Remote Monitoring of Ground Motion Hazards in High Mountain Terrain Using InSAR: A Case Study of the Lake Sarez Area, Tajikistan
Abstract
:1. Introduction
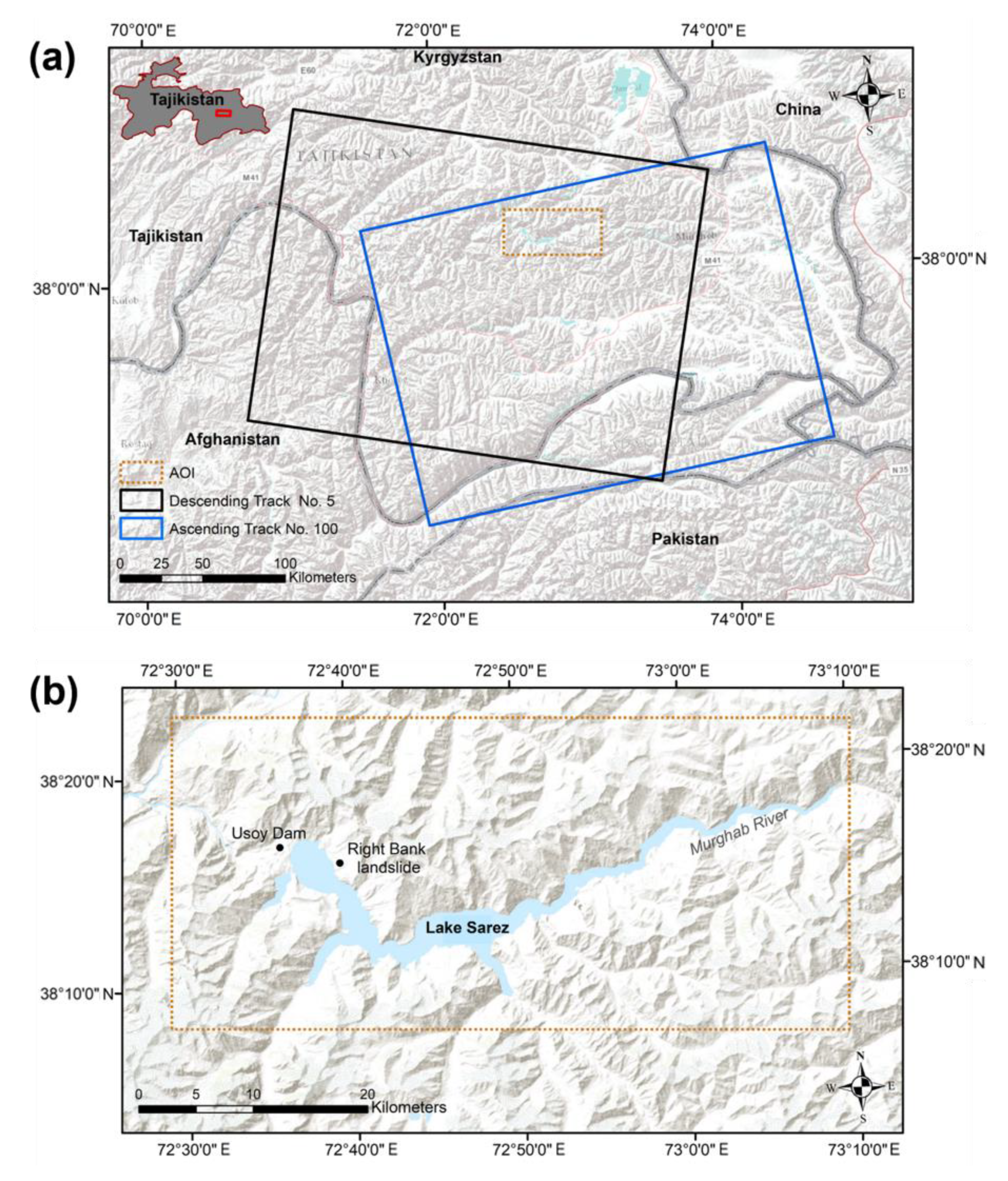
2. Study Area and Data
2.1. Study Area
2.2. InSAR for Remote Ground Motion Monitoring
2.3. Data
3. Methods
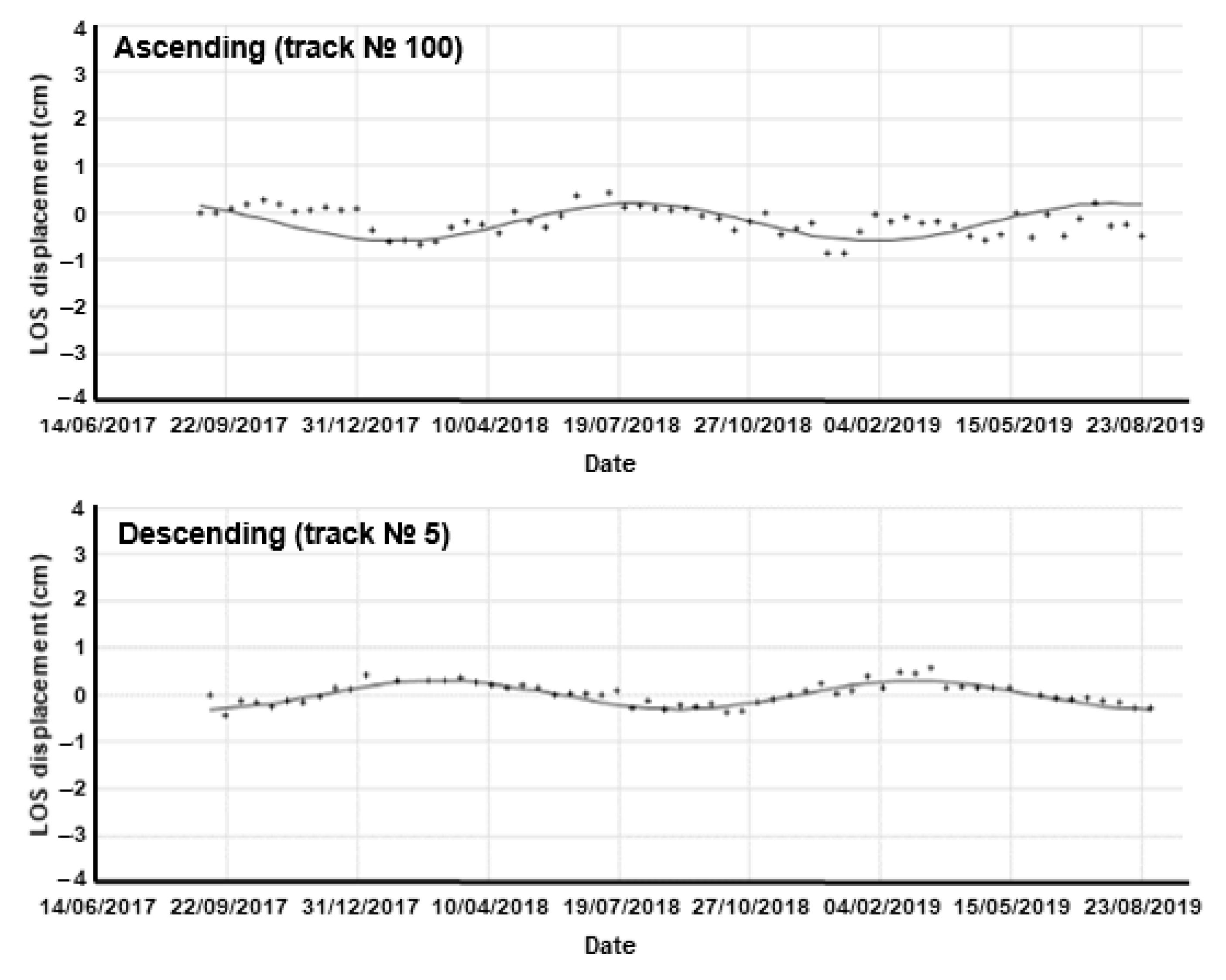
4. Results and Discussion
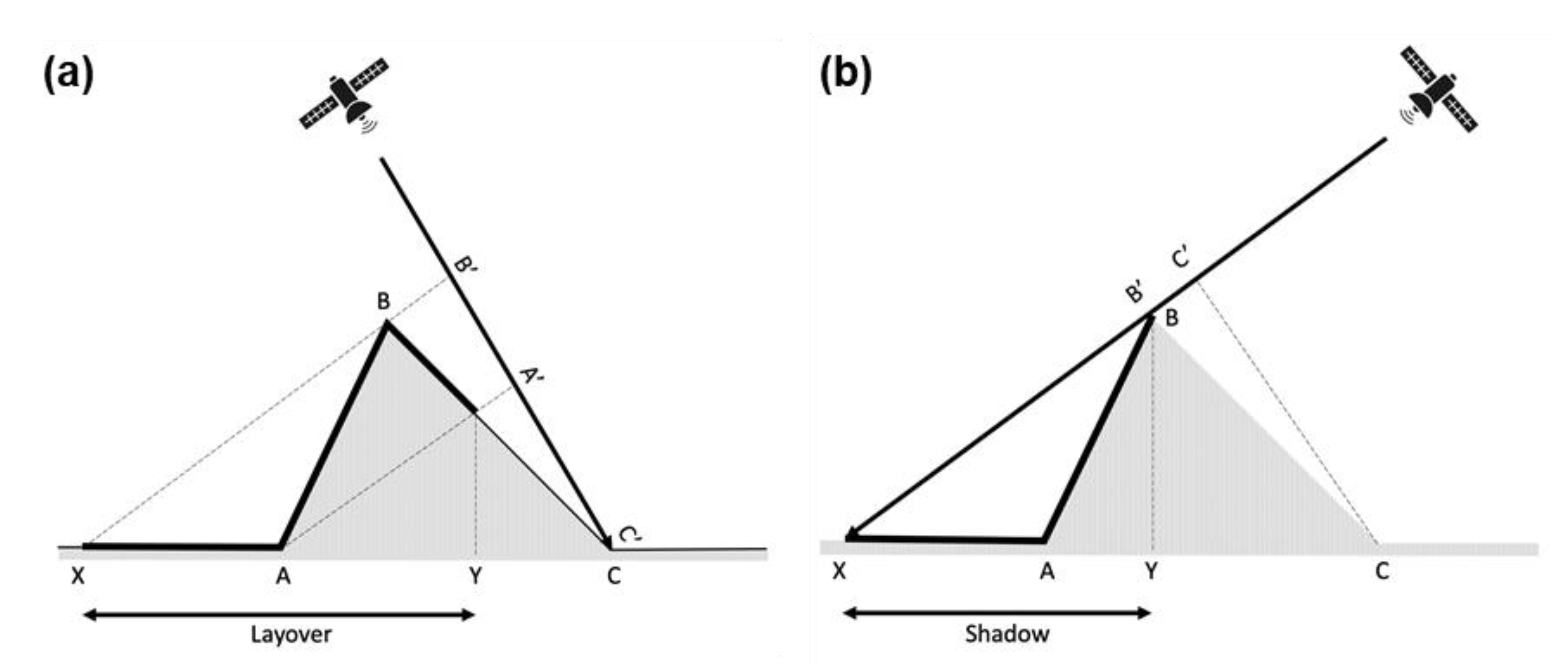
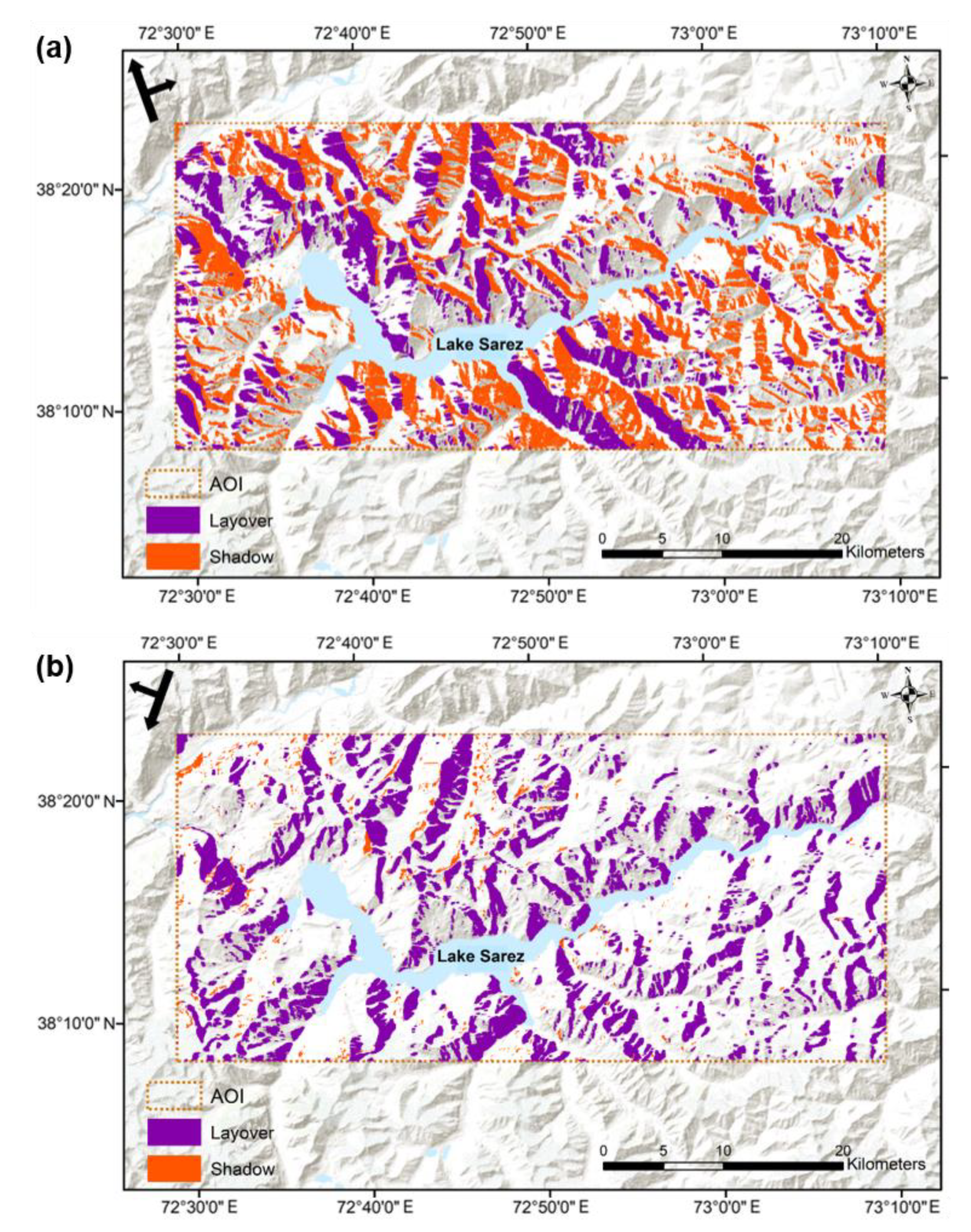
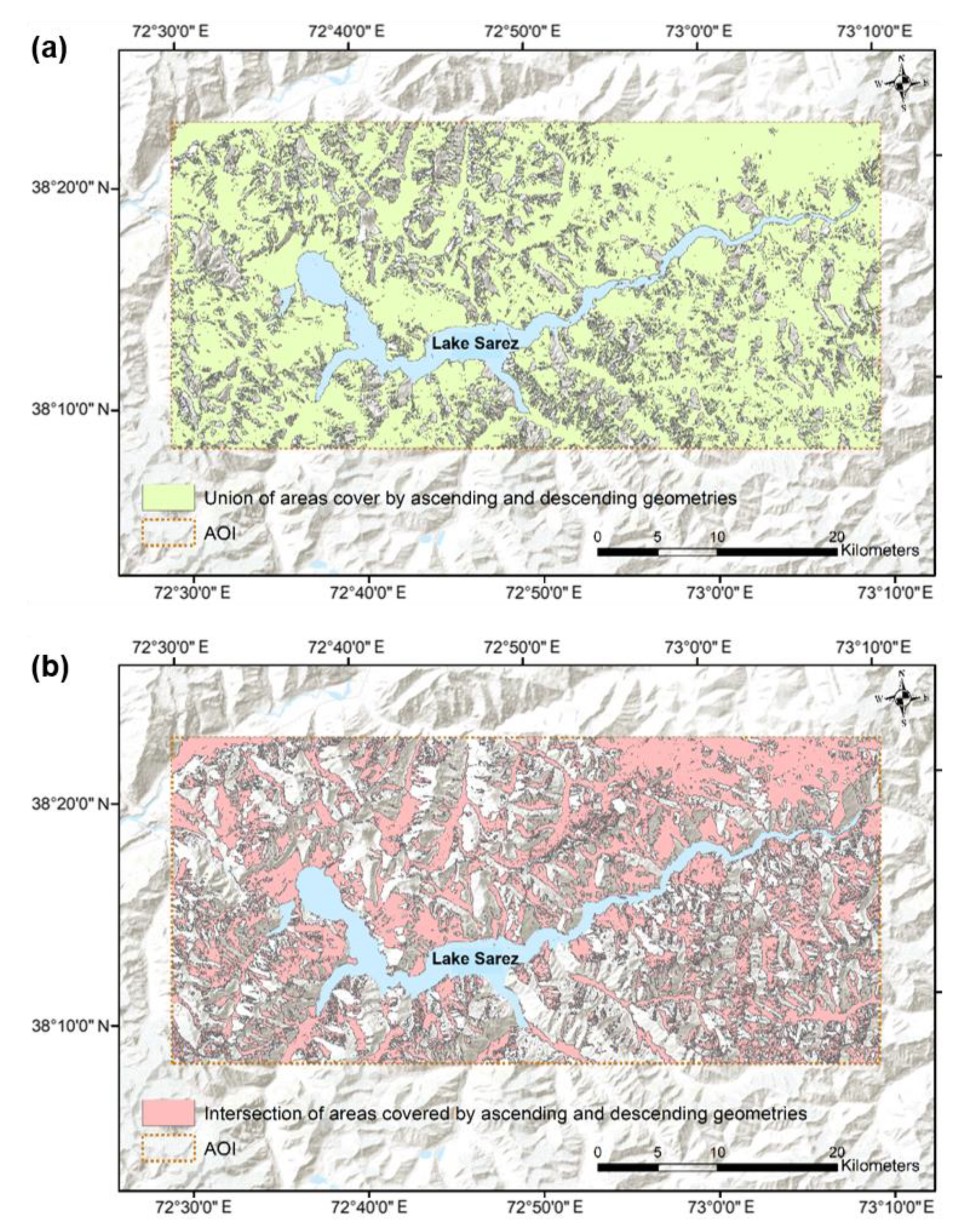
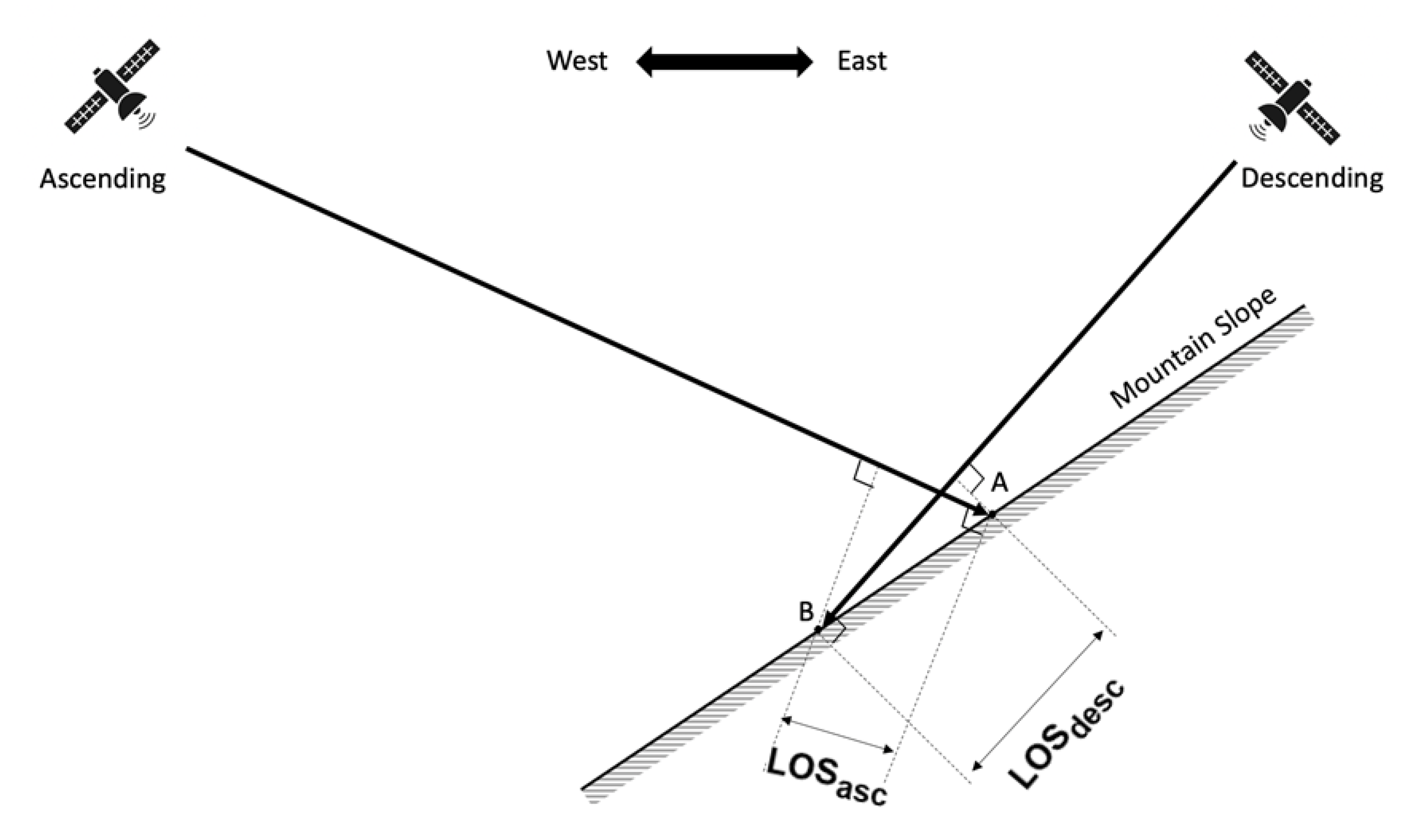
4.1. Effect of Layover and Shadow
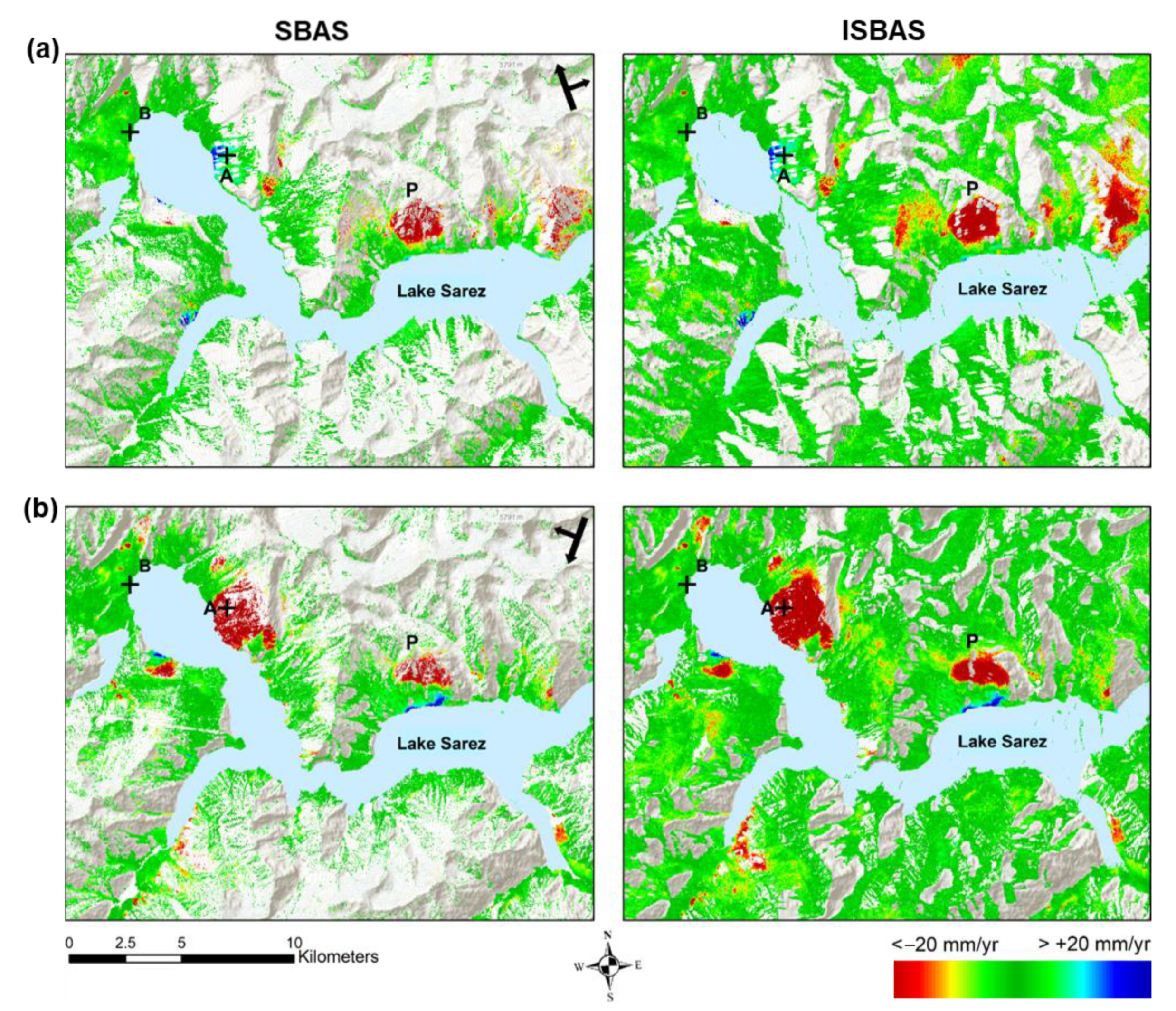
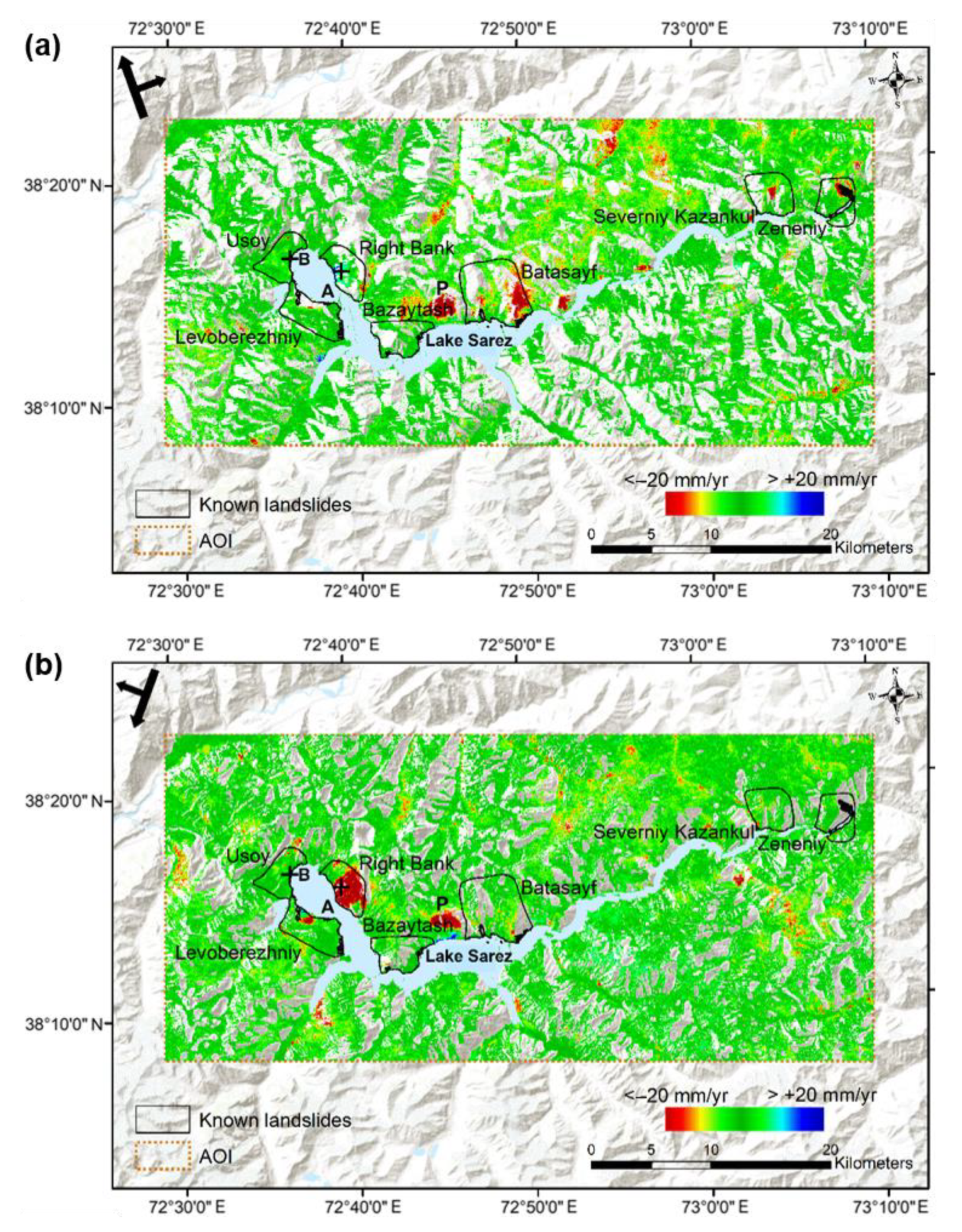
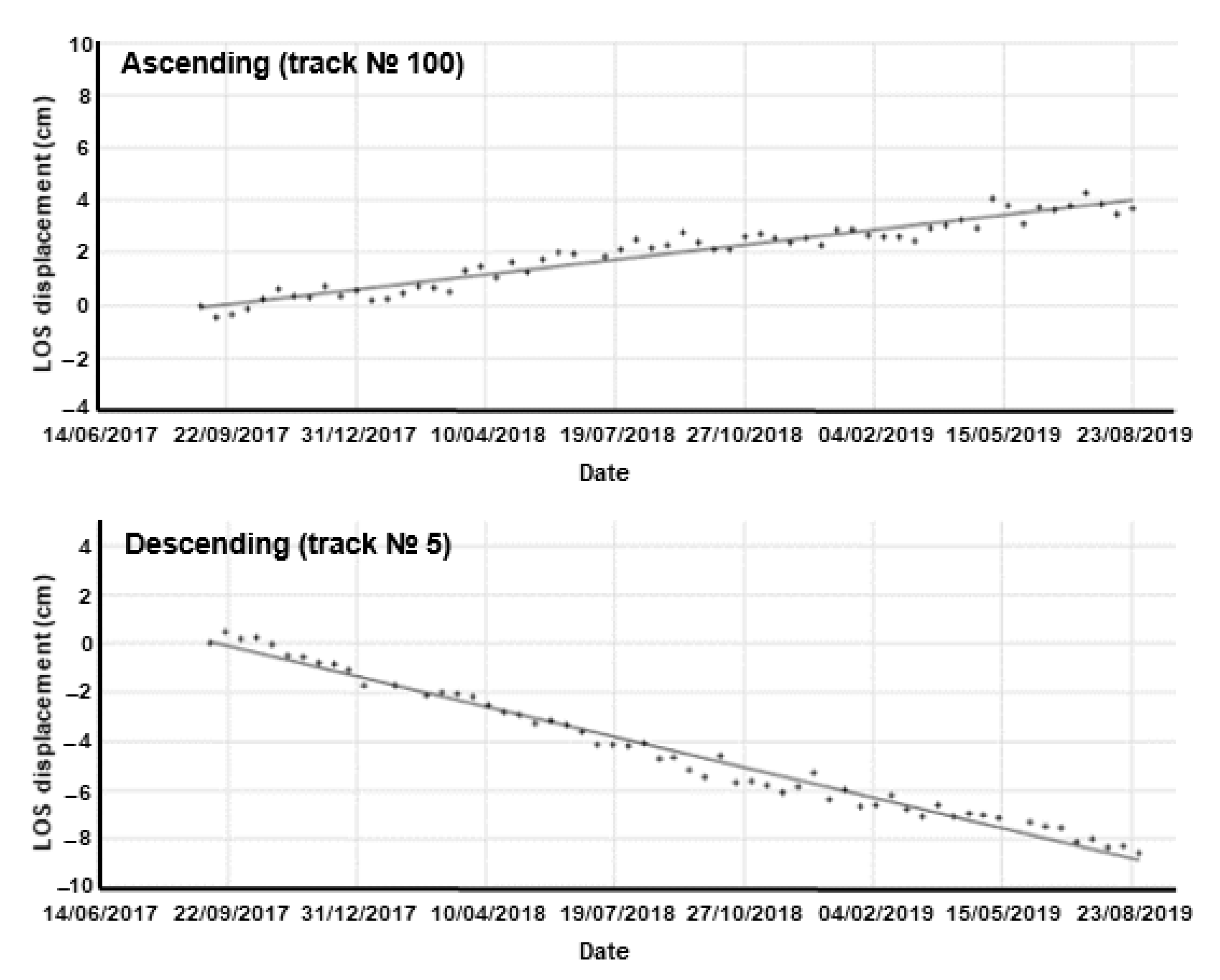
4.2. Ground Motion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Keiler, M.; Knight, J.; Harrison, H. Climate change and geomorphological hazards in the eastern European Alps. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. A 2010, 368, 2461–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kargel, J.S.; Leonard, G.; Crippen, R.; Delaney, K.; Evans, S.G.; Schneider, J. Satellite monitoring of Pakistan’s Rockslide-Dammed Lake Gojal. Eos 2010, 91, 394–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kreutzmann, H. After the flood: Mobility as an adaptation strategy in high mountain oases: The case of Pasu in Gojal, Hunza Valley, Karakoram. Die Erde 2012, 143, 49–73. [Google Scholar]
- Cook, N.; Butz, D. Mobility justice in the context of disaster. Mobilities 2016, 11, 400–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirschbaum, D.; Watson, C.S.; Rounce, D.R.; Shugar, D.H.; Kargel, J.S.; Haritashya, U.K.; Amatya, P.; Shean, D.; Anderson, E.R.; Jo, M. The state of remote sensing capabilities of cascading hazards over high mountain Asia. Front. Earth Sci. 2019, 7, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carlà, T.; Intrieri, E.; Raspini, F.; Bardi, F.; Farina, P.; Ferretti, A.; Colombo, D.; Novali, F.; Casagli, N. Perspectives on the prediction of catastrophic slope failures from satellite InSAR. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 14137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sowter, A. Orthorectification and interpretation of differential InSAR data over mountainous areas: A case study of the May 2008 Wenchuan earthquake. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2010, 31, 3435–3448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Hu, J.; Zhang, L.; Ding, X. Towards slow-moving landslide monitoring by integrating multi-sensor InSAR time series datasets: The Zhouqu case study, Chine. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, C.; Lu, Z.; Zhang, C.; de la Fuente, J. Large-area landslide detection and monitoring with ALOS/PALSAR imagery data over Northern California and Southern Oregon, USA. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 124, 348–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasowski, J.; Bovenga, F. Investigating landslides and unstable slopes with satellite Multi Temporal Interferometry: Current issues and future perspectives. Eng. Geol. 2014, 174, 103–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loibl, D.; Bookhagen, B.; Valade, S.; Schneider, C. OSARIS, the “Open Source SAR Investigation System” for automatized parallel InSAR processing of Sentinel-1 time series data with special emphasis on cryosphere applications. Front. Earth Sci. 2019, 7, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdullaev, U.; Abdullaev, S.; Blaha, P.; Akhmedov, A.; Khudobakhshova, G. The Usoy Dam, Lake Sarez and possibilities of geophysical methods. In Proceedings of the International Journal on Hydropower & Dams, HYDRO 2011, Prague, Czech Republic, 17–19 October 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Lukk, A.A.; Yunga, S.L.; Shevchenko, V.I.; Hamburger, M.W. Earthquake focal mechanisms, deformation state, and seismotectonics of the Pamir-Tien Shan region, Central Asia. J. Geophys. Res. 1995, 100, 20321–20343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hergarten, C. Investigations on Land Cover and Land Use of Gorno Badakhshan (GBAO) by Means of Land Cover Classifications Derived from LANDSAT 7 Data Making Use of Remote Sensing and GIS Techniques. Master’s Thesis, University of Bern, Bern, Switzerland, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Squires, V.R.; Safarov, N. Diversity of plants and animals in mountain ecosystems in Tajikistan. J. Rangel. Sci. 2013, 4, 43–61. [Google Scholar]
- Elliott, A.; Elliott, J.; Hollingsworth, J.; Kulikova, G.; Parsons, B.; Walker, R. Satellite imaging of the 2015 M7.2 earthquake in the Central Pamir, Tajikistan, elucidates a sequence of shallow strike-slip ruptures of the Sarez-Karakul fault. Geophys. J. Int. 2020, 221, 1696–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ischuk, A.R. Usoy natural dam: Problem of security (Lake Sarez, Pamir Mountains, Tadjikistan). Ital. J. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2006, 1, 189–192. [Google Scholar]
- Metzger, S.; Schurr, B.; Ratschbacher, L.; Sudhaus, H.; Kufner, S.-K.; Schöne, T.; Zhang, Y.; Perry, M.; Bendick, R. The 2015 Mw7.2 Sarez strike-slip earthquake in the Pamir interior: Response to the underthrusting of India’s western promontory. Tectonics 2017, 36, 2407–2421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ambraseys, N.; Bilham, R. The Sarez-Pamir earthquake and landslide of 18 February 1911. Seismol. Res. Lett. 2012, 83, 294–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulikova, G.; Schurr, B.; Krüger, F.; Brzoska, E.; Heimann, S. Source parameters of the Sarez-Pamir earthquake of 1911 February 18. Geophys. J. Int. 2016, 205, 1086–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schuster, R.L.; Alford, D. Usoi landslide dam and Lake Sarez, Pamir Mountains, Tajikistan. Environ. Eng. Geosci. 2004, 10, 151–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alford, D.; Schuster, R.L. Introduction and summary. In Usoi Landslide Dam and Lake Sarez. An Assessment of Hazard and Risk in the Pamir Mountains, Tajikistan; Alford, D., Schuster, R.L., Eds.; United Nations: New York, NY, USA; Geneva, Switzerland, 2000; pp. 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Middleton, R.; Thomas, H. Tajikistan and the High Pamirs: A Companion and Guide, 1st ed.; Odyssey Publications: Hong Kong, China, 2008; p. 700. [Google Scholar]
- Bolt, B.A.; Horn, W.L.; MacDonald, G.A.; Scott, R.F. Geological Hazards: Earthquakes—Tsunamis—Volcanoes—Avalanches—Landslides—Flood; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; p. 330. [Google Scholar]
- Stone, R. Peril in the Pamirs. Science 2009, 326, 1614–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiersch, G.A. Vaiont reservoir disaster. Civ. Eng. 1964, 34, 32–39. [Google Scholar]
- Rosen, P.A.; Hensley, S.; Joughin, I.R.; Li, F.K.; Madsen, S.N.; Rodríguez, E.; Goldstein, R.M. Synthetic aperture radar interferometry. Proc. IEEE 2000, 88, 333–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriel, A.K.; Goldstein, R.M.; Zebker, H.A. Mapping small elevation changes over large areas: Differential radar interferometry. J. Geophys. Res. 1989, 94, 9183–9191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osmanoğlu, B.; Sunar, F.; Wdowinski, S.; Cabral-Cano, E. Time series analysis of InSAR data: Methods and trends. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 115, 90–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, A.; Colesanti, C.; Perissin, D.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F. Evaluating the effect of the observation time on the distribution of SAR permanent scatterers. In Proceedings of the Fringe, Frascati, Italy, 1–5 December 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Crosetto, M.; Monserrat, O.; Cuevas-González, M.; Devanthéry, N.; Crippa, B. Persistent scatterers interferometry: A review. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 115, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Snehmani, M.K.S.; Gupta, R.D.; Bhardwaj, A.; Joshi, P.K. Remote sensing of mountain snow using active microwave sensors: A review. Geocarto Int. 2015, 30, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baduge, A.W.A.; Henschel, M.D.; Hobbs, S.; Buehler, S.A.; Ekman, J.; Lehrbass, B. Seasonal variation of coherence in SAR interferograms in Kiruna, Northern Sweden. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2016, 37, 370–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maskey, S.; Uhlenbrook, S.; Ojha, S. An analysis of snow cover changes in the Himalayan region using MODIS snow products and in-situ temperature data. Clim. Change 2011, 108, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Droz, P.; Fumagalli, A.; Novali, F.; Young, B. GPS and InSAR technologies: A joint approach for the safety of Lake Sarez. In Proceedings of the IVth Canadian Conference on Geohazards, Quebec, QC, Canada, 20–24 May 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Lazecky, F.; Comut, F.C.; Nikolaeva, E.; Bakon, M.; Papco, J.; Ruiz-Armenteros, A.M.; Qin, Y.; de Souza, J.J.M.; Ondejka, P. Potential of Sentinel-1a for nation-wide routine updates of active landslide maps. ISPRS Int. Arc. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spatial Inf. Sci. 2016, XLI-B7, 775–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferretti, A.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F. Permanent scatterers in SAR interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berardino, P.; Fornaro, G.; Lanari, R.; Sansosti, E. A new algorithm for surface deformation monitoring based on small baseline differential SAR interferograms. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 40, 2375–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sowter, A.; Bateson, L.; Strange, P.; Ambrose, K.; Syafiudin, M.F. DInSAR estimation of land motion using intermittent coherence with application to the South Derbyshire and Leicestershire coalfields. Remote Sens. Lett. 2013, 4, 979–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sowter, A.; Amat, M.B.C.; Cigna, F.; Marsh, S.; Athab, A.; Alshammari, L. Mexico City land subsidence in 2014–2015 with Sentinel-1 IW TOPS: Results using the Intermittent SBAS (ISBAS) technique. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2016, 52, 230–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gee, D.; Sowter, A.; Novellino, A.; Marsh, S.; Gluyas, J. Monitoring land motion due to natural gas extraction: Validation of the intermittent SBAS (ISBAS) DInSAR algorithm over gas fields of North Holland, the Netherlands. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2016, 77, 1338–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cigna, F.; Bateson, L.; Jordan, C.; Dashwood, C. Simulating SAR geometric distortions and predicting Persistent Scatterer densities for ERS-1/2 and ENVISAT C-band SAR and InSAR applications: Nationwide feasibility assessment to monitor the landmass of Great Britain with SAR imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 152, 441–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schiller, A.; Vecchiotti, F.; Amabile, A.S.; Guardiani, C.; Dhital, M.R.; Dhakal, A.; Pant, B.R.; Ostermann, M.; Supper, R. Ground motion and PSI density analysis from Envisat and Sentinel1a InSAR data in the context of a complex landslide monitoring strategy in Karnali river basin, Far-Western Nepal. In Proceedings of the 22nd EGU General Assembly, EGU2020-21875, Online, 4–8 May 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Cigna, F.; Sowter, A. The relationship between intermittent coherence and precision of ISBAS InSAR ground motion velocities: ERS-1/2 case studies in the UK. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 202, 177–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novellino, A.; Cigna, F.; Sowter, A.; Ramondini, M.; Calcaterra, D. Exploitation of the Intermittent SBAS (ISBAS) algorithm with COSMO-SkyMed data for landslide inventory mapping in north-western Sicily, Italy. Geomorphology 2017, 280, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sowter, A.; Athab, A.; Novellino, A.; Grebby, S.; Gee, D. Supporting energy regulation by monitoring land motion on a regional and national scale: A case study of Scotland. Proc. IMechE Part A J. Power Energy 2018, 232, 85–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grebby, S.; Sowter, A.; Gluyas, J.; Toll, D.; Gee, D.; Athab, A.; Girindran, R. Advanced analysis of satellite data reveals ground deformation precursors to the Brumadinho Tailings Dam collapse. Commun. Earth Environ. 2021, 2, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farr, T.G.; Rosen, P.A.; Caro, E.; Crippen, R.; Duren, R.; Hensley, S.; Kobrick, M.; Paller, M.; Rodriguez, E.; Roth, L.; et al. The shuttle radar topography mission. Rev. Geophys. 2007, 45, RG2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schreier, G. SAR Geocoding: Data and Systems; Wichmann: Karlsruhe, Germany, 1993; p. 435. [Google Scholar]
- Pepe, A.; Calò, F. A review of interferometric synthetic aperture RADAR (InSAR) multi-track approaches for the retrieval of Earth’s surface displacements. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wright, T.; Parsons, B.; Lu, Z. Toward mapping surface deformation in three dimensions using InSAR. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31, L01607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mastro, P.; Serio, C.; Masiello, G.; Pepe, A. The multiple aperture interferometry (MAI) technique for the detection of large ground displacement dynamics: An overview. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hanisch, J.; Söder, C.-O. Geotechnical assessment of the Usoi landslide dam and the right bank of Lake Sarez. In Usoi Landslide Dam and Lake Sarez. An Assessment of Hazard and Risk in the Pamir Mountains, Tajikistan; Alford, D., Schuster, R.L., Eds.; United Nations: New York, NY, USA; Geneva, Switzerland, 2000; pp. 23–42. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations International Strategy for Disaster Reduction. Sarez Lake: The Latest Achievements and Unsolved Problems; United Nations Office for Disaster Risk Reduction: Dushanbe, Tajikistan, 2007; p. 17. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, F.; Tenzer, R.; Jin, S. Water storage variations in Tibet from GRACE, ICESat and hydrological data. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
| Geometry | Angle of Incidence at AOI Centre | Max. Orbital Baseline (m) | Max. Temporal Baseline (days) | Multi-Look (Azimuth: Range) | Coherence Threshold | N° of Interferograms | Interferogram Threshold | Reference Point (lat/long) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ascending | ~37° | 150 | 180 | 7:2 | 0.45 | 710 | 350 | 38.320°/ 72.612° |
| Descending | ~35° | 150 | 180 | 7:2 | 0.45 | 701 | 350 |
| Track | InSAR Method | Coverage (%) | Average Measurement Density (Pixels Per km2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ascending (N° 100) | SBAS | 44 | 1100 |
| ISBAS | 100 | 2500 | |
| Descending (N° 5) | SBAS | 35 | 875 |
| ISBAS | 100 | 2500 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Grebby, S.; Sowter, A.; Gee, D.; Athab, A.; Barreda-Bautista, B.D.l.; Girindran, R.; Marsh, S. Remote Monitoring of Ground Motion Hazards in High Mountain Terrain Using InSAR: A Case Study of the Lake Sarez Area, Tajikistan. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 8738. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11188738
Grebby S, Sowter A, Gee D, Athab A, Barreda-Bautista BDl, Girindran R, Marsh S. Remote Monitoring of Ground Motion Hazards in High Mountain Terrain Using InSAR: A Case Study of the Lake Sarez Area, Tajikistan. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(18):8738. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11188738
Chicago/Turabian StyleGrebby, Stephen, Andrew Sowter, David Gee, Ahmed Athab, Betsabé De la Barreda-Bautista, Renoy Girindran, and Stuart Marsh. 2021. "Remote Monitoring of Ground Motion Hazards in High Mountain Terrain Using InSAR: A Case Study of the Lake Sarez Area, Tajikistan" Applied Sciences 11, no. 18: 8738. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11188738
APA StyleGrebby, S., Sowter, A., Gee, D., Athab, A., Barreda-Bautista, B. D. l., Girindran, R., & Marsh, S. (2021). Remote Monitoring of Ground Motion Hazards in High Mountain Terrain Using InSAR: A Case Study of the Lake Sarez Area, Tajikistan. Applied Sciences, 11(18), 8738. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11188738








