Recent Updates on the Synthesis of Bioactive Quinoxaline-Containing Sulfonamides
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Synthesis and Biological Activities
2.1. Benzothiazole Quinoxaline Sulfonamide Derivatives with Diuretic Activity
2.2. Quinoxaline Sulfonamides with Antibacterial Activity
2.3. Synthesis of Quinoxaline Sulfonamide Derivative with Neuropharmacological Activity
2.4. Quinoxaline Sulfonamide Derivatives with Antileishmanial Activity
2.5. Synthesis of Quinoxaline Moiety-Based Benzene Sulfonamides with Antitumor Activity
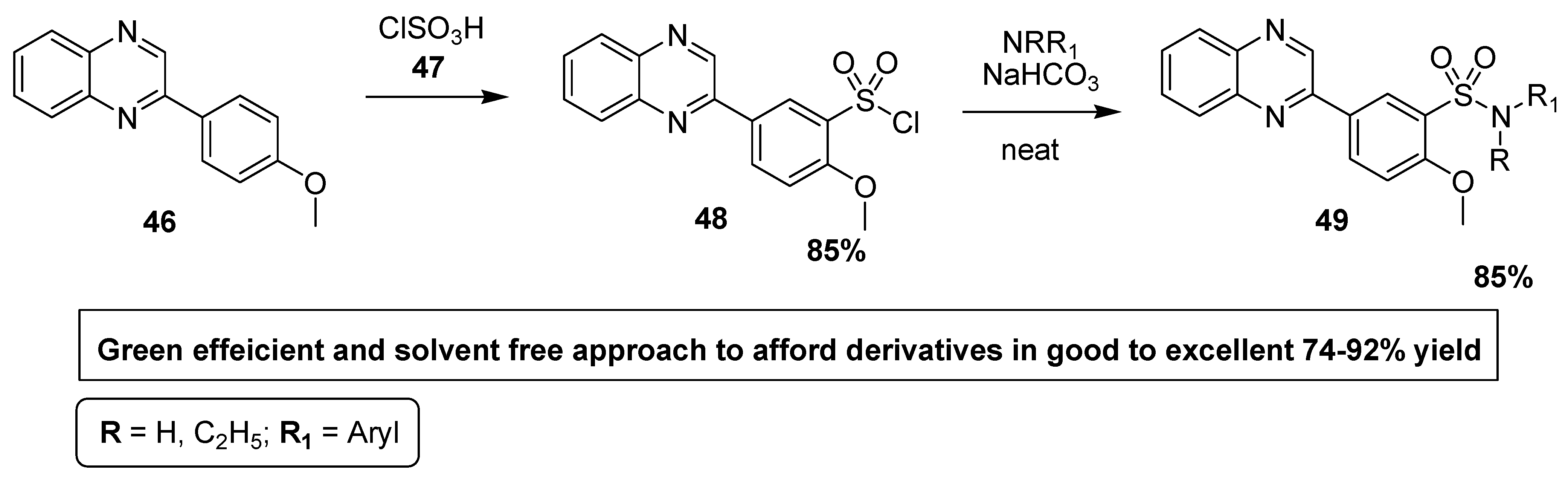
2.6. Synthesis of Quinoxaline-Based Benzene Sulfonamide Derivatives with Anti-Inflammatory Activity
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Seitz, L.E.; Suling, W.J.; Reynolds, R.C. Synthesis and antimycobacterial activity of pyrazine and quinoxaline derivatives. J. Med. Chem. 2002, 45, 5604–5606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, D.J.; Taylor, E.C.; Ellman, J.A. The Chemistry of Heterocyclic Compounds; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Saifina, D.F.; Mamedov, V.A. New and modified classical methods for the synthesis of quinoxalines. Russ. Chem. Rev. 2010, 79, 351–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patidar, A.K.; Jeyakanda, M.; Mobiya, A.K.; Selvam, G. Exploring potential of quinoxaline moiety. Int. J. Pharm. Tech. Res. 2011, 3, 386–392. [Google Scholar]
- Tariq, S.; Somakala, K.; Amir, M. Quinoxaline: An insight into the recent pharmacological advances. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 143, 542–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinheiro, C.A.; Nogueira, M.C.T.; de Souza, M.V.N. Quinoxaline Nucleus: A promising scaffold in anti-cancer drug discovery. Anticancer. Agents Med. Chem. 2016, 16, 1339–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amin, M.K.; Ismail, F.M.M.; Noaman, E.; Soliman, D.H.; Ammar, Y.A. New quinoxaline 1,4-di-N-oxides. Part 1: Hypoxia-selective cytotoxins and anticancer agents derived from quinoxaline 1,4-di-N-oxides. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2006, 14, 6917–6923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotb, R.; Anwar, A.M.; Soliman, S.M.; Salama, A.M. Synthesis and reactions of some novel quinoxalines for anticancer evaluation. Phosphorus Sulfur 2007, 182, 1119–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindsley, C.W.; Zhao, Z.; Leister, W.H.; Robinson, R.G.; Barnett, S.F.; Defeo-Jones, D.; Jones, R.E.; Hartman, G.D.; Huff, J.R.; Huber, H.E.; Duggan, M.E. Allosteric Akt (PKB) inhibitors: Discovery and SAR of isozyme selective inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2005, 15, 761–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carta, A.; Loriga, M.; Piras, S.; Paglietti, G.; La Colla, P.; Busonera, B.; Collu, G.; Loddo, R. Synthesis of variously substituted 3-phenoxymethyl quinoxalin-2-ones and quinoxalines capable to potentiate in vitro the antiproliferative activity of anticancer drugs in multi-drug resistant cell lines. Med. Chem. 2006, 2, 113–122. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, S.A.; Mullick, P.; Pandit, S.; Kaushik, D. Synthesis of hydrazones derivatives of quinoxalinone-prospective antimicrobial and antiinflammatory agents. Acta Pol. Pharm. 2009, 66, 169–172. [Google Scholar]
- Piras, S.; Loriga, M.; Paglietti, G. Quinoxaline chemistry. Part XVII. Methyl [4-(substituted 2-quinoxalinyloxy) phenyl] acetates and ethyl N-{[4-(substituted 2-quinoxalinyloxy) phenyl] acetyl} glutamates analogues of methotrexate: Synthesis and evaluation of in vitro anticancer activity. Farmaco 2004, 59, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahekar, R.H.; Jain, M.R.; Gupta, A.A.; Goel, A.; Jadav, P.A.; Patel, D.N.; Prajapati, V.M.; Patel, P.R. Synthesis and antidiabetic activity of 3,6,7-trisubstituted-2-(1H-imidazol-2-ylsulfanyl)quinoxalines and quinoxalin-2-yl isothioureas. Arch. Pharm. 2007, 340, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shintre, S.A.; Ramjugernath, D.; Islam, M.; Mopuri, R.; Mocktar, C.; Koorbanally, N.A. Synthesis, in vitro antimicrobial, antioxidant, and antidiabetic activities of thiazolidine–quinoxaline derivatives with amino acid side chains. Med. Chem. Res. 2017, 26, 2141–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, N.V.; Revankar, V.K.; Kirasur, B.N.; Hugar, M.H. Transition metal complexes of thiosemicarbazones with quinoxaline hub: An emphasis on antidiabetic property. Med. Chem. Res. 2012, 21, 663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wu, B.; Ma, M.; Mingming, M.; Xin, C.; Xiangyu, Q.; Minlan, H.; Saghir, H.; Chaojun, J.; Bing, M.; Changjin, Z. An efficient synthesis of quinoxalinone derivatives as potent inhibitors of aldose reductase. Chem. Med. Chem. 2012, 7, 823–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, D.; Ghosh, N.N.; Chandra, R. Synthesis and pharmacological evaluation of substituted 5-[4-[2-(6, 7-dimethyl-1, 2, 3, 4-tetrahydro-2-oxo-4-quinoxalinyl) ethoxy] phenyl] methylene] thiazolidine-2, 4-dione derivatives as potent euglycemic and hypolipidemic agents. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2005, 15, 1019–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaso, A.; Zarranz, B.; Aldana, I.; Monge, A. Synthesis of new quinoxaline-2-carboxylate 1,4-dioxide derivatives as anti-Mycobacterium tuberculosis agents. J. Med. Chem. 2005, 48, 2019–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ancizu, S.; Moreno, E.; Solano, B.; Villar, R.; Asunción, B.; Torres, E.; Pérez-Silanes, S.; Aldana, I.; Monge, A. New 3-methylquinoxaline-2-carboxamide 1, 4-di-N-oxide derivatives as anti-Mycobacterium tuberculosis agents. Biorg. Med. Chem. 2010, 18, 2713–2719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Atawy, A.M.; Ezzat, A.; Hamed, E.A.; Alhadi, M.; Omar, A.Z. Synthesis and antimicrobial activity of some new substituted quinoxalines. Molecules 2019, 24, 4198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dharmchand, P.S.; Sanjay, K.D.; Hashim, R.S.; Singhal, G.R. Synthesis and antimicrobial activity of some new quinoxaline derivatives. Pharmaceuticals 2010, 3, 2416–2425. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.B.; Kim, Y.H.; Park, J.Y.; Kim, S.K. Synthesis and biological activity of new quinoxaline antibiotics of echinomycin analogueS. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2004, 14, 541–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarges, R.; Howard, H.R.; Browne, R.G.; Lebel, L.A.; Seymour, P.A.; Koe, B.K. 4-Amino [1, 2, 4] triazolo [4, 3-a] quinoxalines. A novel class of potent adenosine receptor antagonists and potential rapid-onset antidepressants. J. Med. Chem. 1990, 33, 2240–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakata, G.; Makino, K.; Kurasawa, Y. Recent progress in the quinoxaline chemistry. Synthesis and biological activity. Heterocycles 1988, 27, 2481–2515. [Google Scholar]
- Abu-hashem, A.A.; Gouda, M.A.; Badria, F.A. Synthesis of some new pyrimido[2:2,3]thiazolo[4,5-b]quinoxaline derivatives as anti-inflammatory and analgesic agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 45, 1976–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagle, S.; Adhikari, V.A.; Kumari, S.N. Synthesis of some new 2-(3-methyl-7-substituted-2-oxoquinoxalinyl)-5-(aryl)-1,3,4-oxadiazoles as potential non-steroidal anti-inflammatory and analgesic agents. Indian J. Chem. 2008, 47, 439–448. [Google Scholar]
- Ismail, M.M.; Ammar, Y.A.; Ibrahim, M.K.; El-Zahaby, H.S.A.; Mahmoud, S.S. Synthesis and pharmacological evaluation of novel quinoxalines as potential nonulcerogenic anti-inflammatory and analgesic agents. Arzneimittelforschung 2005, 55, 738–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhansay, D.; Kartik, T.N.; Vinay, S.V.; Nagori, K.; Badwaik, H.; Nair, N.; Tripathi, D.K.; Mishra, A. Synthesis and molecular docking study of novel hybrids of 1,3,4-oxadiazoles and quinoxaline as a potential analgesic and anti-inflammatory agents. J. Heterocycl. Chem. 2018, 55, 2901–2910. [Google Scholar]
- Gayathri, R.; Suresh, S.; Thirumurthy, R. Synthesis, characterization and pharmacological evaluation of some potent 2-(substituted phenylimino) quinoxaline-3-one for their analgesic activity. J. Chem. Pharm. 2015, 7, 961–966. [Google Scholar]
- Alswah, M.; Adel, G.; El-Morsy, A.; El-Gamal, K. Synthesis and biological evaluation of some [1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a]quinoxaline derivatives as novel anticonvulsant agents. ISRN Org. Chem. 2013, 587054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Møllerud, S.; Hansen, R.B.; Pallesen, J.; Temperini, P.; Pasini, D.; Bornholt, J.; Nielsen, B.; Mamedova, E.; Chalupnik, P.; Paternain, A.V.; et al. N-(7-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)-2,3-dioxo-6-(trifluoromethyl)-3,4- dihydroquinoxalin-1(2H)-yl)benzamide - a new kainate receptor selective antagonist and analgesic: Synthesis, X-ray crystallography, structure-affinity relationships, in vitro and in vivo pharmacology. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2019, 10, 4685–4695. [Google Scholar]
- Burguete, A.; Pontiki, E.; Hadjipavlou-Litina, D.; Ancizu, S.; Villar, R.; Solano, B.; Moreno, E.; Torres, E.; Pérez, S.; Aldana, I.; Monge, A. Synthesis and biological evaluation of new quinoxaline derivatives as antioxidant and anti-inflammatory agents. Chem Biol. Drug Des. 2011, 77, 255–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Sabbagh, O.I.; El-Sadek, M.E.; Lashine, S.M.; Yassin, S.H.; El-Nabtity, S.M. Synthesis of new 2 (1H)-quinoxalinone derivatives for antimicrobial and antiinflammatory evaluation. Med. Chem. Res. 2009, 18, 782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qing-K, S.; Guo, H.G.; Gao, L.; Mei, J.; Li-Hua Cao, C.; Zhe-Shan, Q. Discovery and evaluation of novel synthetic 5-alkyl-4-oxo-4,5-dihydro-[1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a]quinoxaline-1-carbox-amide derivatives as anti-inflammatory agents. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2020, 35, 85–95. [Google Scholar]
- Tariq, S.; Ozair, A.; Mohd, A. Synthesis, anti-inflammatory, p38α MAP kinase inhibitory activities and molecular docking studies of quinoxaline derivatives containing triazole moiety. Bioorg. Chem. 2018, 76, 343–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manzano, M.T.; Guirado, A.; Martínez-Esparza, M.; Gálvez, J.; García-Peñarrubia, P.; Ruiz-Alcaraz, A.J. 1Quinoxalines potential to target pathologies. Curr. Med. Chem. 2015, 22, 3075–3108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Zahabi, H.S.A. Synthesis, Characterization, and biological evaluation of some novel quinoxaline derivatives as antiviral agents. Arch. Pharm. Chem. Life Sci. 2017, 350, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilhelmsson, L.M.; Kingi, N.; Bergman, J. Interactions of Antiviral Indolo[2,3-b]quinoxaline Derivatives with DNA. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 51, 7744–7750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rongjiao, X.; Tao, G.; Mei, C.; Shijun, S.; He, J.; Xu, T.; Jianga, S.; Xue, W. Synthesis, antiviral and antibacterial activities and action mechanism of penta-1,4-dien-3-one oxime ether derivatives containing a quinoxaline moiety. New J. Chem. 2019, 43, 16461–16467. [Google Scholar]
- Fonseca, T.; Gigante, B.; Marques, M.M.; Gilchrist, T.L.; de Clercq, E. Synthesis and antiviral evaluation of benzimidazoles, quinoxalines and indoles from dehydroabietic acid. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2004, 12, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, I.; Al-Masoudi, I.; Hassan, H.G.; Al-Masoudi, N. Synthesis and anti-HIV activity of new homo acyclic nucleosides, 1-(pent-4-enyl) quinoxalin-2-ones and 2-(pent-4-enyloxy) quinoxalines. Chem. Hetrocycl. Compd. 2007, 43, 1052–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibinskaya, M.O.; Lyakhov, S.A.; Mazepa, A.V.; Andronati, S.A.; Turov, A.V.; Zholobak, N.M.; Spivak, N.Y. Synthesis, cytotoxicity, antiviral activity and interferon inducing ability of 6-(2-aminoethyl)-6H-indolo[2,3-b]quinoxalines. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 45, 1237–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loughran, M.H.; Ziying, H.; Wrobel, E.J.; Sarah, D.E.; Gordon, R.; Bruce, F.D.; Ronald, H.N.; Allen, R.B. Quinoxaline-based inhibitors of Ebola and Marburg VP40 egress. Bioorg Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 26, 3429–3435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Zhi-Cheng, D.; Shao-Song, Q.; Jun-Yan, L.; Yu, X.; Ai-Min, L.; Hai-Liang, Z.; Jian-Xin, W.; Yong-Hao, Y. Design, synthesis, antifungal, and antioxidant activities of (E)-6-((2 phenylhydrazono) methyl) quinoxaline derivatives. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 9637–9643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waring, M.J.; Taibi, B.H.; Kotchevar, A.T.; Ramdani, A.; Touzani, R.; Elkadiri, S.; Hakkou, A.; Bouakka, M.; Ellis, T. 2,3-Bifunctionalized quinoxalines: Synthesis, DNA interactions and evaluation of anticancer, anti-tuberculosis and antifungal activity. Molecules 2002, 7, 641–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Gazzar, M.; Nafie, N.H.; Nocentini, A.; Ghorab, M.M.; Heiba, H.I. Supuran, C.T.; Carbonic anhydrase inhibition with a series of novel benzenesulfonamide-triazole conjugates. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2018, 33, 1565–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Lacorte Singulani, J.; Galeane, M.C.; Ramos, M.D.; Gomes, P.C.; Dos Santos, C.T.; de Souza, B.M.; Palma, M.S.; Fusco Almeida, A.M.; Mendes Giannini, M.J.S. Antifungal activity, toxicity and membranolytic action of a mastoparan analogue peptide. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Shaik, M.B.; Paala, K.; Shaik, T.B.; Chintha, V.; Shafi, S.S.; Naga Raju, C. Synthesis, characterization and antimicrobial activity of boron, silicon and selenium substituted quinoxaline derivatives. Pharma Innov. J. 2019, 8, 627–632. [Google Scholar]
- Soliman, D.H. Synthesis, characterization, anti-bacterial and anti-fungal activities of new quinoxaline 1,4-di-N-Oxide derivatives. IJOC 2013, 3, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shekhar, C.A.; Rao, S.P.; Narsaiah, B.; Allanki, A.D.; Sijwali, P.S. Emergence of pyrido quinoxalines as new family of antimalarial agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 77, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangisetty, J.B.; Gupta, C.N.; Prasad, A.L.; Srinivas, P.; Sridhar, N.; Parimoo, P.; Veeranjaneyulu, A. Synthesis of new arylaminoquinoxalines and their antimalarial activity in mice. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2001, 53, 1409–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonilla-Ramírez, L.; Galiano, S.; Quiliano, M.; Aldana, I.; Pabón, A. Primaquine–quinoxaline 1,4-di-N-oxide hybrids with action on the exo-erythrocytic forms of plasmodium induce their effect by the production of reactive oxygen species. Malar. J. 2019, 18, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillon, J.; Cohen, A.; Gueddouda, N.M.; Das, R.N.; Moreau, S.; Ronga, L.; Savrimoutou, S.; Basmaciyan, L.; Monnier, A.; Monget, M.; Rubio, S.; Garnerin, T.; Azas, N.; Mergny, J.L.; Mullié, C.; Sonnet, P. Design, synthesis and antimalarial activity of novel bis{N- [(pyrrolo[1,2-a]quinoxalin-4-yl)benzyl]-3-aminopropyl}amine derivatives. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2017, 32, 547–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guillon, J.; Moreau, S.; Mouray, E.; Sinou, V.; Forfar, I.; Fabre, S.B.; Desplat, V.; Millet, P.; Parzy, D.; Jarry, C.; et al. New ferrocenic pyrrolo[1,2-a]quinoxaline derivatives: Synthesis and in vitro antimalarial activity. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2008, 16, 9133–9144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillon, J.; Grellier, P.; Labaied, M.; Sonnet, P.; Léger, J.M.; Déprez-Poulain, R.; Forfar-Bares, I.; Dallemagne, P.; Lemaître, N.; Péhourcq, F.; Rochette, J.; Sergheraert, C.; Jarry, C. Synthesis, antimalarial activity, and molecular modeling of new pyrrolo[1,2-a]quinoxalines, Bispyrrolo[1,2-a]quinoxalines, Bispyrido[3,2-e]pyrrolo[1,2-a]pyrazines, and Bispyrrolo[1,2-a]thieno[3,2-e]pyrazines. J. Med. Chem. 2004, 47, 1997–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parhi, A.K.; Zhang, Y.; Saionz, K.W.; Pradhan, P.; Kaul, M.; Trivedi, K.; Pilch, D.S.; LaVoie, E.J. Antibacterial activity of quinoxalines, quinazolines, and 1,5-naphthyridines. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 234, 4968–4974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aravind, K.; Ganesh, A.; Ashok, D. Microwave assisted synthesis, characterization and antibacterial activity of quinoxaline derivatives. J. Chem. Pharm. Res. 2013, 5, 48–52. [Google Scholar]
- Abbas, H.A.S.; Al-Marhabi, A.R.; Ammar, Y.A. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of 2, 3-disubstituted and fused quinoxalines as potential anticancer and antimicrobial agents. Acta Pol. Pharm. 2017, 74, 445–458. [Google Scholar]
- Bayoumi, A.; Ghiaty, A.H.; Abd El-Gilil, S.M.; Husseiny, E.; Ebrahim, M.A. Exploration of quinoxaline derivatives as antimicrobial and anticancer agents. J. Heterocyclic. Chem. 2019, 4, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Marhabi, A.R.; Abbas, H.-A.S.; Ammar, Y.A. Synthesis, characterization and biological evaluation of some quinoxaline derivatives: A promising and potent new class of antitumor and antimicrobial agents. Molecules 2015, 20, 19805–19822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afrough, T.; Bakavoli, M.; Eshghi, H.; Beyzaei, H.; Manesh, M.-M. Synthesis, characterization and in vitro antibacterial evaluation of novel 4-(1-(Pyrimidin-4-yl)Ethyl)-12H-Pyrimido[4′,5′:5,6] [1,4]Thiazino[2,3-b] quinoxaline derivatives. Polycycl. Aromat. Comp. 2019, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, M.; Pinheiro, C.; Fernandes, R.; Noronha, J.P.; Prudencio, C. Antimicrobial activity of quinoxaline 1,4-dioxide with 2- and 3-substituted derivatives. Microbiol. Res. 2014, 169, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicola, O.; O’Neill, A.J. Revisiting unexploited antibiotics in search of new antibacterial drug candidates: The case of MSD-819 (6-chloro-2-quinoxalinecarboxylic acid 1,4-dioxide). J. Antibiot. 2017, 7, 317–319. [Google Scholar]
- Settypalli, T.; Chunduri, V.R.; Maddineni, A.K.; Begari, N.; Allagadda, R.; Kotha, P.; Chippada, A.R. Design, synthesis, in silico docking studies and biological evaluation of novel quinoxaline-hydrazide hydrazone-1,2,3-triazole hybrids as α-glucosidase inhibitors and antioxidants. New. J. Chem. 2019, 43, 15435–15452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umesh, T.P.; Bhautik, T.B.; Dipak, R.K. A green protocol for the synthesis of quinoxaline derivatives catalyzed by polymer supported sulphanilic acid. Arab. J. Chem. 2017, 10, S2902–S2907. [Google Scholar]
- Vijay, K.; Karakavalasa, P.; Vasanthi, R. Synthesis, characterization and pharmacological evaluation of some novel quinoxaline derived chalcones. Der. Pharma. Chemica. 2013, 5, 301–307. [Google Scholar]
- Elkaeed, E.; Ghiaty, A.; El-Morsy, A.; El-Gamal, K.; Sakr, H. Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Some quinoxaline-2-one Derivatives as Novel Anticonvulsant Agents. Chem. Sci. Rev. Lett. 2014, 3, 1375–1387. [Google Scholar]
- Hui, X.; Desrivot, J.; Bories, C.; Loiseau, P.M.; Franck, X.; Hocquemiller, R.; Figadere, B. Synthesis and antiprotozoal activity of some new synthetic substituted quinoxalines. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2006, 16, 815–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- E-Chavez, J.J.; Merino, V.; Cervantes, M.-L.; Cruz, I.-R.; Guerrero, D.-Q.; Quintanar, A.-G. The use of iontophoresis in the administration of nicotine and new non-nicotine drugs through the skin for smoking cessation. Curr. Drug Discov. Technol. 2009, 6, 171–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohde, B.H.; McLaughlin, M.A.; Chiou, L.Y. Existence and role of endogenous ocular Melatonin. J. Ocul. Pharmacol. Th. 1985, 1, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hugo, W.B.; Stretton, R.G. Action of quinacillin on staphylococcus aureus. Nature 1964, 202, 1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carta, F.; Scozzafava, A.; Supuran, C.T. Sulfonamides: A patent review (2008–2012). Expert. Opin. Ther. Pat. 2012, 22, 747–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Actor, P.; Chow, A.W.; Dutko, F.; McKinlay, M.A. "Chemotherapeutics", Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2005; p. 8. [Google Scholar]
- Supuran, C.T. Advances in structure-based drug discovery of carbonic anhydrase inhibitors. Expert. Opin. Drug. Discov. 2017, 12, 61–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carta, F.; Supuran, C.T.; Scozzafava, A. Sulfonamides and their isosters as carbonic anhydrase inhibitors. Future Med. Chem. 2014, 6, 1149–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scozzafava, A.; Owa, T.; Mastrolorenzo, A.; Supuran, C.T. Anticancer and antiviral sulfonamides. Curr. Med. Chem. 2003, 10, 925–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capasso, C.; Supuran, C.T. Sulfa and trimethoprim-like drugs–antimetabolites acting as carbonic anhydrase, dihydropteroate synthase and dihydrofolate reductase inhibitors. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2014, 29, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pareek, A.; Rani, P.; Kishore, D. A Short Review On: Sulphonamides. Int. J. Pharma. BioSci. 2013, 4, 812–820. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, H.U.N.; Zaib, S.; Sultana, K.; Khan, I.; Soume, B.-M.; Nadeem, H.; Hassan, M.; Iqbal, J. Metal complexes of tosyl sulfonamides: Design, x-ray structure, biological activities and molecular docking studies. RSC. Adv. 2015, 5, 30125–30132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hager, T. The Demon Under The Microscope: From Battlefield Hospitals To Nazi Labs, One Doctor’s Heroic Search For. The World’s First Miracle Drug; Broadway Books: New York, NY, USA, 2006; ISBN 1-4000-8214-5. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Mohammed, N.N.; Alias, Y.; Abdullah, Z.; Shakir, R.M.; Taha, E.M.; Hamid, A.A. Synthesis and antibacterial evaluation of some novel imidazole and benzimidazole sulfonamides. Molecules 2013, 18, 11978–11995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsughayer, A.; Elassar, A.A.Z.; Mustafa, S.; Sagheer, F. Synthesis, structure analysis and antibacterial activity of new potent sulfonamide derivatives. J. Biomater. Nanobiotechnol. 2011, 2, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorantla, V.; Gundlac, R.; Jadavc, S.S.; Anugu, S.R.; Chimakurthy, J.; Nidasanametla, S.K.; Korupolu, R. Molecular hybrid design, synthesis and biological evaluation of nphenyl sulfonamide linked n-acyl hydrazone derivatives functioning as cox-2 inhibitors: New anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidant and anti-bacterial agents. New J. Chem. 2017, 41, 13516–13532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Aziz, A.A.M.; Angeli, A.; El-Azab, A.S.; Hammouda, M.E.A.; El-Sherbeny, M.A.; Supuran, C.T. Synthesis and anti-inflammatory activity of sulfonamides and carboxylates incorporating trimellitimides: Dual cyclooxygenase/carbonic anhydrase inhibitory actions. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 84, 260–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capasso, C.; Supuran, C.T. An overview of the alpha-, beta-and gamma-carbonic anhydrases from Bacteria: Can bacterial carbonic anhydrases shed new light on evolution of bacteria. J. Enzym Inhib. Med. Chem. 2015, 30, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isik, K.; Kocak, O.F. Antimicrobial activity screening of some sulfonamide derivatives on some nocardia species and isolates. Microbiol. Res. 2009, 164, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chohan, Z.H.; Rauf, A.; Naseer, M.M.; Somra, M.A.; Supuran, C.T. Antibacterial, antifungal and cytotoxic properties of some sulfonamide-derived chromones. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2006, 21, 173–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chibale, K.; Haupt, H.; Kendrick, H.; Yardley, V.; Saravanamuthu, A.; Fairlamb, A.H.; Croft, S.L. Antiprotozoal and cytotoxicity evaluation of sulfonamide and urea analogues of quinacrine. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2001, 11, 2655–2657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supuran, C.T.; Casini, A.; Scozzafava, A. Protease inhibitors of the sulfonamide type: Anticancer, antiinflammatory, and antiviral agents. Med. Res. Rev. 2003, 23, 535–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, K.T.; Fisher, G.M.; Sumanadasa, S.D.M.; Adams, T.-S.; Moeker, J.; Lopez, M.; S-Poulsen, A. Antimalarial activity of compounds comprising a primary benzene sulfonamide fragment. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 6114–6117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puccetti, L.; Fasolis, G.; Vullo, D.; Chohan, Z.H.; Scozzafava, A.; Supuran, C.T. Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors. Inhibition of Cytosolic/Tumor-Associated Carbonic Anhy-drase Isozymes I, II, IX, and XII with Schiff Bases Incorpo-rating Chromone and Aromatic Sulfonamide Moieties, and Their Zinc Complexes. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2005, 15, 3096–3101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supuran, C.T. Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibition and the Management of Hypoxic Tumors. Metabolites 2017, 7, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbate, F.; Winum, J.Y.; Potter, B.V.; Casini, A.; Montero, L.-J.; Scozzafava, A.; Supuran, C.T. Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors: X-ray crystallographic structure of the adduct of human isozyme II with EMATE, a dual inhibitor of carbonic anhydrases and steroid sulfatase. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2004, 14, 231–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garaj, V.; Puccetti, L.; Fasolis, G.; Winum, Y.J.; Montero, L.J.; Scozzafava, A.; Vullo, D.; Innocenti, A.; Supuran, C.T. Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors: Synthesis and In-hibition of Cytosolic/Tumor-Associated Carbonic Anhydrase Isozymes I, Ii, and Ix with sulfonamides incorporating 1,2,4-Triazine Moieties. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2004, 14, 5427–5433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supuran, C.T. Carbonic anhydrases: Novel therapeutic applications for inhibitors and activators. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2008, 7, 168–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neri, D.; Supuran, C.T. Interfering with pH regulation in tumours as a therapeutic strategy. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2011, 10, 767–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masini, E.; Carta, F.; Scozzafava, A.; Supuran, C.T. Antiglaucoma carbonic anhydrase inhibitors: A patent review. Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2013, 23, 705–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monti, S.M.; Supuran, C.T.; Simone, G.D. Anticancer carbonic anhydrase inhibitors: A patent review (2008–2013). Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2013, 23, 737–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Supuran, C.T. Structure-based drug discovery of carbonic anhydrase inhibitors. J. Enzym Inhib. Med. Chem. 2012, 27, 759–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berredjem, H.; Reggami, Y.; Benlaifa, M.; Berredjem, M.; Bouzerna, N. Antidiabetic and hypolipidemic potential of 3, 4-dihydroisoquinolin-2(1H)- sulfonamide in alloxan induced diabetic rats. Int. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 11, 226–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masereel, B.; Thiry, A.; Dogne, J.M.; Supuran, C.T. Anticonvulsant sulfonamides/sulfamates/sulfamides with carbonic anhydrase inhibitory activity: Drug design and mechanism of action. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2008, 14, 661–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scozzafava, A.; Supuran, C.T.; Carta, F. Antiobesity carbonic anhydrase inhibitors: A literature and patent review. Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2013, 23, 725–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supuran, C.T. How many carbonic anhydrase inhibition mechanisms exist. J. Enzym Inhib. Med. Chem. 2016, 31, 345–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carta, F.; Supuran, C.T. Diuretics with carbonic anhydrase inhibitory action: A patent and literature review (2005–2013). Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2013, 23, 681–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, A.E. Sulfonylurea receptors, ion channels and fruit flies. Diabetes 1988, 37, 847–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carta, F.; Mannelli, L.D.C.; Pinard, M.; Ghelardini, C.; Scozzafava, A.; McKenna, R.; Supuran, C.T. A class of sulfonamide carbonic anhydrase inhibitors with neuropathic pain modulating effects. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2015, 23, 1828–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scozzafava, A.; Supuran, C.T. Carbonic anhydrase and matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors: sulfonylated amino acid hydroxamates with mmp inhibitory properties act as efficient inhibitors of ca isozymes i, ii, and iv, and N-hydroxysulfonamides, Inhibit Both These Zinc. Enzymes J. Med. Chem. 2000, 43, 3677–3687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scozzafava, A.; Supuran, C.T. Protease Inhibitors: Synthesis of potent bacterial collagenase and matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors incorporating n-4-nitrobenzylsulfonylglycine hydroxamate moieties. J. Med. Chem. 2000, 43, 1858–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajeet, A.; Mishra, K.; Kumar, A. Recent advances in development of sulfonamide derivatives and their pharmacological effects- A Review. Am. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2015, 3, 18–24. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, H.; Yamasaki, E.F.; Chan, K.K.; Shen, L.L.; Snapka, R.M. Chloroquinoxaline Sulfonamide (NSC 339004) is a Topoisomerase IIα/β Poison. Cancer Res. 2000, 60, 5937–5940. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kornberg, B.E.; Nikam, S.S. Sulfonamide Derivatives of Substituted Quinoxaline 2,3-Diones as Glutamate Receptor Antagonsts. U.S. Patent 6,096,744, 1 August 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Gaillard, P.; Quattropani, A.; Pomel, V.; Rueckle, T.; Klicic, J.; Church, D. Pyrazine Derivatives and Use as pi3k Inhibitors. U.S. Patent 8,877,757, 4 November 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Allison, B.D.; Hack, M.D.; Rabinowitz, M.H.; Rosen, M.D. Quinoxaline Compounds. U.S. Patent 7,304,051 B2, 4 December 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Pascale, G.; Vincent, P.; J-Isabelle, E.; Jerome, D.; Jasna, K.; Cyril, M. Quinoxaline Compounds and Use Thereof. WO 2008/101979 Al, 28 August 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, X.; Liang, J.T.; Mani, N.; Pandit, C.R. Preparation of Quinoxaline Compounds. U.S. Patent 2008/0103300 A, 1 May 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Bajjalieh, W.; Bannen, L.C.; Brown, S.D.; Mac, M.B.; Marlowe, C.K.; Nuss, J.M.; Tesfai, Z.; Wang, Y.; Xu, W. Phosphatidylinositol, 3-Kinase Inhibitors and Methods of Their Use. U.S. Patent 7,989,622 B2011, 2 August 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Aftab, D.T.; Decillis, A. Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase Inhibitors and Methods of Their Use. WO 2012/065057 A3, 18 May 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Natarajan, A.; Chen, Q.; Bryant, V.C.; Radhakrishnan, P.; Rajule, R.; Chaturvedi, N. Quinoxaline Compounds and Uses Thereof. WO 2012/071414 A2, 31 May 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Harper, S.; Summa, V.; Liverton, N.J.; McCauley, J.A. Macrocyclic Quinoxaline Compounds as HCV NS3 Protease Inhibitors. U.S. Patent 7,973,040 B2, 5 July 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.-L.; Qian, X. Benzenesulfonamide Derivatives of Quinoxaline, Pharmaceutical Compositions Thereof, and Their Use in Methods for Treating Cancer. U.S. Patent 9.295,671 B2, 29 March 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Boezio, C.; Boezio, A.; Bregman, H.; Coats, J.R.; Copeland, K.W.; Dimauro, E.F.; Dineen, T.; Gao, H.; La, D.; Marx, I.E.; Nguyen, H.N.; Peterson, E.A.; Weiss, M. Dhydrobenzoxazine and Tetrahydroquinoxaline Sodium Channel Inhibitors. U.S. Patent 9,346,798 B2016, 28 August 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, L.-Y.; Qian, X. Benzene Sulfonamide Derivatives of Quinoxaline, Pharmaceutical Compositions Thereof, and Their Use in Methods for Treating Cancer. U.S. Patent 9,572,808 B2, 21 February 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Klein, M.; Emde, U.; Buchstaller, H.P.; Esdar, C.; Poeschke, O. Quinoxaline Derivatives. U.S. Patent 2013/0217670 A1, 22 August 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Danig, P.; Dominique, S. Method for Preparing Substituted n-(3-Amino-Quinoxalin-2-yl)-Sulfonamides and Their Intermediates n-(3-Chloro-Quinoxalin-2-yl)Sulfonamides. WO 2012 /052420 Al, 26 April 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Boezio, C.; Boezio, A.; Bregman, H.; Chakka, N.; Coats, J.R.; Copeland, K.W.; Dimauro, E.F.; Dineen, T.; Gao, H.; La, D.; Marx, I.E.; Nguyen, H.N.; Peterson, E.A.; Weiss, M. Tetrahydroquinoxaline Dihydrobenzoxazine and Sodium Channel Inhibitors. WO 2013/122897 Al, 22 August 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Gigstad, K.M.; Cardin, D.P.; Hirayama, T.; Hirose, M.; Hu, Y.; Kakei, H.; Lee, H.M.; Motoyaji, T.; NII, N.; Shi, Z.; Vyskocil, S.; Watanabe, H. Quinoxaline Compounds and Uses Thereof. U.S. Patent 10,144,742 B2018, 4 December 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Husain, A.; Madhesia, D.; Rashid, M.; Ahmad, A.; Khan, S.A. Synthesis and in vivo diuretic activity of some new benzothiazole sulfonamides containing quinoxaline ring system. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2016, 31, 1682–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alavi, S.; Mosslemin, M.H.; Mohebat, R.; Massah, A.R. Green synthesis of novel quinoxaline sulfonamides with antibacterial activity. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2017, 43, 4549–4559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingle, R.; Wadher, S. Synthetic development of antimicrobial novel quinoxaline derivatives. Int. J. Pharm. Chem. 2013, 3, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talari, S.; Karunakaram, D.R.G.; Jupudi, S.; Udhayavani, S. Synthesis of 9-bromo-n-substituted- 6h- indolo [2, 3-b] quinoxaline-3-sulfonamide derivatives containing quinoxaline moiety as prospective antimicrobial agents. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 3, 145–151. [Google Scholar]
- Sharaf El-Din, N. Synthesis of some sulfonamide derivatives with potential antibacterial activity. Chem. Heterocycl. Compd. 2000, 36, 523–528. [Google Scholar]
- Potey, C.L.; Kosalge, B.S.; Hadke, A.M. Synthesis and Antimicrobial Activity of Quinoxaline Sulfonamide. IJOART 2013, 2, 126–134. [Google Scholar]
- Olayiwola, G.; Obafemi, C.A.; Taiwo, F.O. Synthesis and neuropharmacological activity of some quinoxalinone derivatives. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2007, 6, 777–786. [Google Scholar]
- Barea, C.; Pabon, A.; Castillo, D.; Zimic, M.; Quiliano, M.; Galiano, S.; Pérez-Silanes, S.; Monge, A.; Deharo, E.; Aldana, I. New Salicylamide And Sulfonamide Derivatives of Quinoxaline 1,4-Di-N-Oxide with Antileishmanial And Antimalarial Activities. Bioorg Med. Chem Lett. 2011, 21, 4498–4502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farrag, A.A.; Ammar, A.Y.; El-Sehemi, G.A.; Thabet, H.K.; Hassan, N.A.-A.; Samy, A.H. Synthesis And Pharmacological Screening of Novel Sulfamoylphenyl Carbamoyl Quinoxaline Derivatives As Anti-Inflammatory, Analgesic And Antitumour Agents. J. Chem. Res. 2011, 35, 163–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingle, R.; Marathe, R.; Magar, D.; Patel, H.M.; Surana, S.J. Sulphonamido-quinoxalines: Search for anticancer agent. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 65, 168–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingle, G.R.; Marathe, P.R. Sulfonamido Quinoxalines—Search for Anti-Inflammatory Agents. Int. J. Pharm. Res. Allied Sci. 2012, 4, 46–51. [Google Scholar]


























| Compound | Urinary Excretion Percentage | Diuretic Activity | Lipschitz Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 43 | 176.66 | 1.13 | 1.28 |
| 44 | 121.42 | 0.78 | 0.88 |
| 45 | 87.5 | 0.56 | 0.63 |
| Acetazolamide | 155.17 | 1.0 | 1.13 |
| Urea | 136.6 | 0.88 | 1.0 |
| Antibacterial Activity (DMSO, 4 mg mL−1) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Compound | Diameter of Zone of Inhibition (mm) | |
| S. Aureus | E. coli | |
| 50 | 20 | 9 |
| 51 | 22 | 11 |
| 52 | 17 | 18 |
| 53 | 15 | 12 |
| 54 | 11 | 13 |
| 55 | 5 | 5> |
| Chloramphenicol | 19 | 22 |
| Compound | Zone of Inhibition (mm) at 100 μg | |
|---|---|---|
| S. aureus | E. coli | |
| 59 | 10 | 8 |
| 60 | 7 | 6 |
| 61 | 6 | 7 |
| 62 | 9 | 2 |
| Azithromycin | 12 | 10 |
| Compound | Zone of Inhibition (mm) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Antibacterial | Antifungal | ||||
| S. aureus | B. pimilis | E.coli | A. nigar | P. notatum | |
| 67 | 14 | 14 | 16 | 17 | 17 |
| 68 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 12 | - |
| 69 | - | 11 | - | 10 | - |
| Streptomycin | 18 | 20 | 20 | - | - |
| Miconazole nitrate | - | - | - | 23 | 20 |
| Antibacterial Activity (20 mg/mL) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Compound | Zone Diameter (mm) | |
| S. aureus | E. coli | |
| 74 | 15 | 10 |
| 75 | 14 | 8 |
| 76 | 12 | 10 |
| 77 | 10 | - |
| Sulfadiazine | 14 | 13 |
| Antimicrobial Activity | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compound | Zone of Inhibition (mm) | ||||
| Gram-Positive Bacteria | Gram-Negative Bacteria | ||||
| S. aureus | Enterobacteria | V. cholera | E. coli | P. vulgaris | |
| 81 | 19 | 24 | 2 | 22 | 30 |
| 82 | 18 | 18 | 16 | 16 | 16 |
| 83 | 8 | 8 | 6 | 6 | 8 |
| Neuropharmacological Effect | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compound | Activity | Inhibition Effect | Reference Compound | Inhibition Effect |
| 84 | Total locomotor activity | Potent sedative at 40 mg/kg | - | - |
| Anxiolytic activity | 67.3% = time in open arm | Diazepam | 53.3% = time in open arm | |
| 81.0% = entry into open arm, 25.9 = index of open arm avoidance | 82.4% = entry into open arm, 32.2 = index of open arm avoidance | |||
| Dose = 2.5 mg/kg | Dose = 1 mg/kg | |||
| Anticonvulsant activity | Protection effect = 100% against Leptazol at 80 mg/kg and Strychnine at 2.0 mg/kg after 60 min | Phenobarbitone sodium | Protection effect = 90% against both Leptazol at 80 mg/kg. and Strychnine at 2.0 mg/kg after 60 min 15.15 | |
| Dose = 25 mg/kg dose | Dose = 20 mg/kg | |||
| Antileishmanial Activity | |
|---|---|
| Compound | IC50 (µM) |
| 90 | 20.3 |
| 91 | 16.3 |
| 92 | 3.1 |
| Amphotericin B | 0.2 |
| Antitumor Activity | |
|---|---|
| Compound | IC50 (μg m/L) |
| 99 | 0.5 |
| 100 | 4.75 |
| 101 | 6.79 |
| Anti-Inflammatory Activity | ||
|---|---|---|
| Compound | Mean Paw Volume (mL) ± SEM | % Inhibition of Edema |
| 106 | 0.96 ± 0.058 | 4.04 |
| 107 | 0.96 ± 0.052 | 3.82 |
| 108 | 0.98 ± 0.021 | 1.17 |
| Diclofenac sodium | 0.85 ± 0.0085 | 15.15 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Irfan, A.; Ahmad, S.; Hussain, S.; Batool, F.; Riaz, H.; Zafar, R.; Kotwica-Mojzych, K.; Mojzych, M. Recent Updates on the Synthesis of Bioactive Quinoxaline-Containing Sulfonamides. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 5702. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11125702
Irfan A, Ahmad S, Hussain S, Batool F, Riaz H, Zafar R, Kotwica-Mojzych K, Mojzych M. Recent Updates on the Synthesis of Bioactive Quinoxaline-Containing Sulfonamides. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(12):5702. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11125702
Chicago/Turabian StyleIrfan, Ali, Sajjad Ahmad, Saddam Hussain, Fozia Batool, Haseeba Riaz, Rehman Zafar, Katarzyna Kotwica-Mojzych, and Mariusz Mojzych. 2021. "Recent Updates on the Synthesis of Bioactive Quinoxaline-Containing Sulfonamides" Applied Sciences 11, no. 12: 5702. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11125702
APA StyleIrfan, A., Ahmad, S., Hussain, S., Batool, F., Riaz, H., Zafar, R., Kotwica-Mojzych, K., & Mojzych, M. (2021). Recent Updates on the Synthesis of Bioactive Quinoxaline-Containing Sulfonamides. Applied Sciences, 11(12), 5702. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11125702









