Influence of the Protein Content on Fiber Morphology and Heat Treatment of Electrospun Potato Protein–Maltodextrin Fibers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of the Spinning Dispersions
2.2. Electrospinning of the Fibers
2.3. Heating the Fibers
2.4. Visualization of the Fibers
2.5. Determination of the Browning Index
2.6. Determination of the Protein Content According to Dumas
2.7. FTIR-Analysis
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Production Rate of Spinning
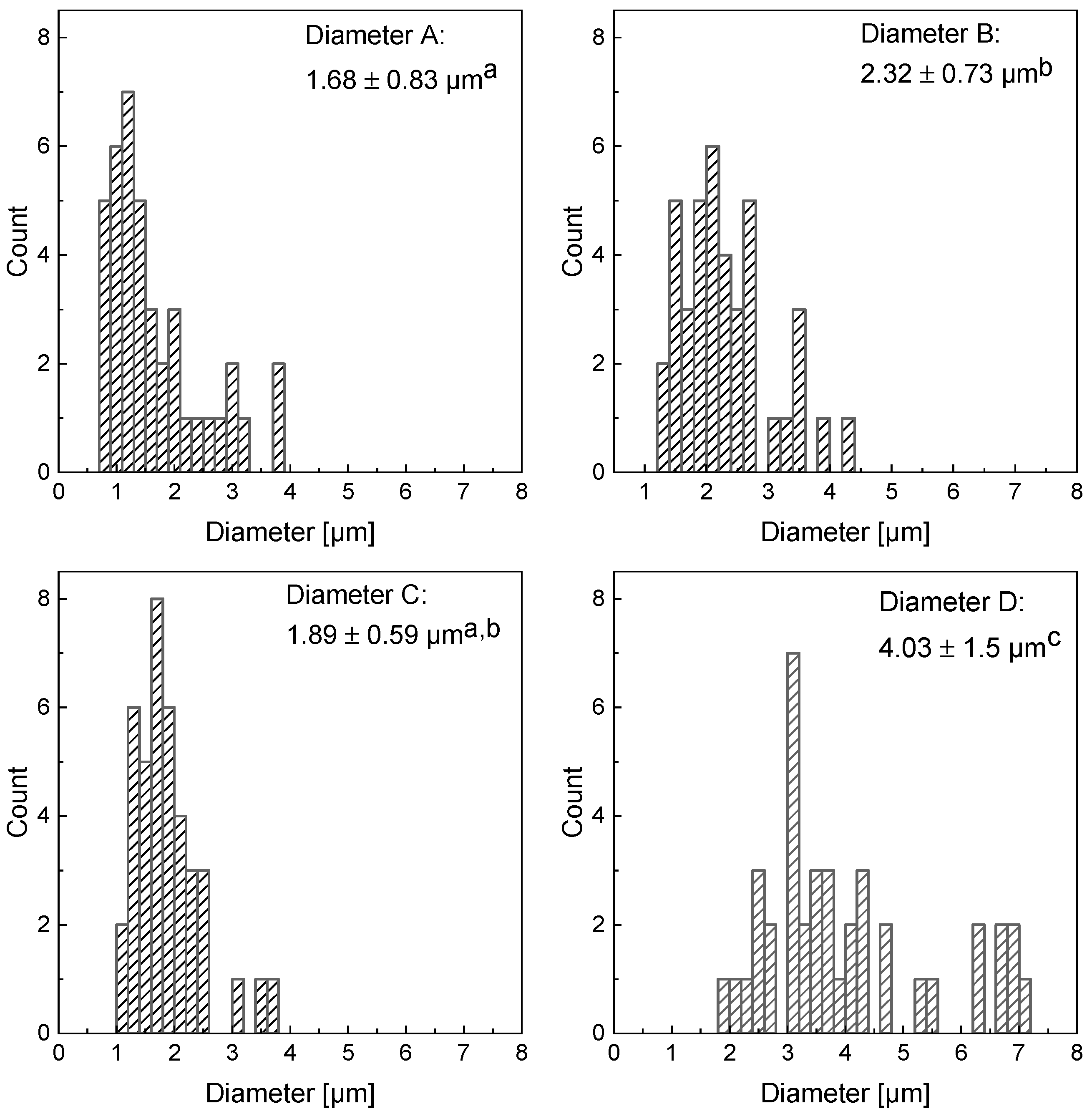
3.2. Visual Appearance of the Fibers
3.3. Protein Content According to Dumas
3.4. Browning Index
3.5. FTIR-Spectra
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schieber, A.; Stintzing, F.; Carle, R. By-products of plant food processing as a source of functional compounds—Recent developments. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2001, 12, 401–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Alfonso, J.E.; Cuadri, A.A.; Franco, J.M. Development and Characterization of Novel Fibers Based on Potato Protein/Polyethylene Oxide Through Electrospinning. Fibers Polym. 2019, 20, 1586–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kofrányi, E.; Jekat, F. Die biologische Wertigkeit von Kartoffelproteinen; VS Verlag für Sozialwissenschaften: Wiesbaden, Germany, 1965; Volume 1582, p. 35. [Google Scholar]
- Waglay, A.; Karboune, S. Chapter 4—Potato Proteins: Functional Food Ingredients. In Advances in Potato Chemistry and Technology, 2nd ed.; Singh, J., Kaur, L., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2016; pp. 75–104. [Google Scholar]
- Alting, A.C.; Pouvreau, L.; Giuseppin, M.L.F.; van Nieuwenhuijzen, N.H. 12—Potato proteins. In Handbook of Food Proteins; Phillips, G.O., Williams, P.A., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2011; pp. 316–334. [Google Scholar]
- van Koningsveld, G.A.; Walstra, P.; Gruppen, H.; Wijngaards, G.; van Boekel, M.A.J.S.; Voragen, A.G.J. Formation and Stability of Foam Made with Various Potato Protein Preparations. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 7651–7659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pots, A.M.; Gruppen, H.; Van Diepenbeek, R.; Van Der Lee, J.J.; Boekel, M.A.J.S.V.; Wijngaards, G.; Voragen, A.G.J. The effect of storage of whole potatoes of three cultivars on the patatin and protease inhibitor content; a study using capillary electrophoresis and MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1999, 79, 1557–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kärenlampi, S.O.; White, P.J. Potato proteins, lipids and minerals. In Advances in Potato Chemistry and Technology, 1st ed.; Singh, J., Kaur, L., Eds.; Elsevier Academic Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Kutzli, I.; Weiss, J.; Gibis, M. Glycation of Plant Proteins via Maillard Reaction: Reaction Chemistry, Technofunctional Properties, and Potential Food Application. Foods 2021, 10, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olías, R.; Becerra-Rodríguez, C.; Soliz-Rueda, J.R.; Moreno, F.J.; Delgado-Andrade, C.; Clemente, A. Glycation affects differently the main soybean Bowman–Birk isoinhibitors, IBB1 and IBBD2, altering their antiproliferative properties against HT29 colon cancer cells. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 6193–6202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aminlari, M.; Ramezani, R.; Jadidi, F. Effect of Maillard-based conjugation with dextran on the functional properties of lysozyme and casein. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2005, 85, 2617–2624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, A.; Sato, T.; Kobayashi, K. Emulsifying Properties of Protein–Polysaccharide Complexes and Hybrids. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1989, 53, 2147–2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Ru, Q.; Ding, Y. Glycation a promising method for food protein modification: Physicochemical properties and structure, a review. Food Res. Int. 2012, 49, 170–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Boekel, M.A.J.S. Kinetic aspects of the Maillard reaction: A critical review. Nahrung Food 2001, 45, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, S.I.; Jongen, W.M.; van Boekel, M.A. A review of Maillard reaction in food and implications to kinetic modelling. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2000, 11, 364–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Damodaran, S.; Lucey, J.A. Formation of Whey Protein Isolate (WPI)—Dextran Conjugates in Aqueous Solutions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 7113–7118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Oliveira, F.C.; Coimbra, J.S.D.R.; de Oliveira, E.B.; Zuñiga, A.D.G.; Garcia-Rojas, E.E. Food Protein-polysaccharide Conjugates Obtained via the Maillard Reaction: A Review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2013, 56, 1108–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baier, S.; Given, P.; Kanjanapongkul, K.; Weiss, J. Formation of Conjugated Protein by Electrospinning. U.S. Patent 20130264731A1, 10 October 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Weiss, J.; Kanjanapongkul, K.; Wongsasulak, S.; Yoovidhya, T. Electrospun fibers: Fabrication, functionalities and potential food industry applications. In Nanotechnology in the Food, Beverage and Nutraceutical Industries; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 362–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutzli, I.; Griener, D.; Gibis, M.; Grossmann, L.; Baier, S.K.; Weiss, J. Improvement of emulsifying behavior of pea proteins as plant-based emulsifiers via Maillard-induced glycation in electrospun pea protein–maltodextrin fibers. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 4049–4056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turan, D.; Gibis, M.; Gunes, G.; Baier, S.K.; Weiss, J. The impact of the molecular weight of dextran on formation of whey protein isolate (WPI)–dextran conjugates in fibers produced by needleless electrospinning after annealing. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 2193–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutzli, I.; Gibis, M.; Baier, S.K.; Weiss, J. Fabrication and characterization of food-grade fibers from mixtures of maltodextrin and whey protein isolate using needleless electrospinning. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2018, 135, 46328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subbiah, T.; Bhat, G.S.; Tock, R.W.; Parameswaran, S.; Ramkumar, S.S. Electrospinning of nanofibers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2005, 96, 557–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P.; Elkins, C.; Long, T.E.; Wilkes, G.L. Electrospinning of linear homopolymers of poly(methyl methacrylate): Exploring relationships between fiber formation, viscosity, molecular weight and concentration in a good solvent. Polymer 2005, 46, 4799–4810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutzli, I.; Gibis, M.; Baier, S.K.; Weiss, J. Electrospinning of whey and soy protein mixed with maltodextrin—Influence of protein type and ratio on the production and morphology of fibers. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 93, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenoy, S.L.; Bates, W.D.; Frisch, H.L.; Wnek, G.E. Role of chain entanglements on fiber formation during electrospinning of polymer solutions: Good solvent, non-specific polymer–polymer interaction limit. Polymer 2005, 46, 3372–3384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarin, A.; Zussman, E. Upward needleless electrospinning of multiple nanofibers. Polymer 2004, 45, 2977–2980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutzli, I.; Griener, D.; Gibis, M.; Schmid, C.; Dawid, C.; Baier, S.K.; Hofmann, T.; Weiss, J. Influence of Maillard reaction conditions on the formation and solubility of pea protein isolate-maltodextrin conjugates in electrospun fibers. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 101, 105535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebert, S.; Gibis, M.; Terjung, N.; Weiss, J. Survey of aqueous solubility, appearance, and pH of plant protein powders from carbohydrate and vegetable oil production. LWT 2020, 133, 110078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Alvarenga, M.; Martinez-Rodriguez, E.; Garcia-Amezquita, L.E.; Olivas, G.; Zamudio-Flores, P.; Acosta-Muniz, C.; Sepulveda, D. Effect of Maillard reaction conditions on the degree of glycation and functional properties of whey protein isolate—Maltodextrin conjugates. Food Hydrocoll. 2014, 38, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kriegel, C.; Arrechi, A.; Kit, K.; McClements, D.; Weiss, J. Fabrication, Functionalization, and Application of Electrospun Biopolymer Nanofibers. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2008, 48, 775–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, A.C.L.; Stephansen, K.; Chronakis, I.S. Electrospinning of food proteins and polysaccharides. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 68, 53–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cengiz-Çallıoǧlu, F.; Jirsak, O.; Dayik, M. Investigation into the relationships between independent and dependent parameters in roller electrospinning of polyurethane. Text. Res. J. 2012, 83, 718–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dosunmu, O.; Chase, G.G.; Kataphinan, W.; Reneker, D.H. Electrospinning of polymer nanofibres from multiple jets on a porous tubular surface. Nanotechnology 2006, 17, 1123–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pham, Q.P.; Sharma, U.; Mikos, A.G. Electrospinning of Polymeric Nanofibers for Tissue Engineering Applications: A Review. Tissue Eng. 2006, 12, 1197–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kumar, T.S.M.; Kumar, K.S.; Rajini, N.; Siengchin, S.; Ayrilmis, N.; Rajulu, A.V. A comprehensive review of electrospun nanofibers: Food and packaging perspective. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 175, 107074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghi, A.K.; Akbari, M. Trends in electrospinning of natural nanofibers. Phys. Status Solidi 2007, 204, 1830–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutzli, I.; Beljo, D.; Gibis, M.; Baier, S.K.; Weiss, J. Effect of Maltodextrin Dextrose Equivalent on Electrospinnability and Glycation Reaction of Blends with Pea Protein Isolate. Food Biophys. 2019, 15, 206–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramakrishna, S. An Introduction to Electrospinning and Nanofibers; World Scientific: Singapore, 2005; p. 382. [Google Scholar]
- Hodge, J.E. Dehydrated Foods, Chemistry of Browning Reactions in Model Systems. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1953, 1, 928–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lertittikul, W.; Benjakul, S.; Tanaka, M. Characteristics and antioxidative activity of Maillard reaction products from a porcine plasma protein–glucose model system as influenced by pH. Food Chem. 2007, 100, 669–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, M. Food Browning and Its Prevention: An Overview. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1996, 44, 631–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kacuráková, M.; Capek, P.; Sasinková, V.; Wellner, N.; Ebringerová, A. FT-IR study of plant cell wall model compounds: Pectic polysaccharides and hemicelluloses. Carbohydr. Polym. 2000, 43, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrondo, J.L.R.; Muga, A.; Castresana, J.; Goñi, F.M. Quantitative studies of the structure of proteins in solution by fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 1993, 59, 23–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Blend | Weight Ratio (MD DE 2:MD DE 21:Potato Protein) | Production Rate 1 (g/h) |
|---|---|---|
| A | (80:10:5) | 3.42 ± 0.17 a |
| B | (80:10:10) | 5.78 ± 0.4 b |
| C | (80:10:15) | 4.59 ± 0.7 c |
| D | (80:10:20) | 2.77 ± 0.5 a |
| Blend | Protein Content of the Spinning Solution (g/100 g) | Protein Content of the Unheated Fibers (g/100 g) | Ratio Protein Content of the Solution to Fiber Protein Content |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | 5 | 4.80 ± 0.01 | 1:0.96 |
| B | 10 | 9.79 ± 0.03 | 1:0.98 |
| C | 15 | 13.57 ± 0.02 | 1:0.90 |
| D | 20 | 20.68 ± 0.29 | 1:1.03 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gibis, M.; Pribek, F.; Kutzli, I.; Weiss, J. Influence of the Protein Content on Fiber Morphology and Heat Treatment of Electrospun Potato Protein–Maltodextrin Fibers. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 7896. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11177896
Gibis M, Pribek F, Kutzli I, Weiss J. Influence of the Protein Content on Fiber Morphology and Heat Treatment of Electrospun Potato Protein–Maltodextrin Fibers. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(17):7896. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11177896
Chicago/Turabian StyleGibis, Monika, Franziska Pribek, Ines Kutzli, and Jochen Weiss. 2021. "Influence of the Protein Content on Fiber Morphology and Heat Treatment of Electrospun Potato Protein–Maltodextrin Fibers" Applied Sciences 11, no. 17: 7896. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11177896
APA StyleGibis, M., Pribek, F., Kutzli, I., & Weiss, J. (2021). Influence of the Protein Content on Fiber Morphology and Heat Treatment of Electrospun Potato Protein–Maltodextrin Fibers. Applied Sciences, 11(17), 7896. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11177896







