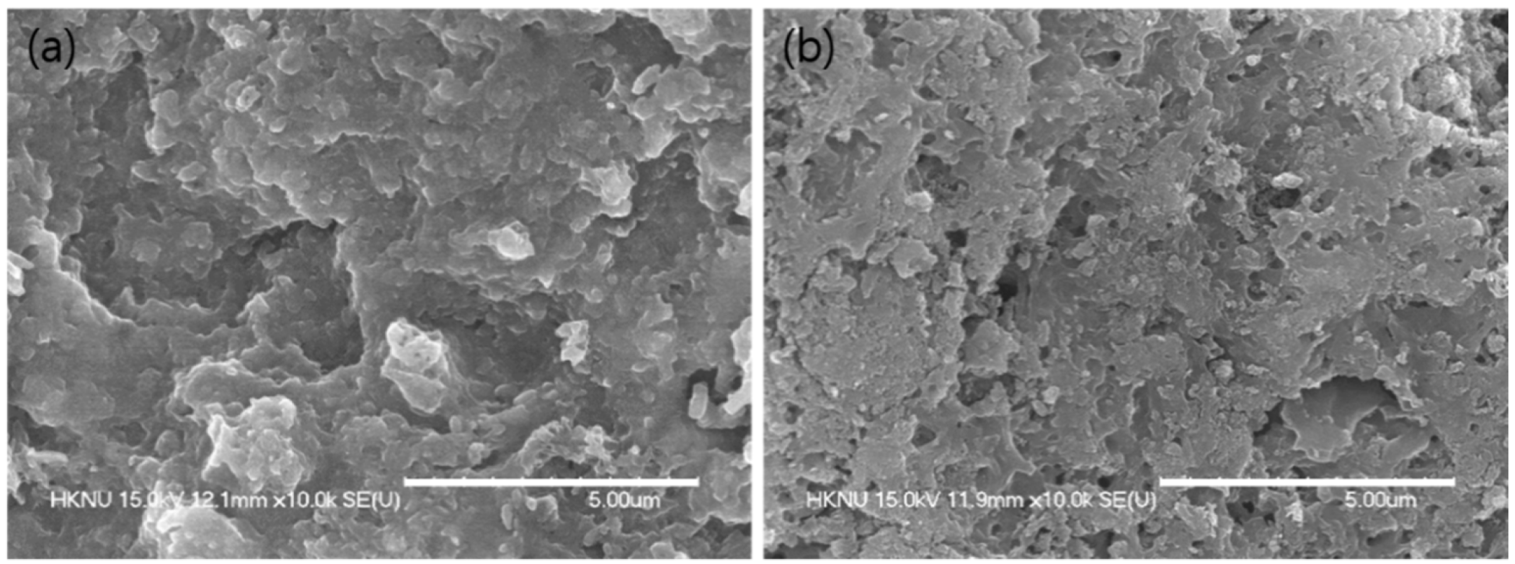
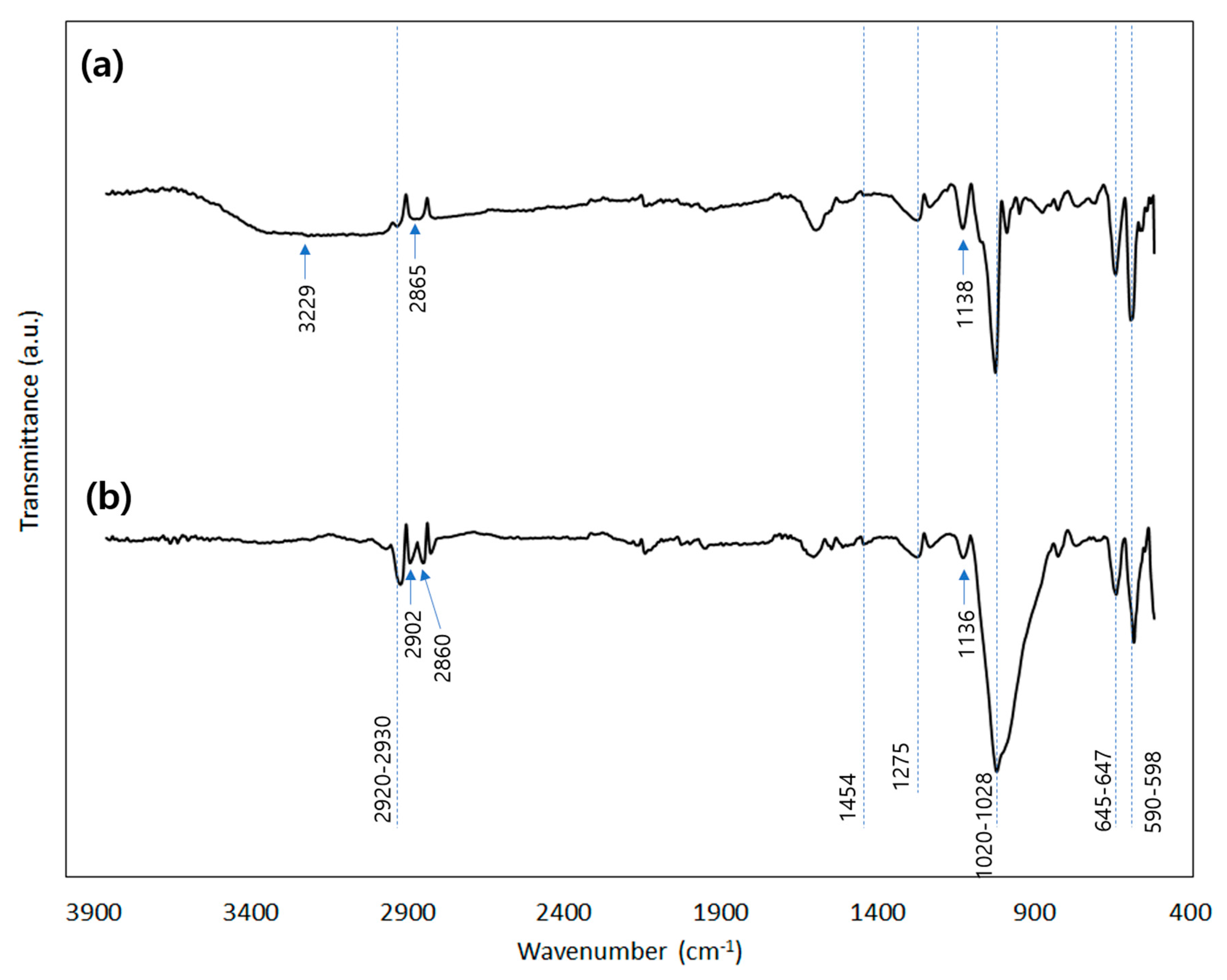
3.1. Physical and Chemical Characteristics of Fe-CMB
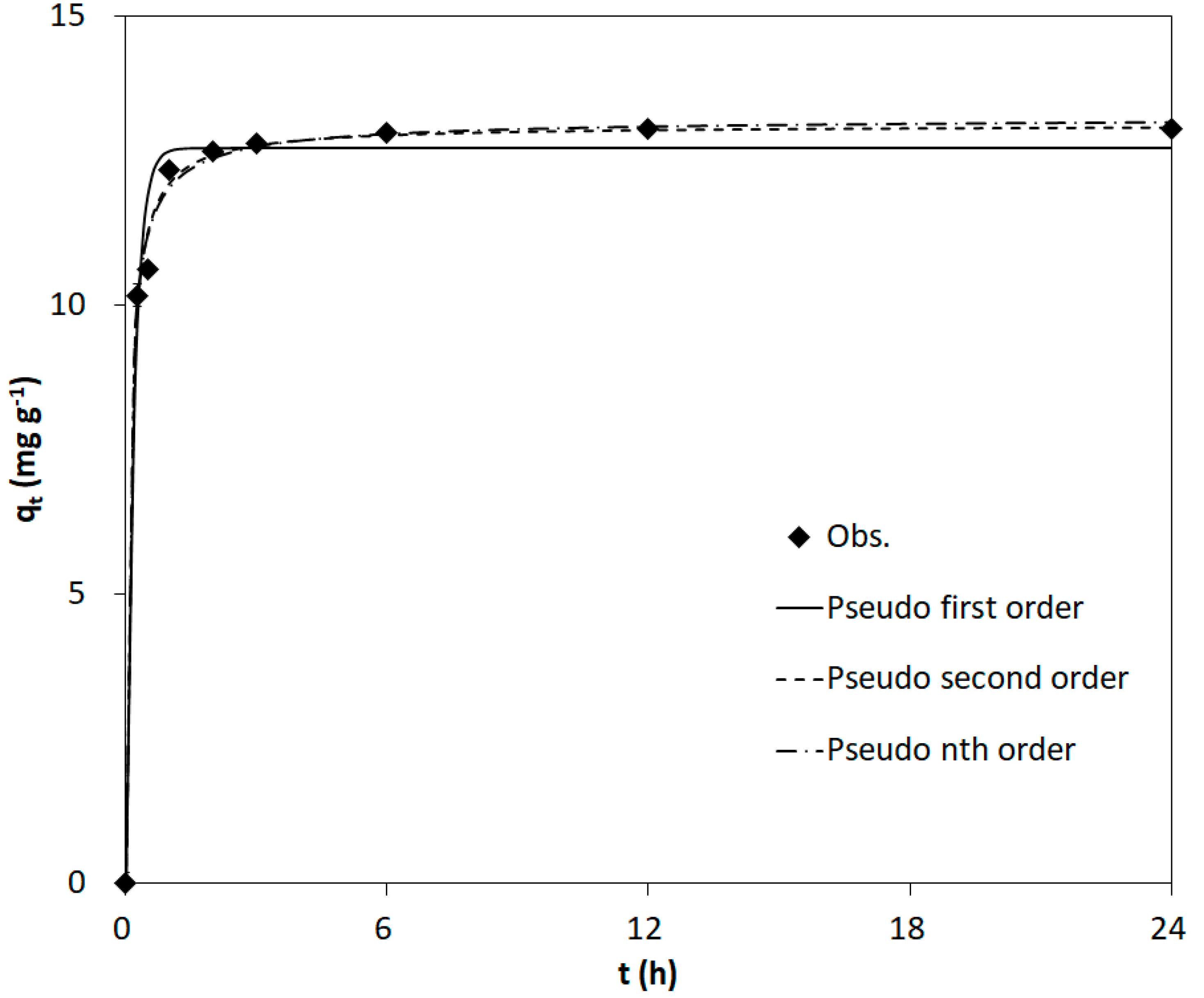
3.2. Kinetic Adsorption Experiments
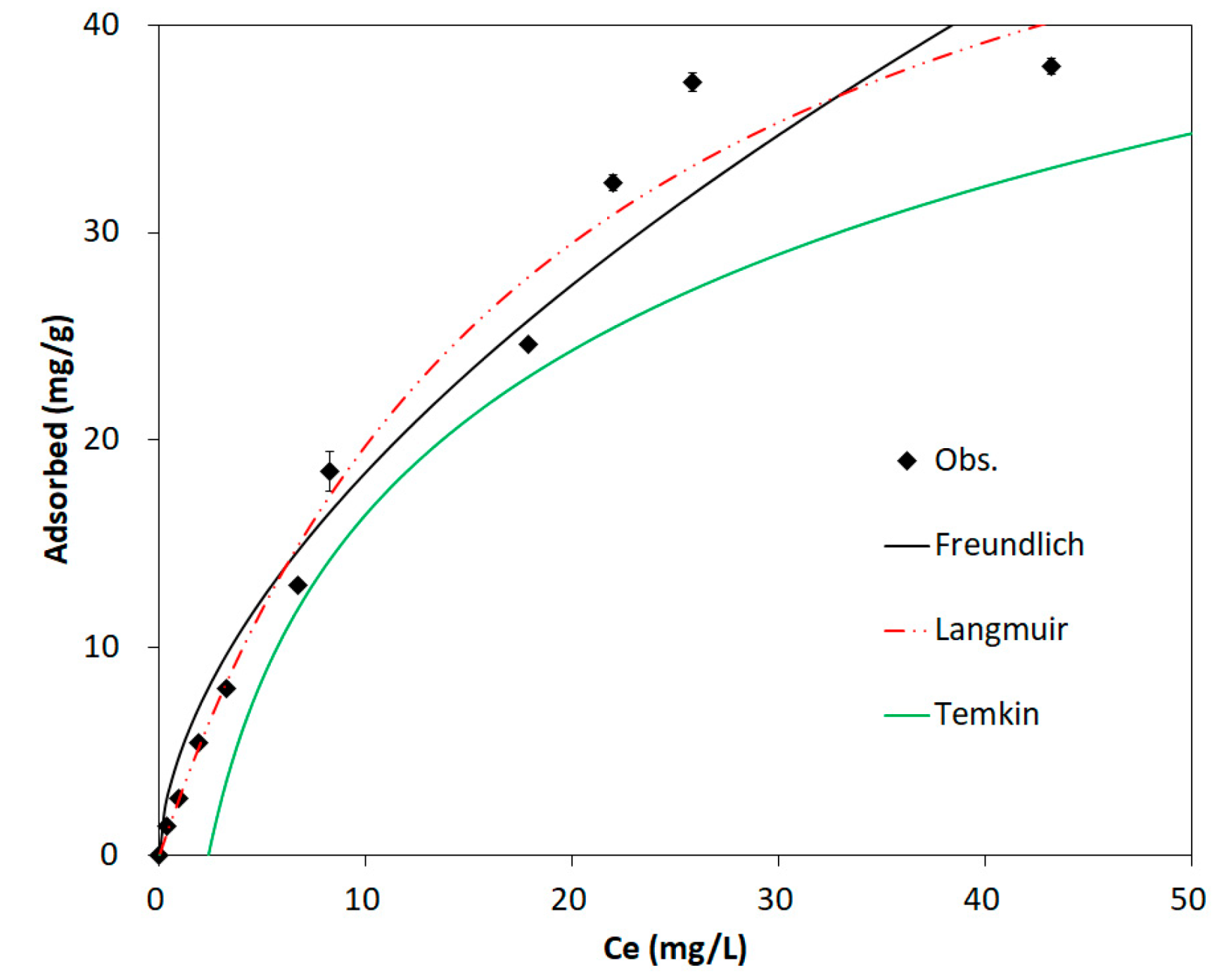
3.3. Equilibrium Adsorption Experiments
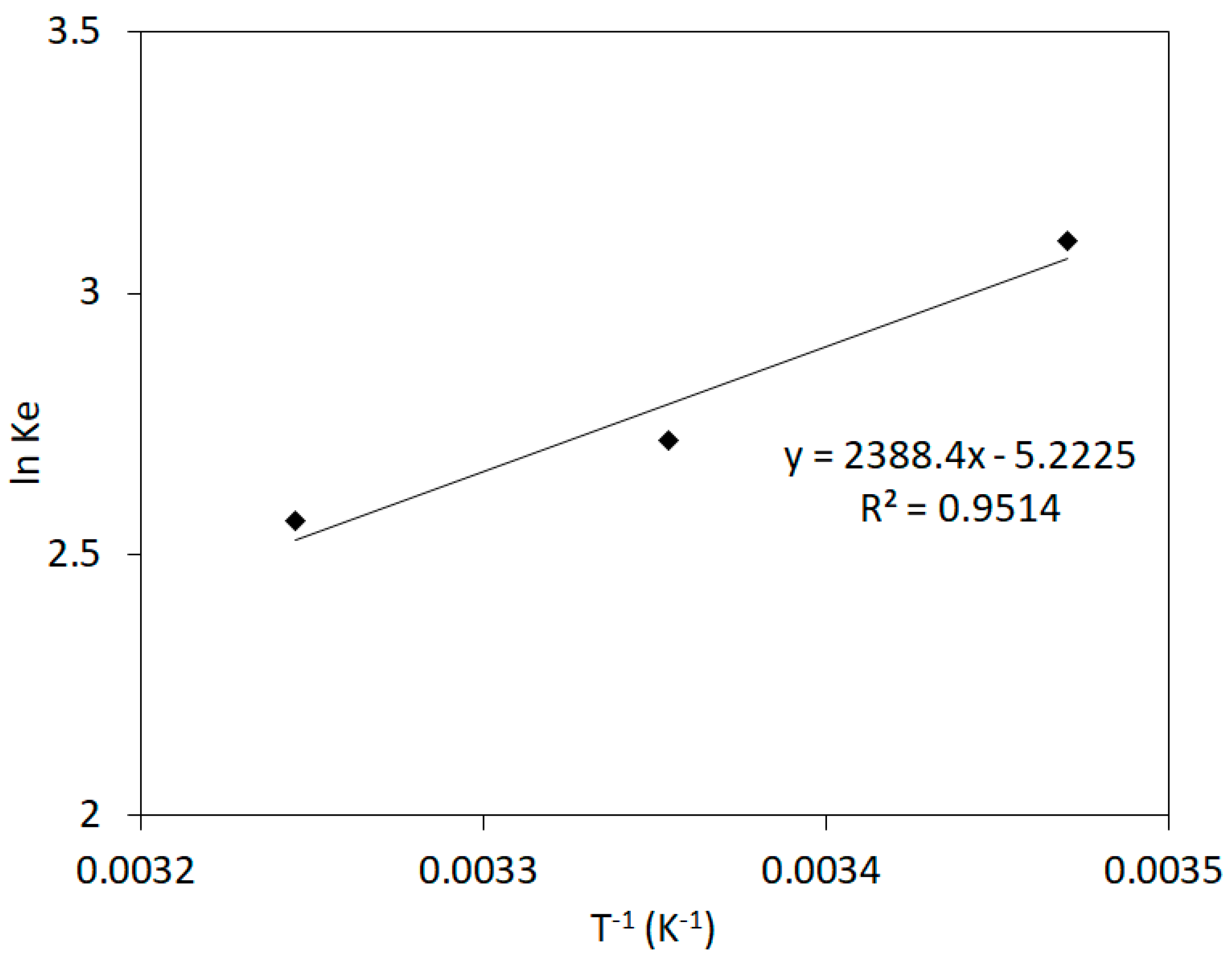
3.4. Thermodynamic Adsorption Experiments
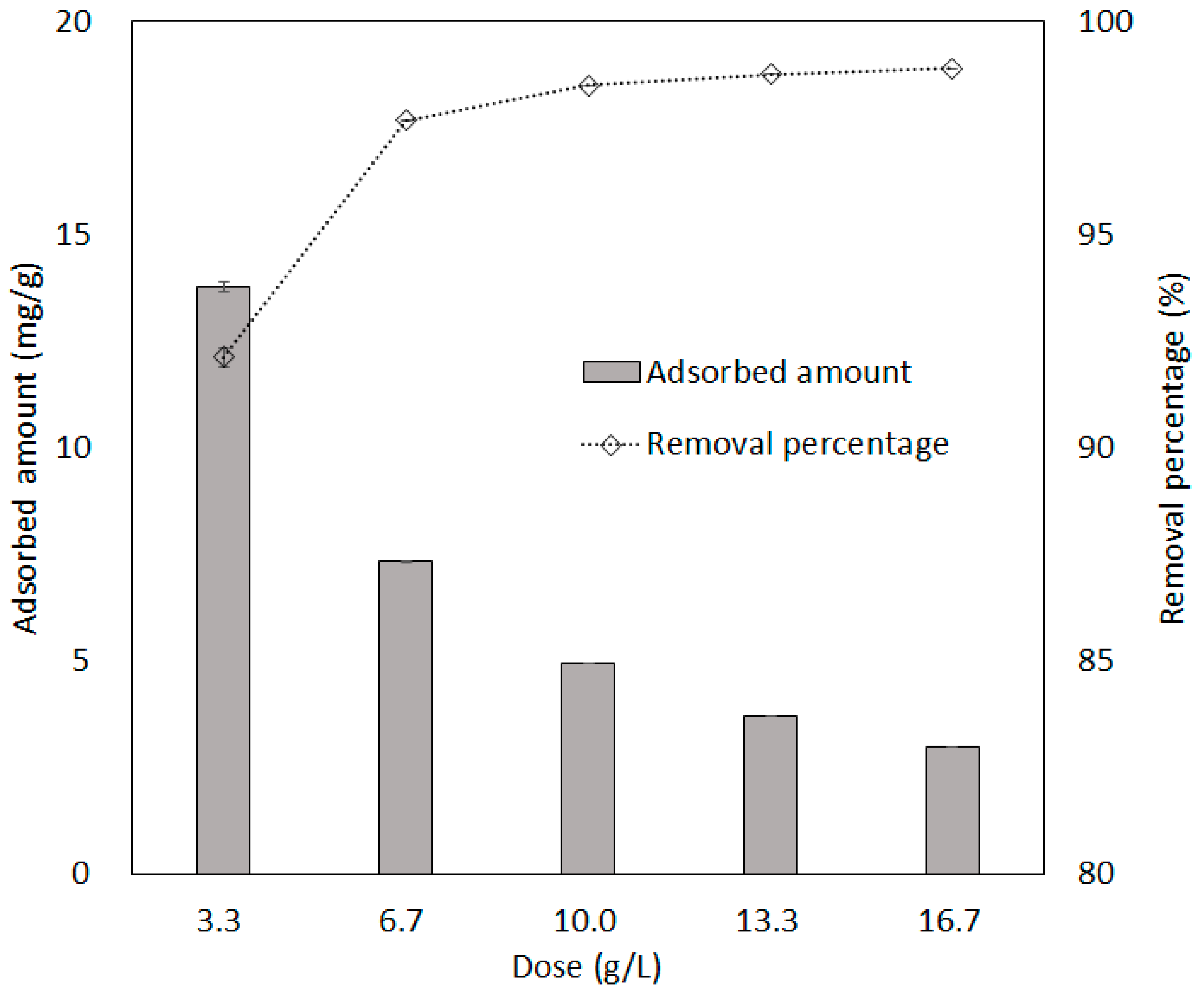
3.5. Effect of Adsorbent Dosage
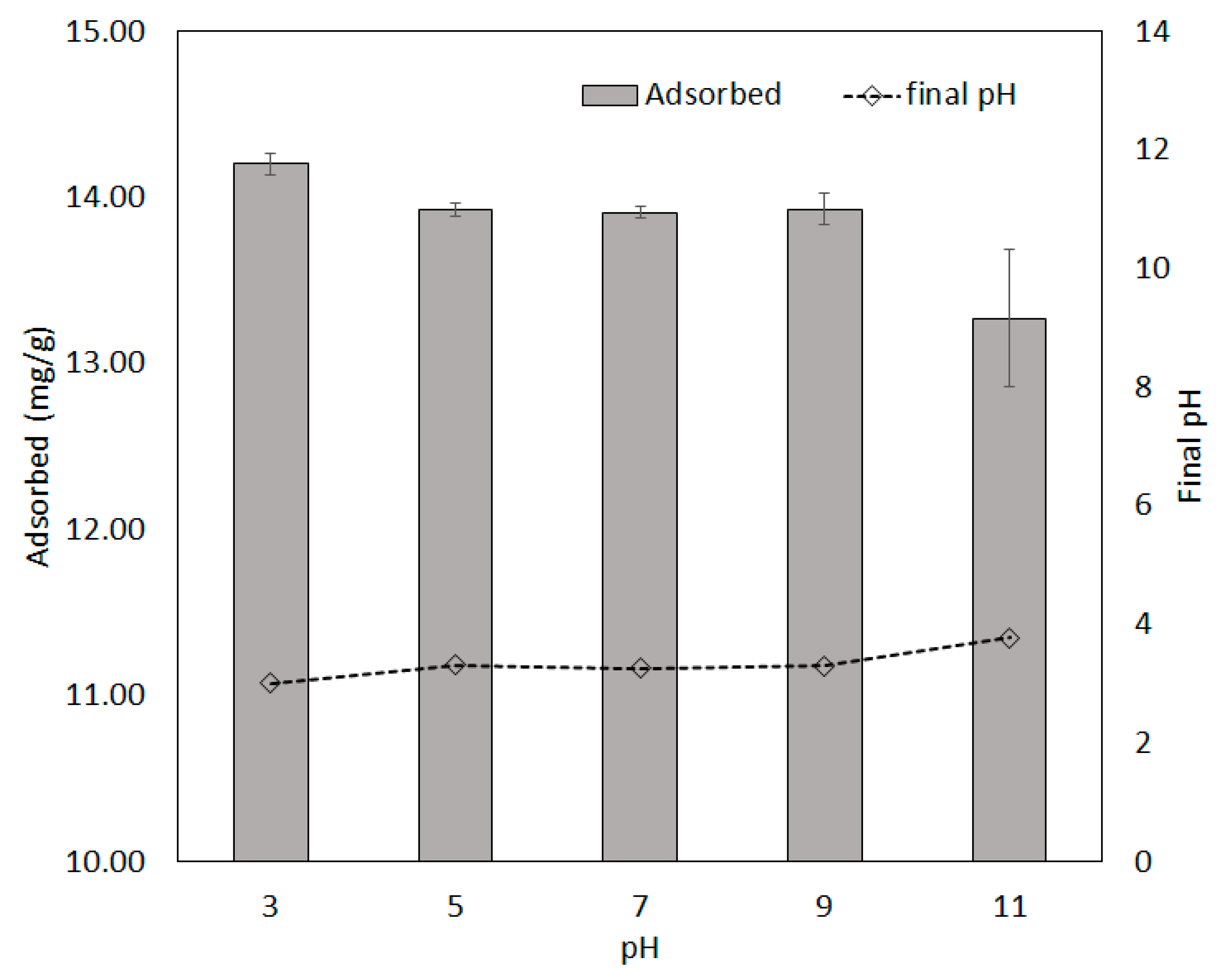
3.6. Effect of Solution pH
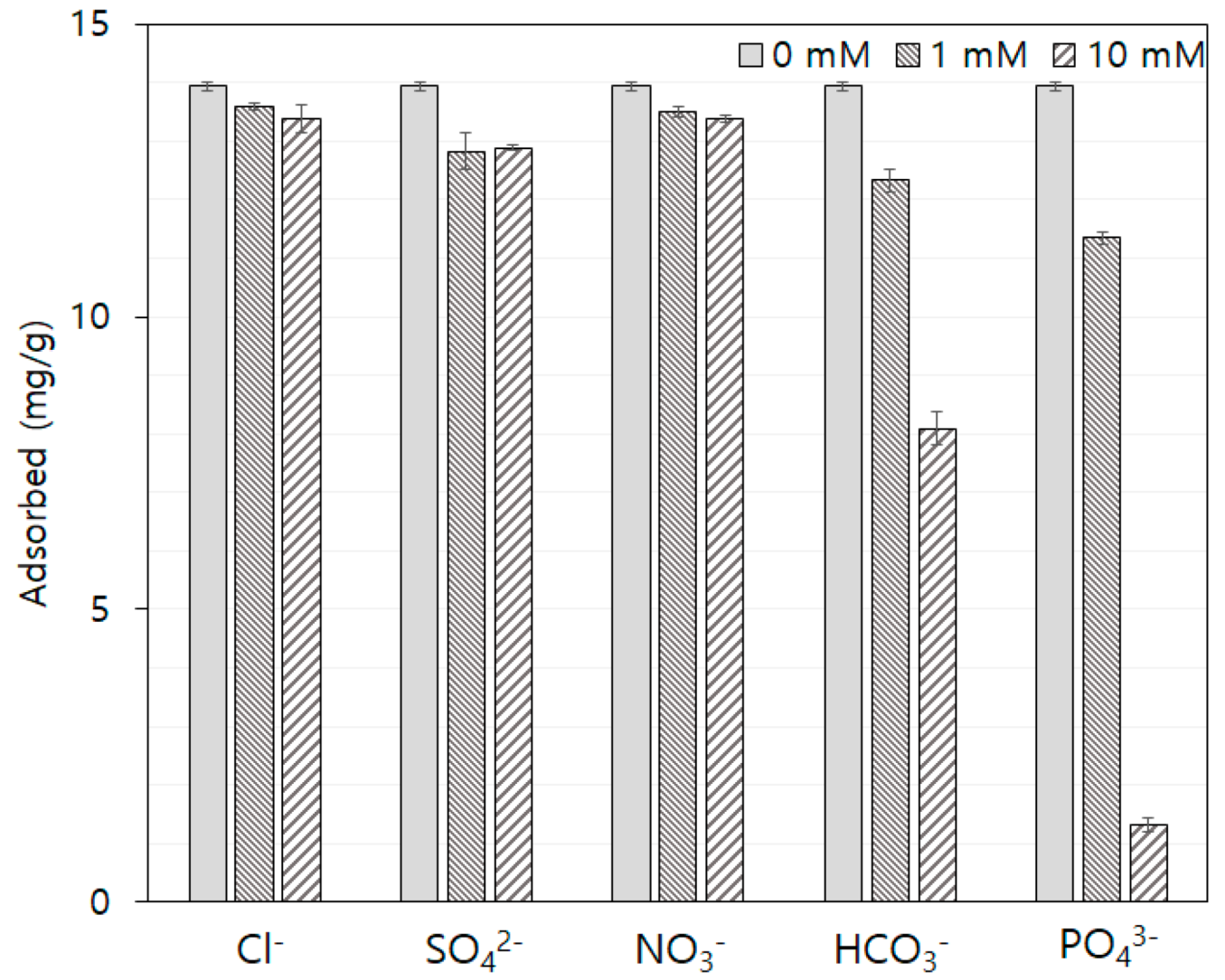
3.7. Effect of the Presence of Anions
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vithanage, M.; Rajapaksha, A.U.; Ahmad, M.; Uchimiya, M.; Dou, X.; Alessi, D.S.; Ok, Y.S. Mechanisms of antimony adsorption onto soybean stover-derived biochar in aqueous solutions. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 151, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Lin, J.; Yuan, Q.; Wang, X.; Zhao, Z.; Hursthouse, A.S.; Wang, Z.; Li, Q. A biochar supported magnetic metal organic framework for the removal of trivalent antimony. Chemosphere 2021, 282, 131068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality. 2011, Volume 38, pp. 104–108. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789241549950 (accessed on 4 October 2021).
- EPA, U.S. Edition of the Drinking Water Standards and Health Advisories. 2018. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/default/files/2018-03/documents/dwtable2018.pdf (accessed on 4 October 2021).
- Asher, B.; Eddo, H. Drinking Water Quality Standards and Regulations. 2012. Available online: https://publications.jrc.ec.europa.eu/repository/handle/JRC61360 (accessed on 4 October 2021).
- Filella, M.; Belzile, N.; Chen, Y.-W. Antimony in the environment: A review focused on natural waters: I. Occurrence. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2002, 57, 125–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zheng, B.; He, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, X.; Ruan, S.; Yang, Y.; Dai, C.; Tang, L. Antimony contamination, consequences and removal techniques: A review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 156, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, D.; Li, B.; Luo, L.; Zheng, Y.; Huang, L.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Y.; Huang, H. Simultaneous adsorption and oxidation of antimonite onto nano zero-valent iron sludge-based biochar: Indispensable role of reactive oxygen species and redox-active moieties. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 391, 122057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z.; Feng, J.; Li, S.; Yan, W. Synthesis of Ce-doped magnetic biochar for effective Sb(V) removal: Performance and mechanism. Powder Technol. 2019, 345, 501–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Zhou, J.; Liu, J.; Liu, P.; Yu, L.; Wen, B.; Feng, Y. The antimony sorption and transport mechanisms in removal experiment by Mn-coated biochar. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 724, 138158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Zhang, N.; Xing, C.; Cui, Q.; Sun, Q. The adsorption, regeneration and engineering applications of biochar for removal organic pollutants: A review. Chemosphere 2019, 223, 12–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inyang, M.I.; Gao, B.; Yao, Y.; Xue, Y.; Zimmerman, A.; Mosa, A.; Pullammanappallil, P.; Ok, Y.S.; Cao, X. A review of biochar as a low-cost adsorbent for aqueous heavy metal removal. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 46, 406–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kılıç, M.; Kırbıyık, Ç.; Çepelioğullar, Ö.; Pütün, A.E. Adsorption of heavy metal ions from aqueous solutions by bio-char, a by-product of pyrolysis. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 283, 856–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, B.; Tao, X.; Wang, H.; Li, W.; Ding, X.; Chu, H. Biochar as a low-cost adsorbent for aqueous heavy metal removal: A review. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2021, 155, 105081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Sun, H.; Ro, K.; Sun, K.; Libra, J.; Xing, B. Removal of antimony (III) and cadmium (II) from aqueous solution using animal manure-derived hydrochars and pyrochars. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 234, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Deng, J.; Li, X.; Wei, X.; Liu, Y.; Liang, J.; Shao, Y.; Huang, W.; Cheng, X. Different adsorption behaviors and mechanisms of a novel amino-functionalized hydrothermal biochar for hexavalent chromium and pentavalent antimony. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 310, 123438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyonga, F.N.; Hong, S.-H.; Cho, E.-J.; Kang, J.-K.; Lee, C.-G.; Park, S.-J. As(III) adsorption onto Fe-impregnated food waste biochar: Experimental investigation, modeling, and optimization using response surface methodology. Environ. Geochem. Health 2021, 43, 3303–3321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leuz, A.-K.; Mönch, H.; Johnson, C.A. Sorption of Sb(III) and Sb(V) to Goethite: Influence on Sb(III) Oxidation and Mobilization. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 7277–7282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, N.; Hong, S.-H.; Lee, C.-G.; Park, S.-J.; Lee, J. Conversion of cattle manure into functional material to remove selenate from wastewater. Chemosphere 2021, 278, 130398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, X.; Lee, S.; Chandrasekaran, R.; Yang, Y.; Caballes, M.; Alamu, O.; Chen, G. Electricity Evaluation and Emission Characteristics of Poultry Litter Co-Combustion Process. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qian, X.; Yang, Y.; Lee, S.W. Design and Evaluation of the Lab-Scale Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger (STHE) for Poultry Litter to Energy Production. Processes 2020, 8, 500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, Y.; Cao, H.; Yuan, Q.; Wang, D. Two-step gasification of cattle manure for hydrogen-rich gas production: Effect of biochar preparation temperature and gasification temperature. Waste Manag. 2017, 68, 618–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Sarmah, A.K.; Kwon, E.E. Chapter 1—Production and Formation of Biochar. In Biochar from Biomass and Waste; Ok, Y.S., Tsang, D.C.W., Bolan, N., Novak, J.M., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, R.-L.; Wu, P.-H.; Wu, F.-C.; Juang, R.-S. A convenient method to determine kinetic parameters of adsorption processes by nonlinear regression of pseudo-nth-order equation. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 237, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberti, G.; Amendola, V.; Pesavento, M.; Biesuz, R. Beyond the synthesis of novel solid phases: Review on modelling of sorption phenomena. Co-Ord. Chem. Rev. 2012, 256, 28–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coates, J. Encyclopedia of Analytical Chemistry; Meyers, R.A., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2000; pp. 10815–10837. [Google Scholar]
- Vithanage, M.; Rajapaksha, A.U.; Dou, X.; Bolan, N.; Yang, J.E.; Ok, Y.S. Surface complexation modeling and spectroscopic evidence of antimony adsorption on iron-oxide-rich red earth soils. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 406, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McComb, K.A.; Craw, D.; McQuillan, A.J. ATR-IR Spectroscopic Study of Antimonate Adsorption to Iron Oxide. Langmuir 2007, 23, 12125–12130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.-I.; Hong, S.-H.; Lee, C.-G.; Park, S.-J. Experimental and model study for fluoride removal by thermally activated sepiolite. Chemosphere 2020, 241, 125094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, Y. Review of second-order models for adsorption systems. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 136, 681–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Edzwald, J.; American Water Works Association. Water Quality & Treatment: A Handbook on Drinking Water; McGraw-Hill Education: Denver, CO, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, X.; Wu, Z.; He, M.; Meng, X.; Jin, X.; Qiu, N.; Zhang, J. Adsorption of antimony onto iron oxyhydroxides: Adsorption behavior and surface structure. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 276, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, Z.; Joshi, T.P.; Liu, R.; Li, Y.; Liu, H.; Qu, J. Adsorption combined with superconducting high gradient magnetic separation technique used for removal of arsenic and antimony. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 343, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Hu, X.; Sun, Y.; Su, S.; Xia, A.; Ge, H. Goethite (α-FeOOH) nanopowders synthesized via a surfactant-assisted hydrothermal method: Morphology, magnetic properties and conversion to rice-like α-Fe2O3 after annealing. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 27091–27096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-I.; Kang, J.-K.; Hong, S.-H.; Lee, C.-G.; Jeong, S.; Park, S.-J. Thermally treated Mytilus coruscus shells for fluoride removal and their adsorption mechanism. Chemosphere 2021, 263, 128328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbamba, C.K. Dynamic Modelling of Minerals Precipitation in Wastewater Treatment. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Queensland Library, Brisbane, QLD, Australia, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- He, Z.; Liu, R.; Liu, H.; Qu, J. Adsorption of Sb(III) and Sb(V) on Freshly Prepared Ferric Hydroxide (FeOxHy). Environ. Eng. Sci. 2015, 32, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.-K.; Seo, E.-J.; Lee, C.-G.; Park, S.-J. Fe-loaded biochar obtained from food waste for enhanced phosphate adsorption and its adsorption mechanism study via spectroscopic and experimental approach. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Fe-CMB | C | O | Cl | Fe | Ca | P | Mg | K | S | Si |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before adsorption | 28.0 ± 1.4 | 15.8 ± 2.1 | 18.0 ± 4.4 | 14.6 ± 0.8 | 10.2 ± 1.5 | 6.2 ± 1.8 | 2.2 ± 0.2 | 2.1 ± 0.1 | 1.9 ± 1.5 | 1.3 ± 0.4 |
| After adsorption | 30.4 ± 1.3 | 19.7 ± 3.1 | 1.8 ± 0.4 | 31.9 ± 3.6 | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 8.4 ± 4.2 | 0.4 ± 0.0 | 0.3 ± 0.0 | 4.2 ± 3.9 | 0.3 ± 0.0 |
| Model Parameter | R2 | SSE | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pseudo-first-order | qe (mg/g) | k1 (1/min) | 0.896 | 2.494 | ||
| 12.7 | 5.512 | |||||
| Pseudo-second-order | qe (mg/g) | k2 (g/mg/min) | 0.977 | 0.562 | ||
| 13.1 | 0.919 | |||||
| Pseudo-nth-order | qe (mg/g) | kn ((mg/g)1−n/h) | n | 0.978 | 0.527 | |
| 13.3 | 0.592 | 2.245 | ||||
| Model Parameter | R2 | SSE | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Freundlich | KF (L/g) | 1/n (-) | 0.960 | 83.8 |
| 4.910 | 0.575 | |||
| Langmuir | Qm (mg/g) | KL (L/mg) | 0.982 | 39.1 |
| 58.3 | 0.051 | |||
| Temkin | BT (kJ/mol) | KT (L/g) | 0.877 | 260.3 |
| 0.217 | 0.423 | |||
| Temp. (°C) | ln Ke | 1/T (1/K) | ΔH0 (kJ/mol) | ΔS0 (J/K∙mol) | ΔG0 (kJ/mol) | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15 | 3.099984 | 0.003470 | −7.35 | |||
| 25 | 2.71791 | 0.003354 | −19.86 | −43.42 | −6.91 | 0.9514 |
| 35 | 2.56438 | 0.003245 | −6.48 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, S.-J.; Lee, Y.-J.; Kang, J.-K.; Lee, J.-C.; Lee, C.-G. Application of Fe-Impregnated Biochar from Cattle Manure for Removing Pentavalent Antimony from Aqueous Solution. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 9257. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11199257
Park S-J, Lee Y-J, Kang J-K, Lee J-C, Lee C-G. Application of Fe-Impregnated Biochar from Cattle Manure for Removing Pentavalent Antimony from Aqueous Solution. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(19):9257. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11199257
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Seong-Jik, Yeon-Jin Lee, Jin-Kyu Kang, Je-Chan Lee, and Chang-Gu Lee. 2021. "Application of Fe-Impregnated Biochar from Cattle Manure for Removing Pentavalent Antimony from Aqueous Solution" Applied Sciences 11, no. 19: 9257. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11199257
APA StylePark, S.-J., Lee, Y.-J., Kang, J.-K., Lee, J.-C., & Lee, C.-G. (2021). Application of Fe-Impregnated Biochar from Cattle Manure for Removing Pentavalent Antimony from Aqueous Solution. Applied Sciences, 11(19), 9257. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11199257








